monomers, polymers, carbohydrates and lipids
1/77
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
78 Terms
what four things do all living things primarily consist of
carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids. These biological molecules are organic, so they contain the element carbon
what is hydrogen bonding
Hydrogen bonds are weak attractions that occur between a hydrogen atom covalently bonded to a highly electronegative atom (like oxygen or nitrogen) and another electronegative atom.
define monomers
Smaller units that combine to make a large molecule (polymer).
define polymers
molecules made from a large number of monomers joined together
give 3 examples of monomers
monosaccharides, amino acids, nucleotides
define condensation reaction
A condensation reaction joins two molecules together with the formation of a chemical bond and involves the elimination of a molecule of water.
what is the monomer and polymer of proteins, carbohydrates and nucleic acids
carbohydrates monomer- monosaccharides, polymer- polysaccharides
proteins monomer- amino acids, polymer- polypeptides
nucleic acids monomer- nucleotides, polymer- polynucleotides
define hydrolysis reaction
A hydrolysis reaction breaks a chemical bond between two molecules and involves the use of a water molecule
what are larger carbohydrates made of (polysaccharides)
their monomer is monosaccharides
name three common monosaccharides and give monosacharide function and number of subunits
glucose, galactose and fructose
main function is energy source
one sub unit (monomer)
what type of bond is formed when two monosaccharides join in a condensation reaction
glycosidic bond
how are disaccharides formed? name the three reactions. give main function and number of sub units
Disaccharides are formed by the condensation of two monosaccharides- pair
glucose + glucose = maltose
glucose + fructose = sucrose
glucose + galactose = lactose
two sub units (dimer)
form of transport
draw the structures of the two isomers of glucose- a-glucose and b-glucose
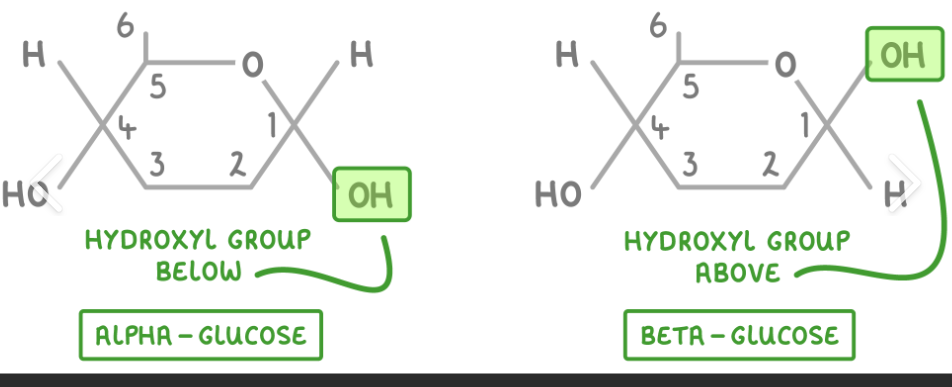
define isomer
molecules which have the same molecular formula but a different arrangement of atoms in space.
how are polysaccharides formed and give function and number of sub units. what properties make them useful in cells
many monosaccharides join in a condensation reaction
many (polymer )
energy storage form
large and insoluble- good as doesnt interfere with osmosis and water potential in the cell
what is a hexose sugar and give an example
contains 6 carbons eg glucose
name 3 polysaccharides and function
glucose, startch , cellulose
startch and glycogen are large energy storage molecules which cannot leave cells
cellulose gives strength in the cell wall for plant and agal cells
how is cellulose fomed
condensation of b-glucose molecules
how is startch anf glycogen formed
condensation reactions between a - glucose molecules
what are monosaccharides
sweet tasting, soluble substances that have the genera formula (CH*2O)n
define polysaccharide- size, type, composed of, what bonding, what reaction
Polysaccharides are large, complex carbohydrates composed of many repeated, monosaccharides joined by glycosidic bonds through condensation reactions.
what property of polysaccharides make them suitable for storage
they are insoluble
describe glycogen- it is a storage molecule in ********, what are they made uo of, what is their structure, 4 factors that made them useful (branching, size, compactness, and solubility)
storage molecule in animals
they are made up of many a-glucose monomers
highly branched structure
more highly branched than starch- enzymes can easily hydrolyse the glycosidic bonds to rapidly release glucose
large- cannot diffuse out of cells
compact- a lot of glucose can be stored in a small space
insoluble- It does not affect the water potential of cells, and so water does not enter cells by osmosis.
differences between monosaccharides and polysaccharides
polysaccharides- 3+ sugar unit, glycosidic bond present, condensation reaction present, not sweet. examples are glycogen and starch
monosacharides- single sugar unit, no glycosidic bond present, no condensation reaction present. examples are glucose, fructose, galactose
what is starch used for
storing excess glucose in plants - can be hydrolysed back inot glucose when plants require energy
name the two forms starch exists in
amylose and amylopectin
describe amylose and amylopectin and how their structure is helpful for starch
amylopectin is branched with 1,4 and1,6 glycosidic bonds, allowing rapid hydrolysis by enzymes to release glucose for respiration
amylose is helical, unbranched structure with 1.4 glycosidic bonds making it compact. This means lots can be stored in a small space
name three properties of starch
Insoluble, preventing osmotic effects in plant cells as it does not affect the water potential.
Large molecule meaning it cannot diffuse out of cells.
Insoluble, preventing osmotic effects in plant cells as it does not affect the water potential.
describe the structure of cellulose (what kind of chains, what are the chains held by, micro**** s are joined together to make macro*****s)
made up of many b(beta)- glucose molecules
it is a long, straight, unbranched chains with 1,4 glycosidic bonds
the straight chains are held together by many hydrogen bonds to form microfibrils.
Microfibrils are joined together to make macrofibrils.
Many hydrogen bonds help give structural strength to cellulose and plant cell walls, preventing plant cells from bursting under osmotic pressure.
if two beta- glucose molecules line up next to eachother. the hydroxyl groups on carbon 1 and carbon 4 are too far apart from eachother to react. For the formation of cellulose, how do they beta - glucose molecules join? and what does this allow to form between the individual chains
|
how is cellulose adapted for it’s role (structure of chains. bonding, *******s)
Long, straight, and unbranched chains - These provide rigidity to the cell wall.
Hydrogen bonds - These cross link the chains to add collective tensile strength.
Microfibrils - These provide additional strength.
describe an explain how the structue and properties of polysaccharides make them useful as energy storage molecules in animals and plants
Polymers of glucose that can be used for respiration
large so insoluble so doesn’t affect the water potential
amylose is coiled- so its compact so it doesnt take up too much space and more can be stored in a smaller area
glycogen is branched, it’s able to be hydrolysed rapidly by enzymes to release glucose
1,4 glycosidic bonds - so they are easy to break down
name which of the 3 polysaccharides arefound in animals and which are found in plants
ONLY GLYCOGEN in animals, starch and cellulose in plants
which of the two polysaccharides contains a-glucose
startch and glycogen- cellulose is made up of beta glucose
true or false- stach, glycogen and cellulose are all structural molecules
false
only cellulose
true or false- starch, glycogen and celluloseare all storage molecules
false only starch and glycogen are. Cellulose is not
which of S, G, C has branched chains
statch and glycogen
which of S , G , C is tightly coiled
starch
describe the iodine test for starch
Place 2 cm3 of your food sample into a test tube.
Add a couple of drops of iodine solution and shake.
If starch is present, the solution will turn from orange to blue-black.
if not, it will stay orange
what is a reducing sugar
Reducing sugars include all monosaccharides and some disaccharides such as maltose and lactose.
A sugar that can donate electrons to another chemical.
what are non- reducing sugars
Non-reducing sugars include some disaccharides such as sucrose and all polysaccharides
describethe test for a reducing sugar
Place 2 cm3 of your food sample into a test tube.
Add an equal volume of Benedict's reagent.
Heat the mixture in a gently boiling water bath for 5 minutes at 80 degrees
If a reducing sugar is present, the mixture will change from a blue solution to a brick red precipitate.
what is the spectrum of colours that indicate concentration of sugars from the benedicts test for reducing sugars
Blue - This indicates no reducing sugar is present.
Green - This indicates a low concentration.
Orange - This indicates a medium concentration.
Brick-red - This indicates a high concentration.
name two more accurate methods that determine the concentration of reducing sugars
Use a colorimeter to measure the absorbance of each solution.
Filter the solution and weigh the precipitate.
what result will non-reducing sugars give for the bendicts reagent
they will give a negative result (blue solution)
Why do lipids form an emulsion in the emulsion test?
Lipids are insoluble in water but soluble in ethanol. When mixed with water, lipid droplets disperse, forming a white emulsion
benedicts test is considered semi-quantative. Why?
it is an approx indication and is subjective
describe the test for non-reducing sugars
Add dilute hydrochloric acid (HCl) and heat to hydrolyse glycosidic bonds. Heat the solution in a water bath gently for 5 mins
Neutralise with sodium hydrogen carbonate (NaHCO₃) which is alkaline..
Repeat the Benedict’s test.
Positive result: Colour change from blue → brick red.
describe the test for lipids
Add ethanol to the sample and shake well.
Pour the mixture into a test tube containing water.
Positive result: A white, milky emulsion forms.
Describe how a student could carry out a chemical test for reducing sugar and suggest how he could estimate the amount of reducing sugar in the sample (the student did not have a colourimeter). (5 marks)
Add Benedict’s reagent
Heat / boil
Forms precipitate / colour change from blue to, green / yellow / orange / brown / (brick) red;
Concentration estimated from EITHER
Observe degree of colour change
Compare colour with known concentration solutions;
OR
Filter and weigh the precipitate
Greater mass/ weight = more reducing sugar present
what are lipids
Lipids are non-polar, hydrophobic molecules made primarily of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen
when are lipids soluble/insoluble
They are insoluble in water but soluble in organic solvents such as alcohols.
are lipids polymers? why/ why not
Lipids are not made up of long chains of monomers, meaning they are not considered as polymers.
name two groups of lipids
triglyceride and phospholipid
what are most lipids made up of
fatty acids comined with an alcohol(usually glycerol)
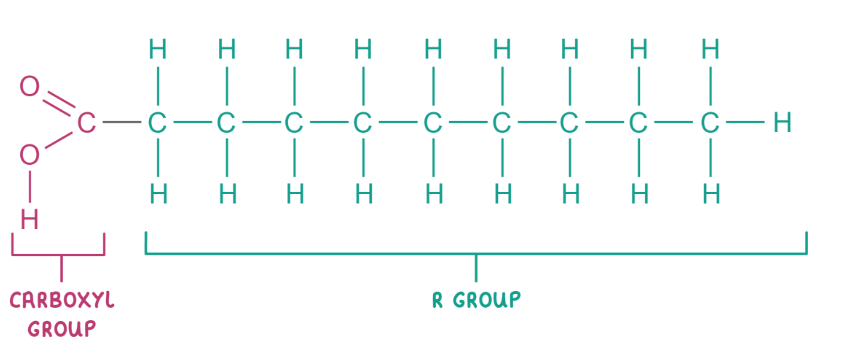
draw and label the groups in a fatty acid
the R group can be unsaturated or saturated
describe a saturated fatty acid (+ describe why they are usually solid at room temp)
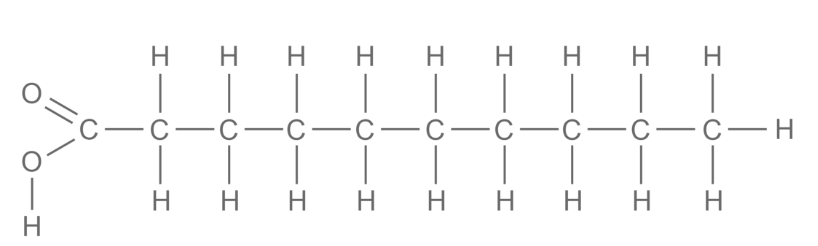
These have hydrocarbon chains that are 'saturated' with hydrogen, meaning all carbon atoms are bonded to the maximum number of hydrogen atoms.
The hydrocarbon chain has no carbon-carbon double bonds.
Lipids that contain saturated fatty acids have higher melting points and so are usually solid at room temperature (fats)- this is because there are mo double bonds to cause a kink in the chain. Saturated fatty acids have stronger intermolecular forces because they are more compact
draw a saturated fatty acid
describe a unsaturated fatty acid (+ describe why they are usually liquid at room temp)
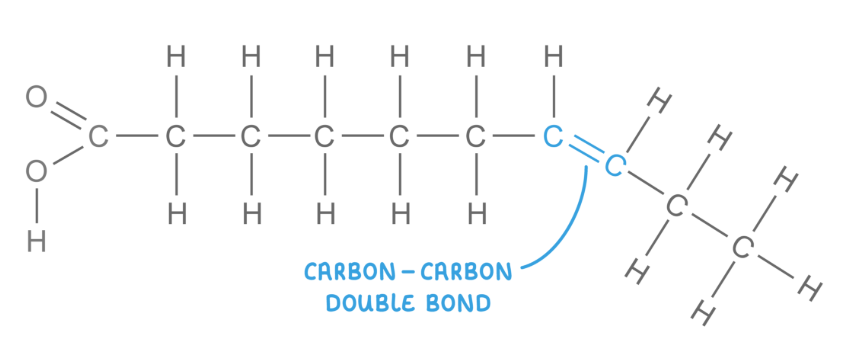
These have hydrocarbon chains that do not contain the maximum number of hydrogen atoms bonded to the carbon atoms.
The hydrocarbon chain has at least one carbon-carbon double bond, which causes the chain to kink - less compact and weak intermolecular forces
Lipids that contain unsaturated fatty acids have lower melting points and so are usually liquid at room temperature (oils).
draw a unsaturated fatty acid
describe some roles of lipids
Energy supply - Lipids can be oxidised to provide energy to cells.
Structural components - Phospholipids are used in cell membranes.
Waterproofing - Insoluble lipids are used to form water-resistant barriers.
Insulation - Lipids can help retain heat or act as electrical insulators.
Protection - Delicate organs are surrounded by a layer of fat.
what is a triglyceride
A triglyceride is a type of lipid used as a store of energy in animals, plants, and some bacteria. |
draw a triglyceride
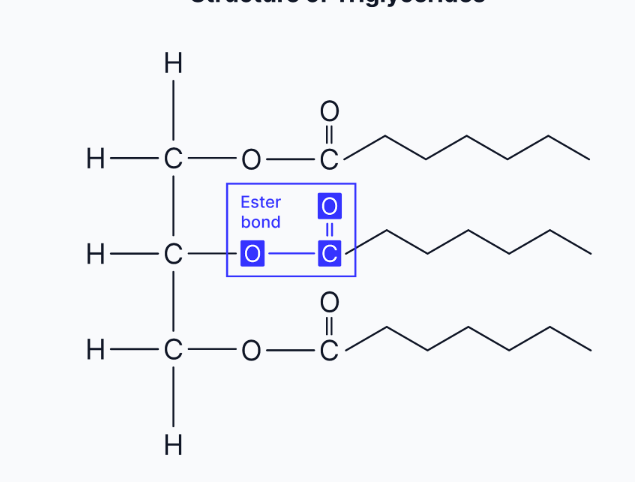
describe the structure of a triglyceride
A triglyceride consists of a glycerol backbone attached to three fatty acid tails. Each fatty acid tail contains a hydrocarbon chain (R) which can vary in length and may be saturated or unsaturated.
how are triglycerides formed
Triglycerides are formed by the condensation of one glycerol molecule and three fatty acid molecules.- which can be saturated or unsaturated
The bond formed between glycerol and each fatty acid is called an ester bond.
Reaction type: Condensation reaction (water is removed).
what bond forms between glycerol and a fatty acid in a condensation reaction
ester bond
describe some features that allow the triglycerides to store energy efficiently
Long hydrocarbon tails - Their many carbon-hydrogen bonds can be broken to release energy.
Low mass to energy ratio - Lots of energy can be stored in a small volume.
Insoluble - They do not affect the water potential of cells as they are large and non-polar.
High ratio of hydrogen to oxygen atoms - Triglycerides will release water when oxidised.
in the condensation reaction between a glycerol and 3 fatty acids to form a triglycerid, where does the ester bond form? what happnes in the hydrolysis of this?
The hydroxyl groups (OH) on the glycerol and on the three fatty acids react together to release three water molecules (H2O).
This results in three ester bonds between the glycerol and the fatty acids.
The addition of three water molecules (H2O) breaks the ester bonds.
This separates the glycerol and the fatty acids.
how many numbers of fatty acid tails does a triglyceride have? how many for a phospholipid?
triglyceride- 3
phospholipid- 2
is a triglyceride and / or a phospholipid polar?
no, only phospholipid is
state the functional difference between a triglyceride and a phospholipid
triglycerides are a energy store, phospholipid is a structural component of a membrane
what is a phospholipid
a type of lipid formed formed by the condensation of one molecule of glycerol, two molecules of fatty acid and a phosphate group
what is polyunsaturated and monosaturated
polyunsaturated- more than one double bond
monosaturated- one bouble bond between carbon atoms
draw the structure of a phospholipid
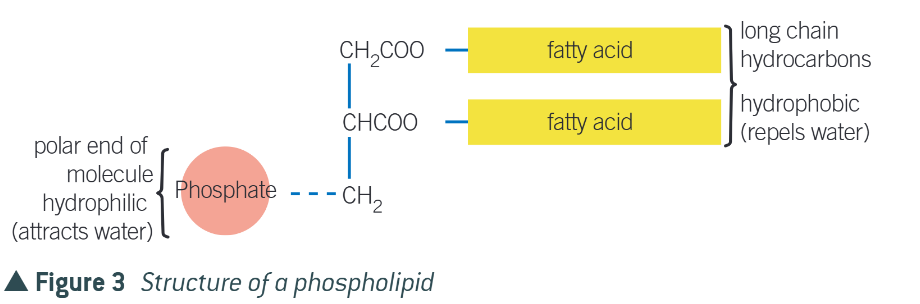
describe the structure of a phosphlipid
Hydrophilic head (phosphate group and glycerol): Attracted to water.
Hydrophobic tails (fatty acids): Repel water.
what happens when phospholipds are placed in water- what region does it create
Because they are polar, they arrange themselves into a double layer (bilayer) so that the hydrophilic heads are facing out (towards the water) and the hydrophobic tails are facing in (away from the water). They form micelles (circle one) when they are in water.
this creates a hydrophobic centre in the bilayer so that water-soluble substances cannot pass through
crucial for compartmentalisation in cells
describe points how the structure of phospholipids relate to their function
in an aqueous enviro, being polar means a bilayer can be formed- essential for compartmentalisation and creates a hydrophobic centre which doesn’t allow any water-soluble substances through
the hydrophillic heads of the phospholipids can be used to hold at the surface of the cell surface membrane
their structure allows them to form glycolipids with carbohydrates which are important on the cell surface membrane for cell recognition
where are saturated and unsaturated fatty acids found
saturated are found in animal fats, uns