DNA damage
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
What are the 6 causes of DNA damage?
endogenous nucleases
replication error
spontaneous errors to bases
Deamination
Depurination (and depyrimidation) , and resulting ssb
Free radical damage
ROS and NOS
Ionising radiation
UV
Alkylating agent
What is endonuclease?
enzymes that cleave the phosphodiester bond within a polynucleotide chain
What is exonuclease?
enzymes that cleaves the phosphodiester bond at the end of a polynucleotide chain
What is polymerase?
enzymes that add ribonucleotides to DNA strands
What is a ligase ?
fosters the joining of DNA strands together by catalysing the formation of a phosphodiester bond
Replication errors - base pairing mismatch during DNA synthsis
energy dfference between correctly paired and incorrectly paired bs is only equivalent to 1 hydrogen bond
Rare tautomeric forms of bases can stabilise incorrect bp
Error frequency of W-C base pairing alone
1-10%
Spontaneous alternation to DNA bases
Deamination
which one is the quickest?
The fastest is 5-methylcytosine to Thymine
Just a deamination at one site from NH2 to =O which creates thymine
Another fast one is from cytosine to uracil
Where is deamination favourable?
Deamination of cytosine is used to increase mutation rates for generation of immunoglobulin diversity
Somatic hypermutation during clonal expansion of B-lymphocytes
In lymphocytes, (activation-induced cytidine deamination) AID deaminates cystidines to yield C to U to create a U -G mismatch repair
Which two pathways induce the removal of induced c to u?
Base excision repair BER or MMR
Mutagenesis by AID in B cell - cause
If AID is targetting the immunoglobulin gene in B cell then the formation of diverse antibodies is useful
but if AID is targetting another gene, it might elicit potential tumour promoting mutations
Spontaneous deamination is not only fastest but also most…
mutagenic at 5-methylcytosine → thymine, which has 4x higher rate of deamination than cytosine.
5-Mec is an important epigenetic mark in DNA, specifically at CpG islands
methylation in CpG islands in promoters are normally hypomethylated, but their hypermethylation can silence tumor supressor gene - Rb
The deamination problem provides a reason why thymine replaced uracil in the evolution of DNA. BER recognises U in DNA as …. and replace with…
BER recognises U in DNA as a deamination product and replace with C
Spontaneous alteration to DNA bases: depurination and depyrimidination
Due to the spontaneous breakage of the … bond
Purine lost … faster than pyrimidines
Due to the spontaneous breakage of the glycosidic bond (hydrolysis), which results in an abasic site lesion
Purine lost x20 faster than pyrimidines
b-elimination can occur at abasic sites because the deoxyribose can convert to the aldehyde (open chain) form.
Free radicals and related ROS
The most important DNA oxidant is OH*, which is generated from the radiolysis of water, or indirectly from the superoxide (O2*-) arising from mitochondrial O2 reduction and from xenobiotic reduction
Main sites of mitochondrial superoxide generation
Complex I = NADH dehydrogenase, involves transfer of electrons from FMNH2 to Fe-S centers and to ubiquinone, which can leak electrons to O2
Complex III
Superoxide formation via redox cycling: Menadione (electrophilic) and Cytochrome P450
menadione (Vit K3) reacts with the enzyme cytochrom P450 which yields the menadione semiquinone radial, which is unstable radial
O2*-
React with itself spontaneously to form H2o2 and this reaction is greatly catalysed by SOD
Catalase convert H2020 into water
Detoxified by GSH and Peroxiredoxins
Are H2O2 and O2*- damaging to DNA, if not, how would they indirectly cause damage?
No, but they can be reduced to OH* by transition metals especially Fe2+
Fe2+ + H202 → Fe3+ + OH* + OH-
RONS play an important physological role in …
How is Hypochlorous acid (HOCl) formed in neutrophils?
defense against bacterial infection
Superoxide is generated at high concentration at respiratory burst by neutrophils
Hypochlorous acid is formd from H2o2, which is catalysed by myeloperoxidase (MPO) in activated neutrophils
Link between colon cancer in inflammatory bowel disease and HOCl
During chronic inflammation, HOCl chlorinates cytosine to form 5-chloroC, which acts 5MeC
→ cause epigenetic silencing mutation
What is peroxynitrite? how can it generate nitrogen dioxide radical and carbonate radial?
ONOO-
from O2*- + NO*
ONOO- can react with CO2 which makes NO2* (nitrogen radical) and CO3*-
Which base has the lowest reduction potential (most easily oxidised)
Guanine → 8-OxoG
8-OxoG does not block DNA polymerase
Mispairs with A (from G-C to O-C) to O-A?
End result : G to T transversion
What can be seen from the oxidative stress and liver cancer in HCV?
8-OxoG upregulation
Positive correlation with hepatic iron storage
Most common dimer generated from UV damage?
T-T
Thymine dimer - 68%
Alkylating agent
What do they do to DNA bases?
Both carcinogen and anticancer
They are electrophillic compounds that add an alkyl group to nucleophilic centres (electron rich) in DNA
Can be both endogenous and exogenous
Alkylating agent: Dimethylnitrosamine
Metabolised by CYP2E1 in the liver, which turns guanine to O6-methyl G
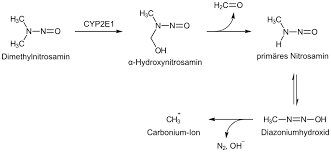
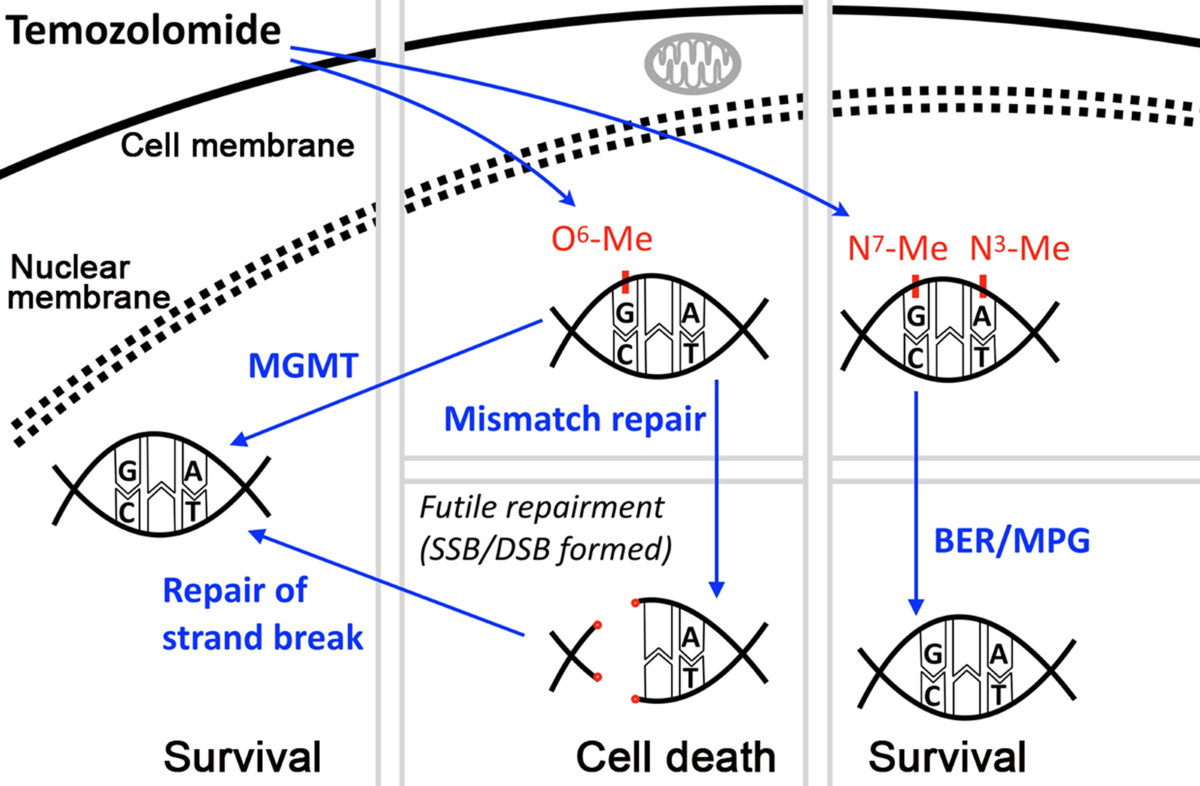
Alkylating agent: Temozolomide
Monfunctional alkylating agent and anticancer agent
It is a prodrug that stimultanously turns into a methylating agent
Used for melanoma and glioblastoma
high oral bioavailability and good tissue distribution
MGMT cause resistance to TMZ by removing O6-MeG
Blocking BER using PARP1 inhibitor can sensitises cells to TMZ by preventing N7-MeG repair
What are some bifunctional alkylating agents and why are they useful
Cisplastin, carboplastin
Induces interstrand crosslink which are highly toxic due to interference with DNA replication
Nitrogen mustard
Bifunctional = two reactive sites on the same molecule
two alkylations on opposite strands
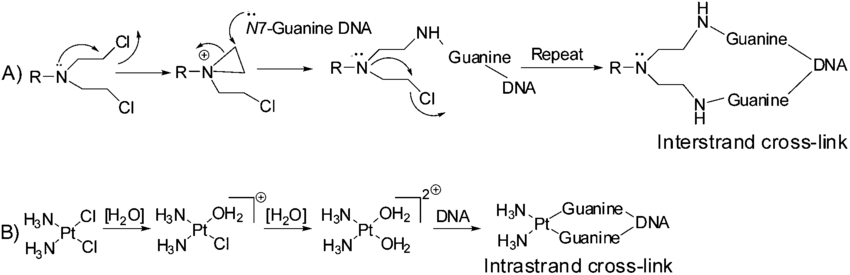
In a retrospective study of liver biopsies from patients infected with hepatitis C virus, levels of iron were found to correlate with the frequency of 8-oxoguanine in DNA, and with the risk of developing hepatocellular carcinoma later in life. These observations can be from
Fenton chemistry produces hydroxyl radicals that oxidise DNA bases