carina government int.
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
36 Terms
why does the government intervene into markets? (7)
1 - earn government revenue; from indirect taxes - the lower the PED of a good the great the amount of tax revenue earned
2 - provide support to firms; financial assistance to small firms so that they can become well established and compete with larger firms, to encourage the growth of firms in industries the government wants to grow (eg: wind and solar power)
3 - provide support to households on low incomes
4 - influence levels of productions of firms
5 - influence levels of consumptions of households/consumers
6 - correct market failure
7 - promote equity
why would the government correct market failure?
to achieve allocative efficiency
what is one way for the government to promote equity?
redistribution of income
what markets does the government intervene in? (10)
1 - healthcare, 2 - weapons, 3- NGOs, 4- housing, 5- roads, 6- alcohol, 7 - cigarettes, 8-public transport, 9 - oil, 10- education
how does the government intervene into markets? (6)
1- price controls, 2- indirect taxes, 3- subsidies, 4- government provisions, 5- regulations, 6- provision of information
price controls definition
The setting of maximum or minimum prices by the govt. or a firm so that prices are unable to adjust their equilibrium level resulting in market disequilibrium. They force a situation of persisting market disequilibrium, causing a shortage.
price ceilings definition
maximum prices set by the government below the equilibrium price
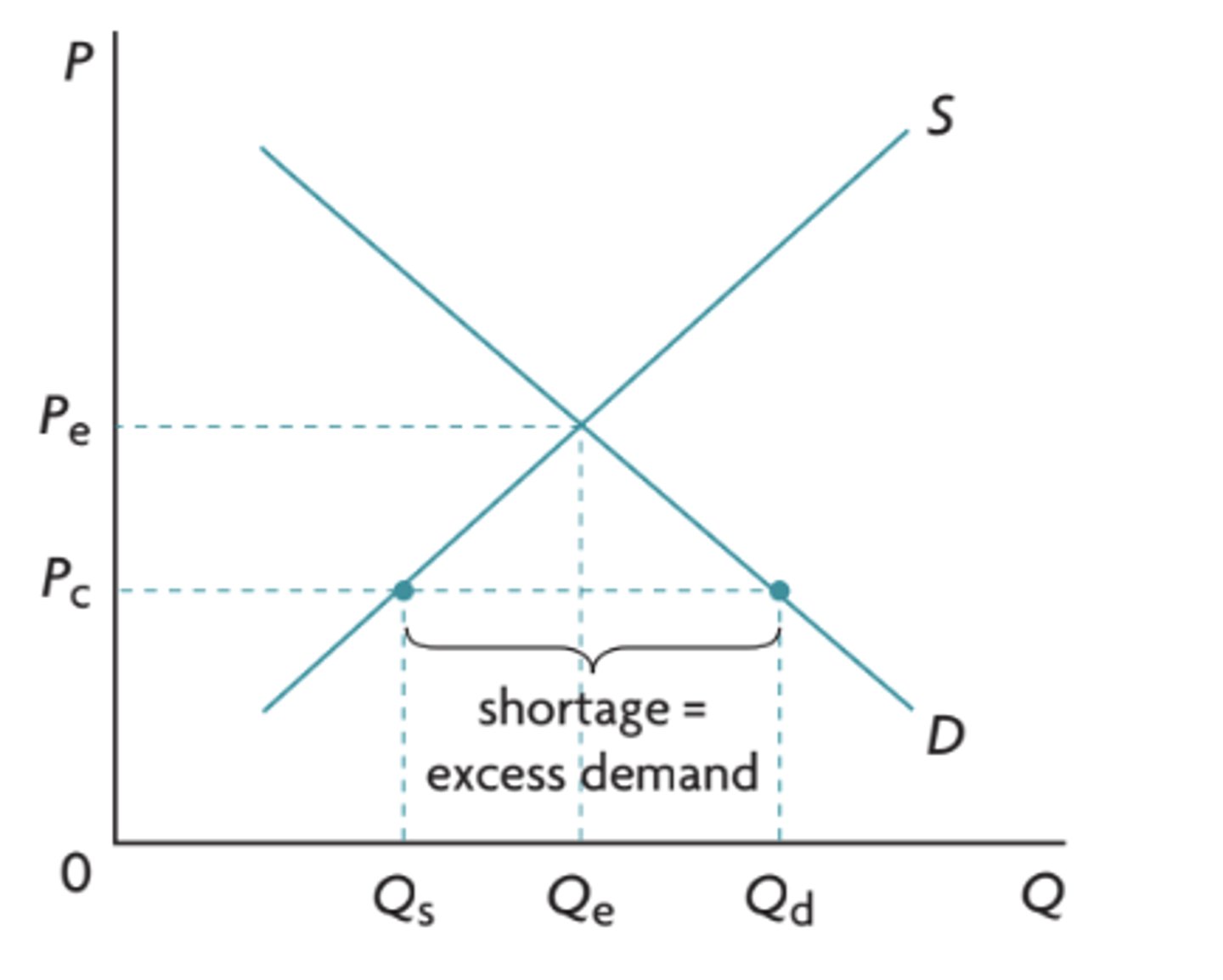
why does the government set price ceilings?
in order to make certain goods/services affordable for people on low incomes
how will a price ceiling benefit/disadvantage consumers?
it will benefit those consumers who were able to receive the good but disadvantage those who were unable due to the shortage.
how will a price ceiling affect producers?
producers are at a disadvantage as it lowers the price they can sell at which thus lowers the quantity they are willing to supply at
how do price ceilings affect consumer and producer surplus?
CS increases, PS decreases,
welfare loss definition
represents the social surplus or welfare benefits that are lost to society because resources are not allocated efficiently.
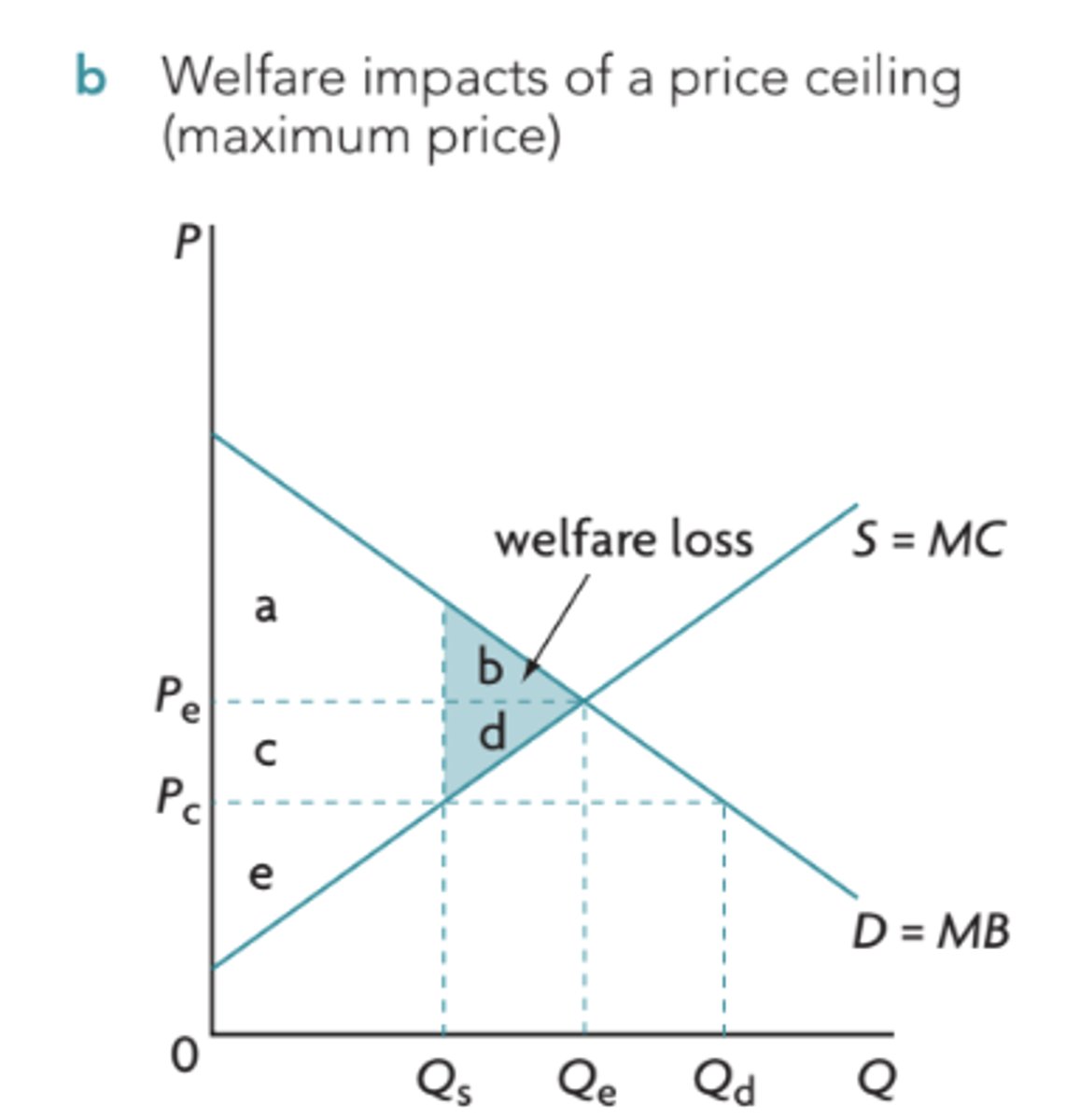
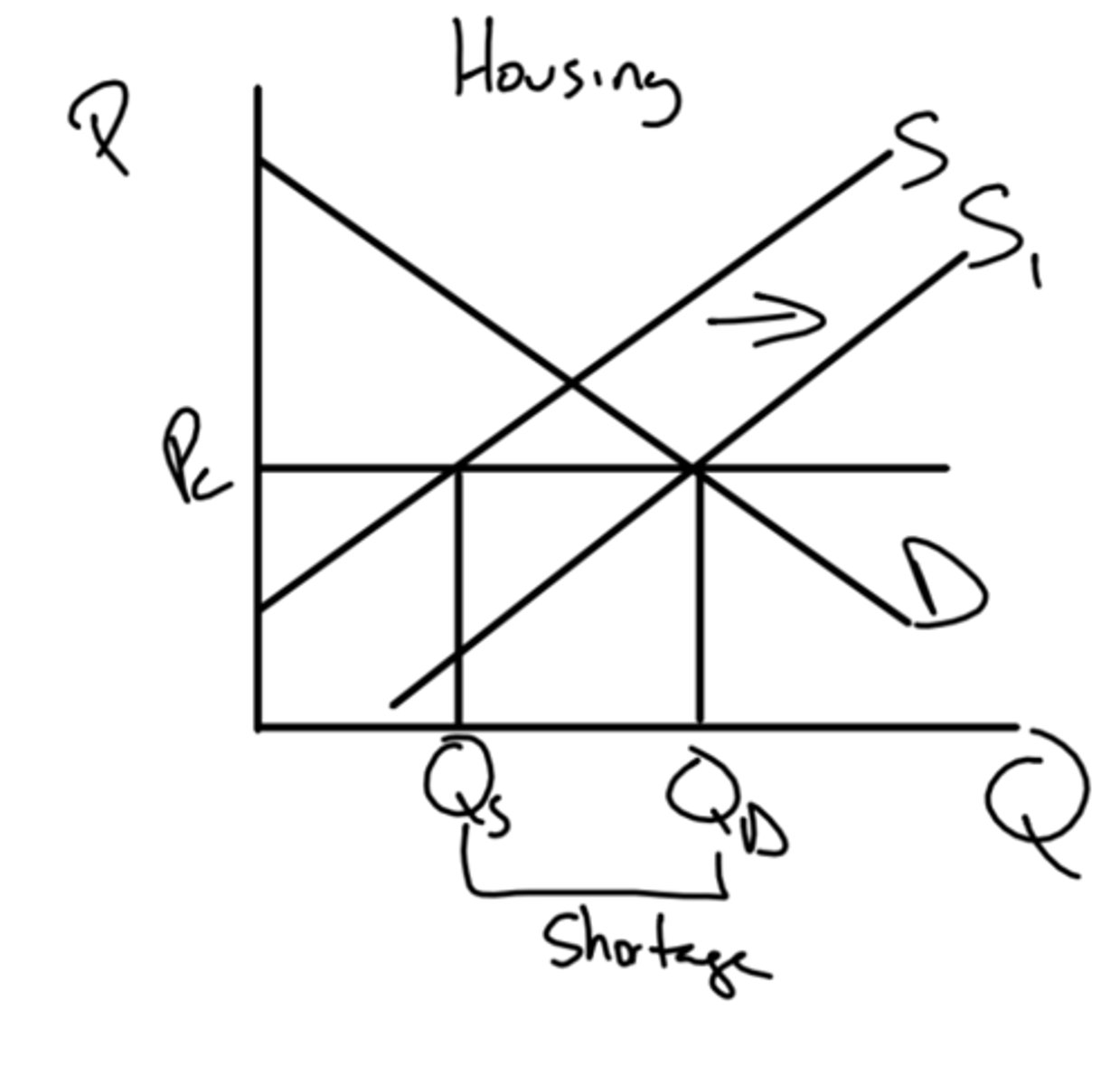
if the government wanted to get rid of the shortage created by the ceiling what policy would they enact?
they could implement a subsidy
what are some examples of price ceilings? (2)
1- rent controls, 2- food price controls
what are some consequences of rent controls? (5)
1- shortages of housing, 2- more affordable for low income households, 3- fall in total revenue for landlords, 4- decreases incentives for landlords to maintain housing 5- could lead to underground markets
price floor definition
minimum prices set by the government above the equilibrium price
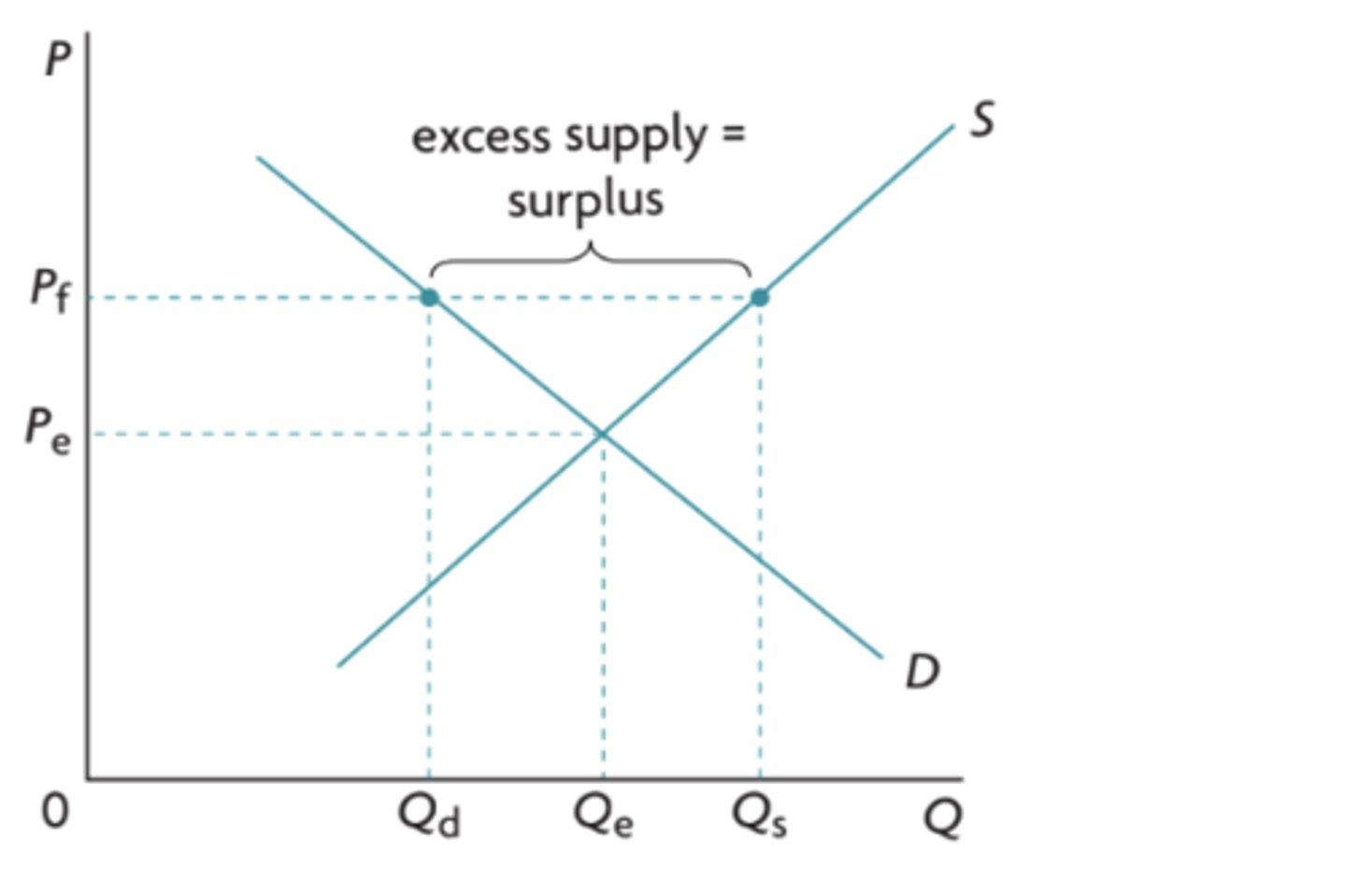
what are the effects of price floors?
they cause surpluses
how do price floors affect consumer and producer surplus?
CS decrease, PS increases
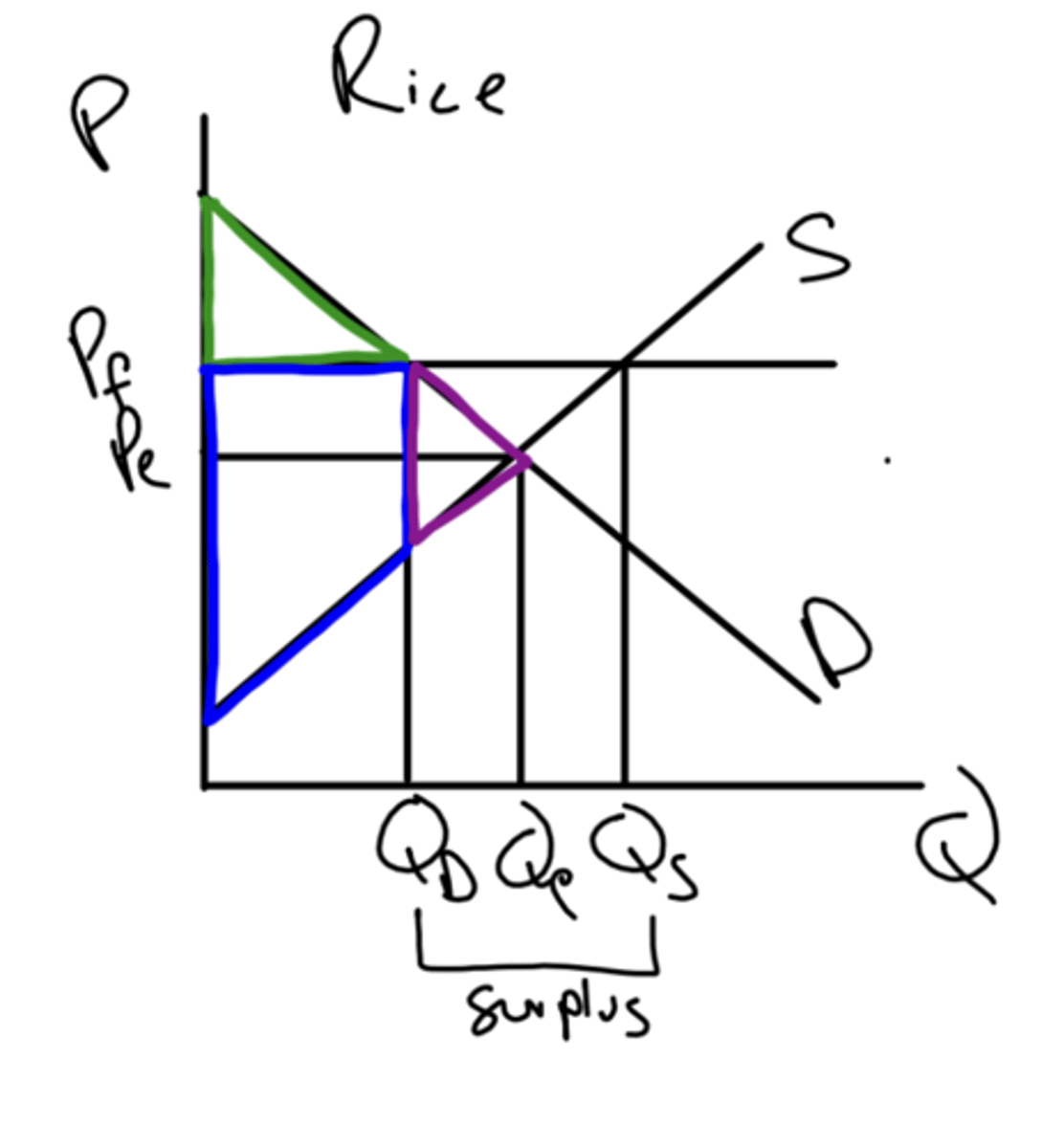
how will a price floor benefit/disadvantage producers?
it will benefit producers that are able to sell their goods but will disadvantage those who cannot
how will a price floor affect consumers?
it will disadvantage them as they now pay a higher price but consume less quantity.
how can governments get rid of the surplus as a result from price floors?
the government can buy up the surplus and then either, store it, send it as foreign aid, or export it
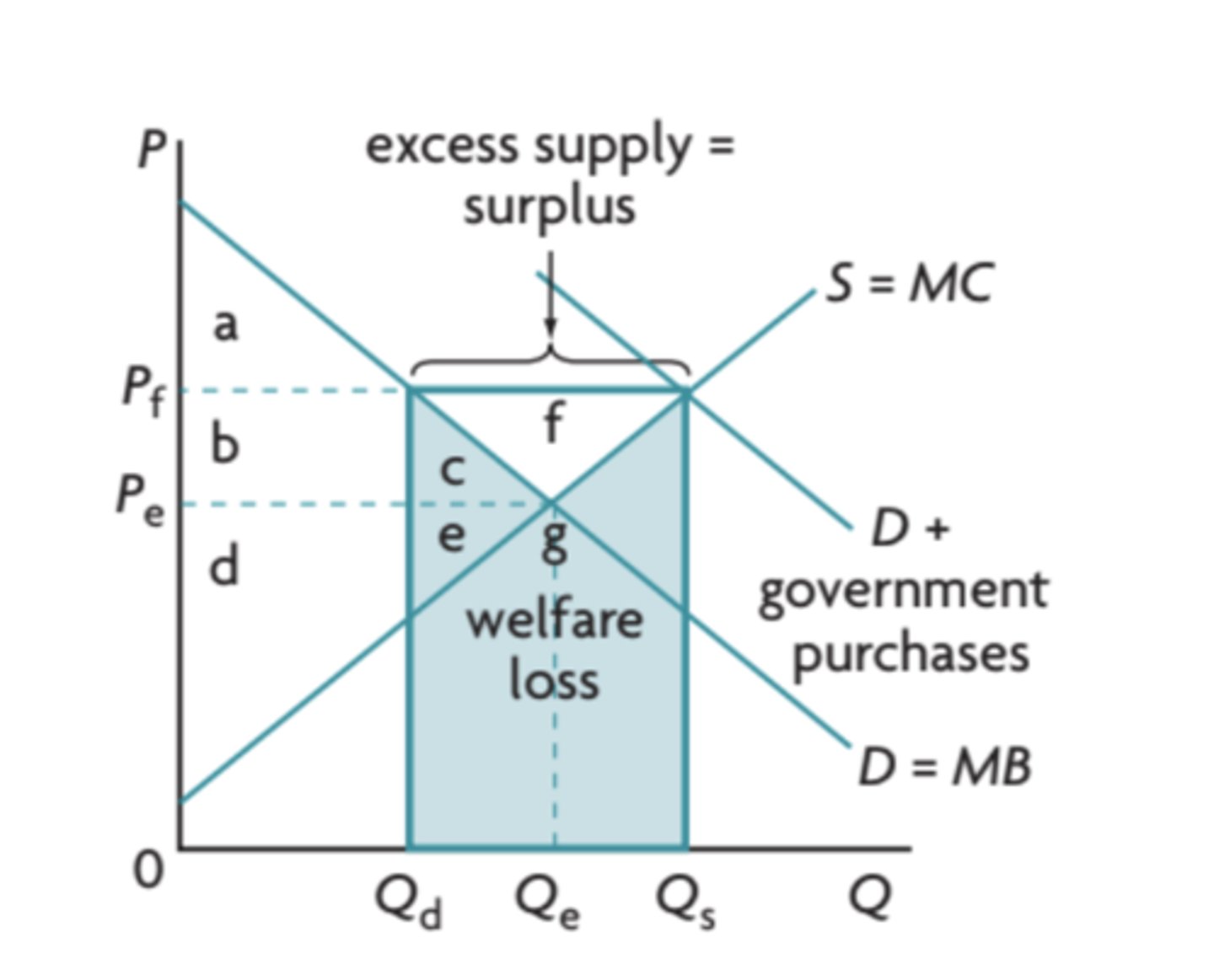
indirect taxes definition
payments made to the government which are partly paid by consumers but are paid to the government by producers.
what are the two types of indirect taxes?
excise taxes and value added taxes
excise taxes definition
taxes that are placed on a specific good/service such as alcohol or tobacco.
VAT definition
taxes added onto the spending of most goods/services
what are the two types of indirect excise taxes?
specific tax and an ad-valorem tax
specific tax definition
a per-unit amount added to a good/service
ad-valorem tax definition
a fixed percentage of the price of the good/service
how will indirect taxes affect the supply curve?
the supply curve will shift to the left (decrease supply, increase prices)
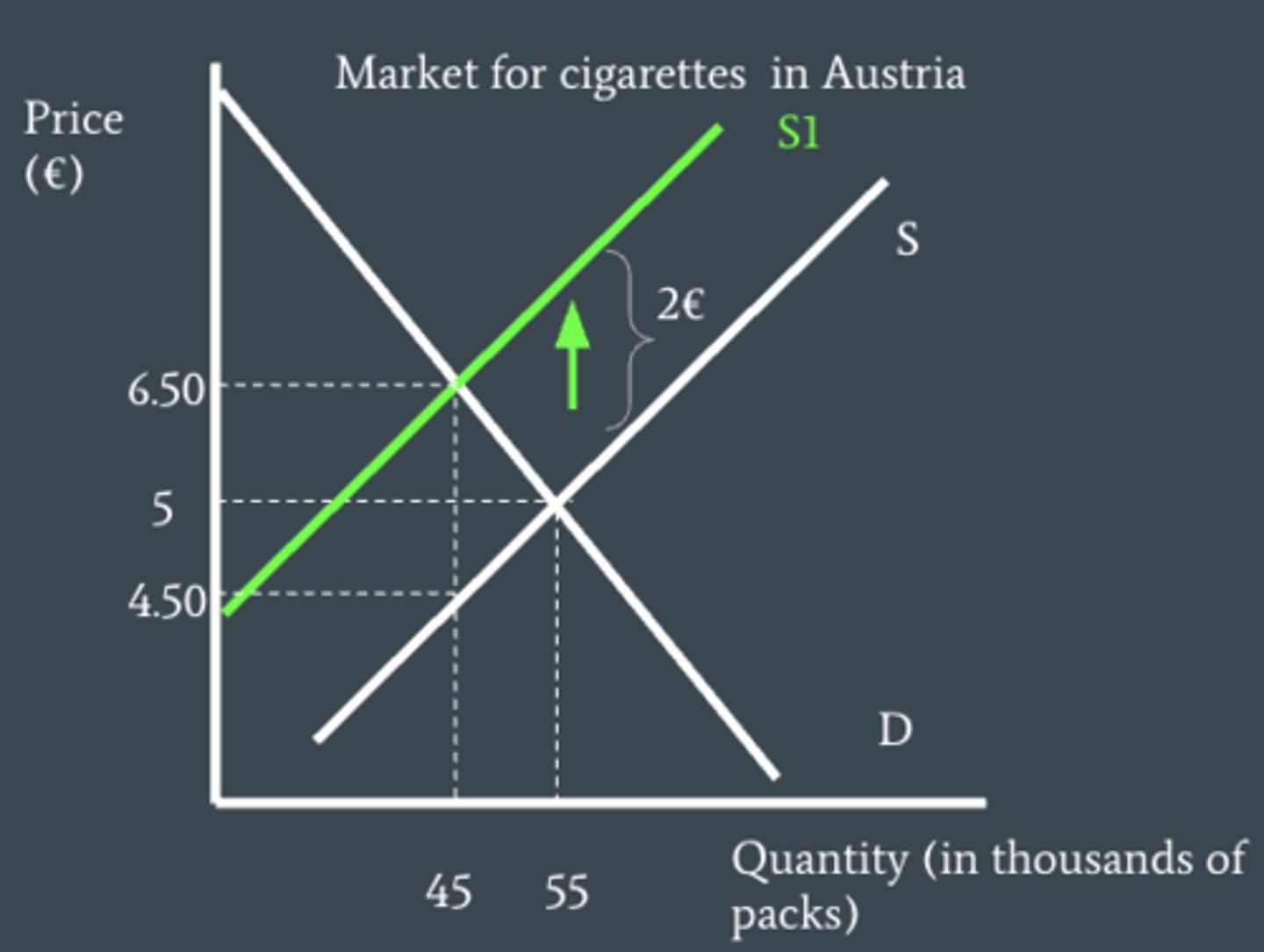
What is a tax burden?
since the tax is shared between both consumers and producers - the amount each of them has to pay is known as their tax burden
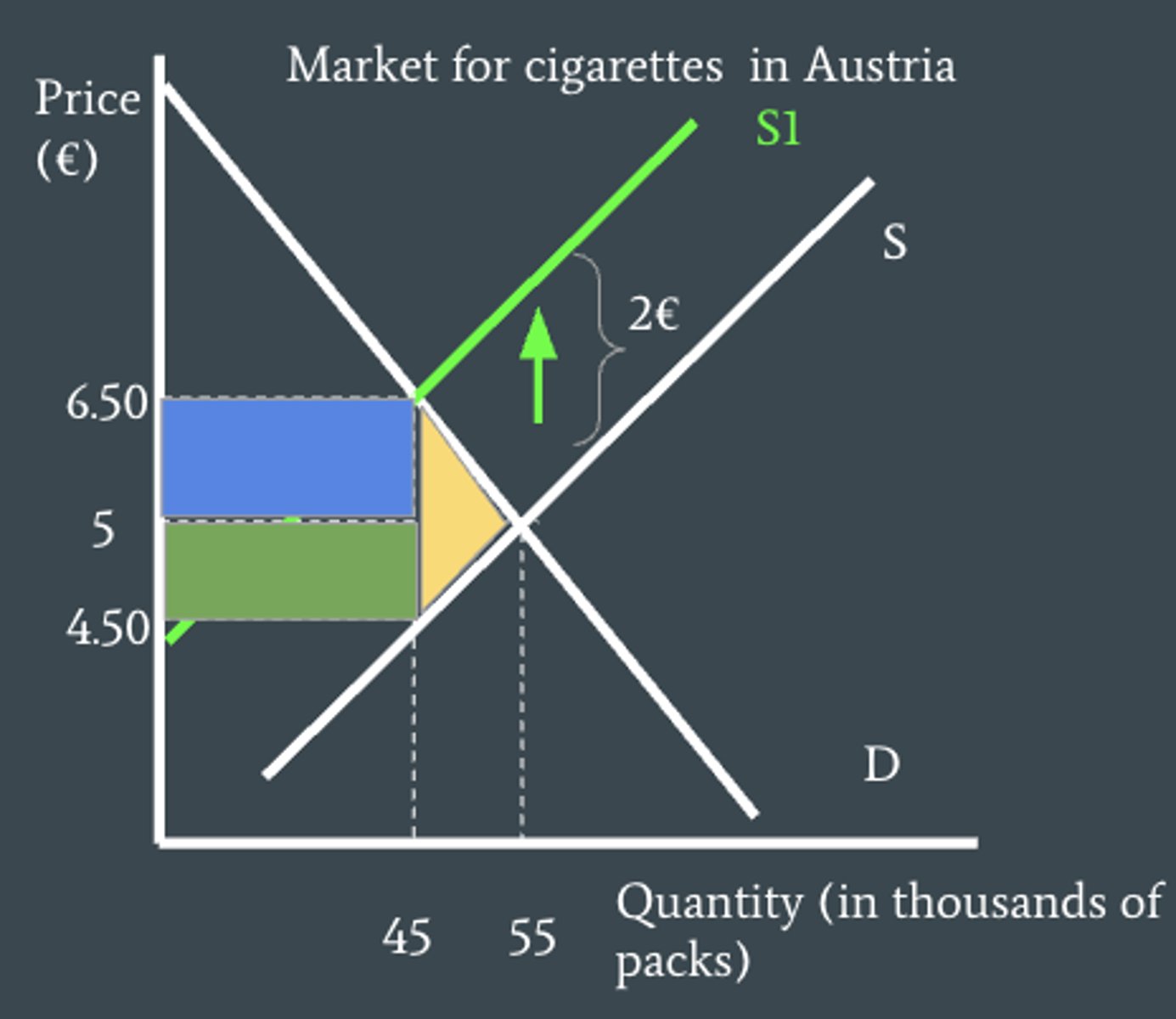
what determines who pays more of the tax?
PED - when demand is elastic producers cannot pass on as much of the tax to consumers, when demand is inelastic they are able to pass on more of the tax to consumers
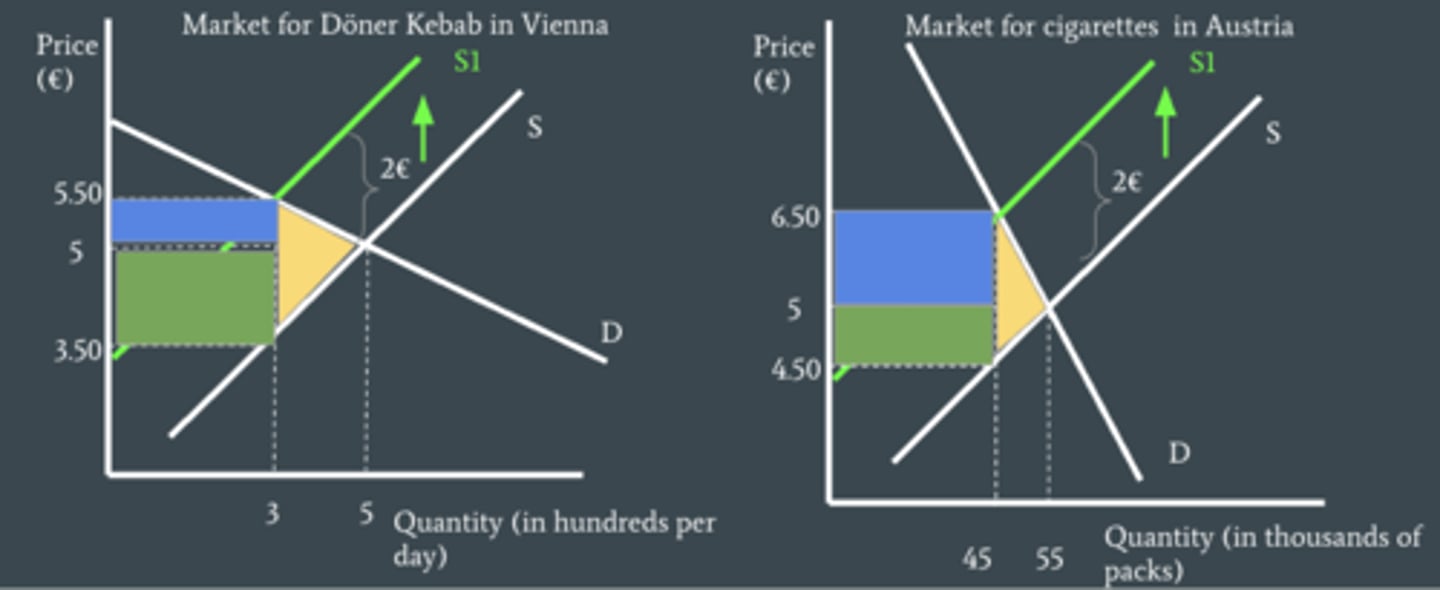
consumer and producer burden on a diagram
consumer burden is at the top above Pe, while producer burden is at the bottom below Pe
producer subsidy definition
a payment from the government to producers which are generally a fixed (specific) amount per-unit of output.
what affect does a producer subsidy have?
it increases the prices producers receive, which incentivizes them to increase their production. It lowers the price for consumers and thus incentivizes them to buy more.
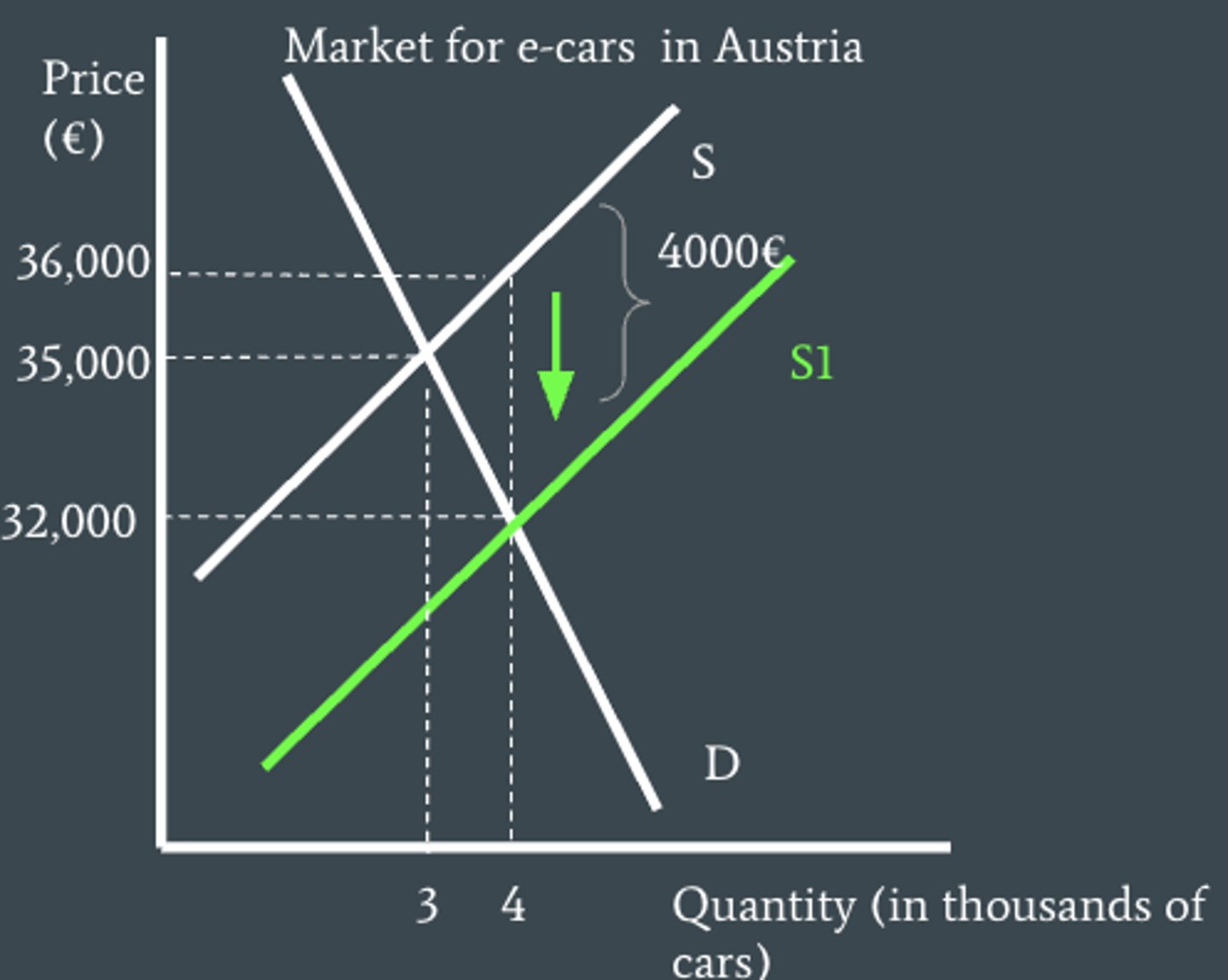
do consumers and producers get a benefit after producer subsidiy?
yes, instead of a tax burden they receive a benefit from the subsidy.
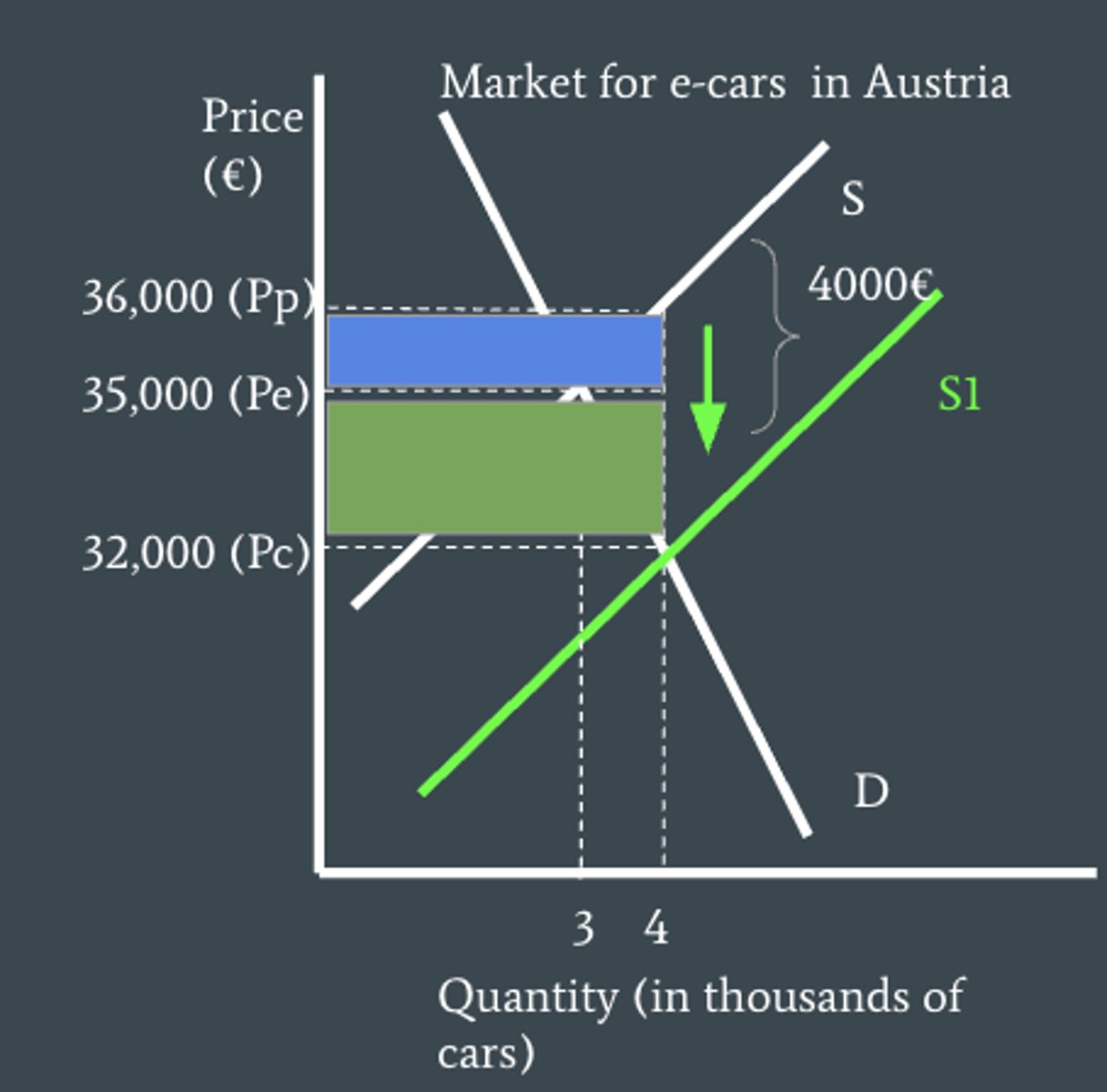
consumer and producer benefit on a diagram
consumer benefit is at the bottom below Pe while producer benefit is at the top above Pe