Cell Parts
1/16
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
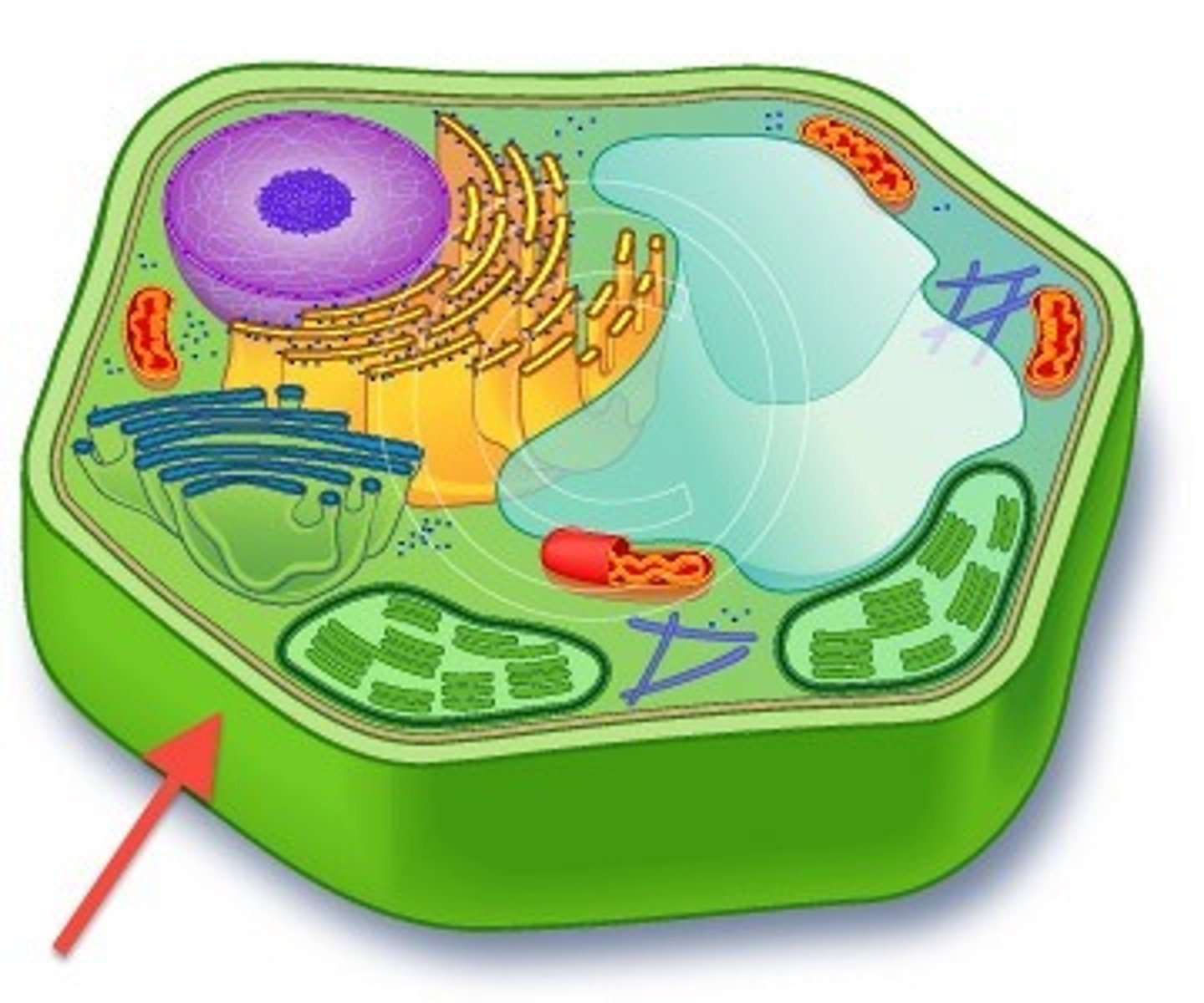
Cell wall
This somewhat rigid structure, made of cellulose, surrounds plant cells providing protection and support
organelle
cell parts with specialized function
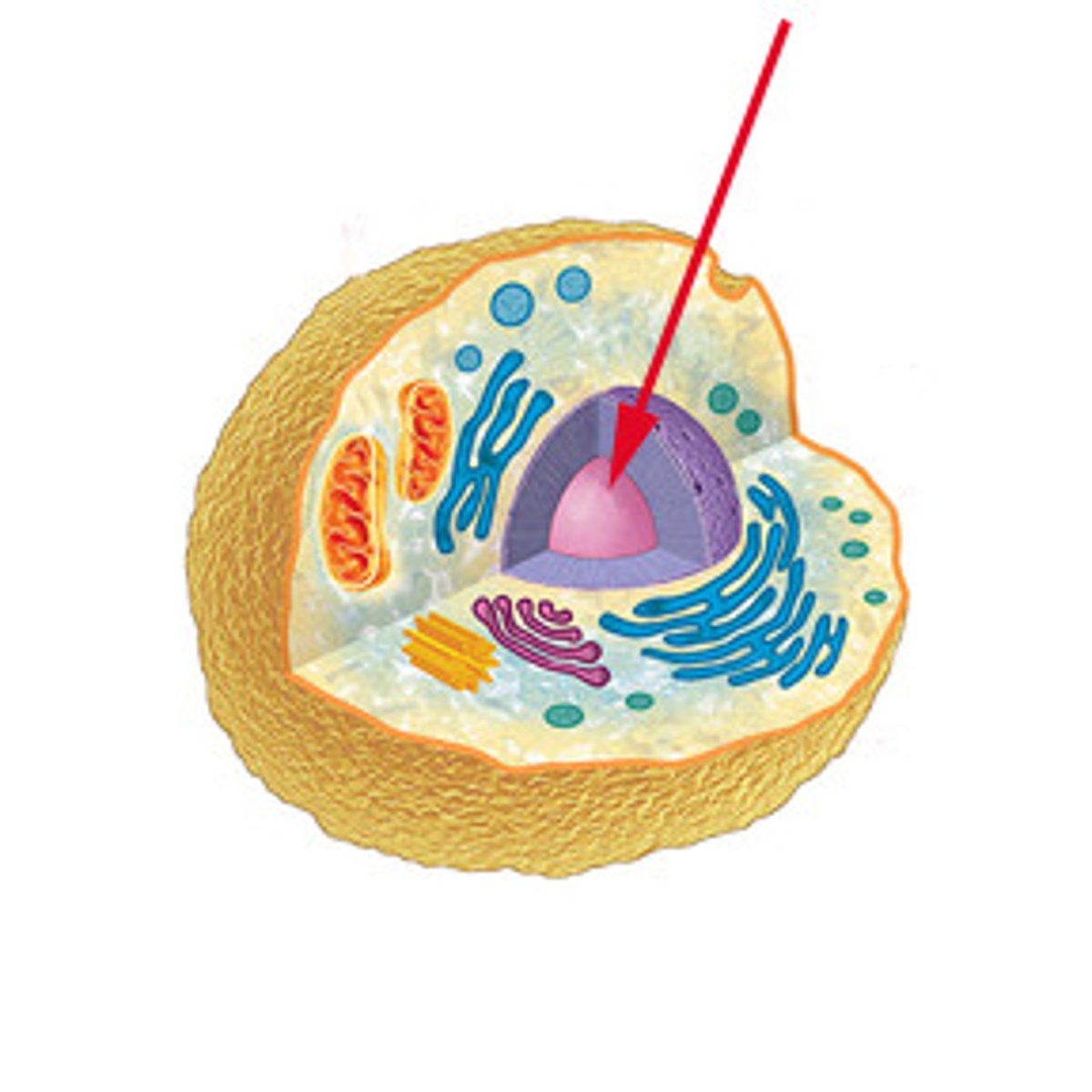
nucleus
large organelle that contains DNA
vesicle
This sac enclosed by a membrane transports things from one part of a cell to another

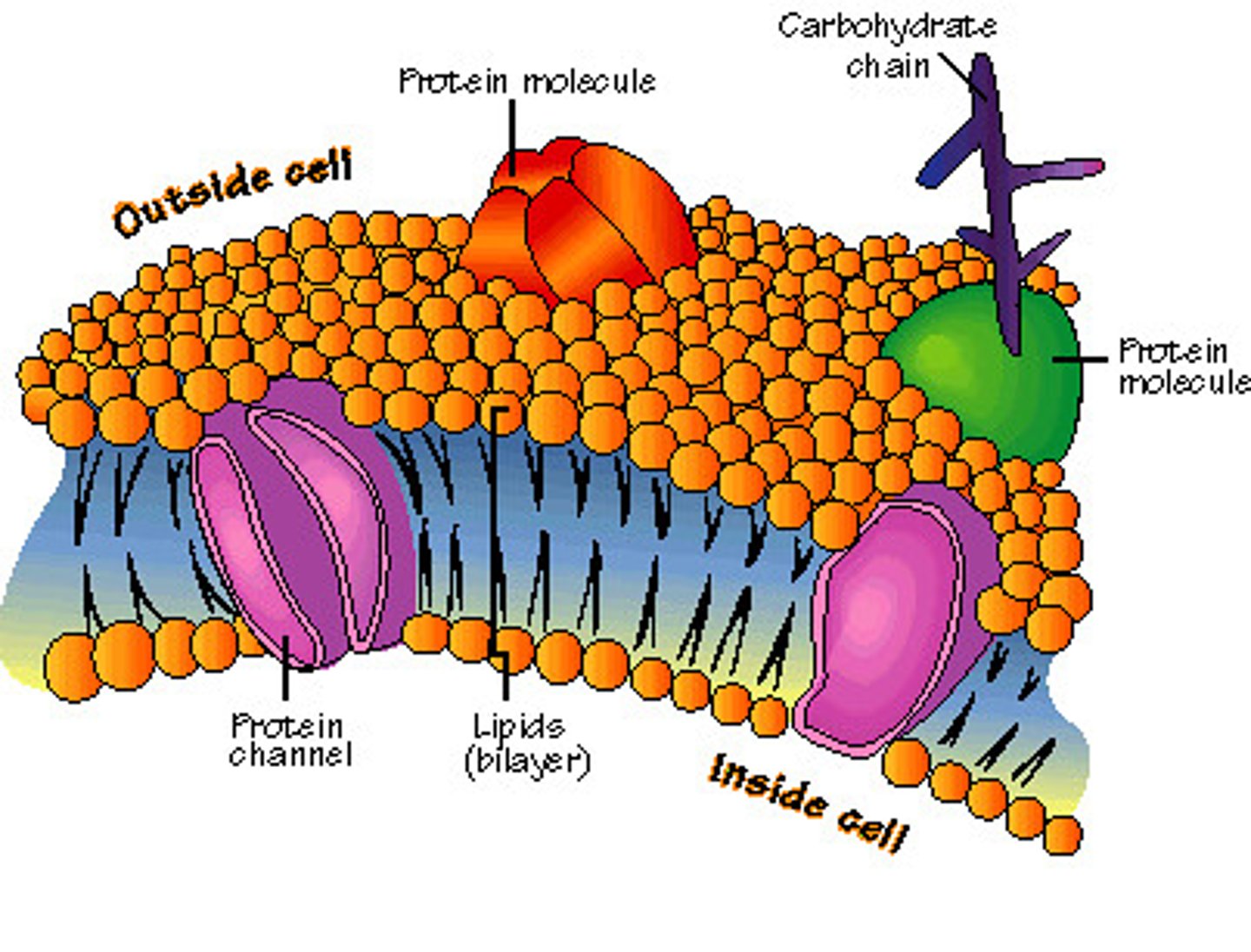
cell membrane
outer boundry of cell; controls what can enter and leave
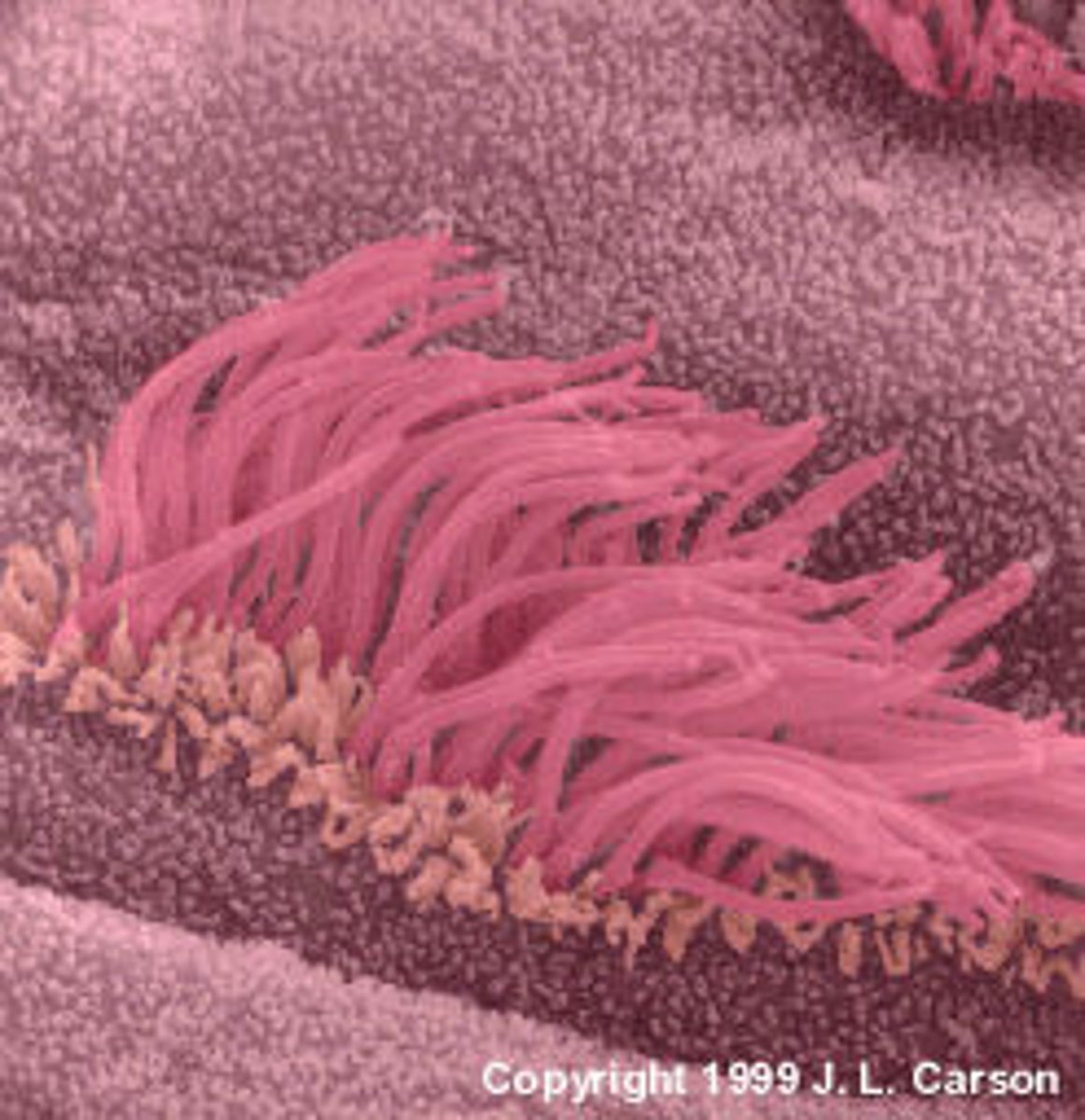
cilia
hair like structure used to move a cell
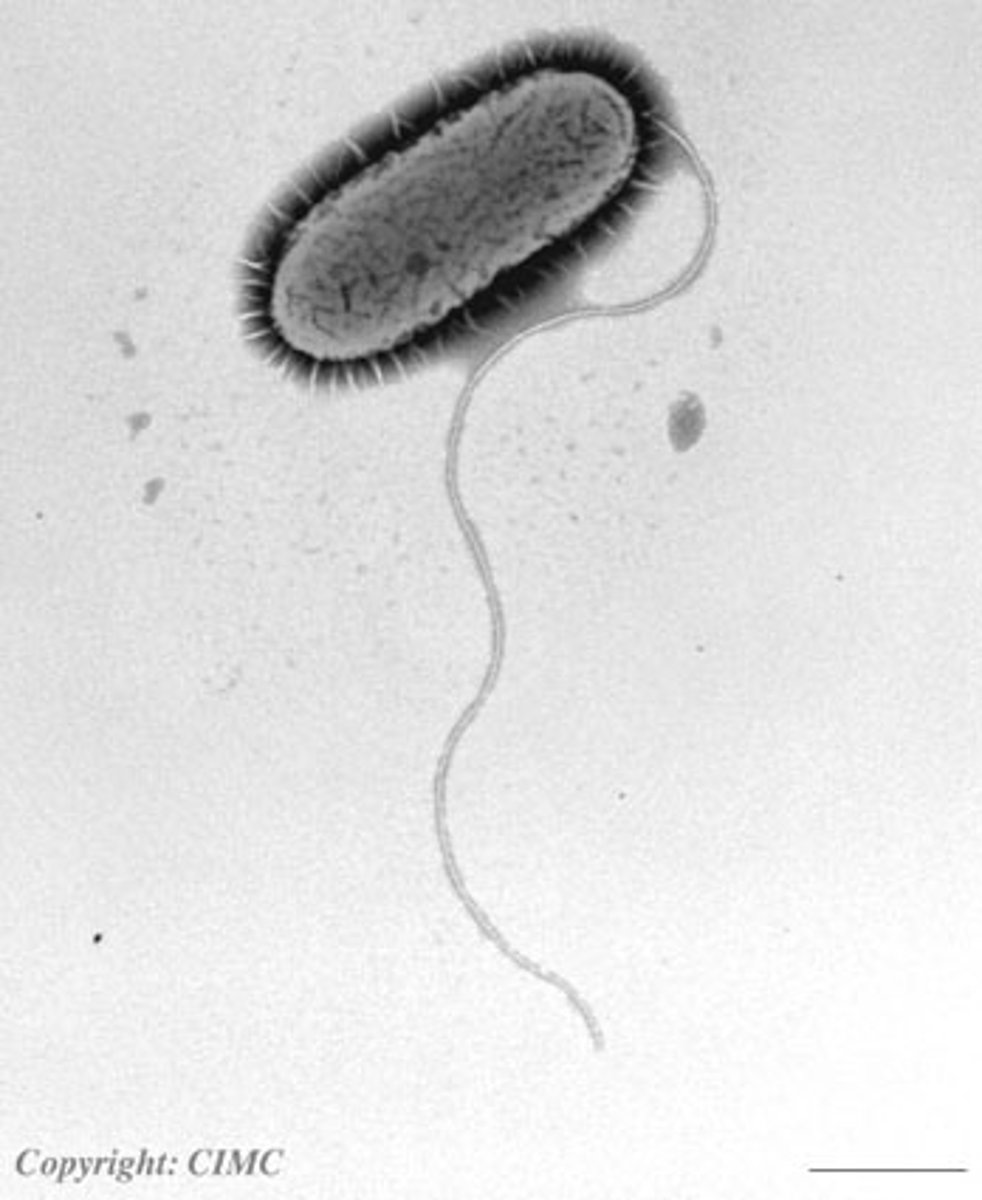
flagella
tail like structure used to move a cell
lysosome
This sac-like organelle contains enzymes that break down material, cell debris and worn out organelles
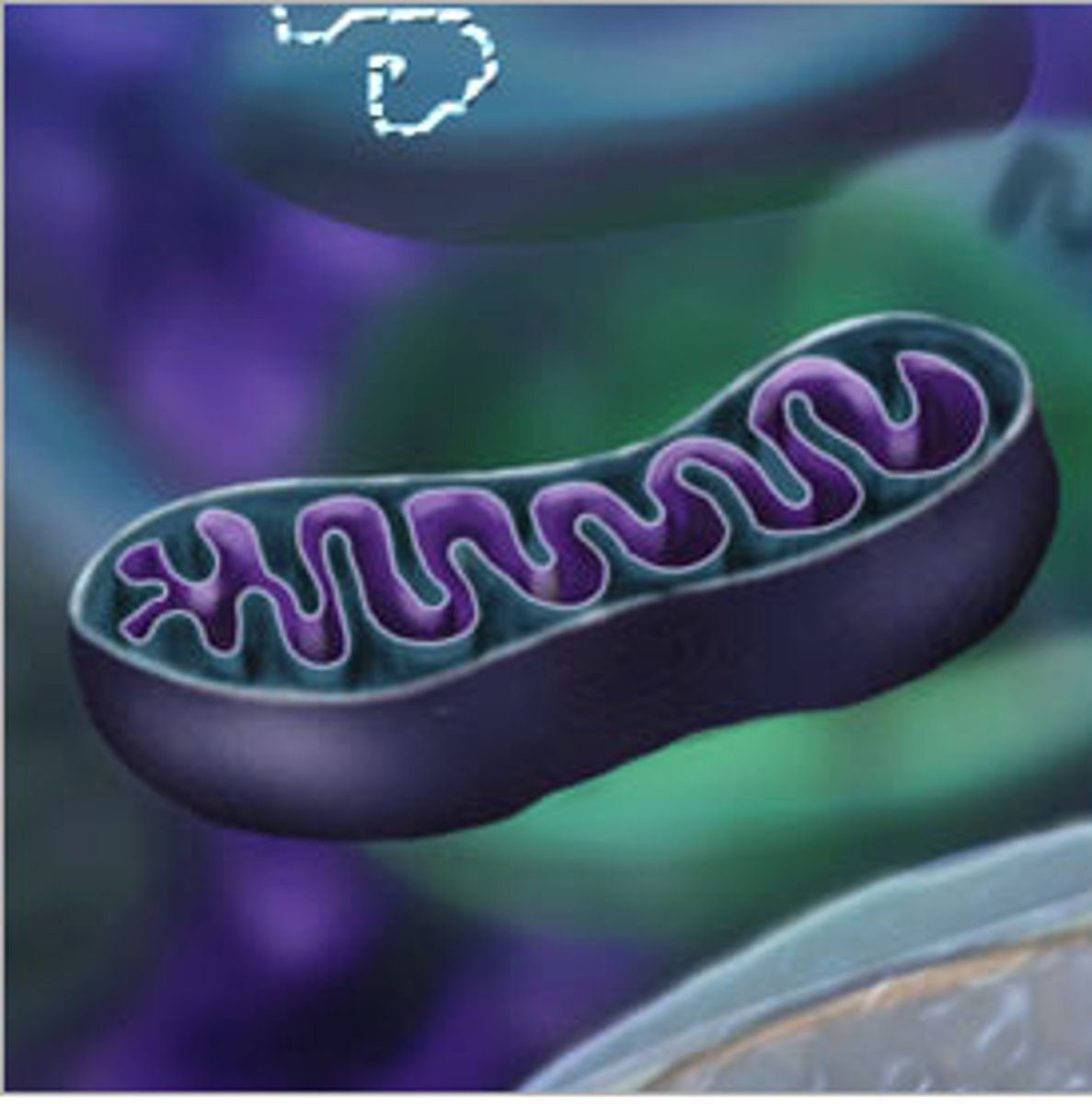
mitochondria
Cellular respiration occurs in this organelle, chemical energy in glucose is converted to ATP
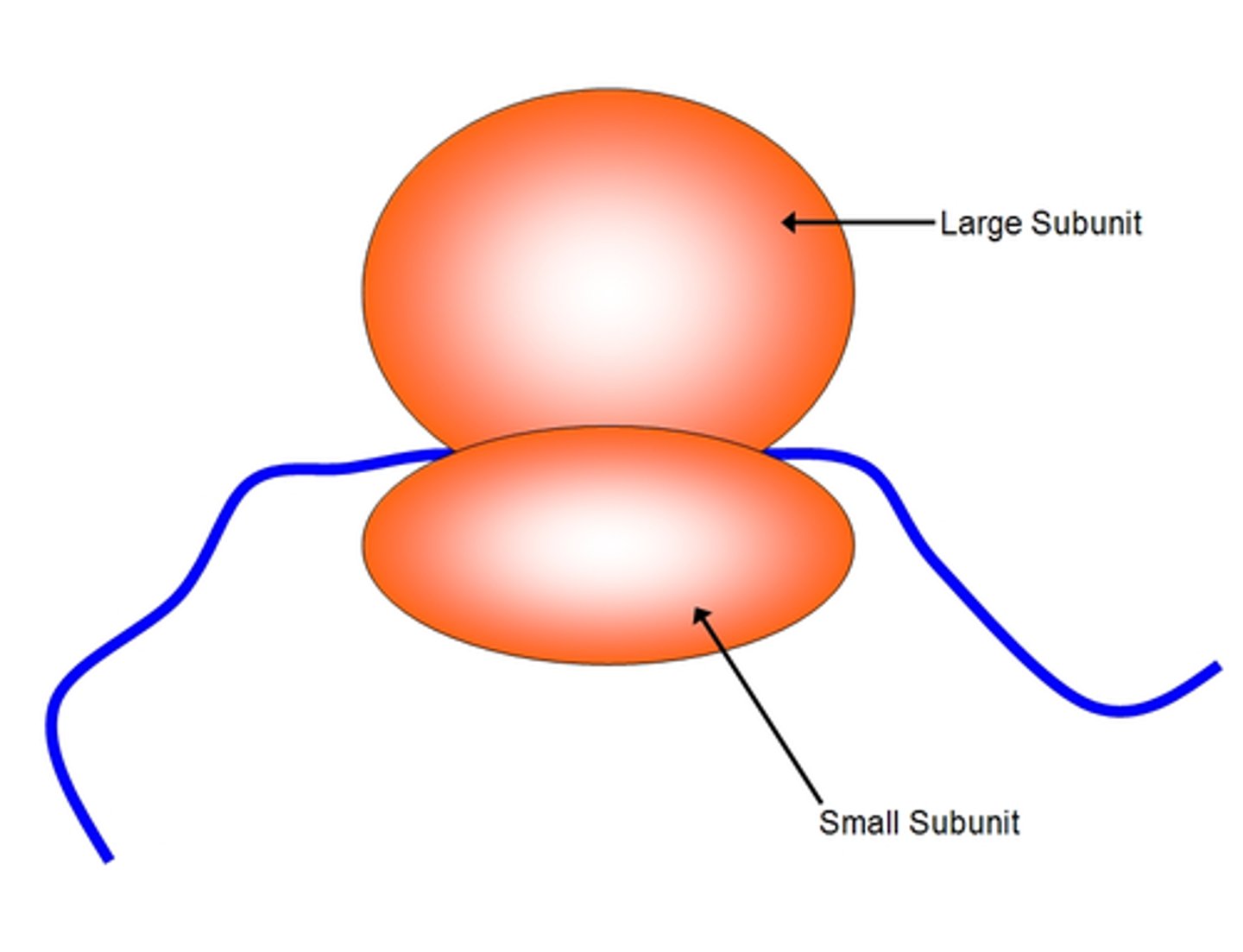
ribosome
Small structures that use the instructions from the nucleus, written in mRNA, to build proteins
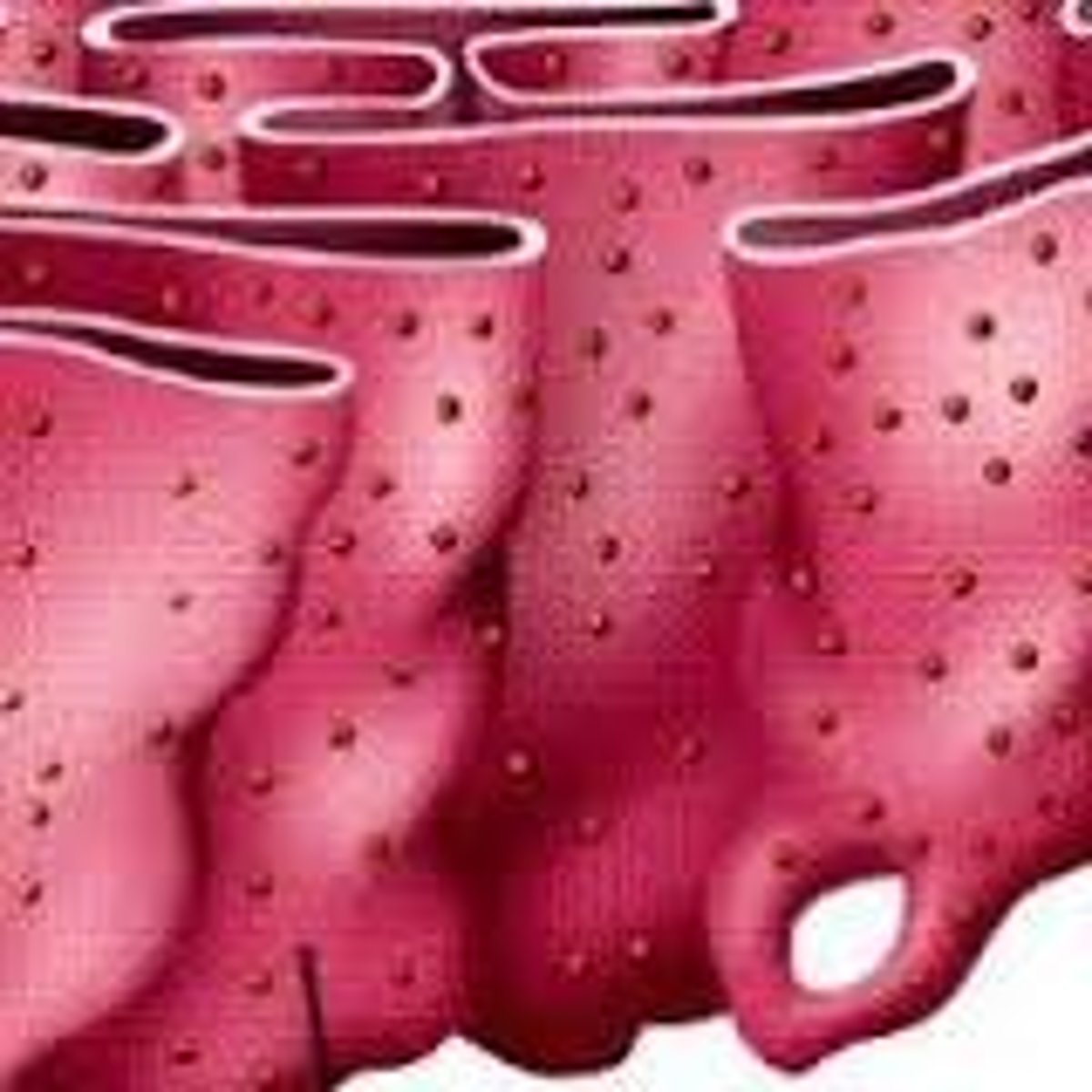
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
This membrane bound network of tubes and flattened sacs lacks ribosomes and its main role is to make lipids and phospholipids.
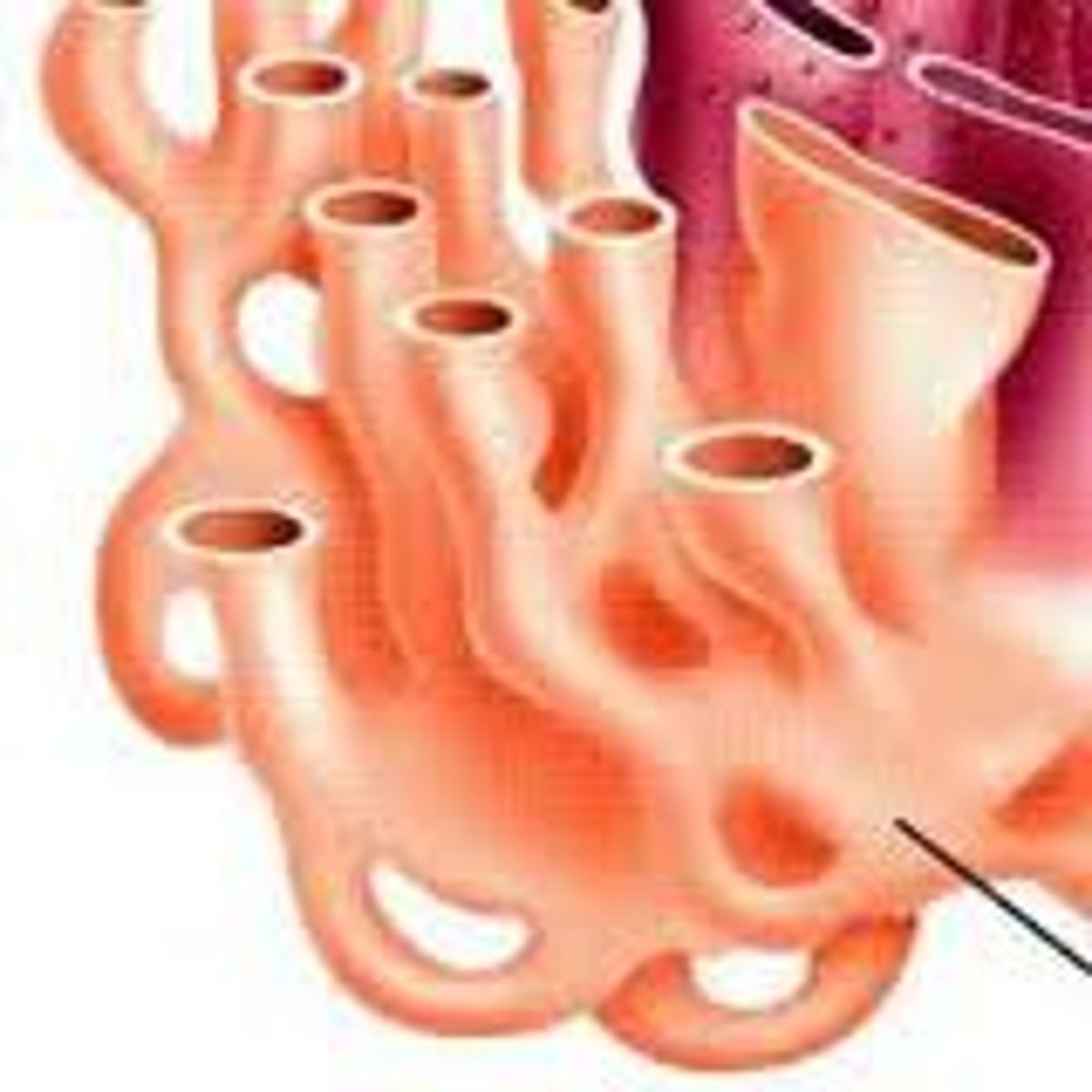
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
This membrane bound network of tubes and flattened sacs has ribosomes attached and is involved in protein synthesis
nuclear envelope
This double membrane controls what can move into and out of the nucleus
cytoskeleton
A network of long protein strands in the cytosol that helps support the cell
vacuole
Large vesicles that act as a storage place and are especially large in plant cells
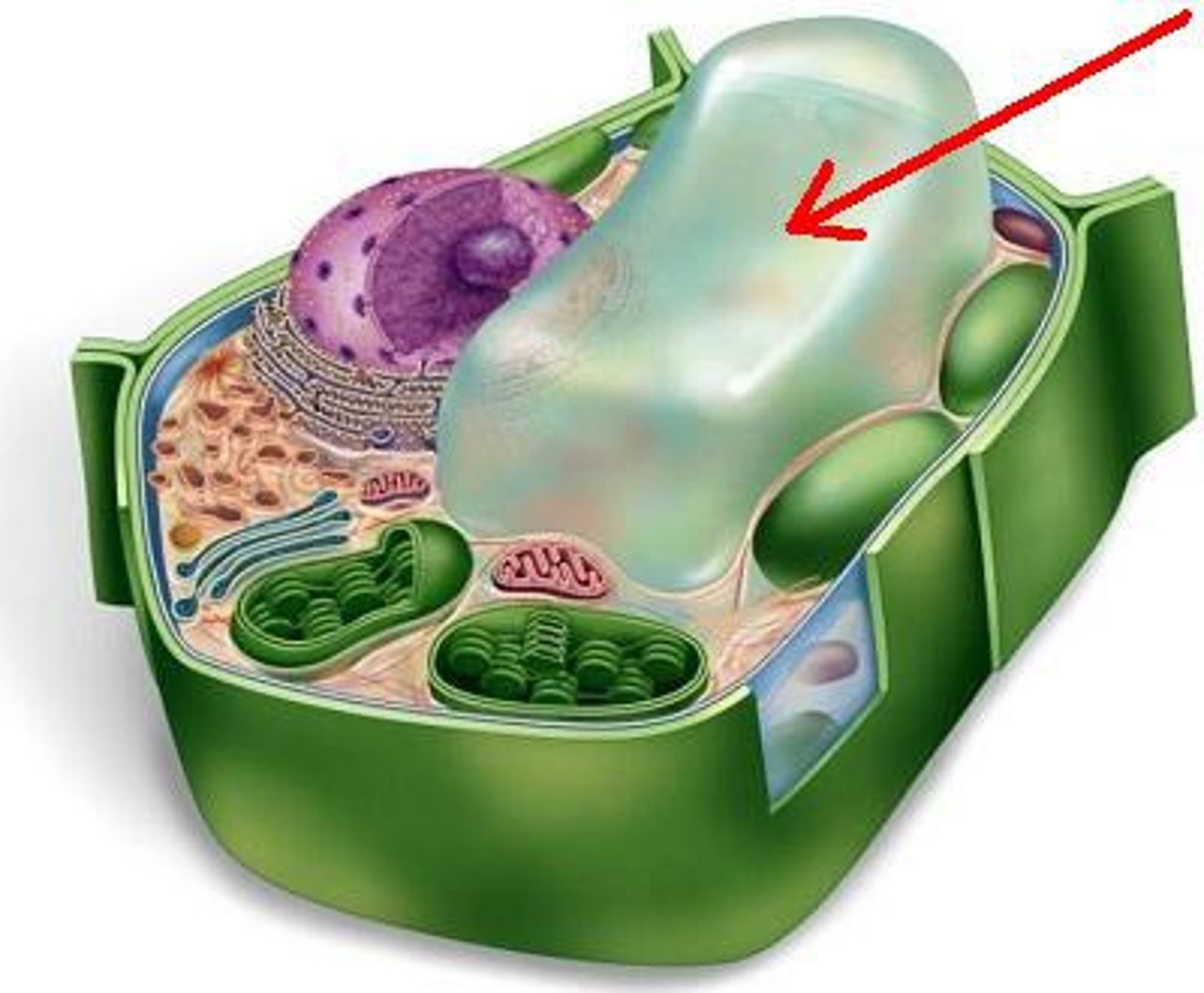
chloroplast
site of photosynthesis - light energy is converted to chemical energy in glucose
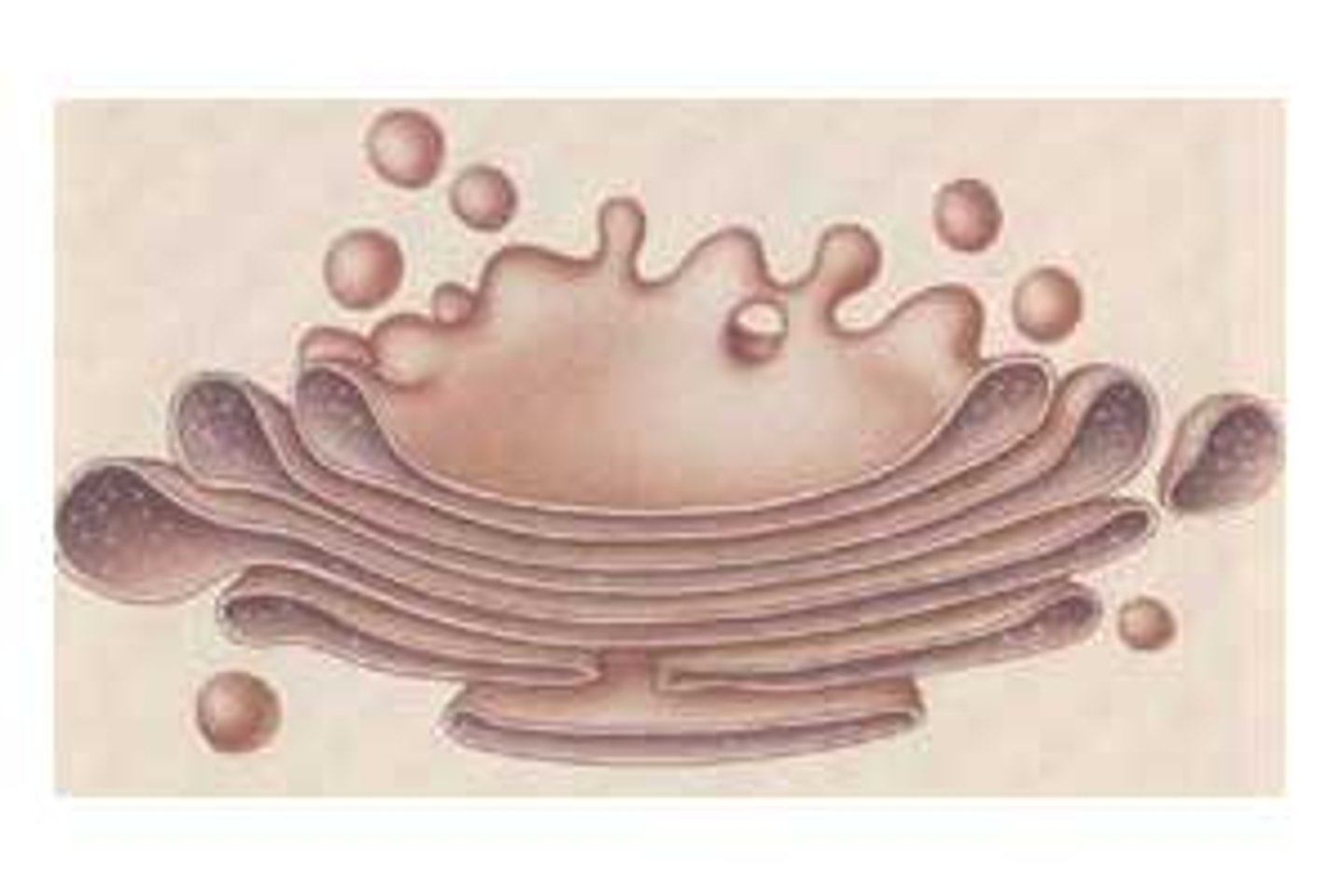
Golgi apparatus
This organelle receives products from the ER, modifies them and prepares them to be "shipped" off to other sites.