AP Micro - Unit 4
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
imperfect competition generalizations
price > MC
firms must lower P to sell additional units
there will be profit
Output lower than ATC minimum (excess capacity, choosing to produce at the efficient point would hurt profits)
To sell more, price must be lowered
Barriers to entry
economics of scale (Coke, McDonalds, etc.)
difficult to compete
legal protection
patents (drugs are initially only sold by one firm)
licenses (stadiums only allow one beer vendor)
ownership or control of essential resources
One company acquires all the coal mines, diamond mines, etc.
pricing and other strategies
Microsoft secured early market dominance by giving away browser for free (killed netscape) and gave OS away to PC manufacturers and then offering Office subscriptions to new users
monopoly
most inefficient, on the way-side of the four market model
types
pure monopoly (has 100% of market share, produces all of one product)
near monopoly (has around 80% of market share)
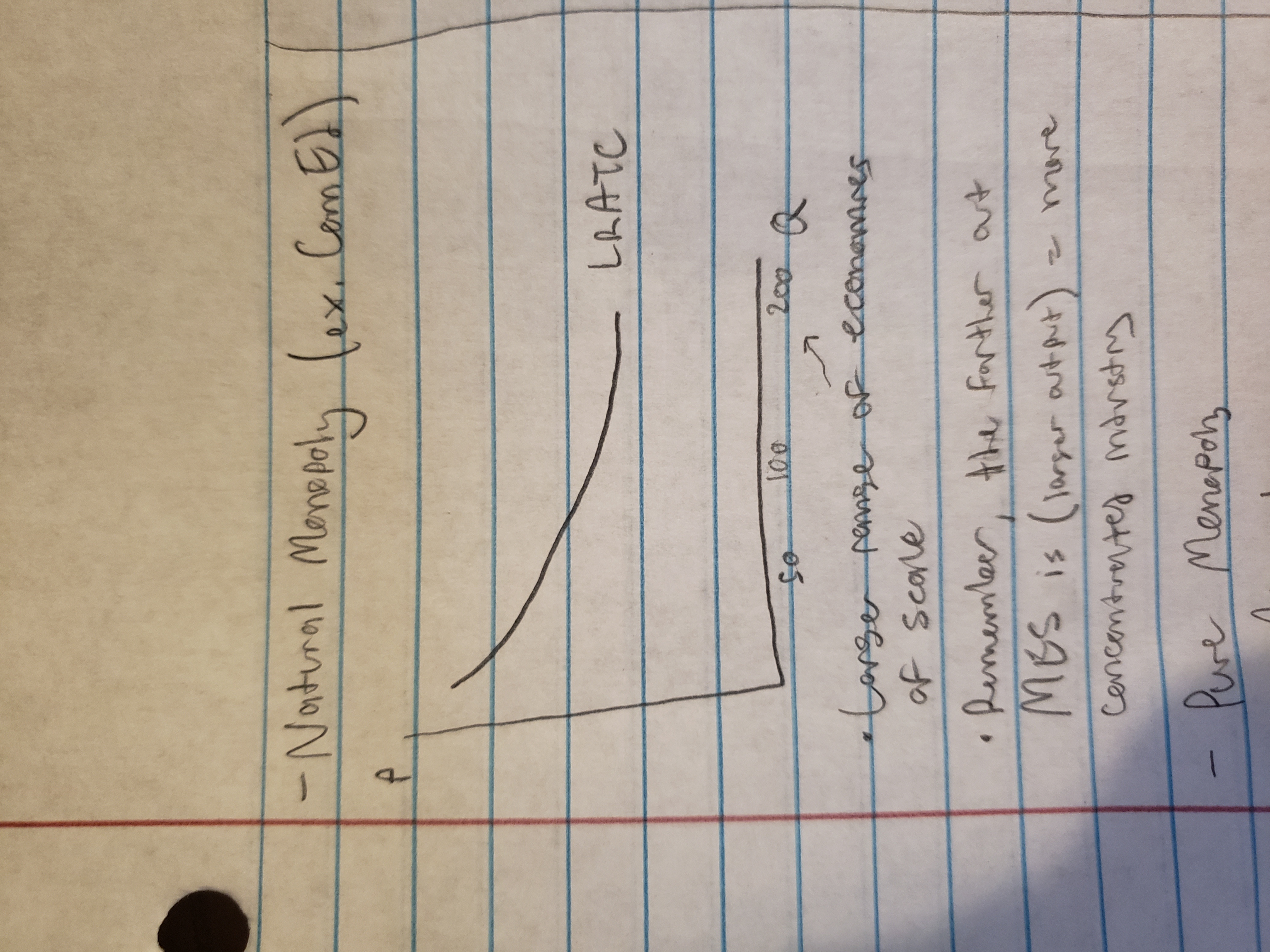
natural monopoly (where it makes sense for one firm to dominate, like electricity wherein infrastructure needed is so expansive and expensive only one firm can really do it) (however, these tend to be..see below)
regulated monopoly
natural monopoly (graph and facts)
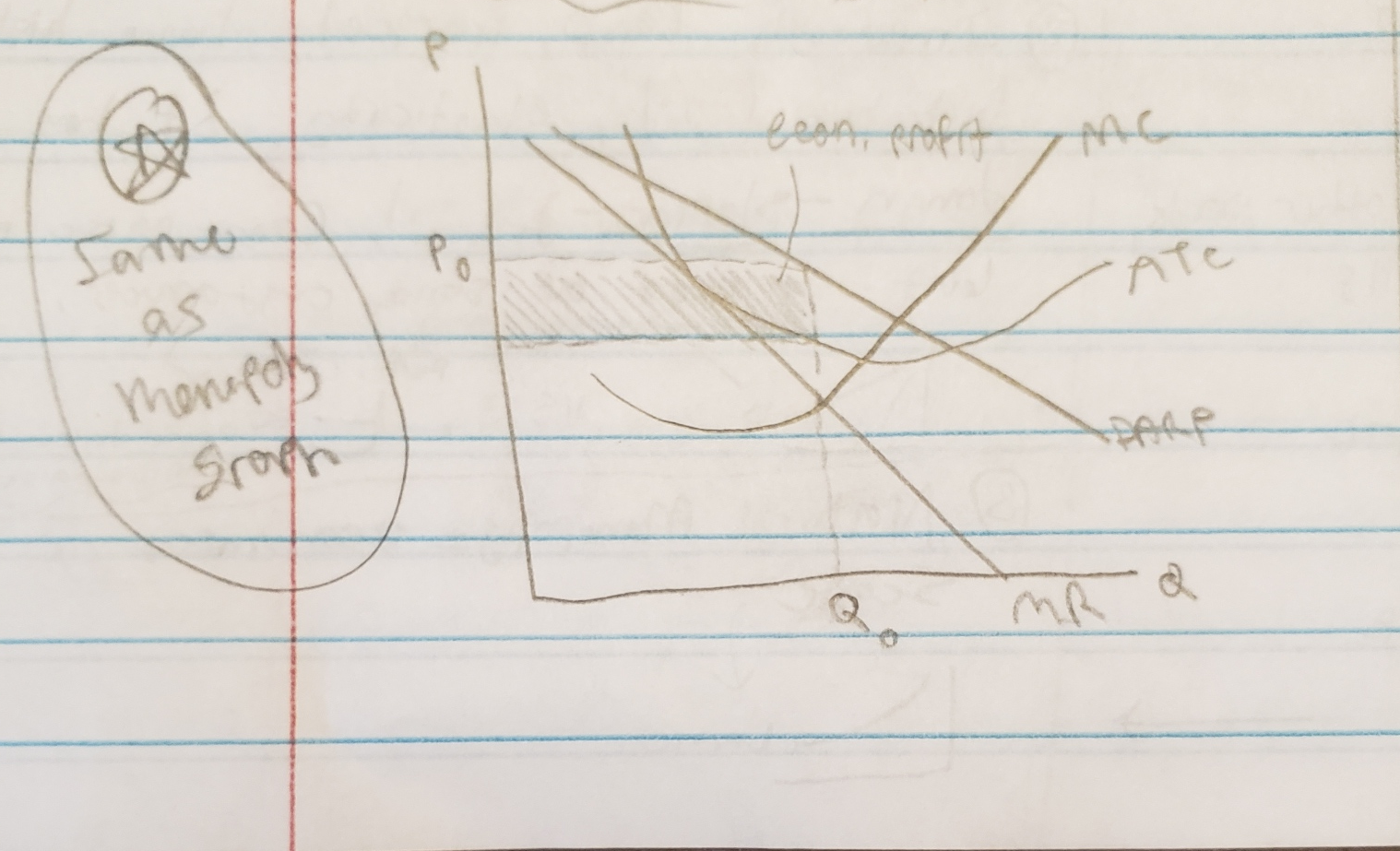
pure monopoly (assumptions, on a table, on a graph)

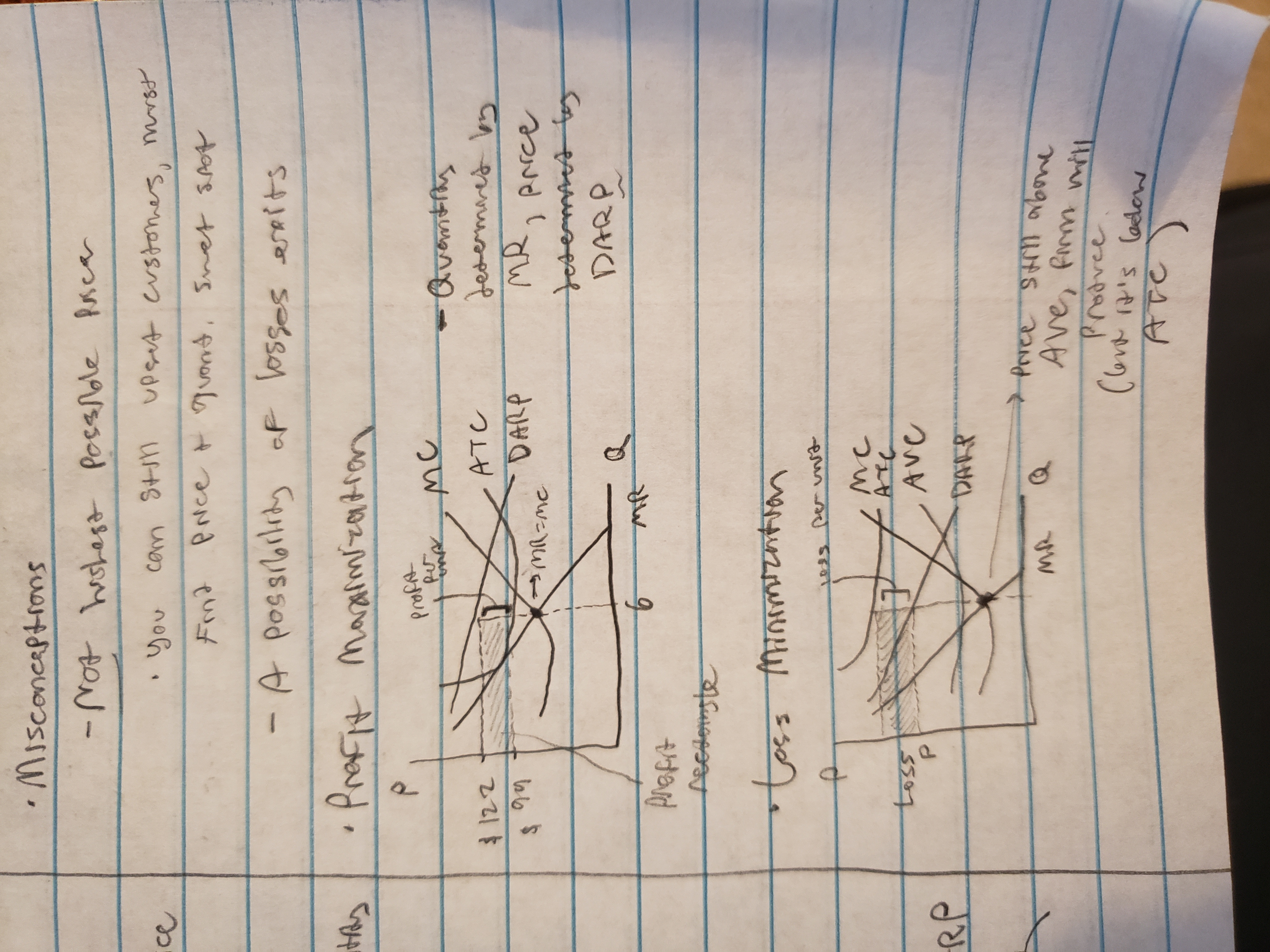
pure monopoly (explain MR and DARP slope relationship, where is profit max, why single graph, misconceptions)

profit maximization / loss minimization in a pure monopoly
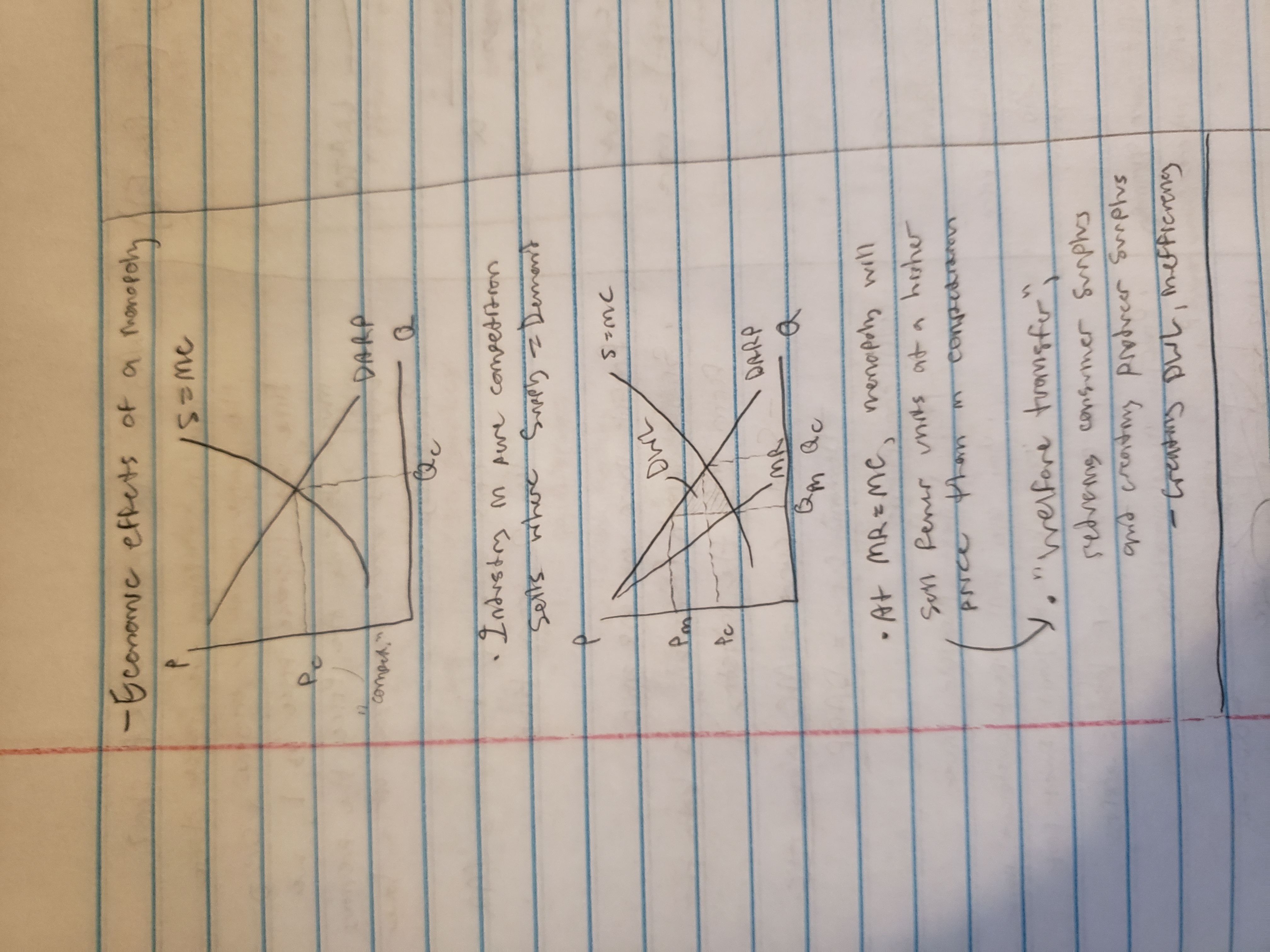
economic effects of monopoly
price discrimination (conditions and effects)
conditions
monopoly
market segregation (how are prices being differently assigned, by race? region? age? etc.)
No resale
Consequences
more profit
more output
price discrimination effects on a graph

monopolistic competition generalizations
large number of sellers
small market shares
no collusion
independent action
easy entry and exit
advertising
differentiated products (product A no longer the same across all firms, can differ in…)
service - how is good served
location - where is it served (think good gas station locations)
brand names, packaging
some control over price
demand is highly elastic (many sellers)
monopolistic competition on a graph
new competition creates other goods, demand for your good falls »
with econ. losses, firms will exit market, less goods, so demand for your good increases »
normal profit only, econ. profit = 0
long-run equilibrium for monopolistic competition

long-run equilibrium for monopolistic competition
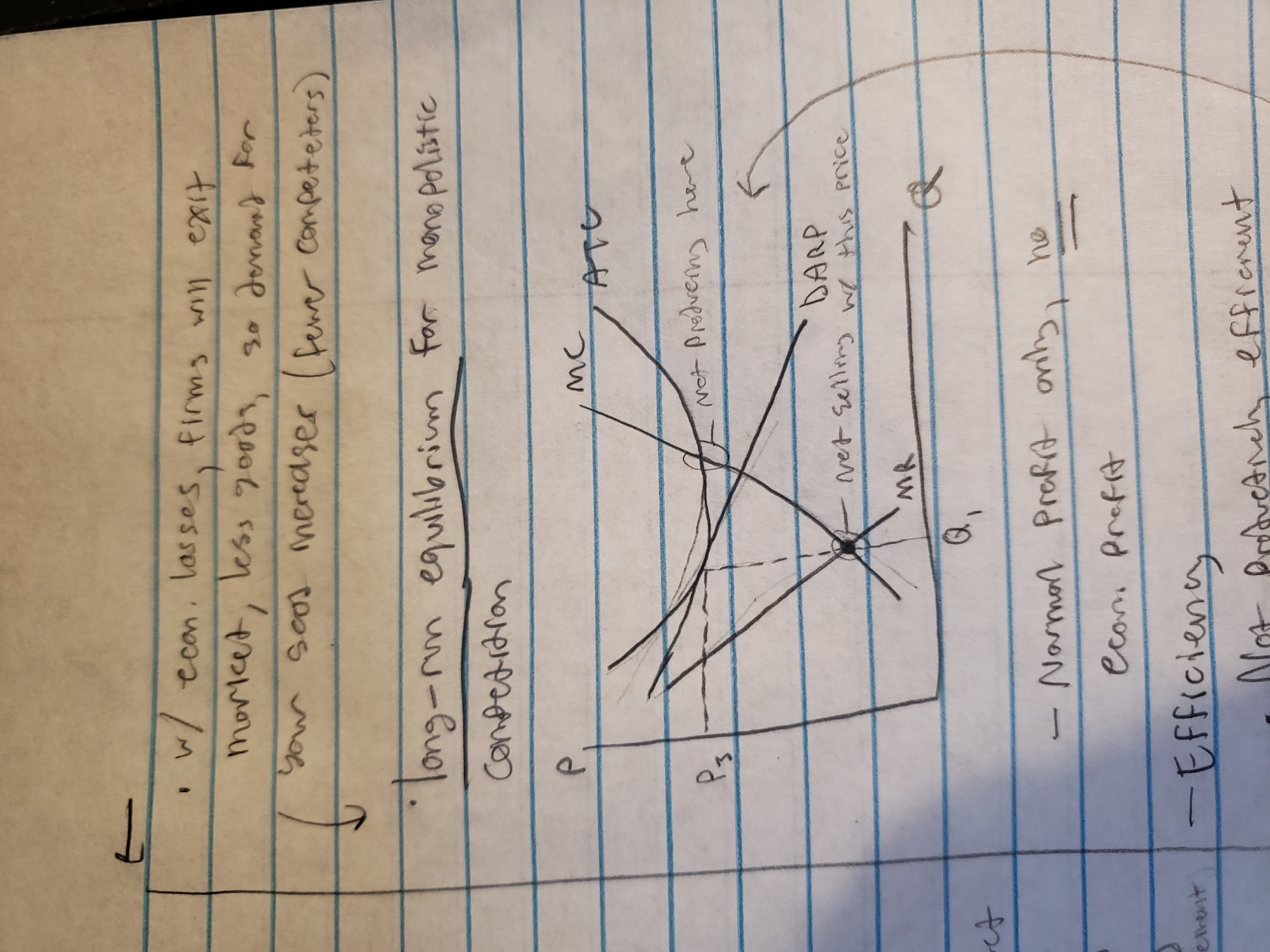
efficiency in monopolistic competition
not productively efficient, economic profit does = 0 but P is not at minimum ATC
not allocatively efficient, P does not equal MC (excess capacity, producing less than we should)
oligopoly
control over price
mutual interdependence
strategic behavior
price wars (slashing prices at a loss to force competitors out)
entry barriers
economies of scale
control of resources
not productively or allocatively efficient
collusive oligopoly
if a few firms face similar demand and costs they will act like a monopoly
they will split monopoly profits
types of collusion in oligopolies
overt collusion (public)
cartels, OPEC
covert collusion
illegal in USA
tacit understandings (“gentlemen’s agreements”)
obstacles to collusion in oligopolies
demand or cost differences
firms can only act together if they have similar DARP and MC lines (monopoly profits shared equally in this case, see graph)
large number of firms (harder to get everyone on the same page)
cheating (double-crossing deals)
potential entry
anti-trust laws
game theory
(refer to Payoff Matrix)
(A) = greatest combined profit
Independent actions stimulate response, if either cheats (B) and (C) are possible
if both cheat, gravitate to (D), Worst Case
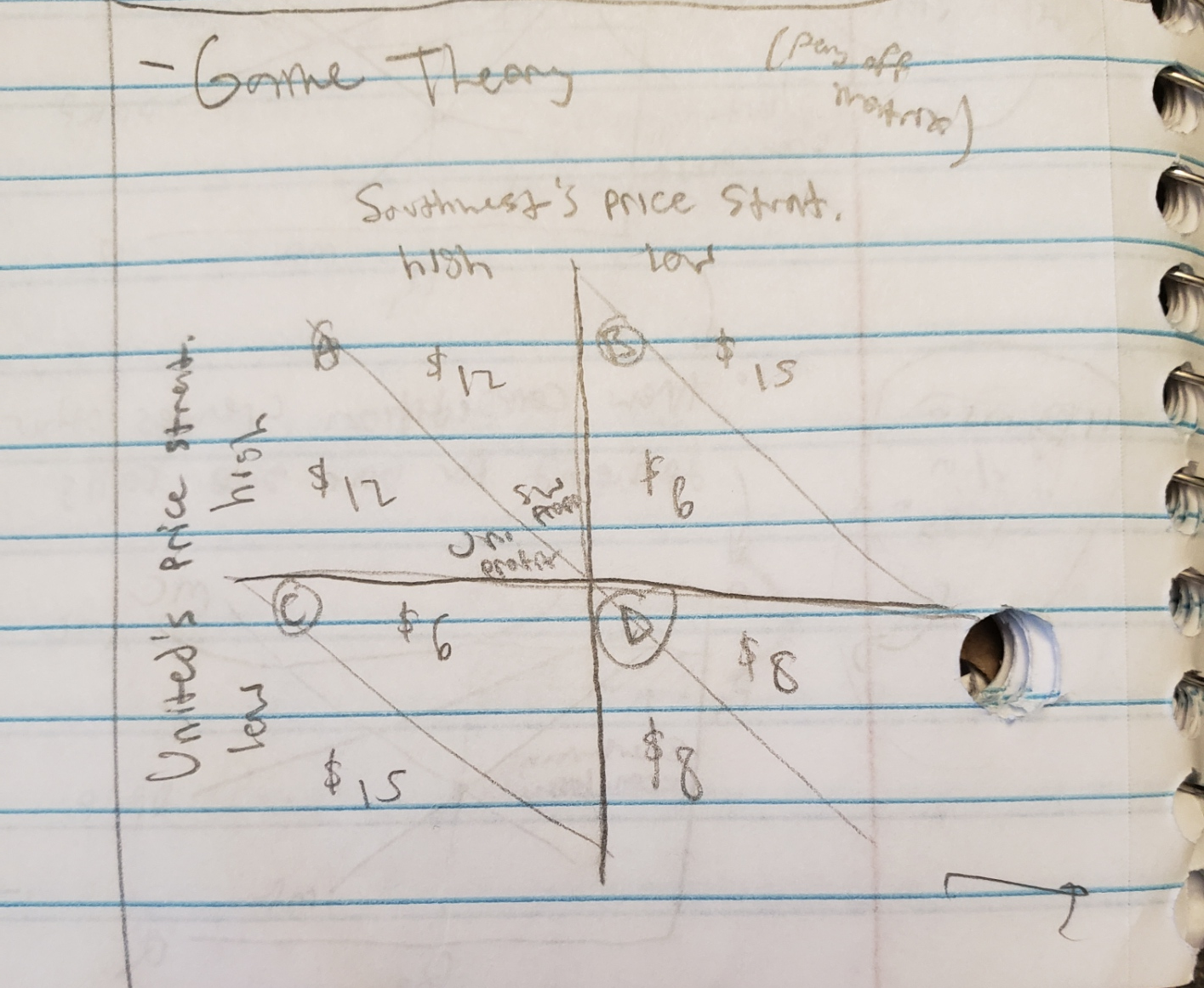
game theory: dominant strategy
when picking one option always yields high profits
Ex) United going low is always higher regardless of Southwest’s decision (12 v 15, 6 v 8)
However, notice that Southwest’s dom. strat. is low too!
thus, if both sides pick dom. strat., they will reach Nash Equilibrium (D), only way to reach (A) is to successfully collude (but incentive to cheat is very real..)
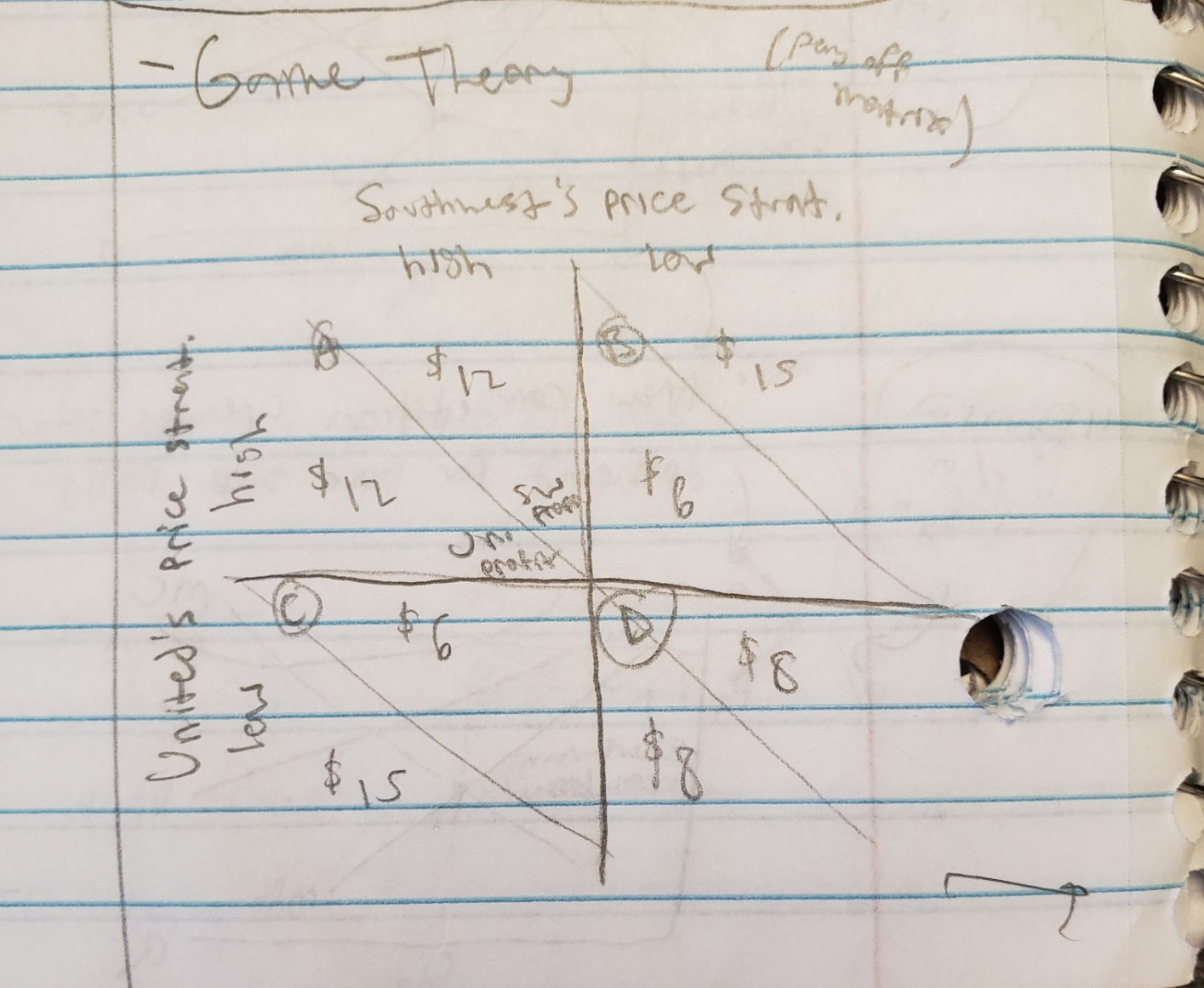
nash equilibrium
point on the payoff matrix wherein no player would gain by changing their strategy (keeping other players’ strategies constant)