Gravitation and Uniform Circular Motion
1/24
Earn XP
Description and Tags
RAFAEL
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
He was just sitting comfortably and the concept just popped out of his mind.
How did Sir Isaac Newton come to discover the Universal Law of Gravitation (popular version)?
It was a product of his careful observation that a falling apple had changing velocities from the point that it was hanging on the tree to the moment it moves towards the ground
How did Sir Isaac Newton come to discover the Universal Law of Gravitation (acceptable version)?
Force; Acceleration
By Newton's 2nd Law there must be a _______________ that acts on the apple to cause this ____________
Gravity
What do you call the force that acts on the apple to cause this acceleration?
Acceleration due to Gravity
What do you call the associated acceleration?
Uniform Circular Motion
It is described as the motion of an object in a circle at a constant speed
Constantly
An object is ______________ changing its direction as it moves in a circle
Tangent
At all instances, the object is moving ________ to the circle
Same; Directed
Since the direction of the velocity vector is the _______ as the direction of the object’s motion, the velocity vector is _______________ tangent to the circle as well
Attracts; Directly proportional; Inversely proportional
In Newton’s Law pdf Gravitation states that, everybody in the universe ________ every other body with a force that is ________________ to the product of their masses and ______________ to the square of the distance between them
Square of the distance between two bodies
In this formula, r2 is defined as
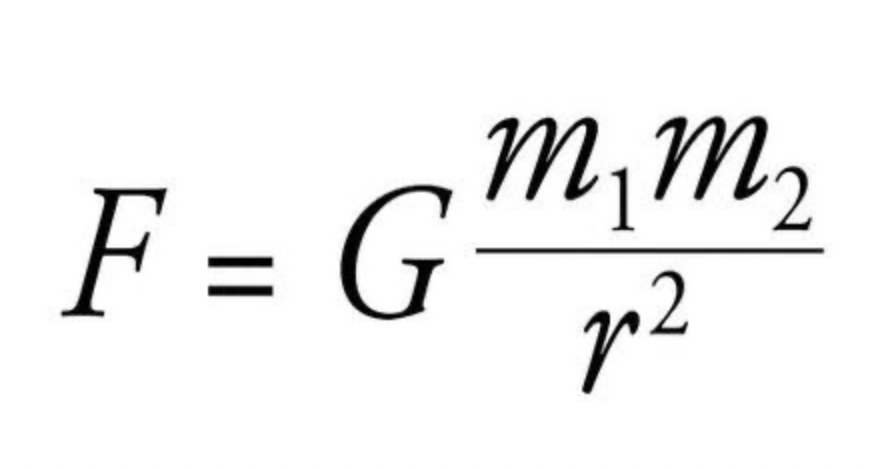
Mass of the smaller body
In this formula, m1 is defined as
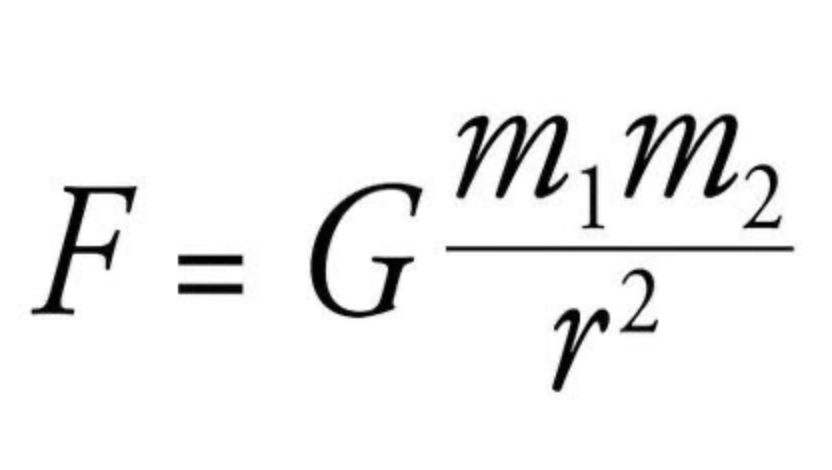
Mass of the bigger body
In this formula, m2 is defined as
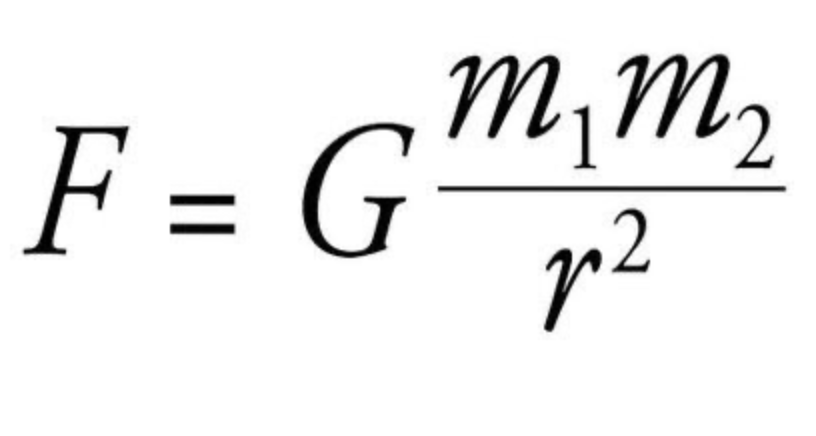
Uniform Circular Motion
It is the motion at constant speed along a curved path of constant radius
Centripetal Acceleration
It is produced by a force known as a centripetal force which is directed toward the center of the circle which the body
Centripental acceleration
In this formula, ac is defined as
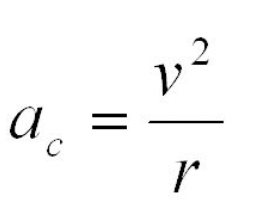
Square of the velocity of a body
In this formula, V2 is defined as
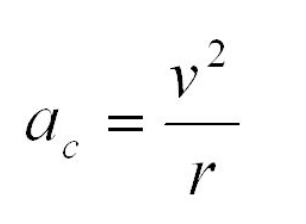
Radius of circular path
In this formula, r is defined as
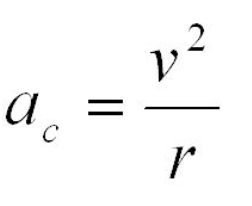
Accelerating; Changes continually
A body in uniform circular motion is ___________ because its direction _______________
Centripetal force
It is the inward force that keeps a body in a circular path
Centripetal force
In this formula, Fc is defined as
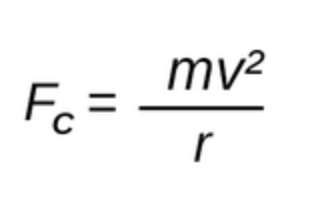
Mass of a body
In this formula, m is defined as
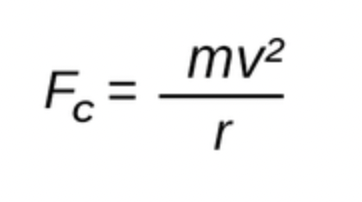
Radius
In this formula, r is defined as
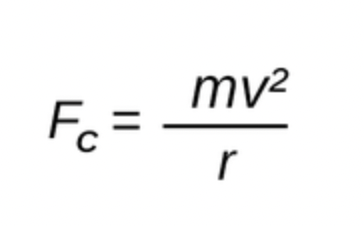
Angle of repose (limiting angle)
Angle just before the block starts to hide
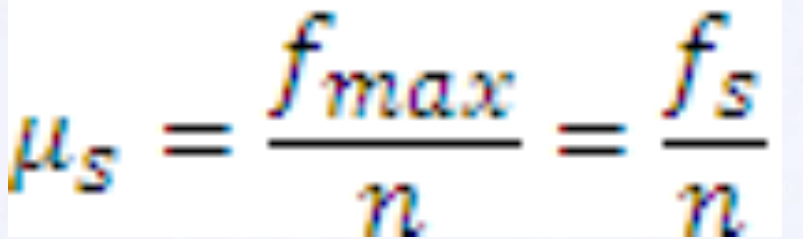
Limiting angle
Angle of repose is also called