bio ch 7 🧬🔬
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
microscope
the invention of the _______ made cell discovery possible
Cells
Robert Hooke used this name to refer to the tiny chambers he saw in the microscope
cell theory
all living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic units of life, and all cells come from other cells
fluorescent dyes
these help scientists see the movement of compounds and structures in living cells
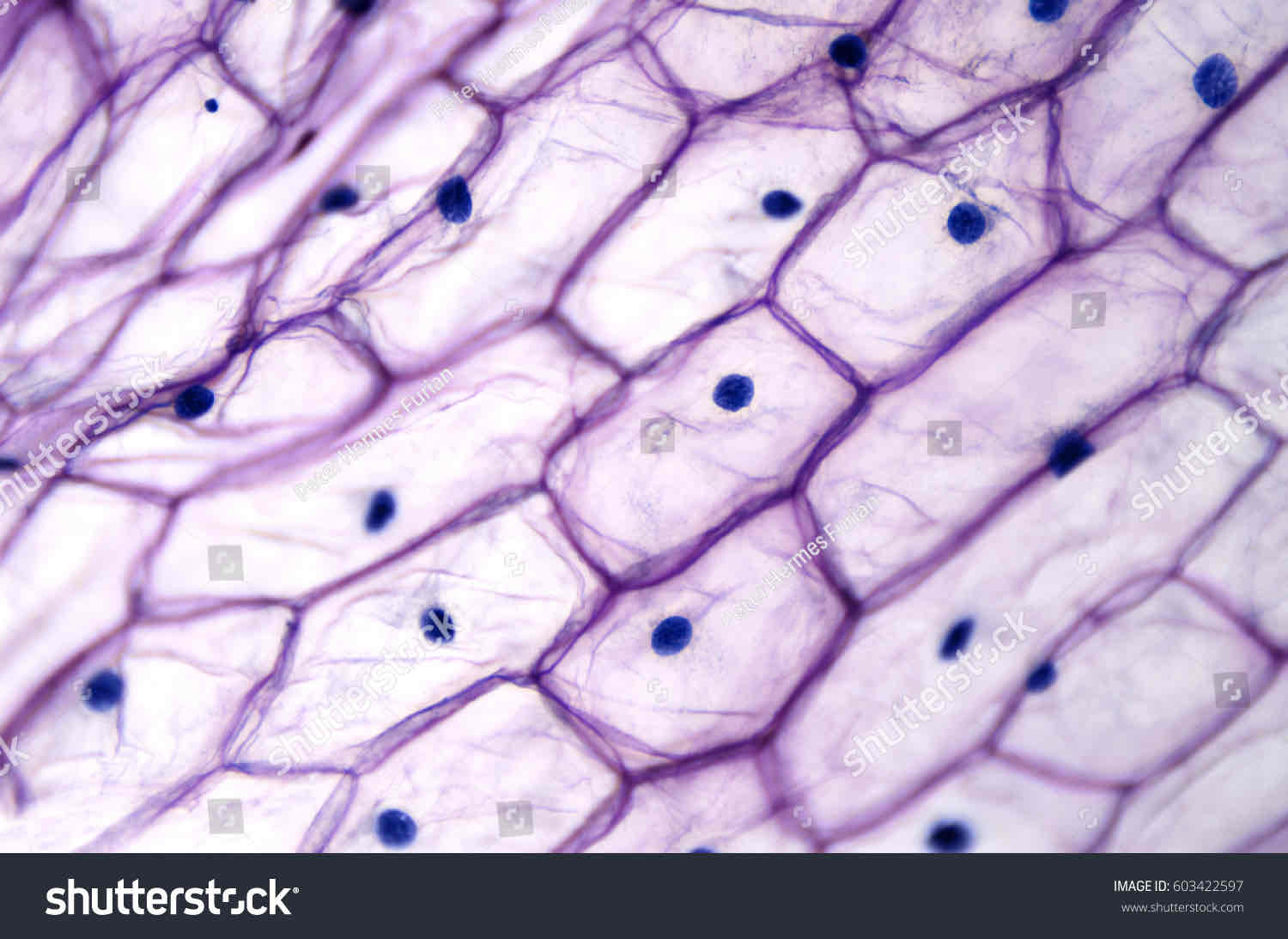
light microscope
microscope w/ image formed by 2 lenses focusing light
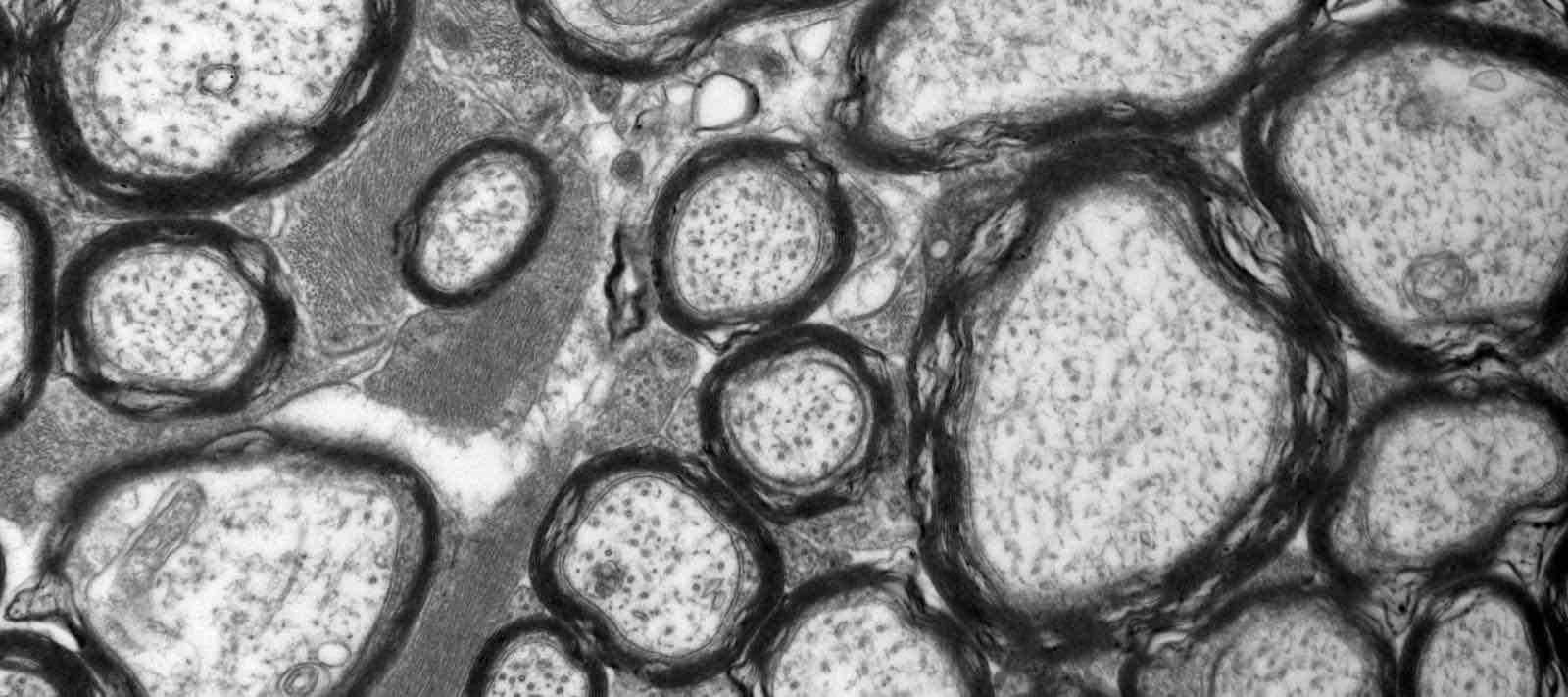
transmission electron microscope
microscope w/ image formed by beams of electrons passing through a thin sample
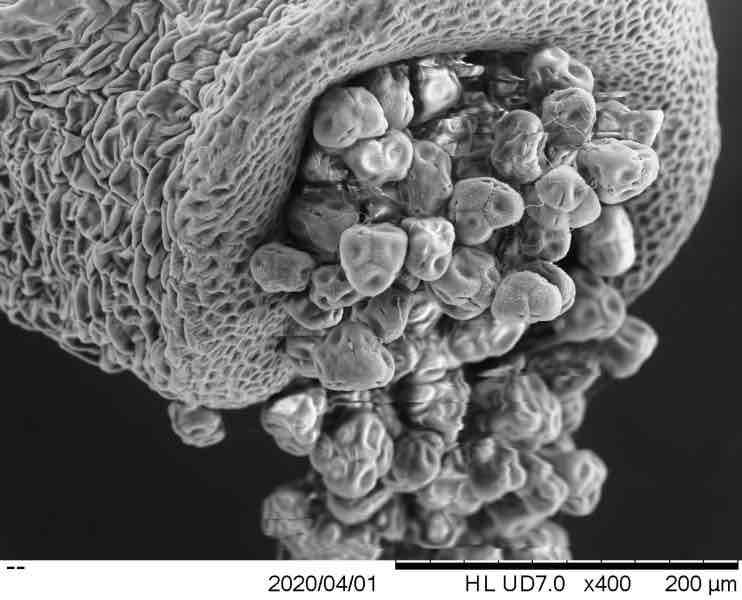
scanning electron microscope
microscope w/ beam of electrons scanning over the surface of a sample
cell membrane
consists of a phospholipid bilayer and controls what enters and leaves the cell
hydrophilic
the heads of the phospholipid bilayer are ________
hydrophobic
the tails of the phospholipid bilayer are _______
prokaryotic cells
cells that do not contain a membrane enclosed nucleus; typically bacteria and archea are composed of this type of cell
eukaryotic cells
cell that contains a membrane enclosed nucleus; describes most cells, except for bacteria and archea
organelle
little organs that are only found in eukaryotic cells
nucleus and ribosomes
organelles involved in the genetic control of the cell
ER, Golgi apparatus, lysosomes, vacuoles, and perixomes
organelles involved in the manufacture, distribution, and breakdown of molecules
mitochondria and chloroplasts
organelles involved in energy processing
cytoskeleton, cell membrane, and cell wall
organelles that provide the cell with structural support, movement, and communication
cell wall, plastics, central vacuole
only plant cells contain these organelles
nucleus
contains most of the cells DNA, directs protein synthesis
nucleolus
makes ribosomes
chromosomes
When a cell is ready to divide the DNA within the cell's nucleus transforms into which form of DNA?
nuclear envelope
double membrane of nucleus that has pores that allow molecules to go in and out of the nucleus
ribosomes
once they leave the nucleus, they are responsible for making proteins
free ribosomes
ribosomes that are suspended in the cytoplasm and they help make proteins to function within the cytoplasm
bound ribosomes
ribosomes attached to the ER and they make proteins that are packed in certain organelles or exported from the cell
smooth ER
responsible for making phospholipids and steroids
rough ER
is the site of proteins that will be transported out of the cell and has attached ribosomes
Golgi apparatus
receives proteins from ER and finishes and sorts them
lysosomes
membranous sac with enzymes from golgi apparatus to help digestion of food particles engulfed by the cell
vacuoles
stores water, food, and nutrients
contractile vacuole
helps to eliminate water
nucleoid
a dense region of DNA in a prokaryotic cell
flagella
a tail structure on a cell
chromatin
dna that needs to be read
peroxisomes
neutralizes harmful toxins so that they do not cause damage in the cells
mitochondria
enclosed by two membranes, conducts cellular respiration and makes all the ATP molecules which provides energy for the cell
vesicles
small membraned "sacks" transport proteins from the ER to the Golgi apparatus
cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, organism
correct order of organization from simplest to most complex
homeostasis
An organism's ability to maintain a balanced internal environment
osmosis
the diffusion of water across a membrane that doesn’t require energy
passive transport
moves from high to low concentration, doesn’t require energy
active transport
goes from low to high concentration requires energy in the form of ATP
isotonic
equal concentration, cell volume won’t react
hypotonic
below level concentration, cell will expand
hypertonic
above level concentration, cell will shrink
osmoregation
the control of water balance
facilitated diffusion
a form of diffusion that gets help from the concentration gradient and doesn’t need energy
exocytosis
used to export bulky molecules such as proteins or polysaccharides
endocytosis
used to import substances useful to the livelihood of the cell, has 2 types of it
phagocytosis
cellular “eating” of a particle by wrapping cell membrane around it to form a vacuole
pinocytosis
cellular “drinking” where a cell takes fluid and dissolved solutes into a vesicle