Geg 010 final exam kutztown
1/132
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
133 Terms
What are plate tectonics?
large-scale motion of the lithosphere
What evidence supports plate tectonic theory?
Evidence from fossils, glaciers, and complementary coastlines helps reveal how the plates once fit together. Fossils tell us when and where plants and animals once existed.
What was Pangaea?
a supercontinent that existed during the late Paleozoic and early Mesozoic eras.
What is a compression tectonic force?
force being pushed on opposite sides
What is the foot wall?
the block of rock below the plane
What is the hanging wall?
the block of rock positioned above the plane,
Why is the New Madrid Fault dangerous?
an earthquake at the fault could leave large parts of St. Louis and Memphis, Tennessee, uninhabitable.
there is a 7-10 percent chance one occurs over the next 50 years
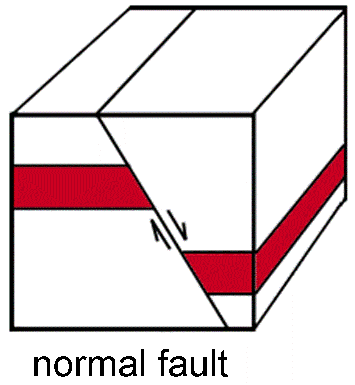
What is a normal fault?
tension fault
footwall above the fault line
hanging wall below the fault line
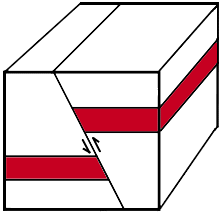
What is a reverse fault?
a high-angled compression fault
hanging wall above the fault line
footwall below the fault line
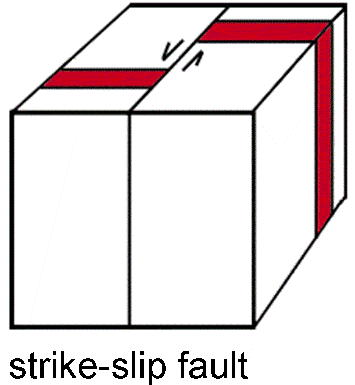
What is a lateral fault?
a strike slip fault
right or left lateral
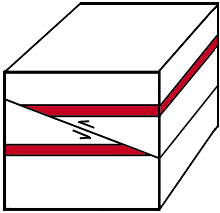
What is a thrust fault?
a shallow-angled compression fault
hanging wall above the fault line
footwall below the fault line
What are earthquakes?
ground motion produced by the release of accumulated tectonic force
Where are earthquakes found?
along fault lines (tectonic plate boundaries)
What is the “focus” of an earthquake?
point inside the earth where the earthquake started
What is the “epicenter” of an earthquake?
the location directly above it on the surface of the earth
What types of waves do we observe in an earthquake?
primary, secondary, and love waves
What is a primary wave?
up and down waves that refract off the earth’s core
What type of wave is a primary wave?
body wave
What is a secondary wave?
side to side waves that go through earth’s core
What type of wave is a secondary wave?
body wave
What is a love wave?
rolling earthquake waves
most destructive
What type of wave is a love wave?
surface wave
What is used to measure an earthquake’s strength?
Richter scale or mercali scale
What is used to measure an earthquake’s magnitude?
the Richter scale
What is a tsunami?
giant waves caused by earthquakes or volcanic eruptions under the sea
How do tsunamis form?
large and sudden displacement of the ocean, usually the result of an earthquake below or near the ocean floor.
what height are open-ocean tsunami waves?
short
what wavelength do open-ocean tsunamis have?
long
what height are shoreline tsunami waves?
tall (potentially)
what wavelength do shoreline tsunamis have?
short
What is coastal shoaling?
the deformation of incident waves on the lower shoreface that starts when the water depth becomes less than about half of the wavelength, causing the waves to become steeper: increase in amplitude and decrease in wavelength.
What is a volcano?
an opening in the ground that allows molten rock to reach the surface
Where are volcanoes found globally?
At tectonic plate boundaries
What is viscosity?
a fluid’s resistance to flow
How is the viscosity of lava determined?
mineral content in magma
Mafic - low in silica. low viscosity
felsic - high in silica. high viscosity
How does the viscosity of lava affect the explosiveness of the volcano?
How do volcanic eruptions impact the climate?
Either climate cooling (ash clouds block the sun) or climate warming (chemicals like co2 being erupted into the atmosphere)
What kinds of volcanoes are there?
Cinder cones (small)
Strato/composite volcanoes (explosive)
Shield volcanoes (big; island formers)
What pyroclastic flows?
a fast-moving current of hot gas and tephra (molten rock)
What are lahars?
mud/debris flow that originate on a volcano. volcanic heat melts snow and ice resulting in a downward water flow that picks up materials
What makes Mt. Rainier so dangerous?
it has numerous glaciers on it, and if it erupted it would trigger huge lahars, wiping out much of the surrounding civilization
What is fracking?
the process of boring into the earth and injecting rock with fluids to force out natural gas and oil
Why is fracking controversial?
it causes air pollution, water contamination, and environmental damage.
What is the Paris Climate Agreement?
An international agreement that covers climate change mitigation, adaptation, and finance.
What is climate?
Average weather patterns in a specific area over a long period of time.
How many years of data is needed to determine average climate?
30
What is weather?
short term patterns of “weather” behavior (rain, snow, temp, etc)
What does anthropogenic mean?
environmental change caused or influenced by people, either directly or indirectly
What is the IPCC?
the scientific group assembled by the United Nations to monitor and assess all global science related to climate change.
How often do the IPCC put out reports?
Every 6-7 years
What does business as usual mean?
A scenario that describes the development of the concentration of greenhouse gas emissions in the atmosphere under the assumption that no further efforts to reduce emissions will be made
What is the Kyoto Protocol?
an agreement among developed nations to reduce carbon dioxide emissions and greenhouse gases to minimize the impacts of climate change.
What was the goal of the Kyoto Protocol?
to reduce the emission of gases that contribute to global warming
What is the Green New Deal?
proposals call for public policy to address climate change along with achieving other social aims like job creation, economic growth, and reducing economic inequality.
What does the green new deal aim to do?
tackle the climate crisis with a 10-year mobilization that puts millions of Americans to work in good-paying, union jobs.
Similar to FDR's New Deal, these jobs would be focused on strengthening the nation's public infrastructure as well as tackling pollution and climate damage.
What is an endogenic force?
occurs inside the earths crust
what is an exogenic force?
occurs outside of the earths crust
What is weathering?
slow erosion of rock material inside and outside the earth
How is weathering accomplished?
physical processes affect rocks, such as changes in temperature or when rock is exposed to the effects of wind, rain, and waves.
What force contributes to mass wasting?
gravity
What is physical weathering?
The physical breakdown of rock caused by pressure, rock exfoliation (rock peeling), etc.
What is chemical weathering?
the erosion or disintegration of rocks, building materials, etc., caused by chemical reactions rather than by mechanical processes.
How can climate affect weathering?
High temperatures and greater rainfall increase the rate of chemical weathering
How can water affect mass wasting?
water can increase slope instability
What is an avalanche?
What triggers avalanches?
A force being exerted on a mass of snow/rock/ice
forces include weather, earthquakes, human activity, etc
What is soil?
A mixture of organic matter, minerals, gases, liquids, and organisms that together support the life of plants and soil organisms
What environmental factors can affect soils?
climate
bacteria presence
mineral presence
organismal/ecological growth
What is leaching?
the process of excess water, through rainfall or irrigation, taking water-soluble nutrients out of the soil.

Why is humus important to soils?
it contains many useful nutrients for healthy soil
How can the pack rat midden give clues to climates of the past?
they represent the local environment at the time the material was gathered, and they can tell scientists a lot about past climates and environments.
If a soil is rich in humus, what color will it be?
Dark brown
If a soil has been leached, what color will it be?
pale yellow or pale brown
What is silt?
granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz/minerals
What is clay?
a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals
What is loam?
soil composed mostly of sand, silt, and a small amount of clay
What is soil porosity?
Open space in soil
What is soil permeability?
Ease in which water can pass through soils
What is the largest cash crop in America?
Corn
What is the largest cash crop in the world?
Sugarcane
What is a desert?
a landscape where little precipitation occurs. This allows for the conditions for geomorphic processes to occur to be easily met.
Which geomorphological process is least effective at work?
Wind-driven change
What is sand?
finely divided/granular rocks and minerals
How does sand form?
erosion and decomposition of rocks over the course of millions of years
What conditions are necessary for aeolian geomorphology to occur?
Strong wind
Loose surface material
Sparse vegetation
What are the two processes at work in aeolian geomorphology?
deflation (removal of loosened material and its transport as fine grains in atmospheric suspension)
abrasion (mechanical wear of coherent material)
What is a haboob?
an intense wind dust storm with a heavy downdraft
What is loess?
Deposits of silt and clay moved by wind
Why are large sections of the American Midwest composed of loess?
During the Ice Age, glaciers advanced down into the mid-continent of North America, grinding underlying rock into fine sediment As temperatures warmed, the glaciers melted and enormous amounts of water and sediment rushed down the Missouri River valley.
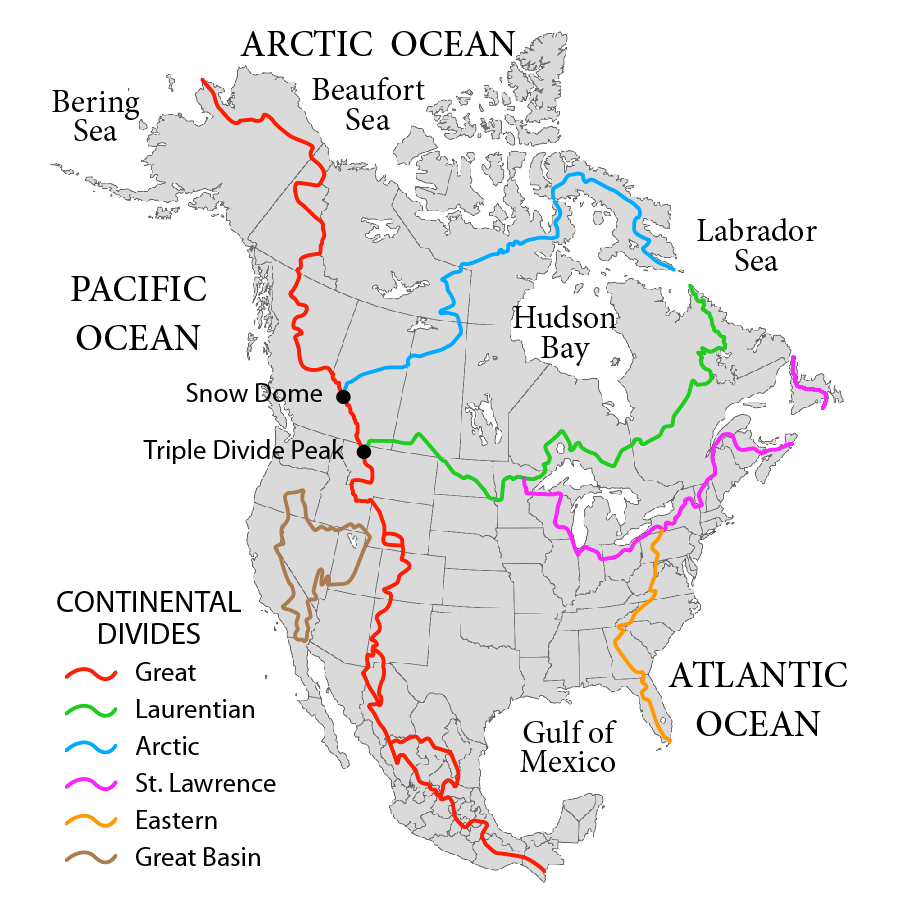
What is the significance of the Continental Divide?
Determines where water in the water cycle will go to
What is a watershed?
an area of land that drains all the streams and rainfall to a common outlet such as the outflow of a reservoir, mouth of a bay, or any point along a stream channel.
Where are watersheds?
Everywhere!
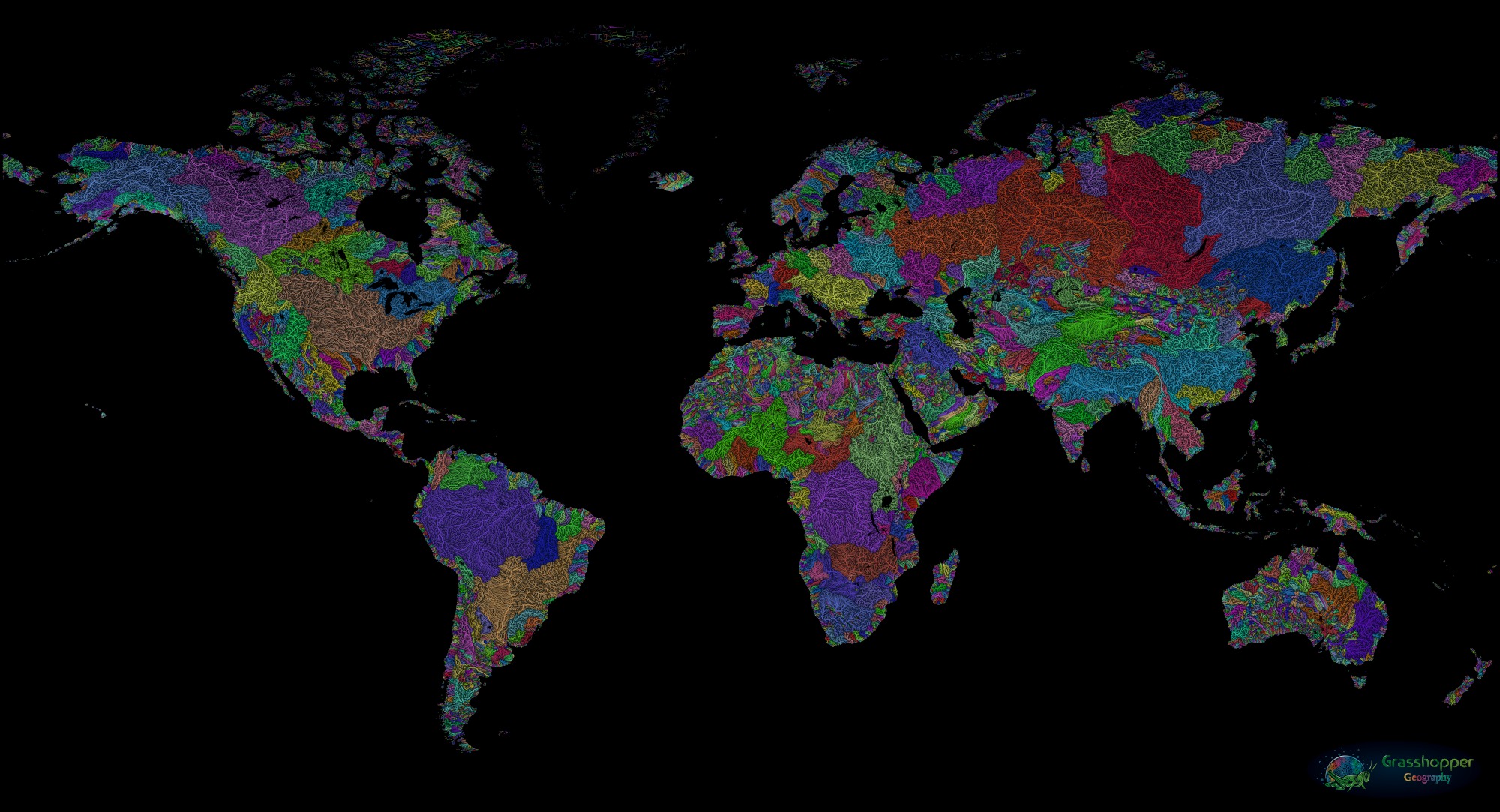
What are fluvial deposits?
sediments that are transported and deposited by rivers in a continental environment
How are plunge pools created?
erosional forces of cascading water impacting the rocks at a formation's base where the water impacts.
How is drainage density calculated?
D = L / A
D = Drainage density
L = Length of all water channels
A = Area of watershed

What drainage pattern is this?
trellis
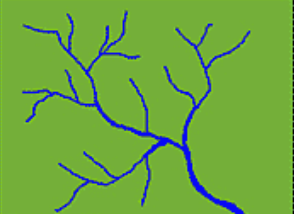
What drainage pattern is this?
Dendritic
What is stream discharge?
amount of water flowing past a point per unit of time
not influenced by river length!
What is stream load?
sediments carried by the water
What is stream competence?
maximum size of the sediment carried by water