Plant Science Exam 2 Study Guide
1/127
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Plant Science with Dr. Kemerait at ABAC
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
128 Terms
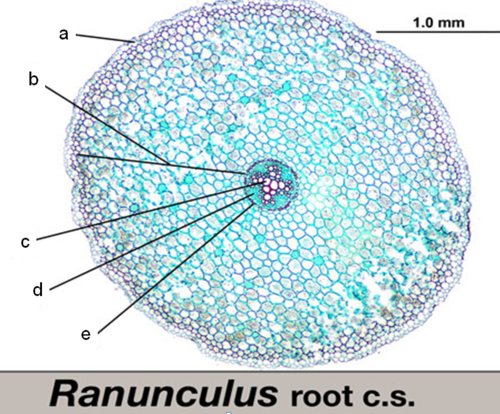
what is ‘A’
epidermis
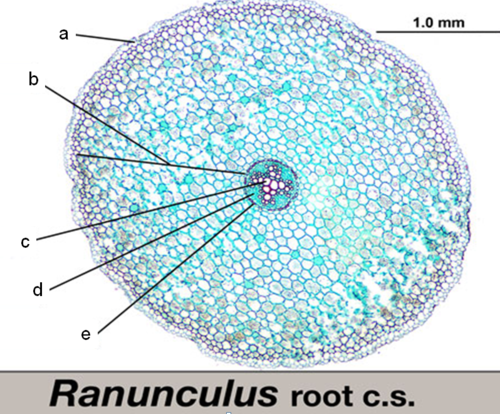
what is ‘B‘
cortex
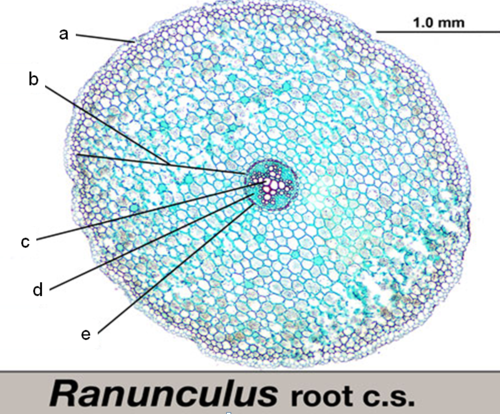
what is ‘C‘
xylem
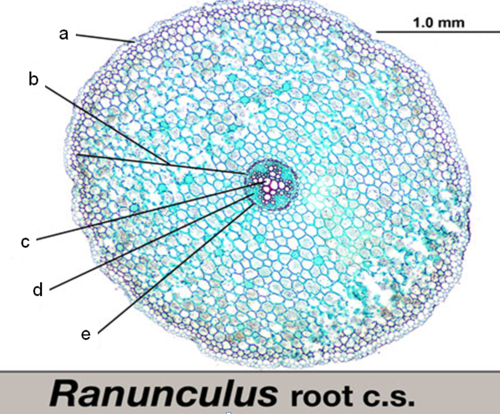
what is ‘D‘
phloem
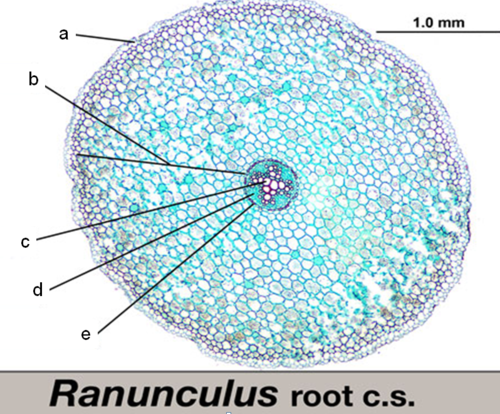
what is ‘E’
endodermis
which of the following is a function of the roots
a. anchorage and support
b. hormone synhthesis
c. nutrient and water absorption
d. all of these
d. all of these
which plant tissue is responsible for the uptake of mineral nutrients and water
a root hair
b phloem
c xylem
d cortex
a. root hairs
where in the root do lateral or branch roots originate
a. epidermis
b. cortex
c. endodermis
d. pericycle
d. pericycle
what is the narrow band or waterproofed material surrounding each endodermal cell called
casparian strip
in what plant tissue do you find root hairs
a. xylem
b. endodermis
c. epidermis
d. phloem
a. epidermis
what are adventatious roots
a roots that seek out pockets of moisture and nutrients in the ground
b main roots from which branch roots grow
c roots that form on any part of the part
d roots with more or less the same length
c. roots that form on any part of the part
*think adventurous
which part of the plant embryo develops into a root and is usually the first structure to emerge upon seed germination
radicle
which type of root system do dicots usually have
a dicot root system
b monocot root system
c taproot
d branching root system
c. taproot system
which is not a function of the stem
a. absorption of water and nutrients
b. photosynthesis
c. transport of metabolites
d. asexual reproduction
a. absorption of water and nutrients
in which type of meristem does secondary growth occur
a. apical
b. intercalary
c. subapical
d. vascular cambium
d. vascular cambium
the annual growth ring in trunks of woody perennials are rings of
a. cork cambium
b.secondary phloem
c. bark
d. secondary xylem
d secondary xylem
which is the reason for the absence of secodnary growth in monocots
a. monocot only have one vascular bundle
b. monocots do not have a continuous vascular cambium
c. monocots have parallel xylem vessle s
d. monocots only live for 1 year
b. monocots do not have a contiinous vascular cambium
what are the persistent shortended stems on branches of woody plants such as apples an pears
spurs
in which of the following crops would you find bulbils
a. onion
b. potato
c.ginger
d.strawberry
a. onion
fleshly terminal portion of undergorun stem
tuber
short vertical swollen undergroudn stem modified for nutrient storage
corm
above ground lateral stem
stolon
below groudn lateral stem
rhizome
highly compressed underground stem with numerous storage leaves
tuber
what is the complete removal of a ring of bark from around a branch or tree trunk
girdling
a leaf would have this/these functions (s)
a. collects solar engery
b. absorbs nutrients and water from the soil
c. in decidous plants, stores nutrients during the winter
d. b and c only
a. collects solar energy
in which part of the leaf does most of the photosynthesis in a plant occur
a vascular bundles
b mesophyll
c stomatas
d epidermis
b mesophyll
a leaf without a petiole is called
a. parallel
b. stipule
c. sessile
d. simple
sessile
the slender stalk by which a leaf is attached to the stem is called the
petiole
which is the best way to tell if a leaf is simple or compound
a. a simple leaf will not have a petiole; a compound leaf will
b. a simple leaf will have parallel veins, and a compound leaf will have branching veins
c. a simple leaf will have a bud at the base of the leaf; a compound leaf will not have a bud at the base of the leaflet
d. a simple leaf has an entire margin, a compound leaf has a lobed margin
a simple leaf will have a bud at the base of the leaf; a compound leaf will not have a bud at the base of the leaflet
Stores food reserves in the seed
a. floral bract
b. sepal
c. spine
d. tendril
e. cotyledon
e. cotyledon
supports the plant: found in climbing plants such as pea
a. floral bract
b. sepal
c. spine
d. tendril
e. cotyledon
d. tendril
usually bright colored as in pointsettia, attracts pollinators
a. floral bract
b. sepal
c. spine
d. tendril
e. cotyledon
a. floral bract
usually found in cacti, helps plant retain water or protects plant from predators
a. floral bract
b. sepal
c. spine
d. tendril
e. cotyledon
c. spine
usually green, protects flower bud during development
a. floral bract
b. sepal
c. spine
d. tendril
e. cotyledon
e. sepal
what statement about transpiration is NOT true
A. distributes metabolites thorughout plant
B. provides the forces that drwas water into the xylem
C. loss of water from a leaf by evaporation
D. helps regulate leaf temp
A. Distributes metabolites throughout the plant
sexual reproduction in angiosperms..
A. occurs in the leaf
B. results in identical offspring
C. involves the fusion of gametes
D. all the above
C. involves the fusion of gametes
alteration of generations in angiosperms involves
A. the occurence of the gametophytic and sporophytic generations
B. the formation of male and female gametes'
C. the fusion of gametes
D. all the above
D. alll the above
a complete flower is a flower with all four of the following parts
A. stipules petals pistil and stigma
B. sepals bracts petals and style
C. sepals, petals. pistil, stamen
D. sessile, petiole, pericarp, and ovary
C. sepals petals pistil stamen
Female productive structure in a flower
a. stamen
b. pistil
pistil
male repoductive structure in a flower
a. stamen
b. pistil
a. stamen
whcih part of the flower produces the pollen grains
anther
the enlarged tip of the stem to which a flower is attached is called the
A. petiole
B. pedicel
C.peduncle
D.receptacle
d receptacle
a flower with both stamen and pistil must be
a. incomplete
b. complete
c. perfect
d. imperfect
c. perfect
a staminate flower
A. does not have a stamen
B. is perfect
C. is incomplete
D. all the above
c. is incomplete
monoencious plants such as squash produce
A. incomplete flowers
B. imperfect flowers
C. pistillate flowers
D. all these types of flowers
d. all these types of flowers
diecious plants such as asparagus, produce…
A. complete flowers
B. perfect flowers
C. pistillate and staminate flowers on separate platns
D. flowers capable of self fertilization
c, pistilate and staminate flowers on separate platns
an inflorescence is
A. a cluster of flowers
B. the female reproductive strucuture within a flower
C. the leaf life structure that protects a flower bud
D. the light that is reflected by the chlorophyll
a. a cluster of flowers
irregular flowers have the following characteristic
A. odd number of flowers in a cluster
B. big and small flowers in a cluster
C. bloom at separate times
D. bilateral symmetry, where the flowers are divisible into equal halves in only one plane
D. Bilateral symmetry where the flowers are divisible into equal halves in only one plane
Monocots and dicots may be differentiated by the number of their flower parts, monotocots have flower parts in…
3s
pistil and stem in the same flower mature at the same time
which is more likely
a. self-pollinated
b. cross-pollination
self
blooming period of male and female flowers in the same plant do not coincide
which is more likely
a. self-pollinated
b. cross-pollination
cross
a flower has stamen and pistil enclosed in a keel petal such as peanuts
which is more likely
a. self-pollinated
b. cross-pollination
self
male flowers are produced in one plant and female flowers are produced in anotehr plant
which is more likely
a. self-pollinated
b. cross-pollination
cross
flowers are big and brightly colored
which is more likely
a. self-pollinated
b. cross-pollination
cross
potential bonus: how would you know a plant is a monocot or dicot just by looking at its leaves
monocot leaves have parallel veins and dicot leaves have web like veins
what is the contiuum of the cytoplasm
symplast
areas of the plant cell outside the cell membrane
apoplast
photosynthesis occurs in what type of roots
aerial
what region of the root zones has root hairs
maturation
what region of the root zones has the largest vacuoles
elongation
1-3 is what
1. apical
2. subapical
3. intercalary
4. lateral
primary growth
TRUE OR FALSE:
A dicot has a palisade mesophyll
true
what are the two types of venation for the external structure of a leaf
parallel and reticulate
___________ - stalk that attaches the leaf blade to the stem
petiole
________ - leafy appendage
stipule
monocot plants have _______ vines
a. parallel
b. web like/reticulate
parallel
what is the centra vein of a leaf a called
midrib
which is NOT a characteristic of the Phloem?
A. mostly dead cells
B. permanent complex tissue
C. transport water and nuteints throughout the plant
D. two way transport
C. transport water and nutrients throughout the plant
which of the following is a function of the roots
A. anchorage and support
B. hormone synthesis
C. nutrient and water absorption
D. all of these are functions of the roots
D. all of these are functions of the roots
which plant tissue is responsible for the uptake of mineral nutrients and water from the soil
A. root hairs
B. phloem
C. cortex
D. pericycle
a. root hairs
what is the narrow band of waterproofed material surrounding each endodermal cell
A. casparian strip
B. cuticle
C. collenchyma
D. cork
a. casparian strip
where in the root do lateral or bracnh roots originate
A. epidermis
B. cortex
C. endodermis
D. pericycle
a. pericycle
in which plant tissue do you find root hairs
root hairs
in which type of meristem does secondary growth occur
subapical
which part of the flower becomes fruit when mature
ovary
what is the processs through which fruit develops without fertilization thus resulting in seedless fruit
a. parenthenocarpy
b. regeneration
c. infertility
d. pollination
a. parenthenocarpy
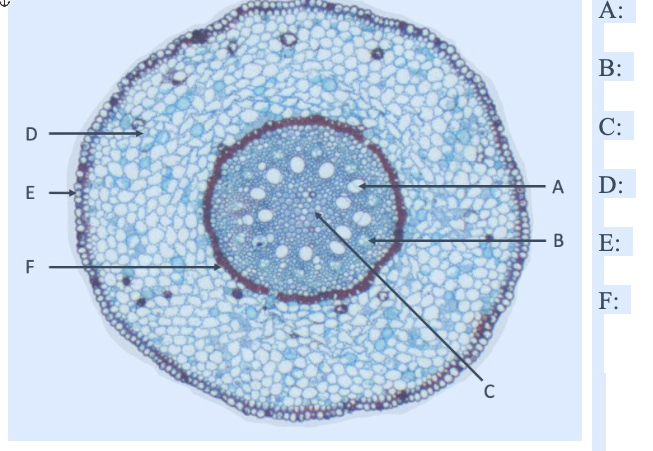
what is A
xylem
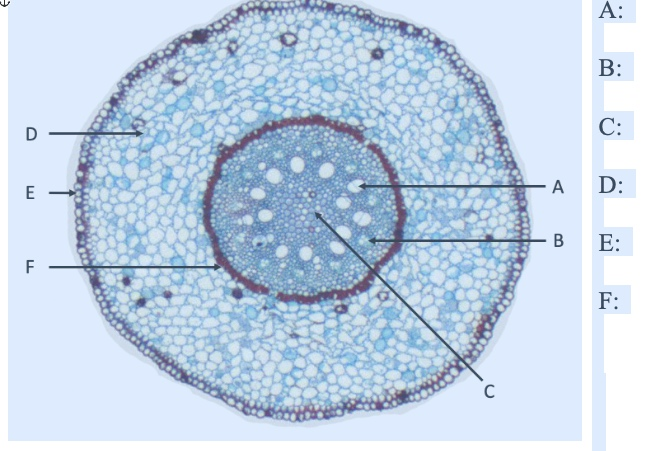
what is B
phloem
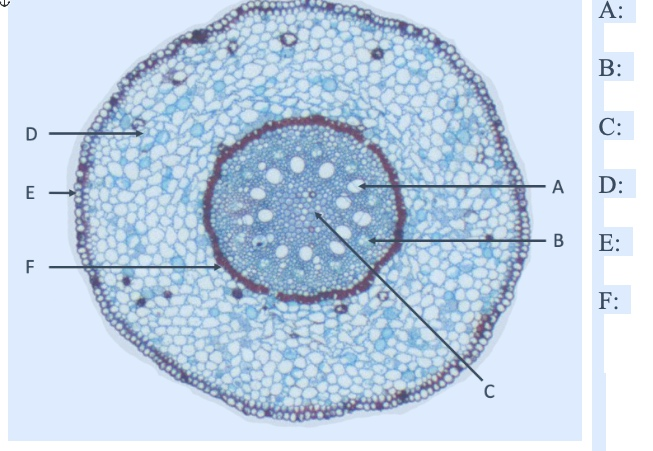
what is C
pith
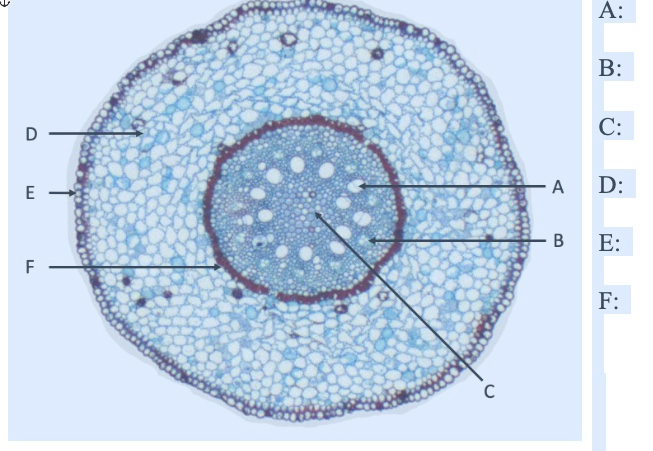
what is D
cortex
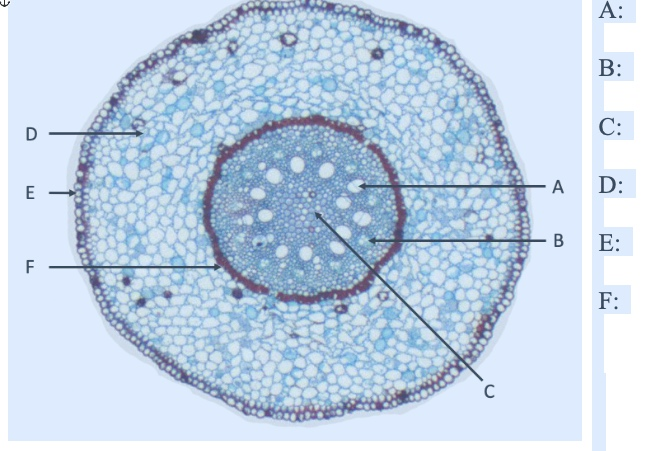
what is E
EPIdermis
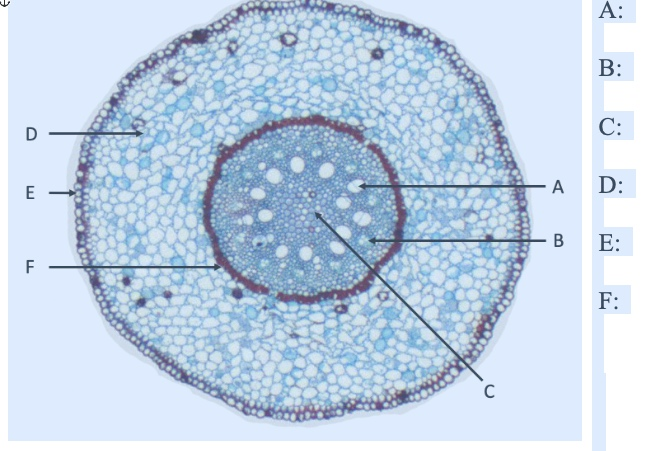
what is F
ENDOdermis
filament + anther =
stamen
Stigma + Style + Ovary =
pistil
protoderm =
epidermis
ground meristem =
cortex
procambium =
vascular cylinder
_________ - outermost layer of the central core and lies just inside the epidermis. Single parenchyma cell layer
A. pericycle
B. stamen
C. petiole
D. stigma
A. Pericycle
what are the four parts of the flower
stamen pistil petal sepal
Petal + Sepal
tepal
Simple fruit
single flower, single ovary
aggregate fruit
single flower several ovaraies single receptable
multiple fruit
several flowers in a mass
pericarp
fruit wall which debvelops from ovary wall after fertilization
exocarp
skin or outermost covering
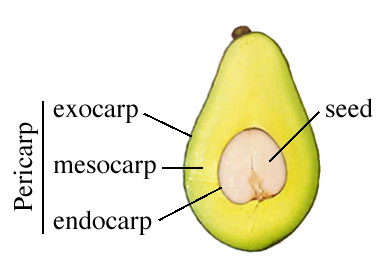
mesocarp
fleshly tissue
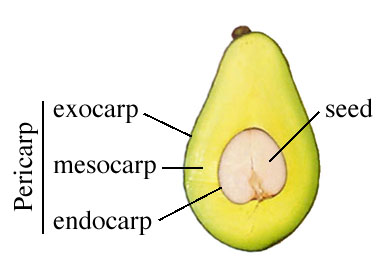
endo carp
boundary around seed which may be hard/stoney/papery
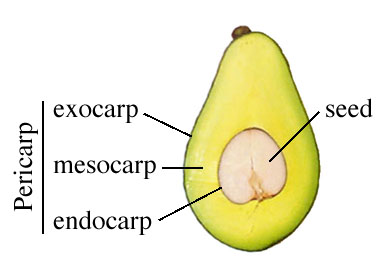
________ - entire paricarp and accesory parts develop into succulent tissue ex. tomato ,apple
simple fleshy fruit
simple dry fruit -
entire pericarp dry at maturity, two types.