Cadaver Project Quiz
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
23 Terms
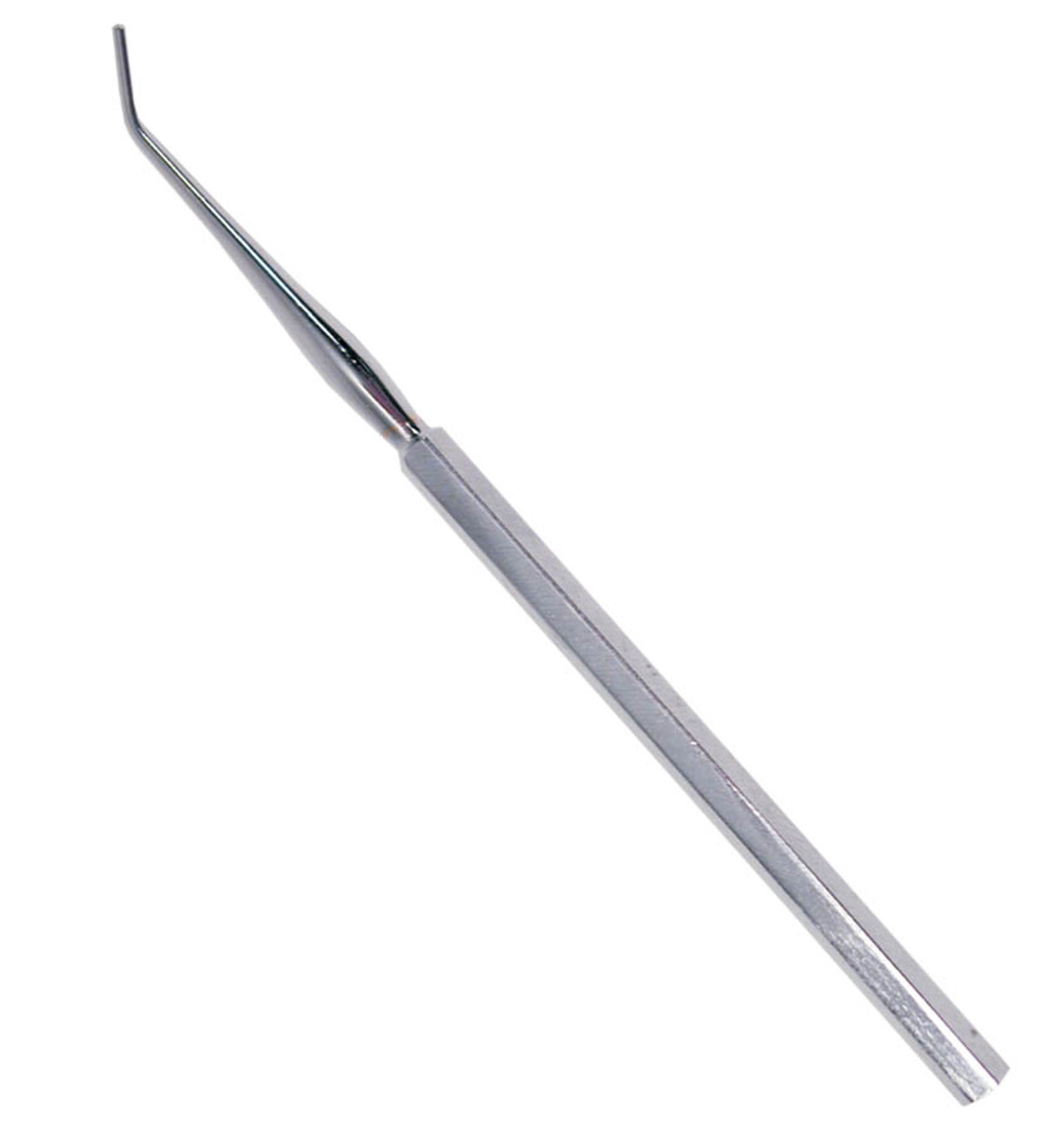
Probe
An excellent blunt dissection tool to be used for investigation of a new region along with your fingers. Designed to tear connective tissue and allow the user to feel the nerves and vessels before they damaged. Can become a primary dissection instrument to isolate and clean delicate structures.

Forceps
Used to lift and hold vessels, nerves, and other structures while blunt dissecting with a probe. Two pairs are needed. One should have tips that are blunt and rounded and the gripping surfaces should be corrugated. Second pair should have teeth (tissue or rat-toothed) for gripping tissue.
Scalpel
Used as a skinning tool. Not recommended for general dissection because they can cut small structures without allowing you to feel them. Handle should be made out of metal. Blade about 3.5 to 4 cm long. Cutting edge must have some convexity near the point. It should be held in a grip similar to holding a pencil. S
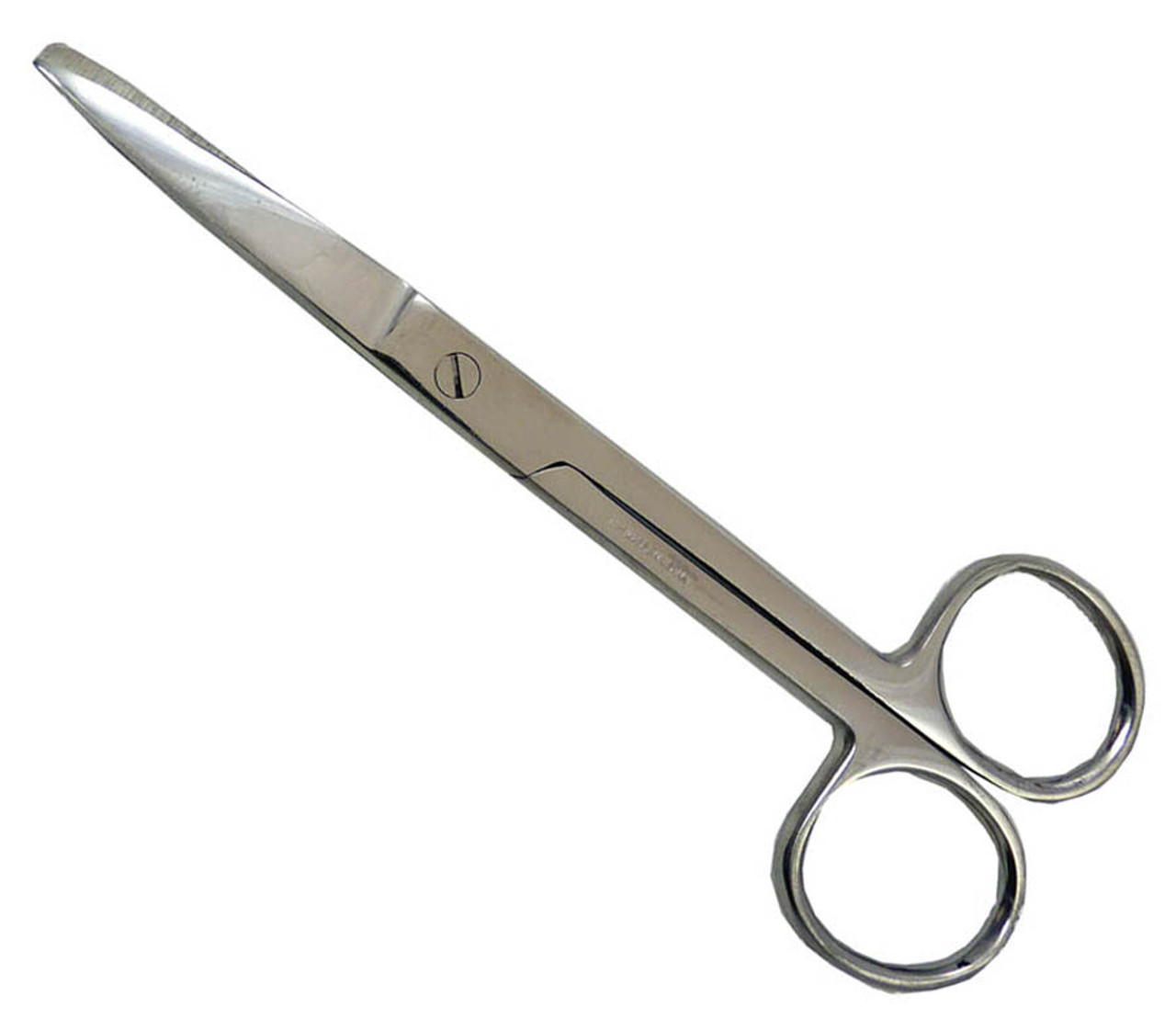
Scissors
Useful in cutting, blunt dissection, and transection. Two pairs are recommended. A large, heavy dissecting one and a small pair with two sharp points for the dissection of delicate structures.

Hemostat
A powerful grasping tool that is helpful in skin removal. Advantage is the ability to lock the grip on slippery surfaces such as skin to facilitate reflection or removal of tissue. But it has two disadvantages, one being that it crushes delicate structures and it cannot be repositioned quickly like forceps can, which slows the progress. Should be held like scissors, thumb and 4th finger in the finger loops.
Dissect
To cut apart. To tear apart or separate. Scalpel should only be used for skin incisions or as a tool of last resort for crude cuts to dissect extremely tough connective tissues.
Blunt Dissection
To separate structures with your fingers, a probe, or scissors by tearing (not cutting) connective tissues.
Scissors Technique
Method of blunt dissection in which the tips of a closed pair of scissors are inserted into connective tissue and then opened, tearing the connective tissue with the back edge of the tips. It is an effective way to dissect vessels and nerves.
Sharp Dissection
To dissect by use of a scalpel or the cutting edge of the scissors. Scalpel or scissors should only be used in conjunction with forceps.
Clean
To remove fat and connective tissue, by means of blunt dissection or sharp dissection, to expose the surface of an anatomical structure for study. Tissue from the surface of a structure can be removed by sharp dissection by cutting through the fascia and connective tissue after it has been separated from the desired structure with blunt dissection.
Clean the surface of the muscle
To remove all fat and connective tissue so the muscle fascicles become obvious and the direction of force can be understood.
Clean the border of a muscle
To define the border of a muscle with blunt dissection by breaking the loose connective tissue that binds the muscle to surrounding structures.
Clean a nerve
To use a probe or scissors technique to strip the connective tissue around a nerve for purposes of observing its relationship and branches.
Clean a vessel
To use a probe or scissors technique to strip the fat and connective tissue off the surface of a vessel or its branches to illustrate relationships.
Define
To use blunt dissection to enhance a structure to better illustrate its relationship. Involves bluntly dissecting the loose connective tissue away from it.
Retract
To pull a structure to one side to visualize another structure that lies more deeply. A temporary displacement and is not intended to harm the retracted structure.
Transect
To cut a structure in two in the transverse plane.
Reflect
To fold back from a cut edge, as in folding back a transected muscle to view what is beneath it. The tissue should remain attached to the specimen.
Strip a vein
To remove a vein and its tributaries from the dissection field so that the artery and related structures can be seen more clearly. Done either by blunt dissection using a probe or carefully with scissors using a combination of blunt and sharp dissection techniques.
Skin Reflection
Portion of the skin is left uncut, typically along the periphery of the region, to have a plane of reflection leaving a section of the skin attached to the underlying tissue.
Skin Removal
Sequential cuts made to completely remove the enitre region of the skin from the dissection field.
Partial Thickness Method
Removes the dermis and epidermis only, leaving the subcutaneous tissue intact to better identify and isolate superficial veins and cutaneous nerves coursing within the fat. Offers the advantage of increased visibility of some structures.
Full Thickness Method
Removal of the dermis, epidermis, and underlying subcutaneous tissue together in a deeper block simultaneously.