Audiology Midterm
1/114
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
115 Terms
What does Audiology mean?
The study of hearing
Who is the father of audiology?
Raymond Carhart
Who is Norton Canfield?
An otologist who worked with Carhart to coin the term Audiology
What is an otologist?
An ear specialist
When and where was the audiometer invented?
1920 at bell laboratories
Why did the profession of audiology gain momentum?
around the time of WWII to address the hearing and communication difficulties experienced by veterans
What did Cordia Bunch do?
Bunch carried out systematic studies of the relations between types of hearing loss and audiometric patterns
What did Bunch teach?
Hearing testing and hearing disorders
What do people call Bunch?
The grandfather of audiology
What is the relations between Bunch and Carhart
mentor and mentoree
Who is the highest employer of audiologists?
From back then to today, it is the veterans association
What are behavioral auditory diagnostic tests?
Raise your hand when you hear a beep
What are physiologic auditory diagnostic tests?
brain stem testing
What are the two main divisions of the auditory system?
Peripheral and central
What is the main function of the outer ear?
Collect and direct sound waves to the tympanic membrane from the environment
What does the outer ear consist of?
Pinna and external auditory canal
What is another word for pinna?
Auricle
What is the Pinna?
It is made completely of cartilage and helps sound localization
What is the abbreviation for external auditory canal?
EAC
What shape is the EAC?
tube
What does the EAC secrete?
sebum from its sebaceous glands
What is ear wax called?
cerumen
What is the purpose of cerumen (ear wax)?
keep the environment out of the ear drum and has perfect temperature
What does the middle ear consist of?
tympanic membrane, ossicles, and Eustachian tube
What is the tympanic membrane also called and what is its shape?
Ear drum and disc shaped
What are the ossicles called?
Malleus, incus, and stapes
What is the middle ear filled with?
Air filled cavity
What is the abbreviation for the tympanic membrane?
TM
What is the first layer of the TM?
translucent and thin seen from EAC
What is the middle layer of the TM?
tough, fibrous, connective tissue
What is the third layer of the TM?
middle ear space which is lined with mucous membrane
What is the pars flaccida?
Moves more freely in the TM
What is the pars tensa?
Tense and towards the bottom of the TM
How is the TM held in place?
At the end of the EAC by the tympanic annulus
What is the Eustachian Tube?
a narrow tube that connects the middle ear to the back of the nose and upper throat
What happens if the Eustachian Tube is not working properly?
air will fill and the ear will feel blocked
What is the mastoid bone and where is it located?
a part of the temporal bone, located behind the ear
What are the windows of the middle ear called?
Oval and round window
What is the round window covered with?
a thin membrane
What does the malleus do?
transmits vibrations from the eardrum to the incus
What does the incus do?
transmit sound vibrations from the malleus (hammer) to the stapes (stirrup)
What does the stapes do?
pushes against the oval window, helps to ensure that sound waves are strong enough to be detected by the inner ear
Which is the correct order fo the ossicles from largest to smallest?
What does the inner ear consist of?
Vestibular and cochlear components
What are the vestibular components?
semicircular canals and otolith organs (utricle and saccule)
What is the vestibular mechanism?
organ of equilbibrium
What is the main need for the cochlea
Hearing
What is perilymph?
Low concentration of potassium ions and high sodium ions
What is endolymph?
high potassium ions, low sodium ions. also has calcium ions
What are the membranous sacs called in the inner ear?
Utricle and saccule
What are the utricle and saccule surrounded by and contain?
perilymph and contain endolymph
What is the utriculosaccular mechanism responsible for?
interpreting linear acceleration like an elevator is going up or a car is picking up speed
What are the utricle and saccule stimulated by?
The rate of change of linear acceleration
What are the semi-circular canals responsible for?
Angular acceleration or rate of change for angular velocity
What do the semi-circular canal receptors do?
report the number of revolutions per minute that the body is turning
What are two symptons of vestibular dysfunction?
Vertigo and nystagmus
What is TMJ?
The jaw will start poking the osseocartilaginous junction causing immense ear pain. can cause popping, clicking, or grinding sounds in jaw
How many turns does the cochlea have and what is it filled with?
2 1/2 turn spiral filled with fluid that is chemically balanced
What would an unrolled cochlea look like?
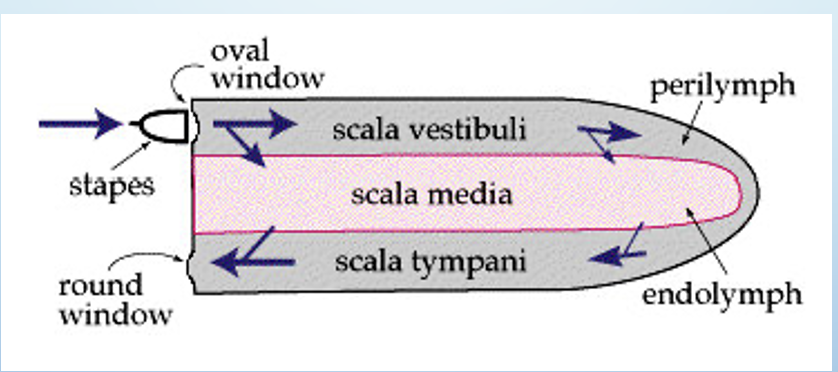
name the places, scala vestibuli, scala media, scala tympani, perilymph, endolymph, round window, oval window, and scapes

How to test for air conduction?
Headphone beep test
How to test for bone conduction?
Device on mastoid bone
What does air conduction test for?
Middle ear problems
What does bone conduction test for?
Inner ear or cochlear problems
What are the three types of hearing losses?
Conductive, sensorineural, and mixed
What is conductive hearing loss entail?
AC is abnormal and BC is normal
Is there an air-bone gap in CHL? If so how much?
Yes, 10dB
What is a sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL)
Both AC and BC are abnormal and they will be near equal
What structures are affected in CHL?
Anything in the middle ear
What is the primary complaint from clients with a CHL?
Sound is not loud enough
What structures are affected in SNHL?
Inner ear or cochlea or beyond
What is the primary complaint from clients who have a SNHL?
trouble hearing and difficulty understanding
What structures are involved in MHL
Middle ear and inner ear
What is mixed hearing loss?
AC and BC abnormal and they are separated by 10dB or more
What degree of hearing loss is -10-15dB??
Normal WNL
What degree of hearing loss is 26-40dB?
Mild
What degree of hearing loss is 16-25dB?
Slight
What degree of hearing loss is 41-55dB?
Moderate
What degree of hearing loss is 56-70dB?
Moderately Severe
What degree of hearing loss is 71-90dB?
Severe
What degree of hearing loss is 91dB and beyond?
Profound
How do you calculate the pure tone average?
You take the dB at 500, 100, and 2000 and add them up, divide by three and you got the average
What is the tuning fork test?
bang the tuning fork against a surface or hand and put it on your mastoid bone. If you can hear it ring, you do not have a problem with your inner ear
What are the instructions for the person taking a pure tone audiometry exam?
tell the person what they will hear, tell them what to do when they hear it, tell them to stop doing it when the sound goes away, and tell them the purpose of the test
What frequency level do you start a pure tone test with?
1000Hz
What tone do you start a pure tone test with?
30dB
If there is no response at 30dB what dB do you raise it to?
50dB
After a response is obtained how much do you lower the dB during a pure tone test?
lower it 10dB and if they did not hear it go up 5dB
What are the rules for masking for air conduction
if the TE and NTE are 40dB or more apart
What is the rule for masking bone and air conduction?
if there is a air-bone gap of 10dB
What is the other rule for air-conduction masking?
If there is a significant air-bone gap in the NTE
What is Interaural attenuation?
Reduction of sound intensity as it goes from the test ear to the non test ear through the bones of the skull

What does this symbol mean?

right ear, unmasked AC

What does this symbol mean?

right ear, masked AC

What does this symbol mean?

left ear, unmasked AC

What does this symbol mean?

left ear, masked AC

What does this symbol mean?

right ear, unmasked BC

What does this symbol mean?

right ear masked BC

What does this symbol mean?

left ear, unmasked BC

What does this symbol mean?

left ear, masked BC