AP BIO: Properties of Life (Unit 1)
1/57
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
58 Terms
matter
occupies weight and has a mass
chemistry
how matter interacts with each other
elements
can not be broken down into simpler substances
atom
basic unit of a chemical element
proton
positive
electron
negative
neutron
uncharged
ion
uneven amount of protons and electrons
high specific heat
hard to change temperature, why large bodies of water are cooler, helps endotherms control their temperature
water
two small atoms of hydrogen and one large oxygen
covalent bond
hydrogen connected to an oxygen atom (strong bond)
hydrogen bond
oxygen connected to a hydrogen atom (weak bond)
high heat of vaporization
water takes a lot to change states; important for sweating
universal solvent
water dissolves everything since it is polar
strong surface tension
due to hydrogen bonding water has___
adhesion
attaches to other substances easily because of hydrogen/ polar substance
cohesion
attaches to water molecules easily because of hydrogen
ph 1-6
acidic, sour, proton donors since there are a lot of H+
ph 8-14
basic, bitter, proton acceptors because they have a lot of OH-
Buffers
help resist changes as life is very sensitive to PH
organic
anything that contains carbon
ionic bond
electron transfer- two oppositely charged ions
covalent bond
molecular bond-sharing electron
hydrogen/dipole bonds
extremely weak; only happens with N O F (very electronegative)
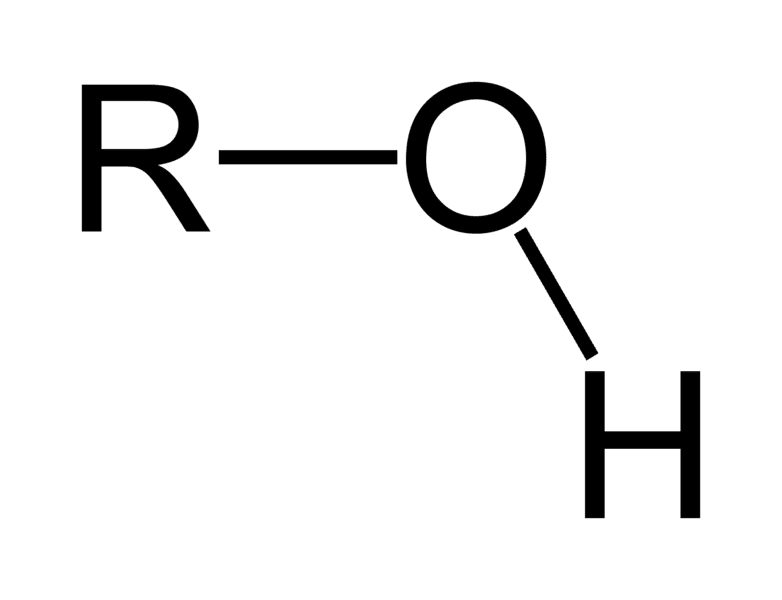
Hydroxyl
very polar; found in all macromolecules
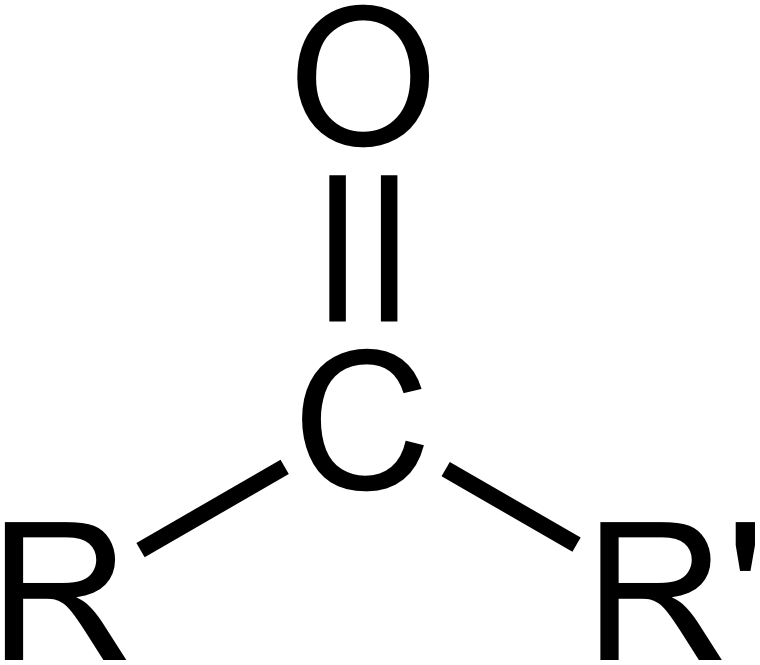
Carbonyl
oxygen double bonded to hydrogen; very polar; found in proteins and lipids only
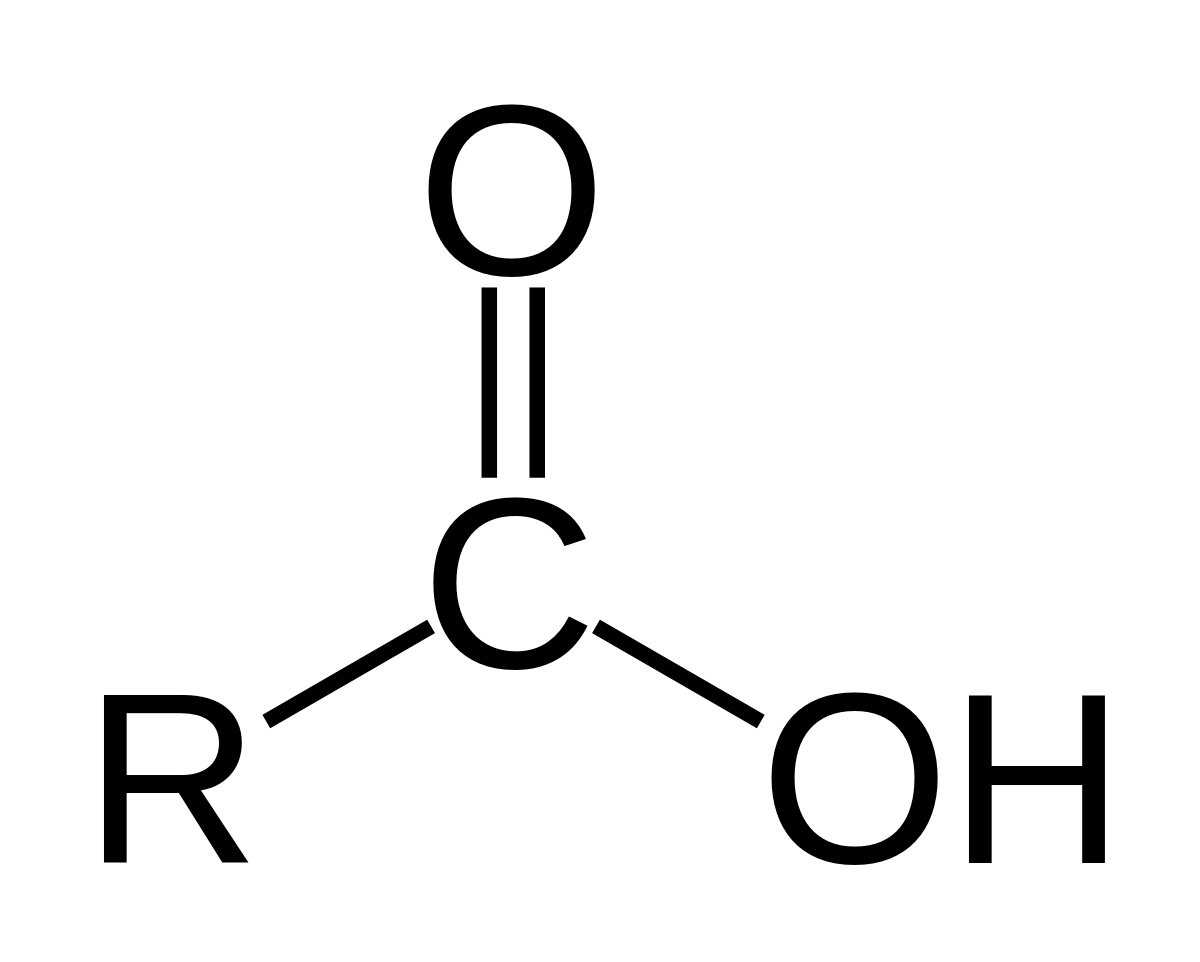
carboxyl
carbonyl with an OH group
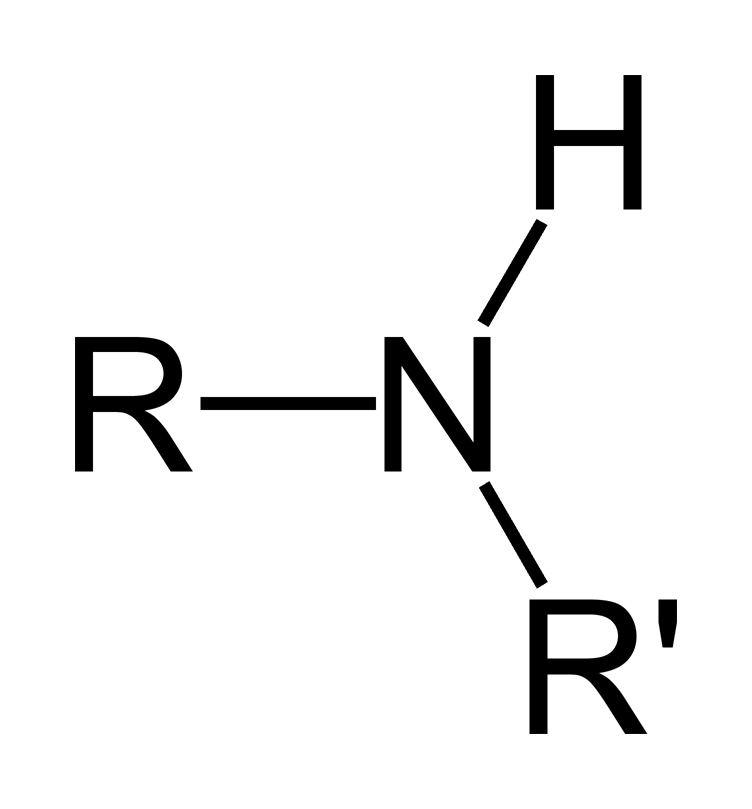
amines
always has nitrogen; found in proteins and nucleic acids only
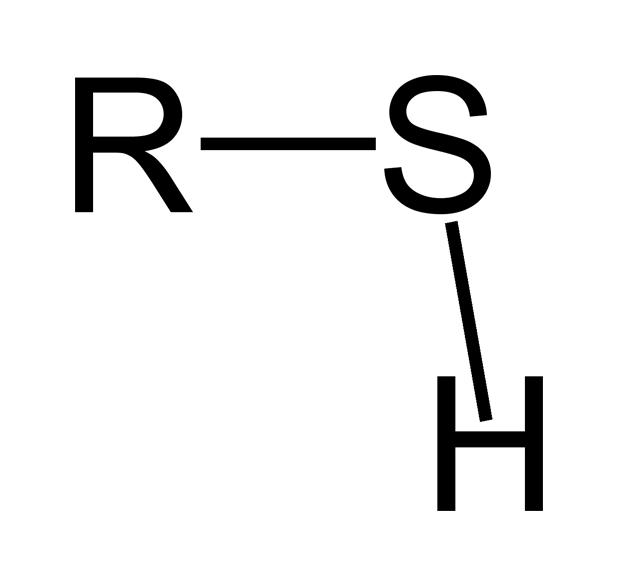
sulfhydryl
always has sulfur; can determine shape of proteins; only found in proteins
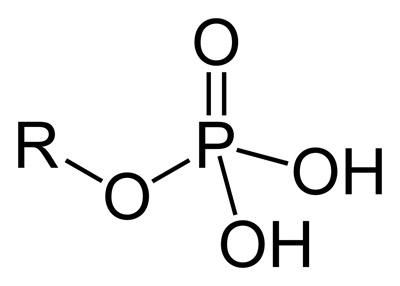
phosphate
makes things more acidic; has a charge to it; only found on phospholipids and in nucleic acids
dehydration synthesis/ condensation reaction
joins two molecules together; takes out hydrogen bonds and oxygen
hydrolisis
separates molecules by adding water molecules
carbohydrate’s bond
glycosidic
proteins/ amino acids’s bond
peptide
lipid’s bond
ester
nucleic acids’s bond
phosphodiester
monomer of carbohydrates
monosaccaride
function of carbohydrates
energy, some for structure
structure of carbohydrates
-ratio 1:2:1
-functional group: carboxyl
-structure: ring
polymer of carbohydrates
polysaccharides
covalent bonds
hold macromolecules together
isomer
same number of atoms, different arrangement, impacts function
monomer of lipids
fatty acid+glycerol
functions of lipids
cellular membrane, energy storage
saturated fatty acid
only single bonds; stack up really easily; mostly solid at room temp
unsaturated fatty acid
has one or more double bond; kinks do not allow them to stack up; liquid at room temp
monomer of proteins
amino acid
function of proteins
cell structures, makes up enzyme, many other things
primary structure of proteins
chain with peptide bonds
secondary structure of proteins
forms an alpha helix or beta sheet
tertiary structure of proteins
three dimensional (R-group interactions)
quaternary structure of proteins
more than one protein subunit
monomer of nucleic acids
nucelotide
function of nucleic acids
stores genetic information in DNA/RNA
structure of nucleic acids
-5 carbon sugar (pentagon)
-nitrogenous base (N)
-phosphate group (P)
DNA
-stores the true blueprint
-double stranded
-very long
-deoxyribose sugar
-uses A, T, G, and C bases
-found in nucleus
-more stable due to the less hydroxyl group
RNA
-converts true blueprint to build proteins
-one stranded
-short
-ribose sugar
-A, U, G, C
-found in nucleolus and moves out of nucleus
-more reactive and not as stable
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
used for energy