Interpersonal Communication -- Exam #1
1/113
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
114 Terms
interpersonal communication
communication between two people --> people are treated as unique individuals with unique livelihood

impersonal communication
communication that treats people as objects --> usually takes form as responding only to their roles rather than to who they are as unique people

I-it
leads to impersonal communication and even disrespectful communication

I-thou
leads to interpersonal deepens bonds and affirms individual uniqueness

mass communication
communication to a large audience that is transmitted by media

small group communication
communication occurring in groups above two

intrapersonal communication
communication with oneself

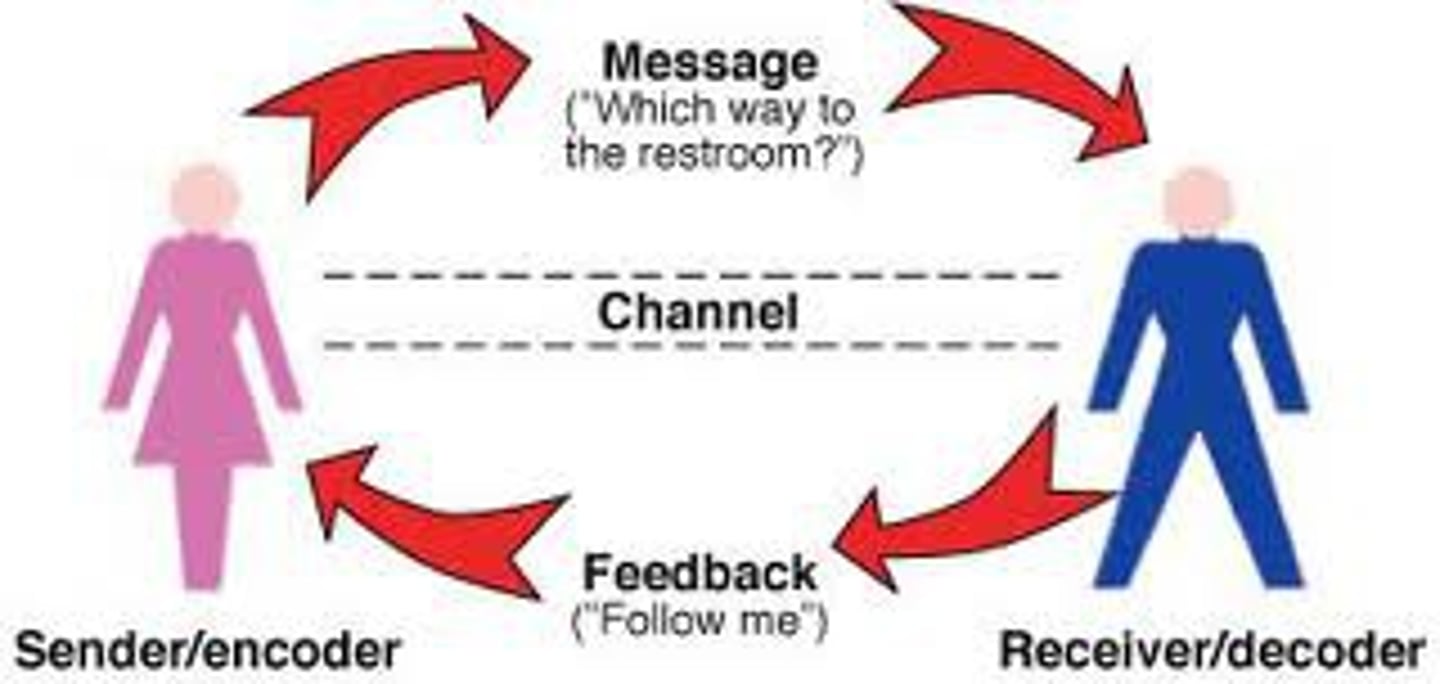
Source
The sender—person, group, or organization—of the message.
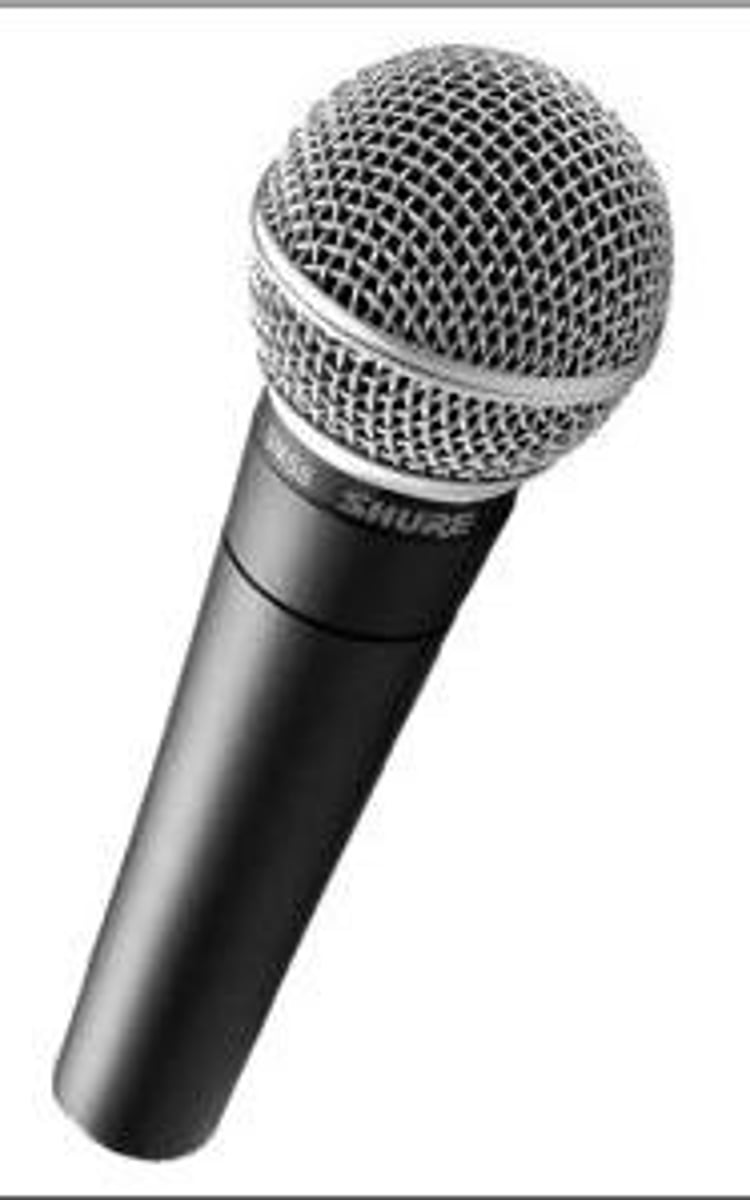

Message
the information transmitted by the source
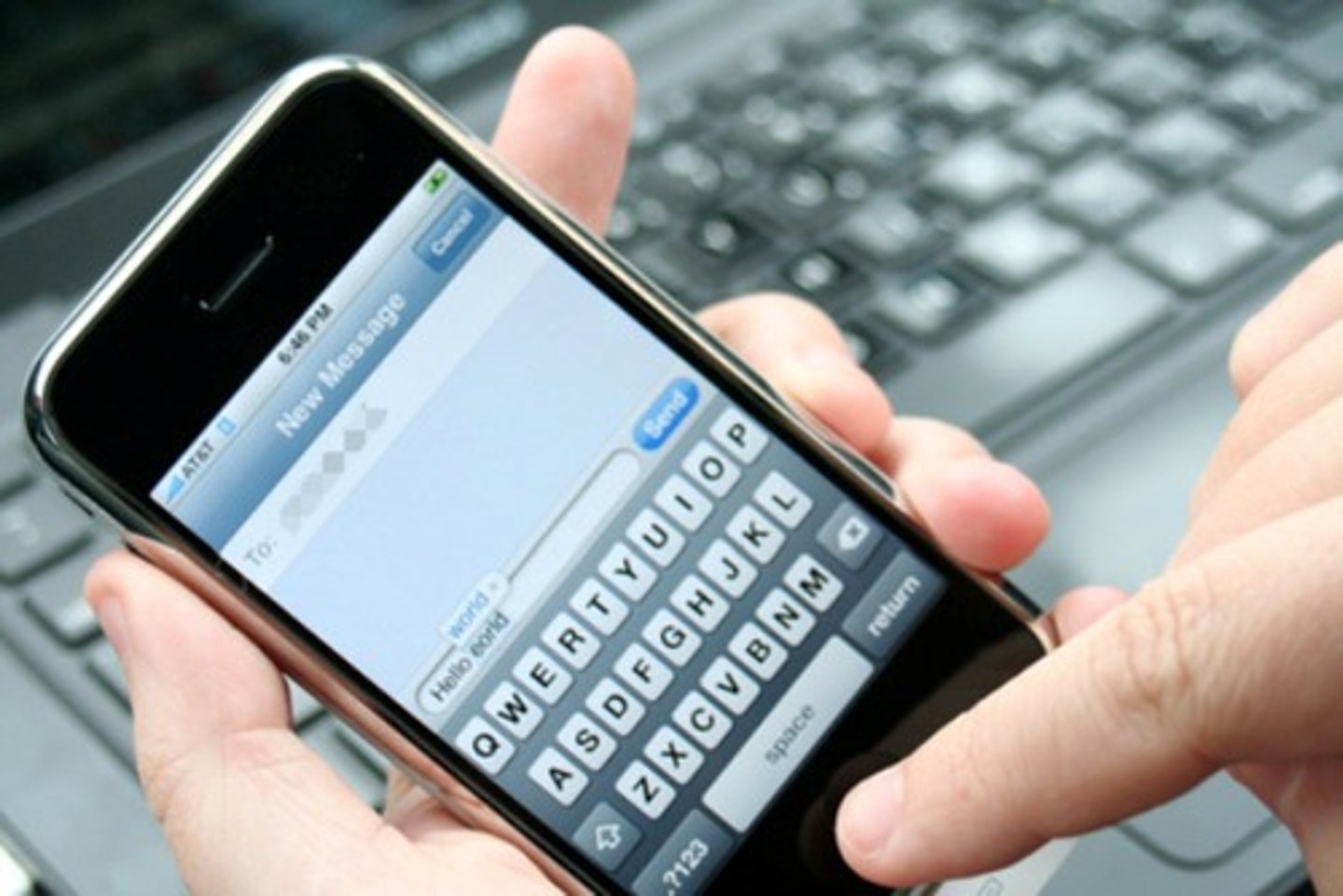

channel
the means by which a message is communicated

Reciever
The person to whom a message is sent / person decoding message / other end of source if it is interpersonal

noise
any disturbance that interferes with the transmission of a message

Feedback
The receiver's response to a message
Linear model
the sender sends the message & the receiver only receives the message. There's no concept of feedback involved.

Interactive Model
The interactive model of communication refers to the back-and-forth communication process that is seen in basic conversations. A source sends out a message to a receiver, who then responds to that message with a reply
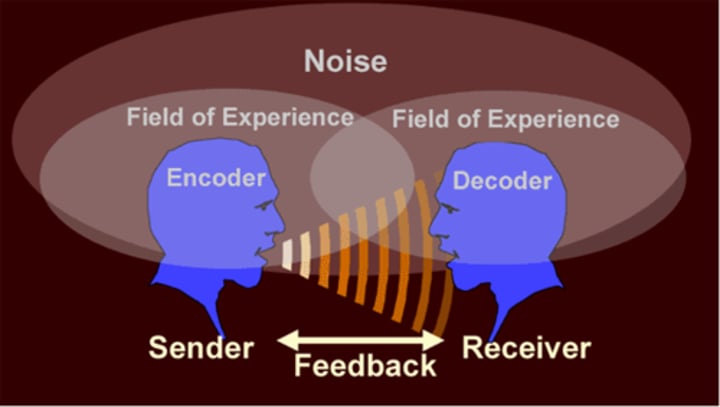
Transactional model
a two-way process that acknowledges the active participation of both the sender and receiver in constructing meaning. This approach contemplates communication as a perpetual dialogue of messages, where both sides shape what is being communicated. this includes ENCODING AND DECODING
Content
Information, ideas, or suggested actions that a speaker wishes to share.

relationship dimension
The aspect of a communication message that offers cues about the emotions, attitudes, and amount of power and control the speaker directs toward others; how something is said. TONE

metacommunication
messages (usually relational) that refer to other messages; communication about communication EX: "I feel like we aren't talking very much lately"

electronically mediated communication
interpersonal communication that takes place via technology

emotional contagion
The process whereby people mimic the emotions of others after watching and hearing their emotional expressions.
asynchronous message
A message that is not read, heard, or seen exactly when it is sent; there is a time delay between the sending of the message and its receipt.
cues-filtered-out theory
The communication of emotion and relationship cues is restricted in e-mail or text messages because nonverbal cues, such as facial expression, gestures, and tone of voice, are filtered out.

Social Information Processing Theory
Theory that suggests people can communicate relational and emotional messages via the Internet, although such messages take longer to express without nonverbal cues.

media richness theory
The richness or amount of information a communication medium has is based on the amount of feedback it permits, the number of cues in the channel, the variety of language used, and the potential for expressing emotions.

self
sum total of who a person is; a person's central inner force
beliefs
Way in which you structure your understanding of reality-what is true and what is false for you.

attitude
Learned predisposition to respond to a person, object, or idea in a favorable or unfavorable way.
values
enduring concept, good versus bad

mindfulness
The ability to think consciously about what you are doing and experiencing.

William James Dimensions of Self
material self (Big cars, fancy clothing, trends
Harmful in how it can impact you), social self (Groups we get involved with) spiritual self (inner self and how we think about ourselves spiritually)
Cooley's Looking Glass Self
see ourselves in a figurative looking glass → you learn who you are based on your interactions with others who reflect back to you

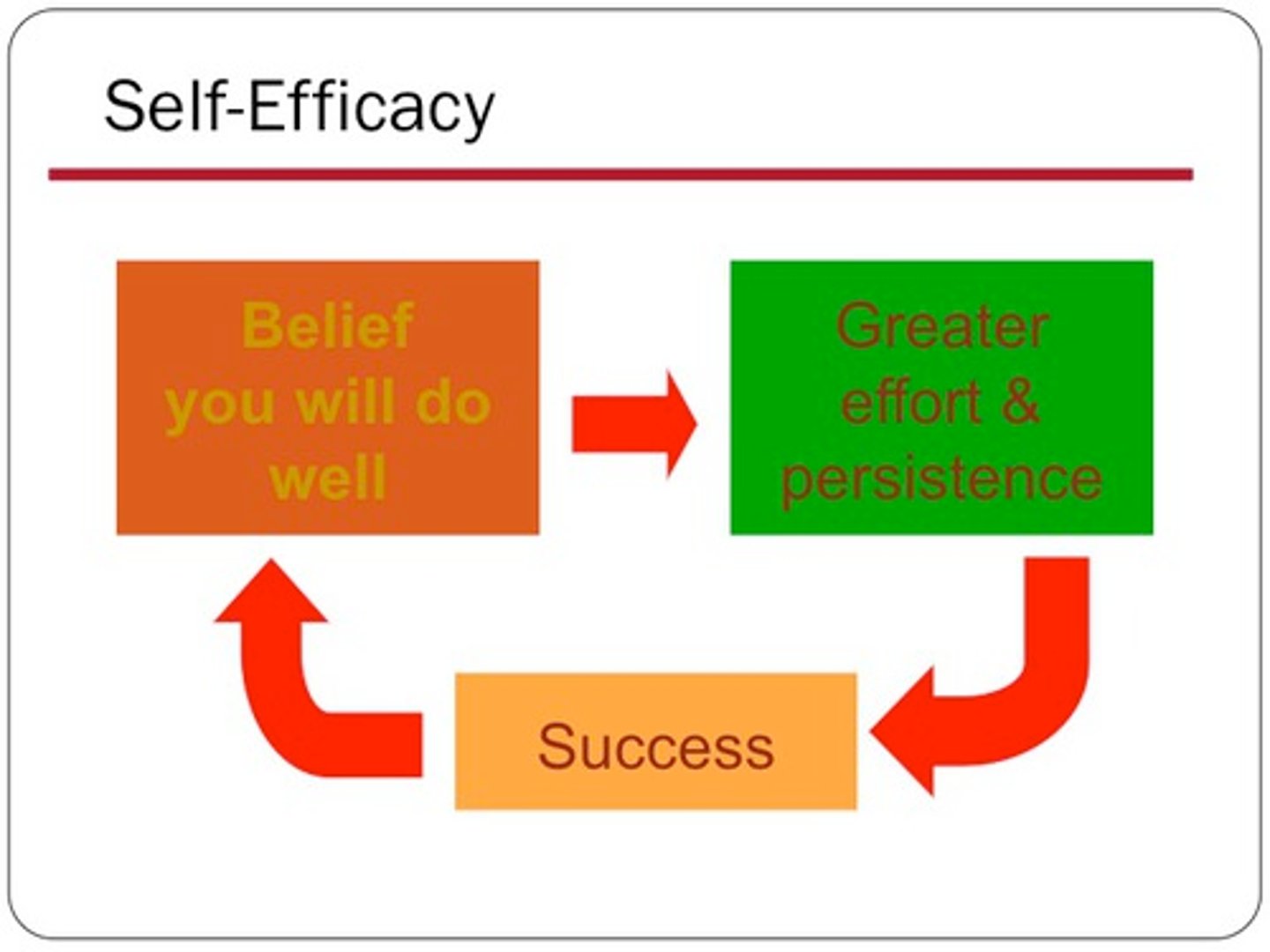
Self-Efficacy
A person's belief in his or her ability to perform a specific task in a particular situation.
facework
Using communication to maintain your own positive self-perception or to support, reinforce, or challenge someone else's self-perception
context
Physical and psychological environment for communication.

systems theory
Theory that describes the intercon- nected elements of a system in which a change in one element affects all of the other elements.
episode
Sequence of interactions between individuals, during which the message of one person influences the message of another.
symbol
A thing that represents or stands for something else, especially a material object representing something abstract.

rule
Followable prescription that indicates what behavior is obligated, preferred, or prohibited in certain contexts.
Hyperpersonal Relationship
A relationship formed primarily through electronically mediated communication that becomes more personal than an equivalent face-to-face relationship because of the absence of distracting external cues, an over-dependence on just a few tidbits of personal information, and idealization of the communication partner.
Social Presence
The feeling that communicators have of engaging in unmediated, face-to-face interactions when messages are being sent electronically.
Ethics
The beliefs, values, and moral principles by which a person determines what is right or wrong.
subjective self-awareness
Ability to differentiate the self from the physical and social environment.
Objective Self-Awareness
Ability to be the object of one's own thoughts and attention-to be aware of one's state of mind and what one is thinking.
Symbolic Self-Awareness
Uniquely human ability to think about oneself and use language (symbols) to represent oneself to others.
Androgynous Role
Gender role that includes both mascu- line and feminine qualities.
Self-Reflexiveness
Ability to think about what one is doing while doing it.
Psychology
The study of how thinking and emo- tional responses influence behavior.
Personality
A set of enduring behavioral character- istics and internal predispositions for reacting to your environment.
Communibiological Approach
Perspective that suggests that genetic and biological influences play a major role in influencing communication behavior.
Social Learning Theory
A theory that suggests people can learn to adapt and adjust their behavior toward others by observing how others behave.
Self-Esteem/ Self-worth
Your evaluation of your worth or value based on your perception of such things as your skills, abilities, talents, and appearance.
life position
Feelings of regard for self and others, as reflected in one's self-esteem.
Positive Face
An image of yourself that will be per- ceived as positive by others.
preventative facework
Efforts to maintain and enhance one's positive self-perceptions.
Face-Threatening Acts
Communication that undermines or challenges someone's positive face.
Politeness Theory
Theory that people have positive perceptions of others who treat them politely and respectfully.
visualization
Technique of imagining that you are performing a particular task in a certain way; positive visualization can enhance self-esteem.
Reframing
Process of redefining events and experiences from a different point of view.
Symbolic Interaction Theory
Theory that people make sense of the world based on their interpretation of words or symbols used by others.
Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
Prediction about future actions that is likely to come true because the person believes that it will come true.
Need for Inclusion
Interpersonal need to be included and to include others in social activities.
Need for Affection
Interpersonal need to give and receive love, support, warmth, and intimacy.
Self-Disclosure
Purposefully providing information about yourself to others that they would not learn if you did not tell them
Communication Social Style
An identifiable way of habitually communicating with others.
Assertiveness
Tendency to make requests, ask for information, and generally pursue one's own rights and best interests.
Responsiveness
Tendency to be sensitive to the needs of others, including being sympathetic to others' feelings and placing the feelings of others above one's own feelings.
Perception
Process of experiencing the world and making sense out of what you experience.
Interpersonal Perception
Process of selecting, organizing, and interpreting your observations of other people.
selective perception
Process of seeing, hearing, or making sense of the world around us based on such factors as our personality, beliefs, attitudes, hopes, fears, and culture, as well as what we like and do not like.
Selective Attention
Process of focusing on specific stimuli, locking on to some things in the envi- ronment and ignoring others.
Selective Exposure
Tendency to put ourselves in situations that reinforce our attitudes, beliefs, values, or behaviors.
Selective Recall
Process that occurs when we remember things we want to remember and forget or repress things that are unpleasant, uncomfortable, or unimportant to us.
Thin Slicing
Observing a small sample of someone's behavior and then making a general- ization about what the person is like, based on that sample.
Superimpose
To place a familiar structure on information you select.
Impressions
Collection of perceptions about others that you maintain and use to interpret their behaviors.
Impression Formation Theory
Theory that explains how you develop perceptions about people and how you maintain and use those perceptions to interpret their behaviors.
Active Perception
Perception that occurs because you seek out specific information through intentional observation and questioning.
Implicit Personality Theory
Your unique set of beliefs and hypoth- eses about what people are like.
Construct
Bipolar quality or continuum used to classify people.
Uncertaintiy Reduction Theory
Theory that explains our information- seeking behavior in our initial interactions with others and also describes the overall process of how we reduce our uncertainty about our social world.
Primacy Effect
Tendency to attend to the first pieces of information observed about another person in order to form an impression.
Predicted Outcome Value Theory
People predict the future of a relation- ship based on how they size up some- one during their first interaction.
Recency Effect
Tendency to attend to the most recent information observed about another person in order to form or modify an impression.
Halo Effect
Attributing a variety of positive qualities to those you like.
Horn effect
Attributing a variety of negative qualities to those you dislike.
Direct Perception Checking
Asking the observed person to confirm an interpretation or a perception about him or her.
Indirect Perception Checking
Seeking additional information through passive perception, such as observing and listening, either to confirm or refute your interpretations.
Other oriented
To be aware of the thoughts, needs, experiences, personality, emotions, motives, desires, culture, and goals of your communication partners while still maintaining your own integrity.
human communication
Process of making sense out of the world and sharing that sense with others by creating meaning through the use of verbal and nonverbal messages.
communication
Process of acting on information.
Attribution Theory
Theory that explains how you generate explanations for people's behaviors.
causal attribution theory
Theory of attribution that identifiesthe cause of a person's actions as circumstance, a stimulus, or the person himself or herself.
Standpoint theory
Theory that a person's social position, power, or cultural background influ- ences how the person perceives the behavior of others.
Barriers to Accurate IP Perception
Stereotype
Ignore information
Impose Consistency
Focus on the negative
Blame others
Fundamental attribution error
Avoid Responsibility
Self-serving bias
Improving IP Perception Skills
Be aware of personal perception barriers
Be mindful
Link details with big picture
Become aware of others' perceptions of you
Check your perceptions
Indirect perception checking
Direct perception checking
Become other-oriented
Predicted outcome theory (POV)
People predict the future of a relation- ship based on how they size up some- one during their first interaction.
public communication
communication directed at an audience that is larger than a small group (NO feedback)

Encode vs Decode
Encode: involves putting thoughts, ideas, or information into a symbolic form.
Decode: how an audience member is able to understand, and interpret the message.
synchronous message
A message that is sent and received simultaneously.
