wavefunctions of the hydrogen atom
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
radial wavefunction
dependent on n and l
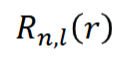
angular wavefunction
dependent on l and ml
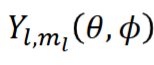
hydrogen atom wavefunction in spherical polar coordinates + what the terms are
wavefunction = radical wavefunction x angular wavefunction
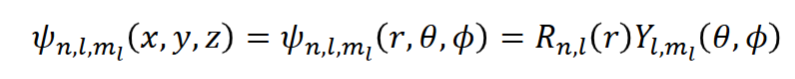
bohr radius
symbol
equation
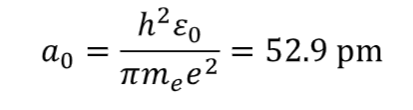
wavefunction of the 1s orbital
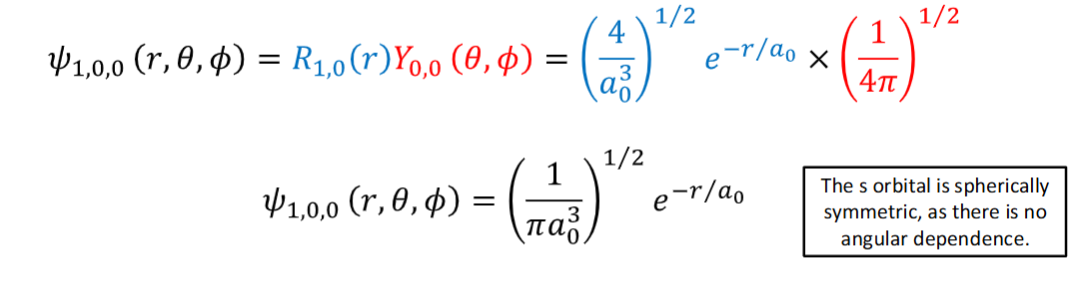
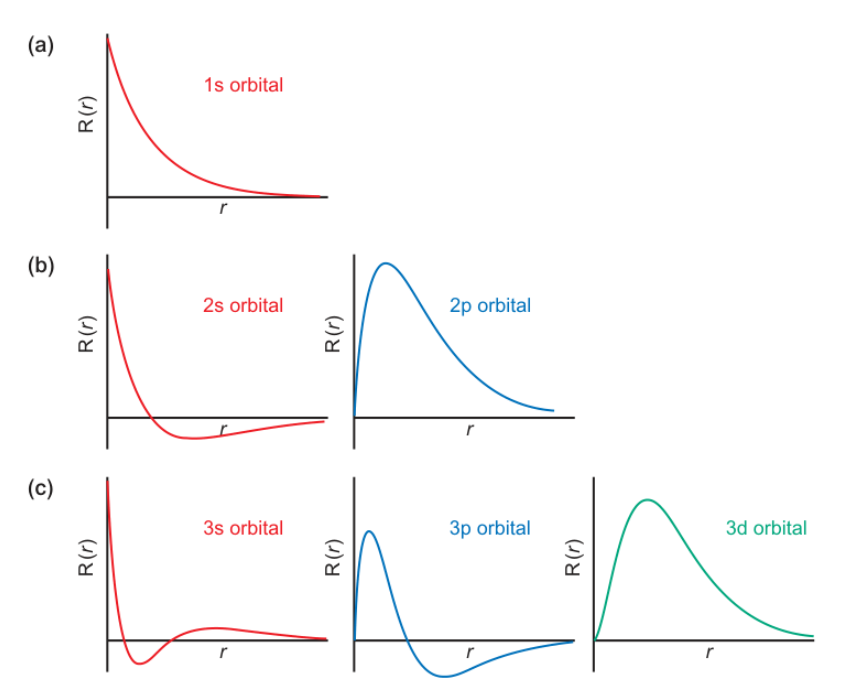
radial nodes for spdf
diagrams for 1s → 3d
when/why do radial nodes occur?
s = (n - 1) nodes
p = (n - 2) nodes
d = (n - 3) nodes
f = (n - 4) nodes
radial nodes occur at R(r) = 0 ie ψ = 0 - the electron cannot exist at this point
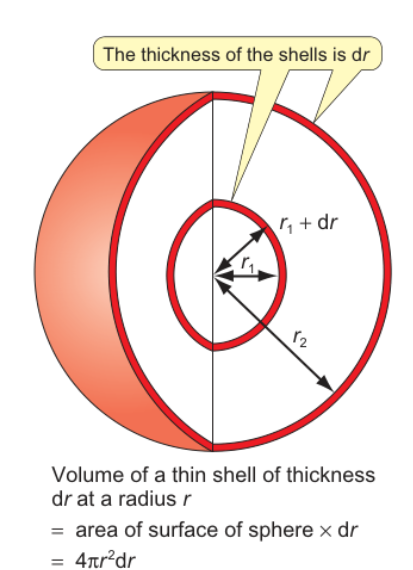
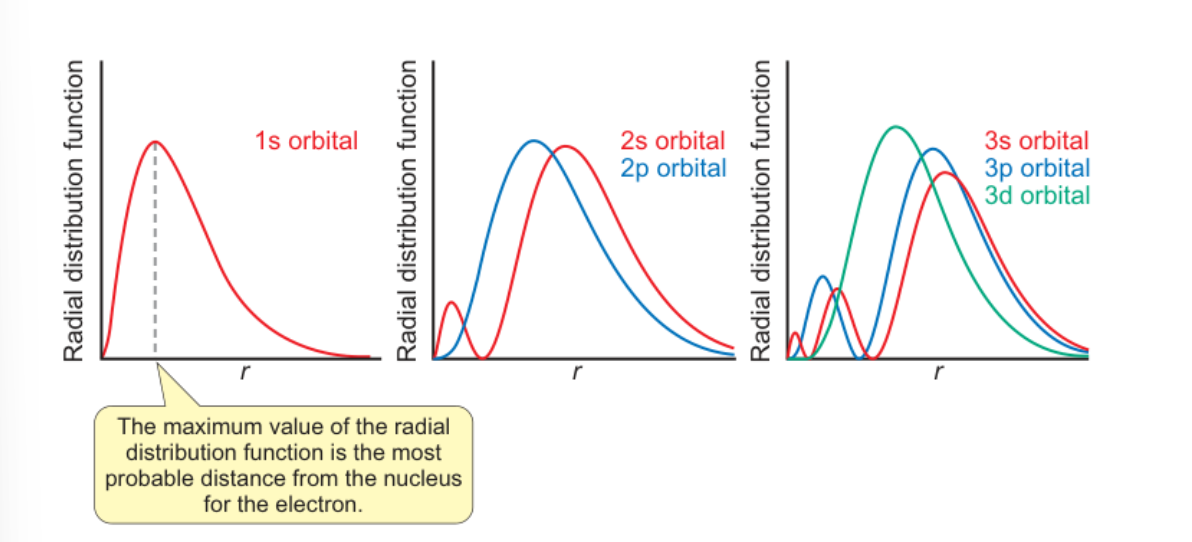
radial distribution function
diagram
equation
radial distribution function = 4πr2R2n,l(r)
radial distribution function plots for n=1 to n=3
what does the peak represent
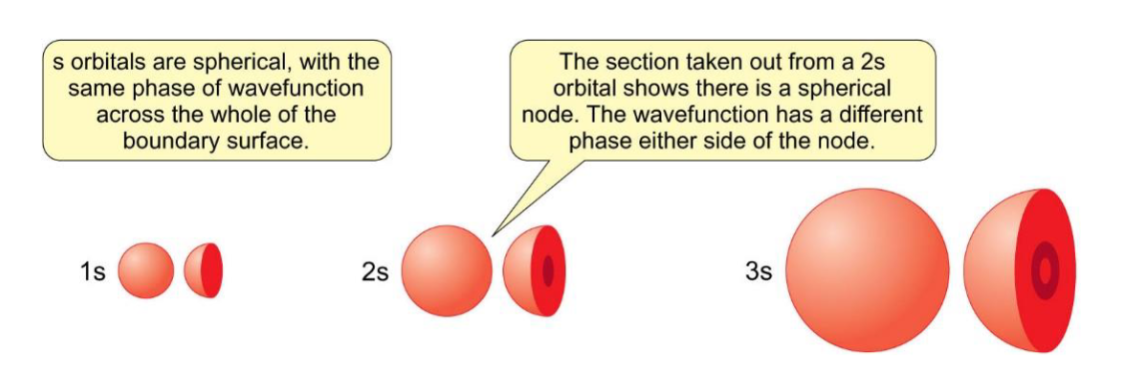
shape and wavefunction (phases) for s orbitals
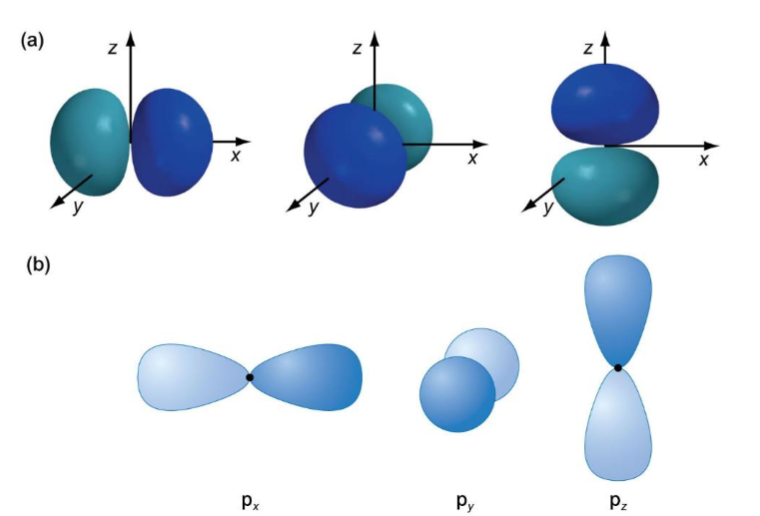
shape and diagrams including wavefunction phases for p orbitals
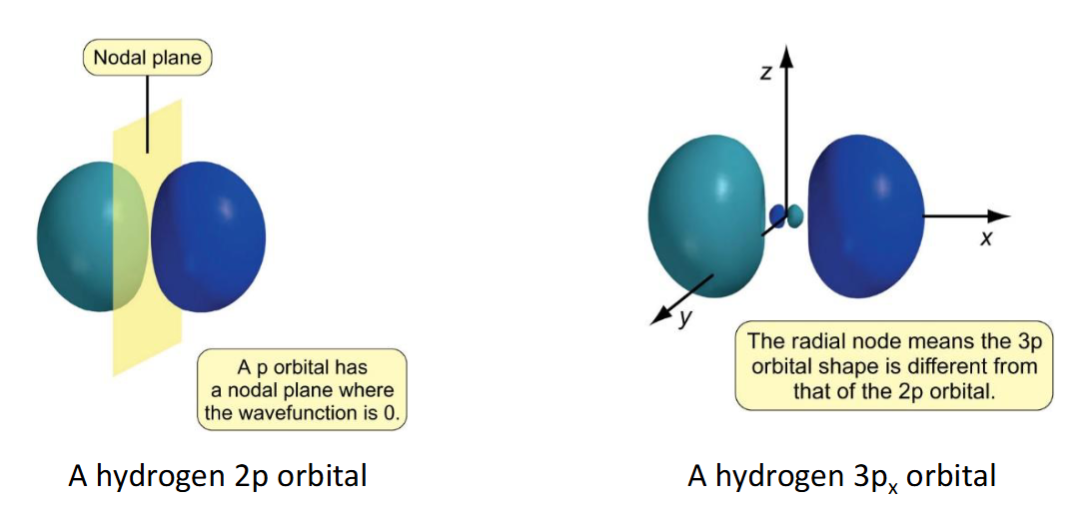
nodes for p orbitals
at the nodal plane, ψ = 0. since this nodal plane arises from the angular wavefunction it is called an angular node
shapes of d orbitals
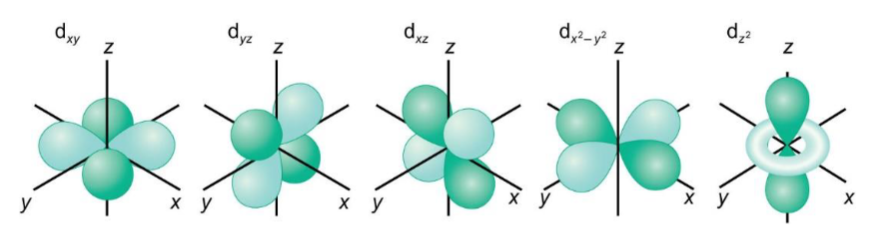
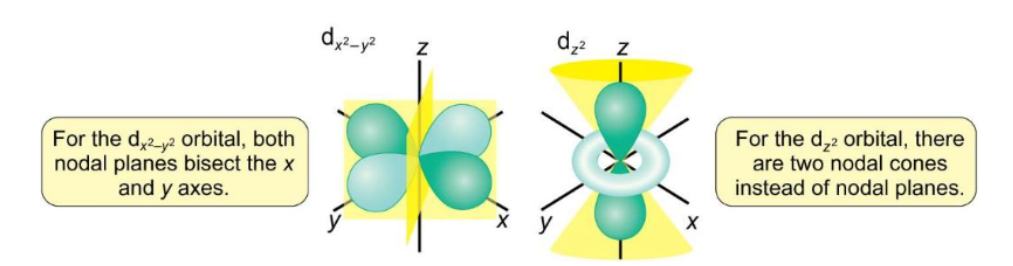
nodal planes for dx2-y2 and dz2
how is the problem of schrodinger only being solvable for two-body problems resolved
using the orbital approximation in which ψ is approximated by the product of N single-electron wavefunctions
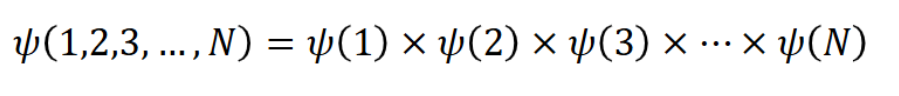
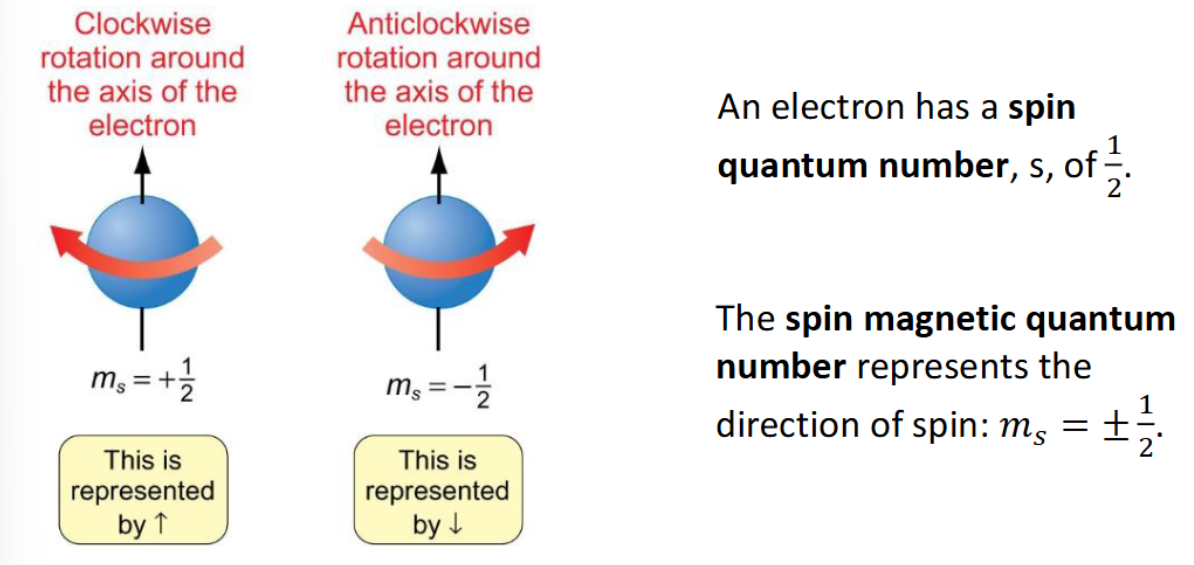
ms quantum number
name
values
diagram
aufbau principle, degeneracy and what is different about hydrogen
lowest energy levels are filled first
energy levels are degenerate for different values of l and ml for any given value of n
but for hydrogen energy levels only depend on n
pauli exclusion principle
principle
what it means for electrons in an orbital
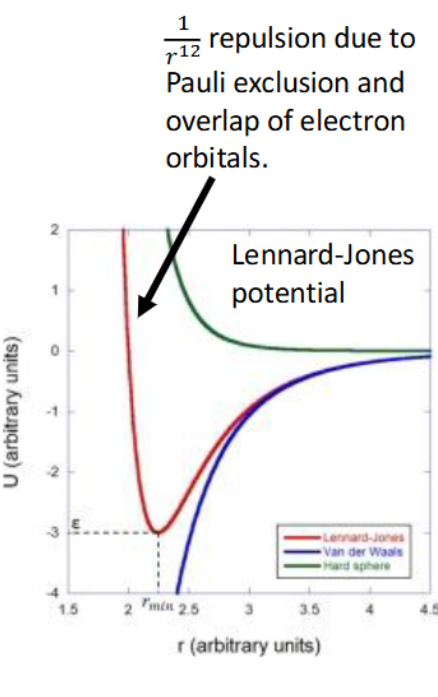
other intermolecular effects
graph?
principle: no two electrons in the same region of space can have the same set of four quantum numbers
so we can have two electrons per orbital with different ms values (±1/2)
this also gives rise to short-range steric repulsion between atoms/molecules - when electrons overlap, electrons in different atoms with the same quantum numbers repel