Overview of Complete Dentures, Edentulous Challenge, and Secondary/Final Impressions
1/139
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
140 Terms
When do we use complete denture pros?
when all else has failed
when system health and adaptability is declining
to restore function (speech and chewing)
to restore facial appearance
maintain health
(we want to keep as much as we can and replace what is needed)
what are the 3 principles of pros?
Support, Stability, and Retention
define: complete denture support
resistance to vertical movement of the denture base toward the ridge (/underlying tissues)
what are the 2 components of support
initial support from bone and mucosa when bilateral simultaneous contact of opposing posterior teeth
long term support - load the tissue areas most resistant to resorption
define: complete denture stability
resistance to horizontal or rotational movements
what are the 4 components of stability
ridge height and conformation
base adaptation
occlusal harmony
neuromuscular control
what are the factors of stability
shape of the alveolar ridges
size of the alveolar ridges/vestibular depth
flange length and shape
intimate fit of prothesis
define: complete denture retention
resistance to displacement of the denture base away from the ridge
what are the 7 components of retention
adhesion - attraction between unlike molecules
cohesion - force between molecules of same material
interfacial surface tension - thin fluid (or saliva) film between 2 closely contacting objects (between gums and denture)
intimate tissue contact - impression technique affects (need to have good reproduction of oral tissues)
border seal - prevent ingress of air (need to seal denture)
atmospheric pressure
Neuromuscular control - (learned phenomenon/how to wear it) external contour of denture bases promote
what is the support found in the natural dentition
45 cm2 in each arch (includes teeth and periodontal ligament)
what is the support of the maxillary complete denture
23 cm2 (has ridge and palate support
what is the support of the mandibular complete denture
12 cm2 (only has ridge support)
what is the first way to minimize residual ridge resorption
remove the dentures for at least 8 hours a day
what is the second way to minimize residual ridge resorption
using proper impression techniques
what is the third way to minimize residual ridge resorption
no contact of anterior teeth in centric relation closure
what is the fourth way to minimize residual ridge resorption
ensure occlusal harmony (clinical remount and occlusal refinement)
what is the purpose of clinical remount
this technique and equilibration at delivery reduce occlusal discrepancies
the first denture problem
dentures move around in the mouth
second problem of dentures
dentures create pressure on supporting mucosa and bone
third denture problem
pressure from dentures cause bone resorption
fourth denture problem
bone resorption results in decreasing horizontal stability and decreasing retention that are possible to achieve with the dentures
fifth denture problem
retention of complete dentures requires saliva of good quality and quantity. However, many denture patients take meds that cause xerostomia
sixth denture problem
the technical quality of dentures in use is not very high. 60% of dentures in use have a least 1 major deficiency
seventh denture problem
denturism is legal in 6 states, dental lab techs petitioning for the right to do dentures directly
eighth denture problem
complete dentures are sometimes prescribed as an economic alternative to more costly fixed and restorative treatments. dentures are not better than natural teeth and they are a substitute for no teeth at all
ninth denture problem
the useful life of a set of complete dentures is 7 - 10 years (ridge will change over time and you need to ensure harmony)
Pt classification: Philosophical
Pt understands that dentures is for their benefit and lets you work on them
Pt Classification: exacting/critical
Pt is very specific, may look up to topic online, they think they know what they want, critical of you when you work with them
Pt classification: Hysterical
Pt is nervous all the time, very emotional (overly), can’t seem to adapt to the situation
Pt classification: indifferent
Pt is only there because a loved one wants them to be there, they really don’t care about getting dentures or not
what do we look for in an intraoral exam for dentures?
mucosa
basal seat
arch form
interarch space
in an intraoral exam, what are we specifically looking for when evaluating the mucosa
the color and contours of the gingiva
in an intraoral exam, what are we specifically looking for when evaluating the basal seat
this is the ridges and the palate. we want to see the height, contour, ridge parallelism, palatal vault shape
in an intraoral exam, what are we specifically looking for when evaluating the arch form
form of the ridge, we specifically are looking for if it is square, tapering, ovoid (might affect fit of complete denture)
in an intraoral exam, what are we specifically looking for when evaluating the interarch space
how much space/room do we have; how much room do we have for the denture teeth, but also for the pink covered base
border molding
allows the intraoral soft tissues to form the length, width and shape of custom tray borders prior to making the secondary impression
intaglio
the interior surface that is determined by the impression
cameo
the viewable portion of the denture that extends in the occlusal direction
interocclusal record
record between the two arches at the appropriate vertical dimension of the face where the bite should be
comorbidities that come with complete edentulism
malnutrition and obesity
increased COPD events
increased pneumonia related hospitalizations
increased risk of head/neck cancer
decline in cognitive function
predictor of cardiovascular disease mortality
reduced, but nonreplaced dentition associated with increased risk of mortality
causes of denture movement
resiliency of tissue
instability of dentures
Almost all of the principles of complete denture fabrication have been formulated to _______ _______ of the dentures or to _________ ___ ______ transmitted to the supporting structures
decrease movement; minimize the forces
due to the few natural adaptive mechanisms left by the time a Pt gets to the edentulous state, the dentures will rest on tissue that…
will change progressively and irreversibly
What are the supports within the natural dentition
dentin, cementum, pdl, alveolar bone
Wolff’s law
living bone responds to functional stress by depositing bone in areas of stress
(remarkable adaptability of natural teeth/masticatory system)
edentulous patients have very little _______ to _________ ________ on alveolar bone
adaptation; functional stress
residual ridge resorption
there is a reduction of bone after the teeth have gone
Who said: “the mean reduction in anterior mandibular ridge is 4 times that of the maxillary ridge”?
Dr. Tallgren
what are the proper impression techniques
record tissues at rest
extend denture base to use maximum support area
placement of pressure on those tissues best able to tolerate pressure
bone is not
a static tissue, it is constantly being remodeled and replaced
bone of the maxillary ridge
partly covered by a layer of cortical bone after teeth are extracted
bone of the mandibular ridge
crest remains spongy, trabeculated and not very resistant to resorption
bone of the buccal shelf (of mandible)
made up of compact bone and is the primary support area for dentures in the mandibular arch
snowshoe principle
decrease the pressure per unit area by extending the denture base to cover the maximum area within physiologic tolerance (support)
in relation to the snowshoe principle we hope to:
have more saliva contact = ….
proper peripheral extension = ….
more contact adhesion (retention)
good border seal (retention)
xerostomia
dryness presents much difficulty for denture wearers— discomfort, ulcerations, retention loss, chewing problems
medical conditions associated with xerostomia
autoimmune and inflammatory conditions
Graft-versus-host disease
Immunoglobulin G4-related sclerosing disease
degenerative disease (amyloidosis)
granulomatous disease (sarcoidosis)
infections: HIV/AIDS, hepatitis C
Salivary gland aplasia or agenesis
medications often associated with xerostomia
anticholinergic drugs
antihistamines
antihypertensive agents (angiotensin blockers/inhibitors, adrenergic blockers, diuretics)
opioids
psychotropic agents (antidepressants, antipsychotics)
skeletal muscle relaxants
adhesion
attraction of unlike molecules for each other (mucosa-saliva-denture base)
the amount of retention attributable to adhesion is directly proportional to…
wettability of denture base material
area covered by the denture base
viscosity of the saliva
Who said: “Our goal … not the meticulous replacement of that which is missing, but the preservation of that which remains”
Dr. M.M. Devan
The patient’s _________ and __________ with the dentist plays a substantial role in overall complete denture success (up to 50%)
personality; relationship
Who said: “Ideal impression must be in the mind of the dentist before it is in his hand. He must literally make the impression rather than take it.”
Dr. M.M. Devan
complete denture impression
a negative registration of the entire denture bearing, stabilizing and border seal areas present in the edentulous mouth
preliminary impression
an impression made for the purpose of diagnosis or for the construction of a tray
(good for records of mouth and occlusion)
what are the three impression philosophies
minimal pressure
functional pressure
selective pressure
minimal pressure impression
attempt is made to exert as little pressure as possible during impression procedures. the objective is to capture tissues in their most undisturbed and undisplaced form
what is the rationale behind minimal pressure impression (aka the “mucostatic technique”)
suggested that if tissues are recorded in an undisturbed state using an accurate, free-flowing impression material, retention and stability of the dentures would be increased
who invented the mucostatic technique
Mr. Page, he was an engineer
in the minimal pressure impression, what material was used and how was it done
material: low viscosity, high flow (metal-oxide paste-ZOE, thin)
minimal pressure was used to seat the tray and to hold it
when do we still use the minimal pressure impression
when we find that the ridge is flabby and moveable (tissue) because the bones has resorbed
functional pressure impression
impression made with the soft tissue under a significant load (material used was more viscous)
how is a functional pressure impression done
the tray is seated and the patient closes the mouth with force while the material sets
what is the theory behind functional pressure impression
that the denture base-tissue contact during the function would be more intimate if tissue is recorded under compression
when is the functional pressure impression technique used today
when we need to add a new liner to a denture base, intaglio surface doesn’t fit very well
Selective pressure impression (what we use)
pressure is applied to certain areas based on dentist’s decision of where and how much. minimal pressure in certain areas, while more on other areas
in selective pressure impression, how do we control the pressure?
wax spacer relief (between tray and ridge)
drill vent holes in tray
grind tray for relief space
combo of all above
why use a custom tray
borders can be modified to control the movable soft tissues around the impression and avoid distorting them
what is the purpose of having space in custom trays
so that the shape of the tissues supporting the denture may be recorded with minimal or selective displacement in the primary support areas
in order to have a successful secondary impression, what is needed?
mucosa should be healthy
impression material of low viscosity
use minimum pressure to seat tray
seat and hold impression until set
purpose of border molding
to define denture border in length, width, shape, and contour. when it is completed, it should resemble anticipated denture border
definition of pre-extraction records
records and measurements obtained of the pt’s natural dentition prior to extraction of the teeth.
what is included in a pre-extraction record?
diagnostic casts
shade and dimensions from natural teeth
facial measurements (profile-assessment of lip position and contour; incisal plane; labio-lingual position of anterior teeth; OVD)
a record of the relationship of the incisal edges of the upper and the lower central incisors to the relaxed lips
Occlusal classification (I, II, III)
clinical photographs
A PVS impression of the labial surfaces of all the anterior teeth
What do pre-extraction records aid in?
determination of the incisal plane
establishing OVD
tooth selection and positioning
shade of teeth
lip position and fullness
re-establishment of natural intraoral relationships
what should we learn during a clinical exam
determine pt’s desires, demands, etc., by listenting and filling out the diagnostics survey
determine possible improvements in esthetics
determine the need for improved phonetics
observe and check: occlusion of denture (centric relation) and relationship of anterior teeth during speech (amount of vertical and horizontal overlap)
remove dentures and examine mouth
observe saliva
examine radiographs
examine previous dentures
What are the three components of the mucosa
masticatory, lining, specialized
masticatory mucosa
highly keratinized, best denture support (bound firmly to bone)
lining mucosa
thin, non-keratinized mucosa of lips and cheek. forms seal against denture, but does not resist stress (think about border molding)
specialized mucosa
dorsal surface of tongue. is keratinized, contains taste buds
the four characteristics for ideal denture bearing tissue
firmly bound, keratinized masticatory mucosa
a zone of connective tissue and submucosa
underlying cortical bone (really important)
muscle attachments nearby (enhance resistance to bone resorption)
centripetal resorption
routine resorption pattern following extraction of teeth results in a smaller maxilla when compared to dentate arch. this is a form of inward and upward resorption
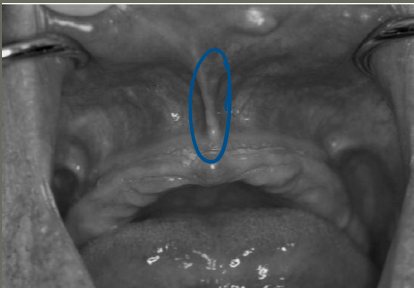
ID
labial frenum
what are the characteristics of the labial frenum
contains no muscle fibers
inserts in vertical direction
little lateral movement in function
notch in denture should be narrow and be accommodating
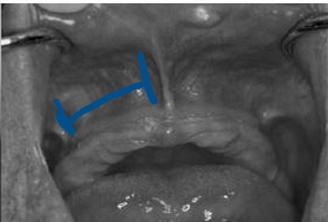
ID
labial vestibule
what is the labial vestibule
space between the labial frenum and buccal frenum. its reflection contains no muscle fibers
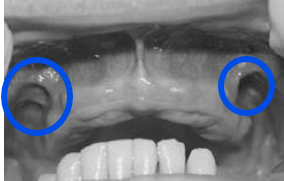
ID
buccal frenum
what is the buccal frenum
either single or multiple
ant-posterior direction of reflection
may contain few fibers of caninus muscle
notch in denture is broad since movement of the frenum is affected by buccinator and orbicularis oris muscle
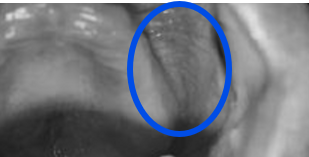
ID
buccal vestibule
what is the buccal vestibule
between buccal frenum and hamular notch
space varies in size
space must be filled vertically and laterally by denture flange to prevent ingress of air and loss of retention of max. denture
what is the other name for the buccal vestibule
retrozygomatic space (because it is the vestibular space posterior to the zygoma)