4.3 Carbon Cycling
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
14 Terms
1
New cards
Carbon Cycle
Processes by which **carbon is exchanged on Earth.**
* Total amount of carbon __**does not change**__ as the planet is a **closed system.**
* Total amount of carbon __**does not change**__ as the planet is a **closed system.**
2
New cards
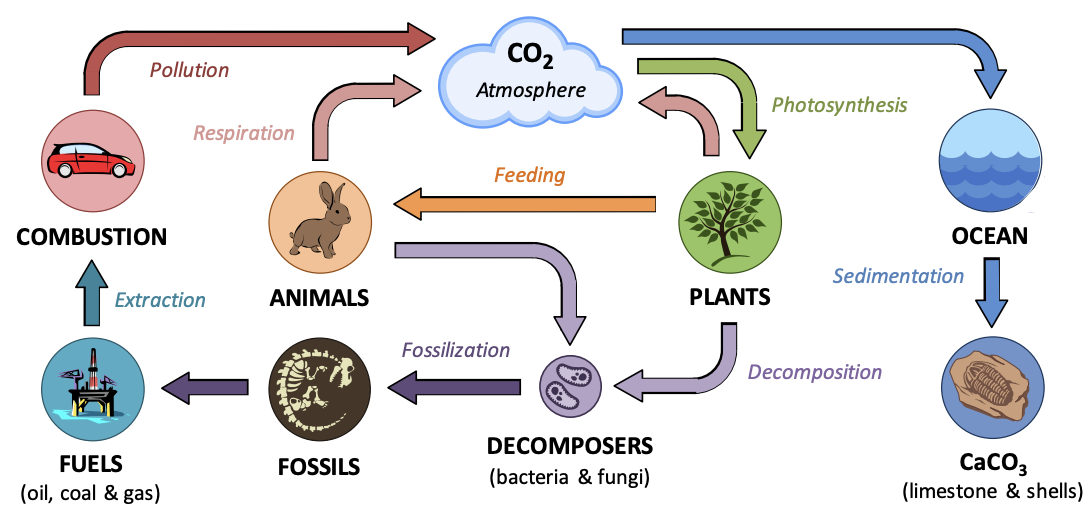
How is carbon is **transferred/sequestered**?
Four environmental spheres:
* **Biosphere** – Carbon %%convert%% into **organic compounds** (e.g. carbohydrate).
* **Hydrosphere** – Carbon %%present%% either as **dissolved CO2 or as HCO3** – ions.
* **Atmosphere** – Carbon mainly %%accumulates%% as **carbon dioxide** (or methane).
* **Lithosphere** – Carbon compounds are %%stored%% in detritus or as **fossil fuels.**
* **Biosphere** – Carbon %%convert%% into **organic compounds** (e.g. carbohydrate).
* **Hydrosphere** – Carbon %%present%% either as **dissolved CO2 or as HCO3** – ions.
* **Atmosphere** – Carbon mainly %%accumulates%% as **carbon dioxide** (or methane).
* **Lithosphere** – Carbon compounds are %%stored%% in detritus or as **fossil fuels.**
3
New cards
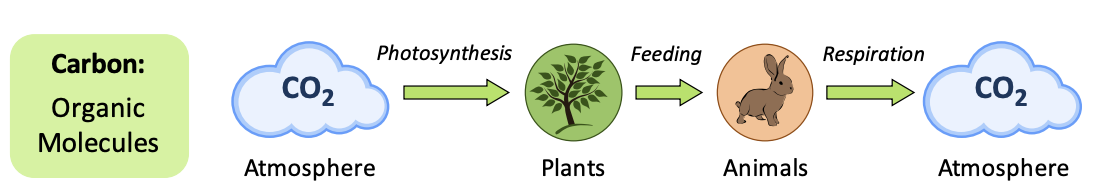
Biosphere: Organic Conversions
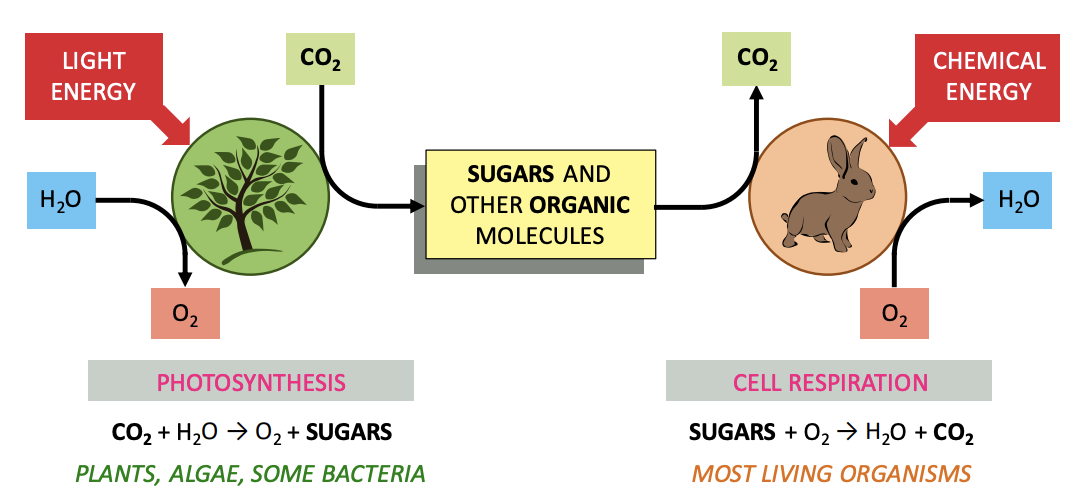
**Carbon dioxide** is **converted into organic compound**s by autotrophs (*producers*).
* Taken from air/water by *producers* and used for %%photosynthesis.%%
* %%Photosynthesis%% **fixes CO2** into **carbon compounds** (*e.g. carbohydrates*).
* Heterotrophs (*consumers*) may acquire the **organic compounds by feeding.**
* **Both** *producers* and *consumers* **produce CO2 as a by-product of respiration.**
* Taken from air/water by *producers* and used for %%photosynthesis.%%
* %%Photosynthesis%% **fixes CO2** into **carbon compounds** (*e.g. carbohydrates*).
* Heterotrophs (*consumers*) may acquire the **organic compounds by feeding.**
* **Both** *producers* and *consumers* **produce CO2 as a by-product of respiration.**
4
New cards
Biosphere: Carbohydrates
Carbon dioxide is **produced by respiration** and diffuses out of organisms into **water** or the **atmosphere.**
5
New cards
Hydrosphere: Aquatic Conversions
In water, carbon exists as dissolved gas (*CO2* ) **or** hydrogen carbonate ions (*HCO3 –* ).
* **Dissolved** carbon dioxide forms **carbonic acid in water** (CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2 CO3 ).
* **Carbonic acid** dissociates into **hydrogen carbonate ions** (H2 CO3 ⇌ HCO3 – + H+ )
As this conversion produces **H+ ions**, %%high levels%% of dissolved *CO2* lowers the *pH.*
* **Dissolved** carbon dioxide forms **carbonic acid in water** (CO2 + H2O ⇌ H2 CO3 ).
* **Carbonic acid** dissociates into **hydrogen carbonate ions** (H2 CO3 ⇌ HCO3 – + H+ )
As this conversion produces **H+ ions**, %%high levels%% of dissolved *CO2* lowers the *pH.*
6
New cards
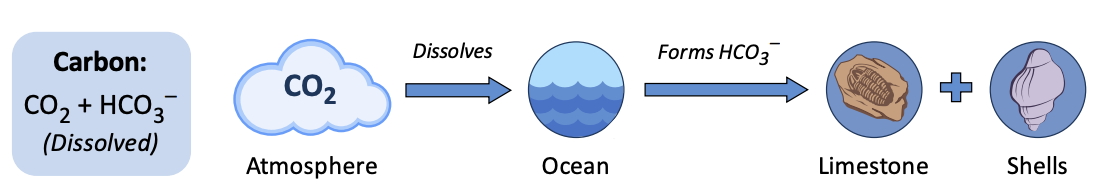
Hydrosphere: Calcium Carbonate
When HCO3 – **contacts rocks and sediments** on the **ocean floor**, they acquire __metal ions__ to **form calcium carbonate.**
\
Animals such as reef-building corals and molluscs also form hard exoskeletons composed of calcium carbonate.
* When these organisms die, these hard components may become fossilised.
\
Animals such as reef-building corals and molluscs also form hard exoskeletons composed of calcium carbonate.
* When these organisms die, these hard components may become fossilised.

7
New cards
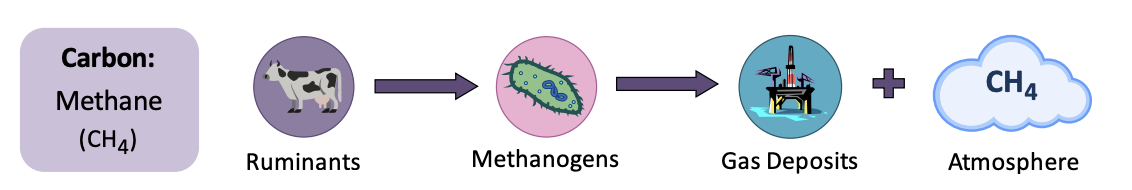
Atmosphere: Gaseous Conversions
**Methane (CH4)** is **produced from organic matter** by methanogenic archaeans under %%**anaerobic**%% conditions – which may include locations such as:
* Wetlands (*e.g. swamps and marshes*).
* Marine sediments (*e.g. in the mud of lake beds*).
* Digestive tracts of ruminant animals (*e.g. cows, sheep, goats, etc*.)
* Wetlands (*e.g. swamps and marshes*).
* Marine sediments (*e.g. in the mud of lake beds*).
* Digestive tracts of ruminant animals (*e.g. cows, sheep, goats, etc*.)
8
New cards
Atmosphere: Methane
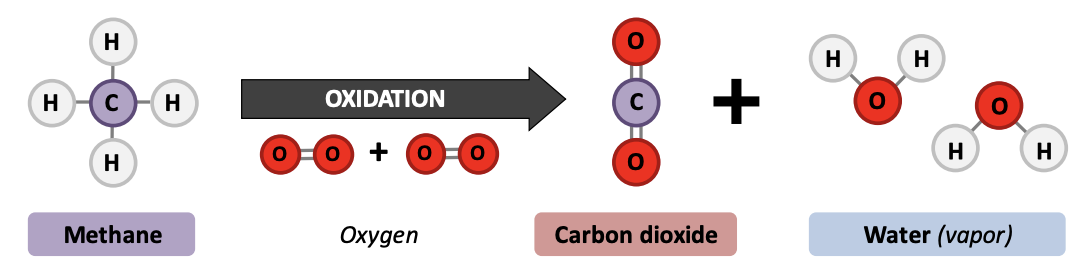
Methane **accumulate** in the __ground__ **or diffuse** into the __atmosphere__.
* Organic matter buried in anoxic conditions (oxygen deficient) condition may form natural gas deposits.
* Methane released into air oxidises into **carbon dioxide and water** (*~12 years*)
* Organic matter buried in anoxic conditions (oxygen deficient) condition may form natural gas deposits.
* Methane released into air oxidises into **carbon dioxide and water** (*~12 years*)
9
New cards
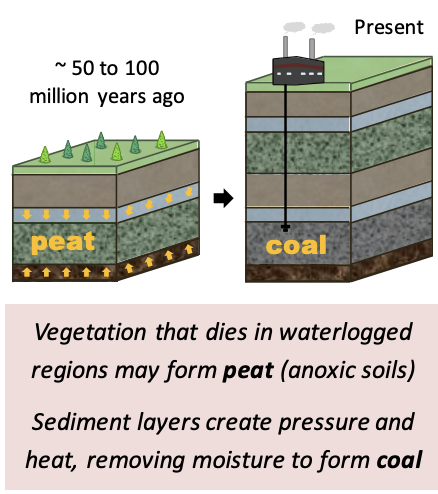
Lithosphere: Peat / Coal
**Waterlogged soils** lack __oxygenated air spaces__, resulting in **anoxic and/or acidic** soil conditions.
Organic matter not fully decomposed will form into **peat**, which compressed under sediment layers, causing it to become **coal.**
Organic matter not fully decomposed will form into **peat**, which compressed under sediment layers, causing it to become **coal.**
10
New cards
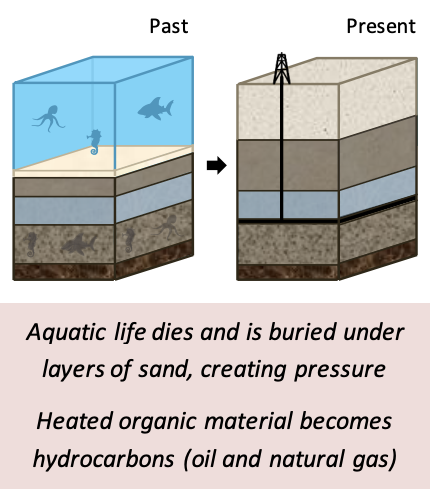
Lithosphere: Oil / Gas
Marine organisms may be buried **under layers of sediment** on the **ocean floor** after death.
* Burial creates %%anaerobic%% conditions. Compaction generates **pressure and heat.**
Organic matter is **transformed into natural gas and oil**, which accumulates in porous rock. It takes *millions* of years.
* Burial creates %%anaerobic%% conditions. Compaction generates **pressure and heat.**
Organic matter is **transformed into natural gas and oil**, which accumulates in porous rock. It takes *millions* of years.
11
New cards
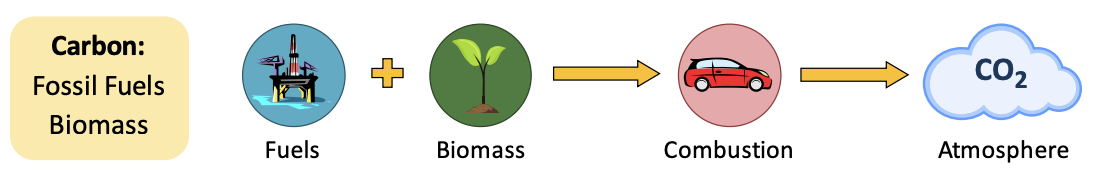
Combustion
**Fossil fuels** are converted into **usable energy via combustion** (*exergonic reaction*).
* Hydrocarbons are **heated** **to release CO2 and H2O.**
* Fossil fuels are __non-renewable.__
* Hydrocarbons are **heated** **to release CO2 and H2O.**
* Fossil fuels are __non-renewable.__
12
New cards
Carbon Fluxes
Describe **rate** of **carbon exchange** between sinks and reservoirs.
* Carbon fluxes are estimates measured in gigatonnes (one billion metric tonnes).
* Fluxes are driven by many processes (*photosynthesis, combustion, respiration, etc*.)
* Carbon fluxes are estimates measured in gigatonnes (one billion metric tonnes).
* Fluxes are driven by many processes (*photosynthesis, combustion, respiration, etc*.)
13
New cards
Main causes for carbon flux change
* **Climate** - **light** affects %%photosynthesis%%, while ==**heat**== impacts ^^CO2^^ dissolution in oceans.
* **Natural Events** - **forest fires**/**volcanic eruptions** can release large CO2 quantities.
* **Human Activity** - **deforestation/combustion**.
* **Natural Events** - **forest fires**/**volcanic eruptions** can release large CO2 quantities.
* **Human Activity** - **deforestation/combustion**.
14
New cards
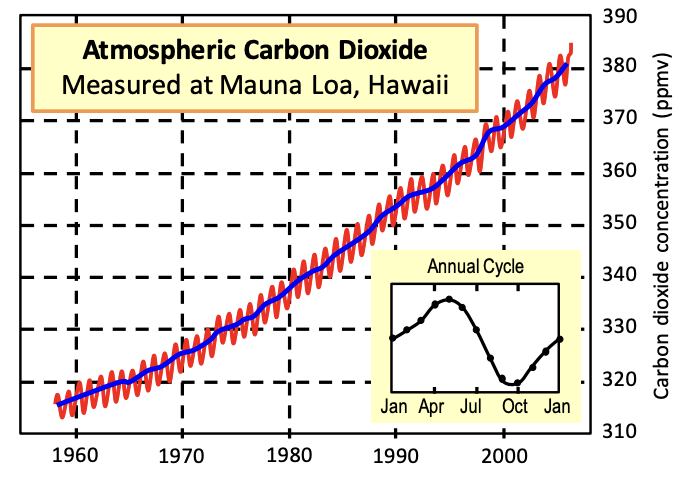
Carbon Flux Trends
* Annual fluctuations.
* **Lower in summer months** (⬆ light = ⬆ photosynthesis).
* **CO2 levels are on the rise** (combustion & deforestation).
* **Global trends** conform to the northern hemisphere
* **Lower in summer months** (⬆ light = ⬆ photosynthesis).
* **CO2 levels are on the rise** (combustion & deforestation).
* **Global trends** conform to the northern hemisphere