PNB 2264 Practical 1
1/145
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
epidermis
The epithelium covering the surface of the skin
dermis
The connective tissue layer beneath the epidermis of the skin.
subcutaneous tissue
the layer of loose connective tissue below the dermis; also called hypodermis or superficial fascia
dermal papillae
small, conical projections of the dermis into the epidermis. they can be observed at the surface of the skin in the hands and feet as papillary ridges (known as fingerprints)
sweat gland
have coiled, tubular secretory portion located in the reticular layer of the dermis. produce a watery solution that performs thermoregulation, secretion, and protection.
sebaceous gland
glands that secrete sebum; normally associated with hair follicles
pacinian corpuscle
pressure receptors in the skin and various internal organs.
tactile corpuscle
large, encapsulated oval receptors for fine touch and texture within the dermal papillae of the skin
free nerve endings
least complex of the tactile receptors and are in the papillary layer of the dermis. detect pain and temperature stimuli
hair follicle
accessory structure of the integument; tube lined by stratified squamous epithelium that begins at the surface of the skin and ends at the hair papilla
arrestor pili
smooth muscle whose contractions force hairs to stand erect
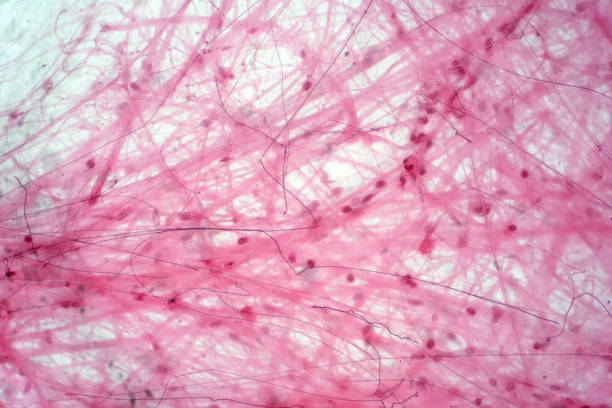
areolar connective tissue
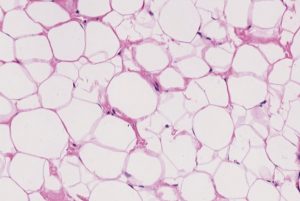
adipose tissue
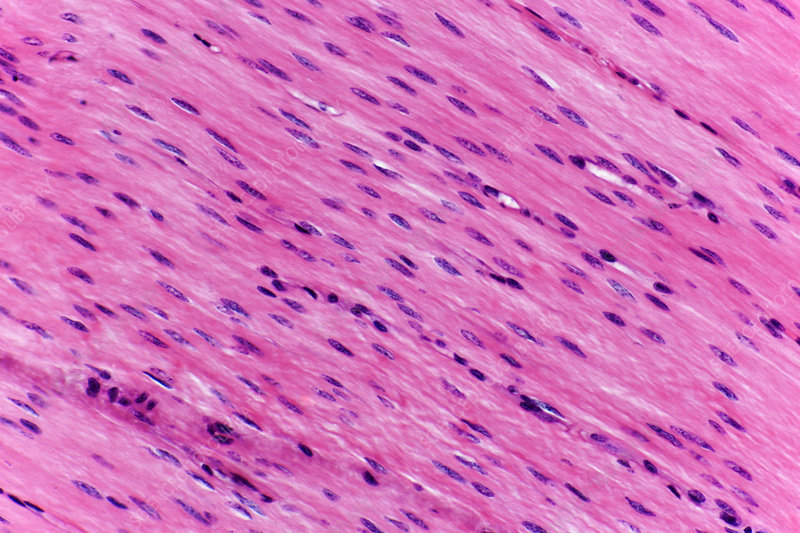
smooth muscle
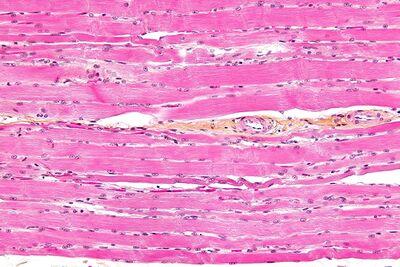
skeletal muscle
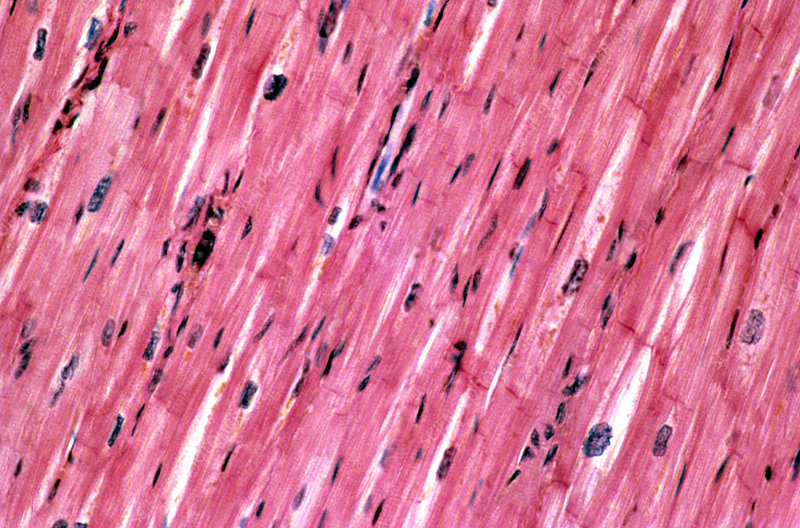
cardiac muscle
The two basic tissues that compose the skin are:
dense irregular connective tissue; stratified squamous epithelium
what characteristics relating to location or gland structure allow you to differentiate sebaceous and sweat glands?
sweat glands release their secretions directly to the surface of the skin whereas sebaceous glands release their secretions into the hair follicle
Which part would you adjust in order to examine a specimen under light microscope with two eyes at the same time?
ocular lenses to adjust the inter pupillary distance
What are general features of all connective tissues?
protein fibers in an extracellular matrix; ground substance in an extracellular matrix; specialized cells
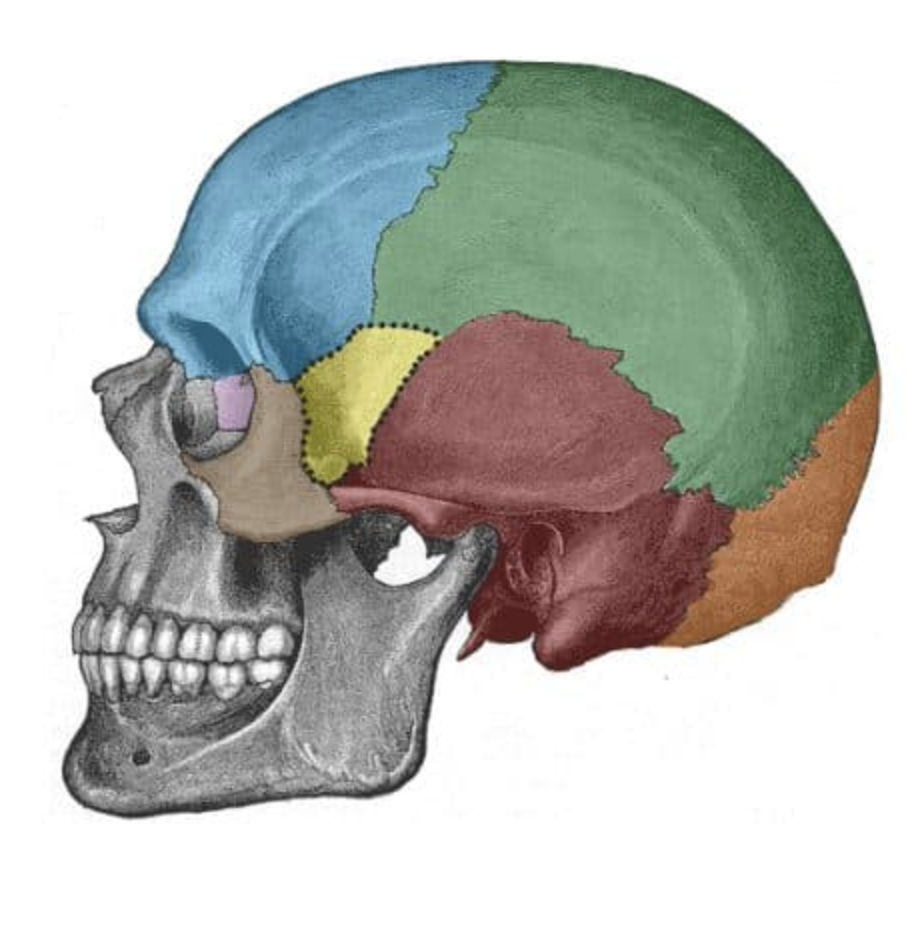
What is the blue bone?
Frontal
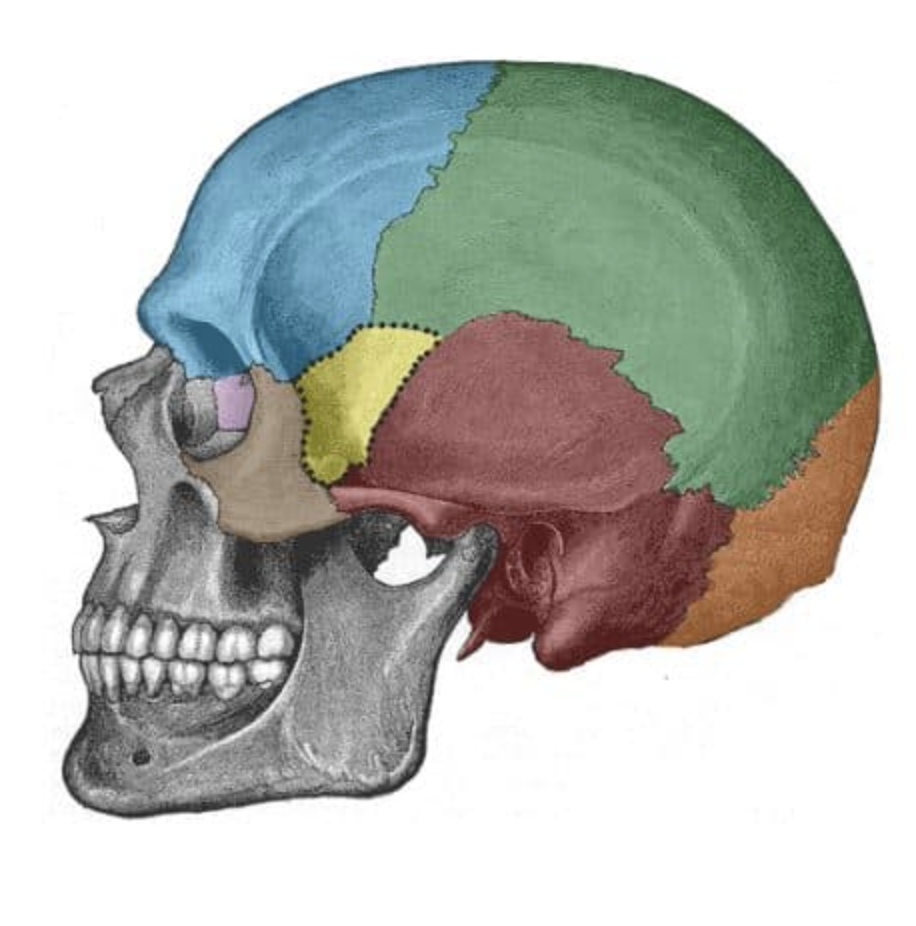
What is the green bone?
parietal
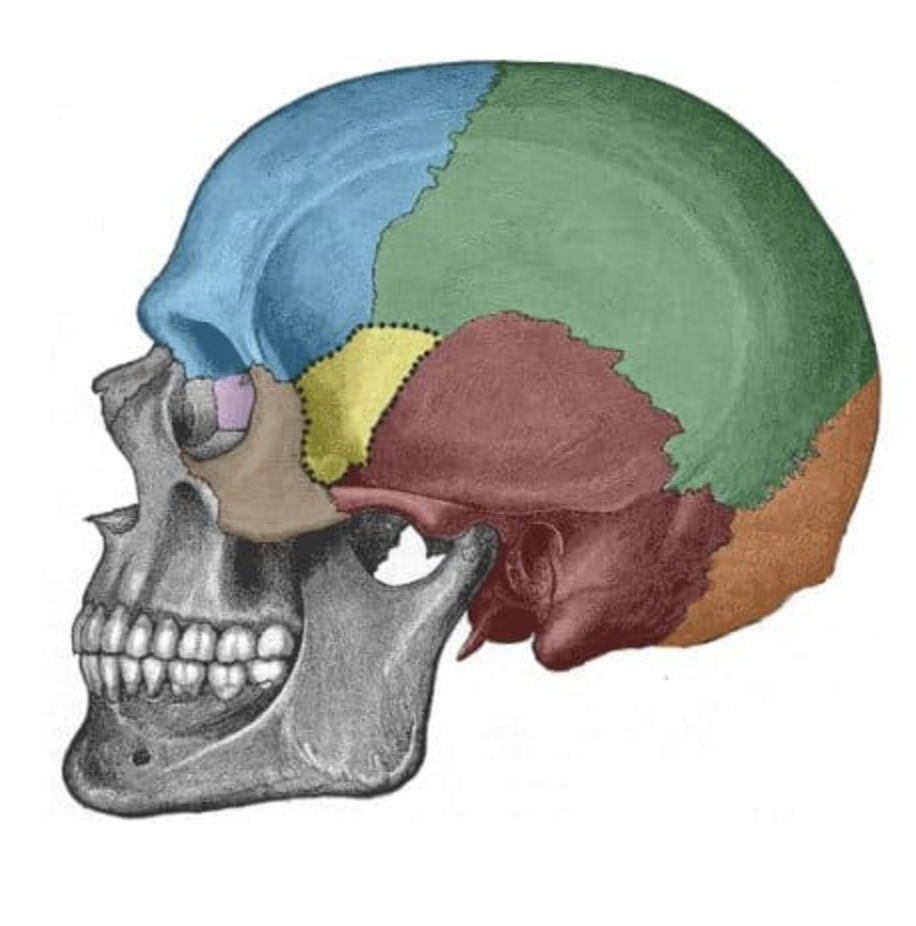
What is the red bone?
temporal
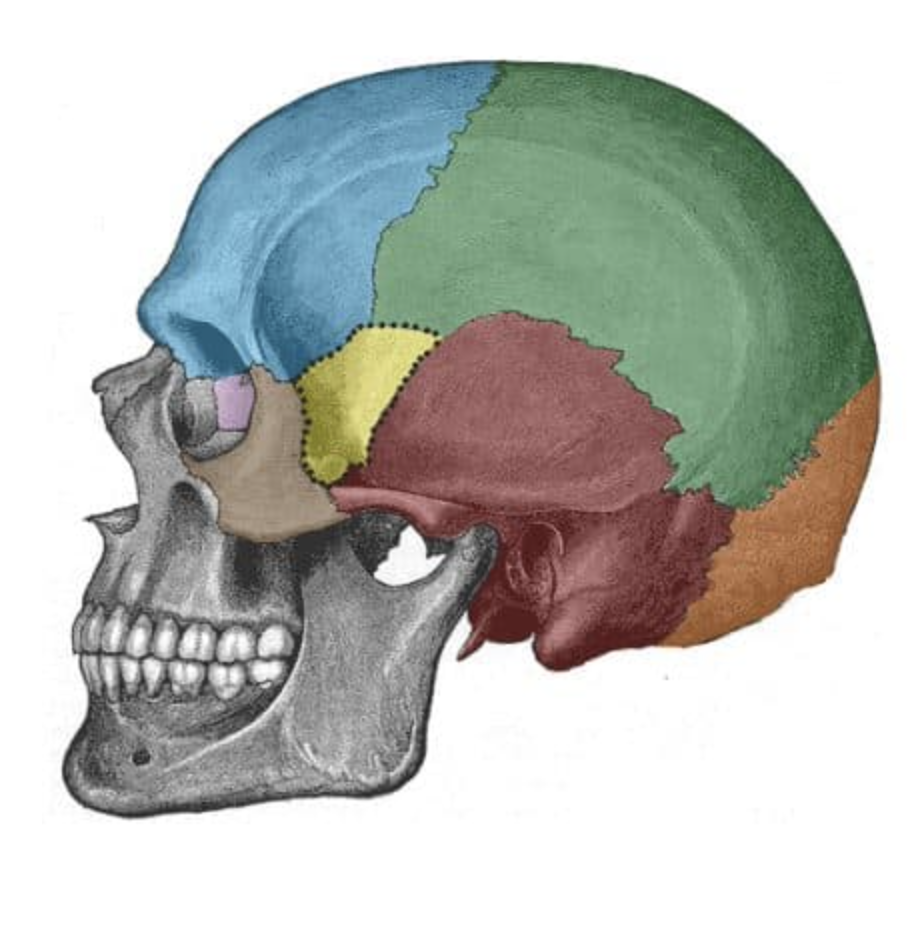
What is the yellow bone?
sphenoid
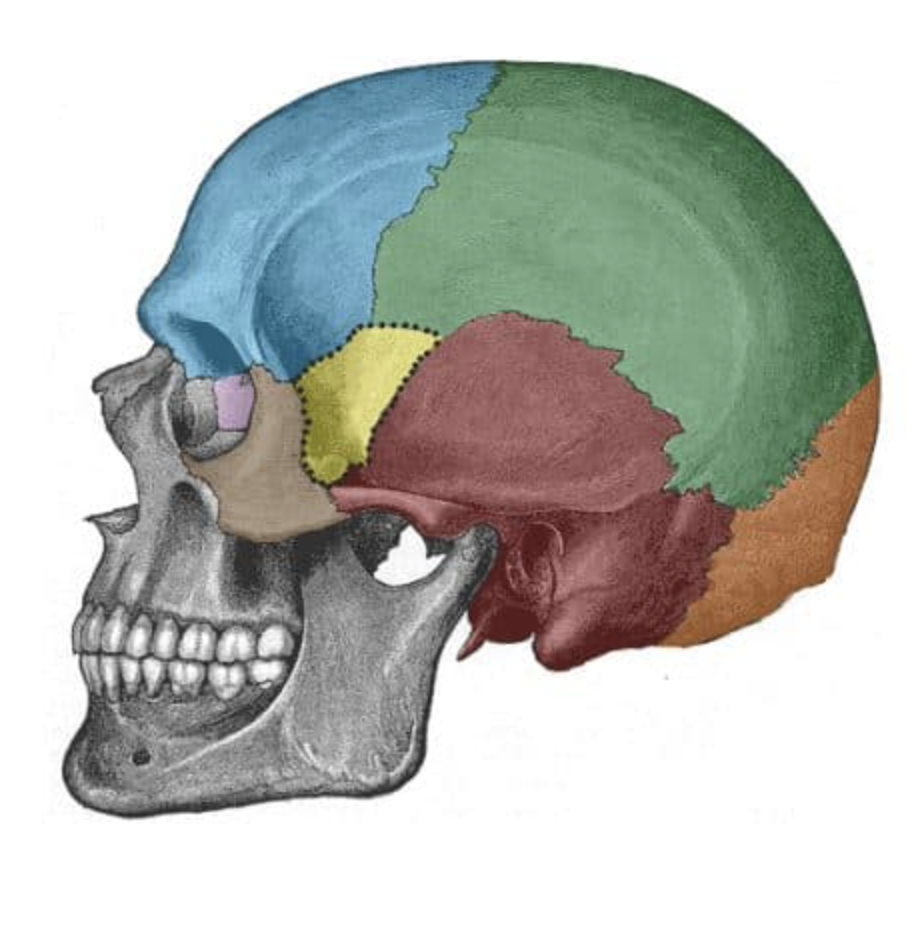
What is the orange bone?
occipital
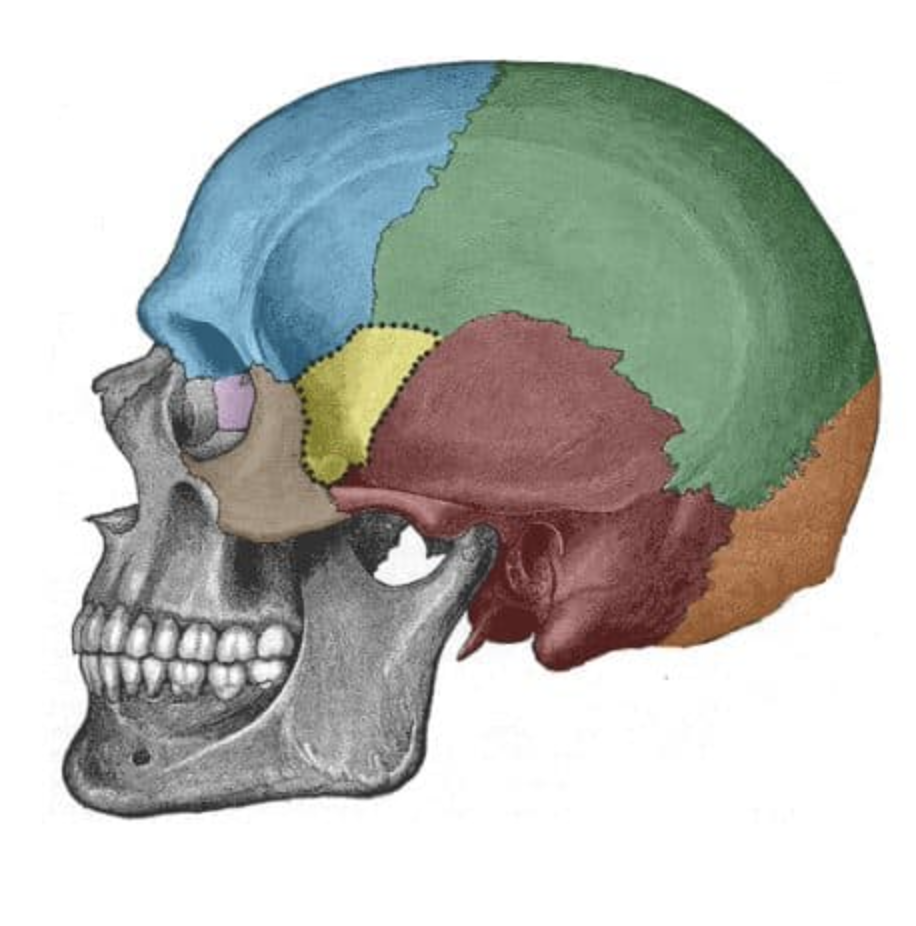
What is the purple bone?
ethmoid
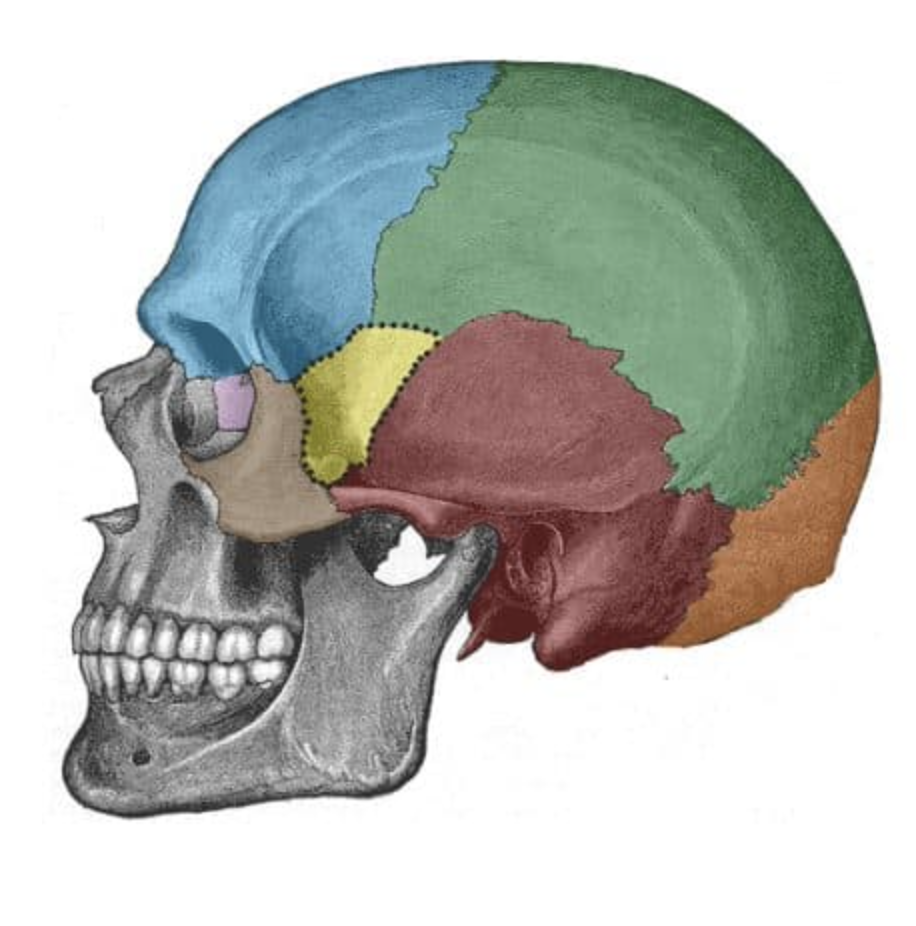
What is the brown bone?
zygomatic
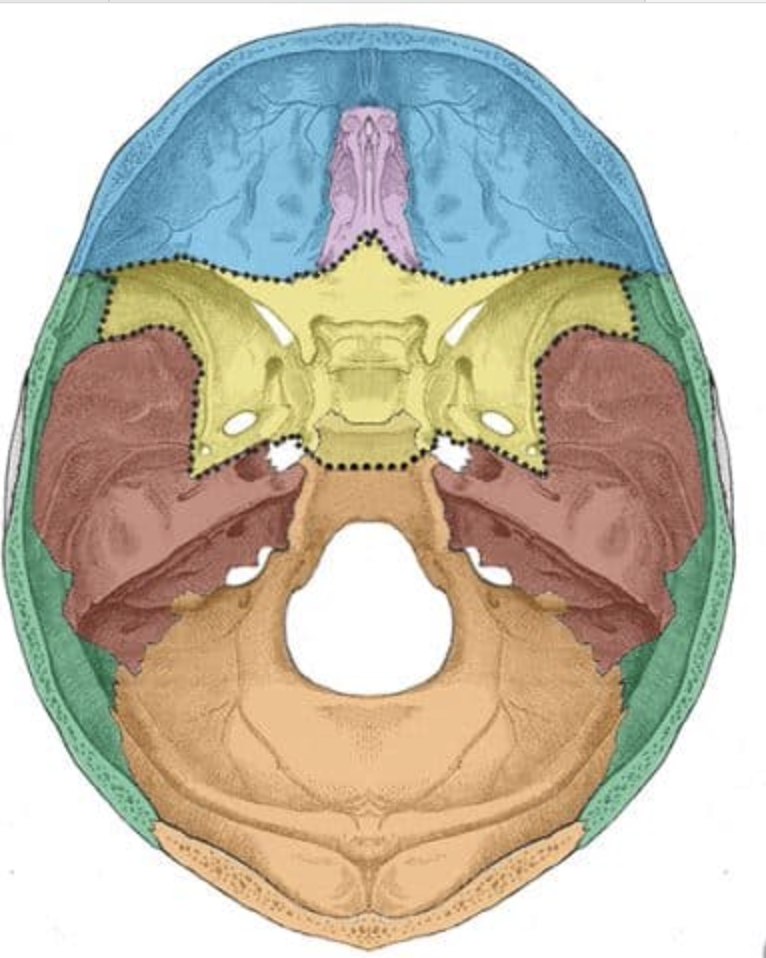
What is the purple bone?
ethmoid
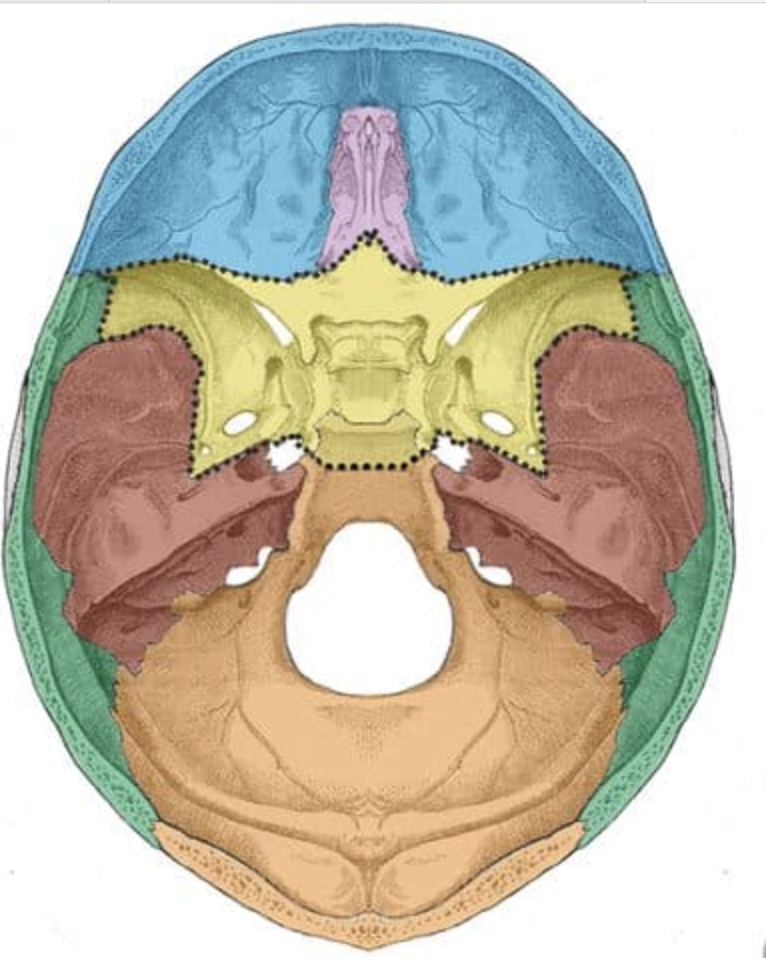
What is the yellow bone?
Sphenoid
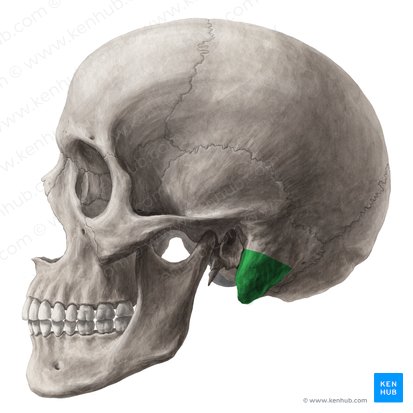
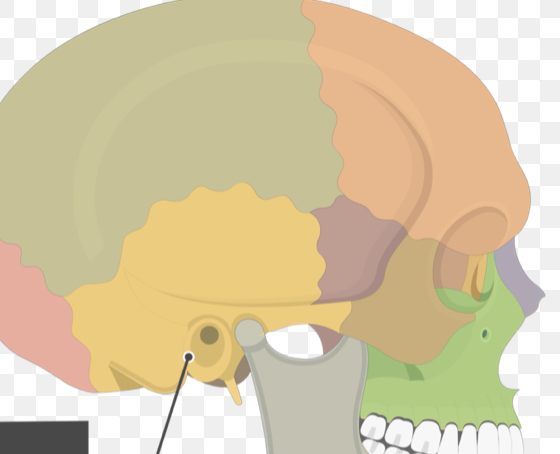
What does this represent?
mastoid process
What does this represent?
occipital condyles
What does this represent?
mandibular fossa
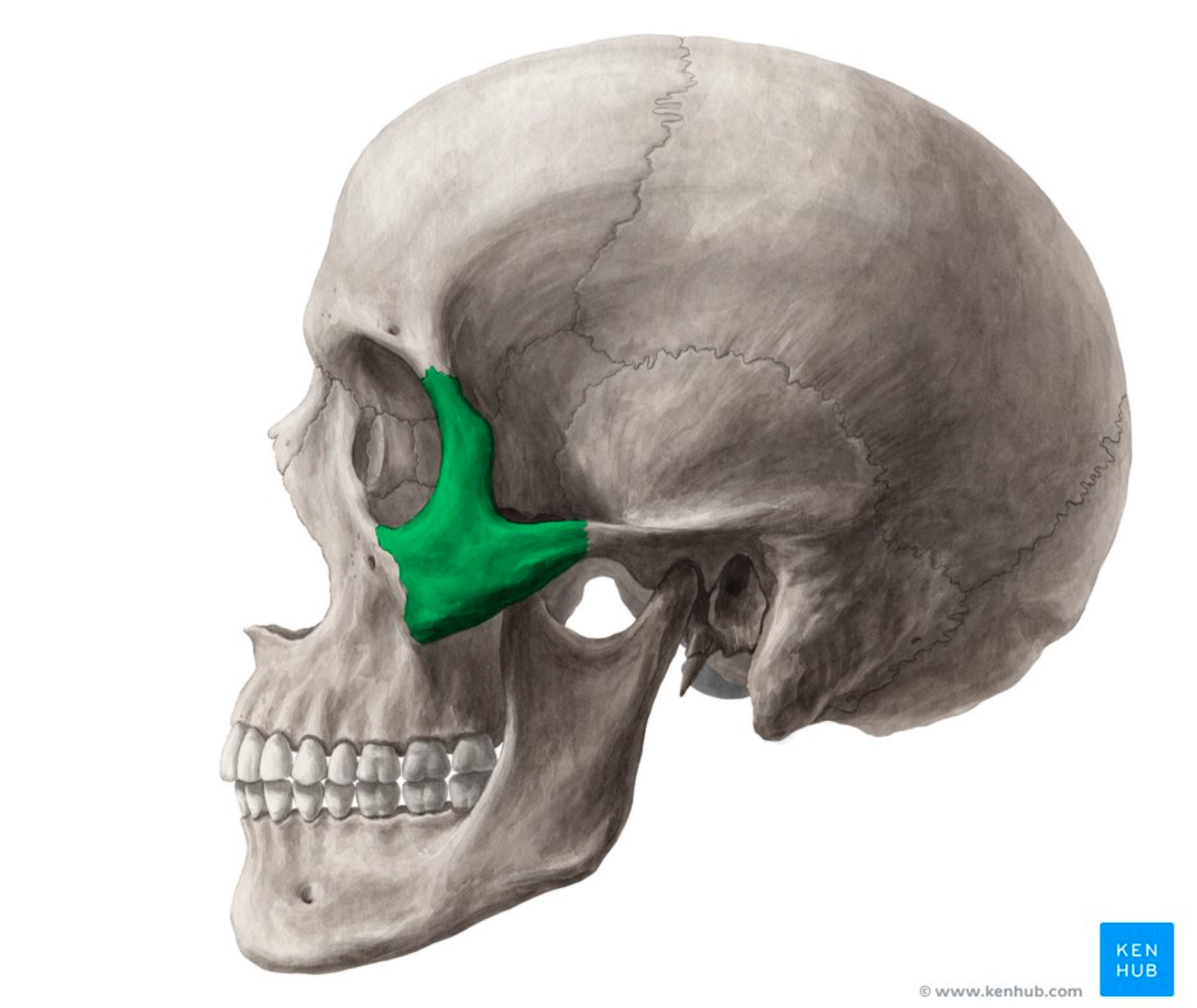
What does this represent?
zygomatic process
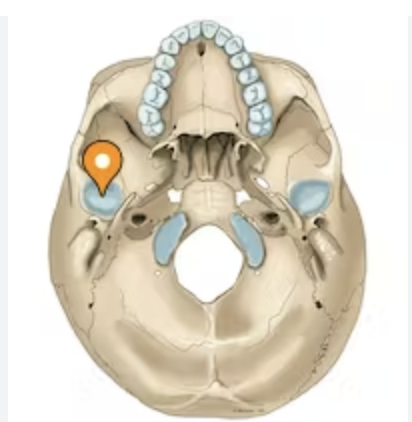
What does this hole represent?
external auditory meatus
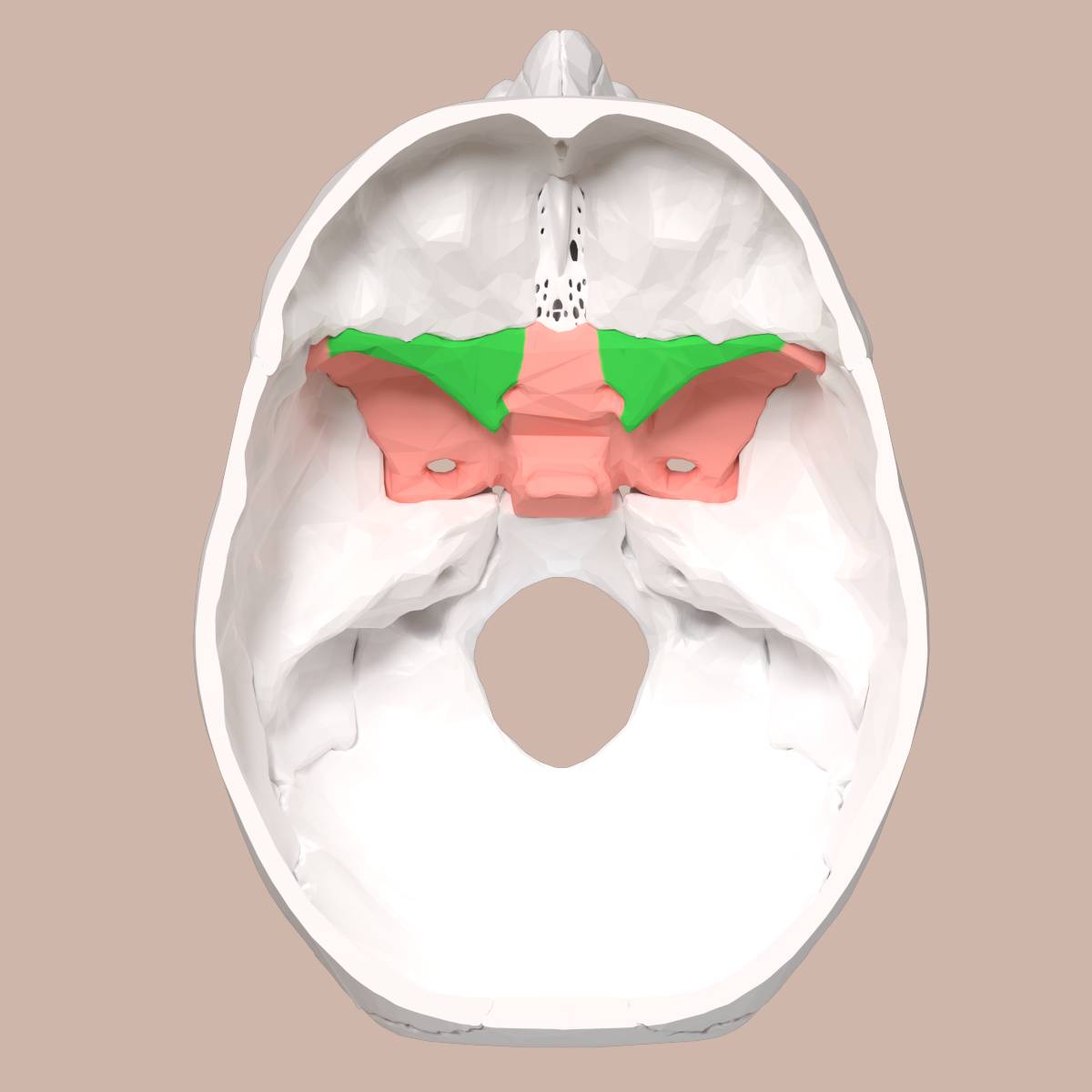
What does the green structure correspond to?
lesser wing of sphenoid
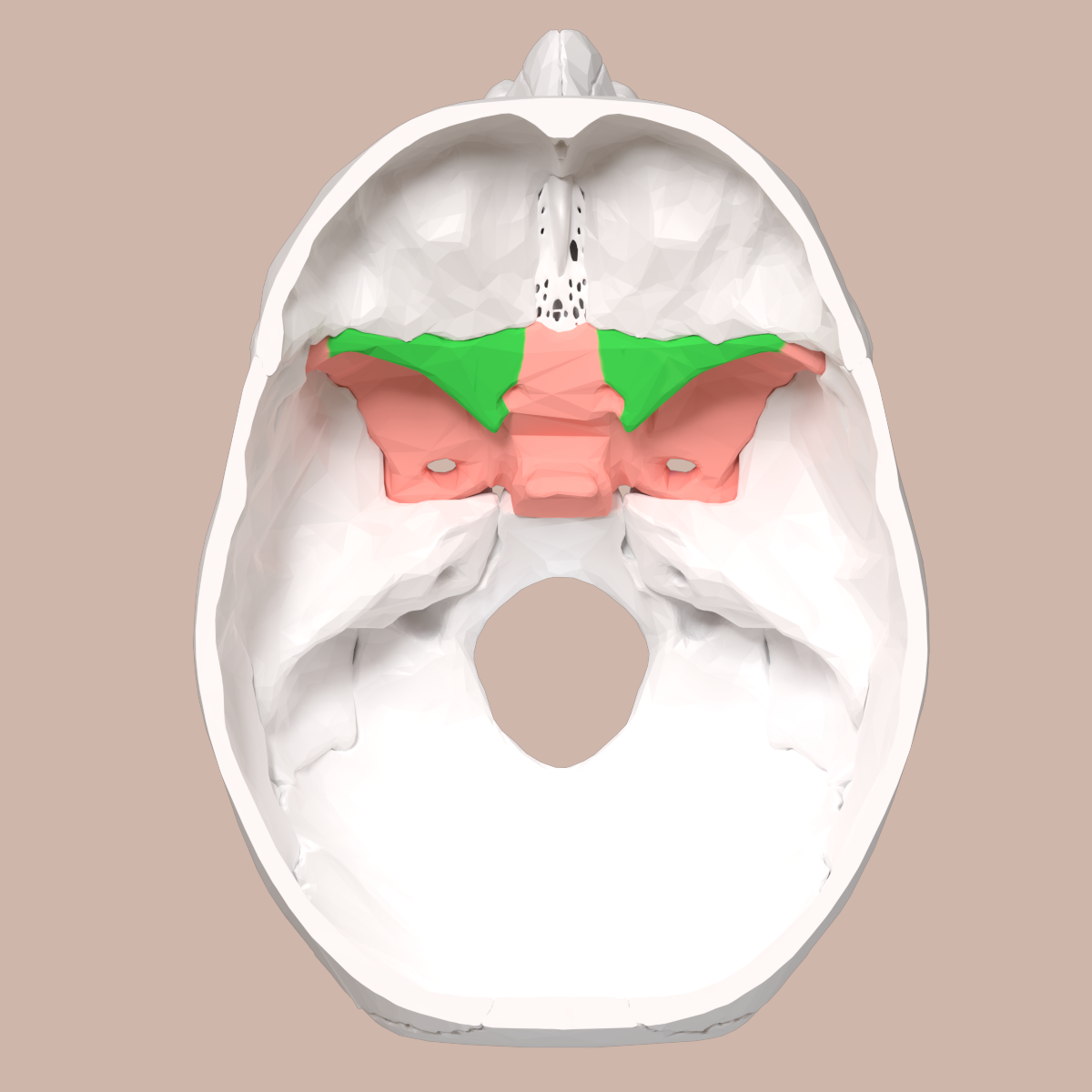
What does the pink structure correspond to?
greater wing of sphenoid
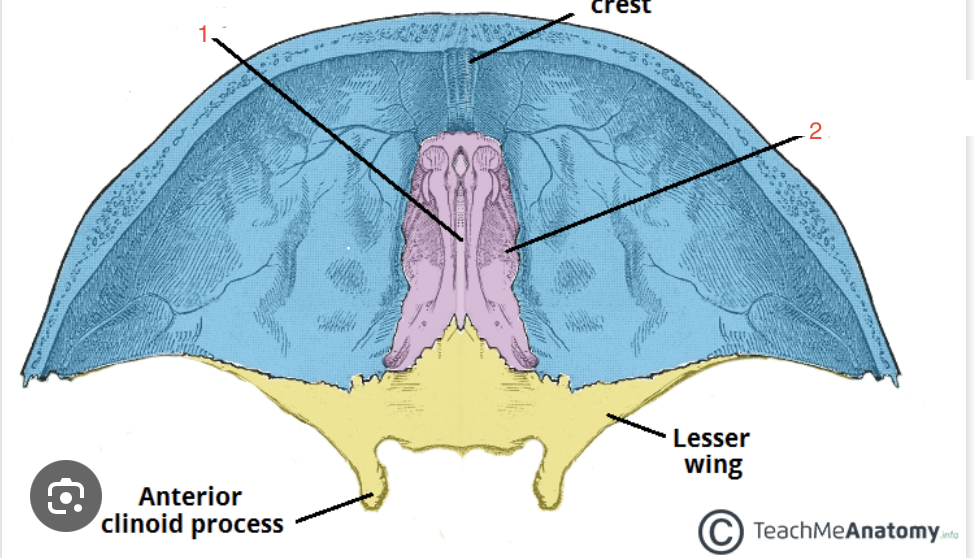
What structure does arrow 1 correspond with?
crista galli
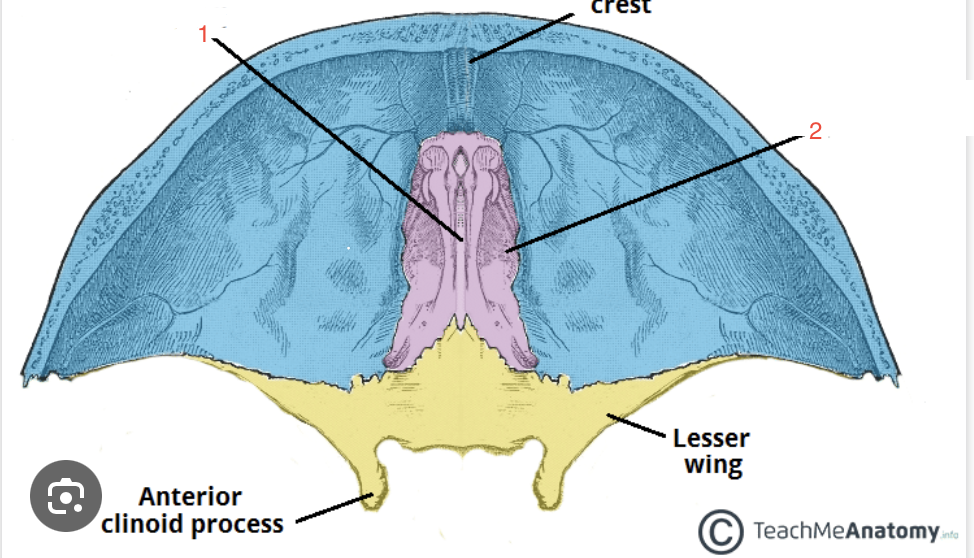
What structure does arrow 2 correspond with?
cribriform plate
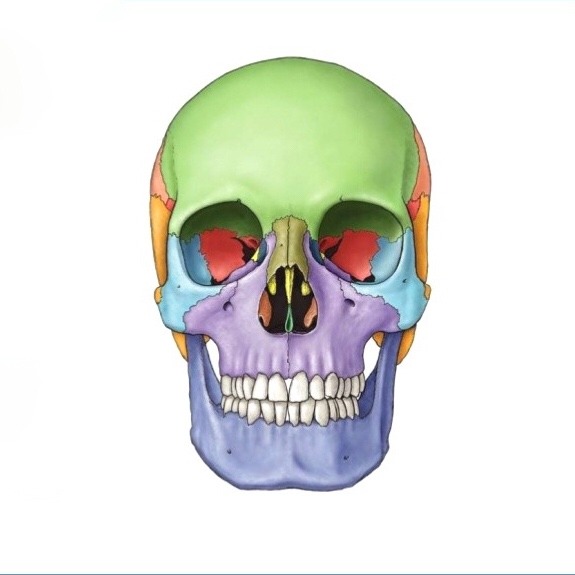
What does the purple structure correspond to?
Maxillae
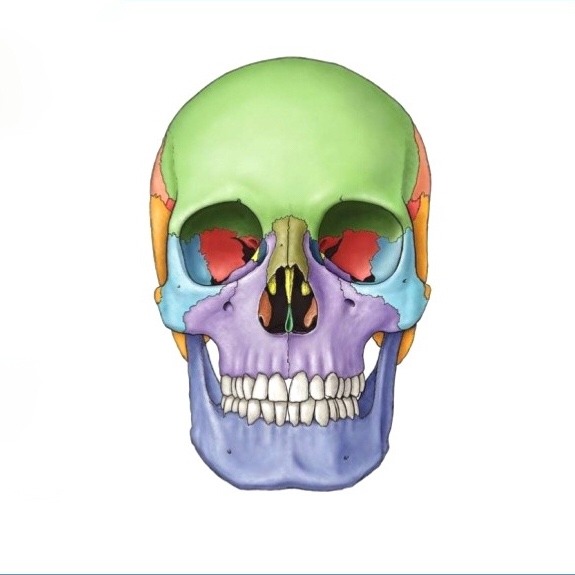
What does the dark green structure correspond to?
Nasal
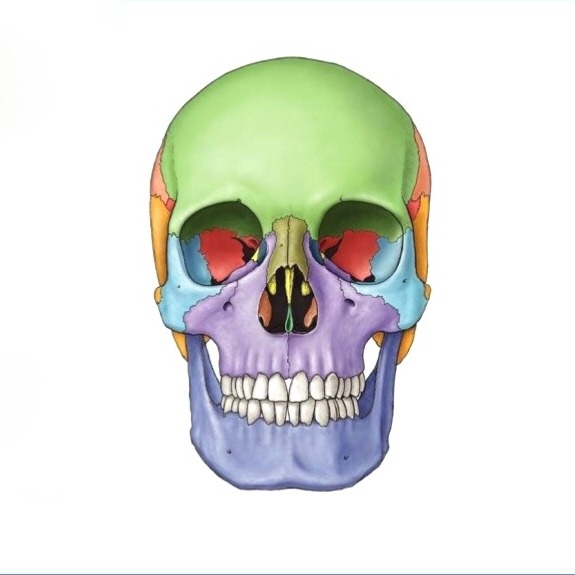
What does the dark blue structure correspond to?
mandible
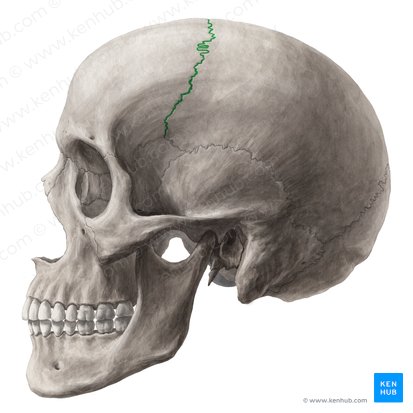
What does this structure correspond with?
coronal suture
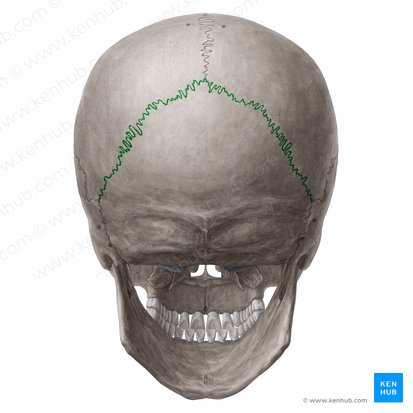
What does this structure correspond with?
lambdoidal suture
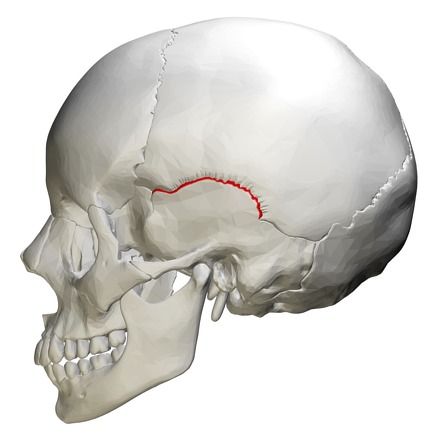
What does this structure correspond with?
squamous suture
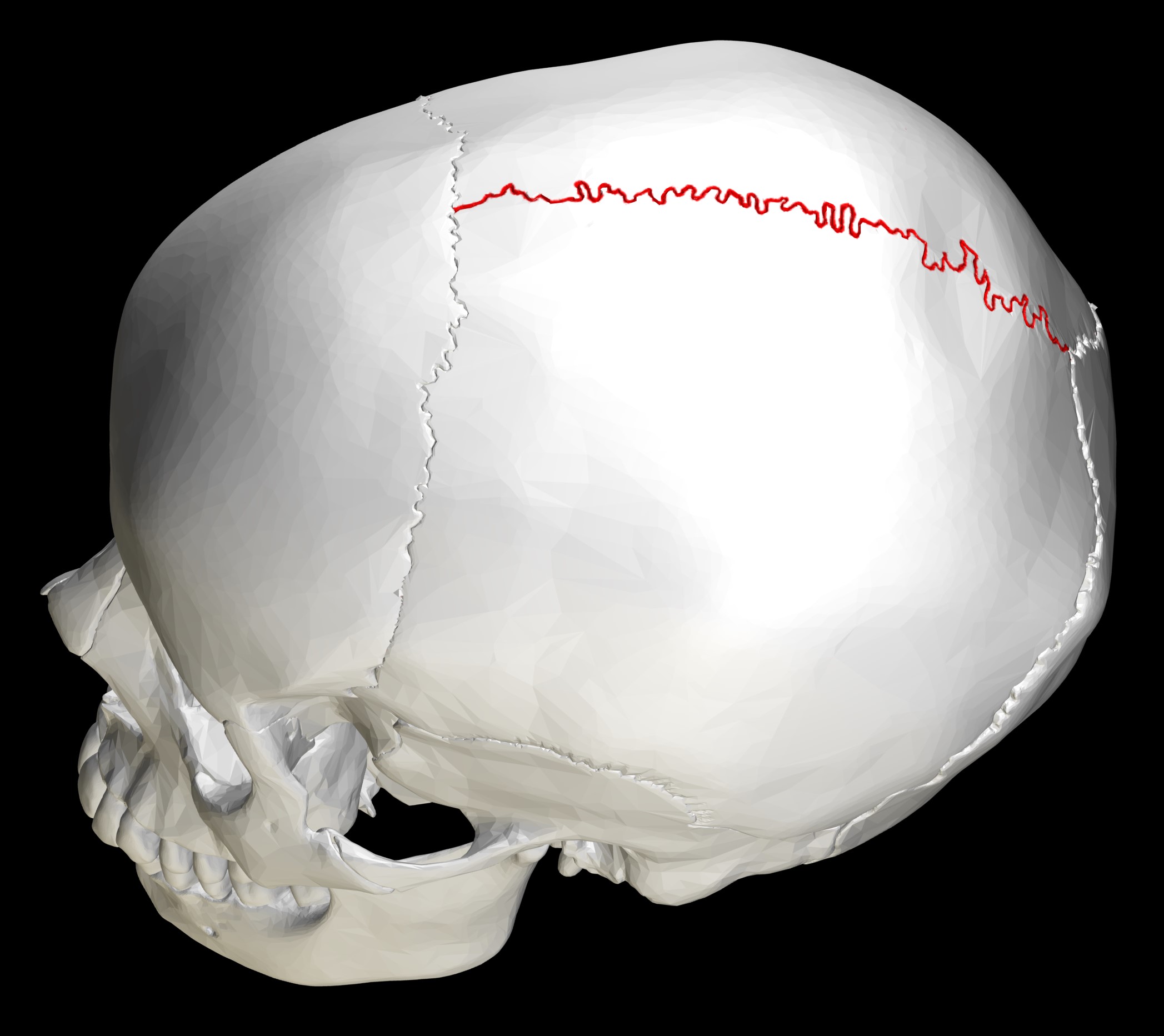
What does this structure correspond with?
sagittal suture
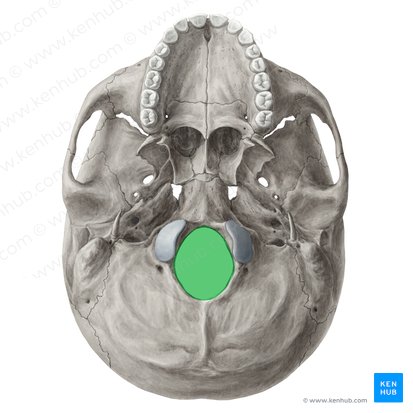
What does this structure correspond with?
formen magnum
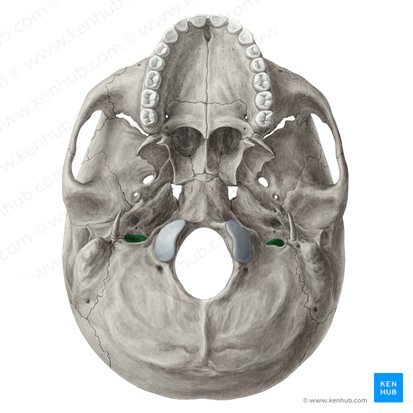
What does this structure correspond with?
jugular foramen
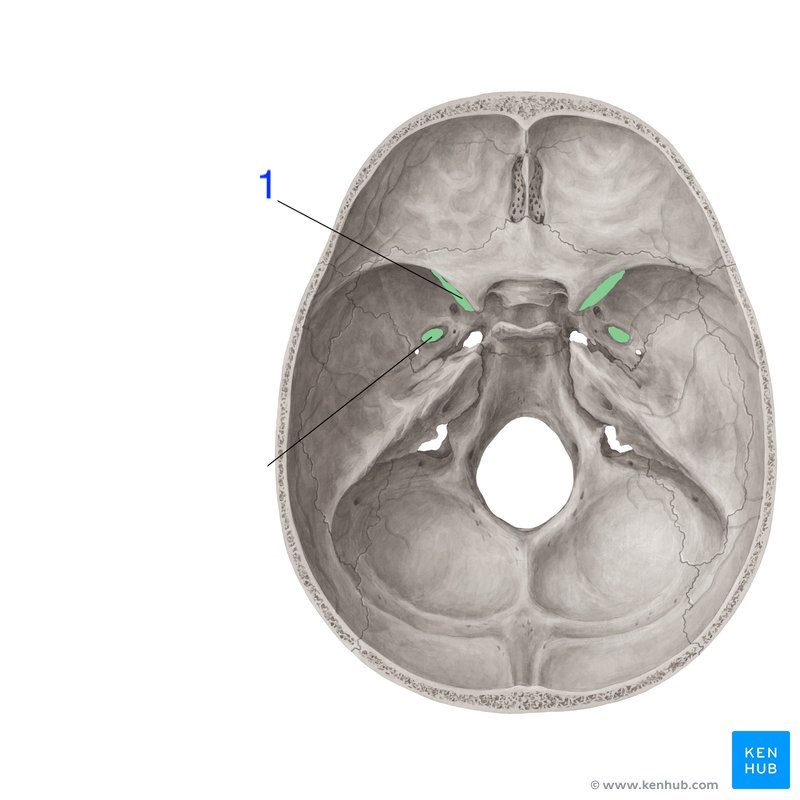
What does this structure correspond with?
carotid canal
What does this structure (1) correspond with?
superior orbital fissure
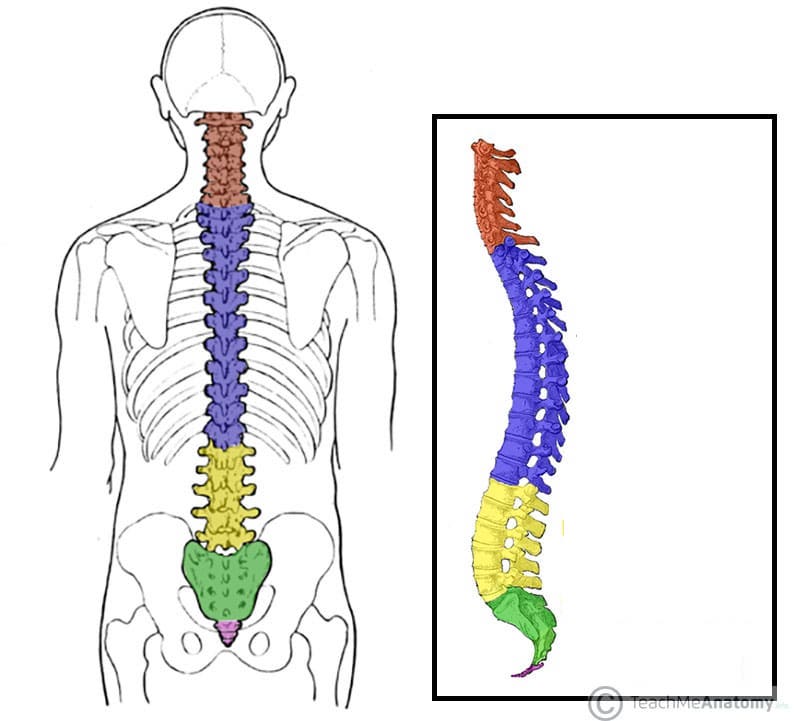
What does the red structure correspond with?
cervical vertebrae
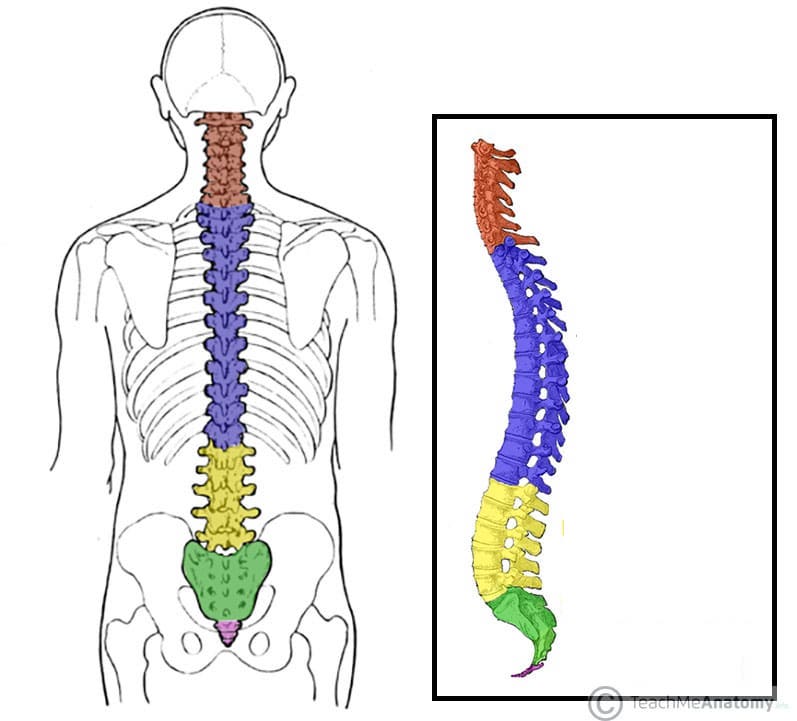
What does the purple structure correspond with?
thoracic vertebrae
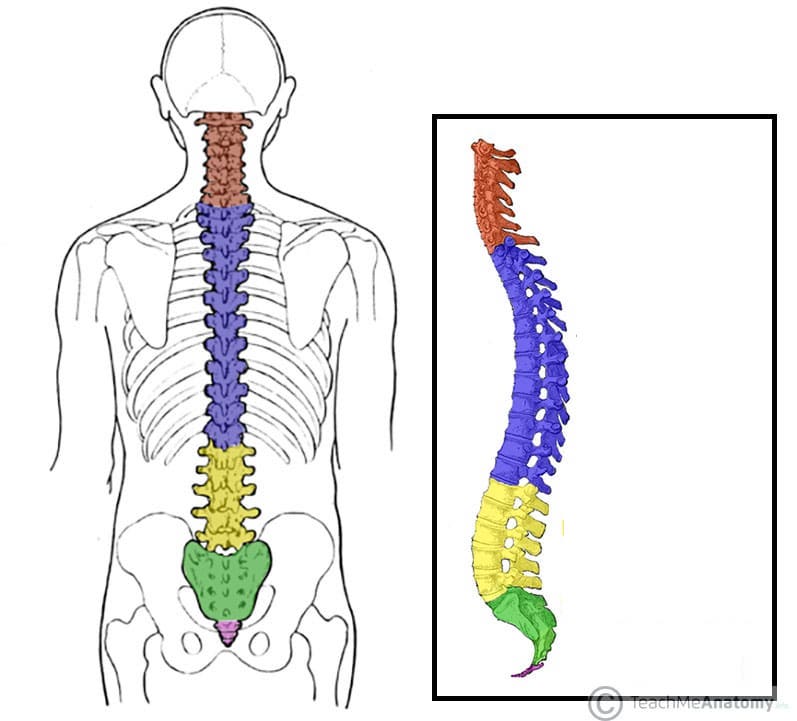
What does the yellow structure correspond with?
lumbar vertebrae
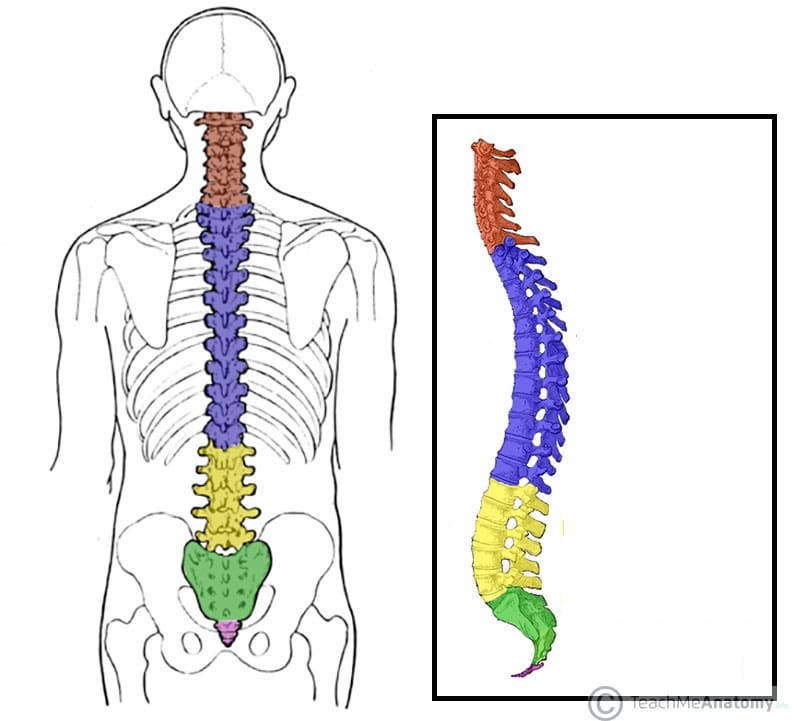
What does the green structure correspond with?
sacrum
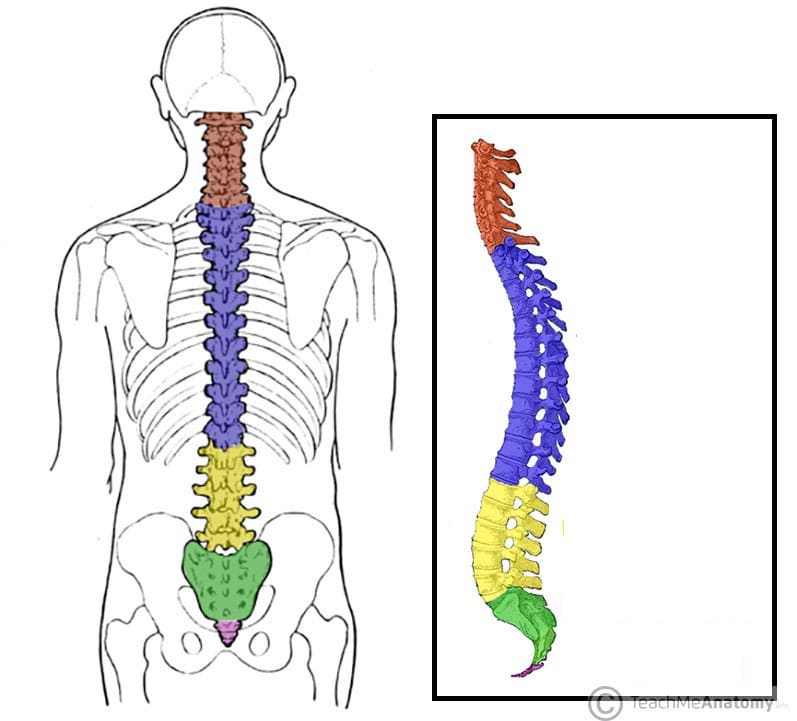
What does the pink structure correspond with?
coccyx
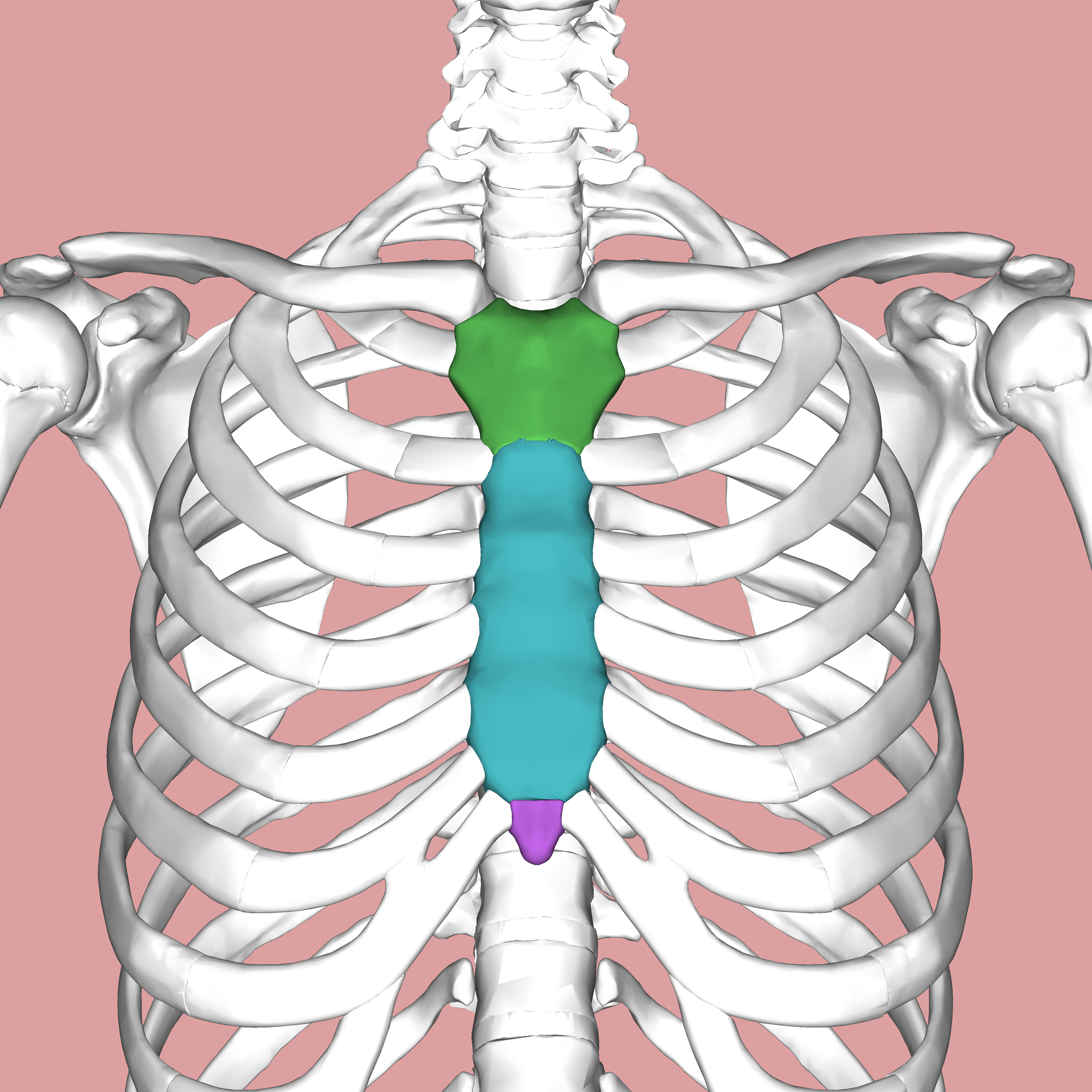
What does the green structure correspond with?
manubrium of sternum
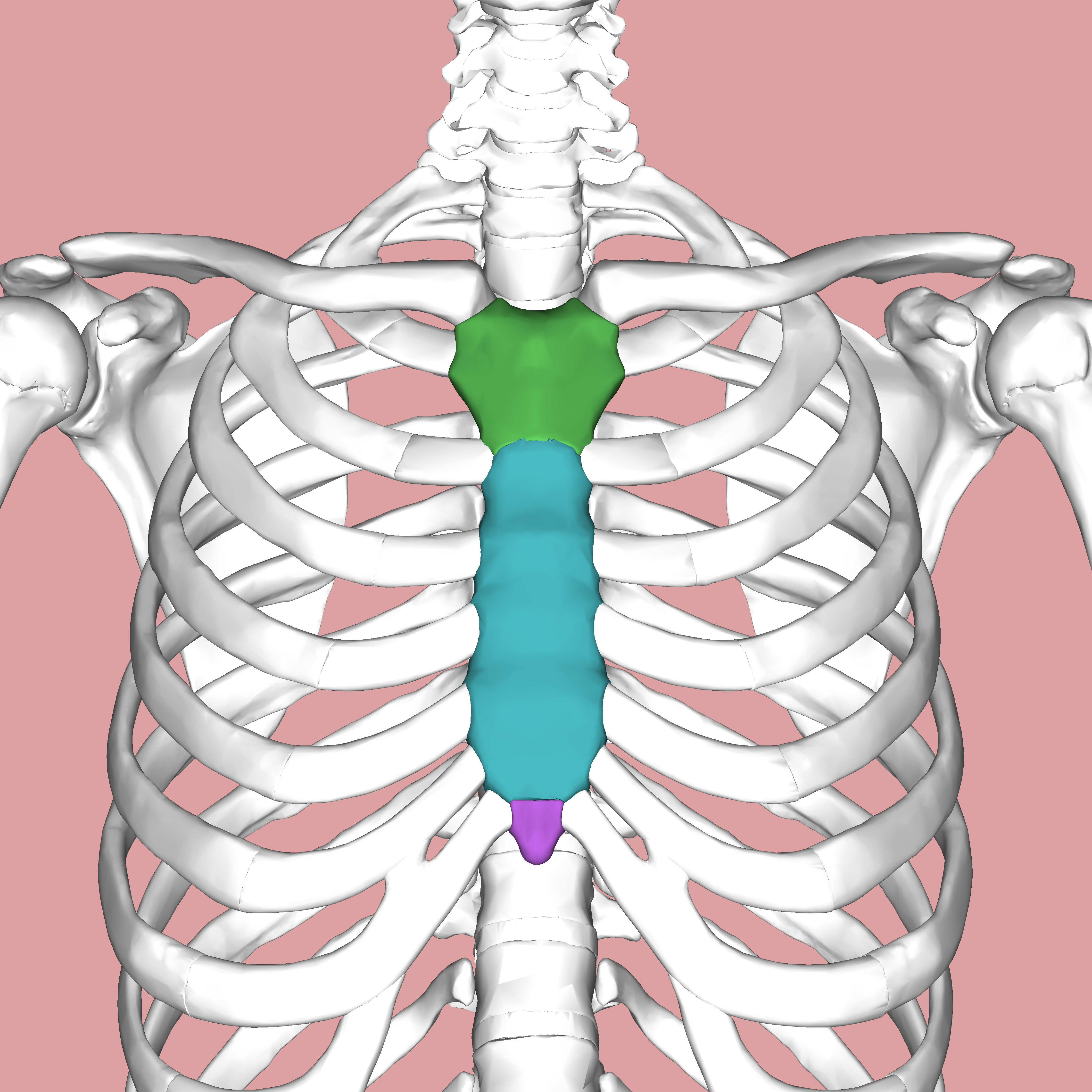
What does the blue structure correspond with?
body of sternum
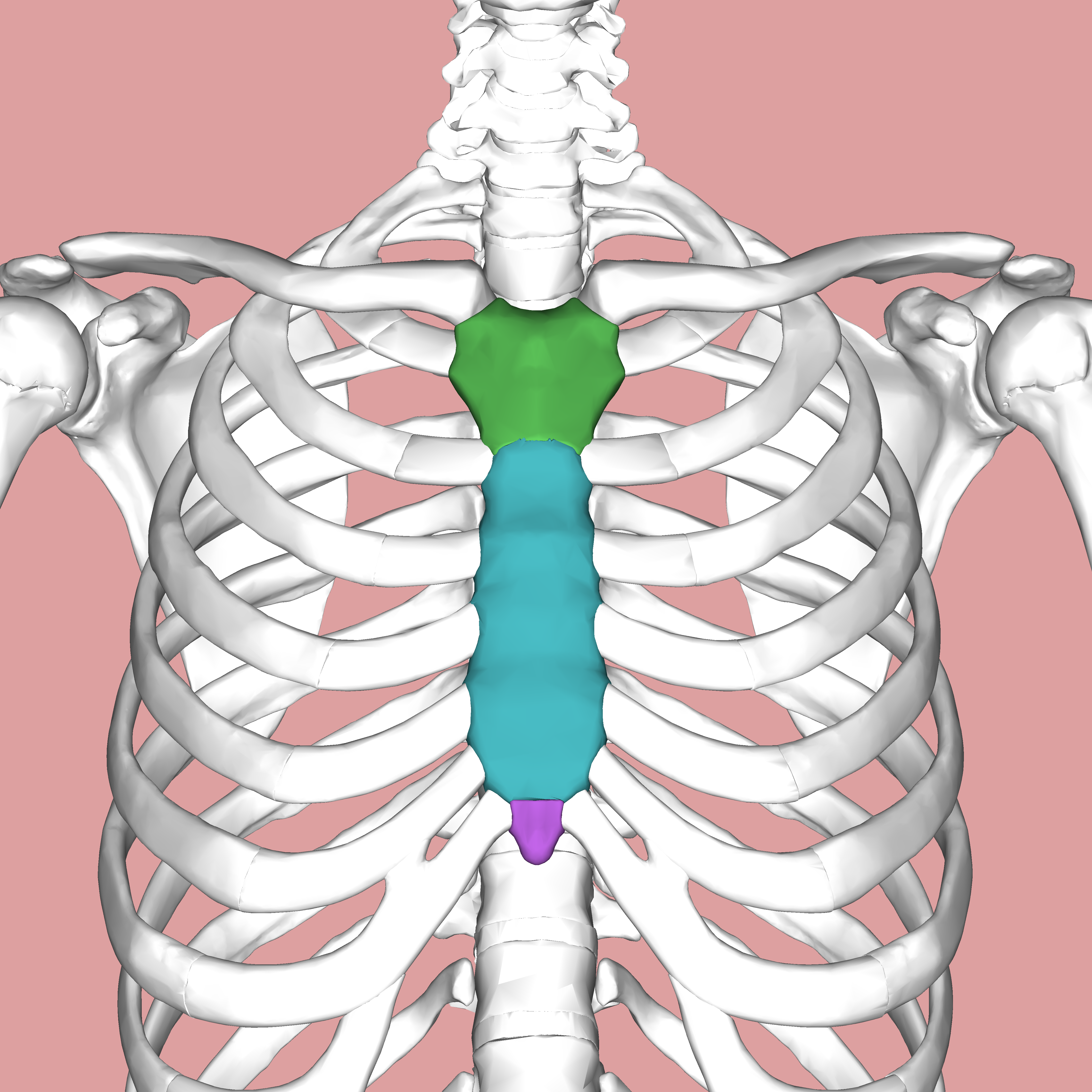
What does the purple structure correspond with?
xiphoid process of sternum
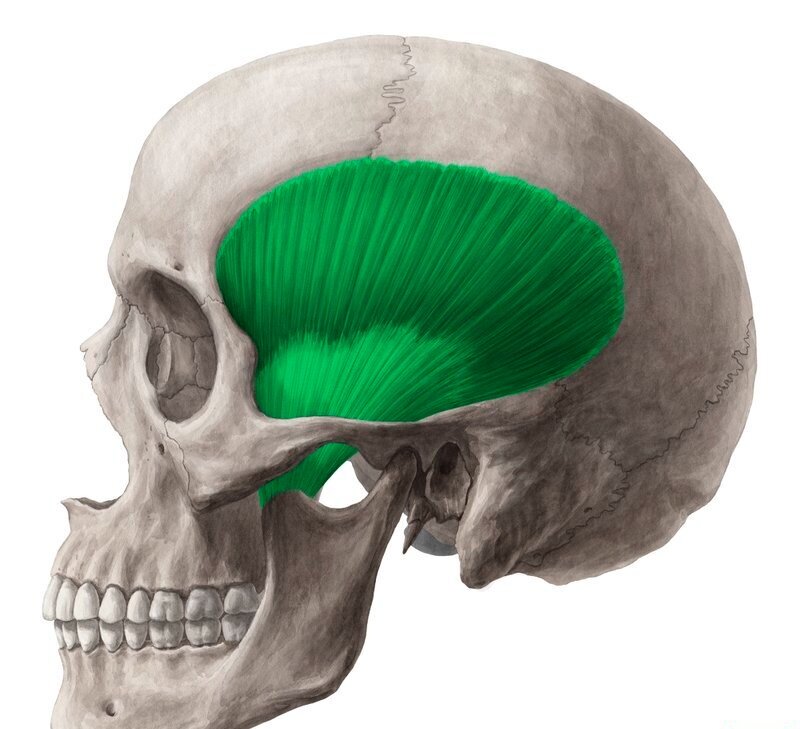
What does this structure correspond with?
temporalis; closes jaw (elevates mandible)
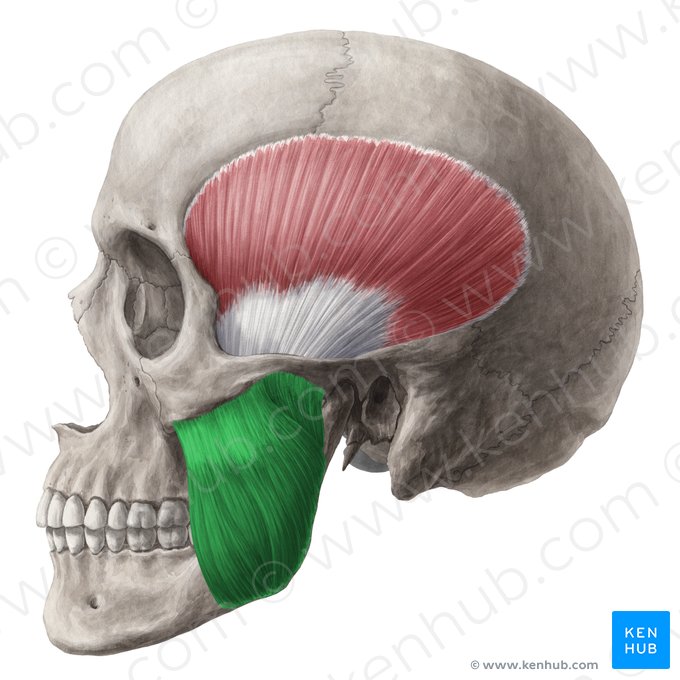
What does this structure correspond with?
masseter; closes jaw (elevates and retracts mandible)
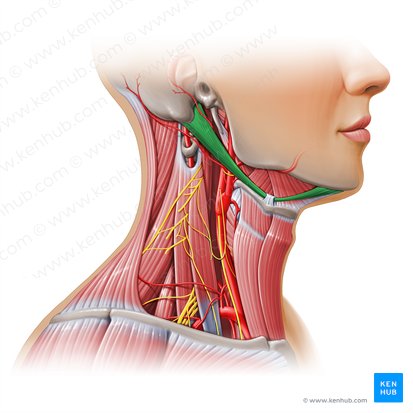
What does this structure correspond with?
digastricus; open mouth (lowers mandible), elevates and holds hyoid
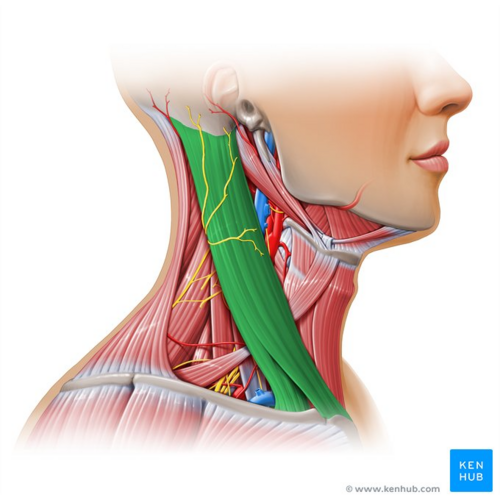
What does this structure correspond with?
sternocleidomastoid; rotates/tilts head sideways
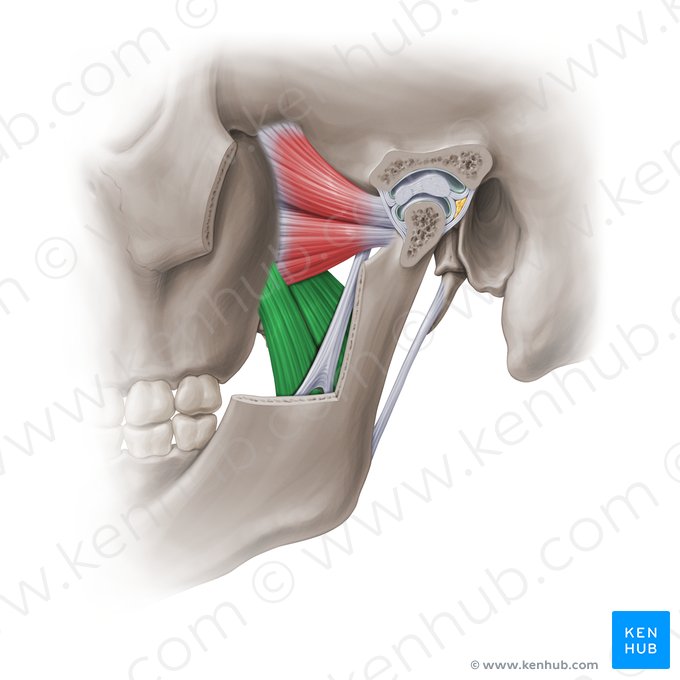
What does this structure correspond with?
medial pterygoid; closes jaw
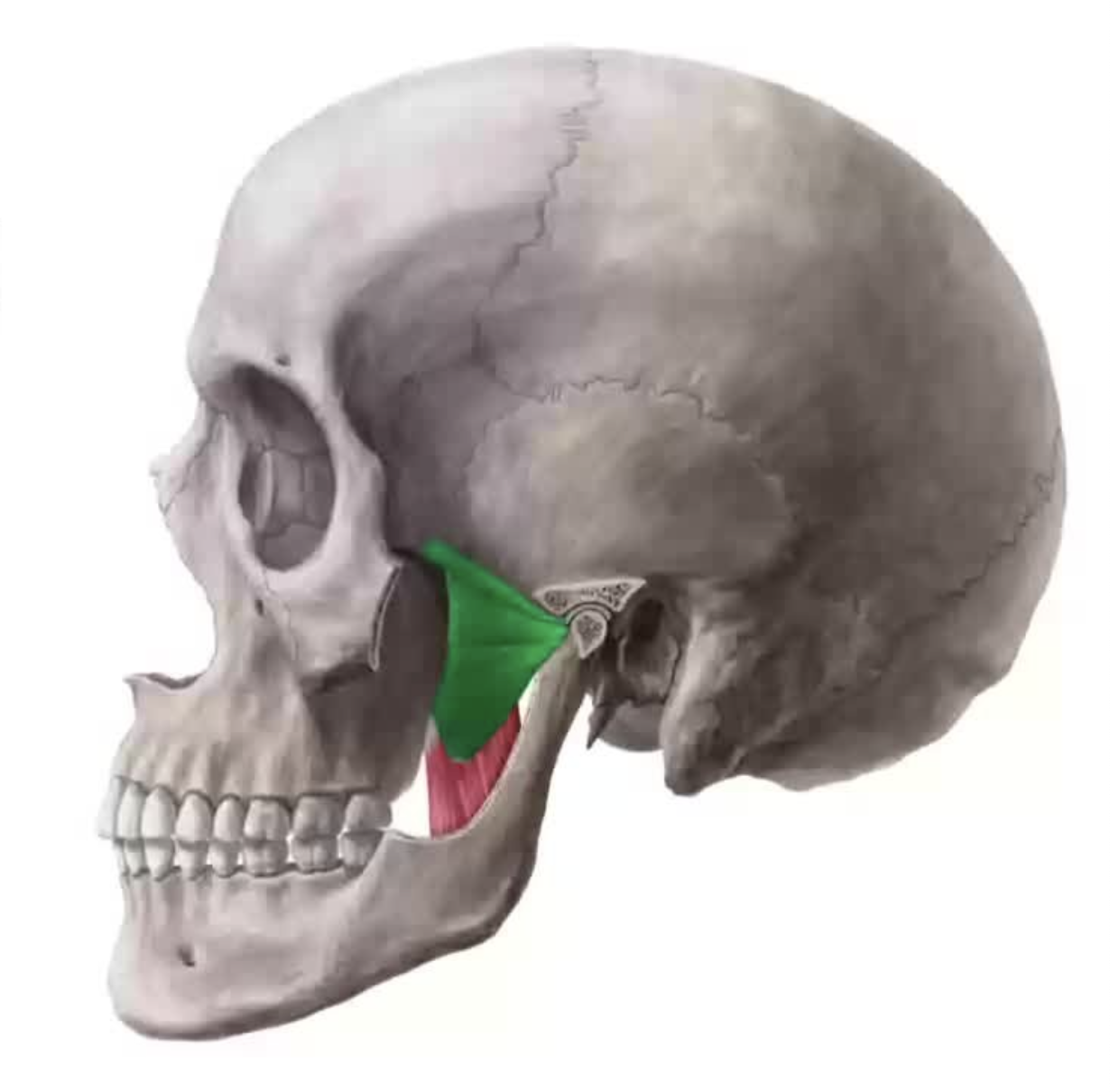
What does this structure correspond with?
lateral pterygoid; opens jaw
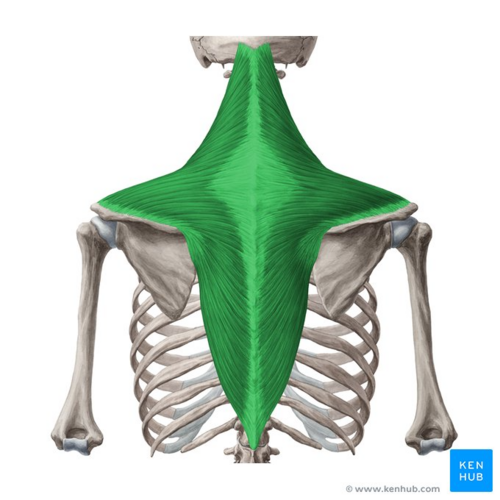
What does this structure correspond with?
trapezius; elevates, depresses, and retracts scapula
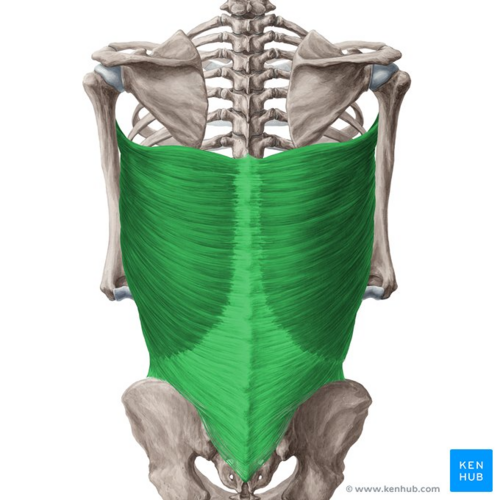
What does this structure correspond with?
latissimus dorsi; adducts and extends shoulder, rotates shoulder, draws shoulder down and backward
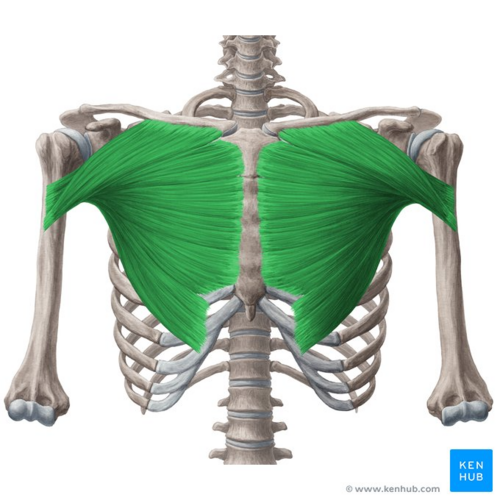
What does this structure correspond with?
pectoralis major; flexion, abduction, medial rotation of shoulder
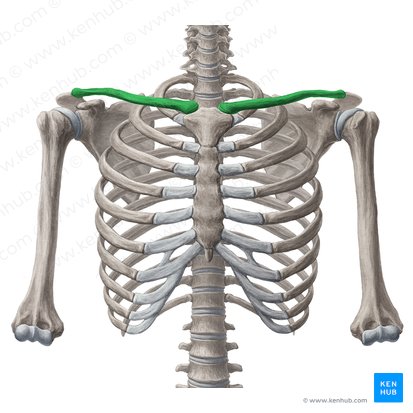
What does this structure correspond with?
clavicle
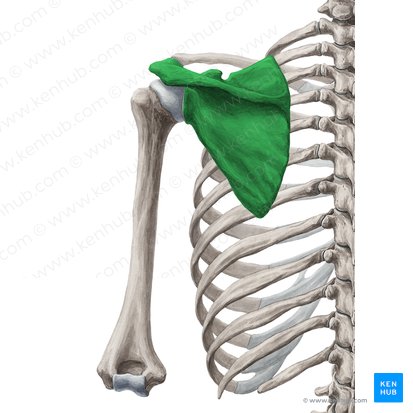
What does this structure correspond with?
scapula
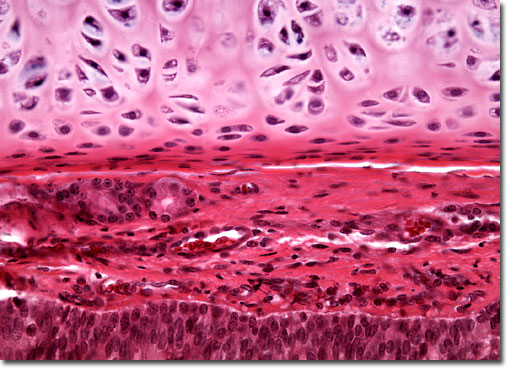
What type of tissue is this?
hyaline cartilage
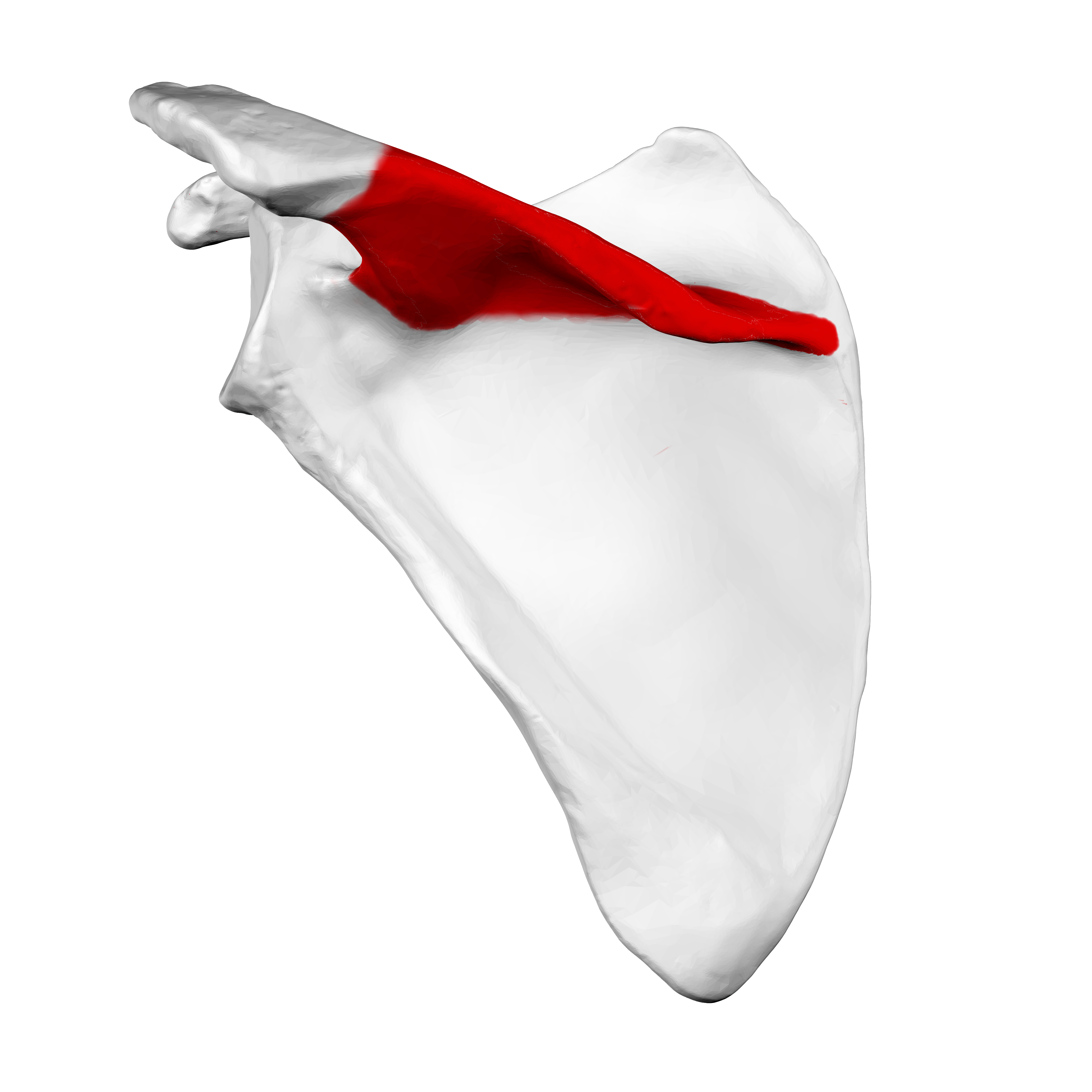
What does this structure correspond with?
spine of scapula
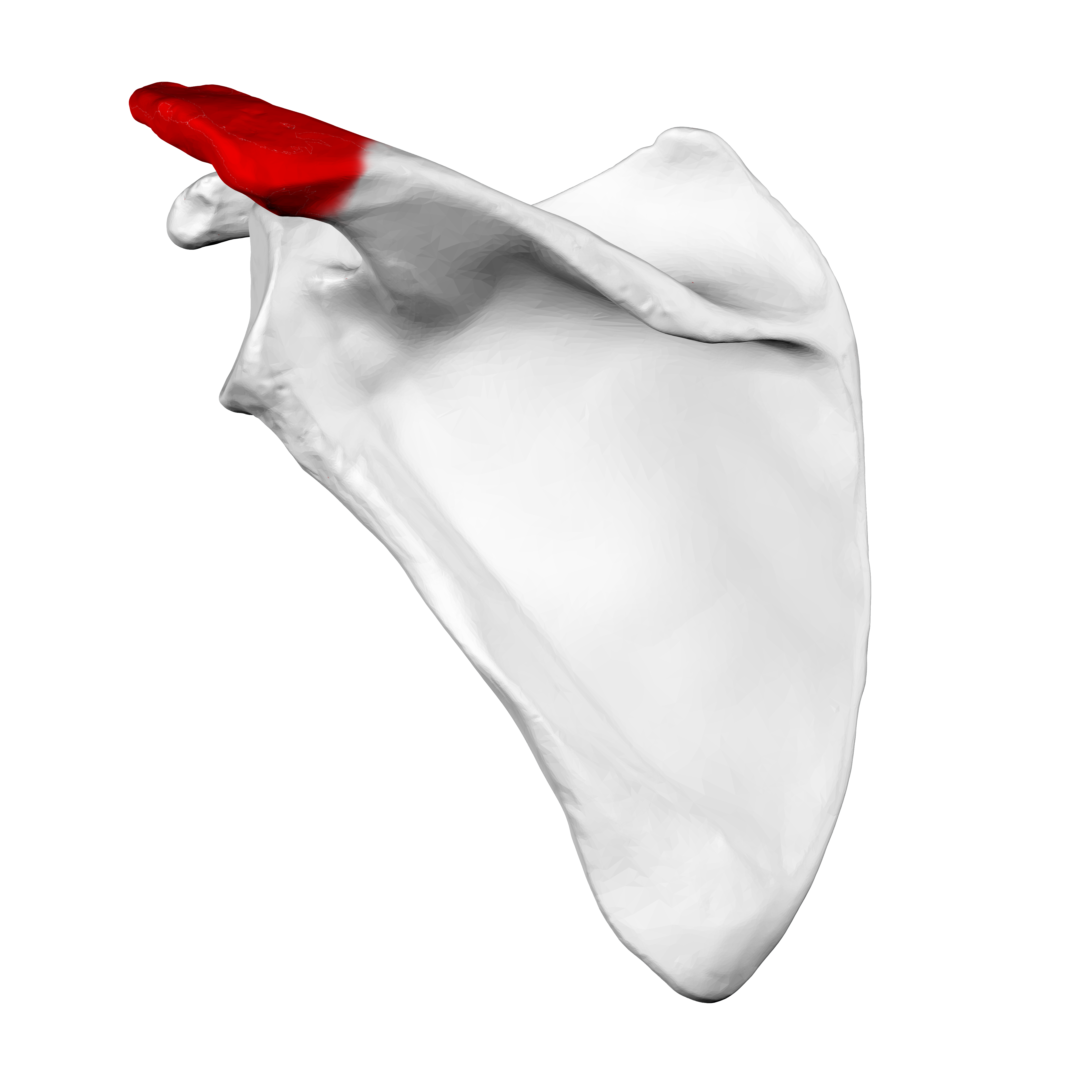
What does this structure correspond with?
acromion of scapula
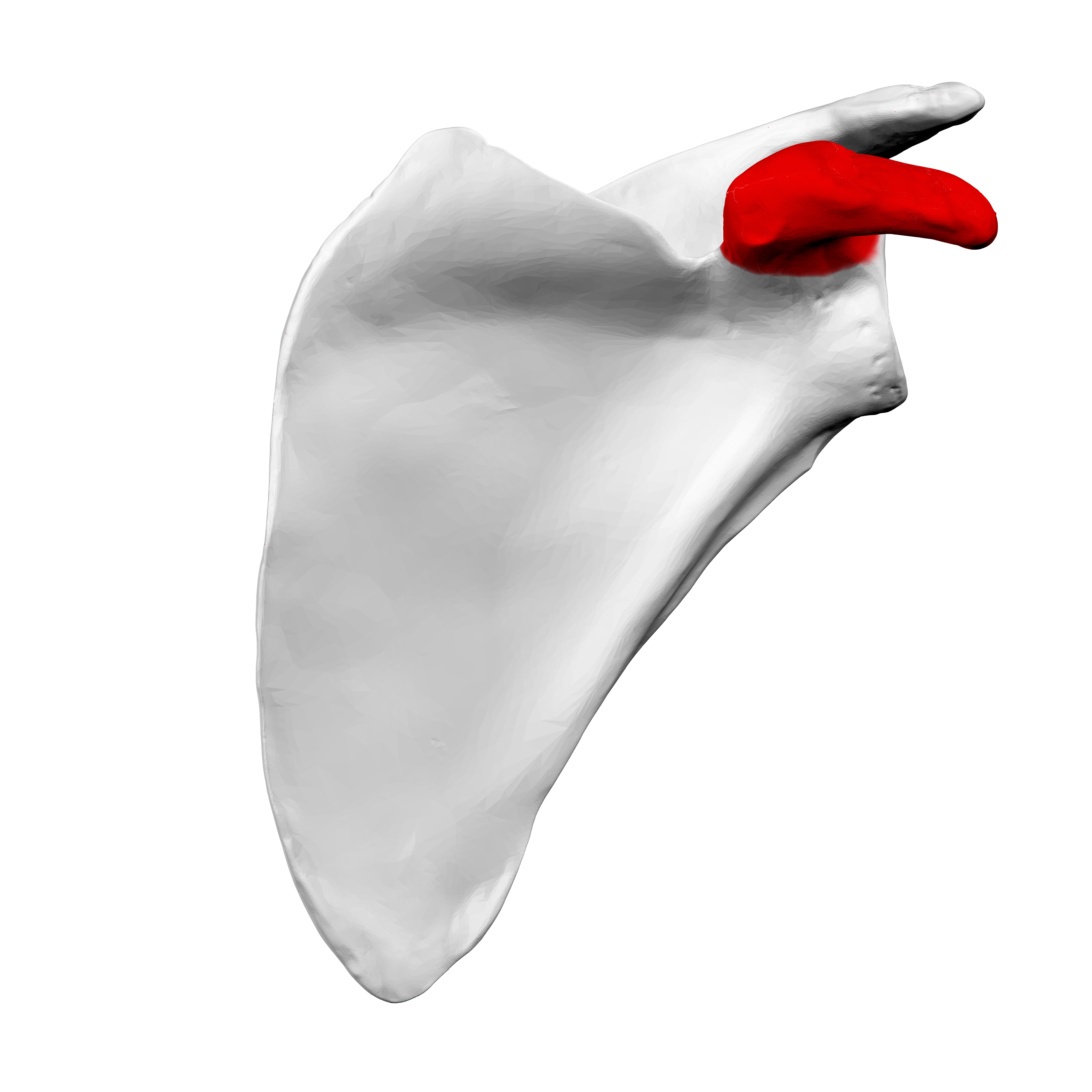
What does this structure correspond with?
coracoid process of scapula
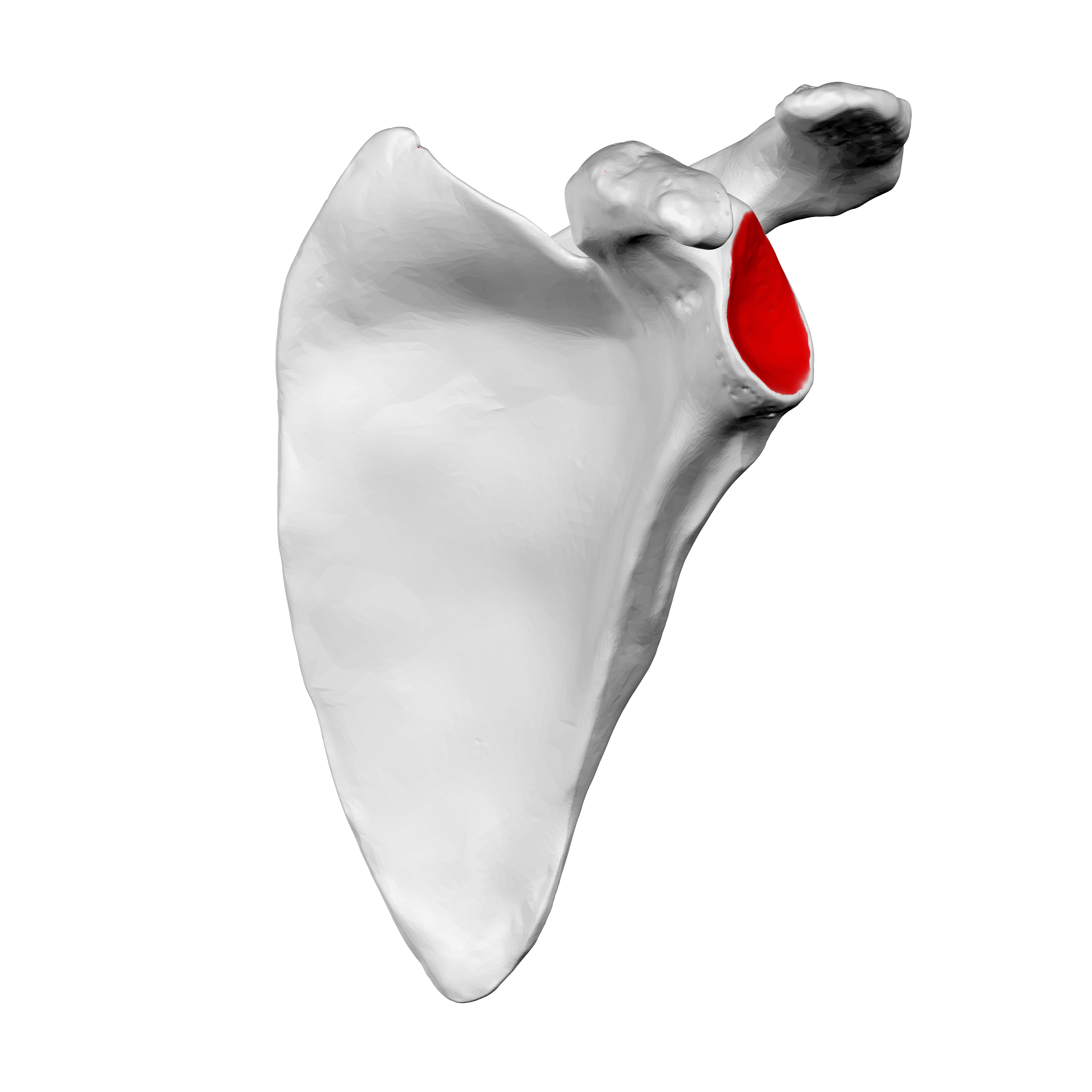
What does this structure correspond with?
glenoid cavity of scapula`
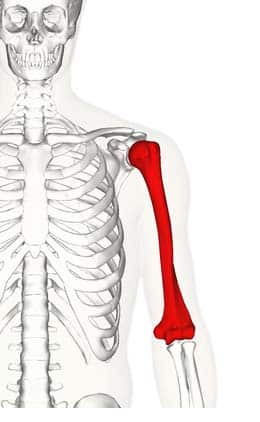
What does this structure correspond with?
humerus
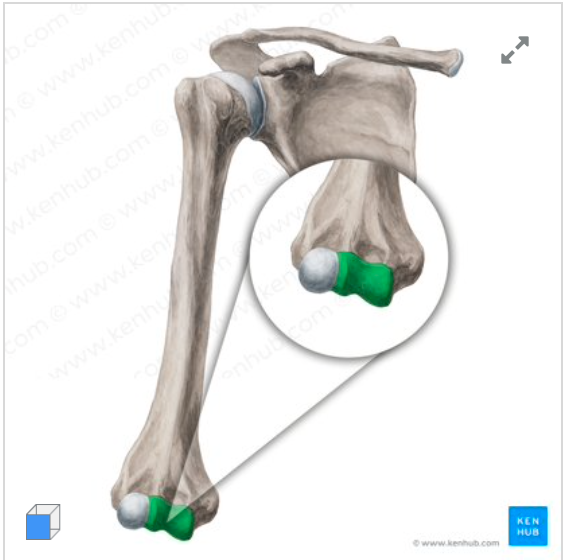
What does this structure correspond with?
trochlea of humerus
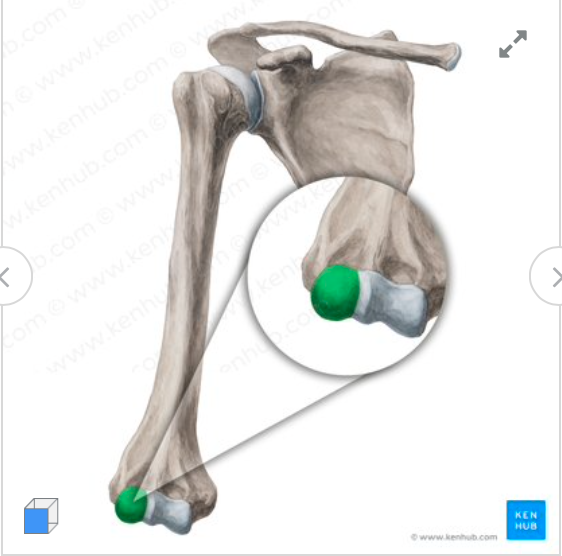
What does this structure correspond with?
capitulum of humerus
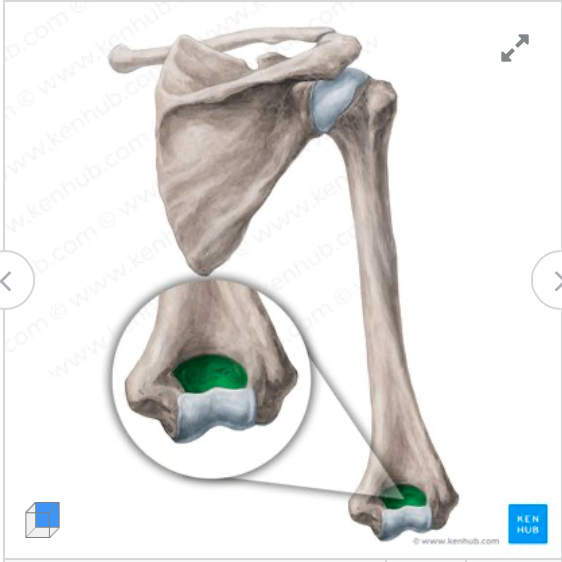
What does this structure correspond with?
olecranon fossa of humerus
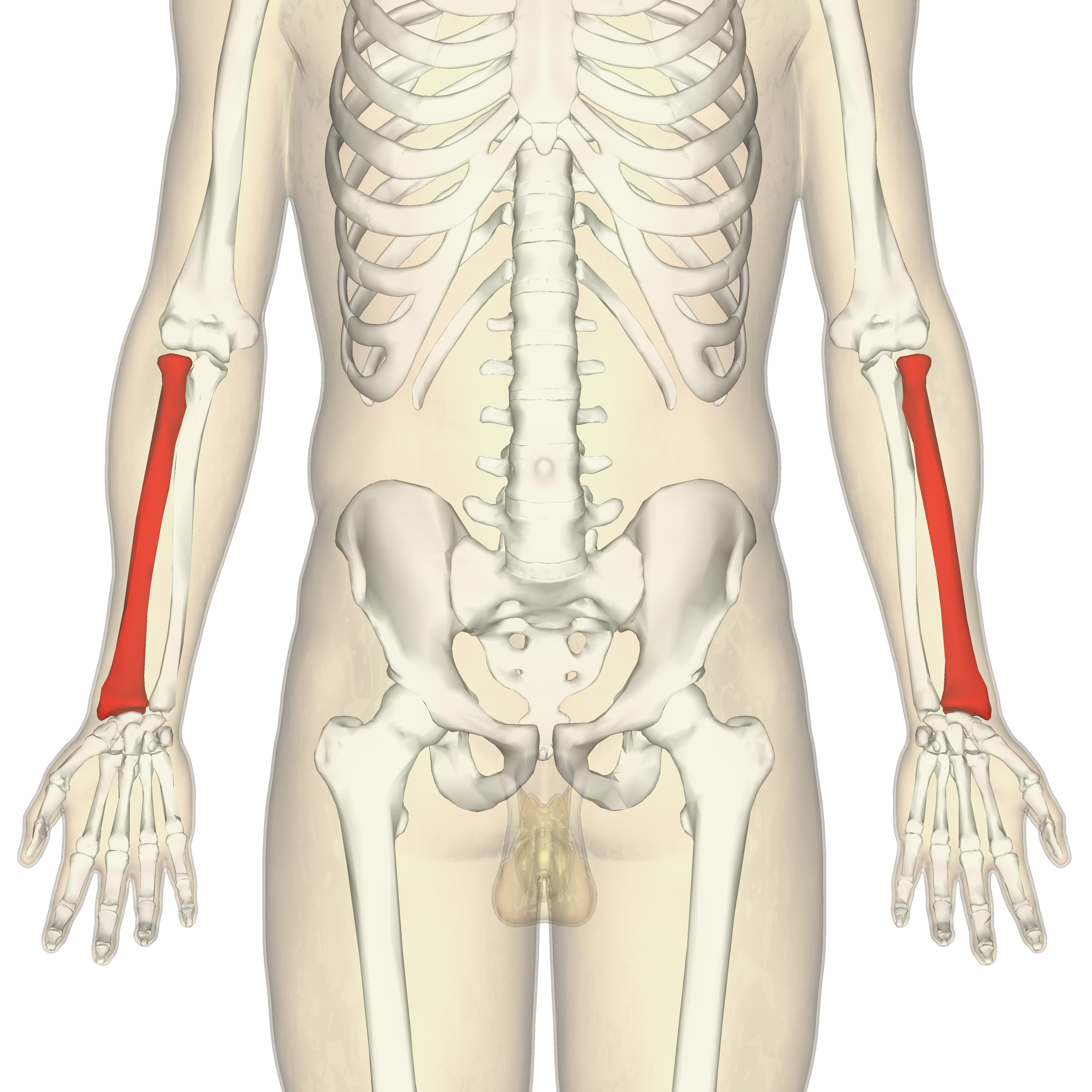
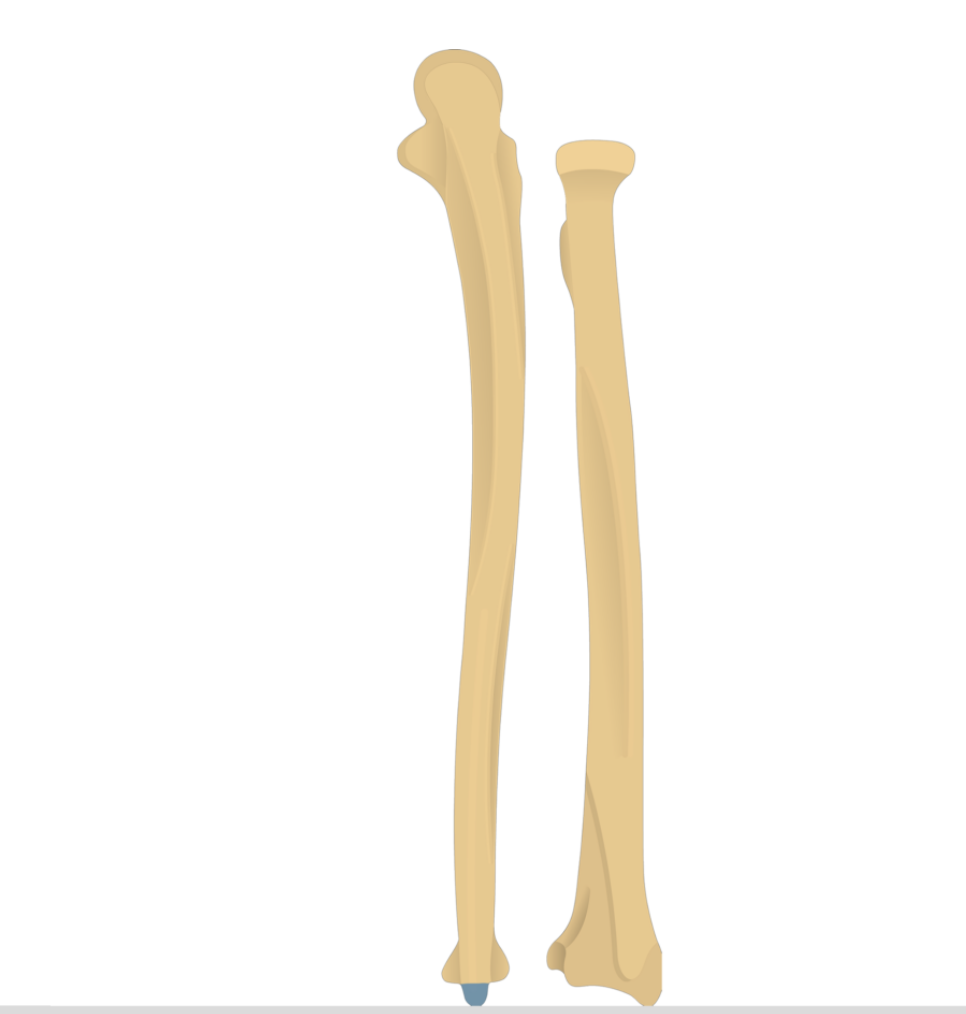
What does this structure correspond with?
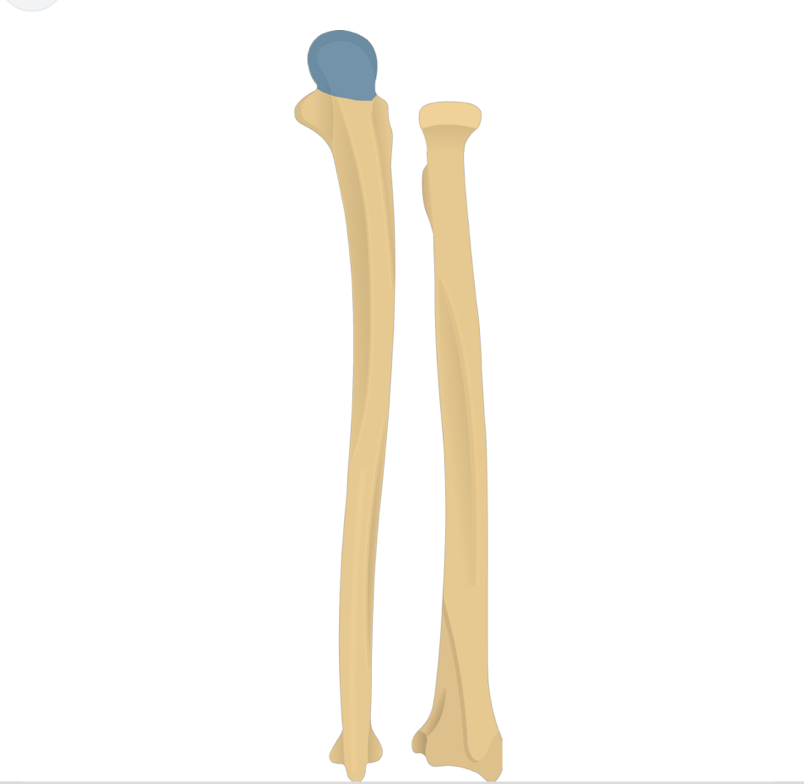
radius

What does this structure correspond with?
radial tuberosity

What does this structure correspond with?
styloid process
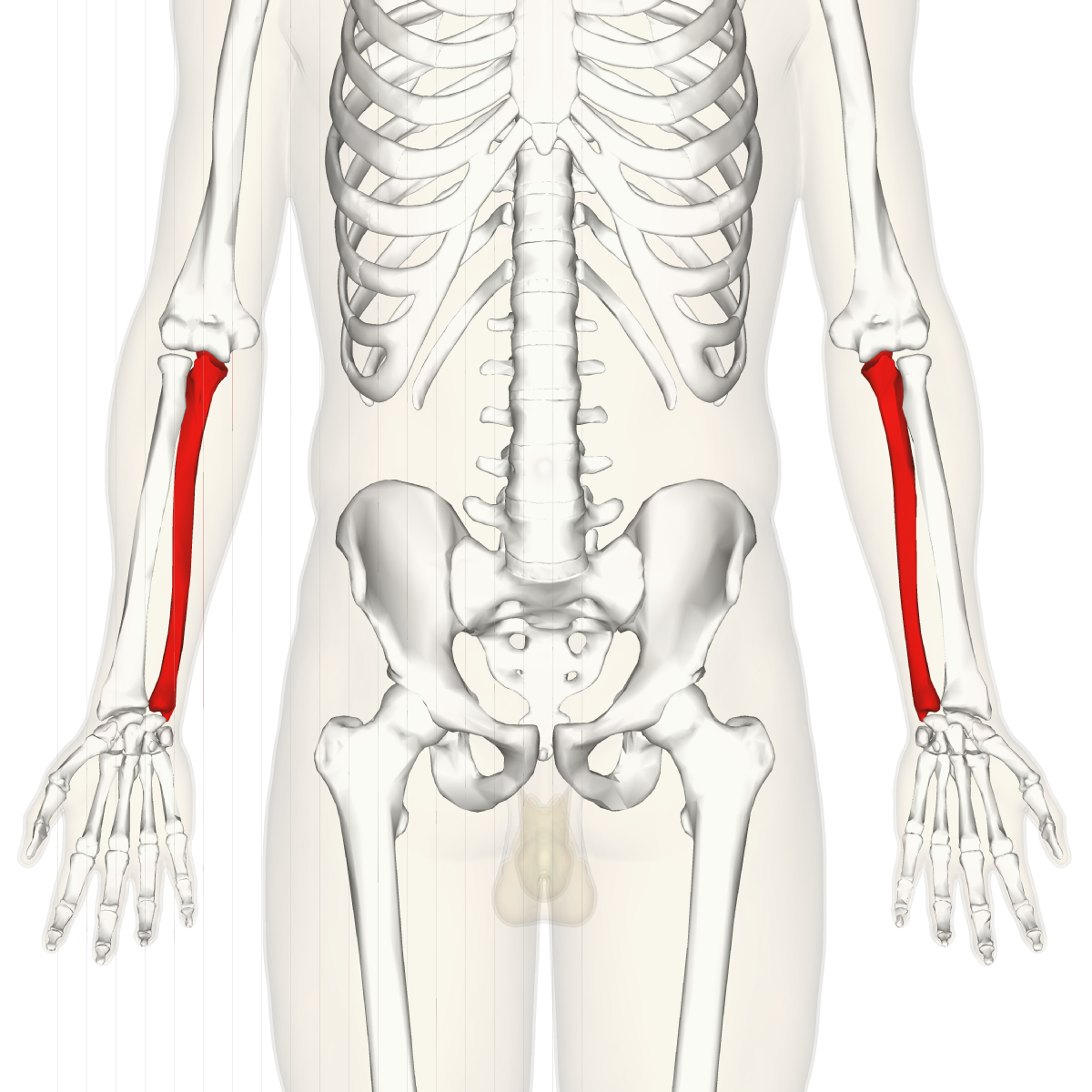
What does this structure correspond with?
ulna
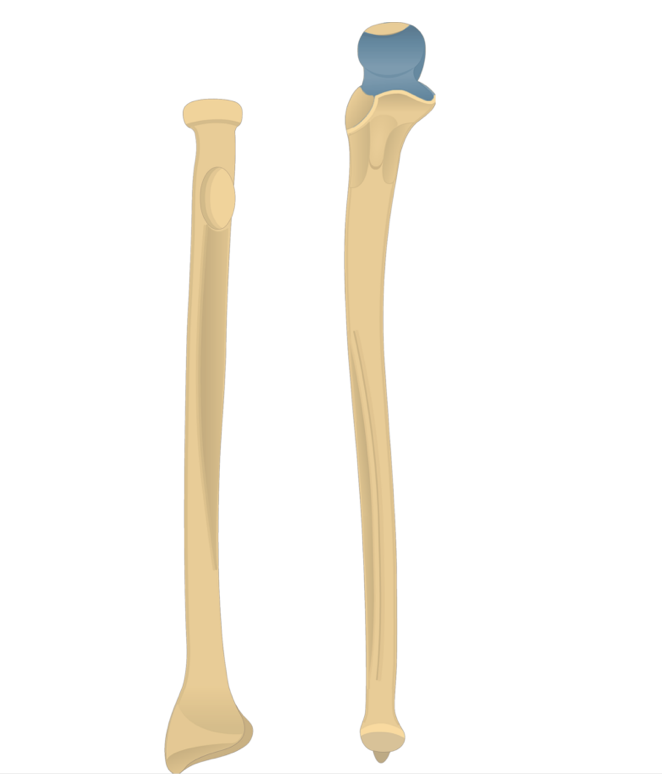
What does this structure correspond with?
trochlear notch
What does this structure correspond with?
olecranon process
What does this structure correspond with?
styloid process
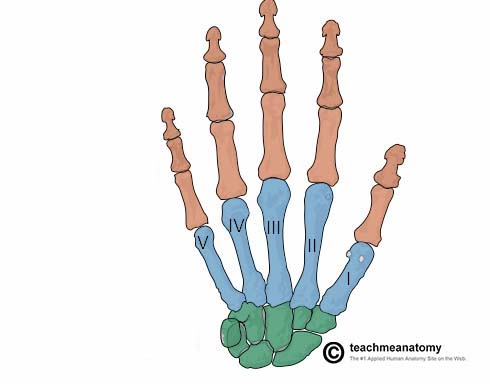
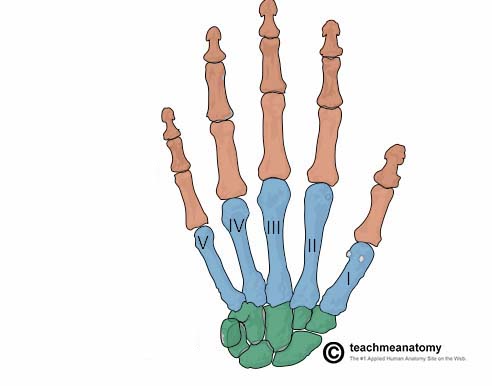
What does the green structure correspond with?
carpus
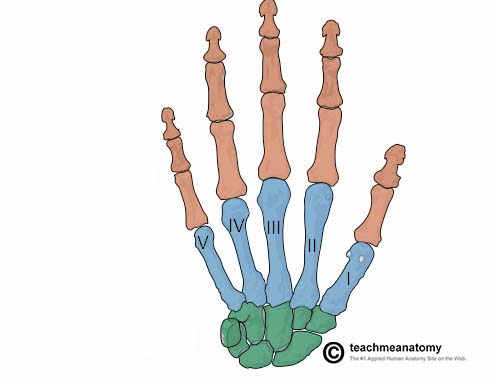
What does the blue structure correspond with?
metacarpus
What does the red structure correspond with?
phalanges
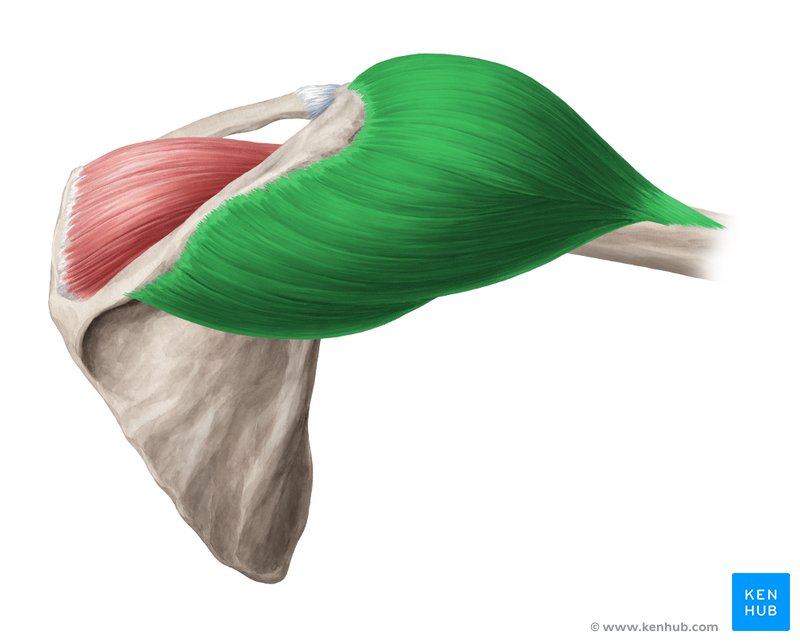
What does this structure correspond with?
deltoid; abducts shoulder; posterior deltoid- extension of shoulder; anterior deltoid- flexes shoulder
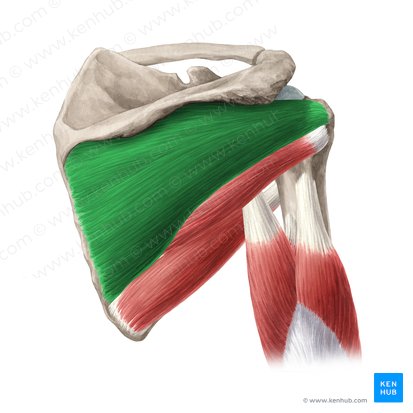
What does this structure correspond with?
infraspinatus; lateral rotation of shoulder, horizontal adduction of shoulder
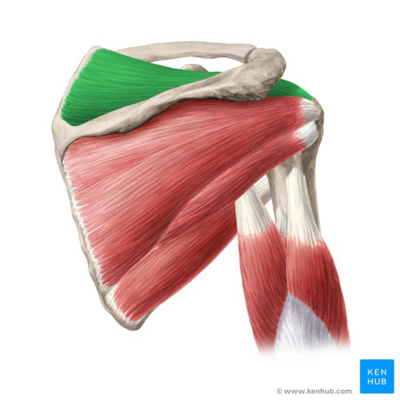
What does this structure correspond with?
supraspinatus; abduction of shoulder, stabilizes joint
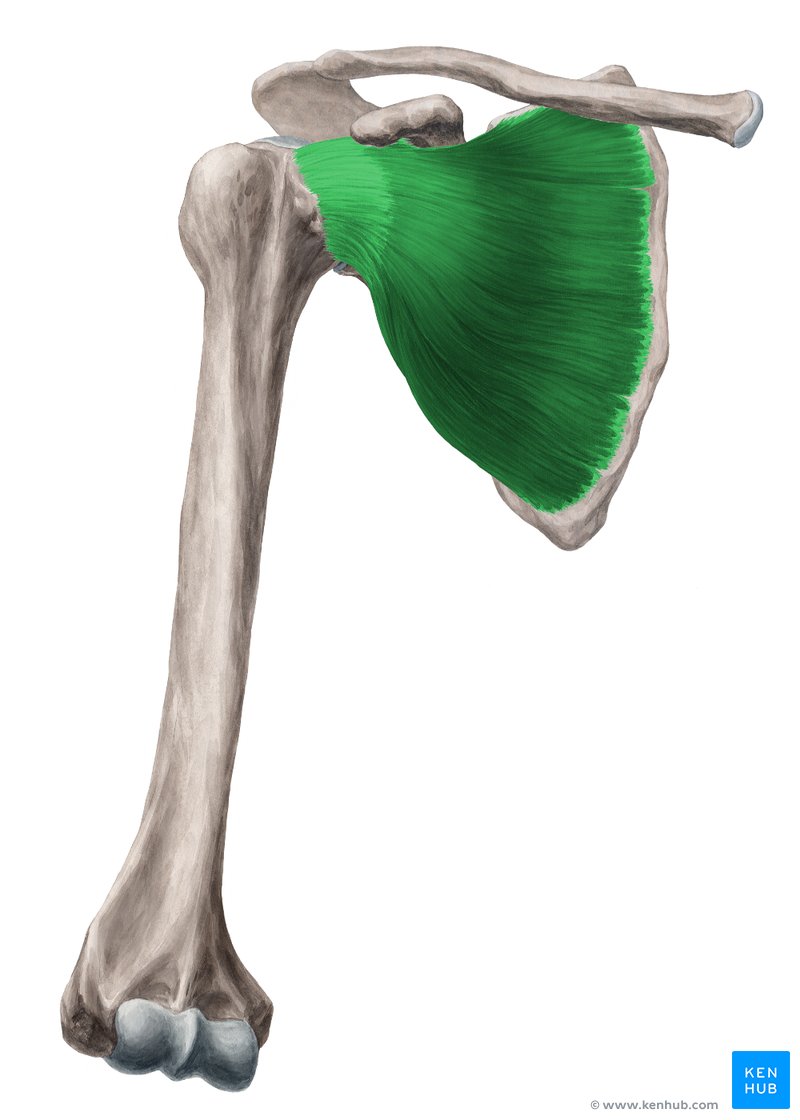
What does this structure correspond with?
subscapularis; medial (internal) rotation of humerus, stabilizes joint
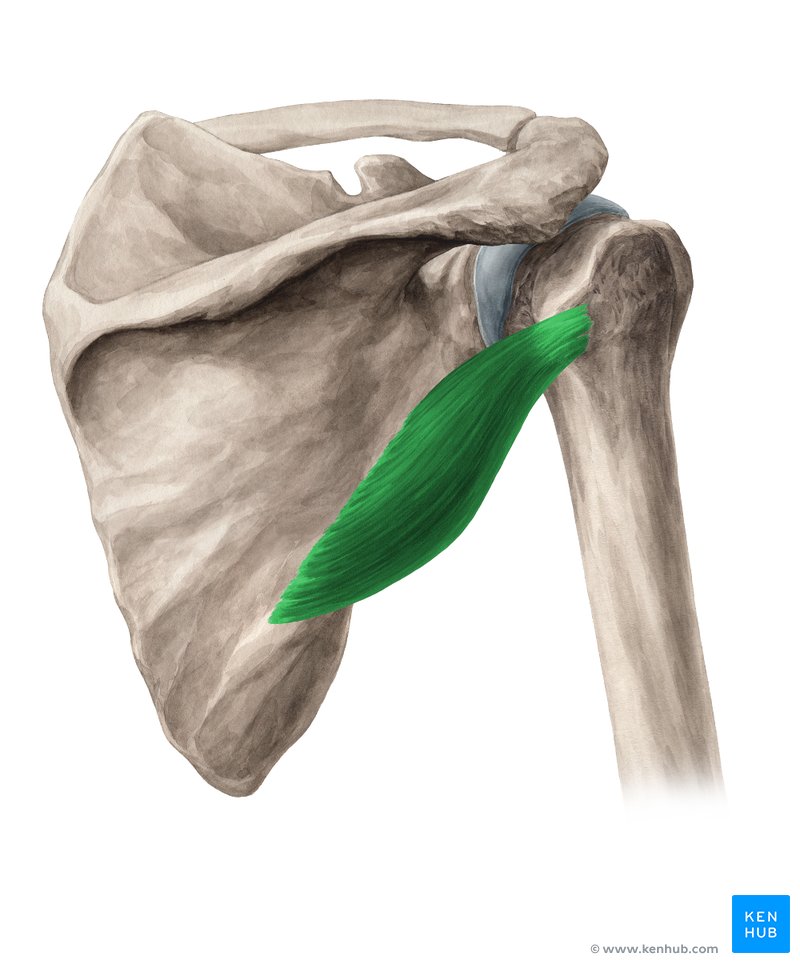
What does this structure correspond with?
teres minor; lateral (external) rotation of humerus
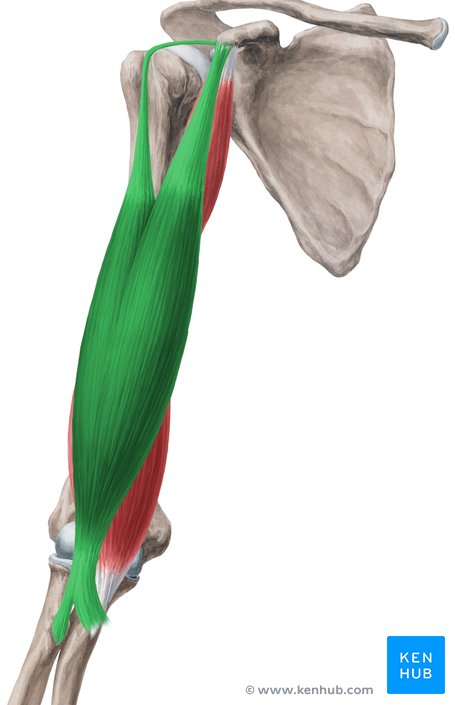
What does this structure correspond with?
biceps brachii; flexes elbow, supination of forearm
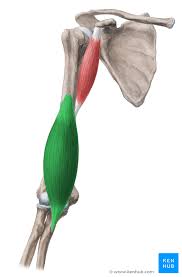
What does this structure correspond with?
brachial; flexes elbow
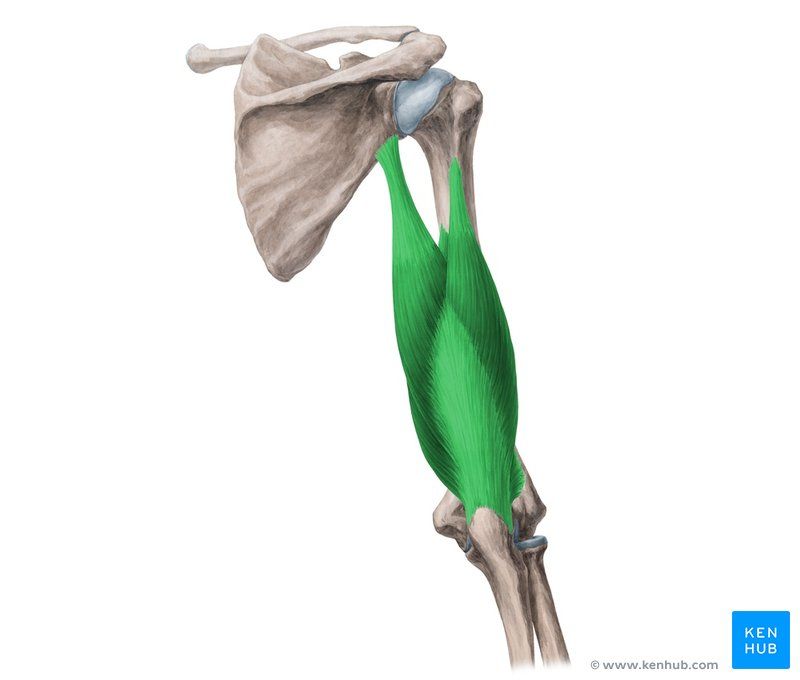
What does this structure correspond with?
triceps brachii; extends elbow and shoulder
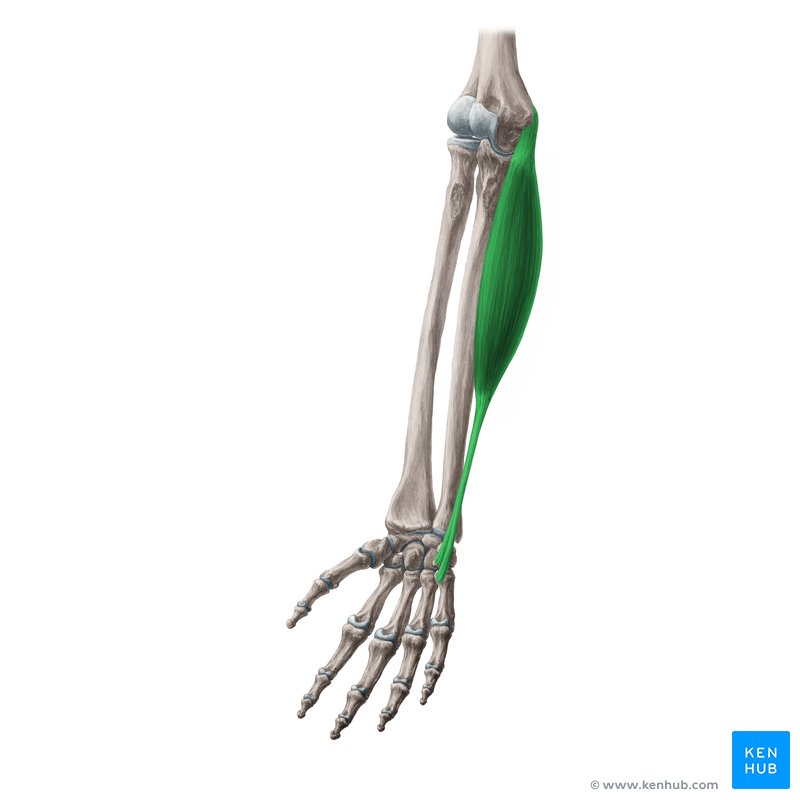
What does this structure correspond with?
flexor carpi ulnaris; flexes wrist, acts with Extensor carpi ulnaris to adduct wrist
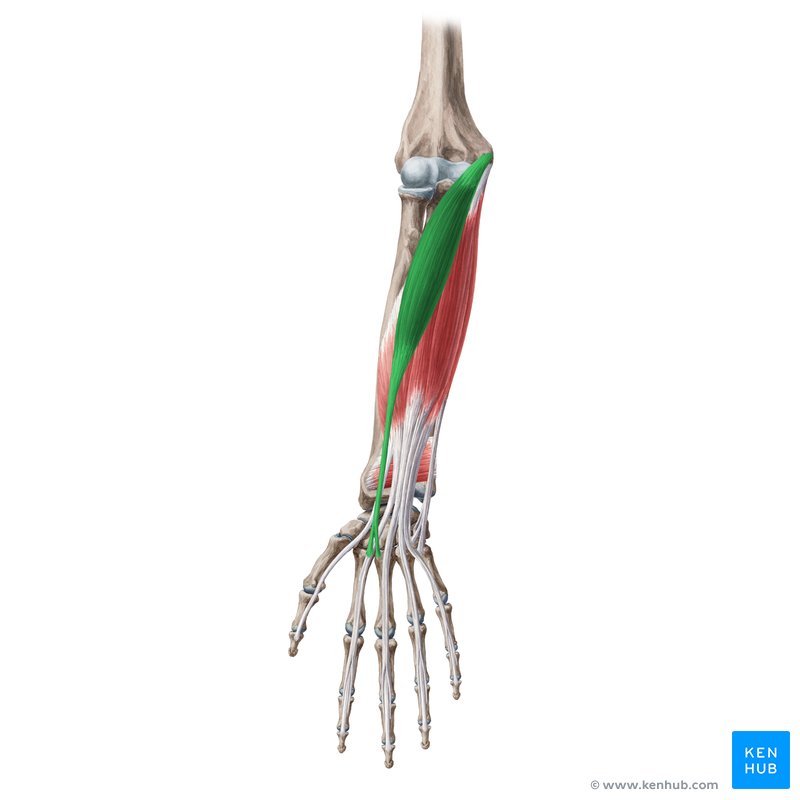
What does this structure correspond with?
flexor carpi radialis; flexes and abducts wrist
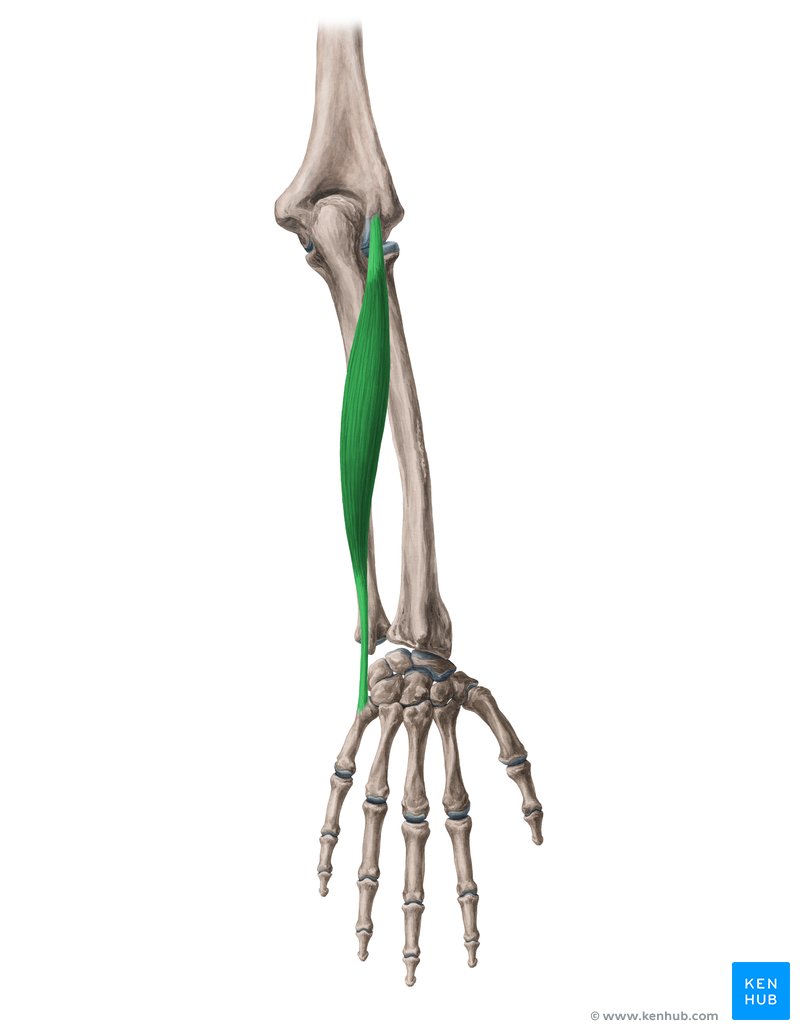
What does this structure correspond with?
extensor carpi ulnaris; extends and adducts wrist, acts with flexor carpi ulnaris to adduct wrist
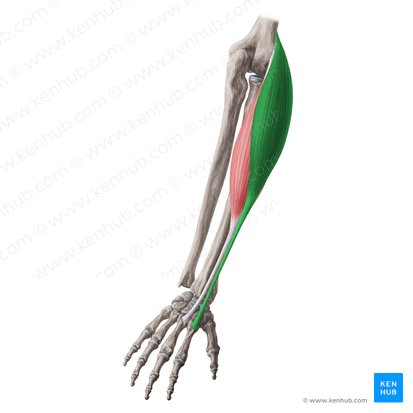
What does this structure correspond with?
extensor carpi radialis (longus & brevis); extends and abducts wrist, acts with Flexor carpi radialis to abduct wrist
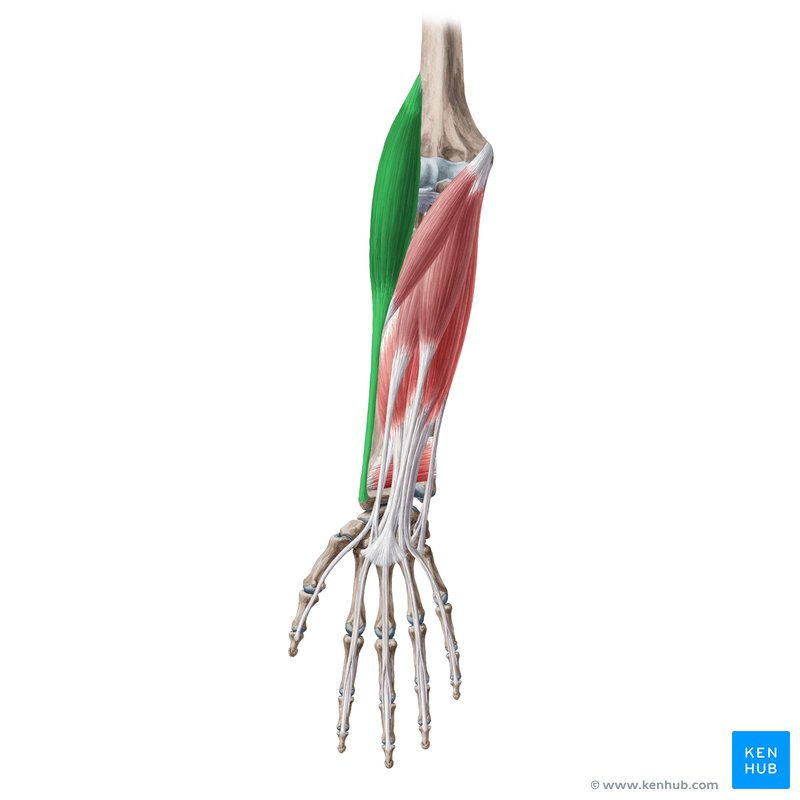
What does this structure correspond with?
brachioradialis; flexes elbow