3.3 - unemployment
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
unemployment
people of working age who are able and willing to work and are actively looking for a job but who are not employed
underemployment
people of working age with part time jobs when they could work full time
overqualified people in low skilled occupations
labor force
the number of people who are employed plus the number of people of working age who are not working but seeking work
unemployment rate formula
unemployment rate = (number of unemployed / labor force) x 100
difficulties in measuring unemployment
hidden unemployment
unemployment excludes discouraged workers
unemployment excludes underemployment
unemployment excludes people on retraining or early retirement
unemployment excludes people working in underground economy
doesn’t distinguish between population groups in society as its an average
region
gender
ethnic group
age
occupation
discouraged workers
people who are not actively seeking employment as they were unable to find work and have given up looking.
economic costs of unemployment
loss of real GDP
increased government spending on social services fewer people work than available, decreasing actual output produced
loss of income for unemployed
loss of income tax revenue for government
costs to government of providing unemployment benefits
costs to government of dealing with social problems arising from unemployment
larger budget deficit
tax revenues<government expenditures
personal and social costs of unemployment
personal problems
loss of income
increased indebtedness as people borrow to survive
loss of self esteem
psychological stress
lower health
family tensions and breakdowns
suicide
greater social problems
crime
violence
drug use
homelessness
growing poverty
types of unemployment
structural
frictional
seasonal
cyclical (not part of natural rate of unemployment)
structural unemployment
resulting from changes in the economy that create a mismatch between:
supply of labor (the skills of workers)
and
the demand for labor (skills needed for available jobs.)
*serious as it tends to be long term
determinants of structural unemployment
change in demand for particular labor skills
technological advancements
changes in structure of the economy
change in geographical location of industries/ closing down of industries
inability to move from one region with fall in demand for labor to region with increased demand where the business relocates to
labor market rigidities
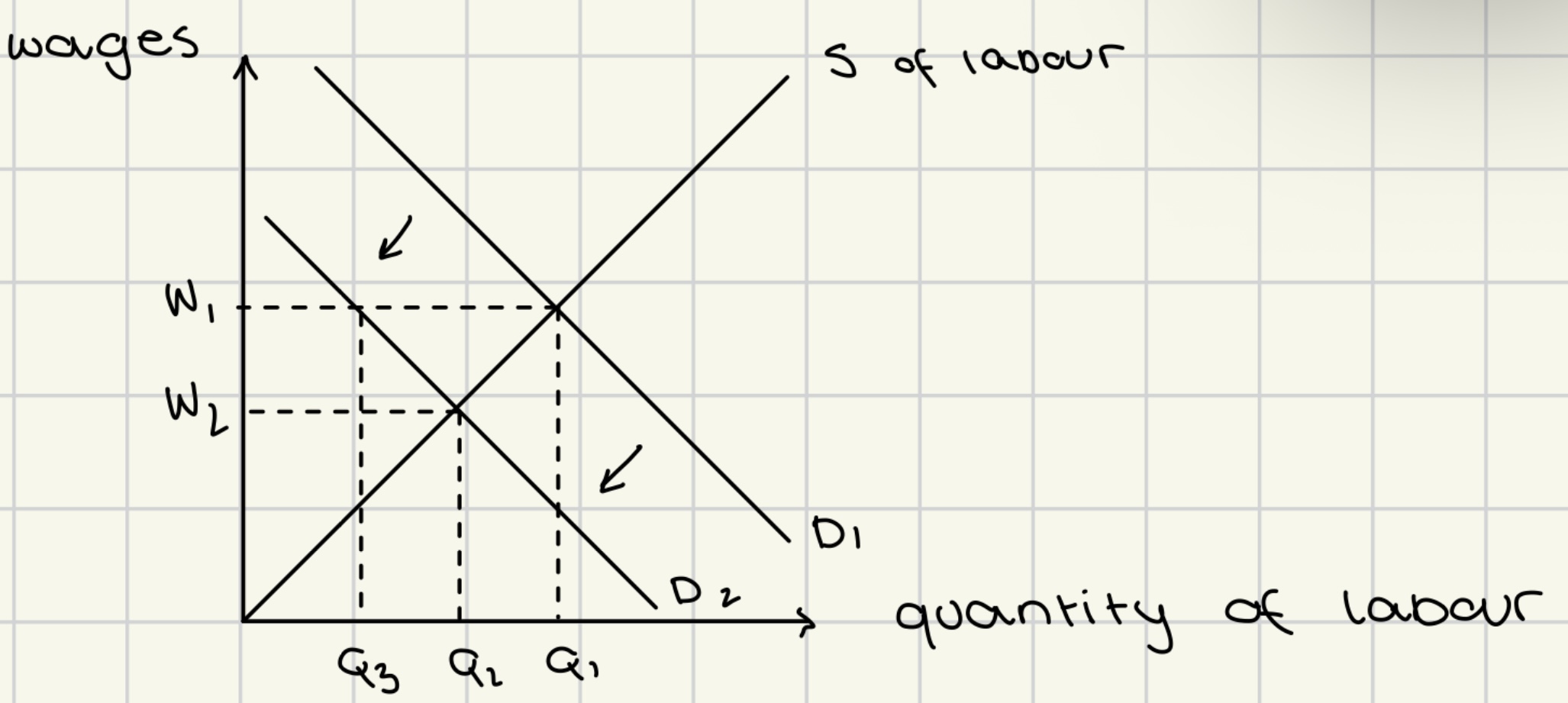
structural unemployment graph
equilibrium → S, D1, W1, Q1
fall in demand due to one of the determinants of structural unemployment (D1 → D2)
in theory:
at S, D2, W2, Q2 , workers would want to work even at lower wages, there
in practice:
wages do not fall easily over short-time → wages remain at W1
this gives rise to excess supply of labor at Q3
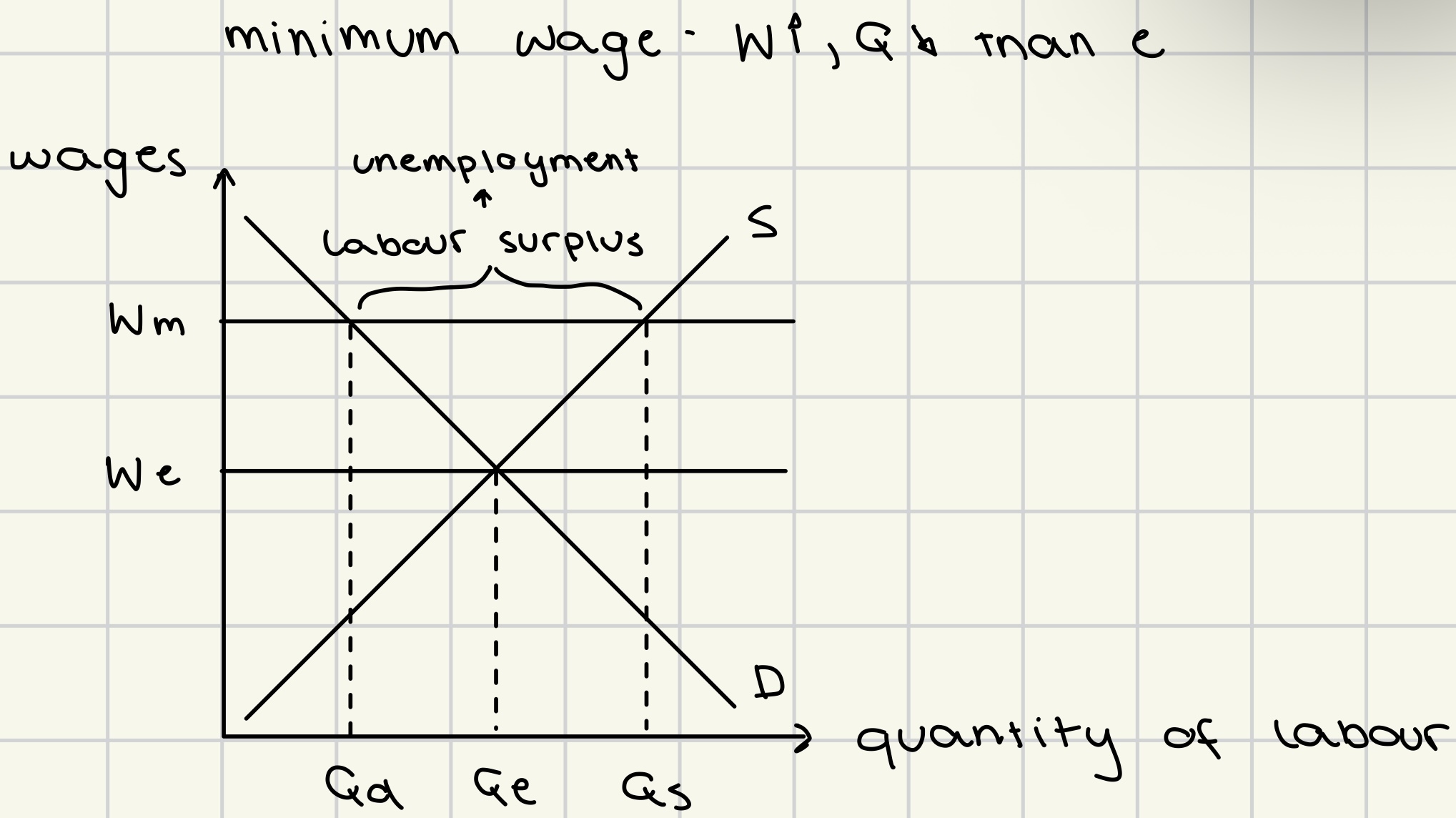
labor market rigidities
features of labor market that increase production costs preventing it from reaching equilibrium
minimum wage
labor unions
employment protection laws
costly due to compensation for firms to fire workers → more cautious hiring process
generous unemployment benefits
increase ‘attractiveness’ of remaining unemployed and reduce incentives to work
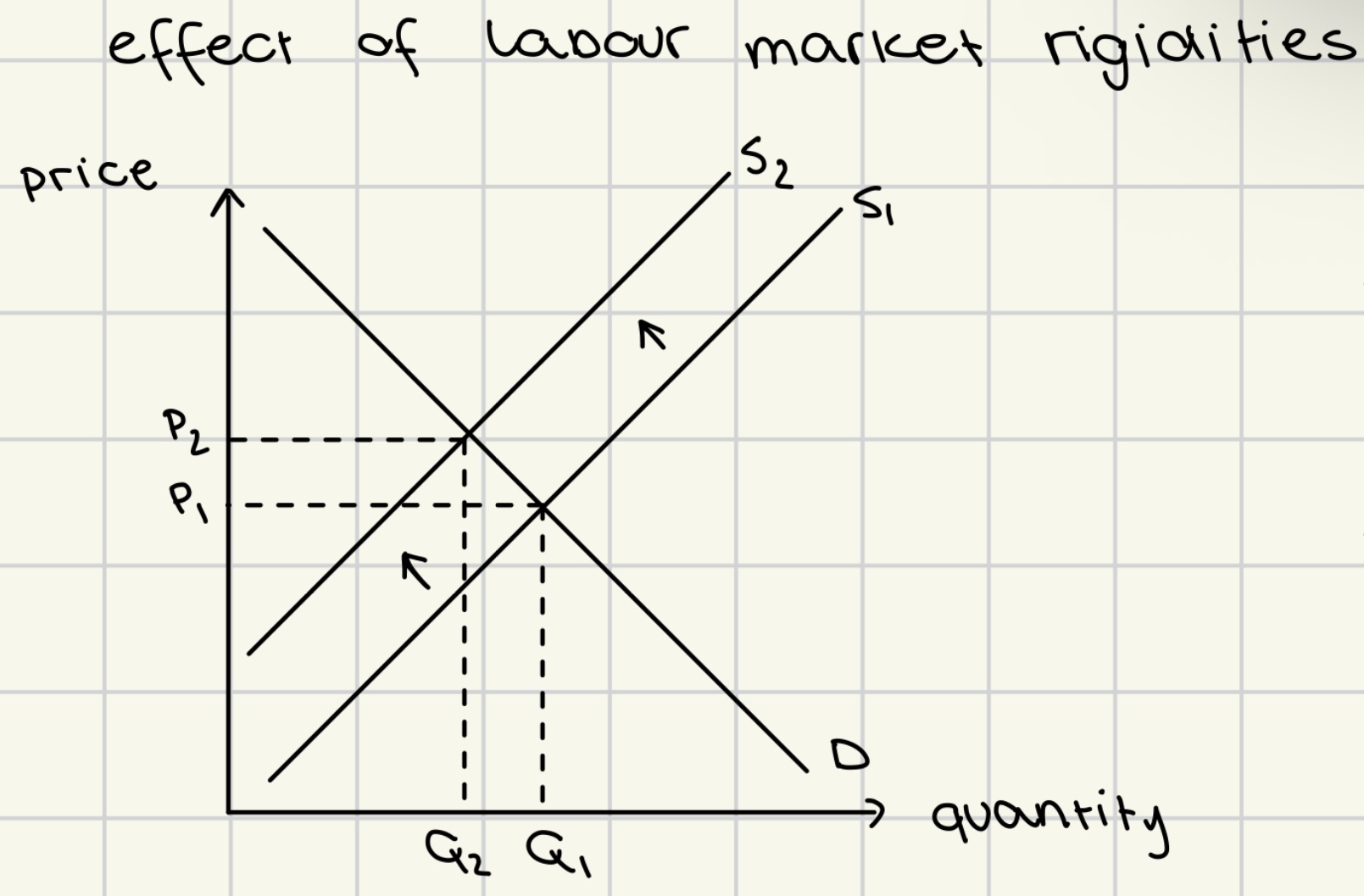
unemployment arising from labor rigidities shown indirectly through product supply and demand diagram
policies to reduce structural unemployment
encouraging workers ro retain and obtain new skills
relocate to areas with greater employment opportunities
providing incentives to firms to hire structurally unemployed workers
frictional unemployment
temporary unemployment that occurs when people are:
in between jobs
entering the workforce for the first time.
*tends to be short-term
*due to incomplete information about job opportunities and required qualifications
*inevitable in any growing, changing economy
policies to reduce frictional unemployment
aim at reducing time a worker spends in between jobs
improving information flow between workers and employers
seasonal unemployment
periodic unemployment due to seasonal fluctuations in demand for certain jobs
cyclical (demand-deficient) unemployment
unemployment that occurs during downturns of a business cycle, when there is insufficient demand for goods and services.
deficiency of AD
AD↓ = rGDP ↓ = unemployment ↑ due to layoffs
*no cyclical unemployment when economy produces rGDP at the level or above the potential output
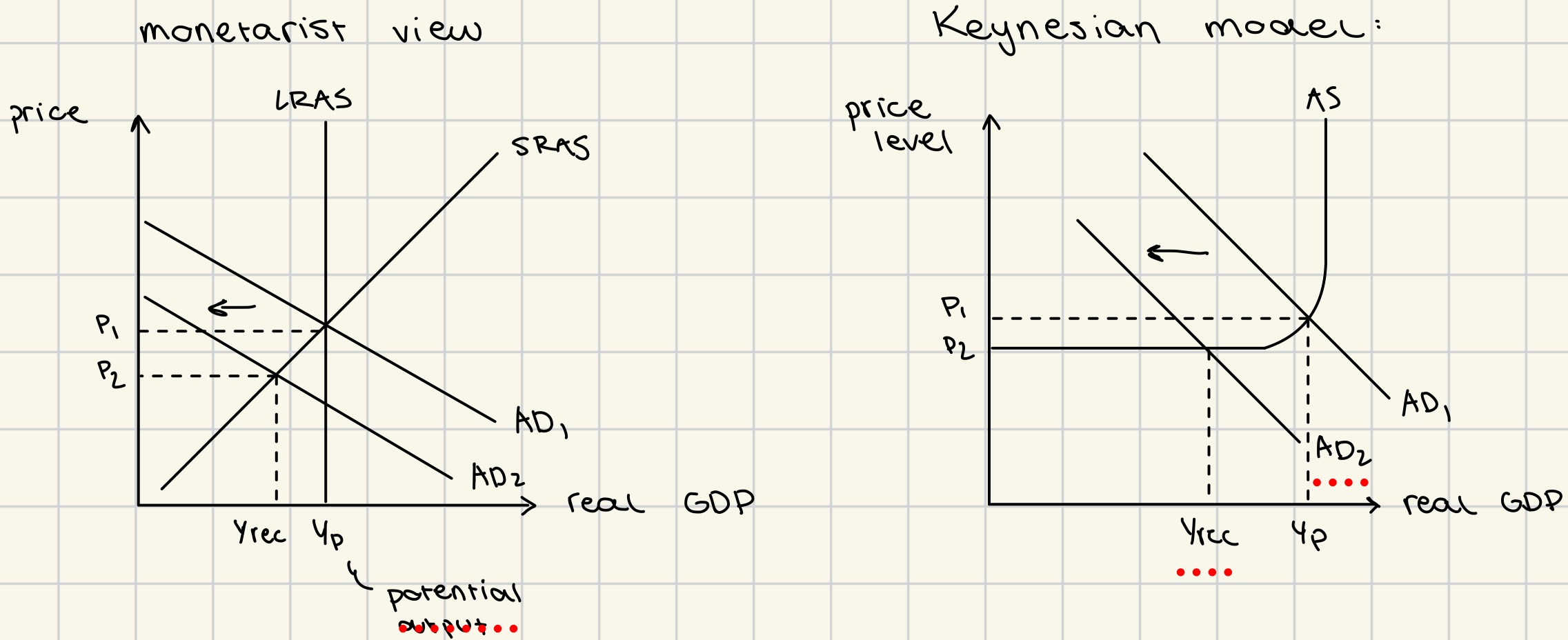
cyclical unemployment graph (monetarist + Keynesian)
at Yp there is no cyclical unemployment
fall in AD
deflationary gap (Yp → Yrec)
new unemployment created