MGMT 30B Ch 2
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
Absorption costing
all manufacturing costs (fixed and variable) are assigned to units of product that fully absorb manufacturing costs
All nonmanufacturing costs are treated as period costs and aren’t assigned to products
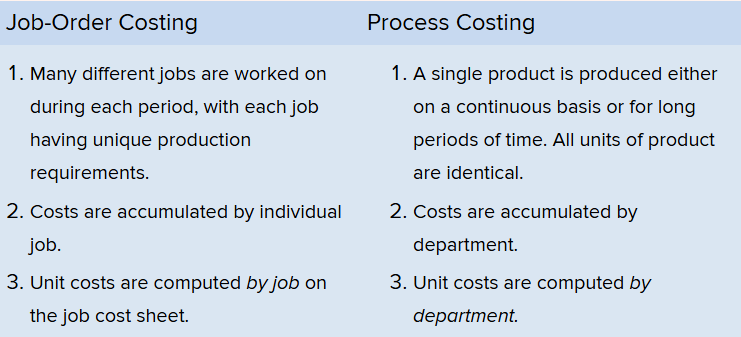
Job-order costing
used by companies that make many different products, each with unique features
Costs are traced and allocated to jobs and then divided by the number of units to have a cost per unit (unit product cost)
Bill of materials
document that lists the quantity of each type of direct material needed to complete a unit of product
Materials requisition form
specifies the type and quantity of materials to be drawn from the storeroom and identifies the job charged for the cost of the materials
Used to control flow of materials into production and for making journal entries in accounting records
Job Cost Sheet
records materials, labor, and manufacturing overhead costs charged to a job
Time ticket
provides and hour-by-hour summary of employee’s activities throughout the day
Allocation base
a measure (like direct labor hours) that’s common to all products and used to assign overhead costs to them
Predetermined overhead rate (POHR)
computed by dividing the total estimated manufacturing overhead cost for the period by the estimated total amount of the allocation base

4 step process to compute POHR
1. Estimate total amount of allocation base for next period (denominator)
2. Estimate the total fixed manufacturing overhead cost for the next period and the variable manufacturing overhead cost per unit of the allocation base
3. Use the cost formula (y = a + bX) to estimate total manufacturing overhead cost for the next period (numerator)
4. Compute POHR
Overhead application
process of assigning overhead costs to jobs

Normal cost system
applies overhead costs to jobs by multiplying a predetermined overhead rate by the actual amount of the allocation base incurred by the jobs
Cost driver
factor that causes overhead costs (like machine hours, beds occupied, computer time, flight hours, etc)
Should DRIVE the overhead cost for POHR to be accurate
Cost-plus pricing
pricing method in which a predetermined markup is applied to a cost base to determine the target selling price
5 step process to calculate the selling price
1. Calculate the estimated total manufacturing overhead cost for each department (fixed manufacturing cost + ($ per hour * amount of hours))
2. Calculate the POHR for each department
3. Calculate the amount of overhead applied from both departments for the job (POHR * hours for job)
4. Calculate the total cost for the job (direct materials + direct labor + applied manufacturing overhead)
5. Multiply the total cost by the markup to get the selling price
To find COGS
1. Figure out total job cost
2. Divide by units completed for get unit product cost
3. Multiply unit product cost by units sold
When a company applies less overhead to production than it actually incurs…
it’s underapplied overhead = needs to be adjusted and increases COGS = decreases net operating income
When a company applies more overhead than it actually incurs…
it’s overapplied overhead = needs to be adjusted and lowers COGS = increases net operating income
Process costing
used in industries that convert raw materials into uniform products (bricks, soda, paper, etc) on a continuous basis
Differences between Job-Order Costing and Process Costing