REN R 210 FINAL
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
Inorganic Carbon
CO2 and carbonates in lithosphere (limestone, sodium carbonate, etc…)
Organic Carbon
SOM (C, O, H)
SOC
Active Carbon Reserve
3000 Pg
Pg= 10^15 g
Turnover = CO2, COH(SOM), CO2
Inactive Carbon Reserve
100,000,000 Pg
inorganic (carbonate), rock
Global Carbon Pools
Largest to Smallest
Carbonate(75,000,000), Oceans/Lakes (36,000) Fossil (5,000) fuels, Soil (2,400), Atmosphere (750), Vegetation(550)
Anthropogenic release of C
Tg - 10^12
420 ppm CO2
Soil Health
A soils capacity to continue to function as a vital living ecosystem that sustains plants, animals, and humans.
SOM Composition
Living Biomass: 0.5-3% - roots, microbes, animals
Residue/Detritus: 5-40%- litter, fibers, dead roots, feces (L, F layer)
Humus:
non-humic substances: 5-10% - Biopolymers, low molecular weight(known chemically)
humic substances: 40-90% - SOC stabalization
New SOM theory
accessibility to microbes, temperature for enzymes and adsorption, forms soluble in water, emphasis on carbon flow. OM is protected by minerals
Old theory
OM quality=emission prediction, stable humus, temperature sensitive, solubility in alkaline solution, emphasis on carbon stocks.
Humin – Humic Acid – Fulvic Acid
Decomposition
CHO + O2 (enzymes and microbes) = CO2, H2O,
Mineralization
Release of soluble or gaseous inorganic constituents during decomposition (e.g., nutrients, CO2).
R-NH2 (organic) —> NH4 (inorganic)
Humification
Old: - OLD theory - Condensation Rxn: low MW biopolymer to high MW biopolymer
New: NEW theory – stabilization of SOC by three mechanisms. Minerals, aggregates, decreasing molecular size.
Non-Humic substances
Known biopolymers, Easily identified chemically, Decomposition rate depends on chemical composition
Cellulose (cell wall) - 30%
Hemi-cellulose - 20%
Lignin - 20%
Lipids: 20%
Proteins: 5% (contains N)
Most to least tightly packed N
Protein, hemi-cellulose, cellulose, lignin, lipids
C/N ratio
dictates recalcification
Micro-organisms need an AVG of 8 C atoms for every 1 N atom to build biomass.
With respiration: every 24 C, microbes need to find 1 N to build biomass
C<20 = fast decomp
C>30 = slow decomp
Mean residence
time of atoms to cycle through pools
Plant residue: biopolymers, some chemical resistance
SOM “Pools”
Chemical protection (active?)
Physical protection (aggregates, slow)
Organo-mineral associations (passive)
Energy source
Photo - energy from radiation
Chemo – Energy from Org. C
Litho – Energy from soil REDOX Rxn
Human and Fungi Energy source
Organic Carbon
Chemo-Heterotrophs
Nitrogen Fixation
78% of atmosphere
Organic N
C-NH2
Inorganic N
N2, NH4, NO3, N2O
Biological Fixation (lots of energy)
Rhizobium (legumes)
Frankia (alders)
N2 — nitrogenase — NH4
Nitrogenase (enzyme) must be protected from O2. Leghemoglobin scrubs O2 out of nodule.
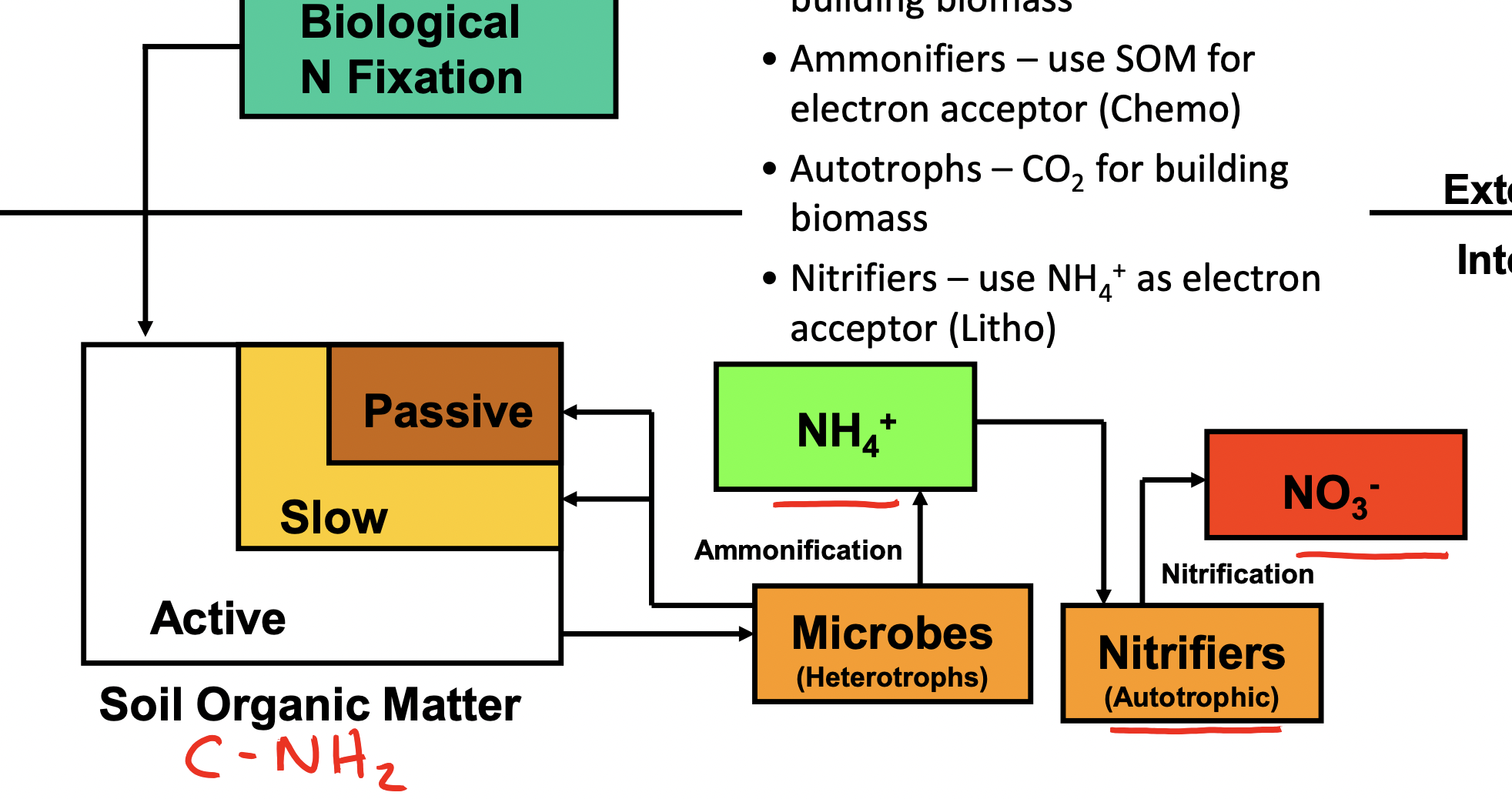
Nitrogen Cycle
Autotrophs use CO2 to build CNH2 — microbes(heterotrophs) (ammonifiers) use SOM for e acceptor and produce NH4— nitrifiers(autotrophs) use NH4 as e acceptor and produce NO3.
Pyrogenic C (wildfire)
“passive” pool
REDOX – REDuction / OXidation Reactions
O2 +NH4 — NO3 + H2O + H2(reduction reaction)
Ammonification
Immobilized/mineralization — used by microbes to build biomass
When there is access (lower C/N ratio) — nitrification
Nitrification
NH4 + O2 = NO2 + H2O
NO2 (toxic) + O2 = NO3 + H2O
Anaerobic process
Lithoautotrophs
Denitrification
without O2, NOx is used as an e receptor
NO3— NO2 — NO — N2O— N2
Mineral Fixation
NH4 bonds to clay (very strong)
Haber Bosch Process
CH4 + N2 + O2 + H2O = NH4 + CO2 + H2O
Cuts out SOM and microbes from cycle
Eutrophication
N + P = increase in nutrients = algae = increased turbation, decreased oxygen, decreased water quality
Fresh water – 0.5-1.0 mg/L
Marine water - <0.5 mg/L
Solutions for Nutrients leaching
Plant root stimulators
Grass buffer
Capture sites (plant fireweed, aspens)
Precision ag, Regenerative ag
Acid rain
Sulfer and nitric oxide react with oxygen and water in atmosphere = Sulferic acid and nitric acid
N measurements in AOSR
IER – captures wet and dry N deposition, showed that its high on the mine sites
How is phosphorus cycle different than N cycle?
only in inorganic form (PO4 -3), no oxidation, from lithosphere
P Cycle
1.Mineral Dissolution 2.Uptake from Solution 3.Leaching/Runoff 4.Organic matter release 5.Precipitation
is insoluble when attached to Al and Fe
6.5 is best for P availability
K cycle
no redox, from lithosphere
Sulphur Cycle
redox rxn, from lithosphere
1. Mineral dissolution
SOM turnover
Atmosphere Dep
Organic forms of S
• C-S – carbon bond
• C-O-S – ester bond • Electron acceptor in anaerobic environments (WETLANDS)
Edatopic Grid
System for identifying diff ecosystems
Macrofauna
OM shedders
Bioturbation
Predatory
Ants, beetles, earthwormsetc…
Megafauna
bioturbation
predatory
gophers, moles, etc…
Mesofauna
predation
OM consumers/shedders
mites (0.1-1mm)
Microfauna
Nematodes, Protozoa (Ciliates, Amoebe, Flagellates)
Microflora
Fungi, Bacteria(prokaryotes), Archaea (prokaryotes)
Types of Mycorrhiza
1. Ecto (outside cell)
2. Erricoid (species specific)
3. Arbuscular (inside cell)
4. Orchid (species specific)
Microbial Size Class
Nematode, Protists, Fungi, Bacteria, Virus, Clay Particle
6 C’s of soil conservation
1. Compaction reduction 2. Conservation tillage 3. Continuous living plants 4. Cover crops 5. Crop +animal diversity 6. Composts and amendments