Bio Lab Exam 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/54
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 11:54 PM on 3/22/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
1
New cards
What are the 4 parts of the microscope?
1. fine adjustment
2. coarse adjustment
3. objective lenses
4. ocular
2
New cards
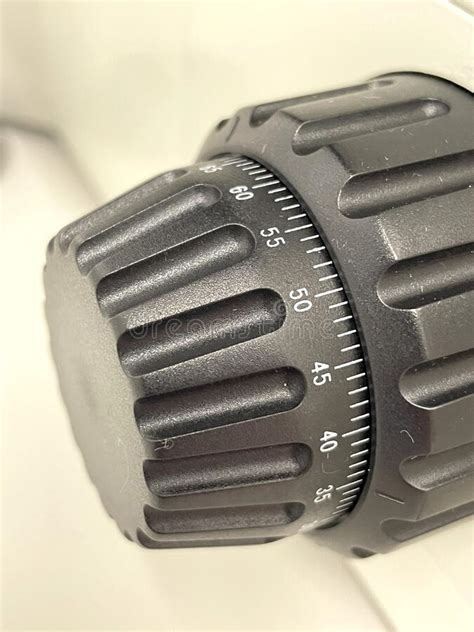

bigger notch
coarse adjustment
3
New cards
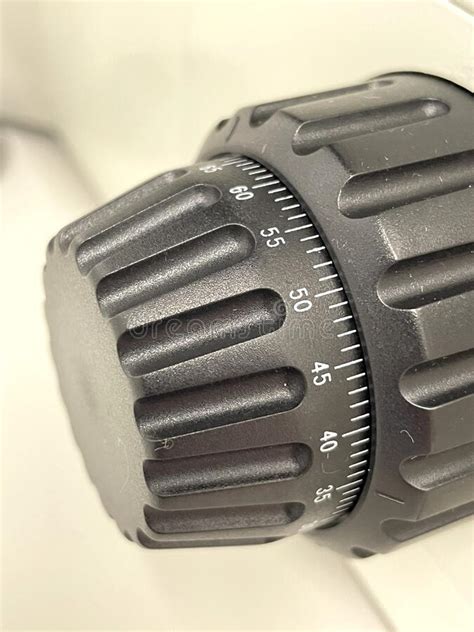

smaller notch
fine adjustment
4
New cards
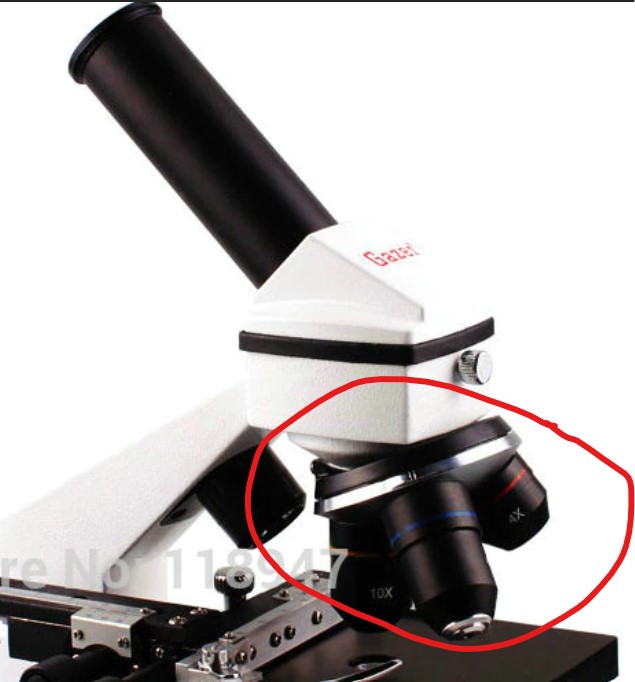

objective lenses
5
New cards
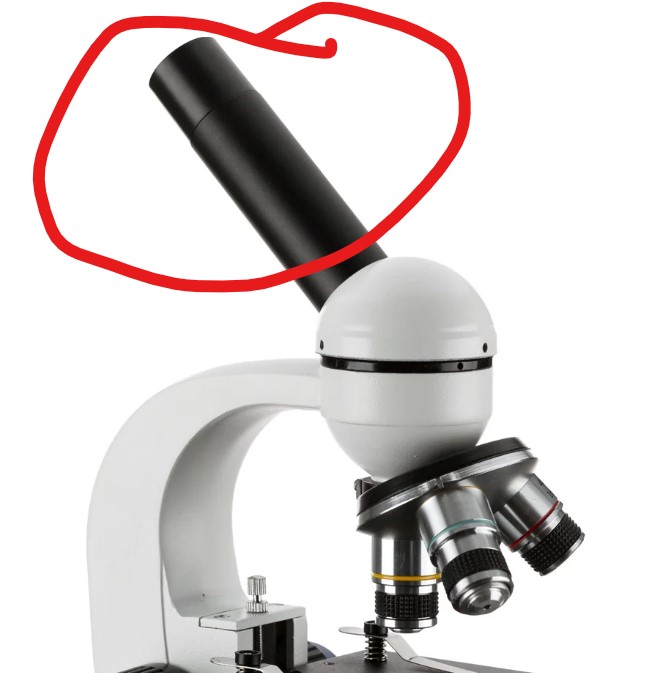

oculars
6
New cards
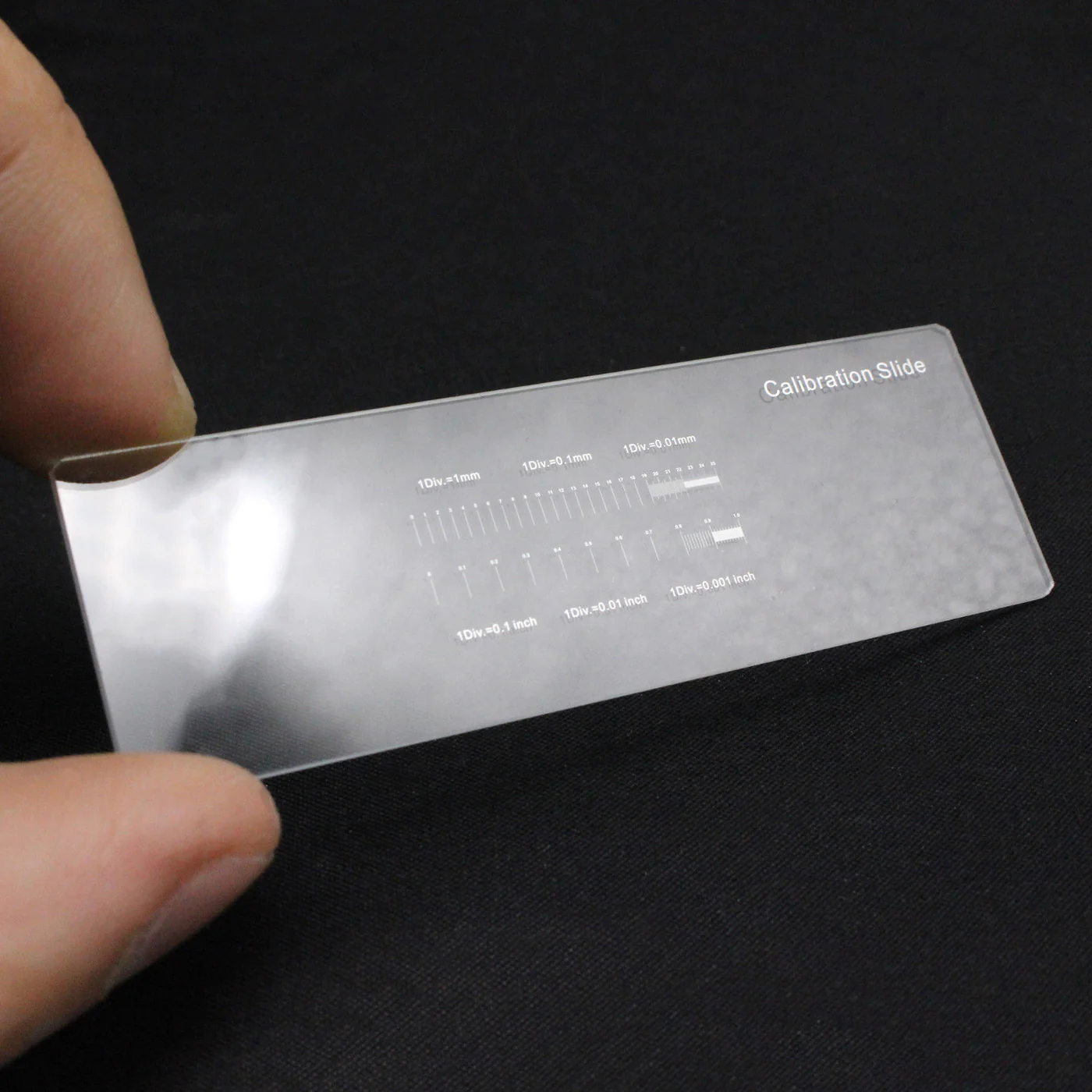

what is it and what is it used for?
* stage micrometer
* 1 space = 10 micrometers (μm)
* used to convert pixels to micrometers
* 1 space = 10 micrometers (μm)
* used to convert pixels to micrometers
7
New cards
define total magnification
ocular magnification x objective magnification (multiply objective lens magnification by 10)
8
New cards
define working distance
* space between objective lens and slide
* the greater the magnification the less working distance
* the greater the magnification the less working distance
9
New cards
field of view
* amount of space that can be seen
* the greater the magnification the smaller field of view
* the greater the magnification the smaller field of view
10
New cards
what to do when finished with microscope
* turn off
* rotate to 4x objective
* rotate to 4x objective
11
New cards
what is the software used with microscope?
LAS EZ
12
New cards
independent variable
variable you manipulate in experiment (changes)
13
New cards
dependent variable
variable you measure to see if there was an effect
14
New cards
potentially confounding variables
factors that are kept constant b/c they may change results
15
New cards
null hypothesis
“there is no effect of independent variable on dependent variable”
Ex: there is no effect of music on studying habits
Ex: there is no effect of music on studying habits
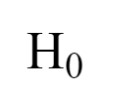
16
New cards
alternative hypothesis
“independent will have blank affect on dependent variable”
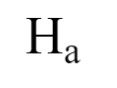
17
New cards
controlled experiment
changing one factor and observing its affect on another while keeping all other factors constant
18
New cards
how to calculate size of cell given scale + length of cell in pixels or # of spaces of stage micrometer
scale = line distance / known distance
19
New cards
what is scale when determining cell size?
pixels/unit
20
New cards
what is line distance when determining cell size?
size measured of cell in pixels
21
New cards
what is known distance when determining cell size?
\# of spaces x 10 μm
22
New cards
what is the size difference between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
eukaryote is 6.642 times bigger than the prokaryote
23
New cards
explain paper chromatography
* isolates pigment molecules from leaves of plant
* uses properties of molecules to separate the 4 pigment molecules
* carotenes
* xanthophylls
* chlorophyll a
* chlorophyll b
* uses non-polar solvent to dissolve non-polar pigments
* the higher it travels up the paper, the more polar/non polar it is (depends on the solvent)
* uses properties of molecules to separate the 4 pigment molecules
* carotenes
* xanthophylls
* chlorophyll a
* chlorophyll b
* uses non-polar solvent to dissolve non-polar pigments
* the higher it travels up the paper, the more polar/non polar it is (depends on the solvent)
24
New cards
what would happen if water was used as solvent in paper chromatography?
Pigments would not dissolve and remain at the origin because water is polar
25
New cards
what would happen if pigment line is submerged in solvent in paper chromatography?
pigments will dissolve in solvent (leaves green liquid in jar)
26
New cards
how to calculate Rf value?
distance of pigment from origin / distance of solvent from origin
27
New cards
what does Rf value tell you about solubility?
Greater = more soluble
smaller = less soluble
smaller = less soluble
28
New cards
what does Rf value tell you about polarity?
* if solvent is polar, the higher it is the more polar it is
* if solvent is non-polar, the higher it is the more non-polar it is
* if solvent is non-polar, the higher it is the more non-polar it is
29
New cards
how does color of pigment relate to absorbance spectrum in chromatography?
* colors with no peaks are the colors reflected (we see the reflected color)
\
\
30
New cards
What is purpose of setting the scale in imageJ?
To convert pixels into micrometers so that we can measure cells at any magnification.
31
New cards
what pipettes are used with green pump?
* 5mL
* 10mL
* 10mL
32
New cards
what pipettes are used with blue pump?
2 mL
33
New cards
How to use 2 mL pipette?
* draw liquid up to 0 mL mark
* dispense to # needed
* dispense to # needed
34
New cards
5 Steps to extract DNA from strawberries?
1. mash strawberry
2. add DNA extraction buffer
3. Filter
4. Meat tenderizer
5. alcohol
35
New cards
Purpose of mashing strawberry step
replicate breaking cell/disturbing membrane
36
New cards
purpose of adding DNA extraction buffer step
soap: breaks down cell membrane
salt: stabilizes DNA molecules and removes proteins bound to DNA
salt: stabilizes DNA molecules and removes proteins bound to DNA
37
New cards
purpose of filter step
remove large cellular debris (cell membrane/organelles)
38
New cards
purpose of meat tenderizer step?
releases DNA by breaking down histone proteins with digestive enzymes
39
New cards
purpose of alcohol step?
DNA is not soluble in alcohol and will be able to be picked up.
40
New cards
How to determine purity of DNA sample from A260/A280 ratio?
* pure DNA sample has ratio of 1.8
* lower ratio = protein impurities
* lower ratio = protein impurities
41
New cards
describe structure of nucleotide and its 3 main components
* monomer of nucleic acids (like DNA/RNA)
* contains 3 bases: nitrogenous, sugar, phosphate group
* contains 3 bases: nitrogenous, sugar, phosphate group
42
New cards
describe nitrogenous base
* 5 types: adenine, guanine, cytosine, thymine, uracil
* contains genetic information
* contains genetic information
43
New cards
describe sugar base
* pentose (5 carbon) sugar
* backbone of nucleotide
* deoxyribose/ribose
* backbone of nucleotide
* deoxyribose/ribose
44
New cards
describe phosphate group
* attached to sugar molecule
* 4 phosphate 1 oxygen
* negative charge stabilizes structure of nucleic acid
* 4 phosphate 1 oxygen
* negative charge stabilizes structure of nucleic acid
45
New cards
what type of bond connects components of a nucleotide
2 covalent bonds:
* glycosdic
* phosphodiester
covalent bond stronger than hydrogen bonds
* glycosdic
* phosphodiester
covalent bond stronger than hydrogen bonds
46
New cards
what type of bond connects complementary bases?
hydrogen bonds, weaker than covalent bonds
47
New cards
identify complementary base pairs
A-T : two hydrogen bonds
C-G : three hydrogen bonds
C-G : three hydrogen bonds
48
New cards
what part of the DNA molecule interacts with the cellular environment and whether that part is hydrophobic or hydrophilic
sugar-phosphate backbone, which is hydrophilic
49
New cards
how to tell that the two strands of a DNA molecule are anti-parellel?
They run in opposite directions
* you can look at the orientation of the sugar molecules in the backbone. This creates a repeating pattern of a sugar-phosphate backbone with a free @@**5' phosphate group**@@ at one end and a free **3' hydroxyl group** at the other end.
* you can look at the orientation of the sugar molecules in the backbone. This creates a repeating pattern of a sugar-phosphate backbone with a free @@**5' phosphate group**@@ at one end and a free **3' hydroxyl group** at the other end.
50
New cards
what does red represent on dna molecule
oxygen atoms
51
New cards
what does yellow represent on dna molecule
phosphorus atoms
52
New cards
what does gray represent on dna molecule
carbon atoms
53
New cards
what does blue represent on dna molecule
nitrogen
54
New cards
what does white represent on dna molecule
hydrogen
55
New cards
what does grey and red central ring represent
sugar (gray + red), base (central ring)