Heart Structure & Circulation Terms | Physiology Lecture 20
1/73
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
74 Terms
Pulmonary (lung) circulation
this type of circulation carries blood bewteen the heart and lungs
Systemic circulation
this type of circulation carries blood between heart and organ system
Pulmonary (lung circulation)
This circulation moves O2 from inhaled air into blood
Systemic circulation
This circulation moves O2 to tissues and CO2 back to lungs
systemic circulation
This system maintains appropriate blood pressure
Pulmonary (lung) circulation
This system removes CO2 from blood and releases it into the atmosphere
2
the heart is a four-chamber ___ sided pump
right atrium
deoxygenated blood from the body enters the _____ ____
right ventricle
from the right atrium, the blood flows into the ____ ____
lungs
from the right ventricle, the blood flows to the
left atrium
from the lungs the blood flows to the
left ventricle
from the left atrium the blood flows to the
body
from the left ventricle the blood flows to the
(superior/inferior) vena cava, right atrium, tricuspid (right atrioventricular) valve, right ventricle, pulmonary semilunar valve, pulmonary arteries, lungs, pulmonary veins, left atrium, mitral (bicuspid, leftatrioventricular) valve, left ventricle, aortic semilunar valve, aorta
Say the order of blood flow, starting with the vena cava
tricuspid valve
what is another name for the right atrioventricular valve
mitral or biscuspid valve
what is another name for the left atrioventricular valve
Left
Which side of the ventricular muscle walls is thicker?
Higher systemic blood pressure
the left side needs to have a much thicker/stronger ventricular walls due to the __________ ____________ ___________________ ________on the other side
lower pressure
The right ventricle pumps blood to pulmonary circulation with a ______ ______
Endocardium
this is the inner lining of the heart
Myocardium
this is the middle layer of tissue in the heart, made up of cardiac muscle
Pericardium
this is the membrane surrounding the heart also called the “heart sac”
4
How many layers of the pericardium are there?
Pericarditis
this is inflammation of the pericardium
Cardiac tamponade
this is fluid accumulation in the pericardial cavity
Myocardial infarction
this is another word for a heart attack, it's whena part of the myocardium fails to receive enough oxygen
Cardiac myocyte (cardiomyocyte)
these are another word for cardiac muscle cell
Deoxygenated
the right side of the heart (atrium and ventricle) carries this kind of blood, before going to the lungs
Oxygenated
the left side of the heart (atrium and ventricle) carries this kind of blood after going to the lungs, then delivering it to tissues
Angle
the heart is positioned at an _________ on the left side of the thoracic cavity
Apex
this is the tip of the heart
Relaxed
when the ventricles are _____________, blood enters the atria, pushing the atrioventricular valves down
Contracted
When the ventricles are _________________, blood presses up against the AV valve cusps, forcing the valves closed, and the blood will flow through the semilunar valves
Chordae tendineae
these are bands of fibrous tissue in the ventricles that can be tightened by papillary muscles, and prevent the AV valves from being pushed inside out into the atria when the ventricles are contracted
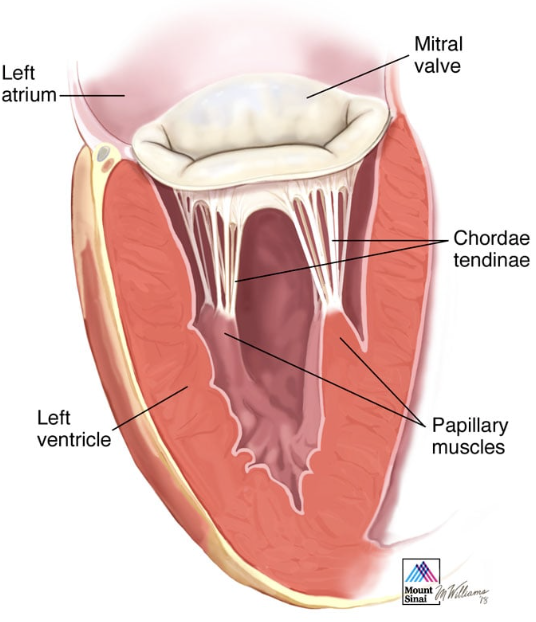
Cardiac Skeleton
this is the fibrous layer of connective tissue that's composed of rings of that connective tissue around the 4 valves, but it's not a bone., forms a single spatial plane that contains teh 4 valves
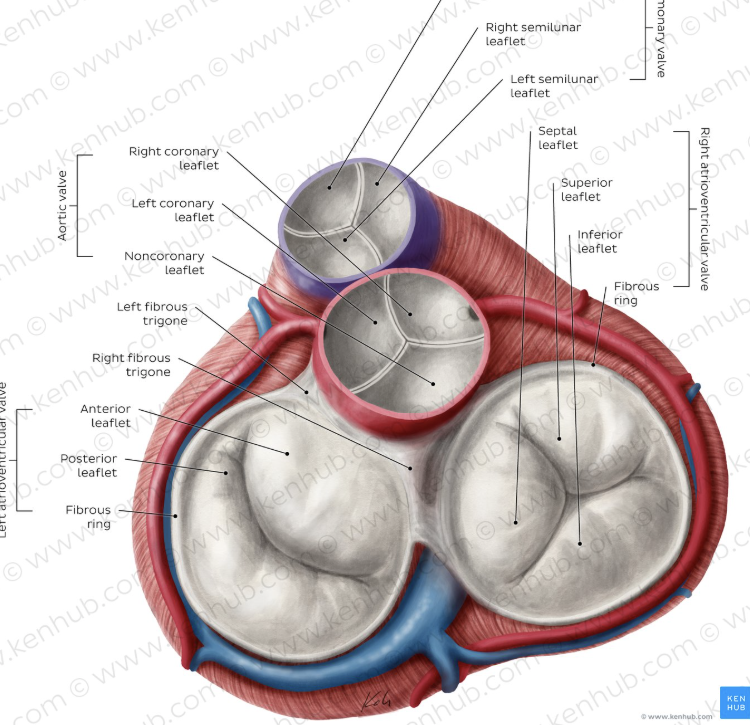
Anchors valves
anchors atrial muscles above and ventricular muscles below
acts as an electrical insulator between atria and ventricles
these are the 3 roles of the cardiac skeleton
Echocardiogram
ultrasound of the heart
Stenosis
this is a condition when the valve flaps become thick or stiff, and maybe fuse together, resulting in a norrowed valve opening and reduced blood flow through the valve
Regurgitation
this is a condition when the valve flaps don't close properly, which causes blood to leak backwards into the heart, and occurs due to a condition called prolapse
Atresia
this is a condition where the valves are not formed, and a solid sheet of tissue blocks the blood flow between the heart chambers
Atrium
In terms of the 3 waves of depolarization, the first wave of depolarization goes from the top of the _________ to its bottom
Intermittent period
After the atria are depolarized, the period that follows is called the _________________ ______________ and is a delay
Ventricle`
After the intermittent period, the next wave of depolarization happens from the bottom of the ____________ to its top
simultaneously
the left and right atria contract _______
simultaneously
left and right ventricles contract ______
Preload
the intermittent period is needed because of the necessity to fill the ventricles with blood, which is known as this
preload
volume of blood in the ventricles at the end of diastole, right before the muscle contracts
Arrhythmia
this is irregular electrical activites that lead to abnormal contractions
Ventricular fibrillation
this is an extreme case of arrhythmia which causes the ventricles to twitch uselessly, which eventually can lead to sudden death, can be solved by CPR and AED
Intercalated discs
these are specialized structures in cardiac muscle cells that has desmosomes and gap junctions, which help the cardiac muscle to initiate its own muscle contractions
Gap Junctions
these are in the intercalated discs taht are areas of low electrical resistance that allows action ptoentials to spread from cell to cell
Desmosoems
these are in the intercalated discs that are a type of adherence junction which holds the cells together
Functional syncytium
this is the concept that is an action potential is initiated in any cell of the heart, it will spread throughout to the connected muscle cells
myogenic
cardiac muscle = myogenic/neurogenic
Myogenic
the heart has the ability to initiate its own muscle contractions, and when removed from the body, it'll still beat spontaneously
neurogenic
skeletal muscle = myogenic/neurogenic
Neurogenic
skeletal muscle is this, which means that the muscle needs to be initiated by a motor neuron in order to contract
2
there are this many subgroups of syncytia, which contract sequentially with delay
AV node
there is only one connecting path between the atrial and ventricular syncytia, which is this
Cardiac pacemakers
these are cells that are specialized and devoted to generation and conduction of rhythmic, pacemaker potentials, which help the rhythm of circulation
Pacemaker potentials
spontaneous depolarization in the resting membrane potential
SA node
this is the place where the pacemaker potentials are initiated, and it is at the top right of the heart
AV node
after the pacemaker potential is generated in the SA node, it spreads to this, which is the only way to get a depolarization wave to get from the atria to the ventricles
AV nodal delay
the conduction through the AV node is slow, which creates a delay between the atria and ventricular contraction, called this
Doesn't
the wave of depolarization from the AV node ________(does/doesn't) spread uniformly over the vnetricular myocardium
Bundle of His
After the AV node, the electrical impulse spreads to this
Left and right blude branches
After the Bundle of His, the electrical impulse spreads to this
Purkinje fibers
After the left and right bundle branches, the elecrtrical impulse spreads from the apex upward through these, and enable ventricular contraction beginning primarily at the apex, pushing blood upward towards the pulmonary and aortic valves
SA node
which node has the fastest rate of conduction?
SA node
what node determines the heart rate and direction of conduction?
AV node
which node has the slowest conduction speed?
Delay
AV node has the slowest conduction speed, and during this __________ caused by this, and the atria contract, and ventricles become filled
Tachycardia
if the heart beats too fast, it is called this
Brachycardia
if the heart beats too slow, it is called this