Life is Cellular Quiz
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
This part of the cell is underneath the cell wall in plant cells and the outside layer of animal cells.
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Cell Membrane (Plasma Membrane)
It controls what goes in and out of the cells
This part of the cell is the outermost layer of the plant cell and animals do not have this
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Cell Wall
It provides structural support and protection
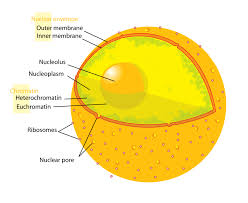
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and acts as the control center for all cellular activities, such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction
What is the part of the cell that surrounds the nucleus
What part of the cell is that and what is its function?
The Nuclear membrane
to act as a barrier that keeps the nucleus from the cytoplasm
What is the structure inside of the eukaryotic cells
What part of the cell is that and what is its function
Nucleolus
Primary responsible for carrying out the process of synthesizing ribosomal RNA and assembling it with proteins to form ribosomal subunits
What is the fluid that is found in both cells
What part of cell is that and what is its function
Cytoplasm
It keeps all the organelles in place in the cell
What are all the little dots found in both cells and also found on the rough ER
What part of the cell is that and what is its function?
Ribosomes
To synthesis proteins by translating messenger RNA into chains of amino acids

Kind of looks like sea coral and has lots of interconnecting tubes. Close to the nucleus
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Smooth ER
synthesis of lipids and detoxifies harmful substances like drugs and poisons
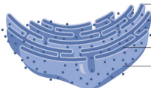
Has ribosomes attached to it and it is close to the nucleus
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Rough ER
Responsible for folding, synthesizing, modifying, and transporting proteins
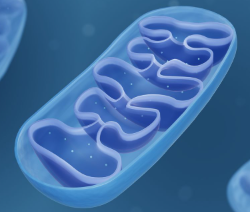
What is known as the powerhouse of the cell
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Mitochondria
Produces energy in the form of ATP by breaking down nutrients from food
Both plant and animal cells have this but plants have one big one, while animals have many smaller ones
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Vacuole
Stores water, nutrients, and waste products
Only found in animal cells and sometimes they fuse together with the vacuole
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Lysosomes
They are the cells digestion system, because they break down waste and foreign invaders like bacteria (basically a recycling center)
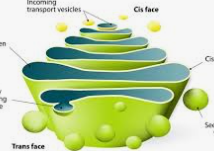
Kind of look like a sad stack of pancakes and they’re the post office of the cell
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Golgi Body/Apparatus
modify, sort, and package proteins and lipids from the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) for transport to their final destinations
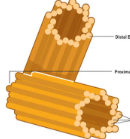
cylindrical organelles found in the cytoplasm animal cells, typically arranged in pairs within a region called the centrosome
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Centrioles
organize microtubules and are essential for cell division and the formation of cilia and flagella
Only found in plant cells and has green coloring
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Chloroplast
Responsible for photosynthesis
Kind of looks like loose fibers or hair in the cell
What part of the cell is this and what is its function
Cytoskeleton
providing structural support, maintaining cell shape, enabling cell movement, and organizing cellular contents
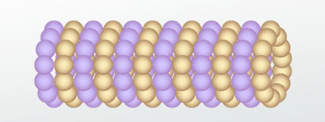
rigid, hollow tubes, and a key component of the cytoskeleton
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Microtubules
Maintain cell shape, organize cells interior, facilitates cell division, and provides tracks for intracellular transport

Thin protein filaments and main part in cell’s cytoskeleton
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Microfilaments
important for cell’s motility, maintain shape, cellular contractility, and cytokinesis

the complex of DNA and proteins that forms chromosomes in the nucleus (The pasta looking stuff in the nucleus)
what part of the cell is this and what i its function
Chromatin
tightly package DNA to fit inside the cell nucleus, regulate gene expression, and enable essential DNA processes like replication, repair, and recombination

thread-like structures found in the nucleus of cells that are made of DNA tightly coiled around proteins
What part of the cell is this and what is its function?
Chromosome
storing and transmitting genetic information, and controlling cell division and growth
Robert Hooke
observed a thin slice of cork (Plant material) called what he ended up seeing cells
Leeuwenhoek
observed living organism in pond water under a microscope
Schleiden
concluded plants have cells in 1839
Schwann
concluded animals are made of cells in 1839
Virchow
In 1855 he concluded that new cells can only come from pre-existing cells
What are the 3 parts of the cell theory
Cells are the basic units of life
All organism are made of one or more cells
All cells come from other cells by cell reproduction
Prokaryotes (Pro: no)
Cells do NOT contain nuclei or cell bound organelles (little organs)
Smaller and simpler than eukaryotes
Have genetic material (DNA)
Carry out same activities as eukaryotes (reproduce, move, respond to environment
Examples: Bacteria
Eukaryotes (Eu: do)
Cells that DO contain a nucleus
Larger and more complex than prokaryotes
Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists (Amoeba, paramecium)
What two organelles do plant cells have that animal cells do not?
Cell Wall and chloroplasts
Cell membrane is _____ _________
semi preamble
N ——> R ——→ P
Nucleolus makes ribosomes which then makes proteins
Cell wall has a lipid ____ ____
Lipid bi layer (heads like water and tails hate it)
Describe what an “e” looks like under the microscope compared to the naked eye
Its upside down under a microscope
How much does the ocular lens in our microscopes magnify an image?
10x
What units do we use when measuring with a microscope?
millimeter??
diaphragm
regulates the amount of light going through the stage
nosepiece
revolves to allow changing various objects
objectives
High power objectives provides a magnification of 40x low power objectives provides a magnification of 10x
coarse adjustment knob
Moves stage up and down approximately to correct distance
fine adjustment knob
Permits finer focusing by moving the stage in smaller increments
ocular
Contains lens to increase magnification usually 10x
What is resolving power of a microscope?
Its ability to distinguish between two closely spaced objects as separate entities
How to view specimens on the microscope
place the slide on the stage, turn on the light, and position the lowest power objective lens over the specimen. Look through the eyepiece and use the coarse adjustment knob to slowly move the stage down until the image comes into focus, then use the fine adjustment knob for a sharper image.
Calculate the total magnification
multiply the magnification of the objective lens by the magnification of the eyepiece (ocular) lens (eyepiece is 10x)
Calculate the diameter of the field of view
Field number/ magnification
Determine number of cells in a specimen at different magnifications when
given only 1 field of view
first determine the diameter of the field of view at each magnification, then estimate the number of cells that fit across the diameter
Specimen size
divide the field of view diameter by the estimated number of specimens that fit across it
Know the formula for calculating the diameter of the high power field of
view. And be able to use it
High-Power Diameter = (Low-Power Magnification / High-Power Magnification) x Low-Power Diameter
If a student views 10 bacteria cells under high power (40x), how many would
you expect the student to see under low power (10x)?
160