BIOL Topic 13
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Anterior
-near head
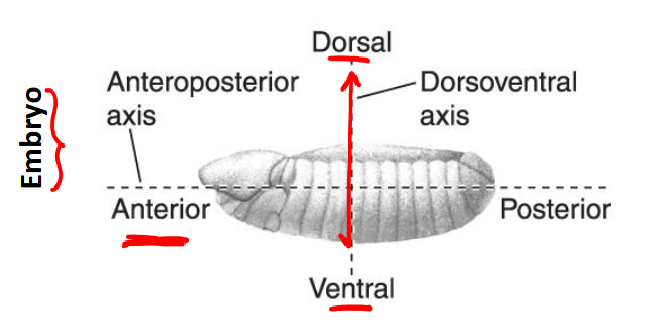
posterior
-near abdomen
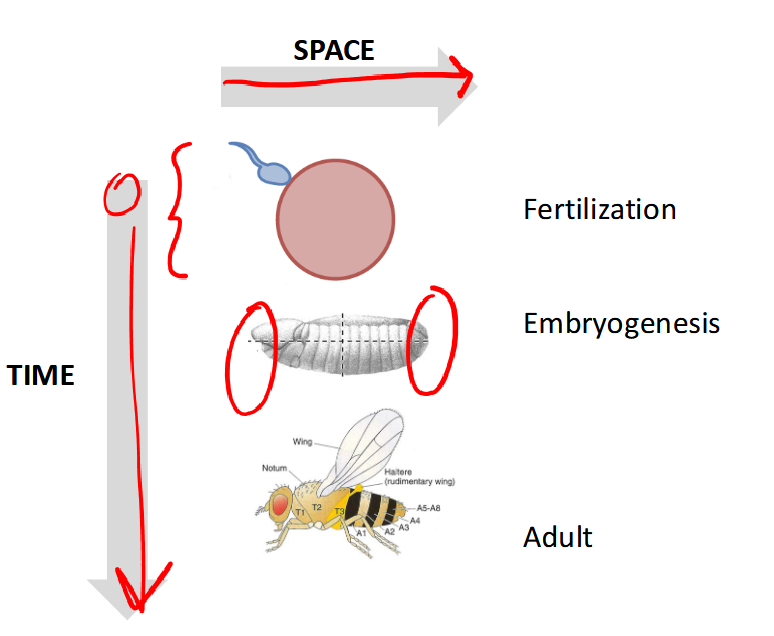
gene expression over time
fertilization, embryogenesis, adult
toolkit genes
-the set of genes responsible for the regulation of animal development
-there are only ~few dozen to 100s of tool kit genes
-mostly encode cell signalling proteins and transcription factors
-highly conserved across diverse species of animals
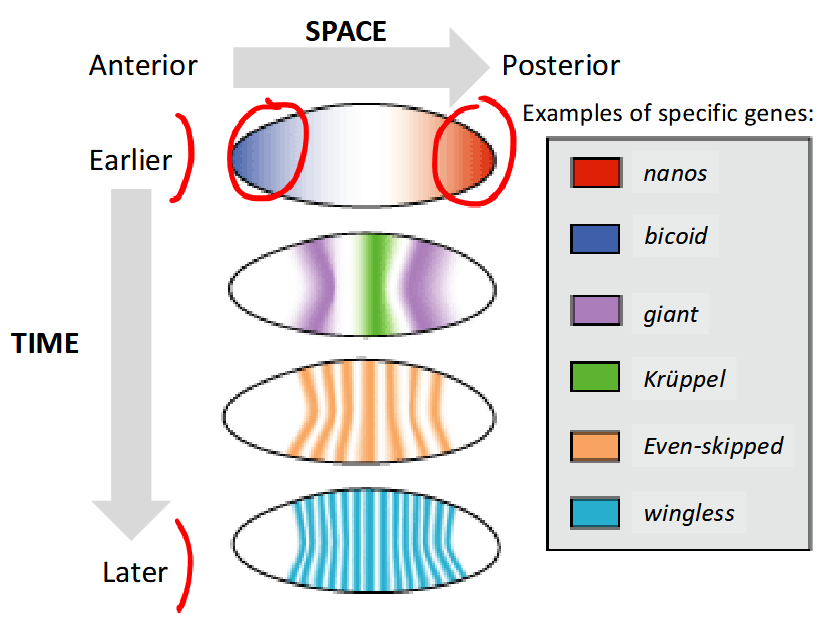
classes of toolkit genes involved in regulating the anteroposterior body axis
earlier-maternal effect genes, gap genes, pair-rule genes, segment-polarity genes, hox genes-later
maternal-effect genes establish the A-P axis
-bicoid and nanos mRNA are tetherd to the anterior and posterior ends of the unfertilized egg
-upon fertilization, the proteins are expressed and form a gradient
-bicoid and nanos encode transcription factors that regulate expression of the next set of genes
-maternally expressed
-function: determine the major body axis
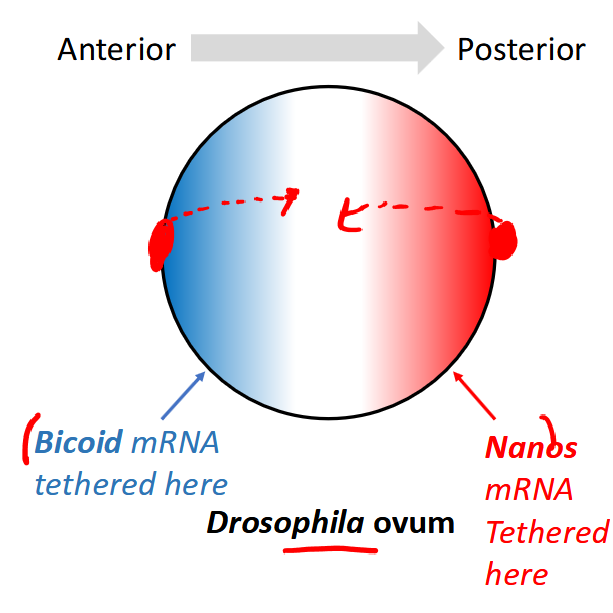
maternal-effect genes
mutant phenotypes of maternal-effect genes depend only on the genotype of the egg parent
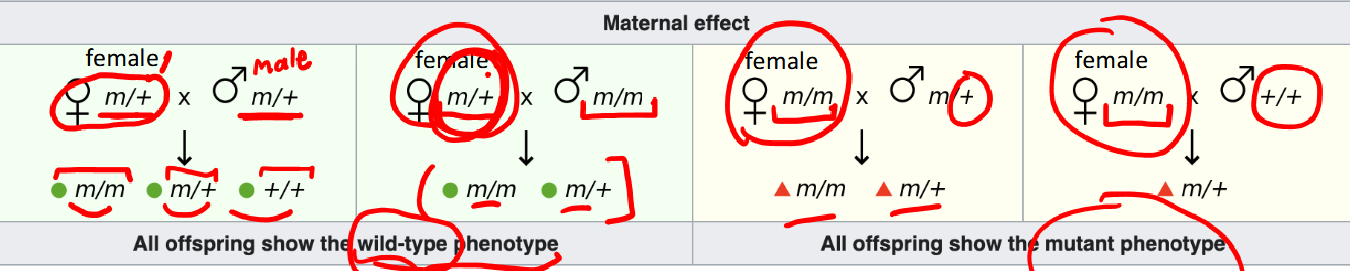
segmentation genes
-gap genes, pair rule genes, segment polarity genes (in that order)
--zygotically expressed
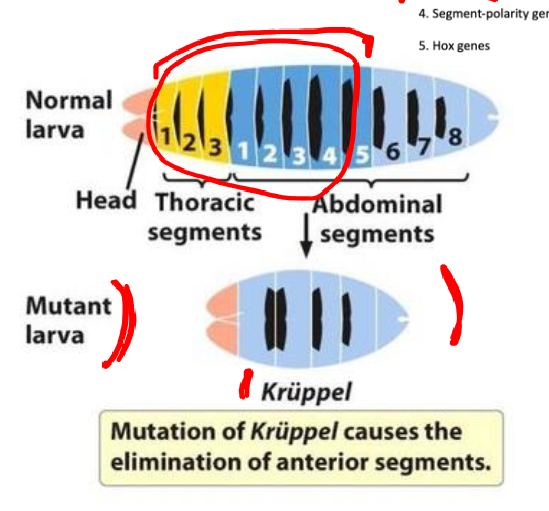
gap genes
-divide embryo into broad regions and turn on next gene
-Mutations in gap genes lead to large gaps in segmentation
-zygotically expressed
-function: define broad sections
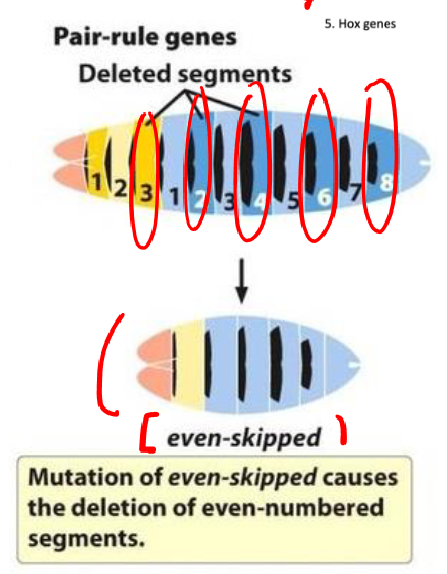
pair-rule genes
-affect the development of pairs of segments and turn on next gene
-act in more narrow regions that do gap genes
-alternating (turn on the next)
-zygotically expressed
-function: define individual segments
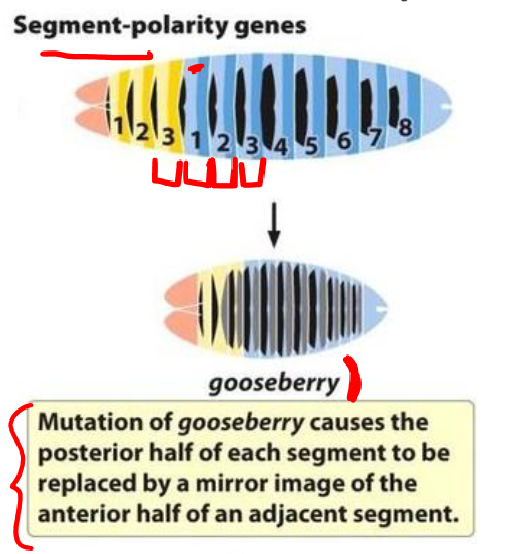
segment polarity genes
-affect the organization of segments
-mutations in segment polarity genes lead to defects in segment polarity
-zygotically expressed
-function: organization within a segment
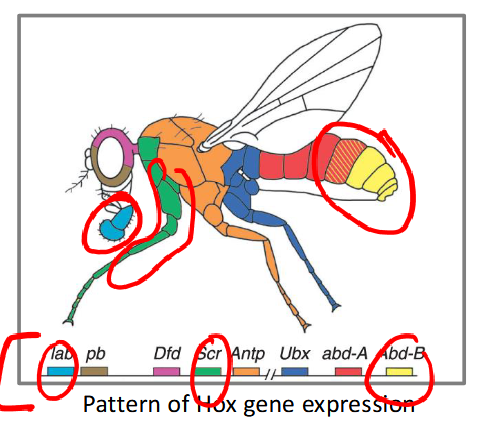
hox genes
-determine the identity of a structure or segment
-encodes transcription factors
-zygotically expressed
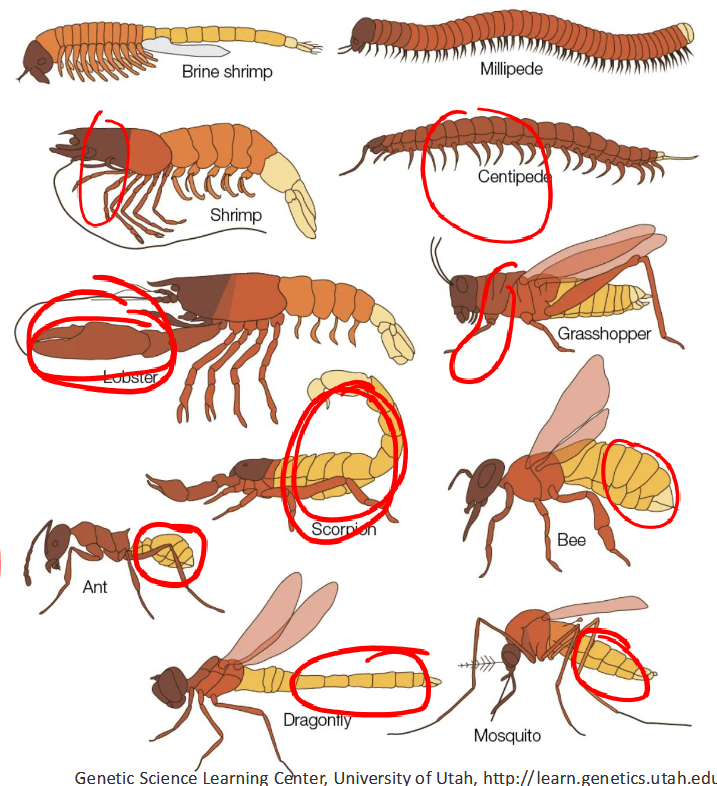
hox proteins
-turn on similar genetic programs in different species
-these genes play a fundamental role in the development of most animals
How do Hox genes control the identify of segments and appendages?
-they regulate the expression of networks of other genes
-hox genes encode sequence specific DNA-binding proteins (transcription factors)
-they bind to cis-acting regulatory elements (enhancers and/or promoters) of other genes to activate or repress them