MRI Brain Labelling 2
1/161
Earn XP
Description and Tags
ANAT 305 - Cross Sectional Anatomy
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
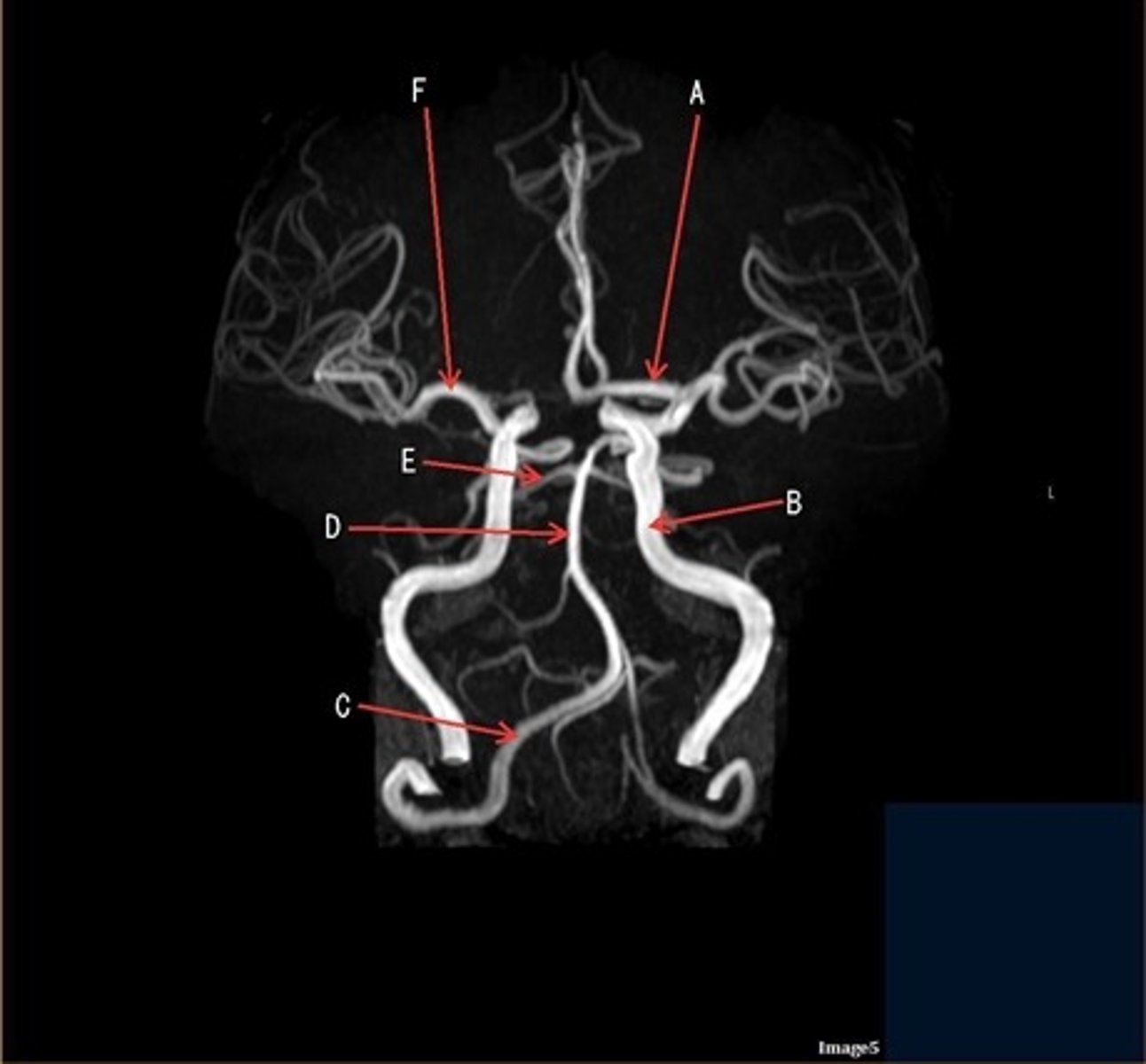
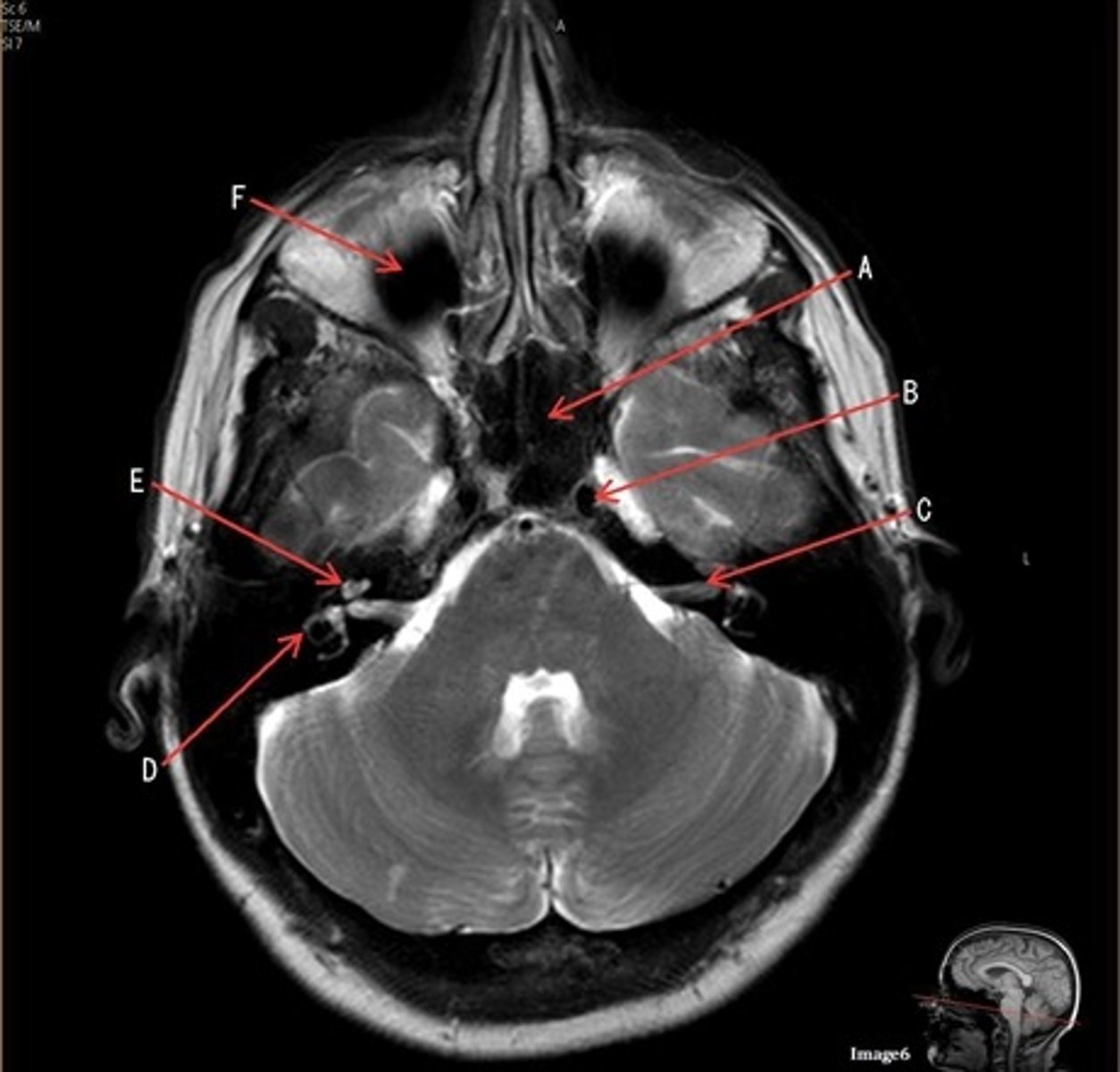
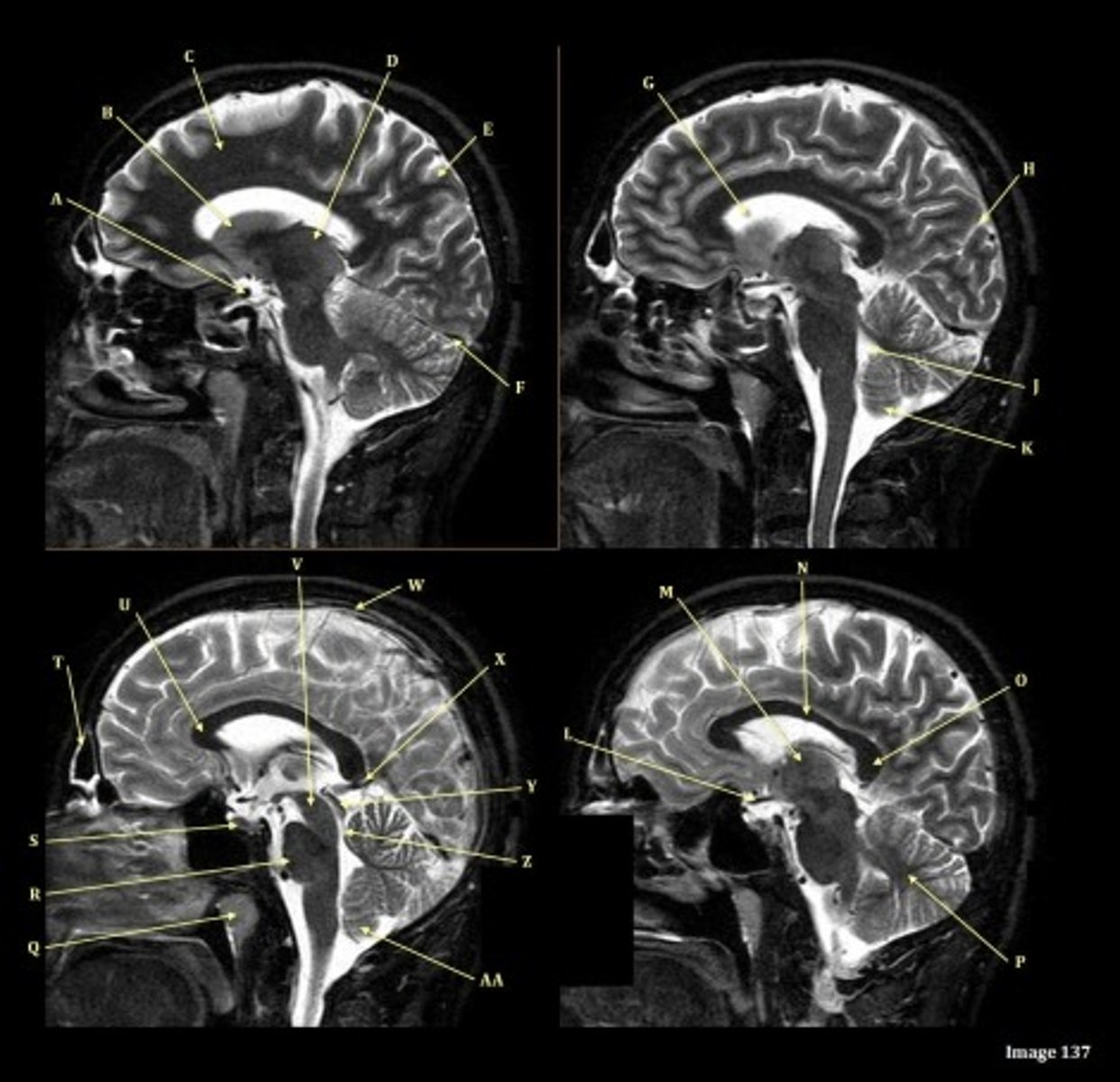
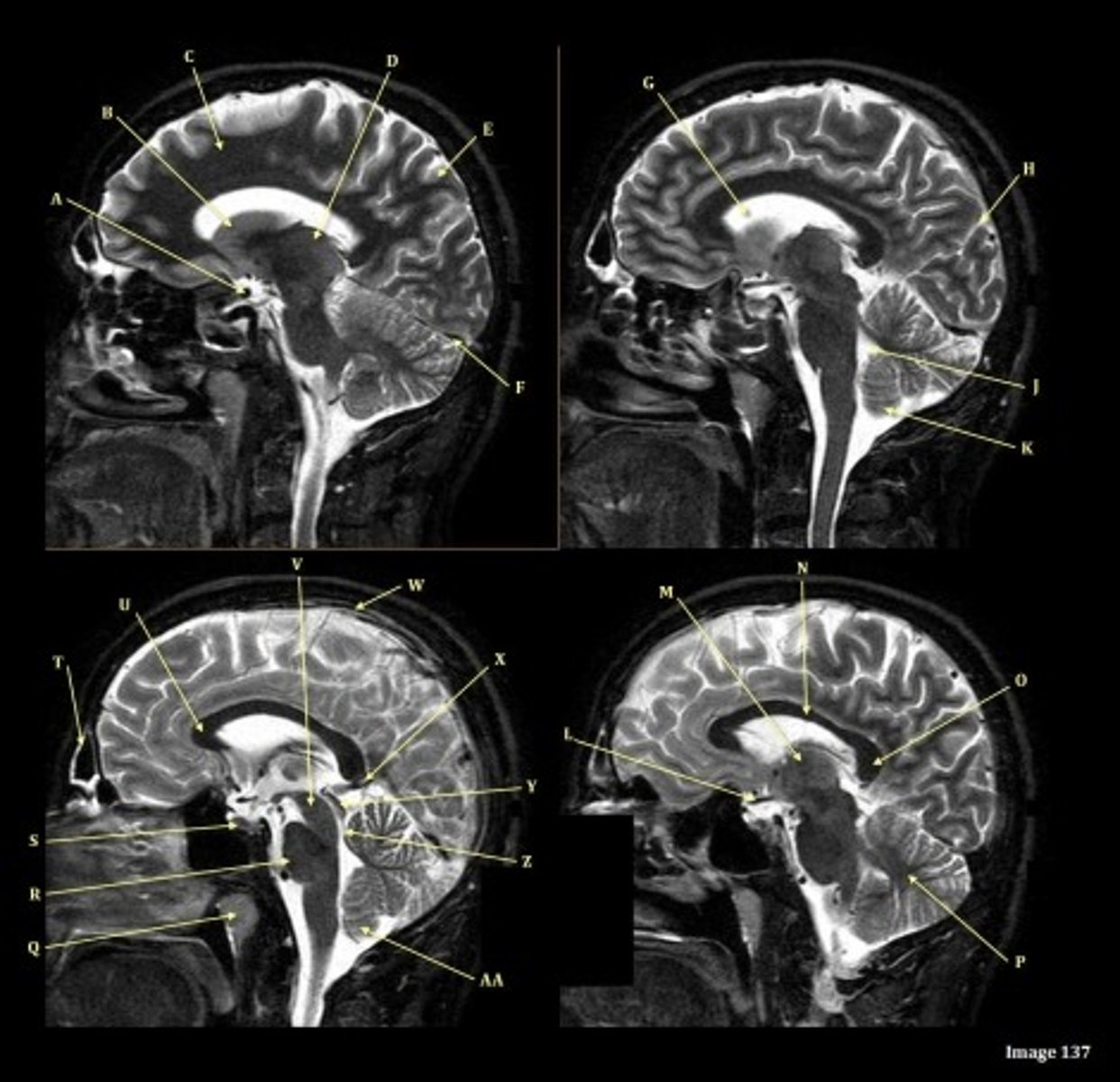
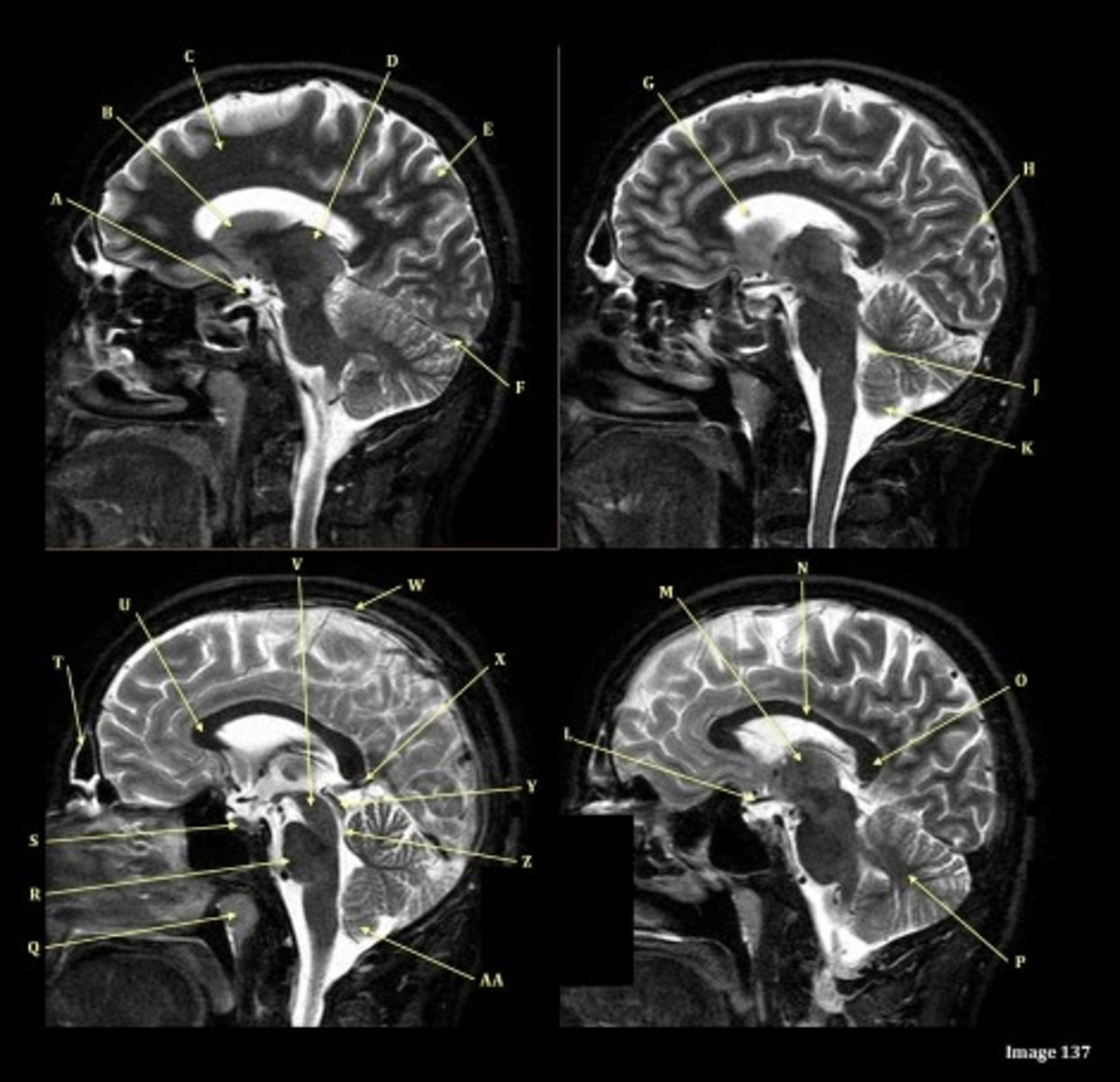
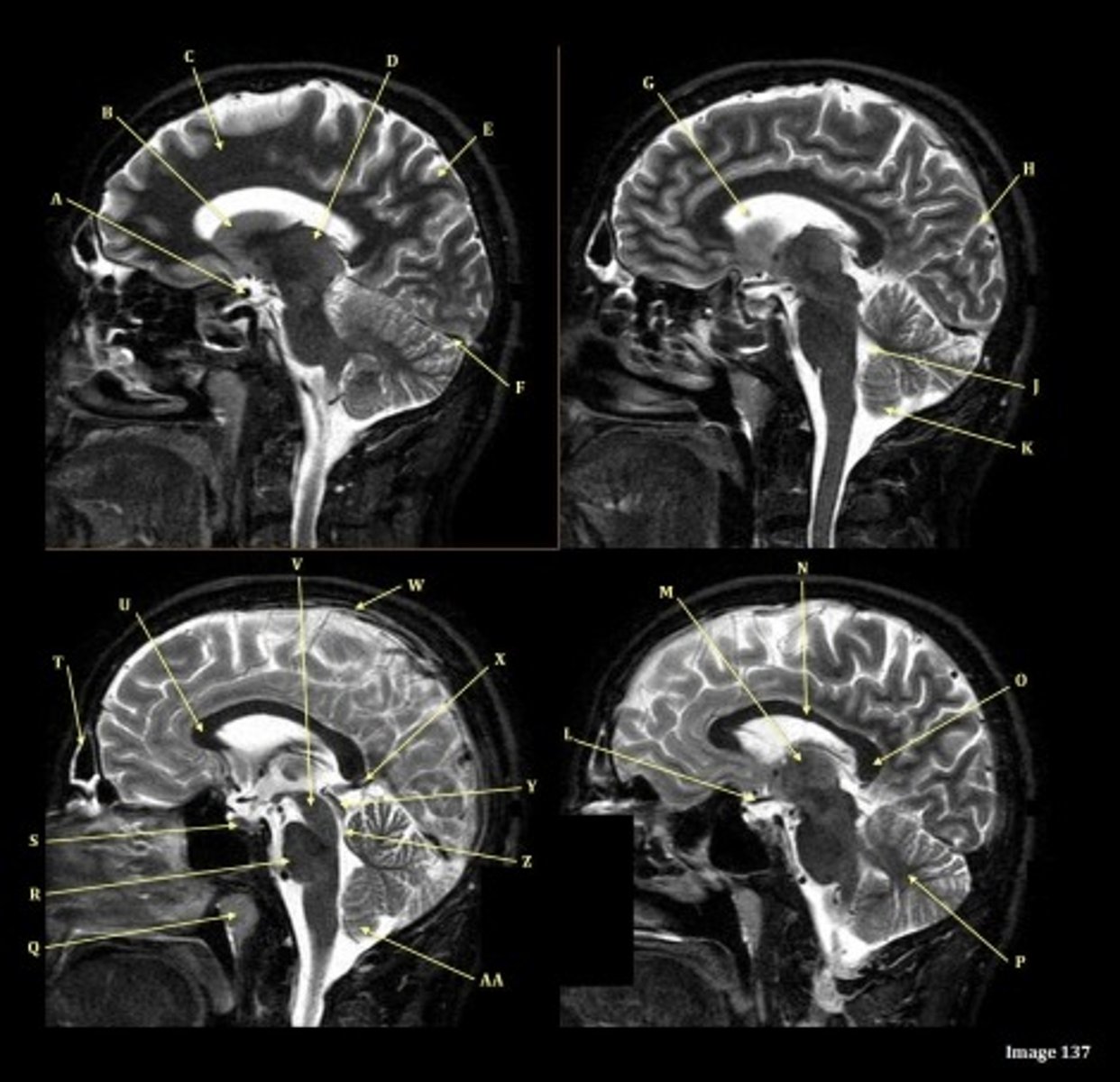
A
A- anterior cerebral artery
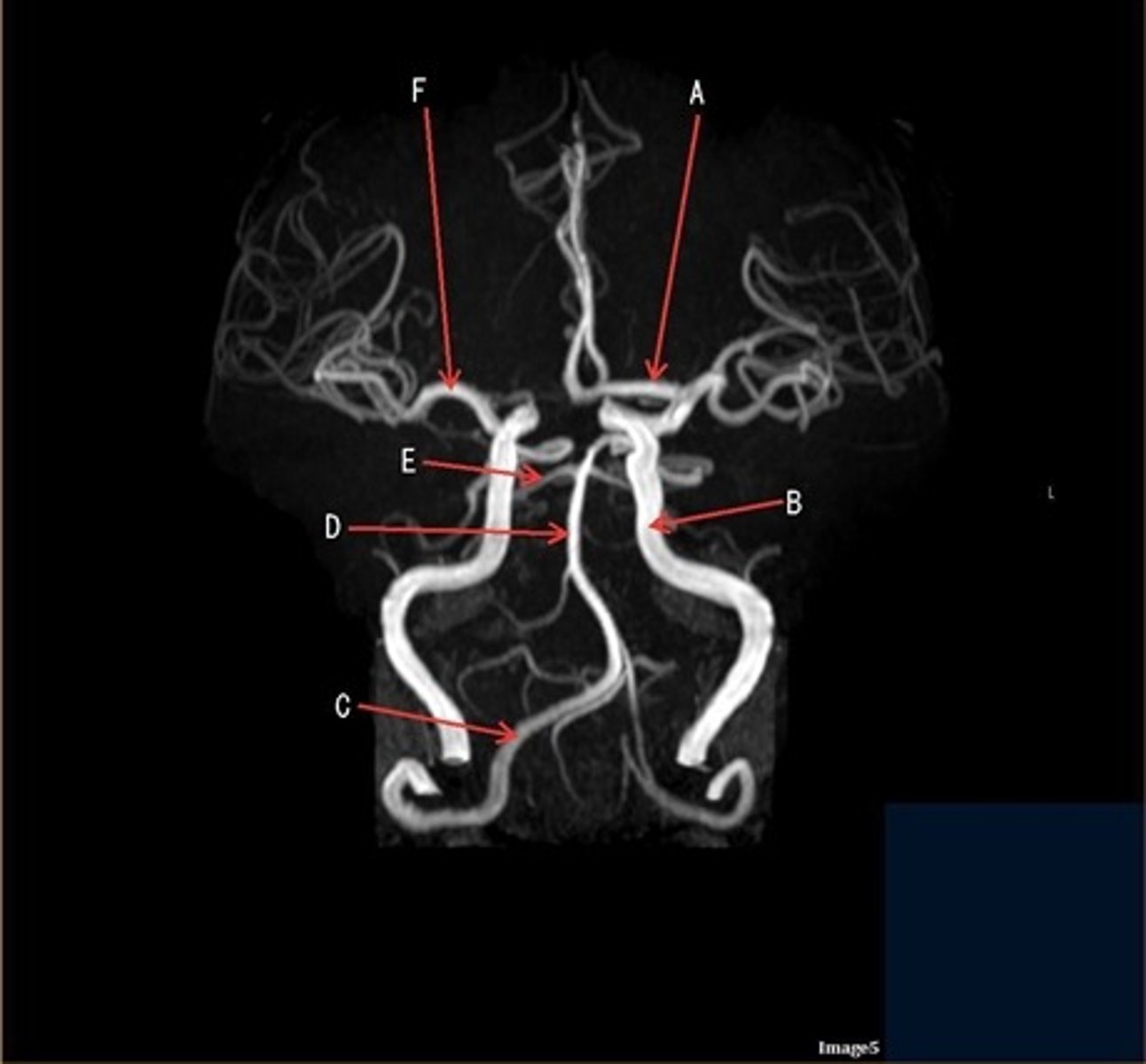
B
B- internal carotid artery
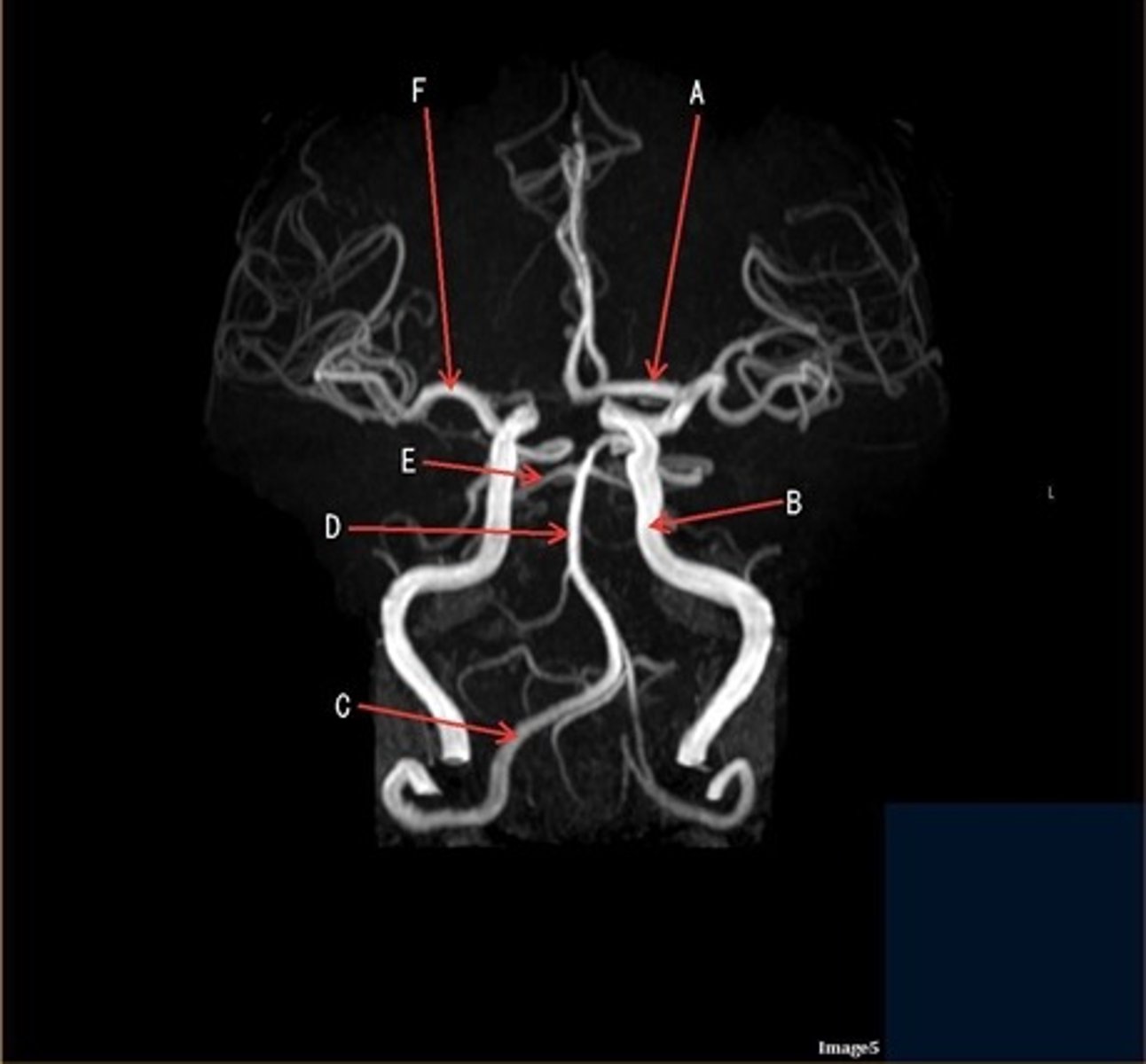
C
c- vertebral artery
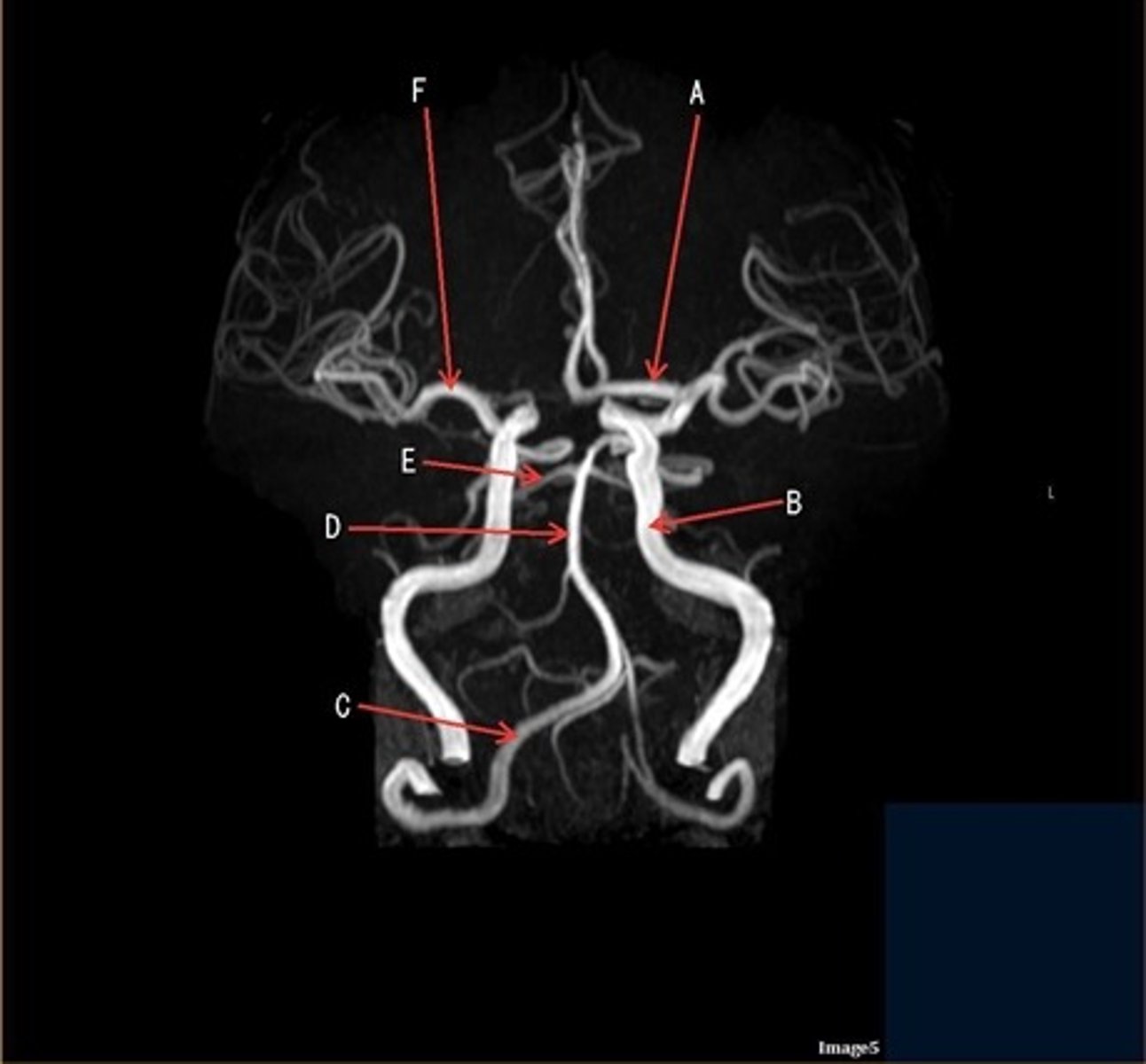
D
D- basilar artery
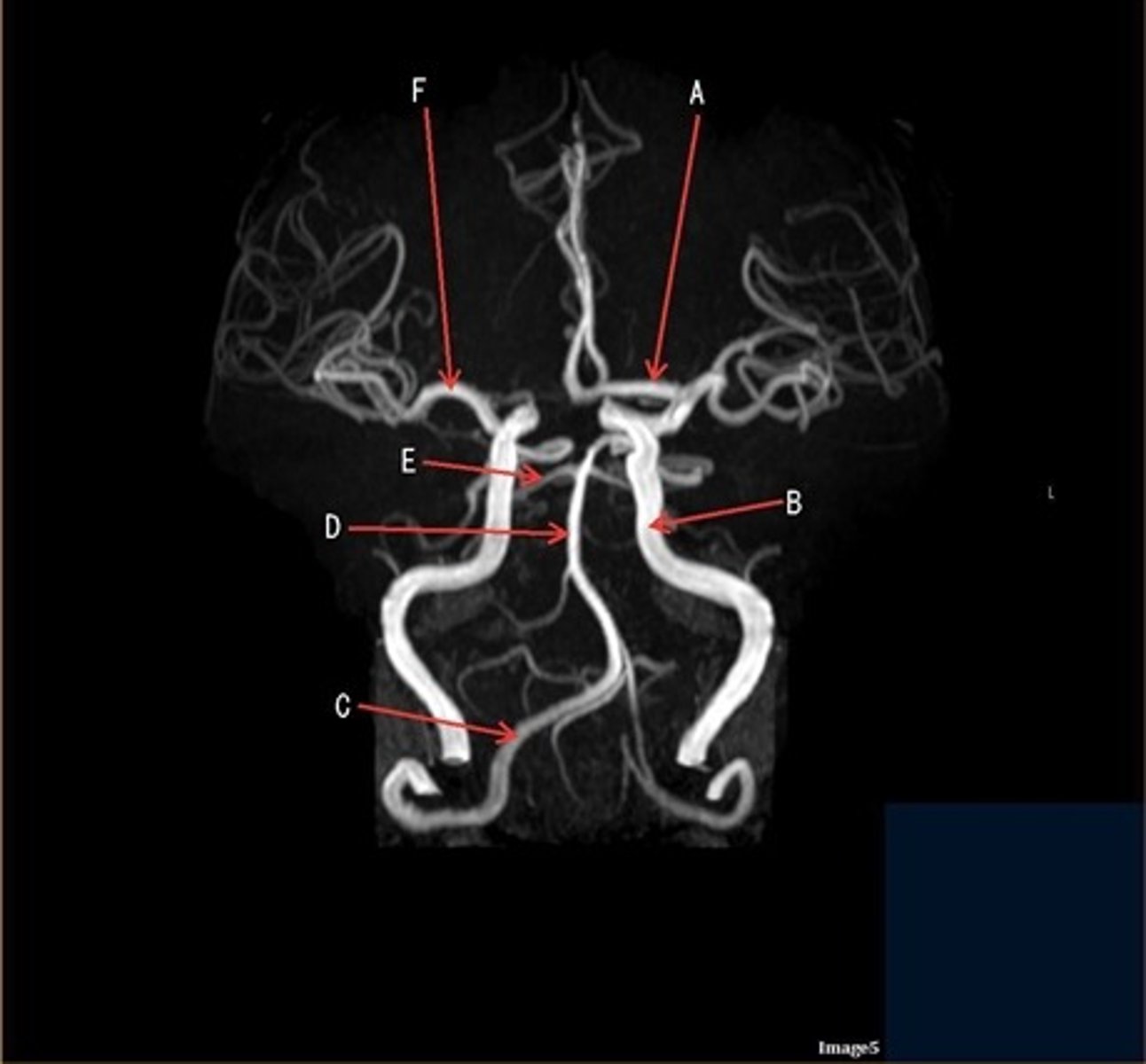
E
E- posterior cerebral artery
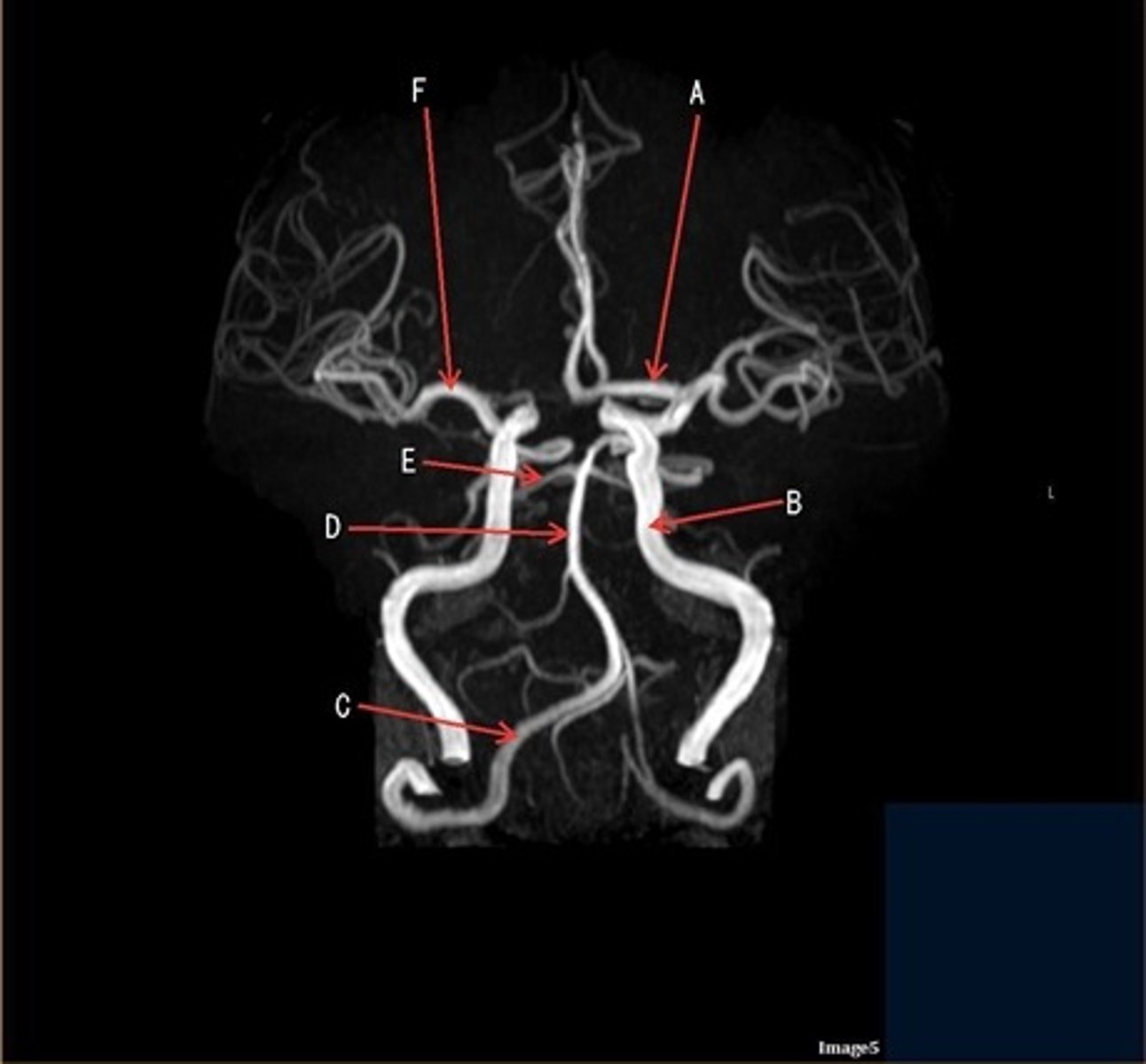
F
F- middle cerebral artery
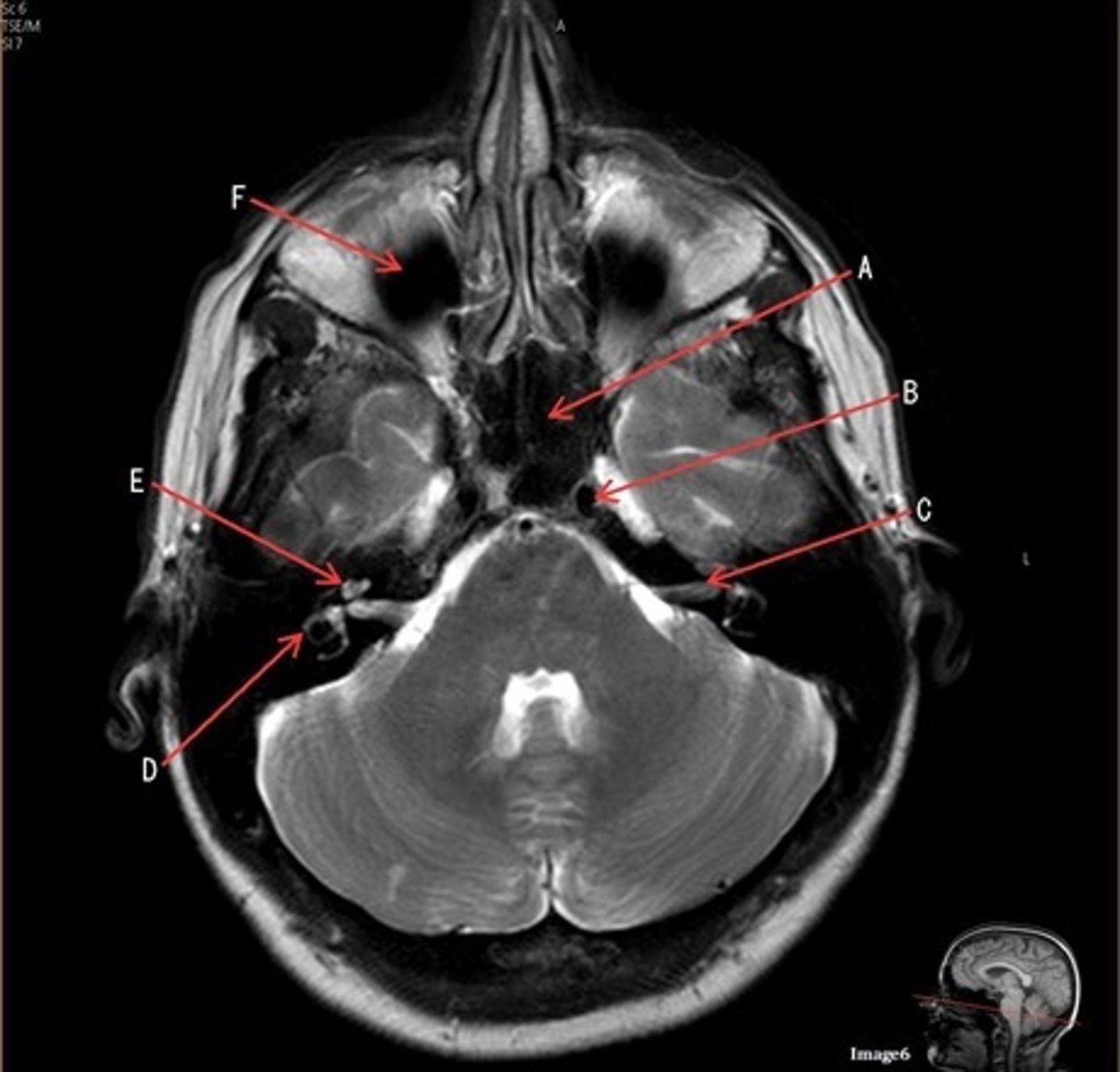
C
C- 7th cranial nerve, facial nerve
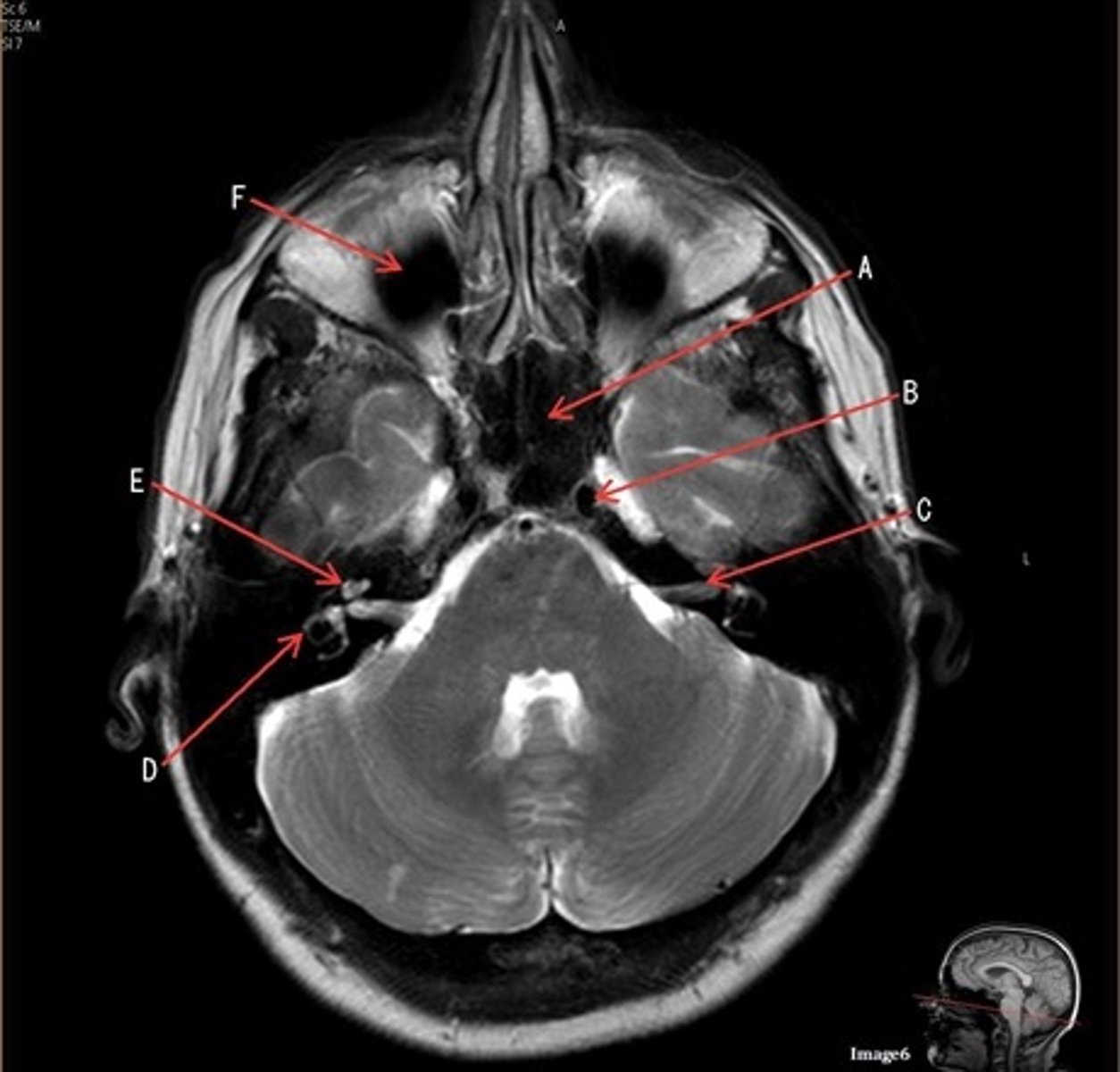
D
D. semi-circular canal
E
E- cochlea
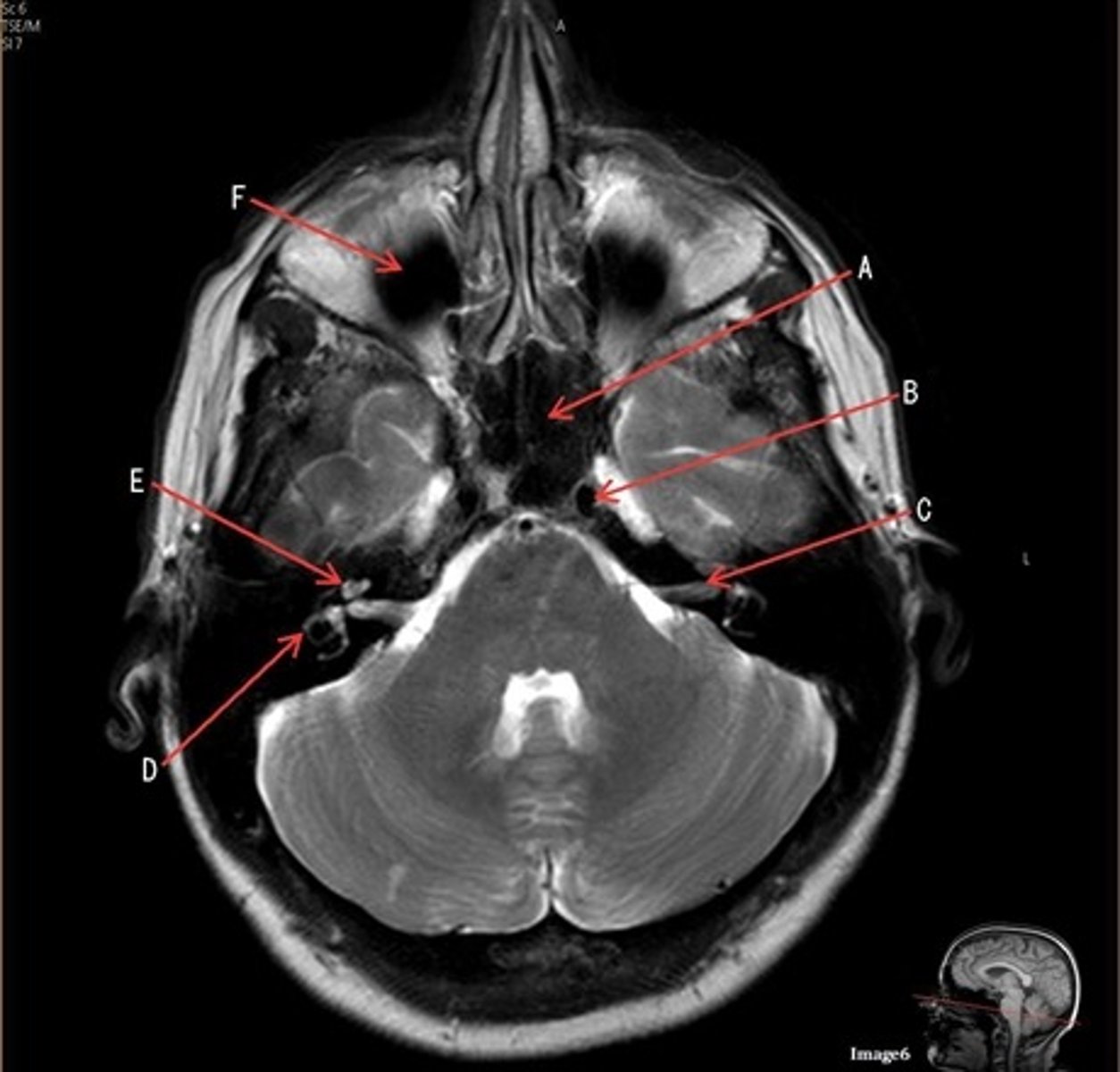
F
F- maxillary sinus
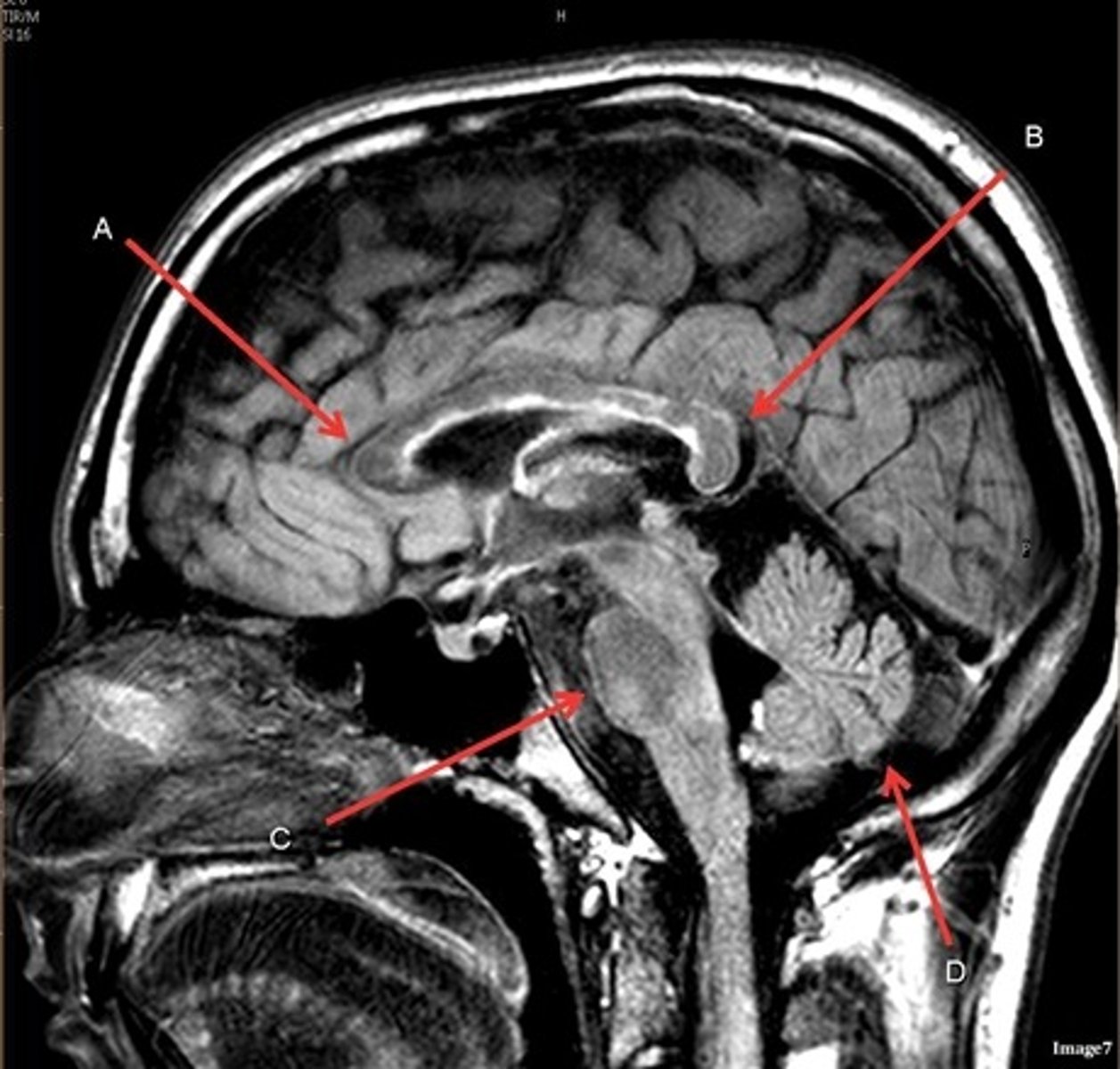
What type of sequence?
T2 FLAIR; Sagittal
A FLAIR (Fluid Attenuated Inversion Recovery) sequence is utilized to suppress signal from cerebrospinal fluid (CSF).
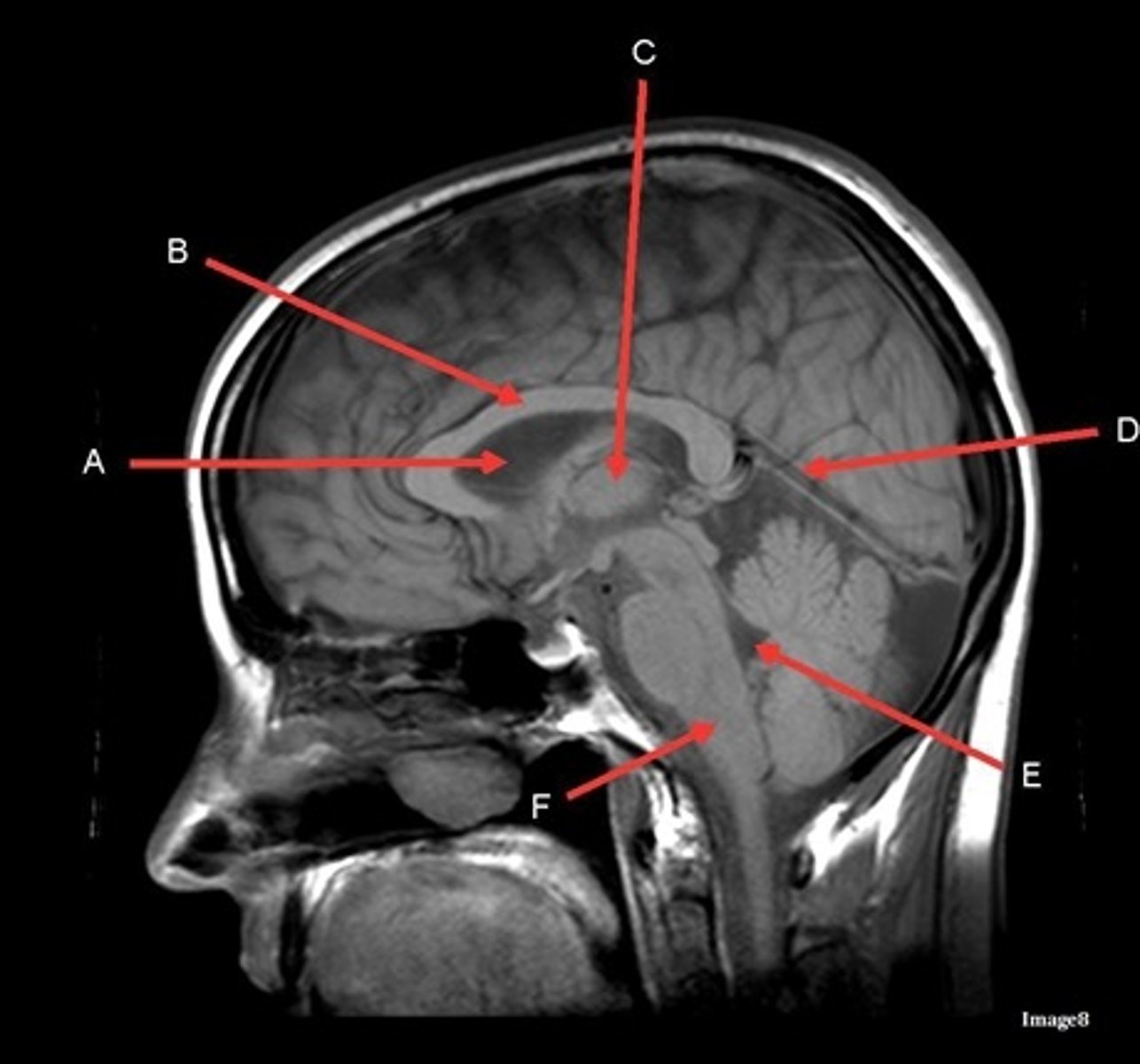
What type of sequence?
T1, sagittal
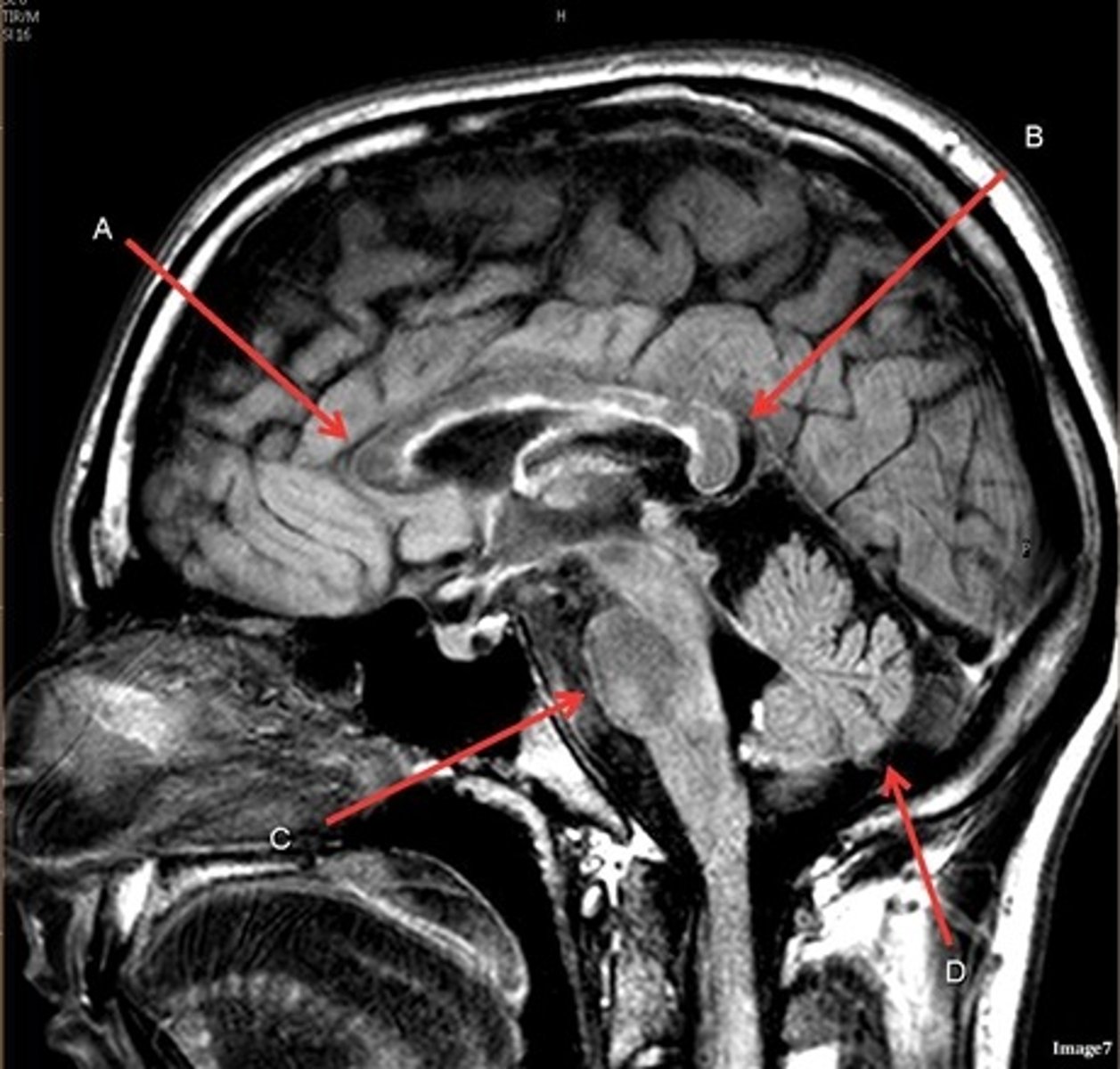
A- region
Genu of Corpus Callosum
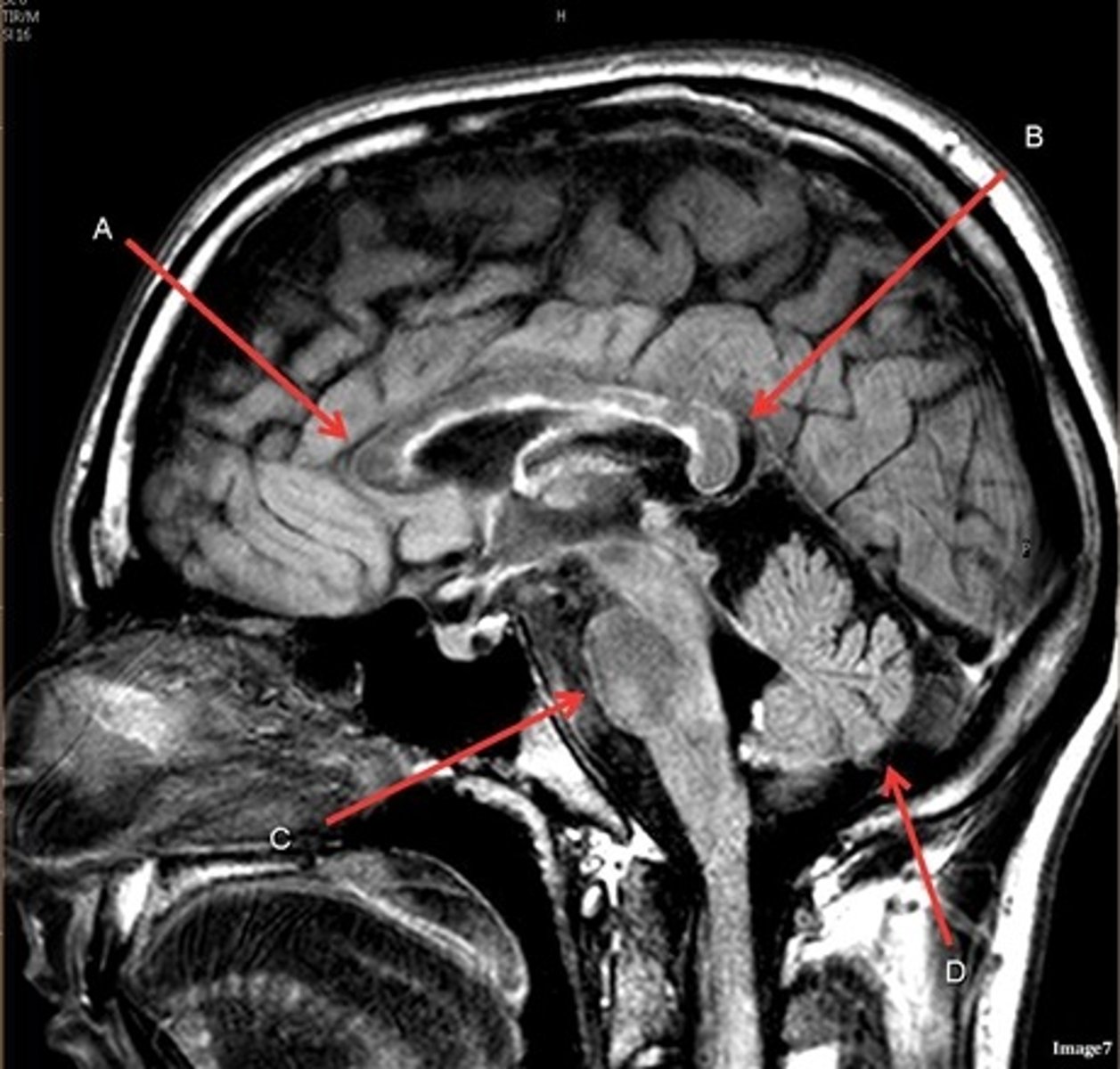
B- region
Splenium of Corpus Callosum
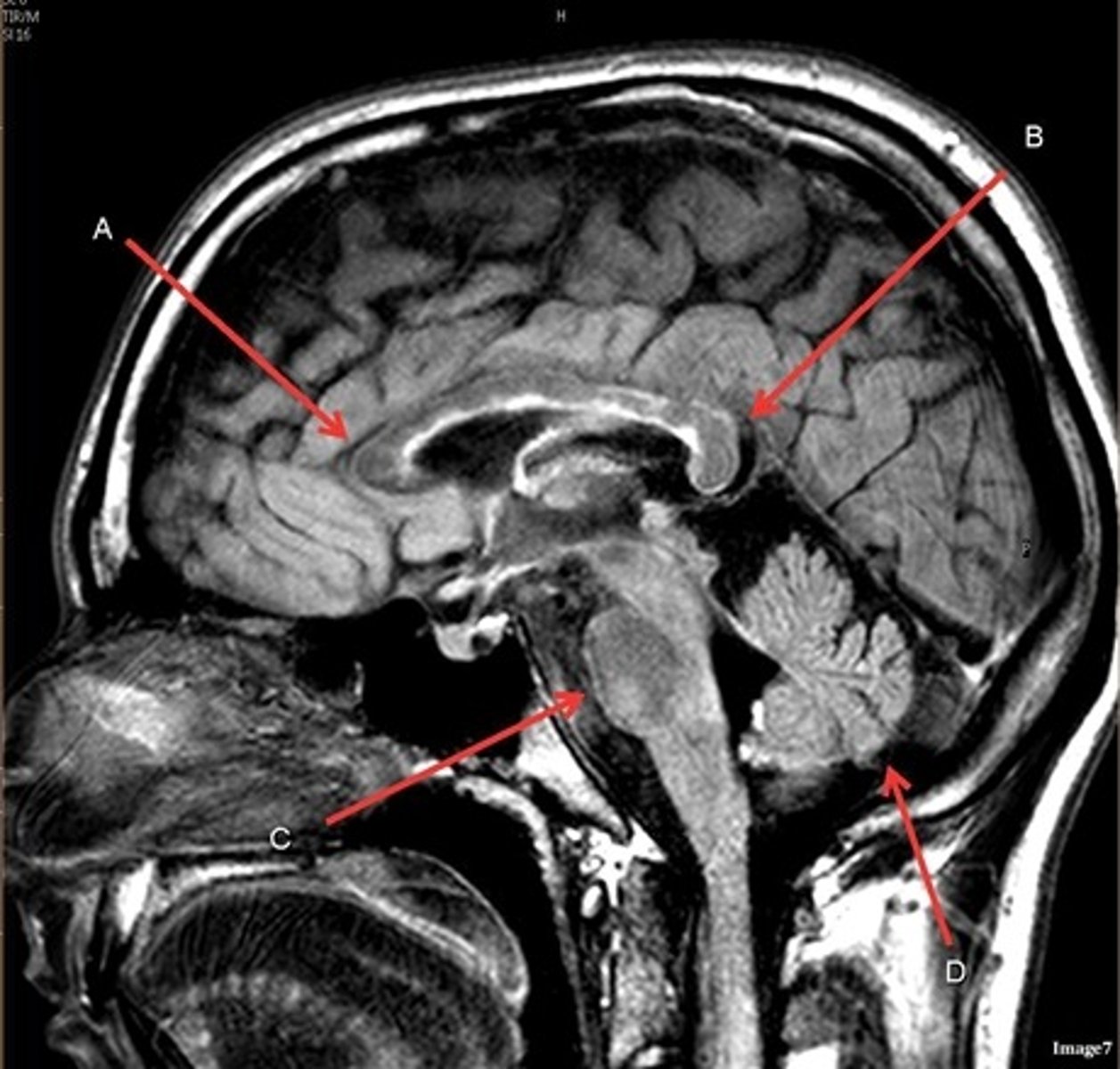
C
pons
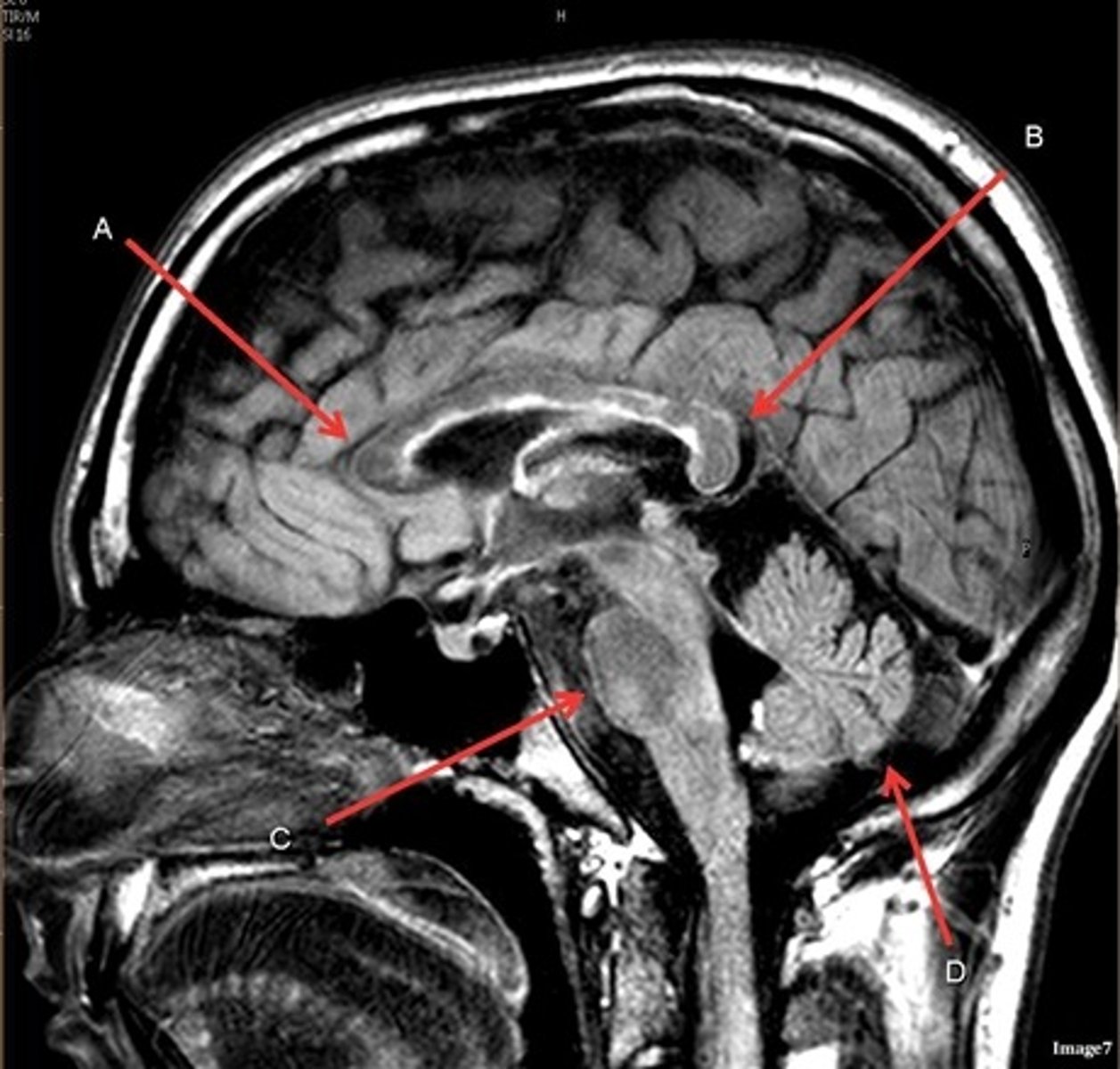
D
cerebellum
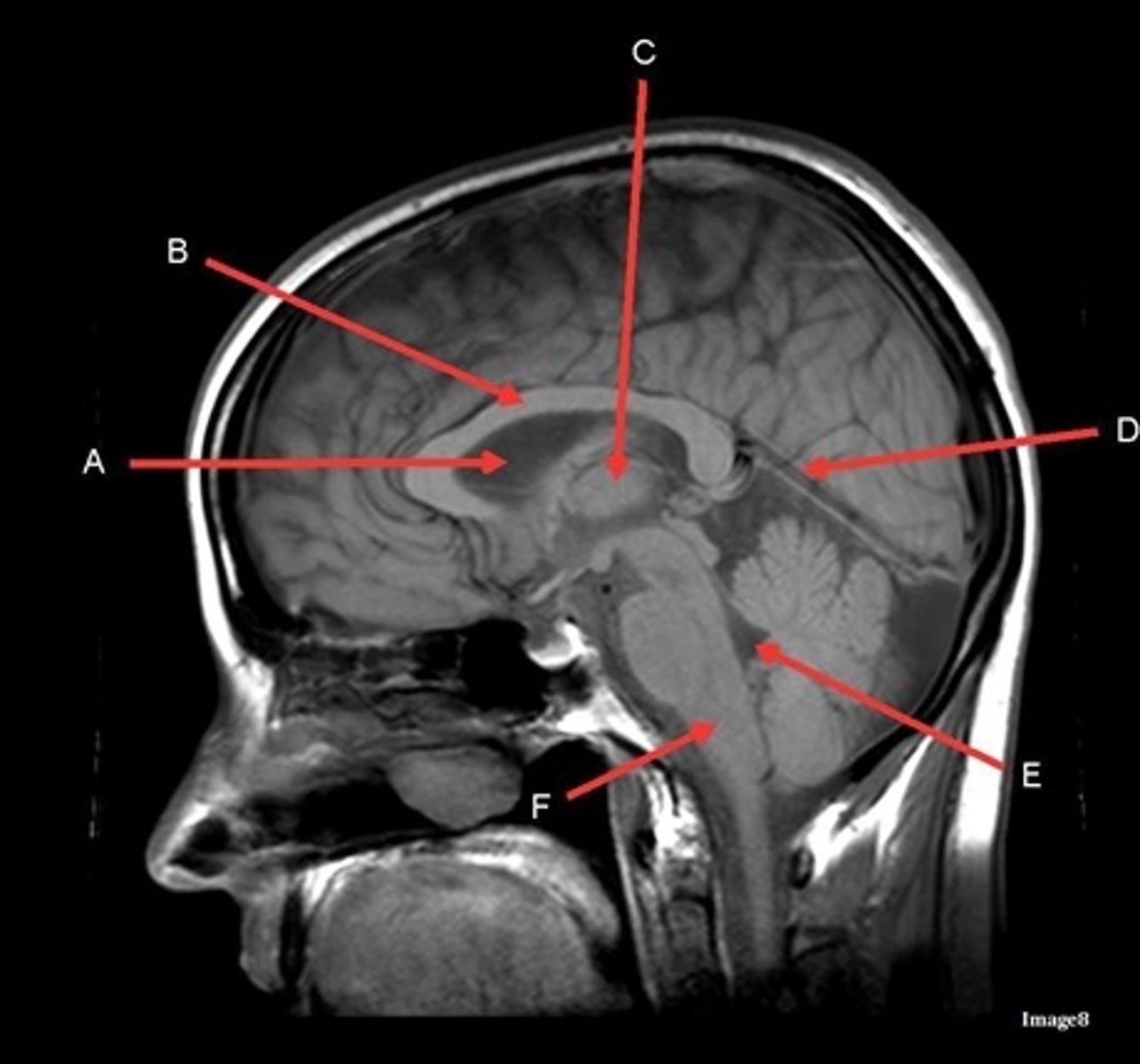
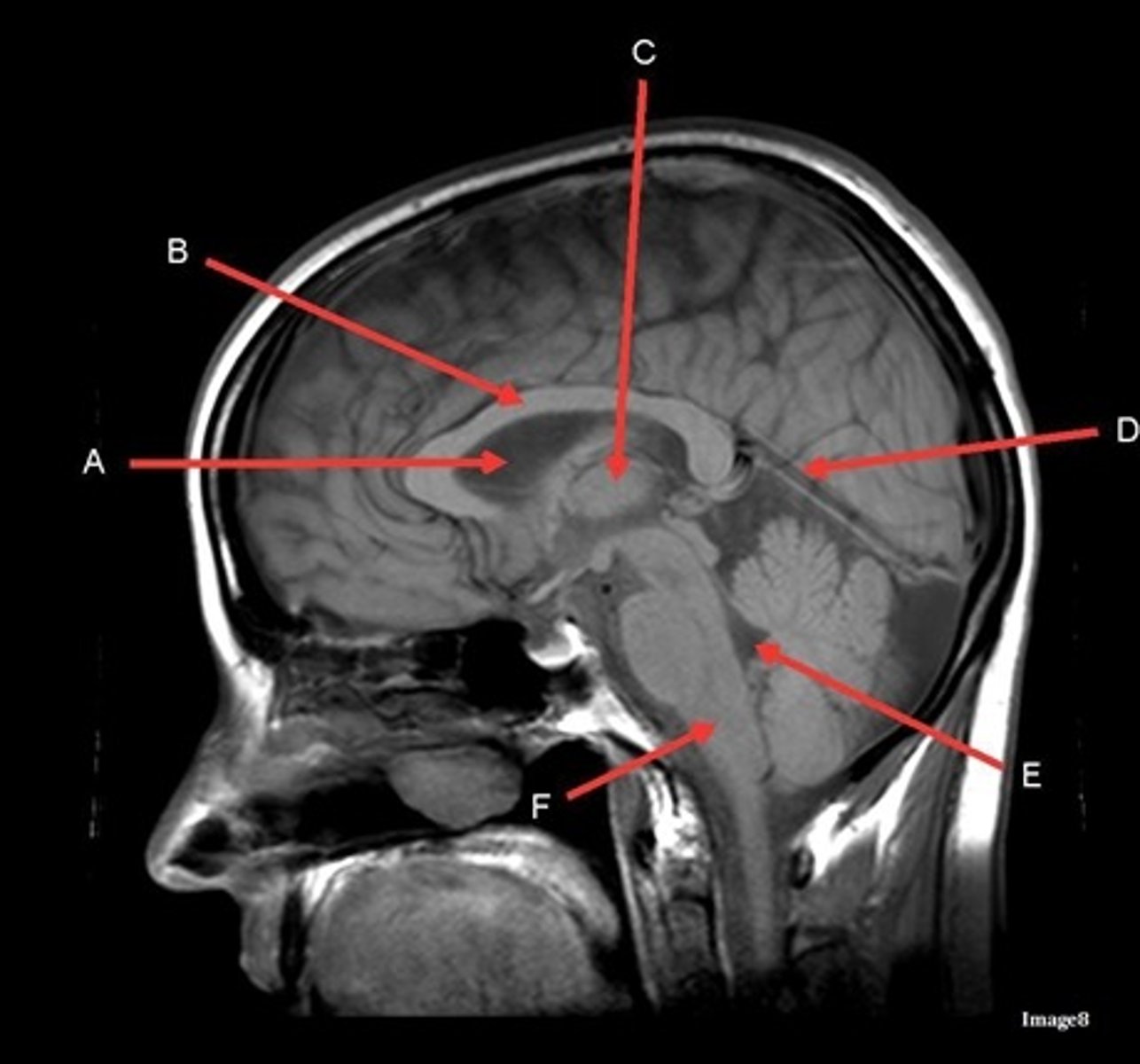
A
lateral ventricle
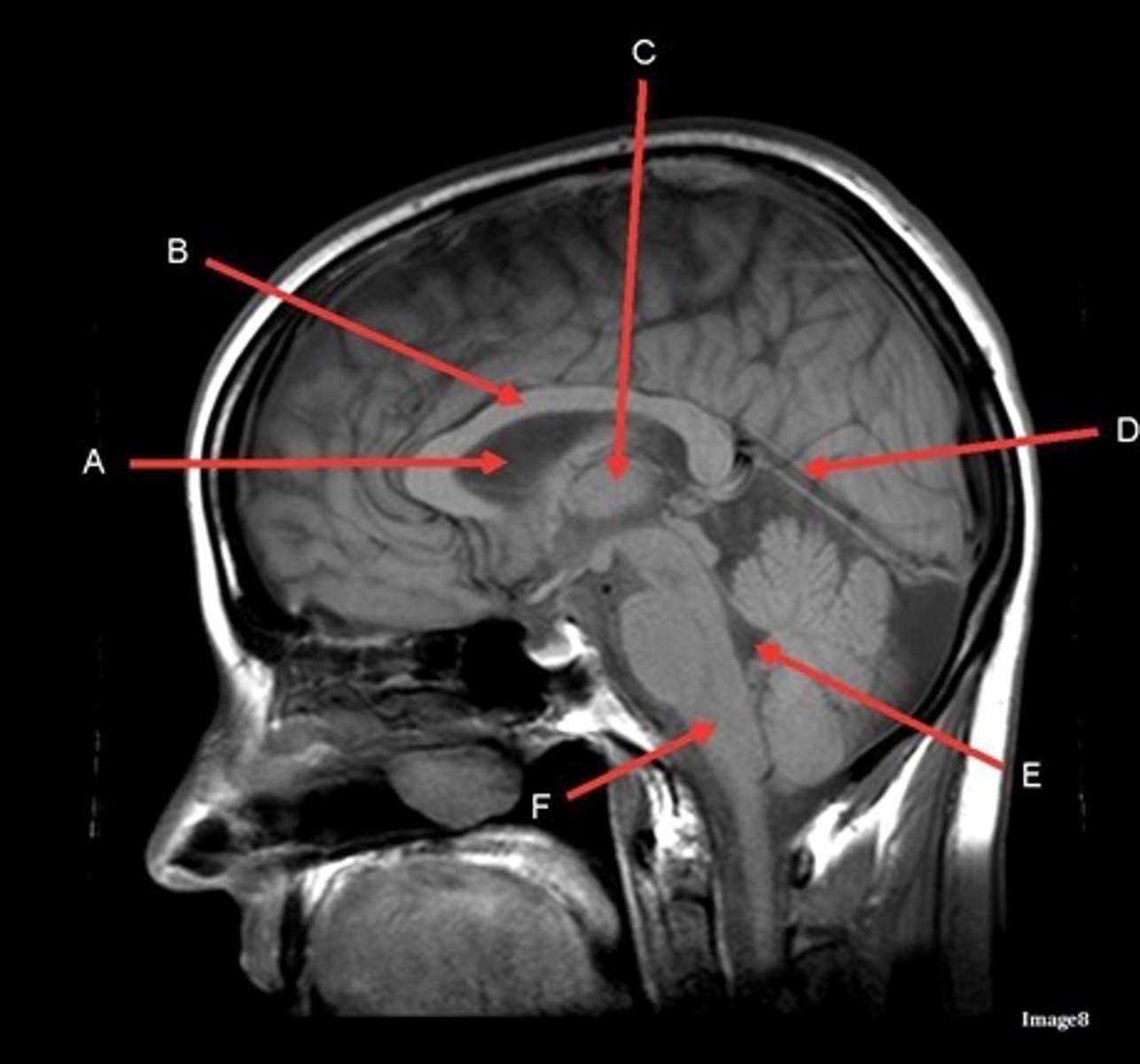
B
corpus callosum
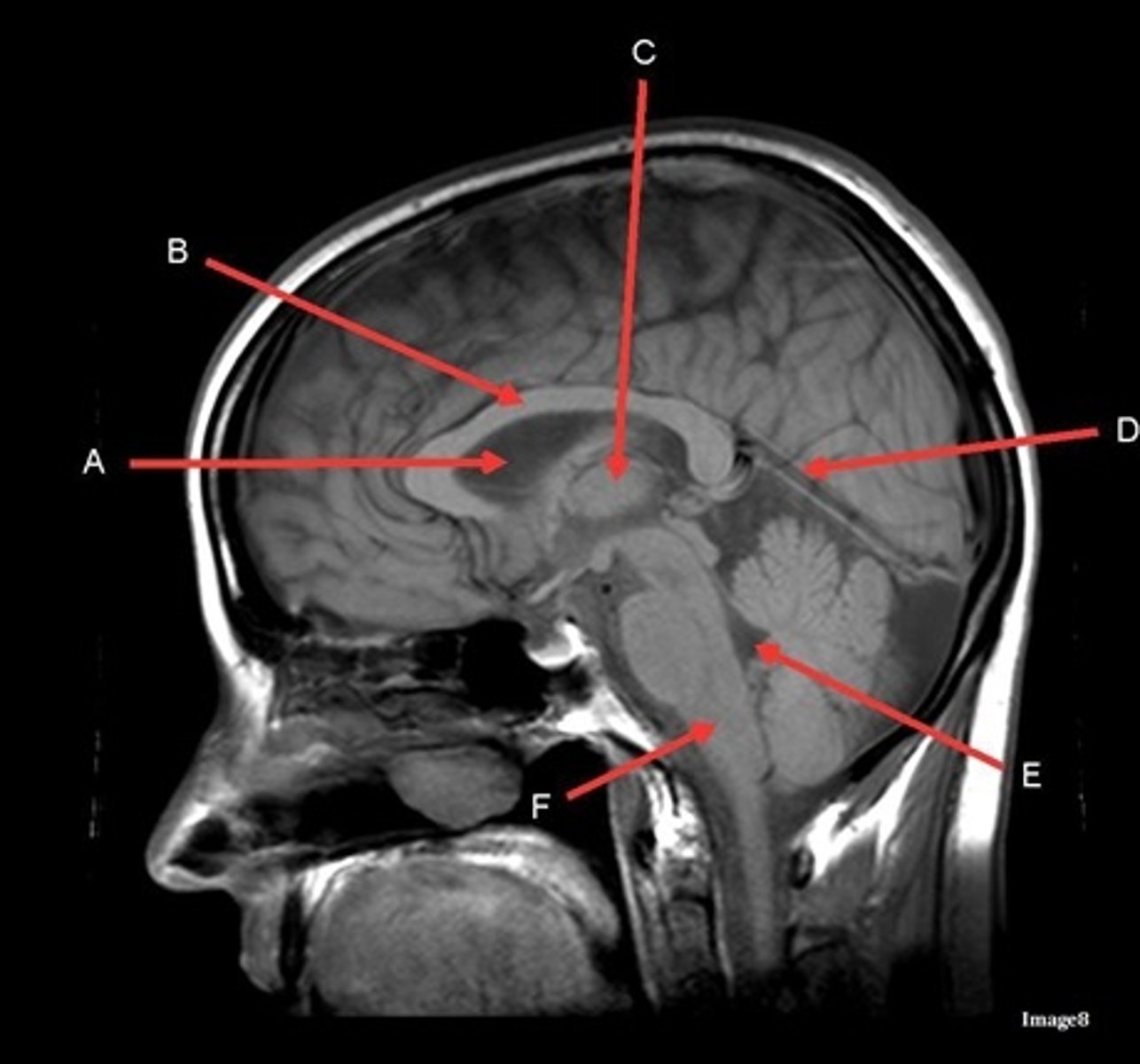
C
thalamus
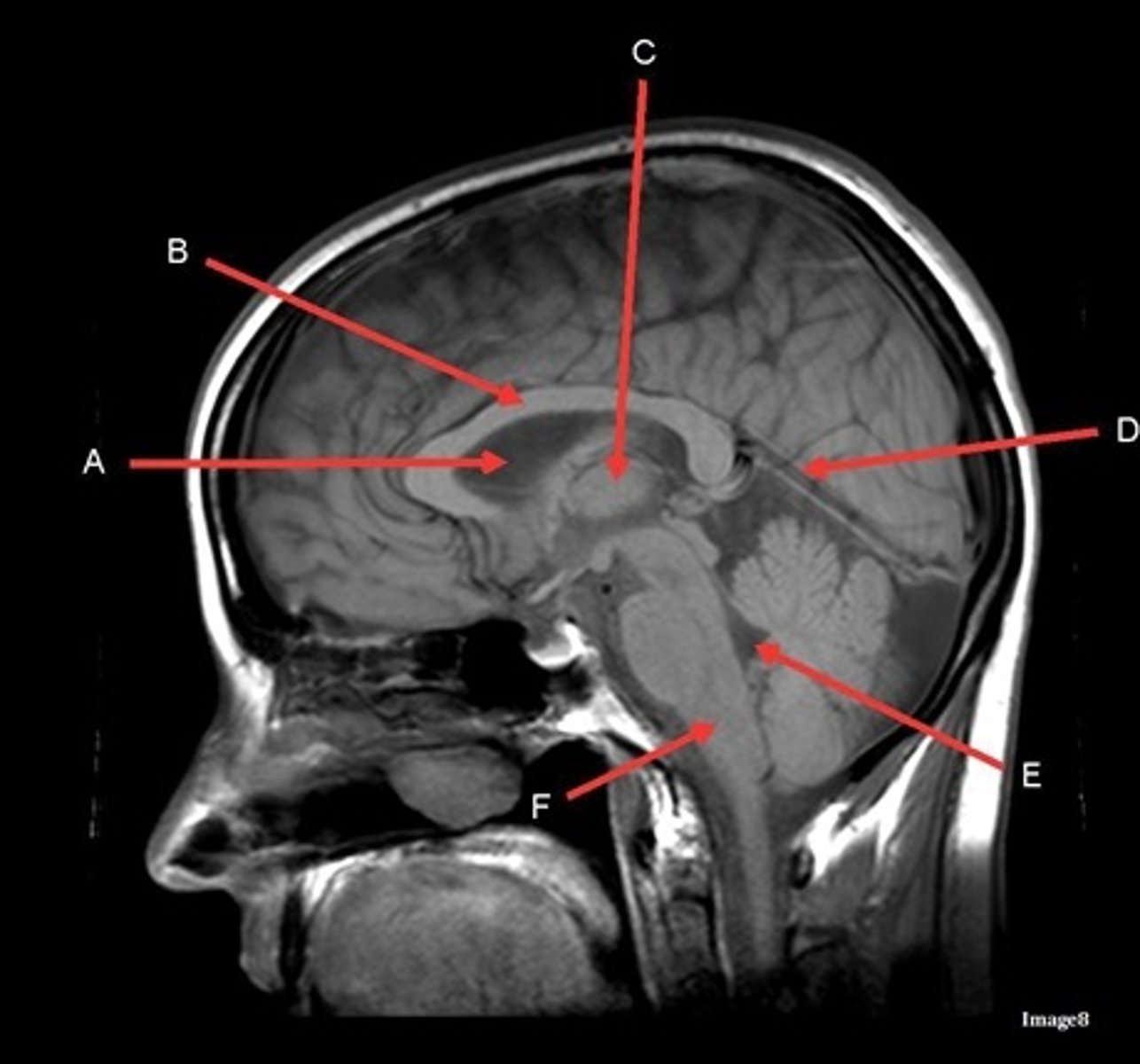
D- separates what
tentorium cerebelli- cerebrum (occipital and temporal lobes) from brainstem and cerebellum
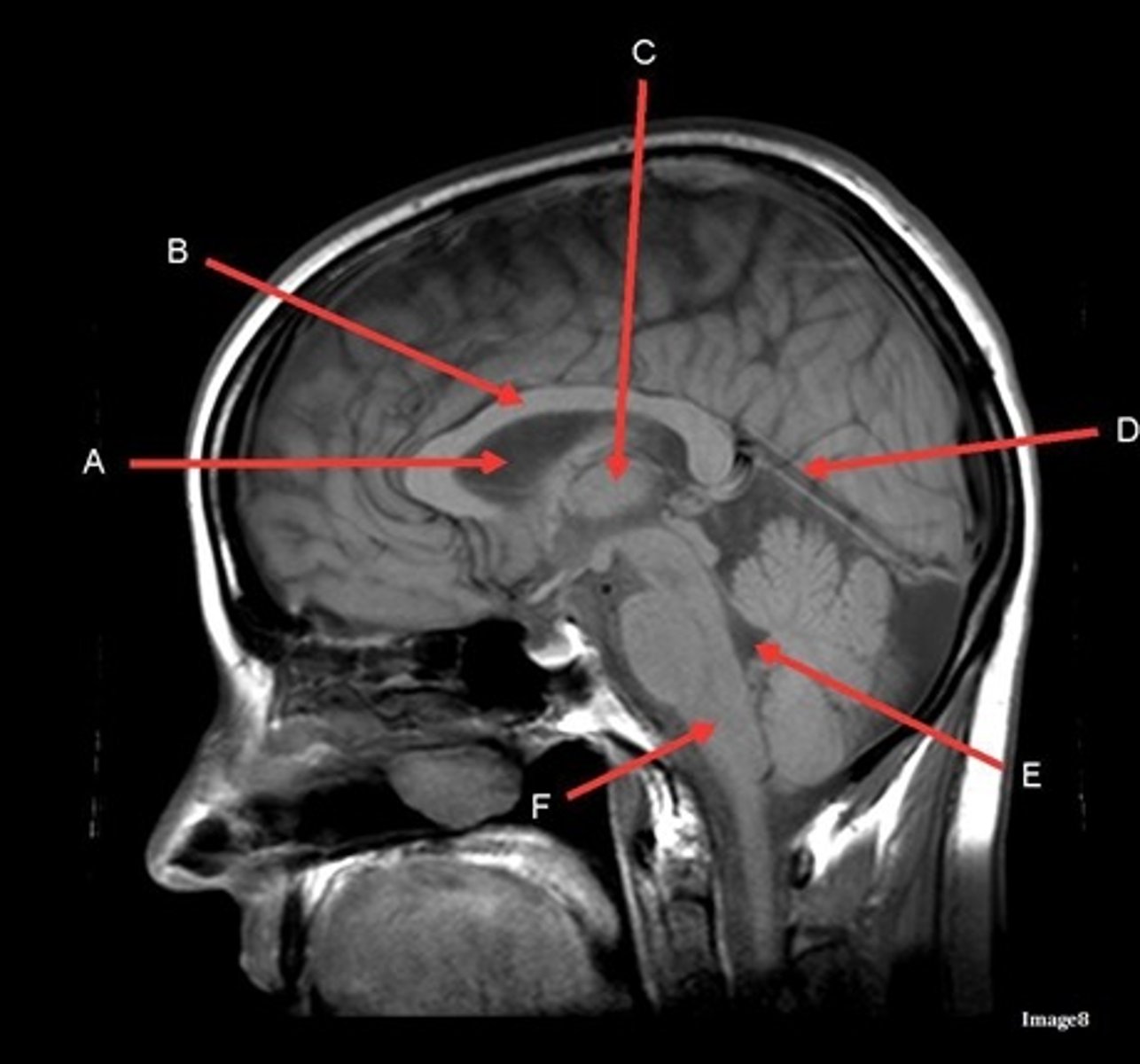
E
fourth ventricle
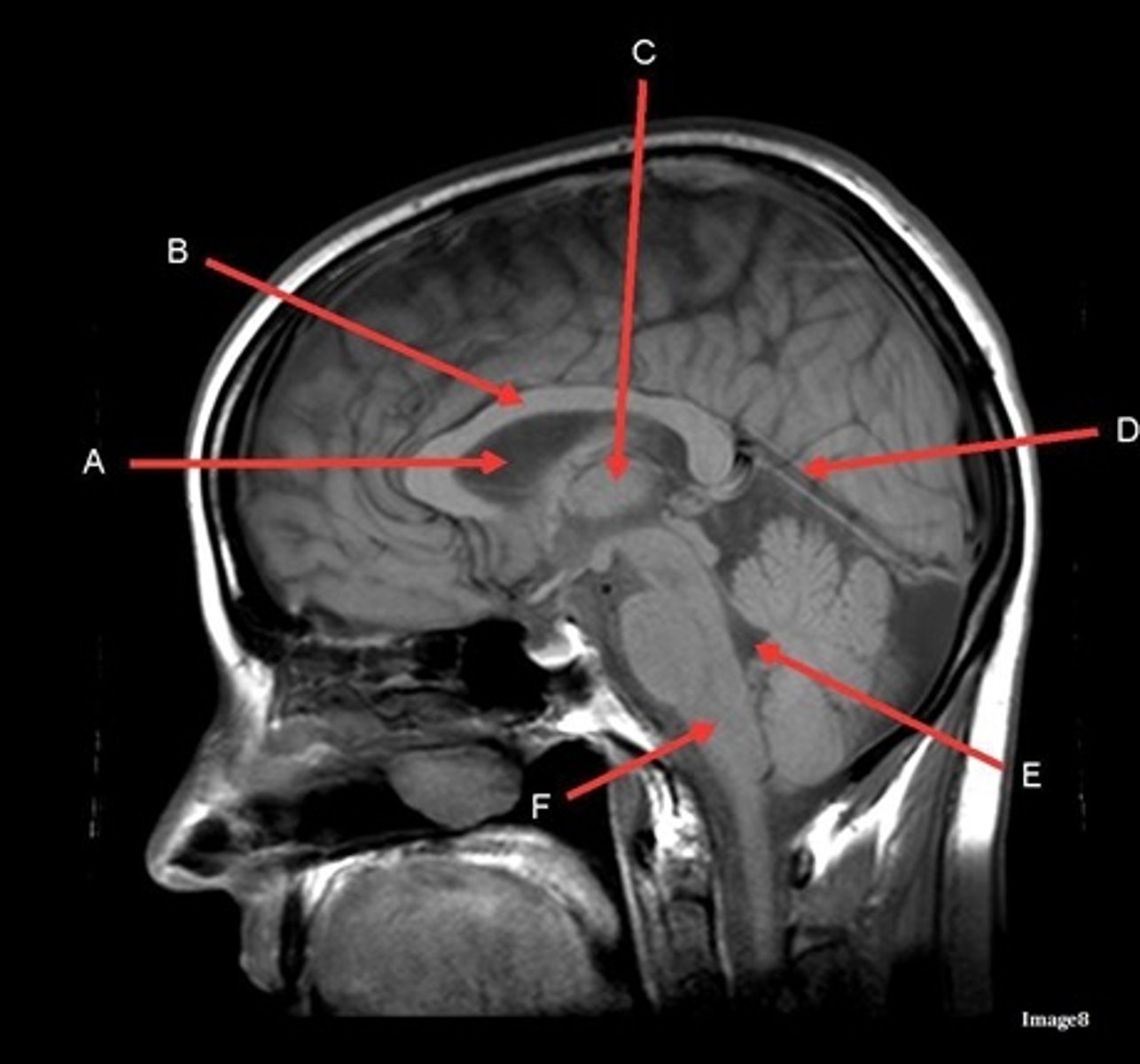
F
medulla oblongata
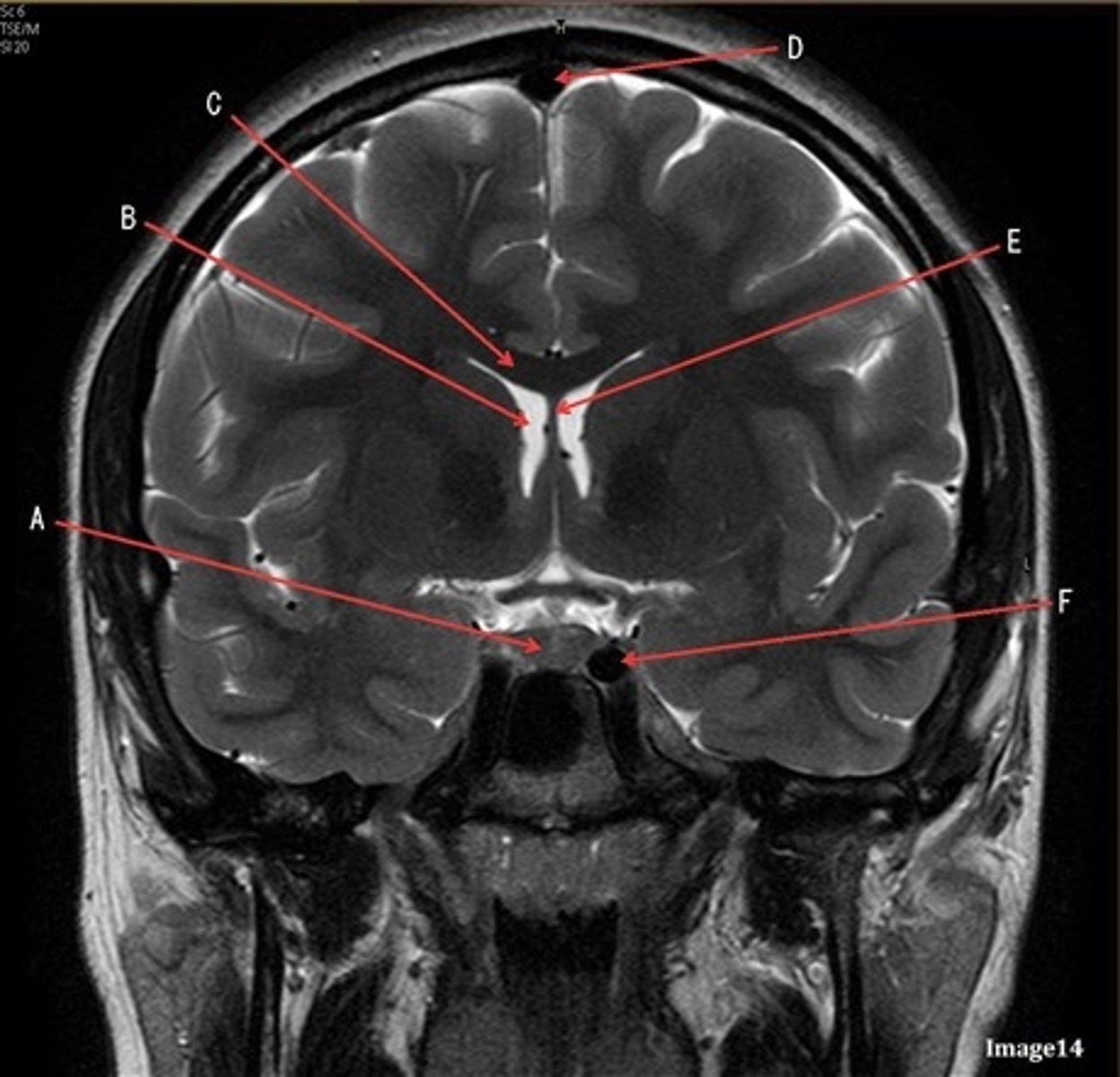
A
caudate nucleus
B
thalamus
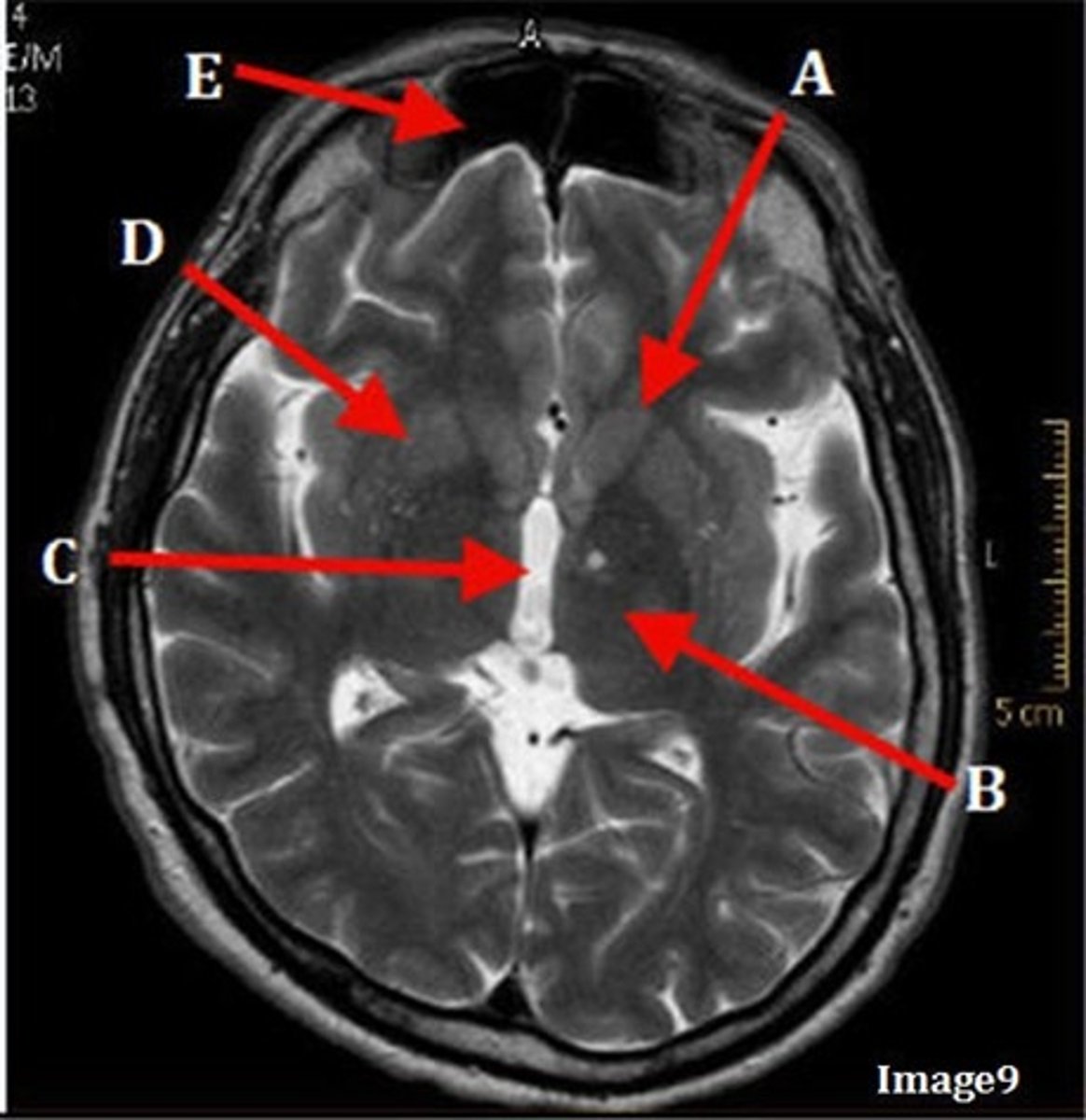
C
third ventricle
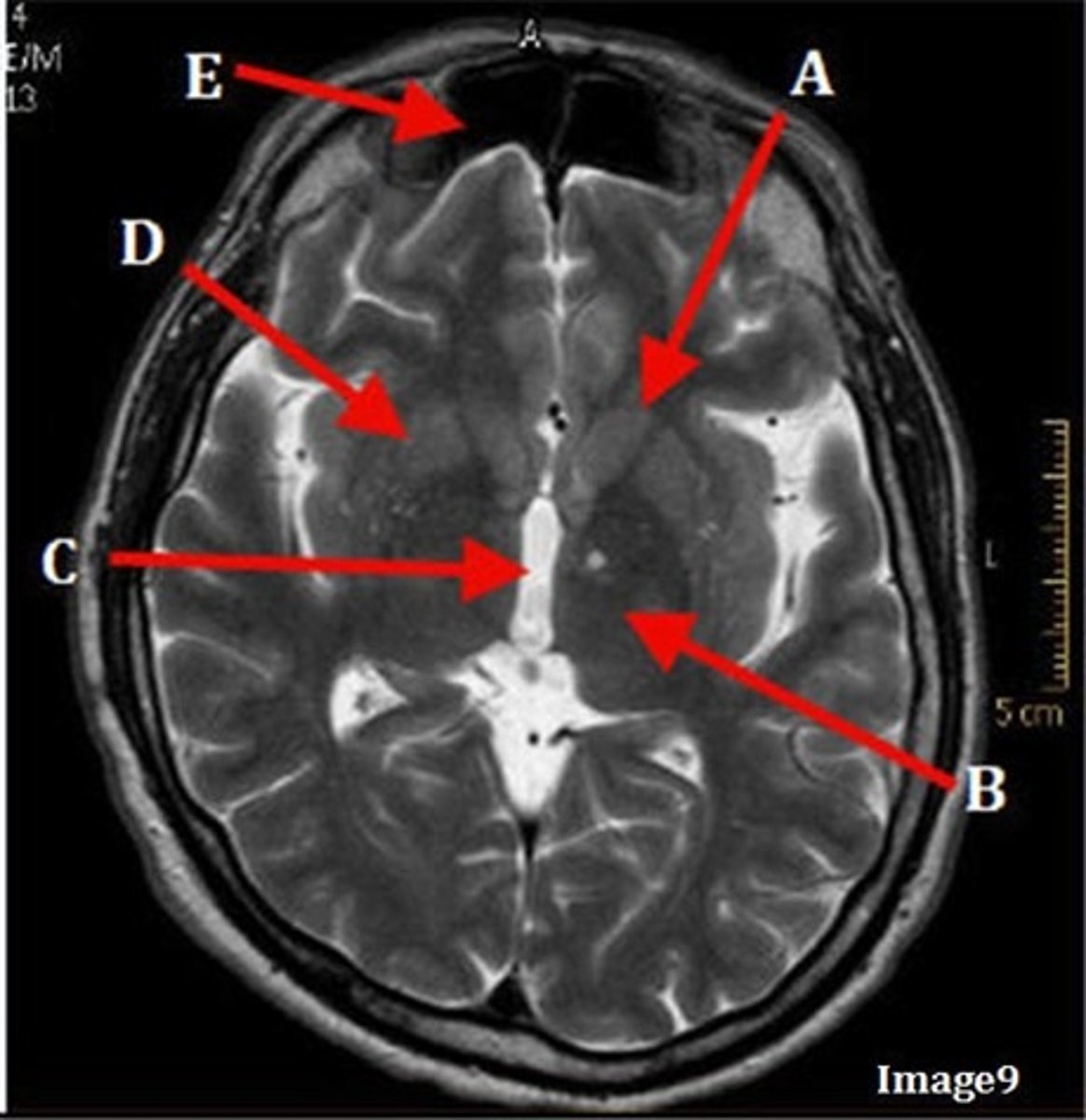
D
lentiform nucleus
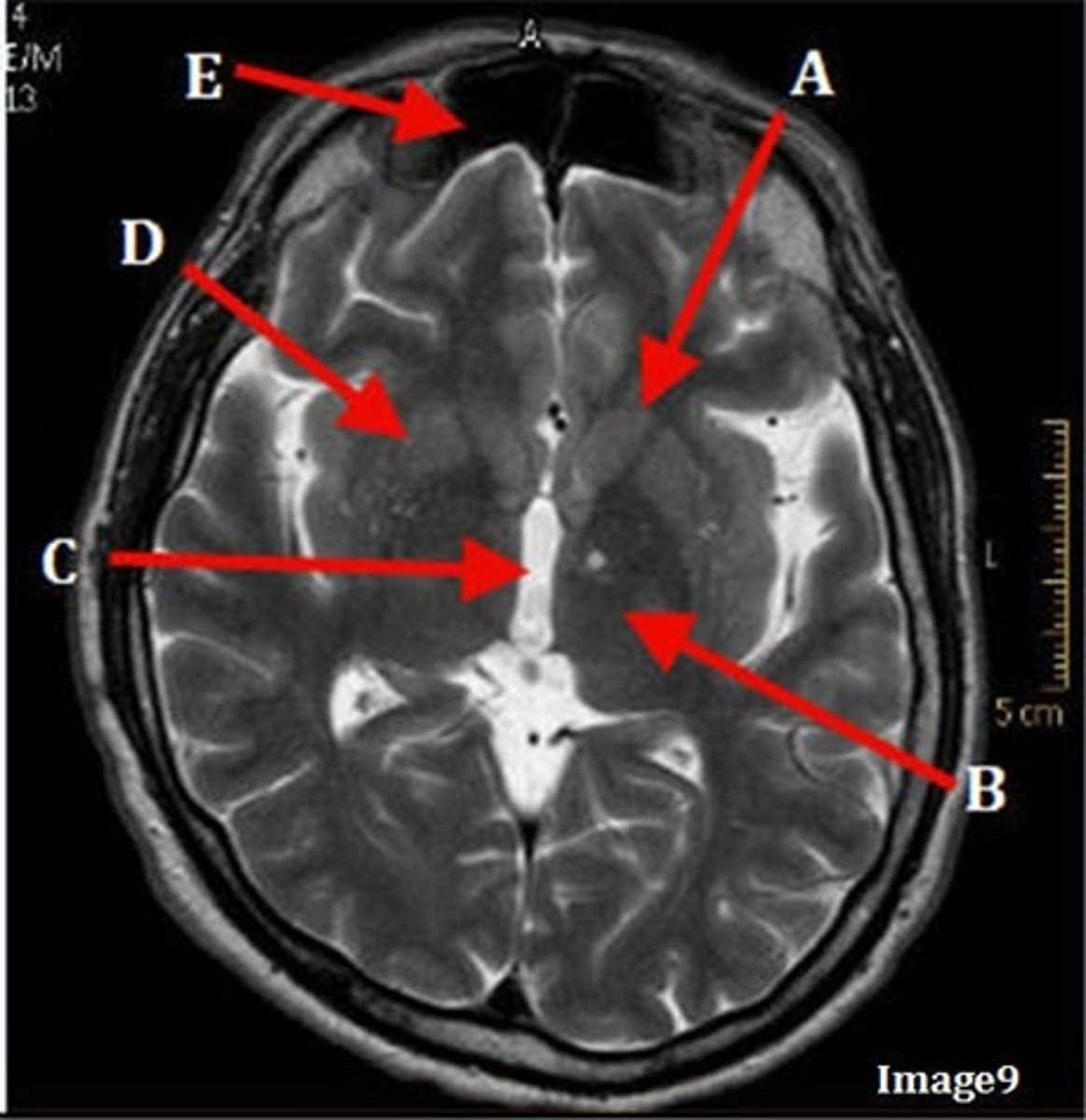
E
frontal sinus
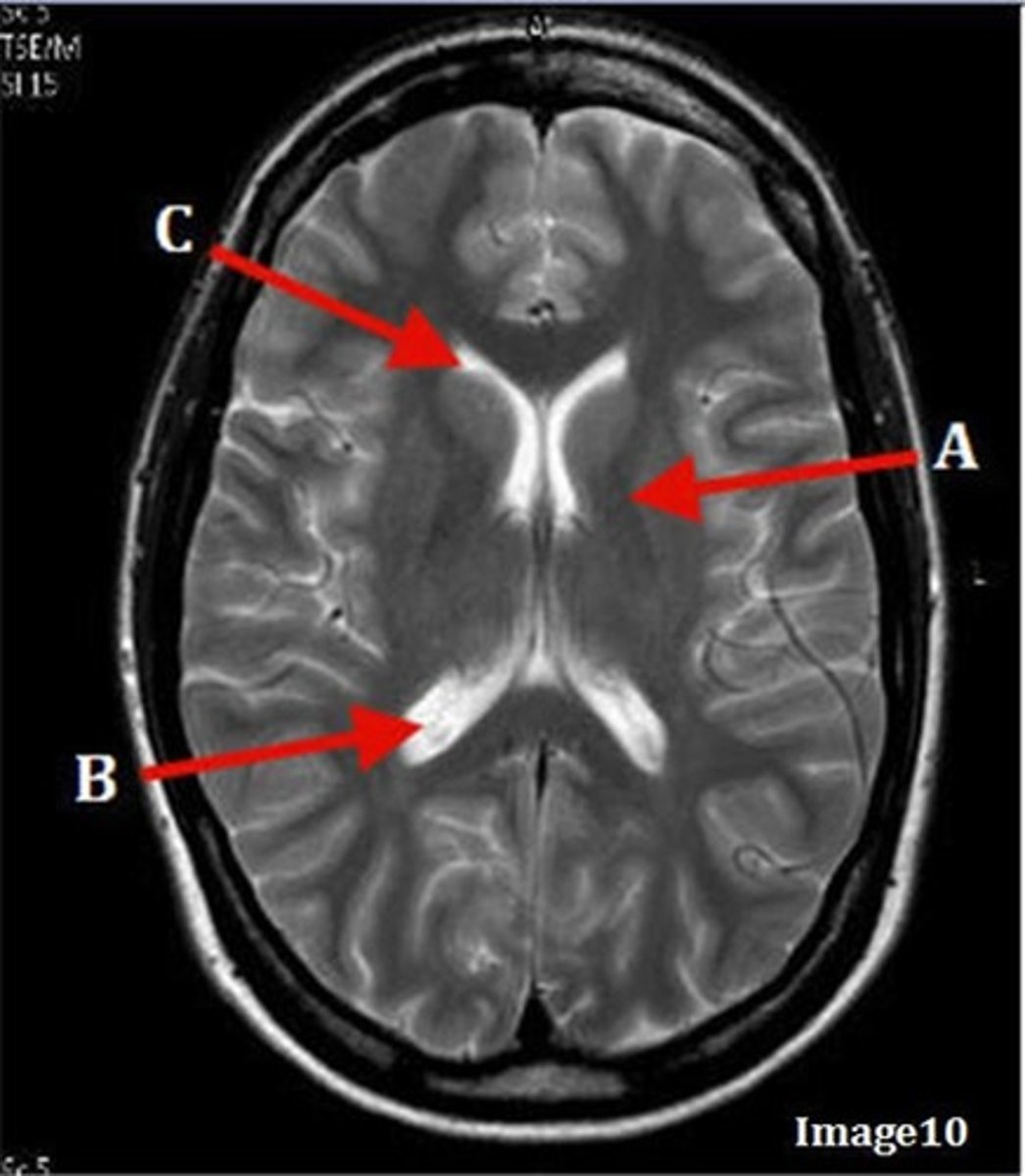
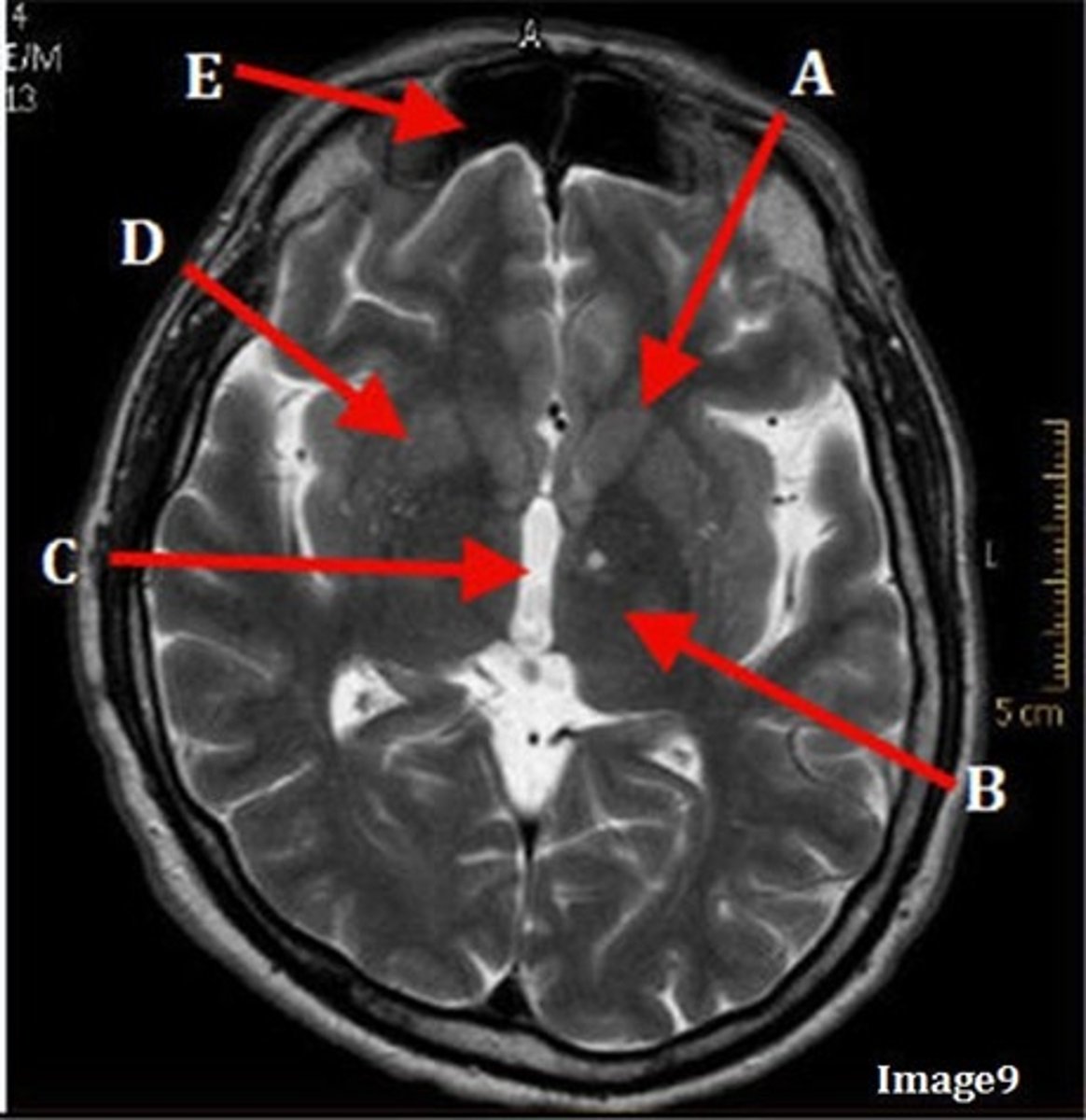
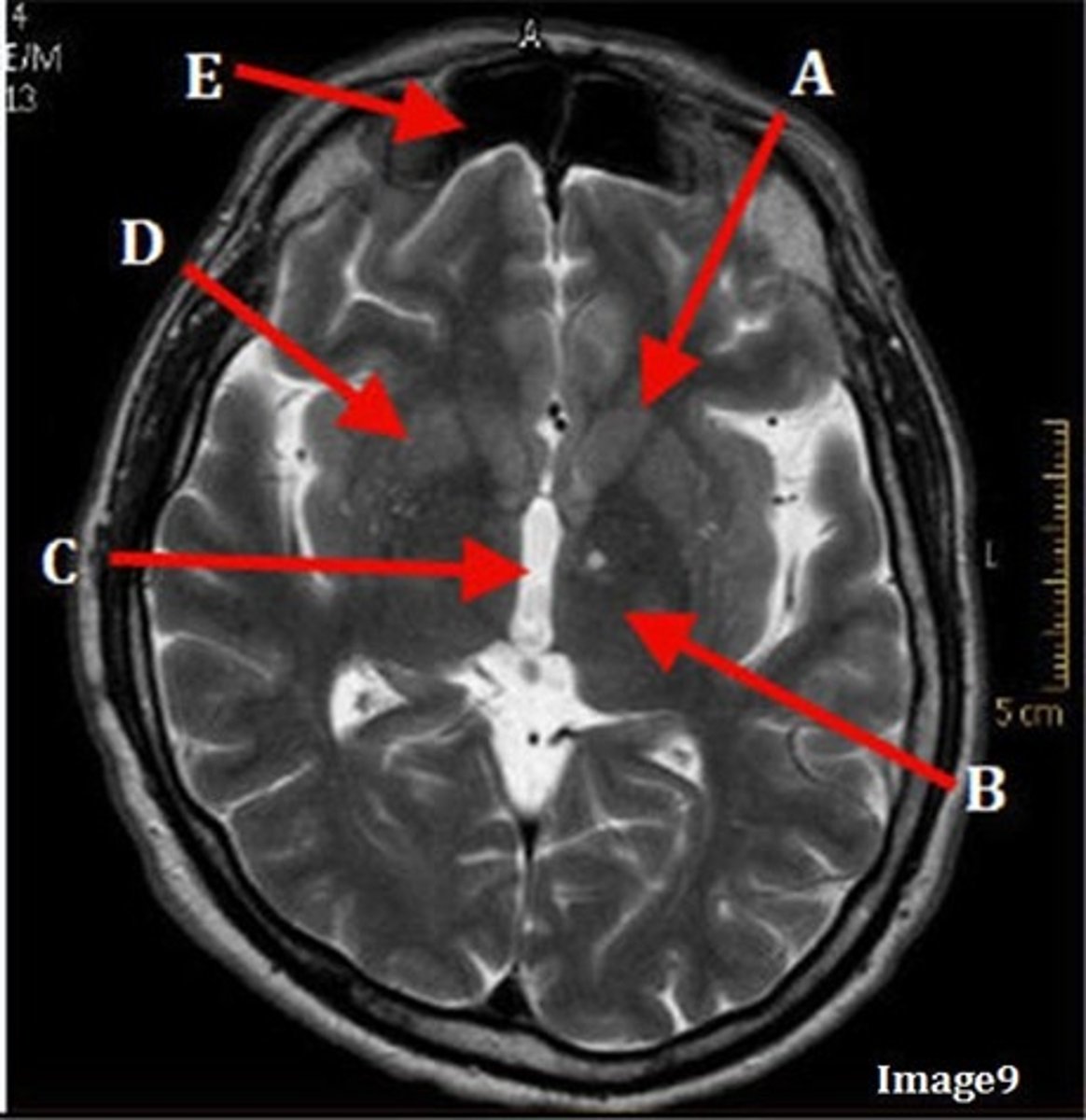
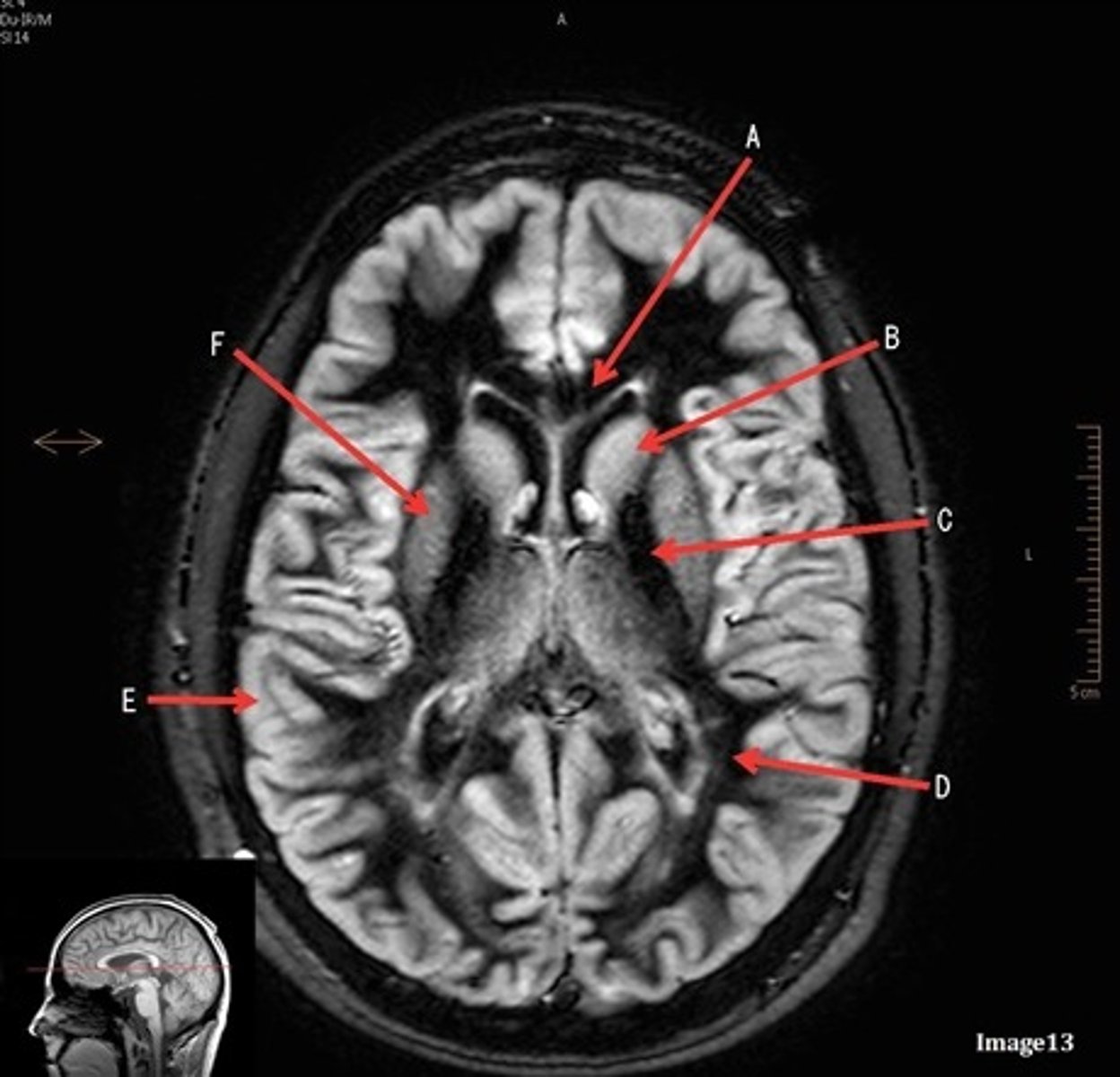
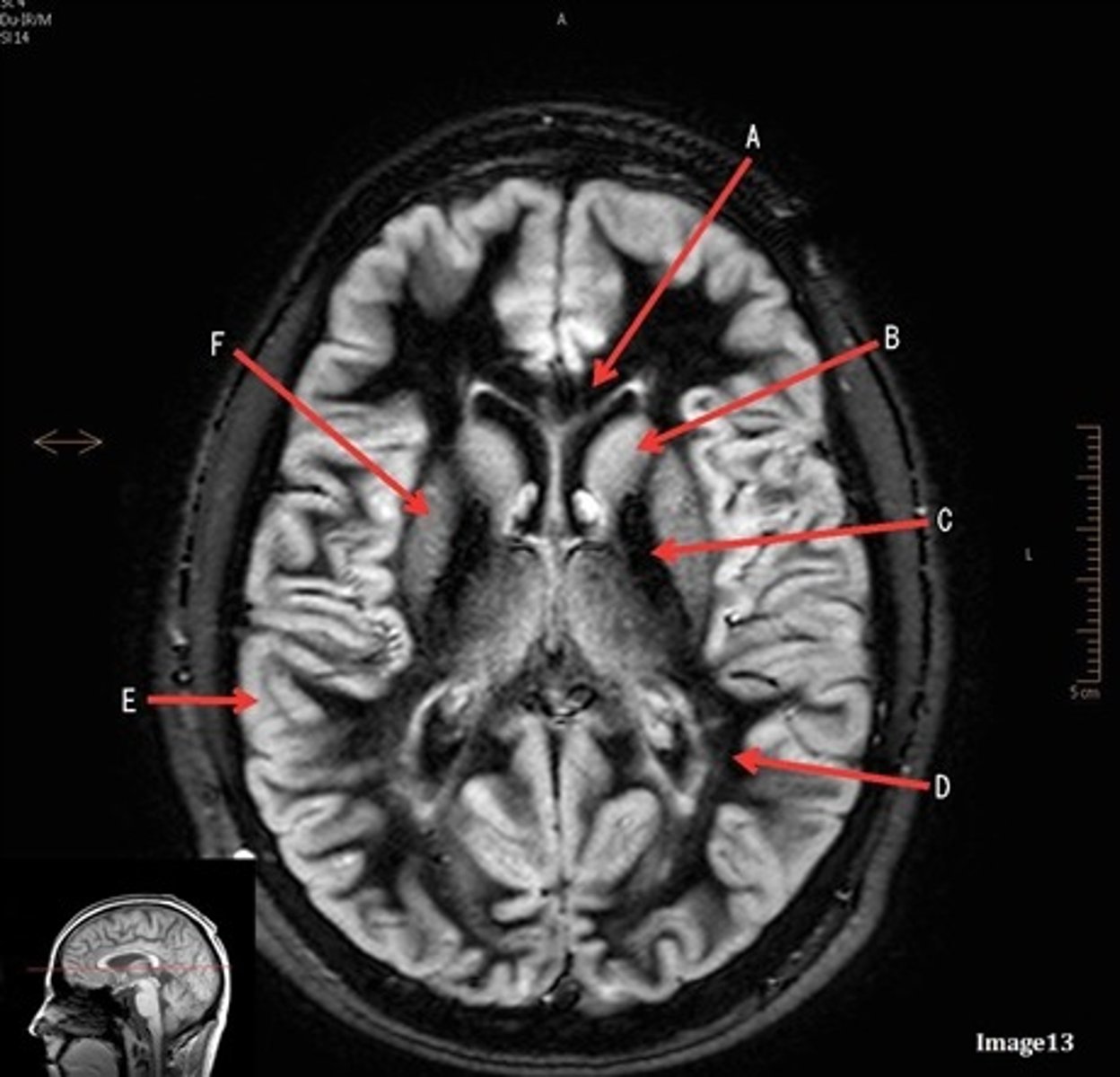
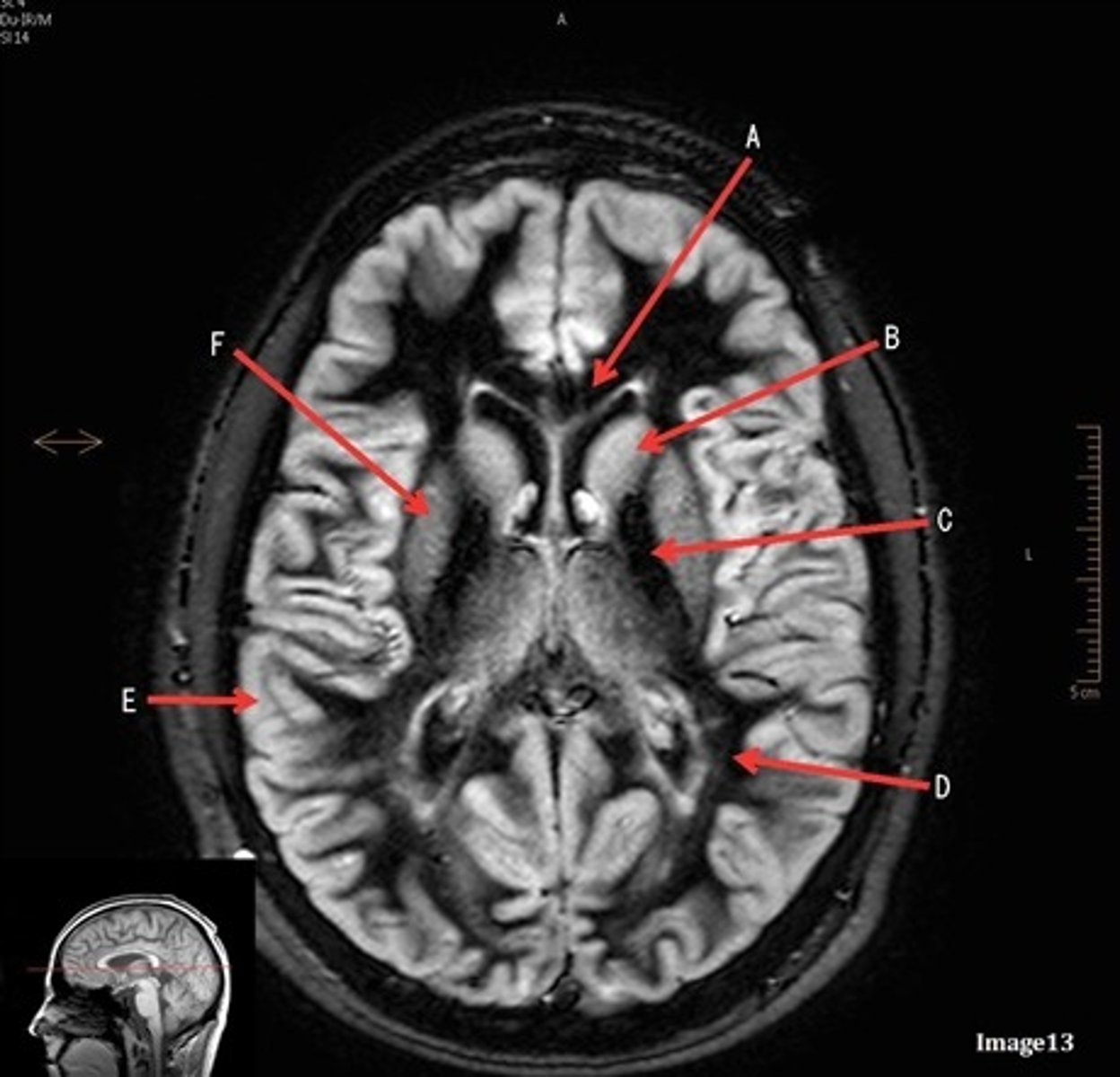
A (region)
dark band is called?
basal ganglia region
internal capsule
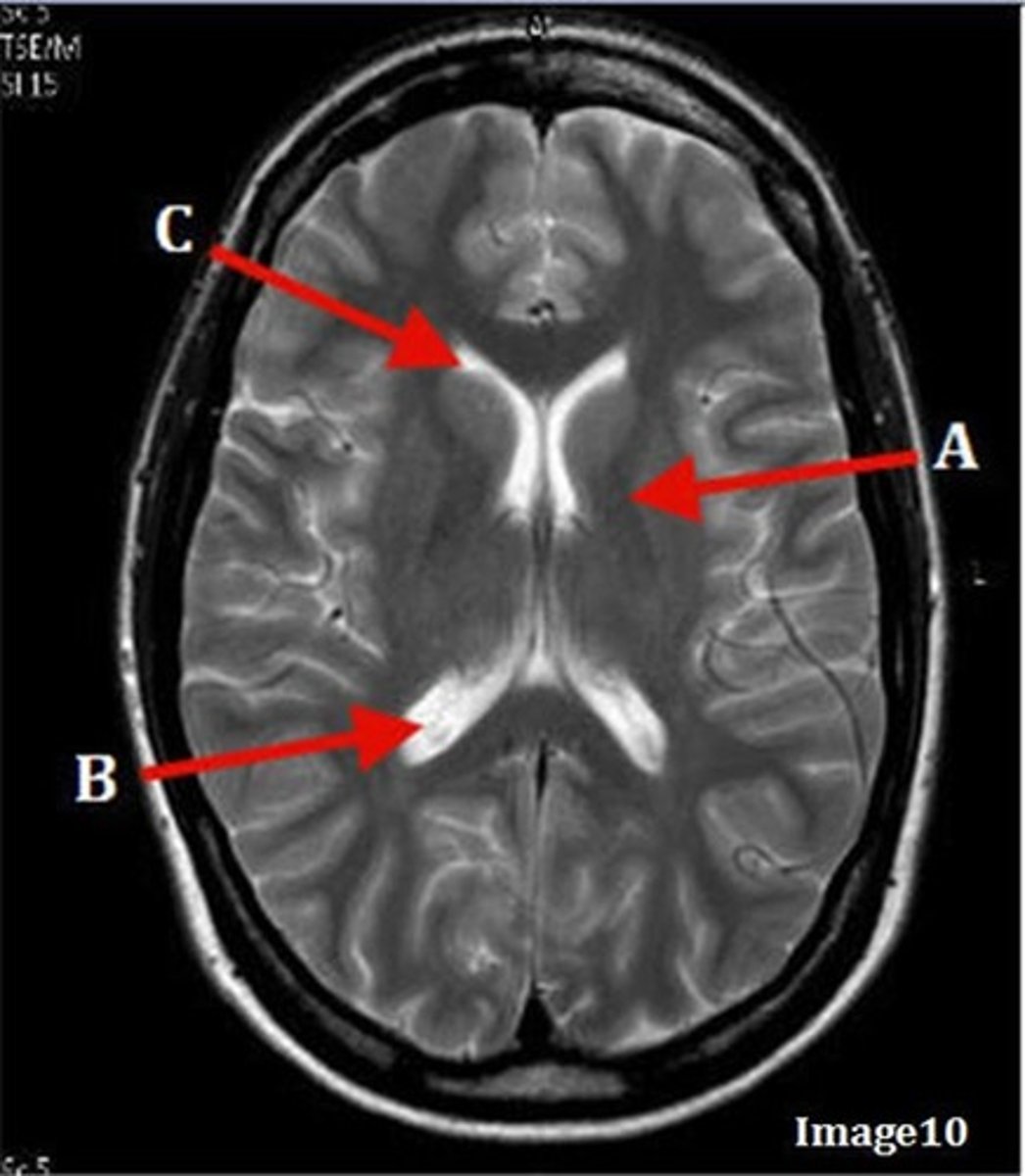
B
posterior horn of lateral ventricle
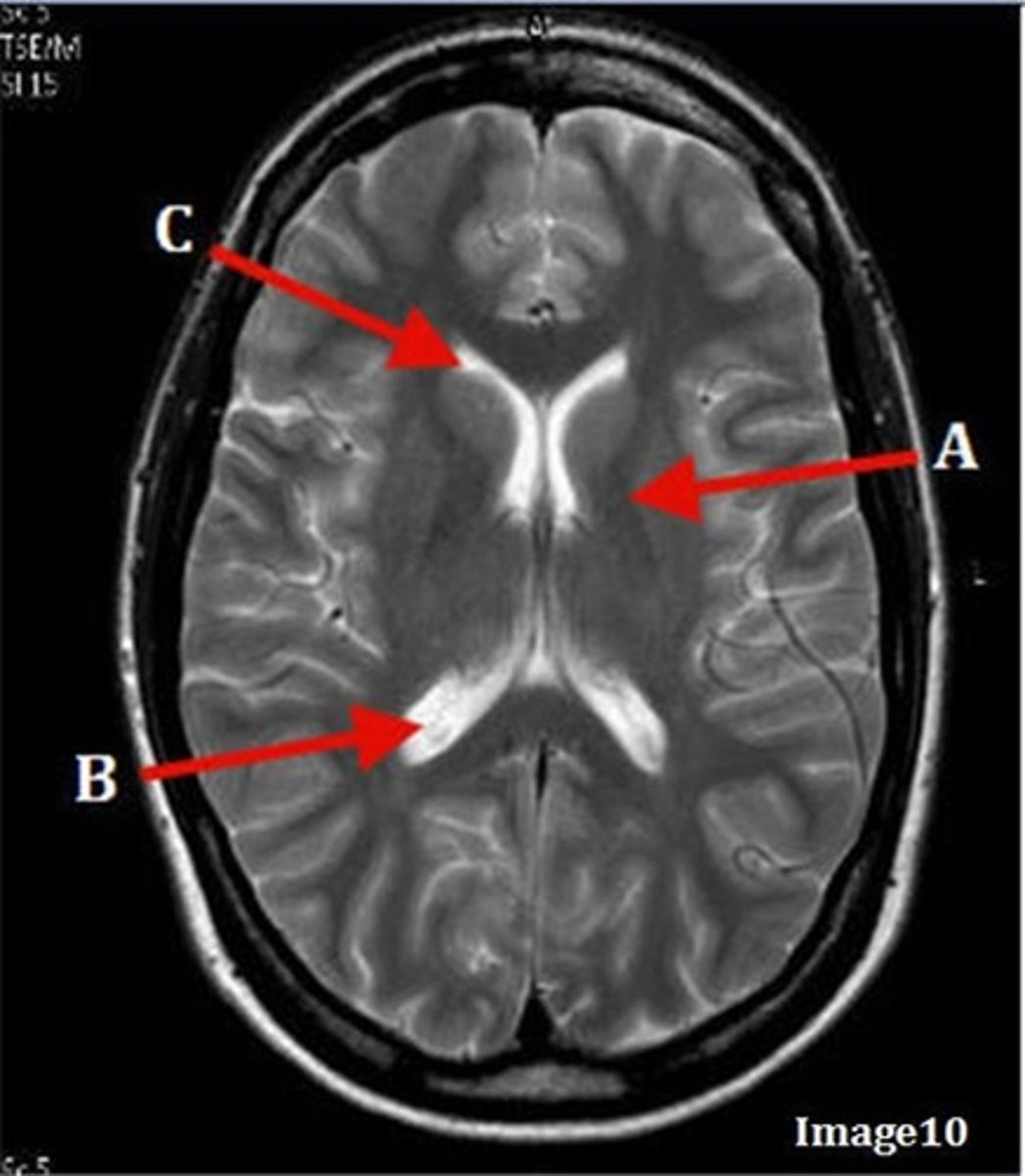
C
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
D
white matter
B
caudate nucleus
C
internal capsule
F
lentiform nucleus
E
gray matter
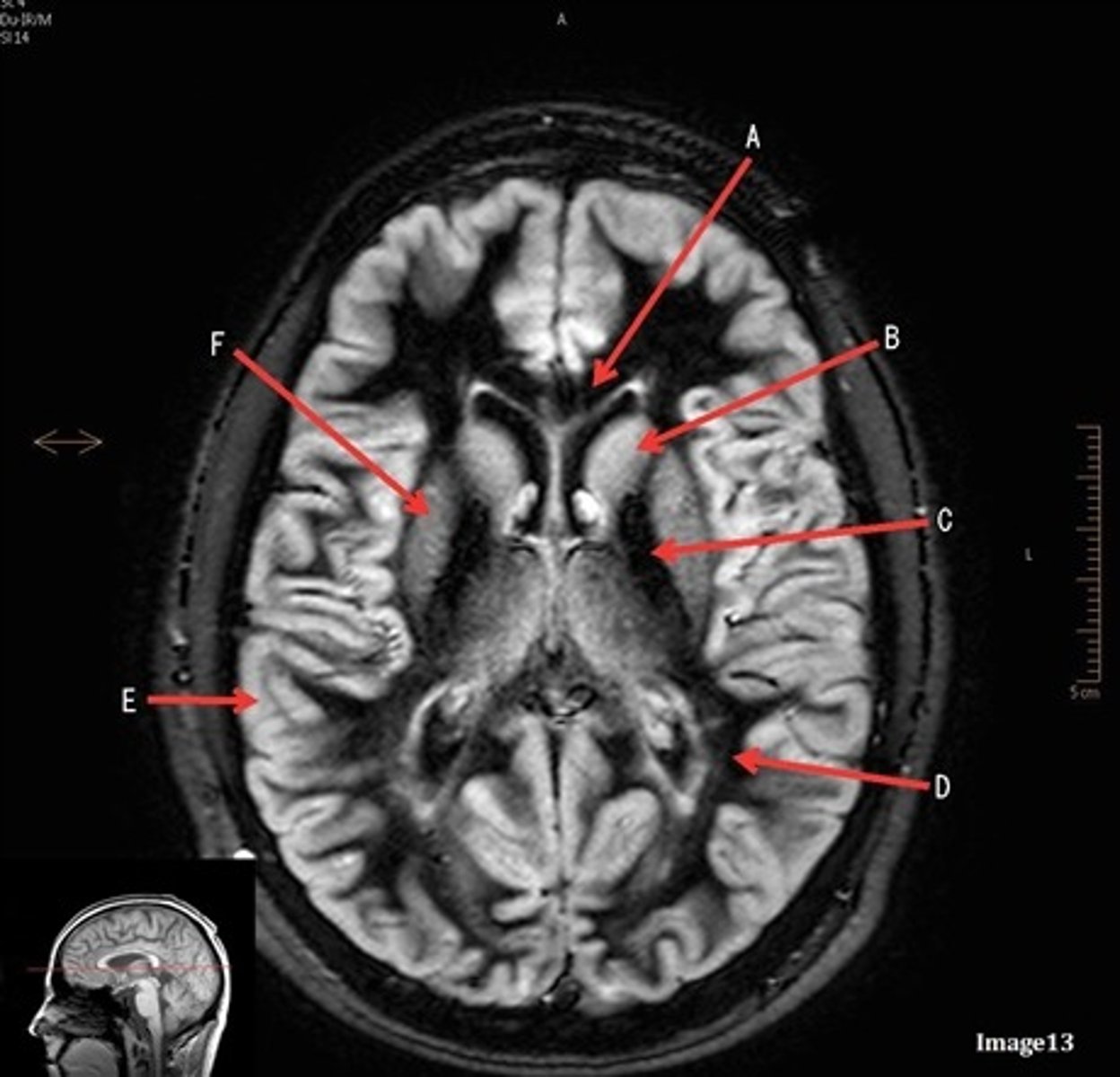
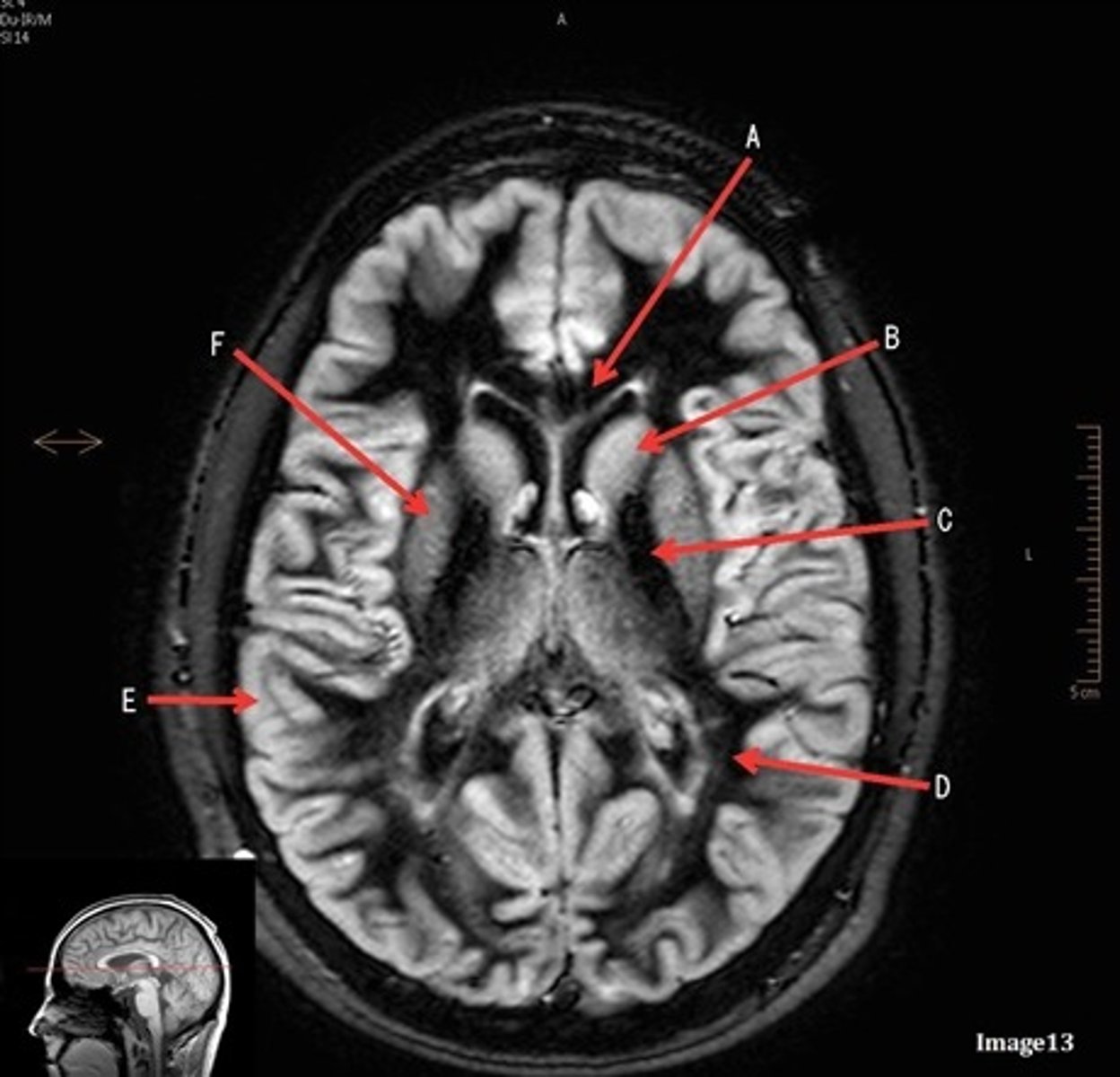
A
pituitary gland
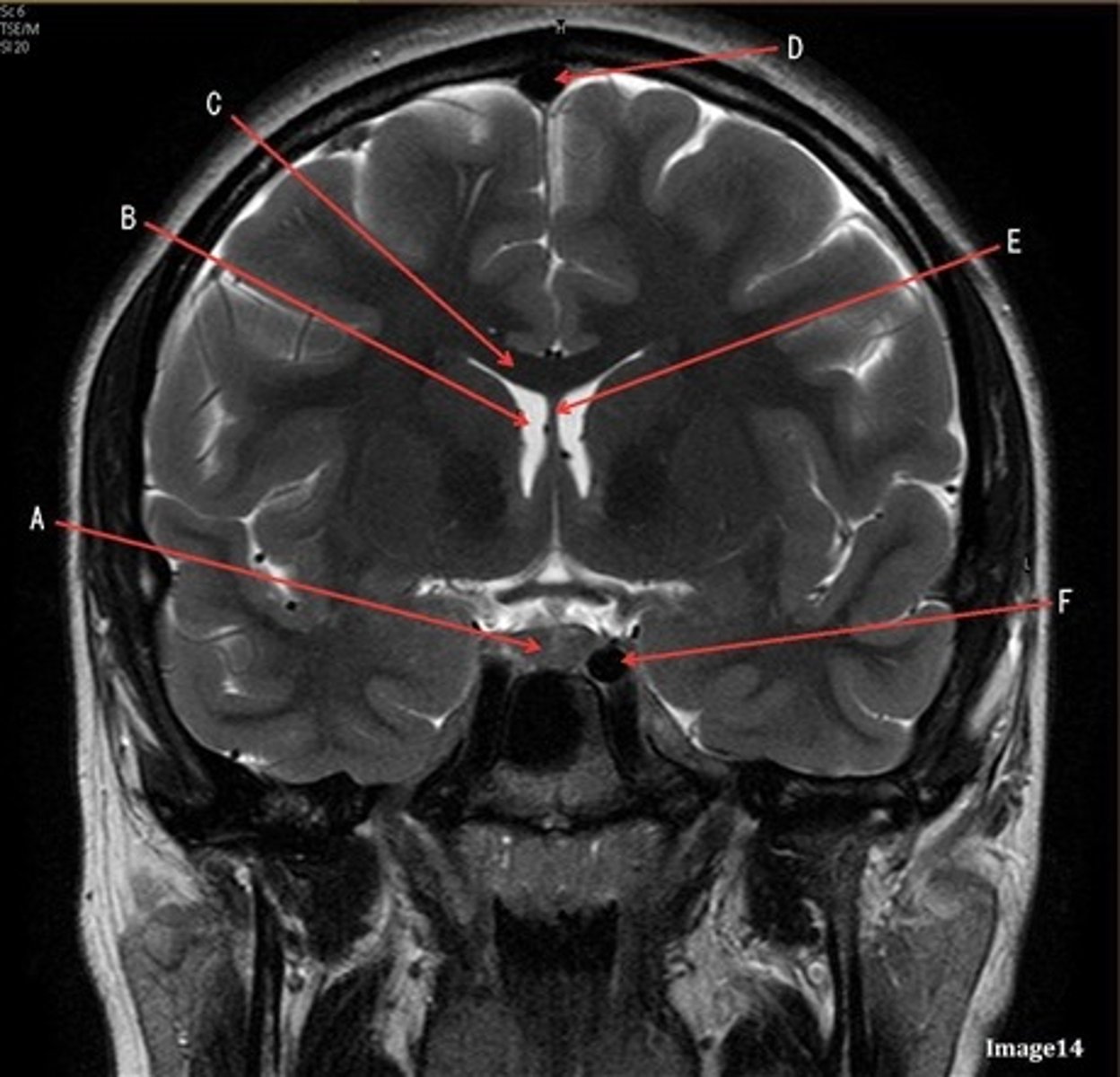
B
lateral ventricle
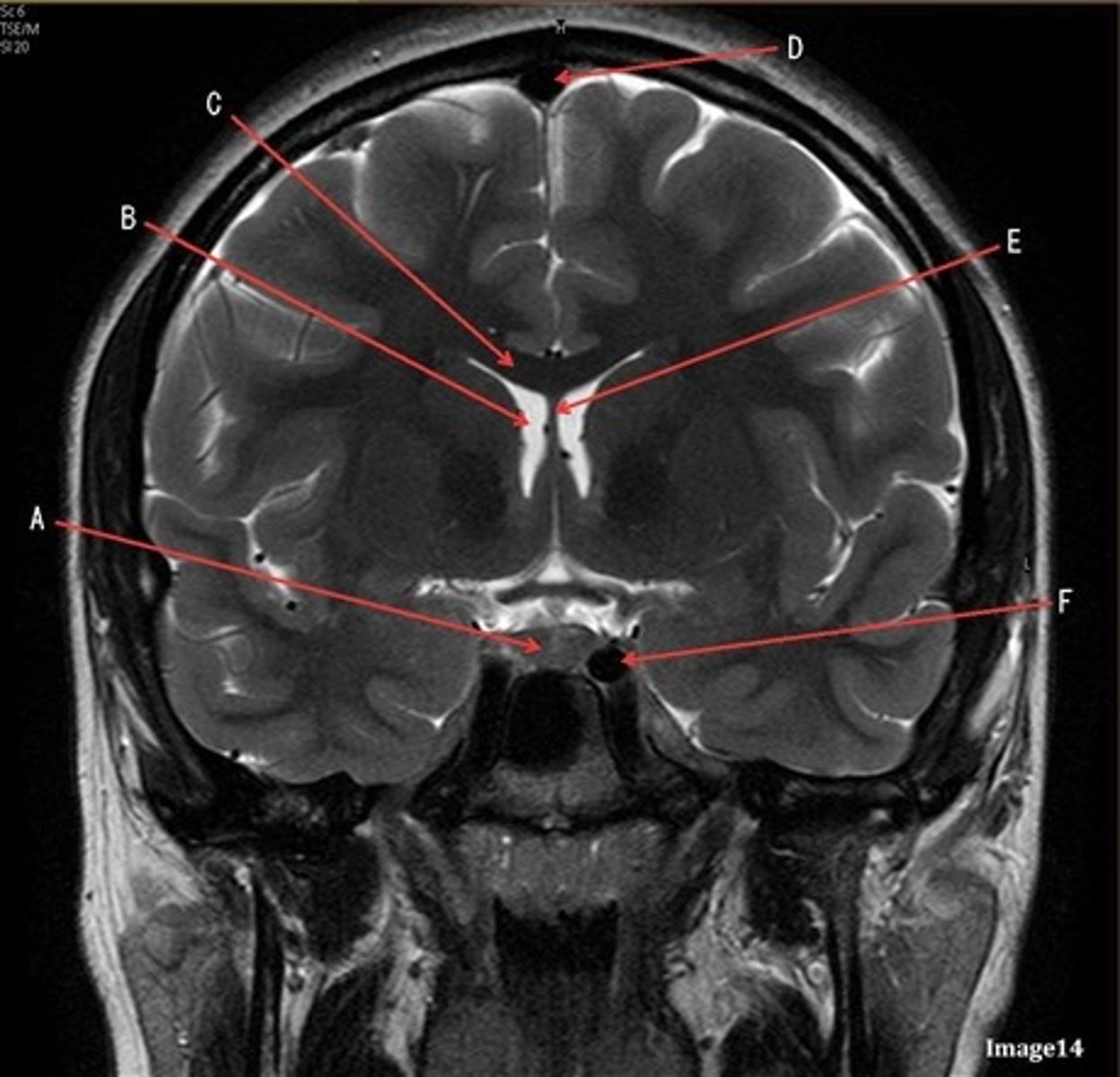
C
corpus
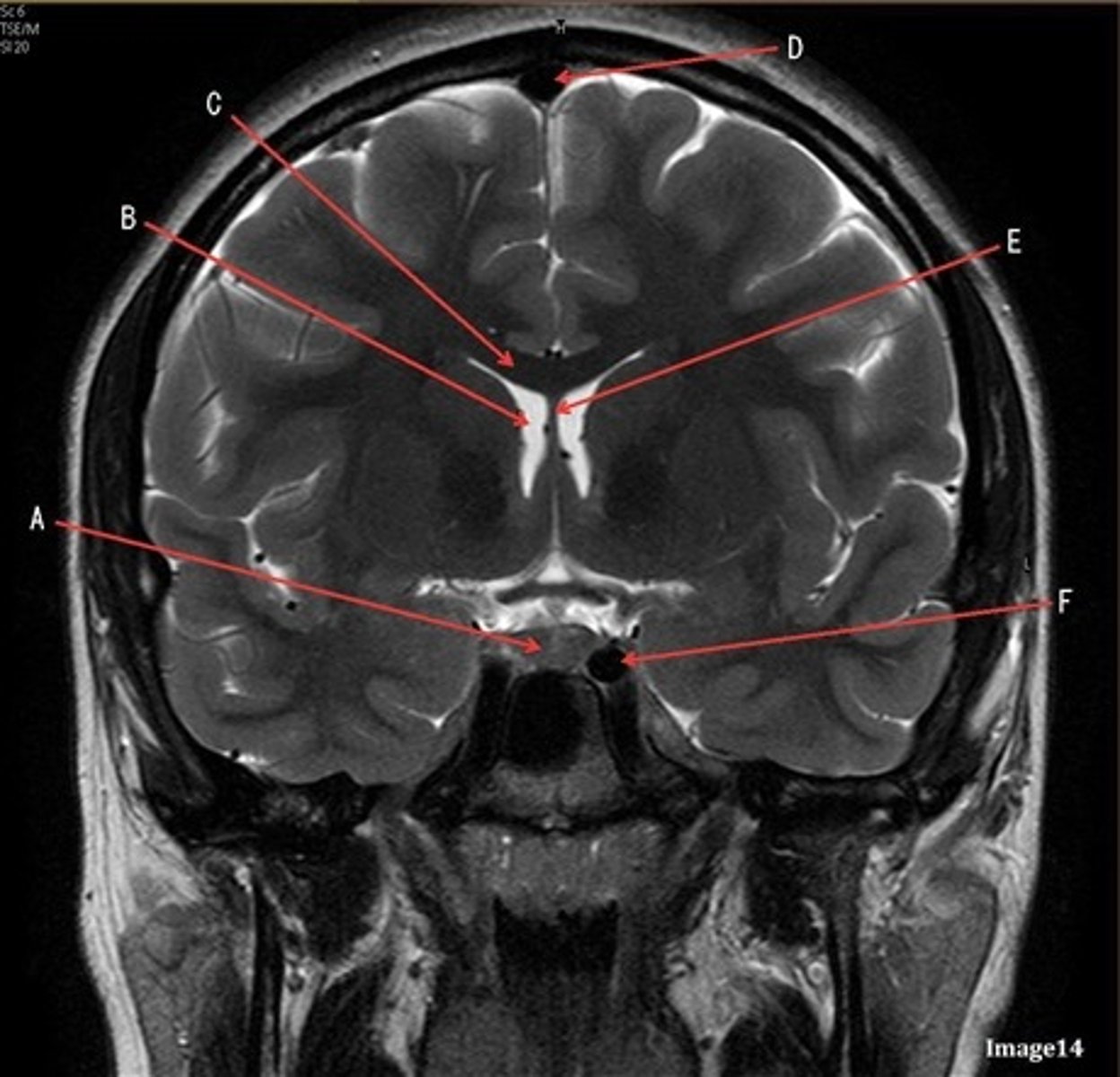
E
fornix
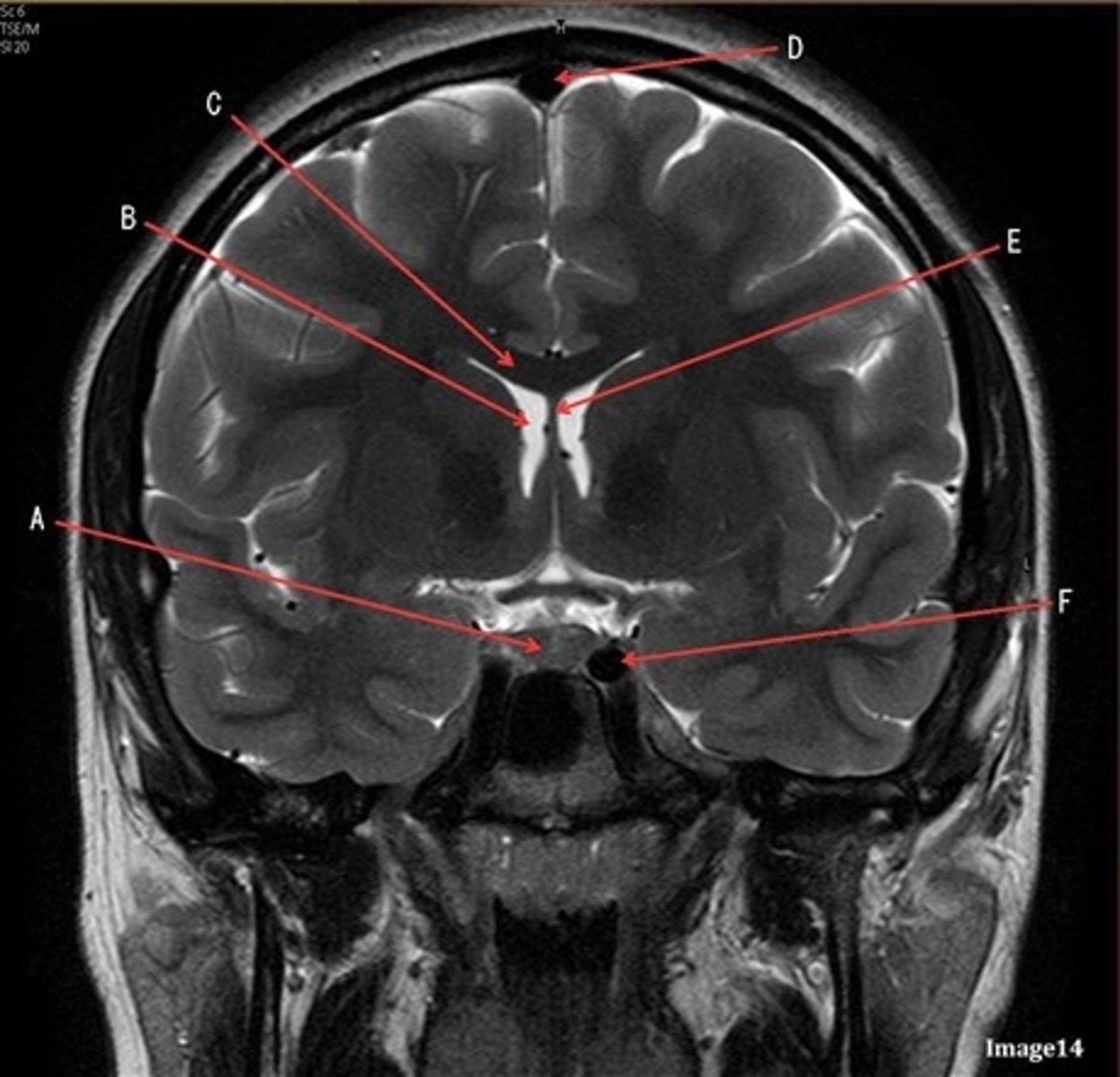
F
internal carotid artery
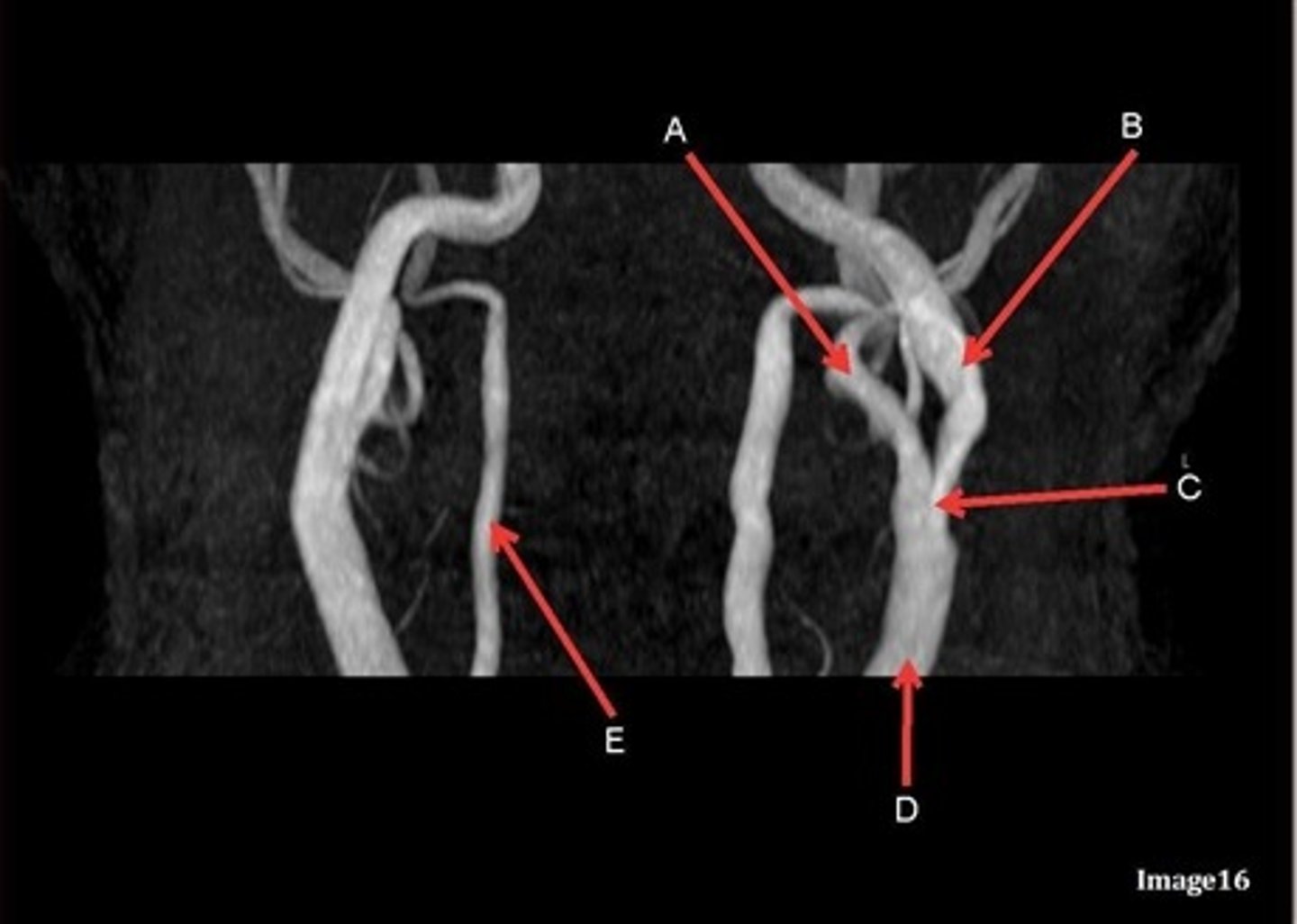
A, where does it supply blood to?
external carotid artery
face
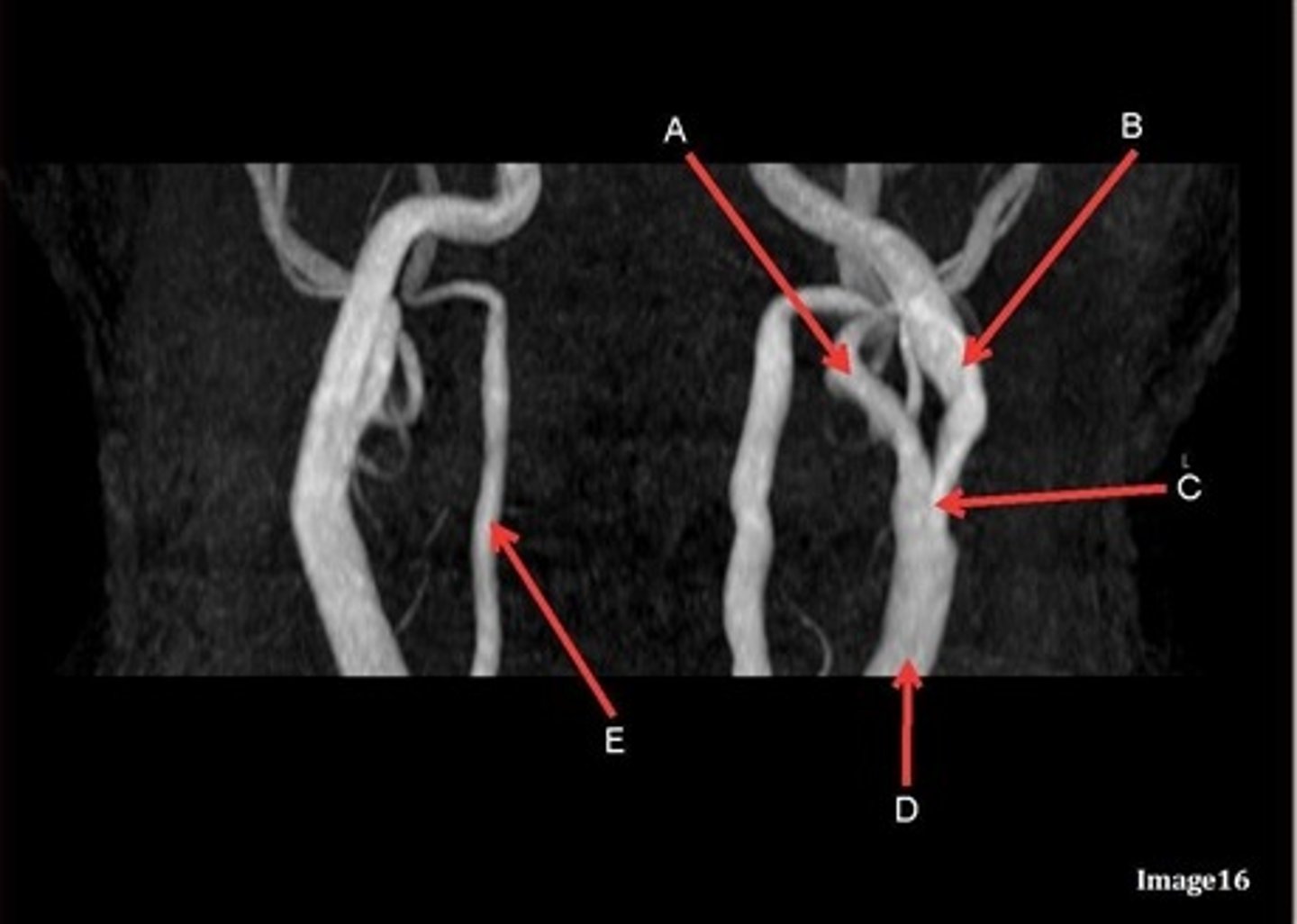
B, where does it supply blood to?
internal carotid artery, anterior brain
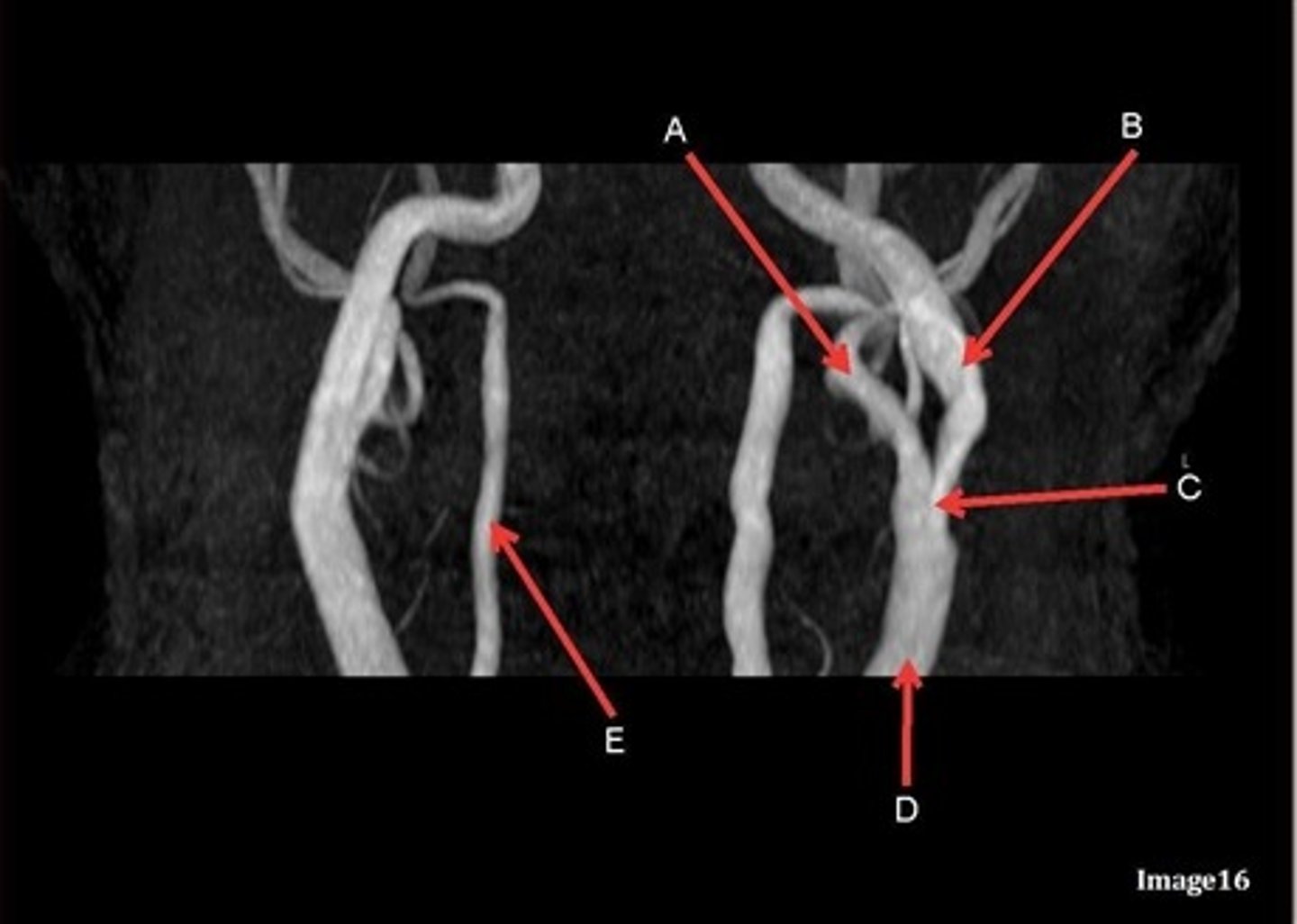
C
Common carotid bifurcation
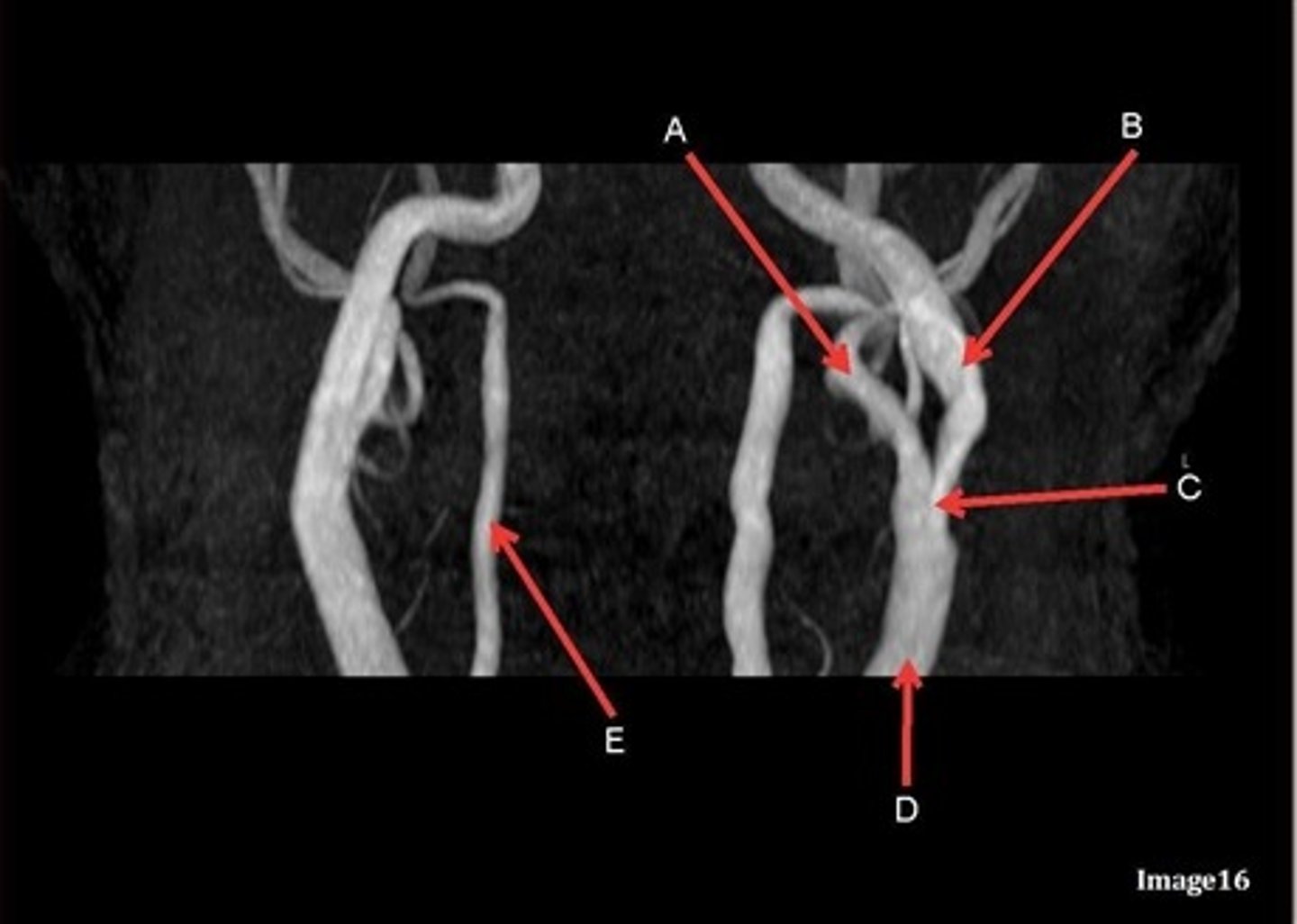
D
common carotid artery
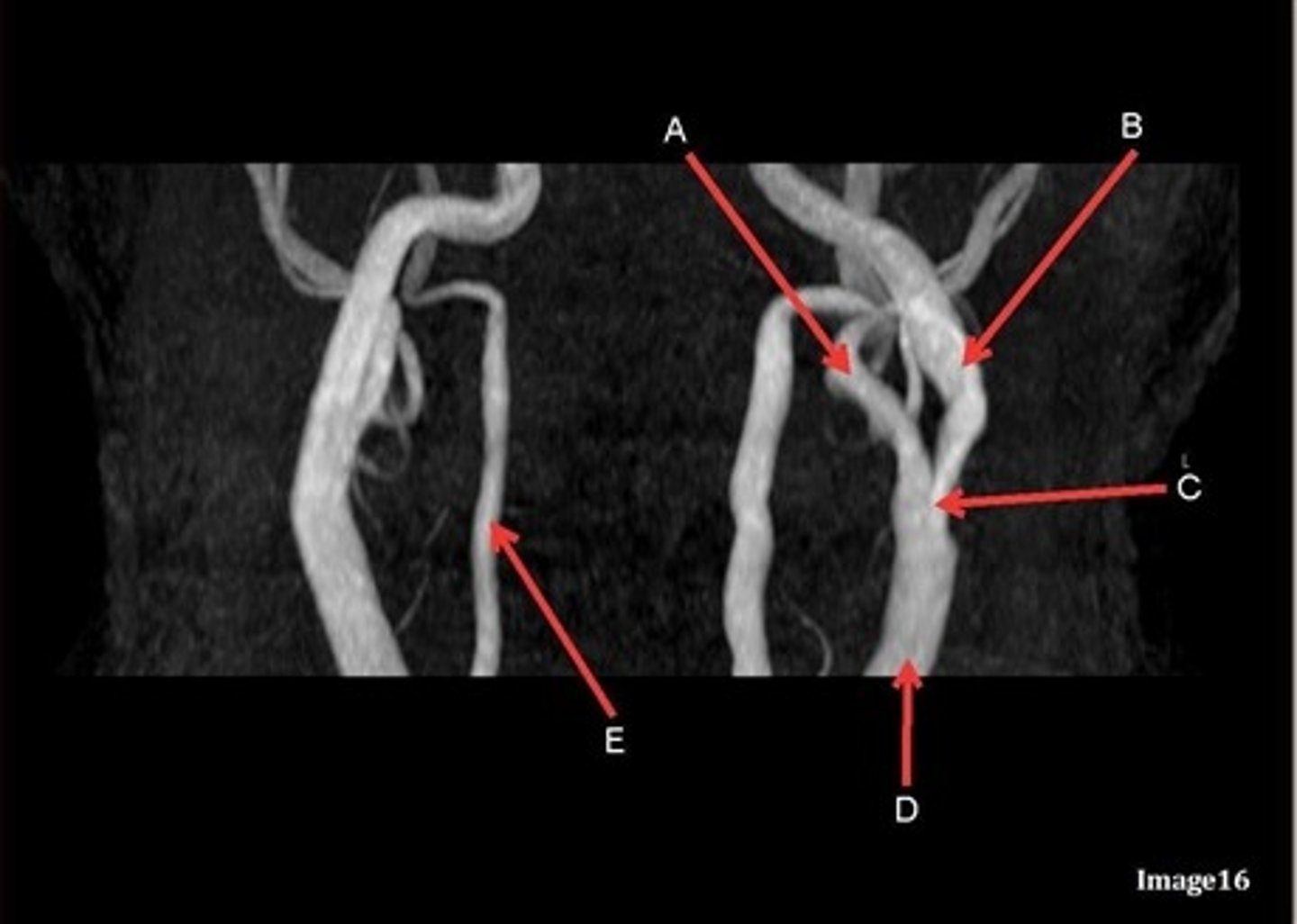
E, where does it supply blood to?
vertebral artery, posterior brain
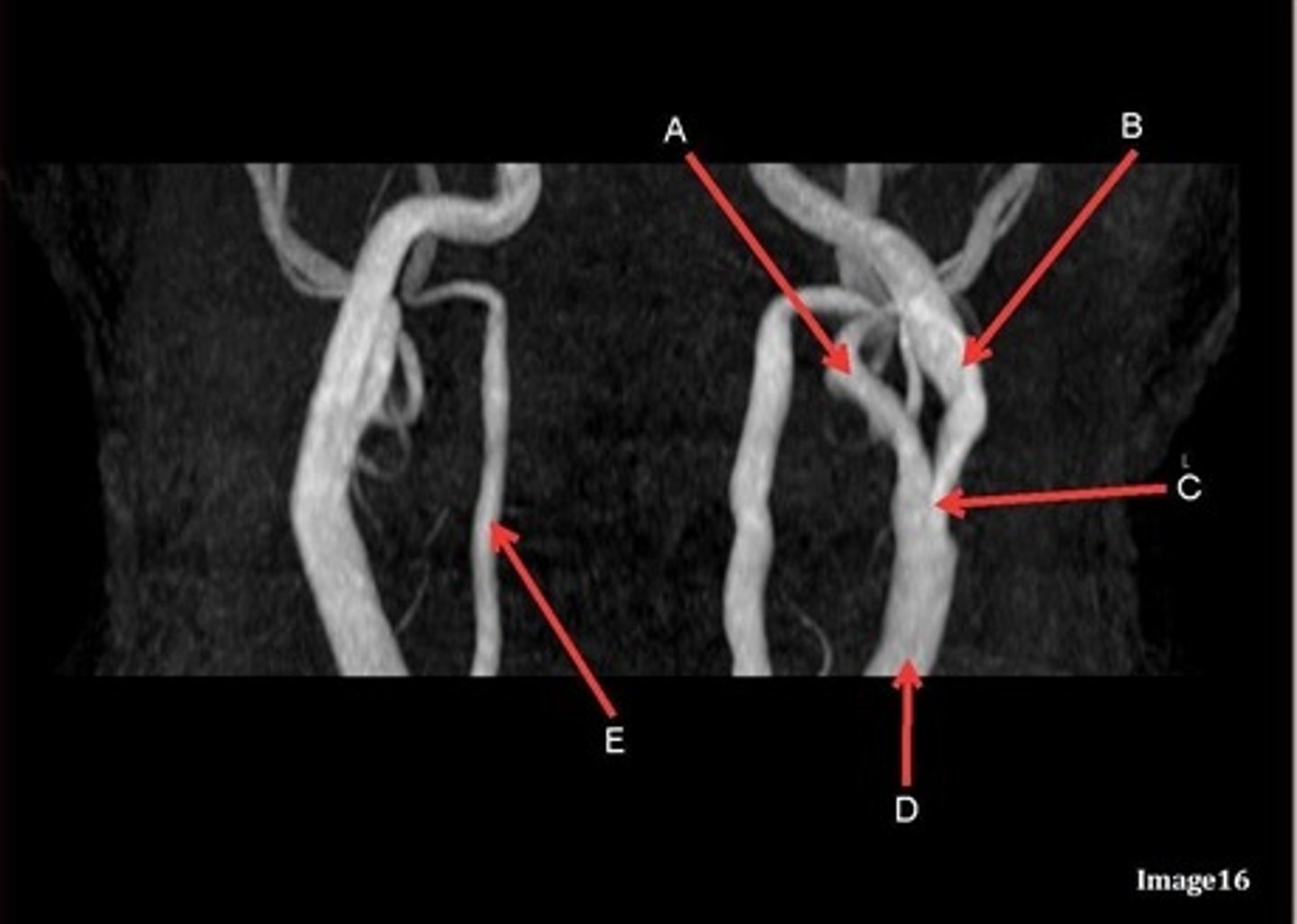
what kind of image is this?
MRA extracranial circulation
E
Torcular herophili
B
thalamus
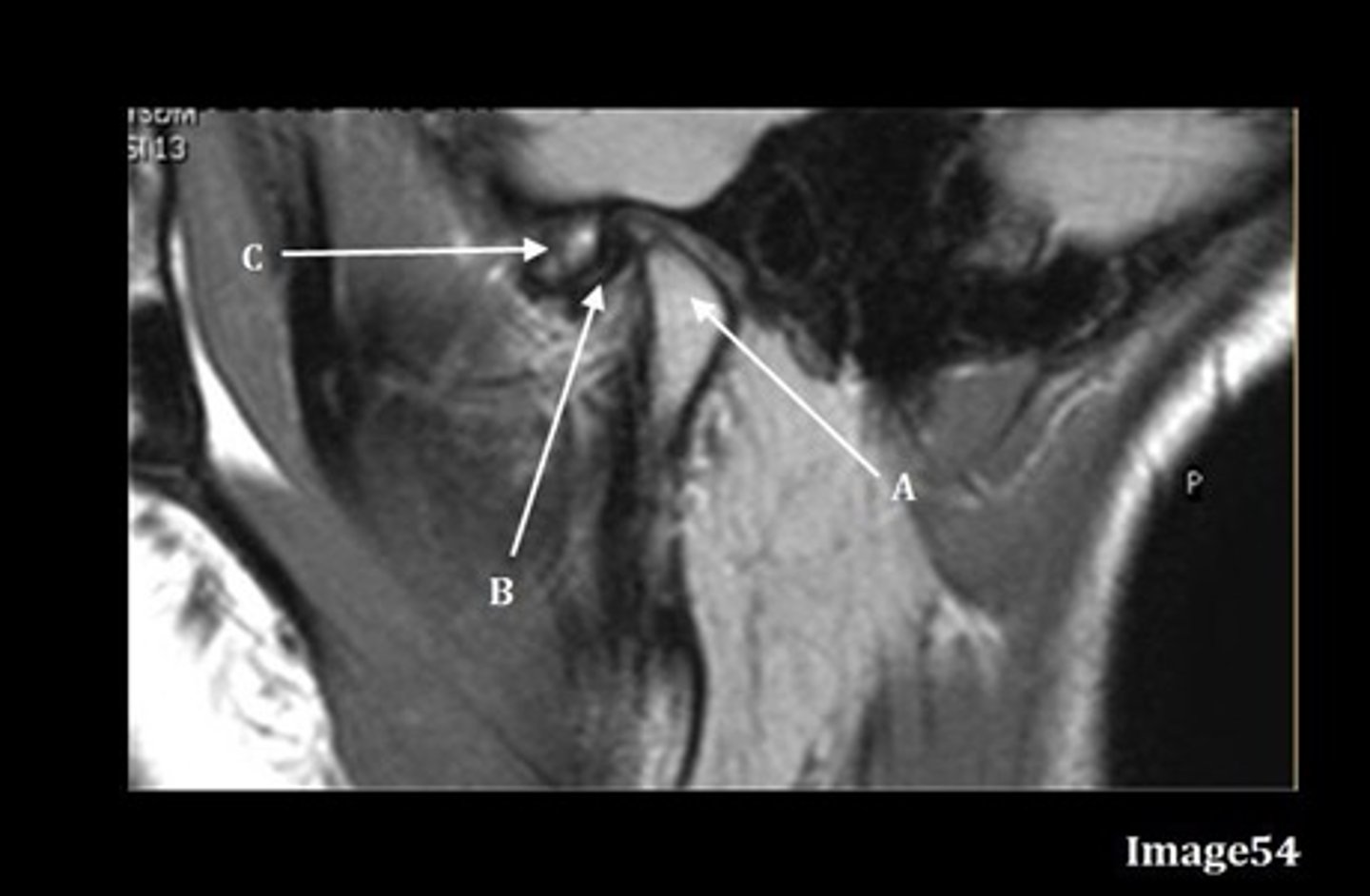
A
B
C
A- mandibular condyle inside mandibular fossa of temporal bone
B- articular disc
C-articular tubercle
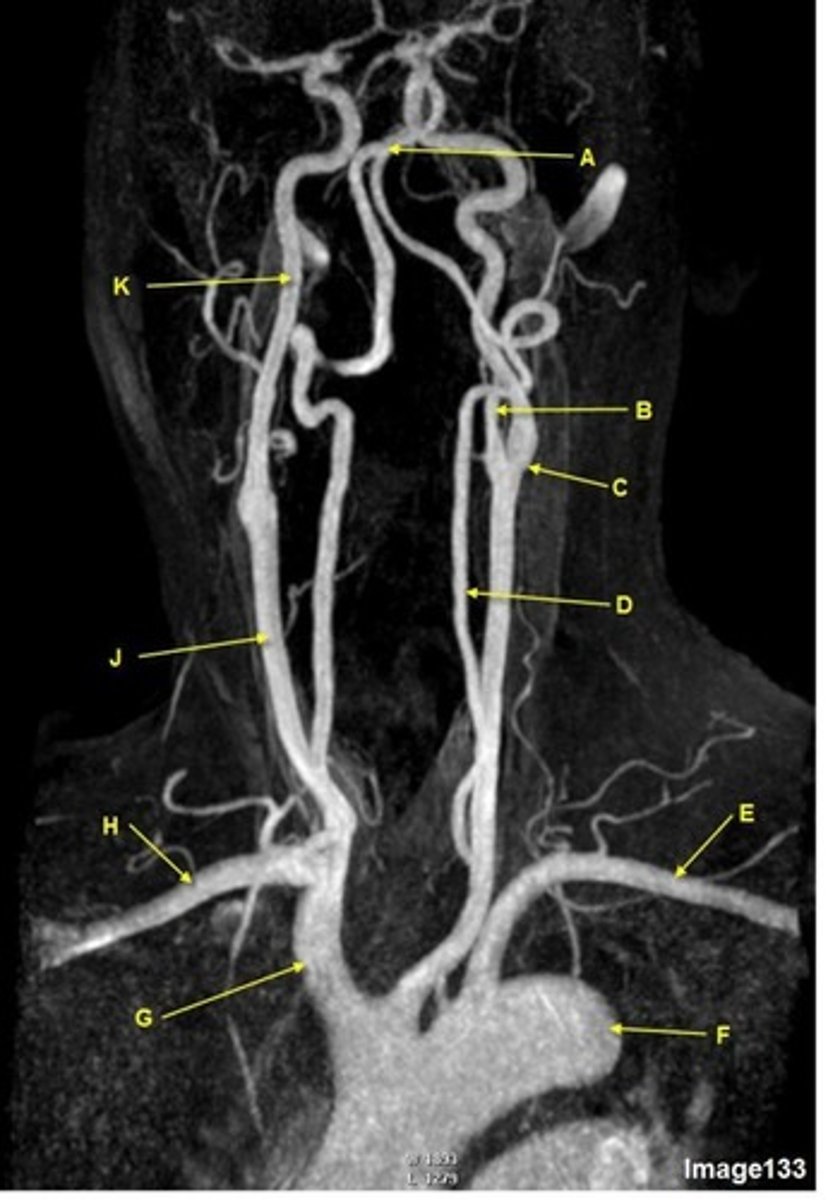
G
brachiocephalic trunk, innominate artery
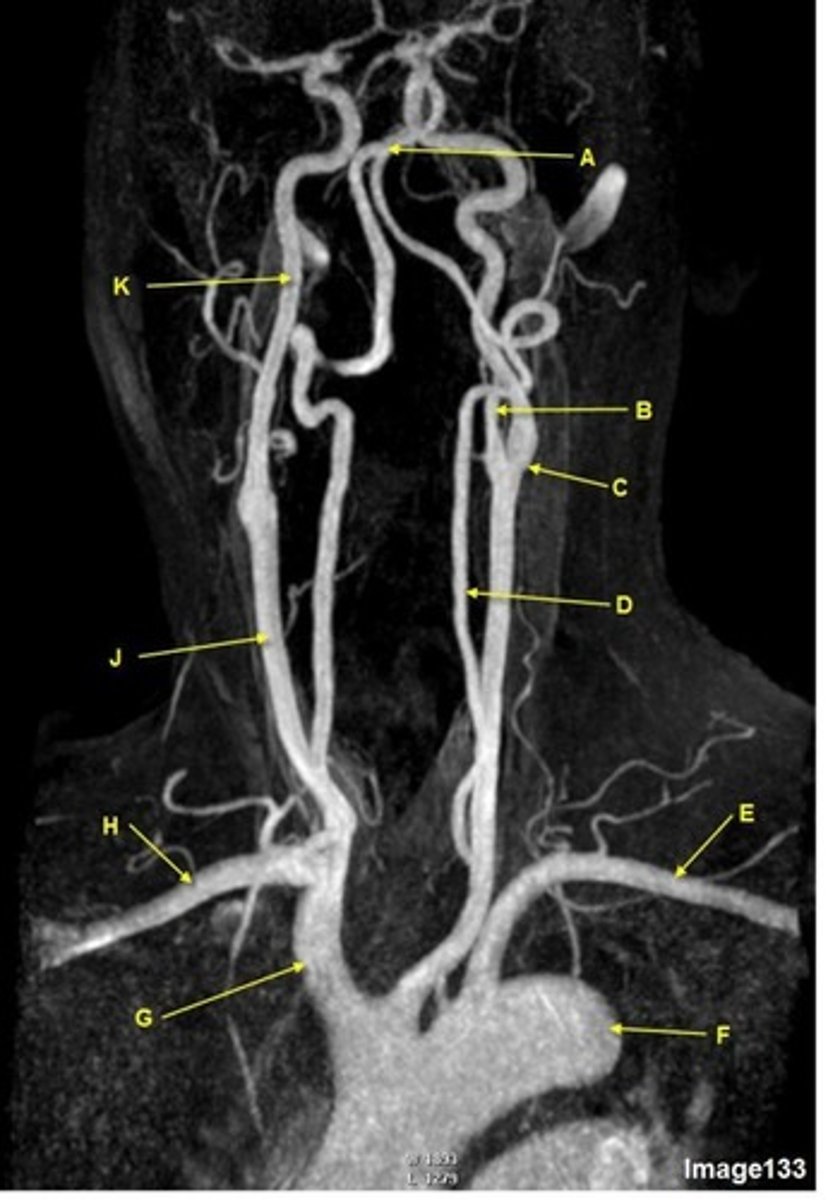
H
R subclavian artery
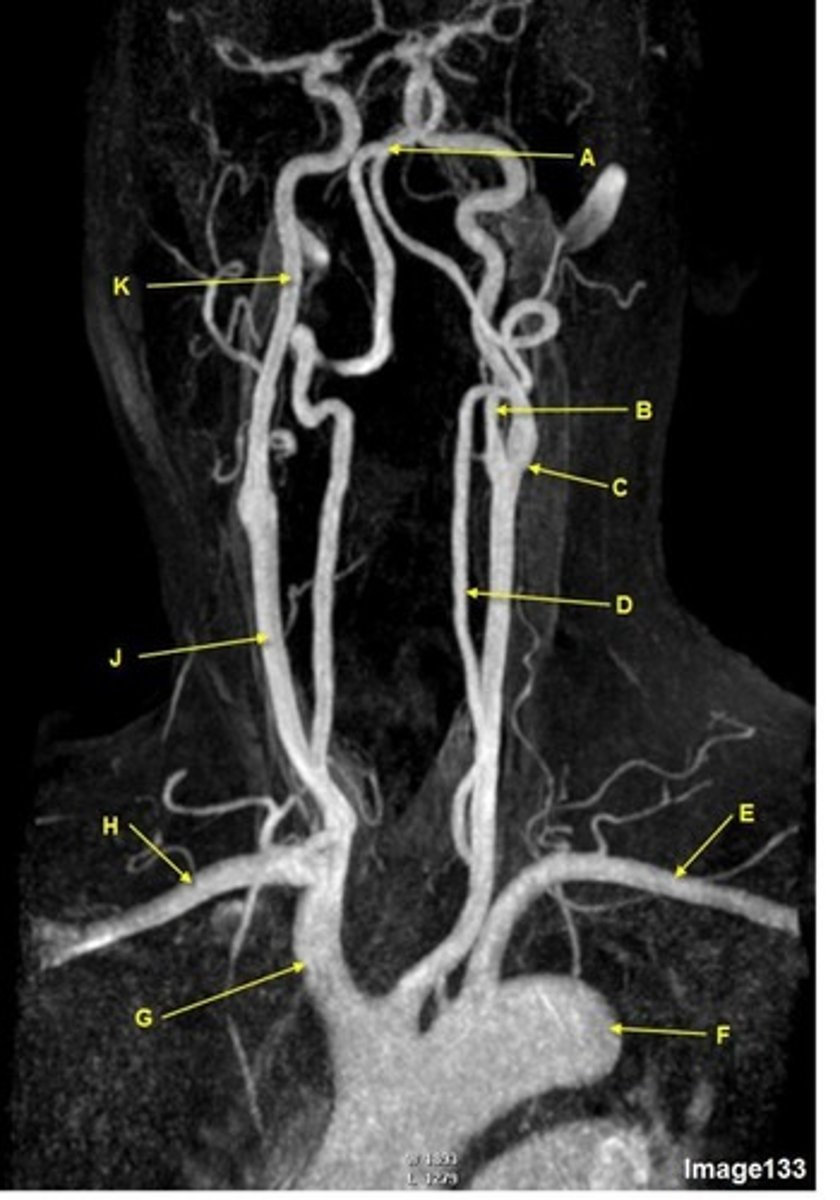
K
internal carotid artery
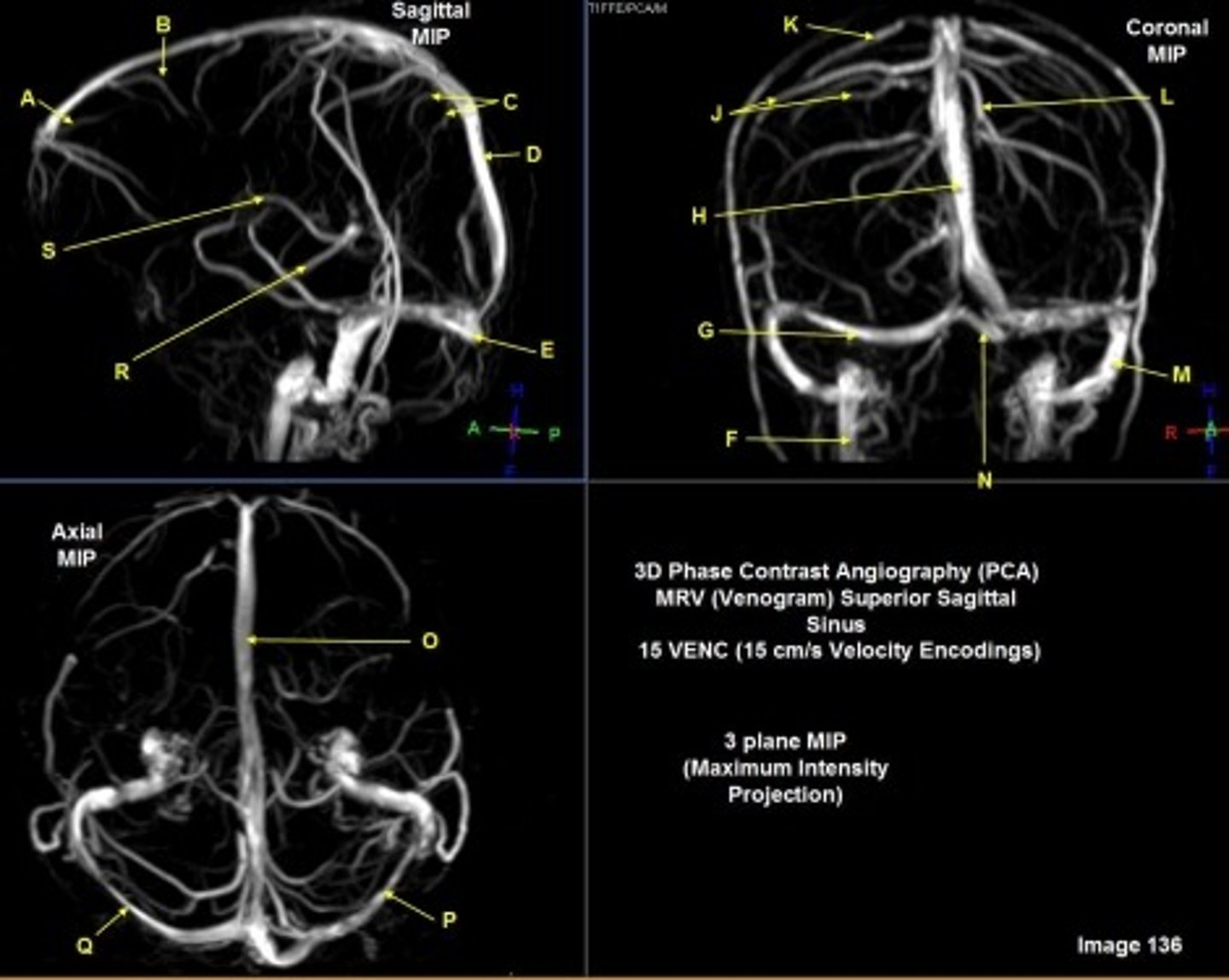
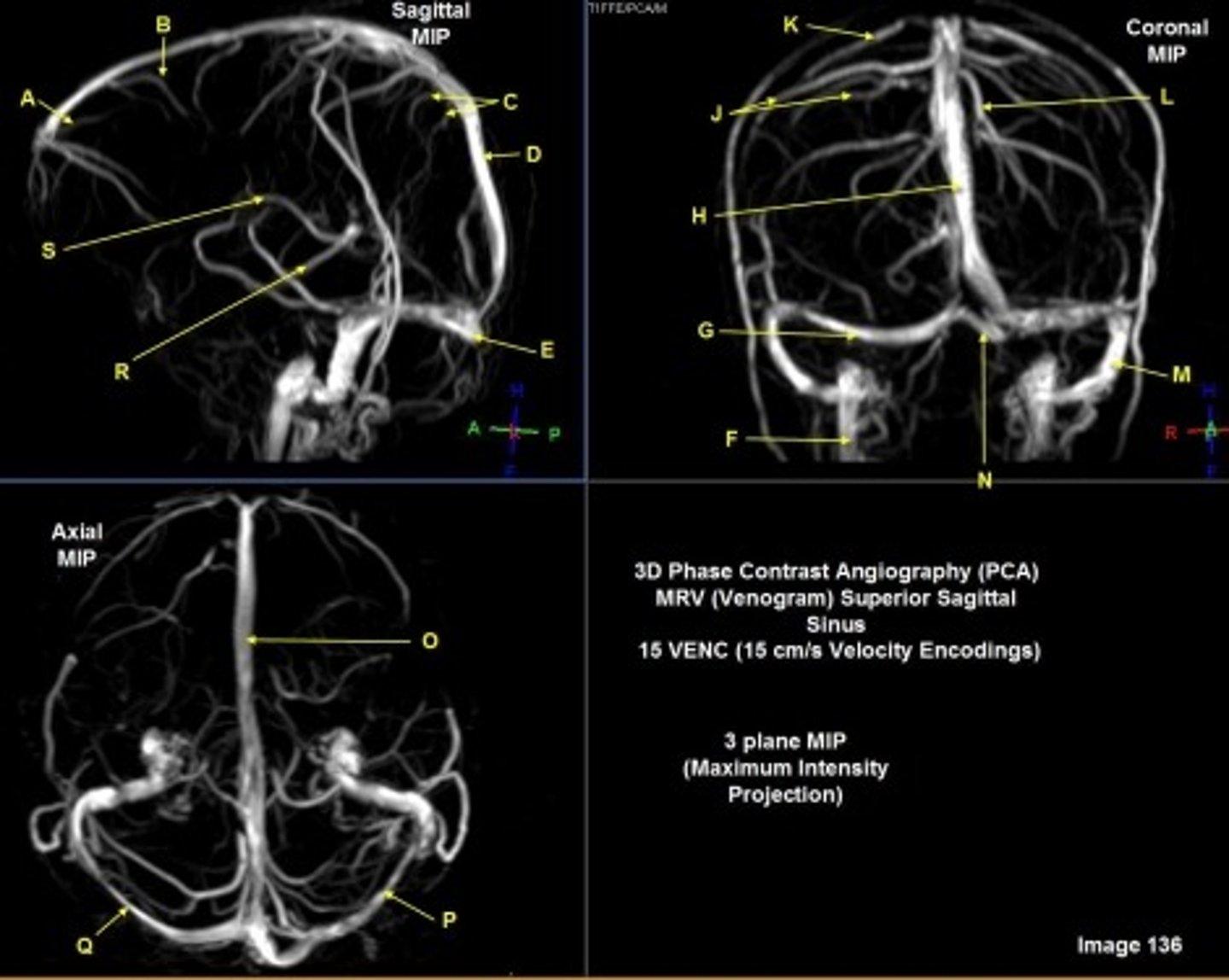
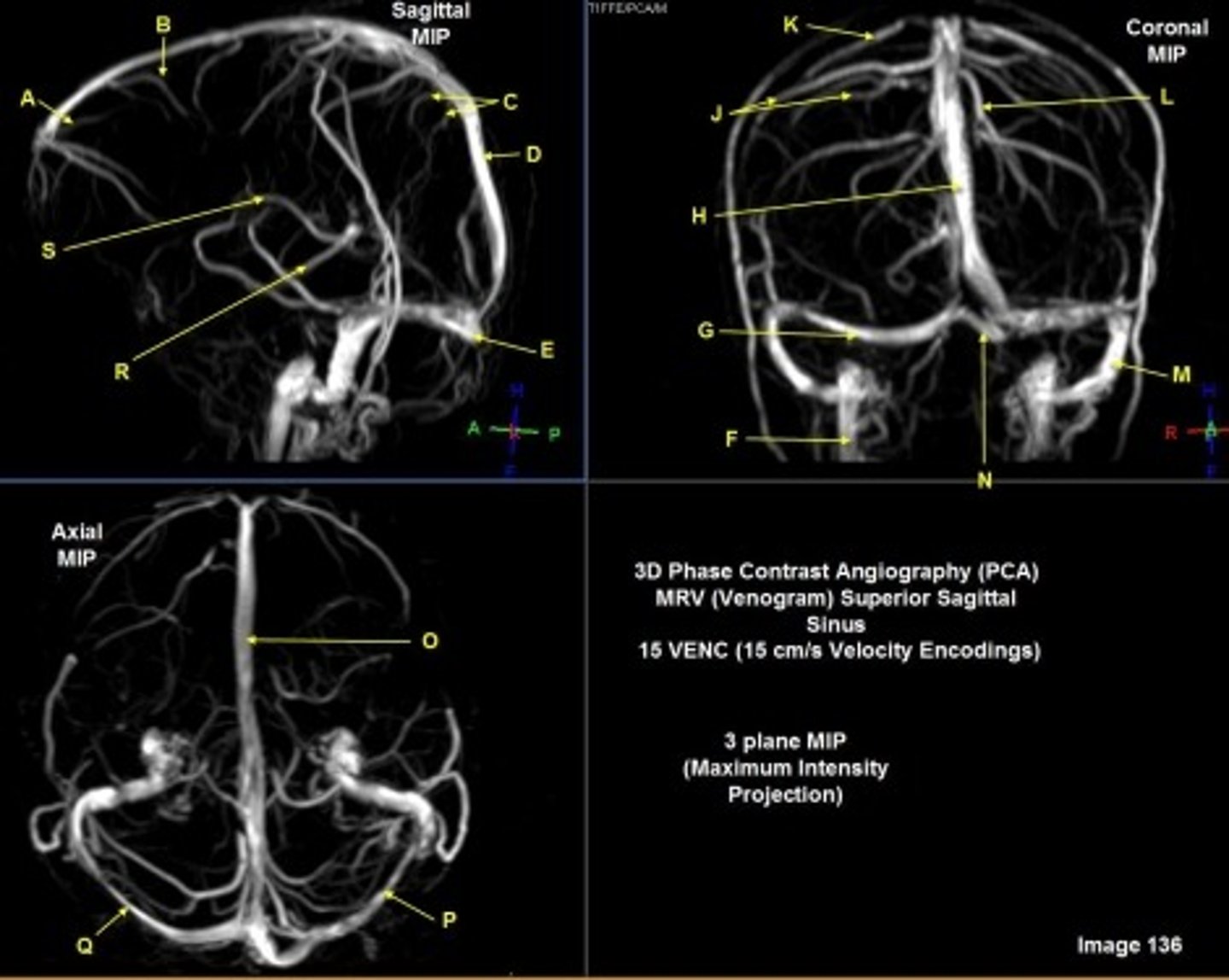
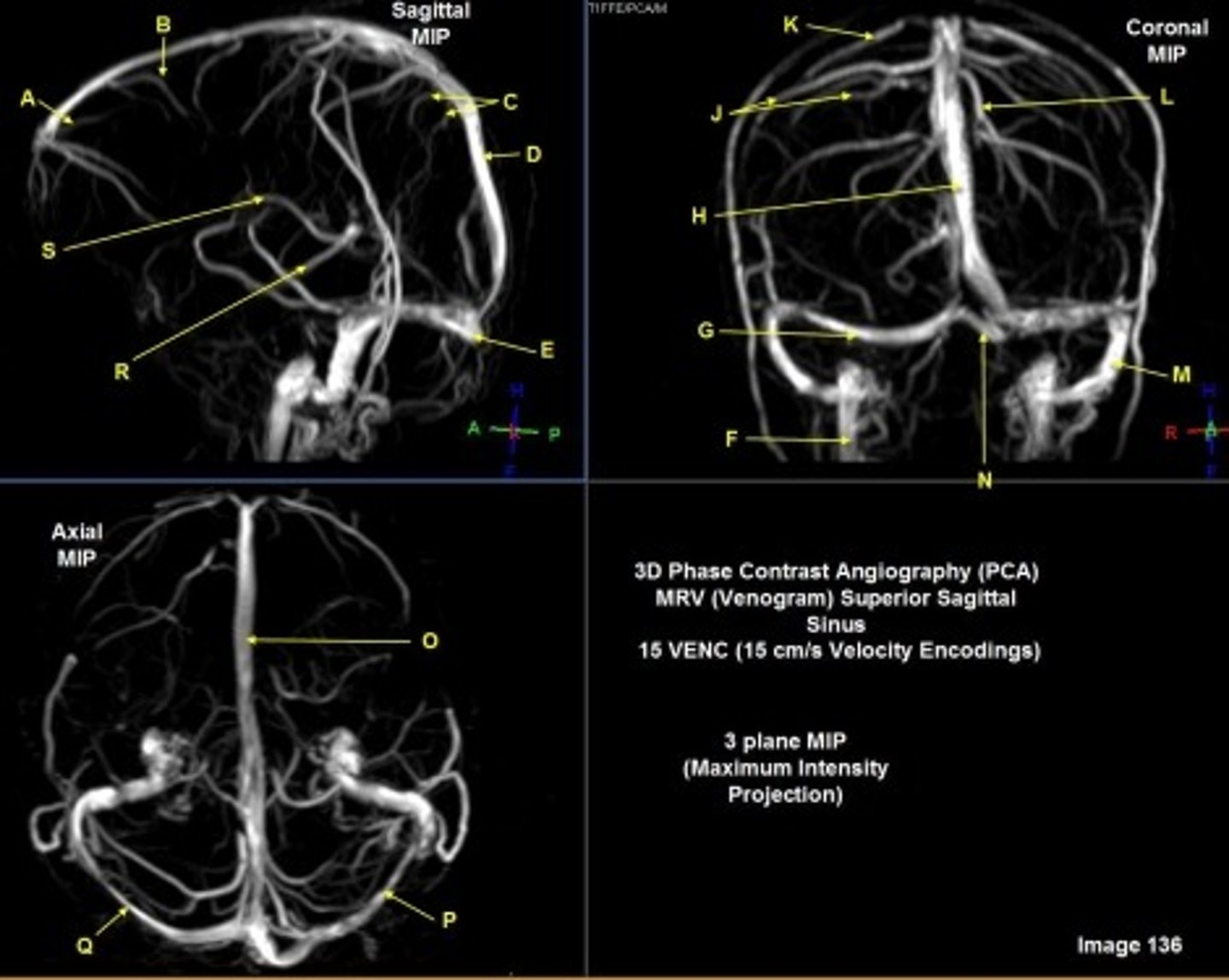
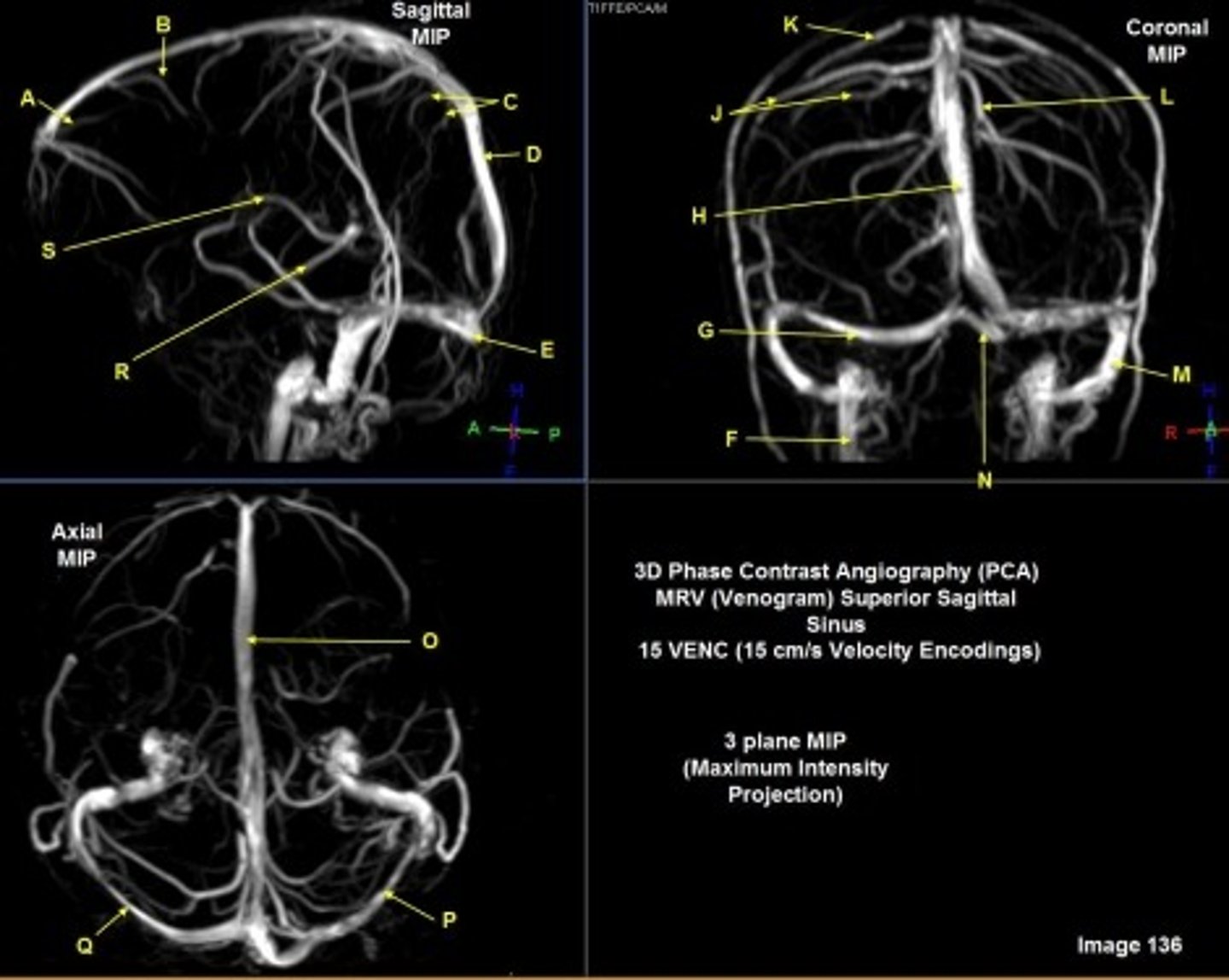
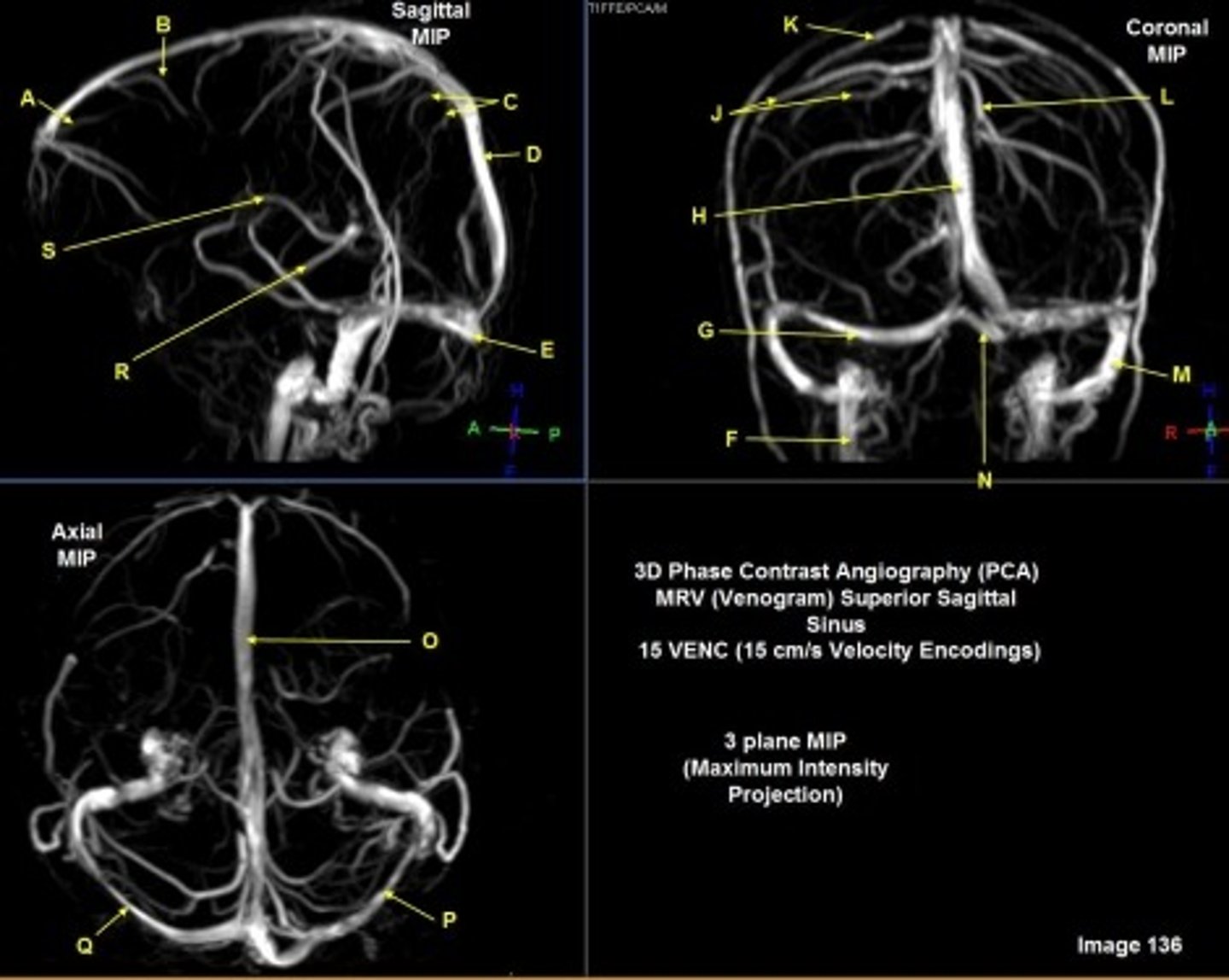
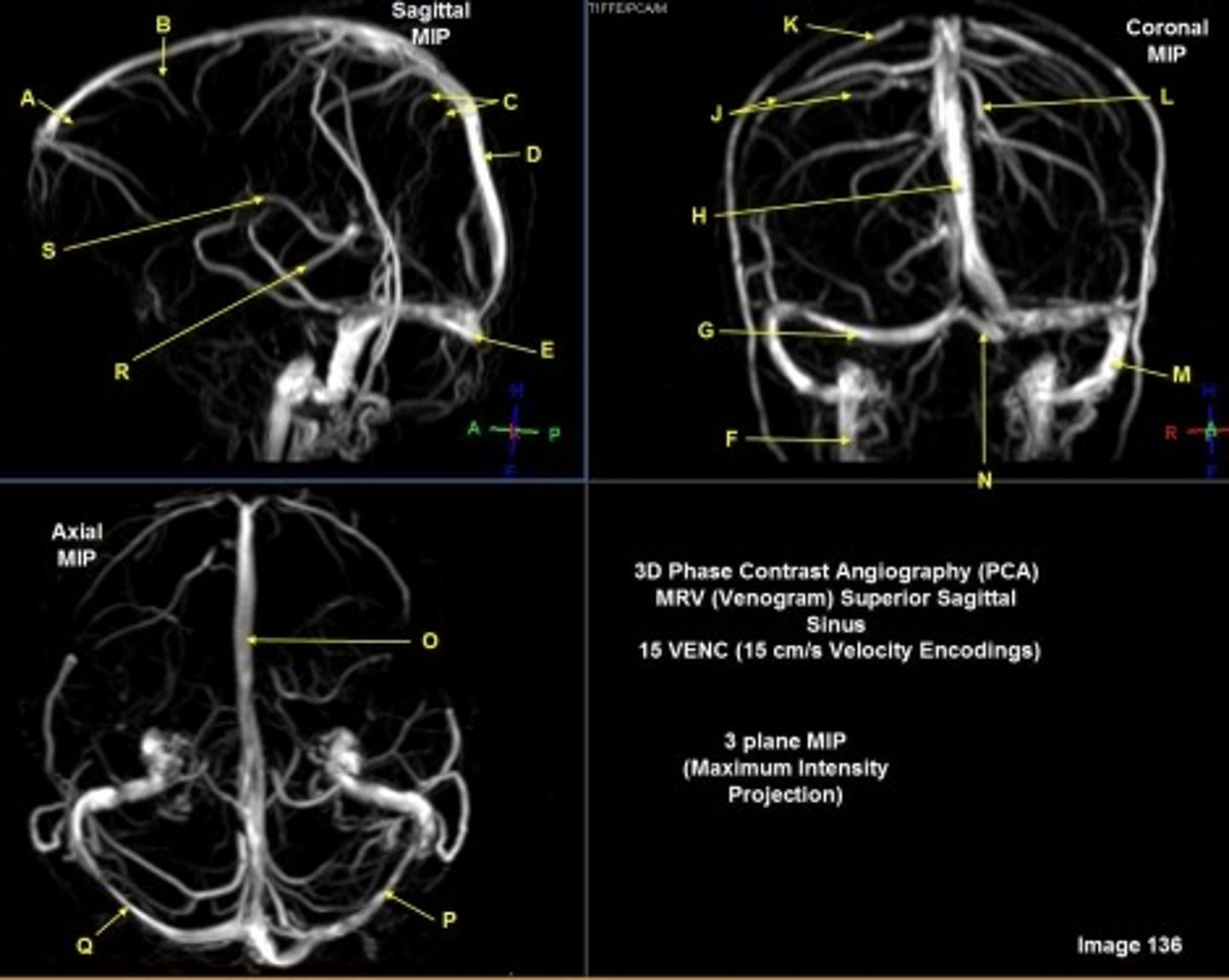
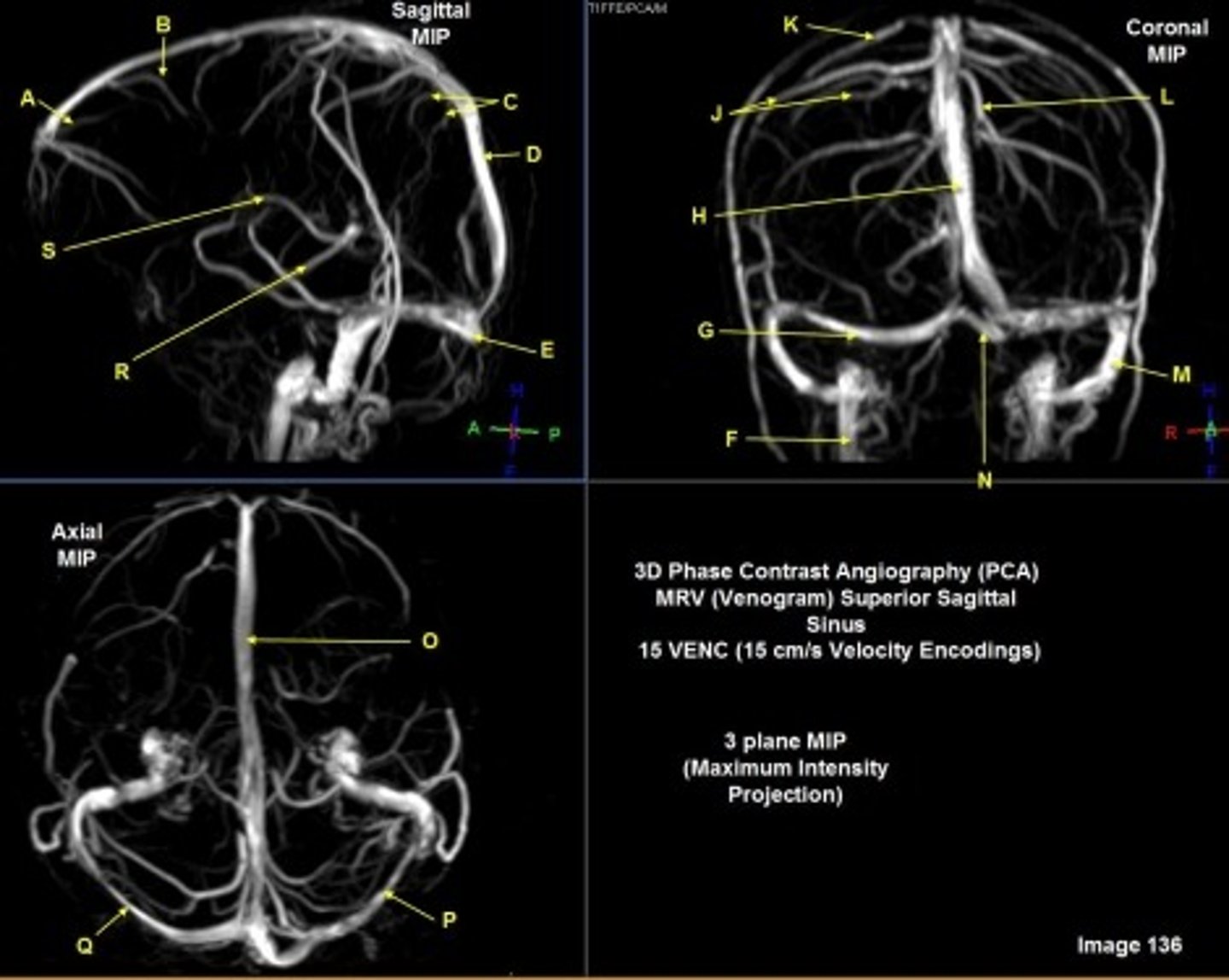
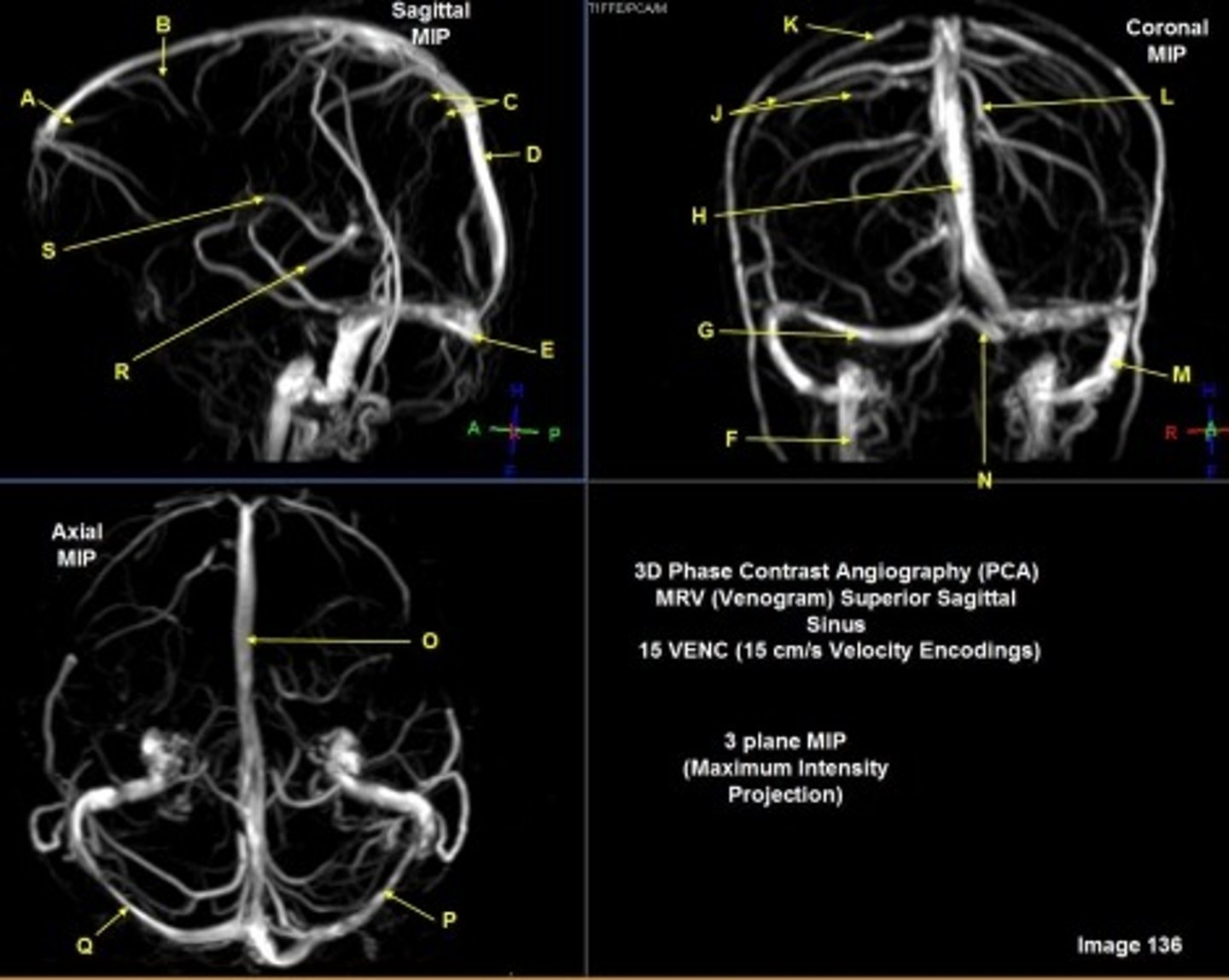
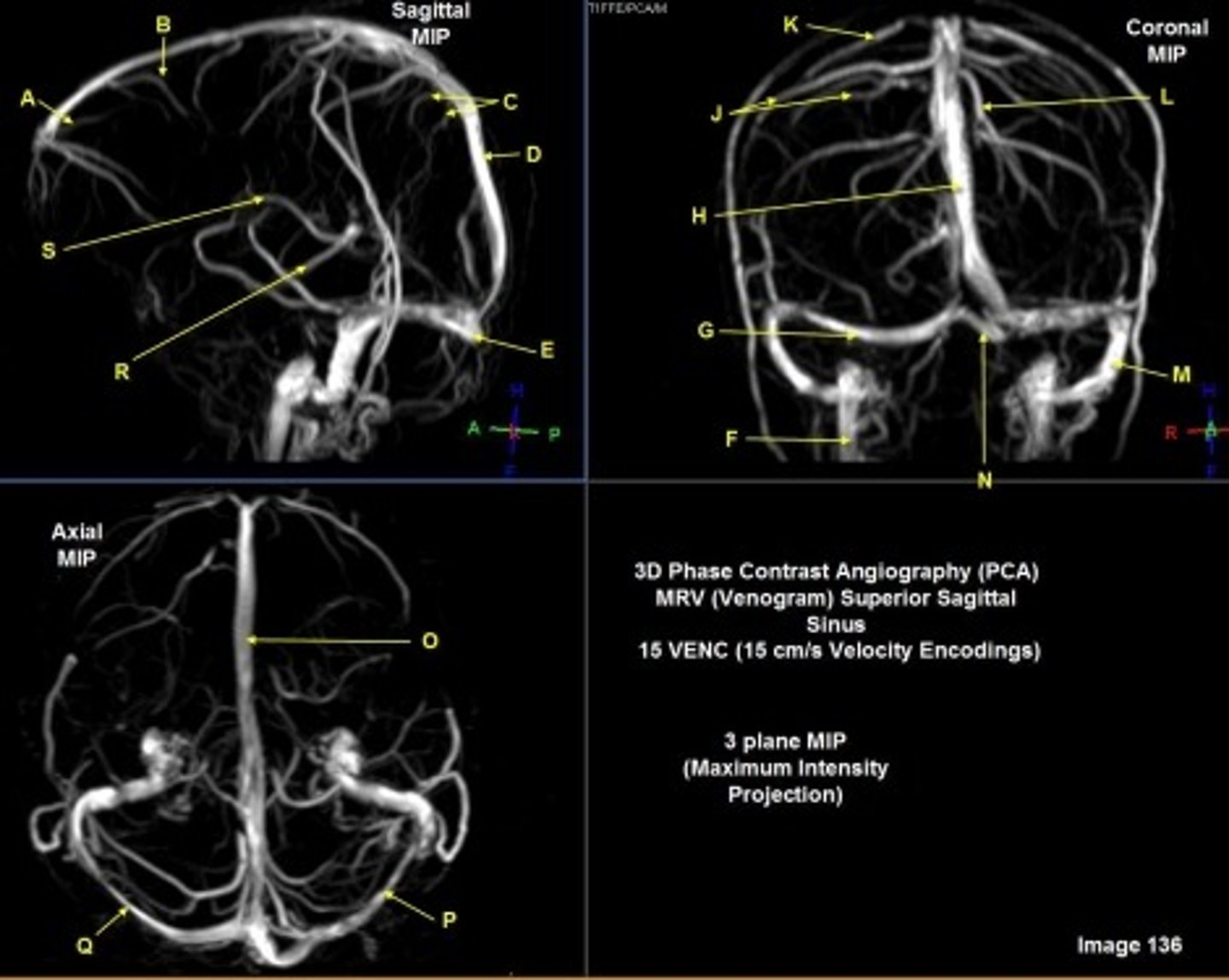
B
posterior frontal vein
C
parietal veins
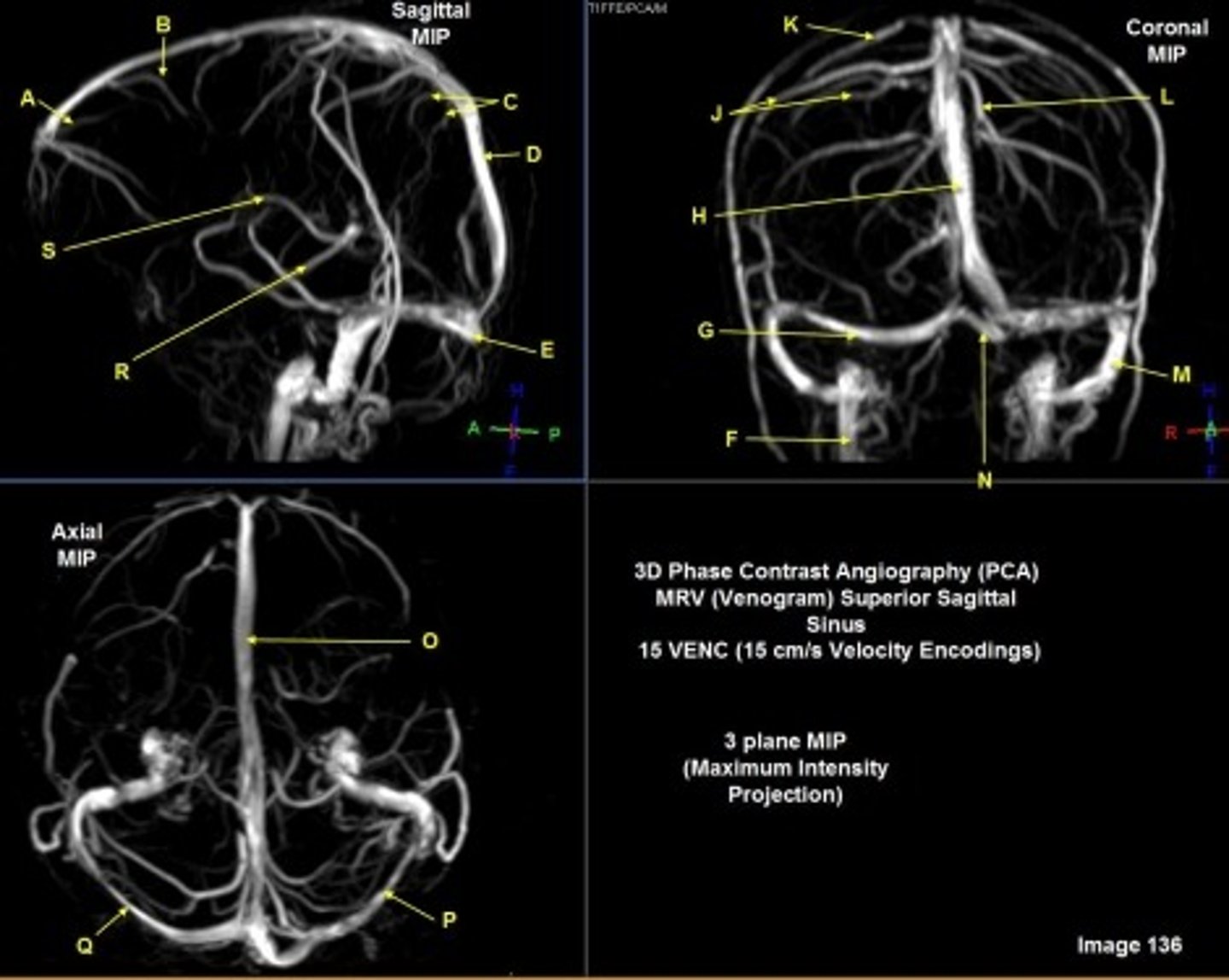
D
superior sagittal sinus
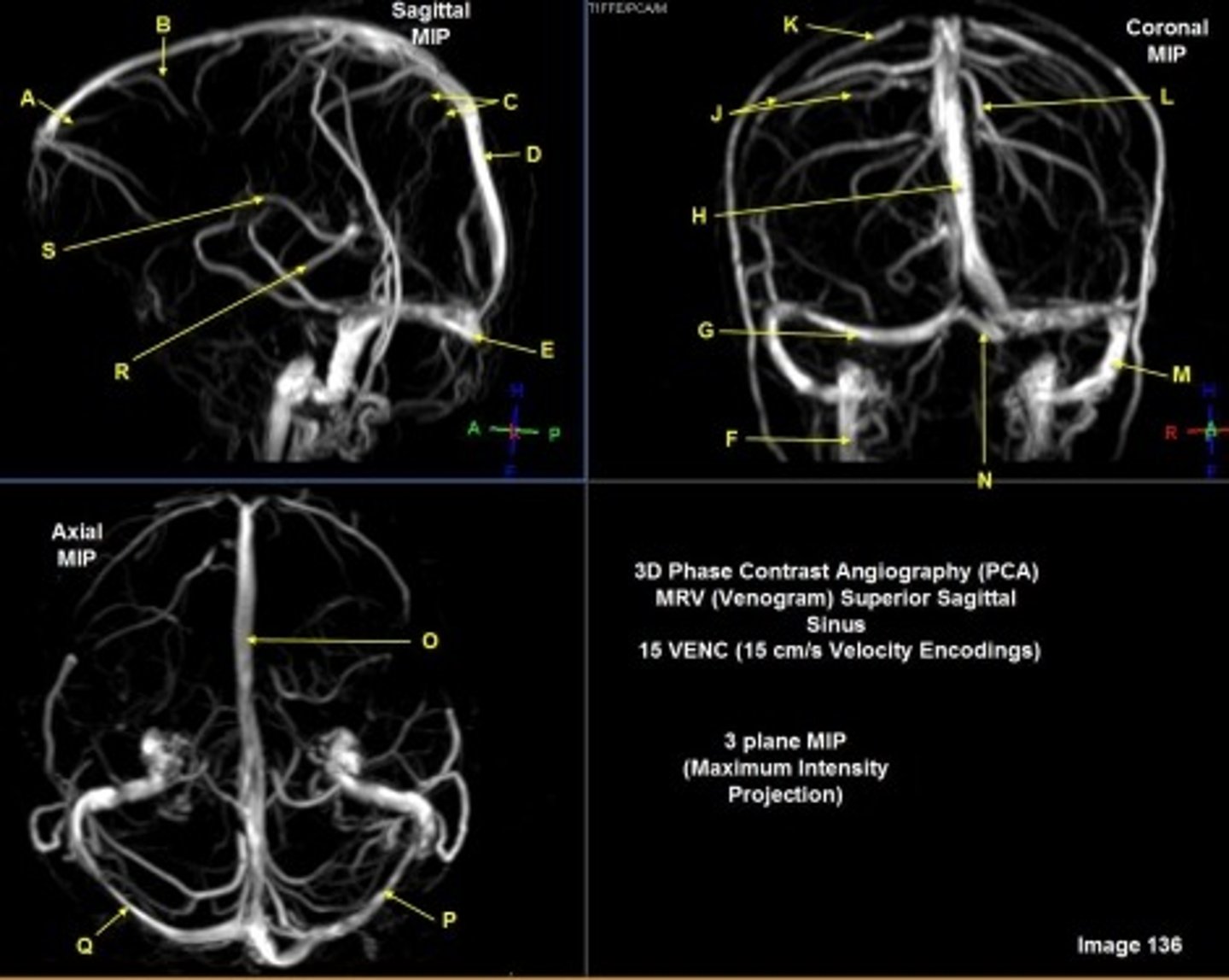
E
Torcular herophili
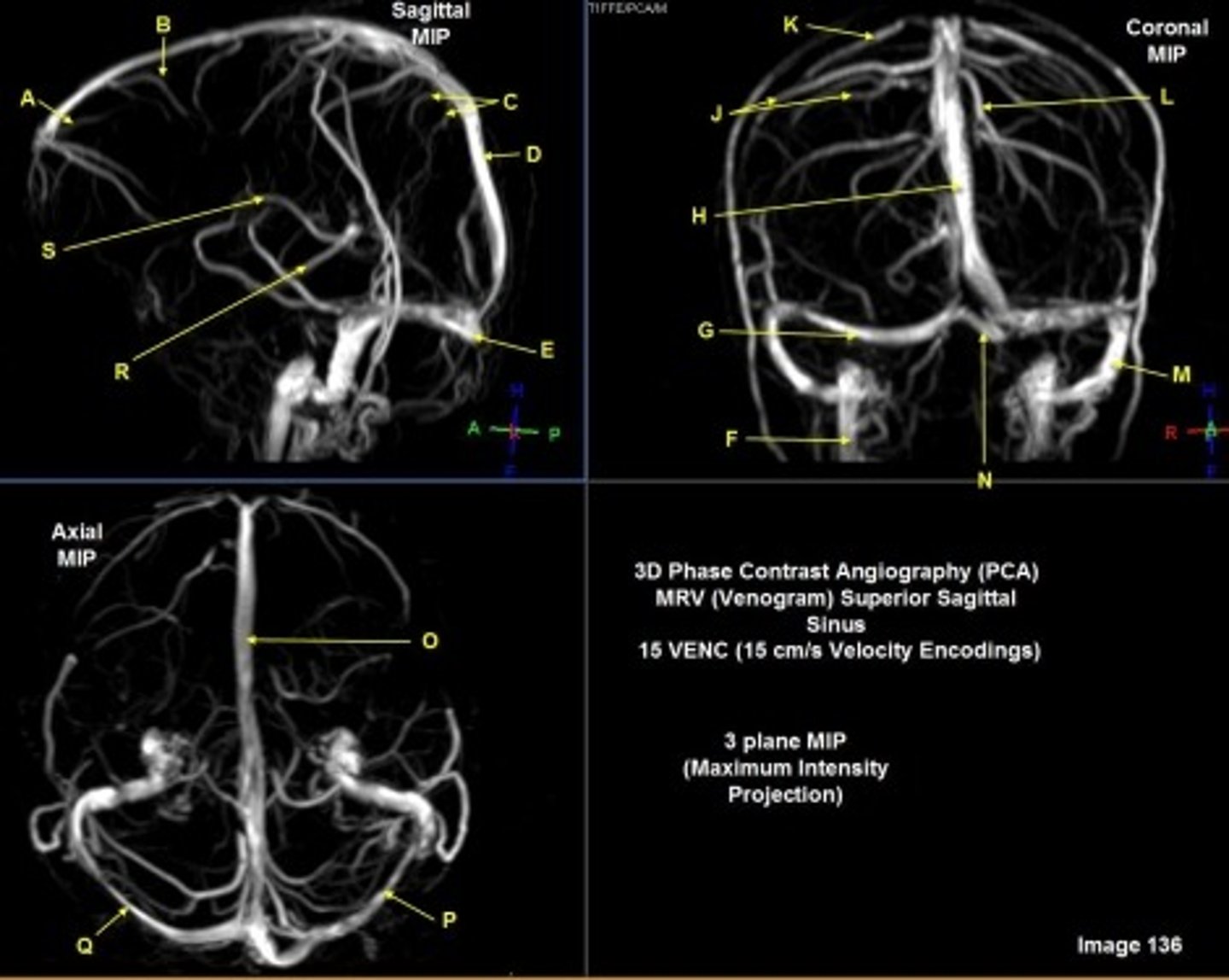
F
internal jugular vein
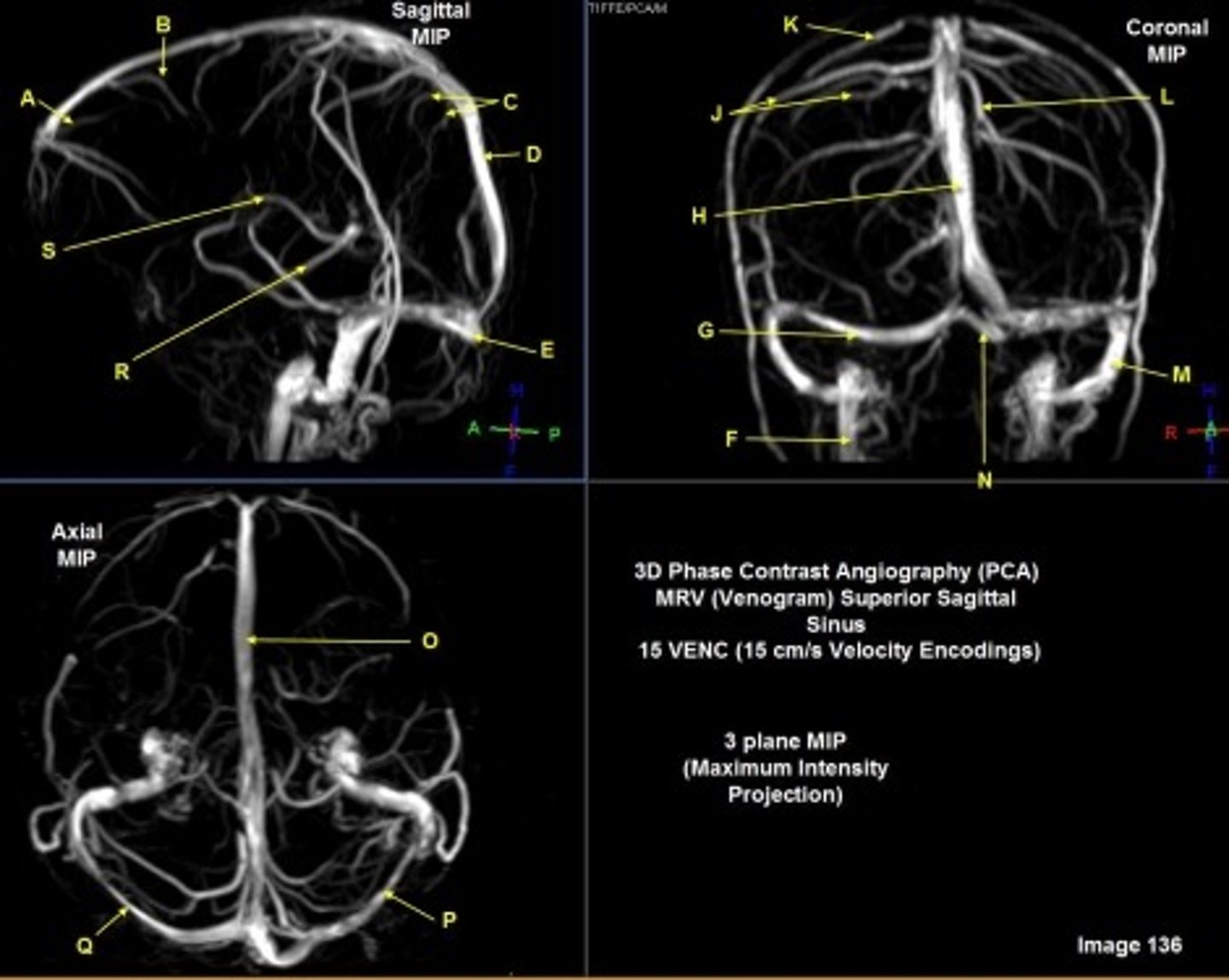
G
R transverse sinus
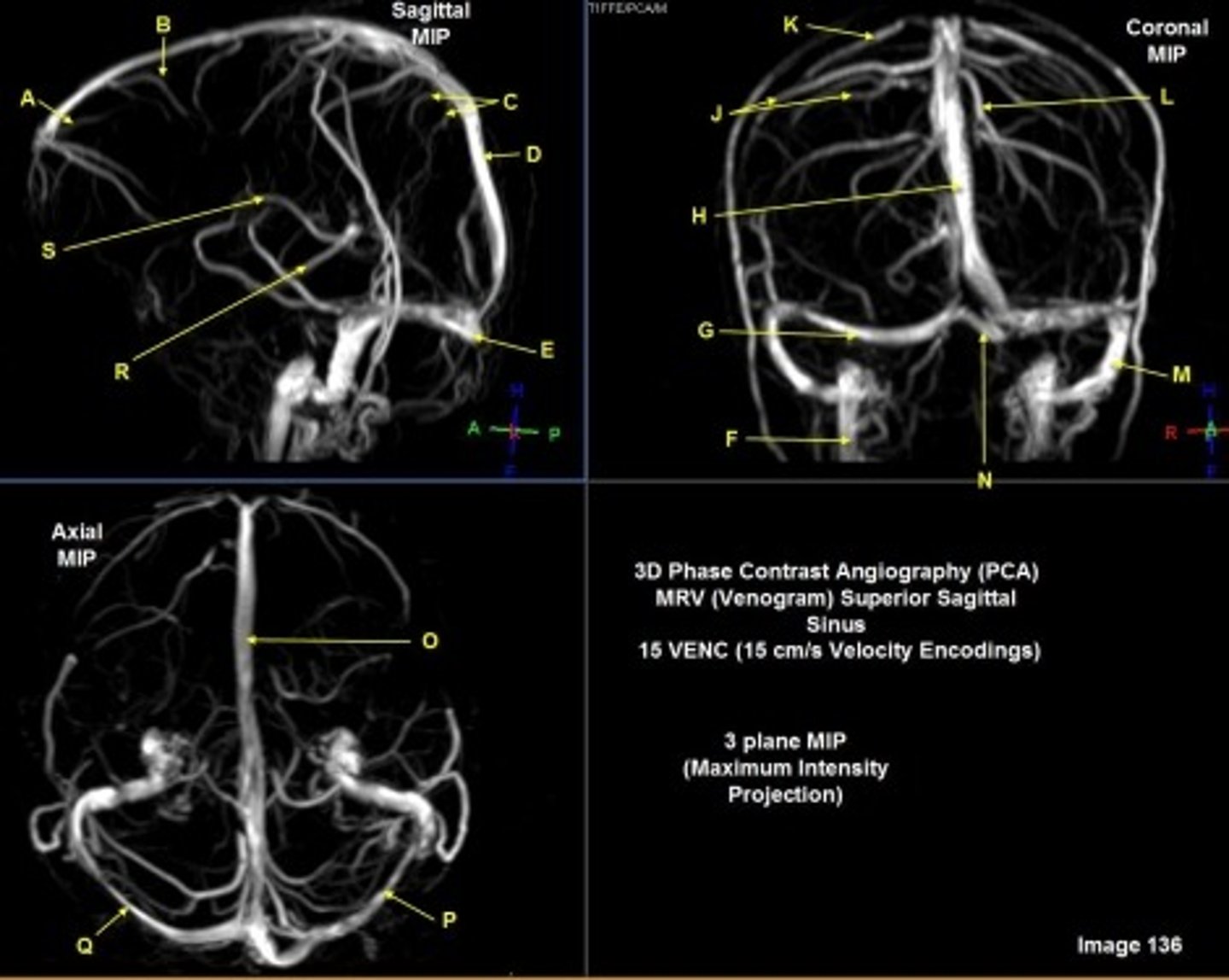
H
Superior sagittal sinus
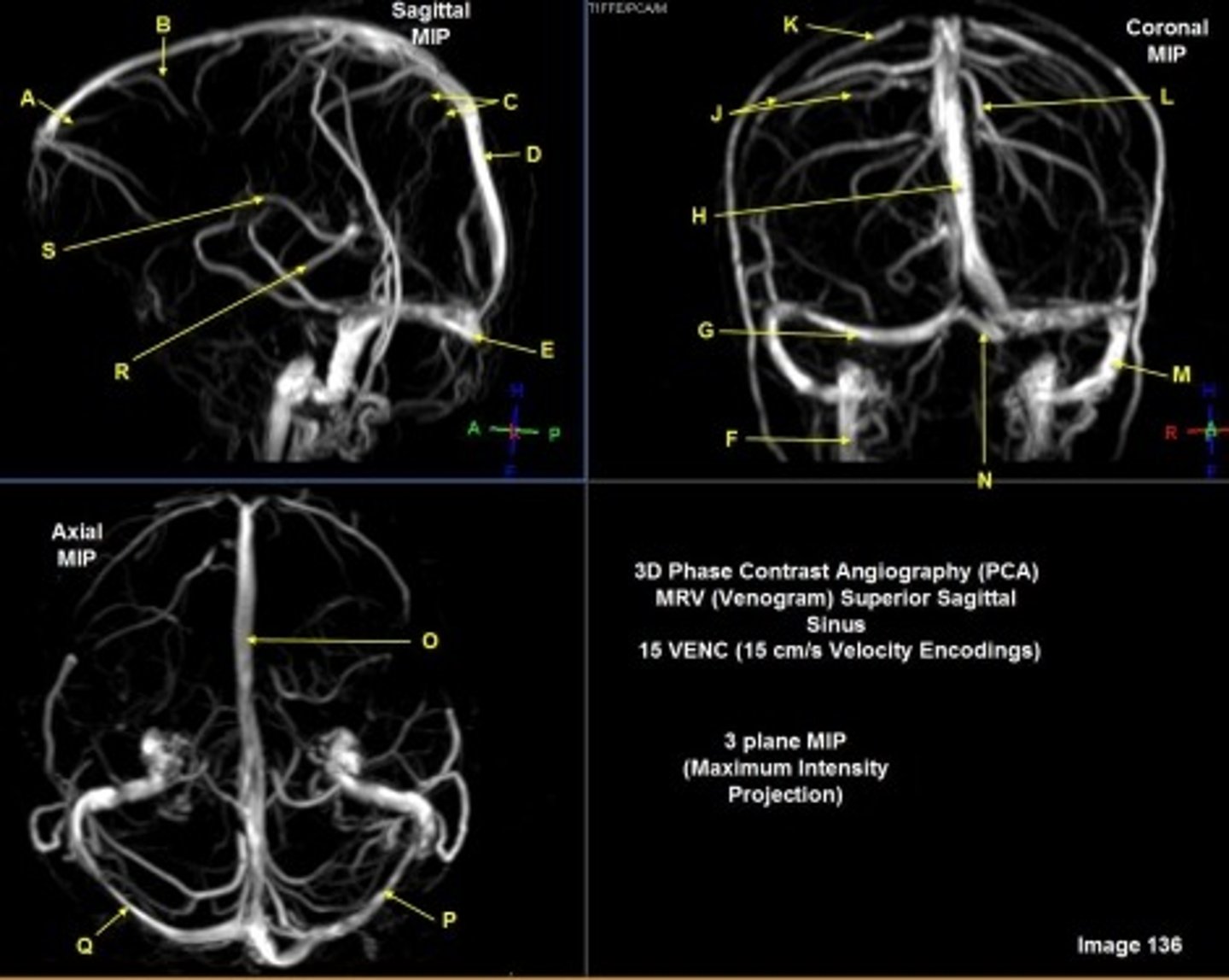
J
R parietal veins
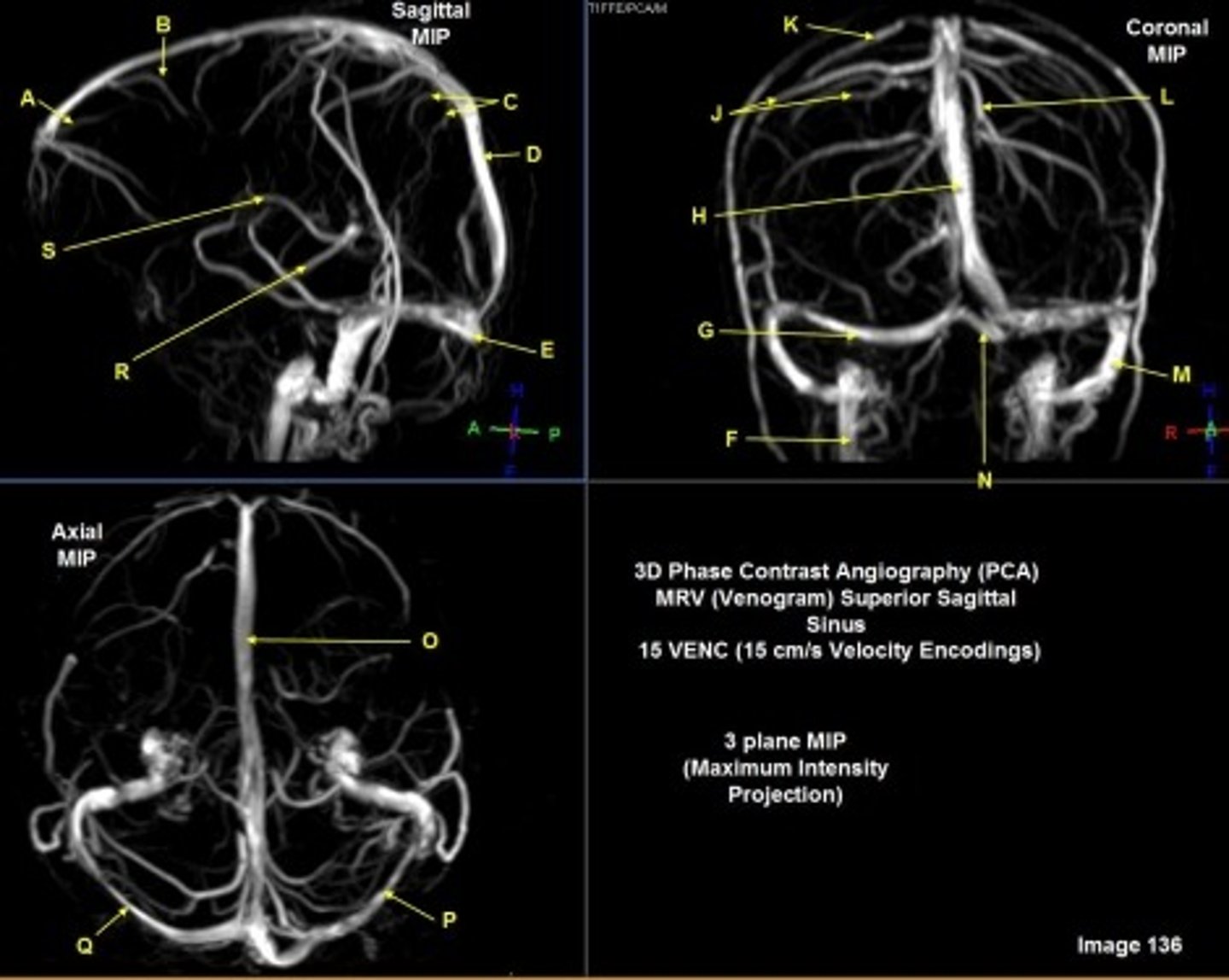
L
L parietal veins
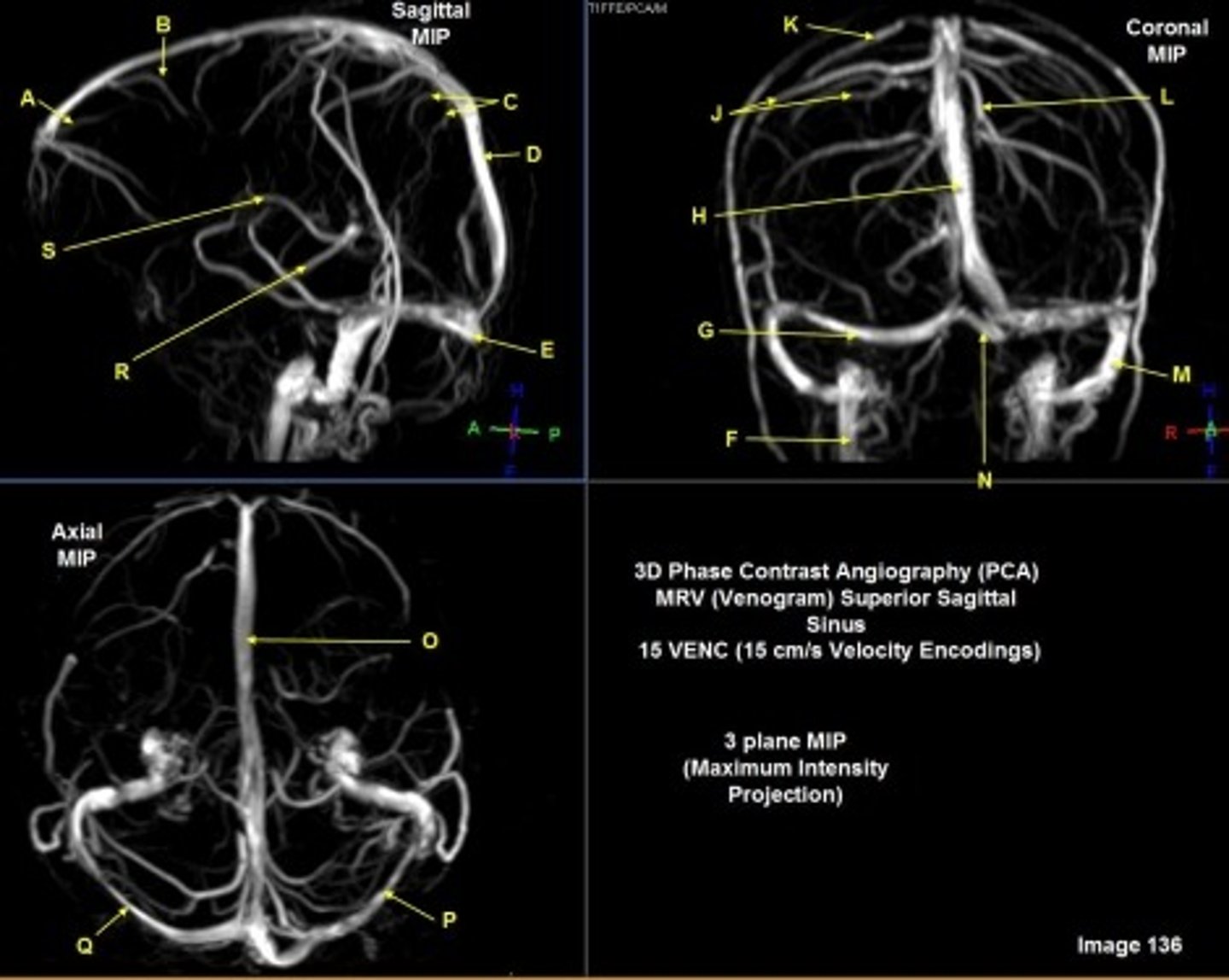
K
Vein of trolard (superior anastomotic vein)
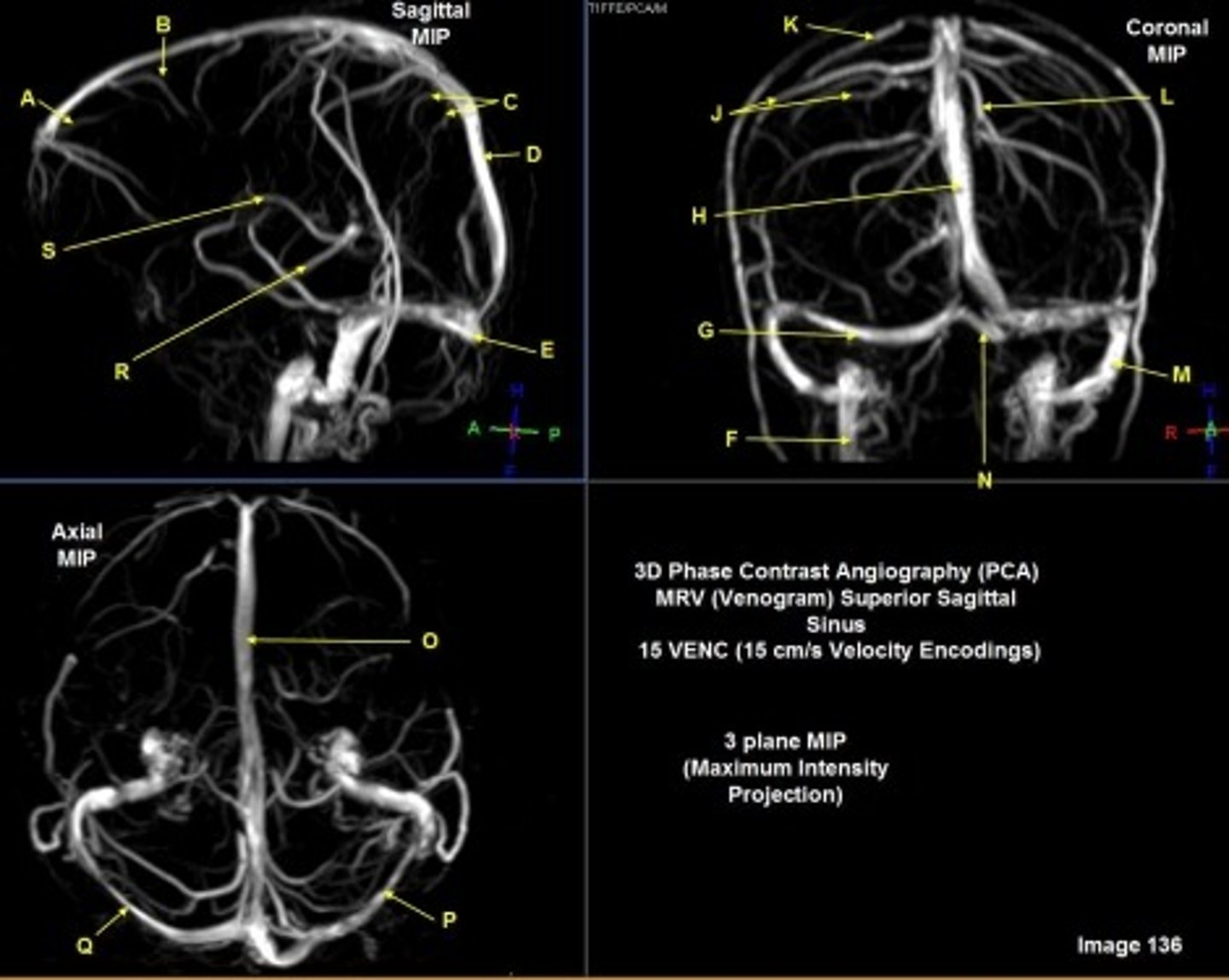
M
Left sigmoid sinus
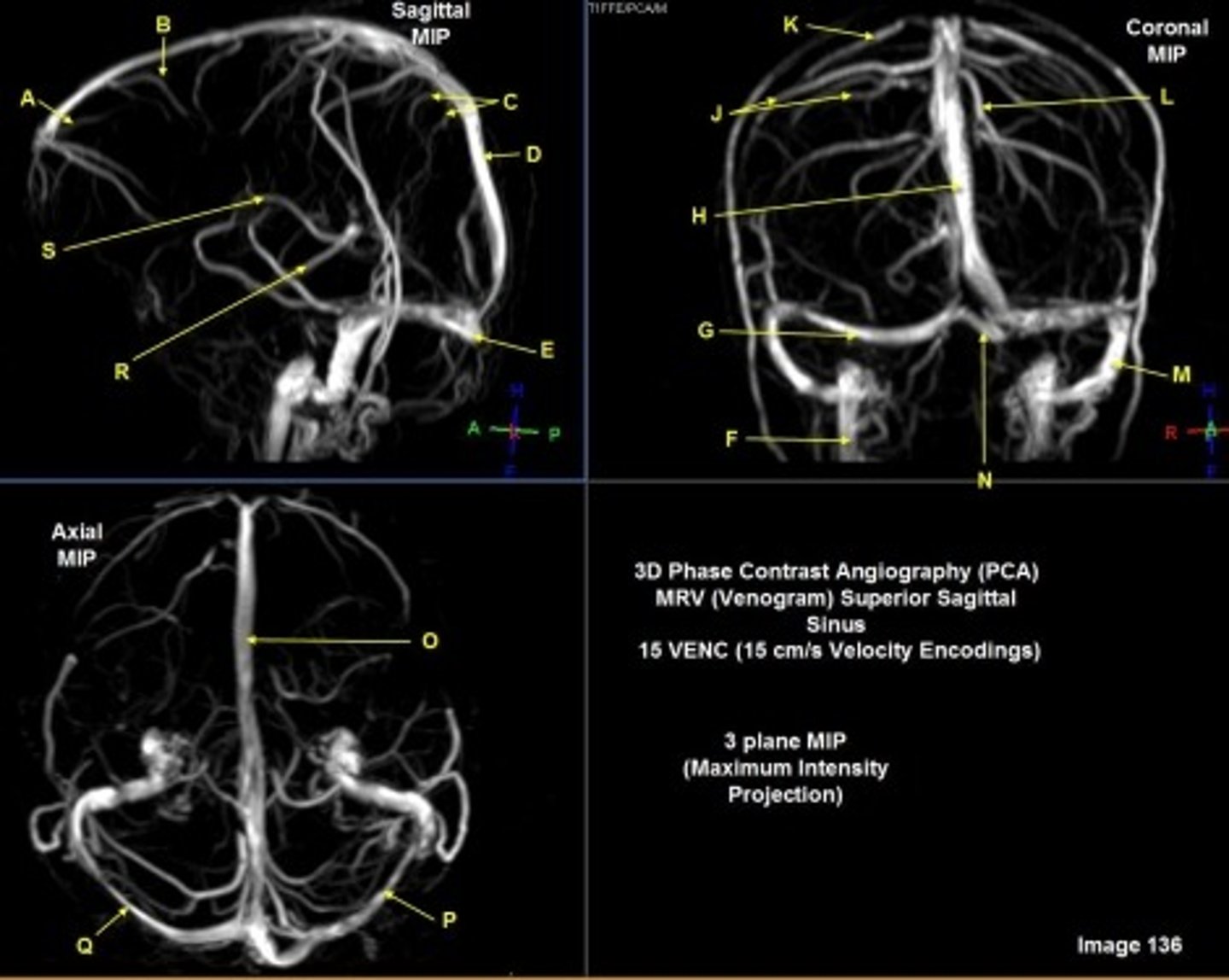
N
Torcular herophili
O
Superior sagittal sinus
P
Left transverse sinus
S
Internal cerebral vein
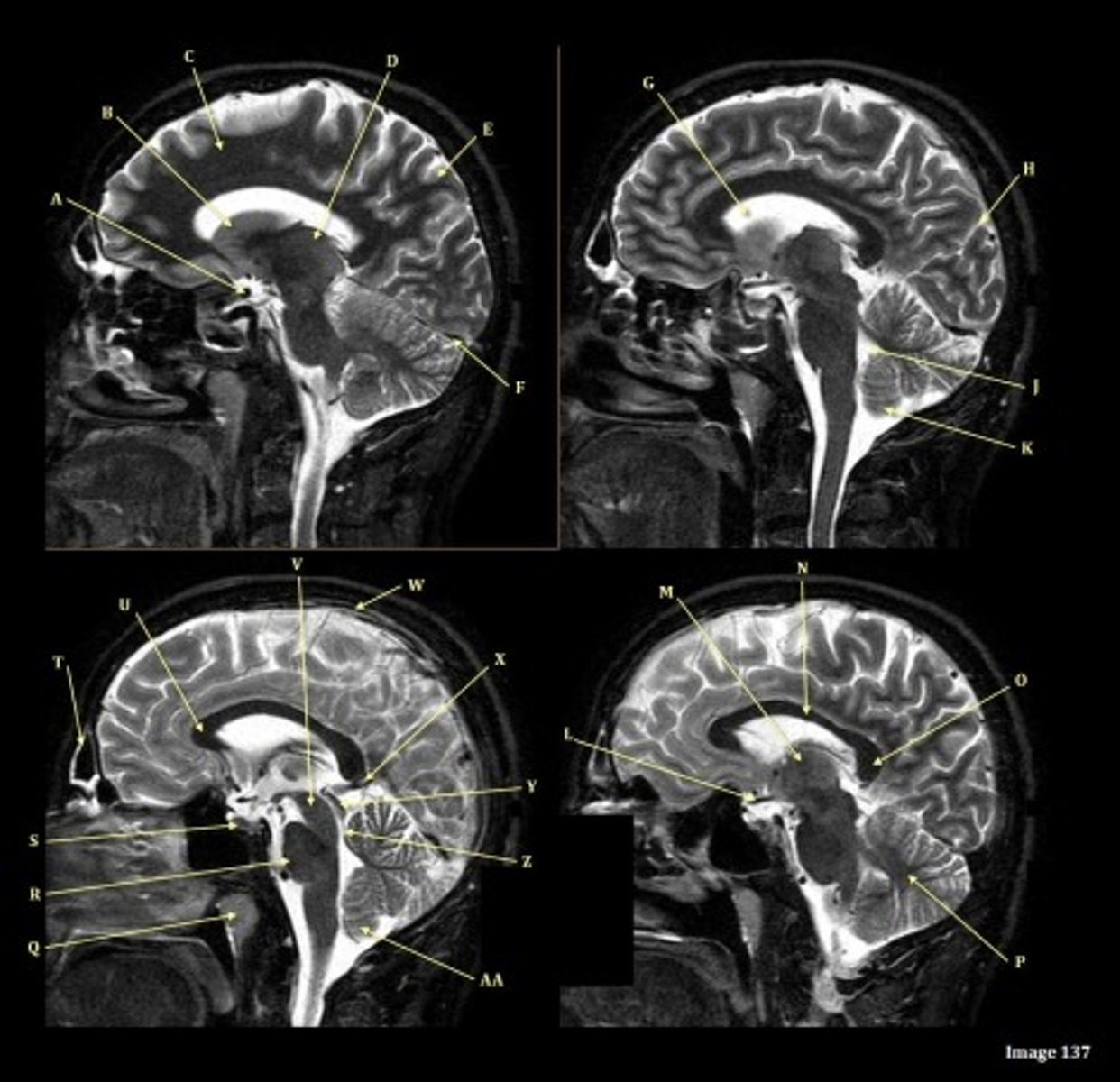
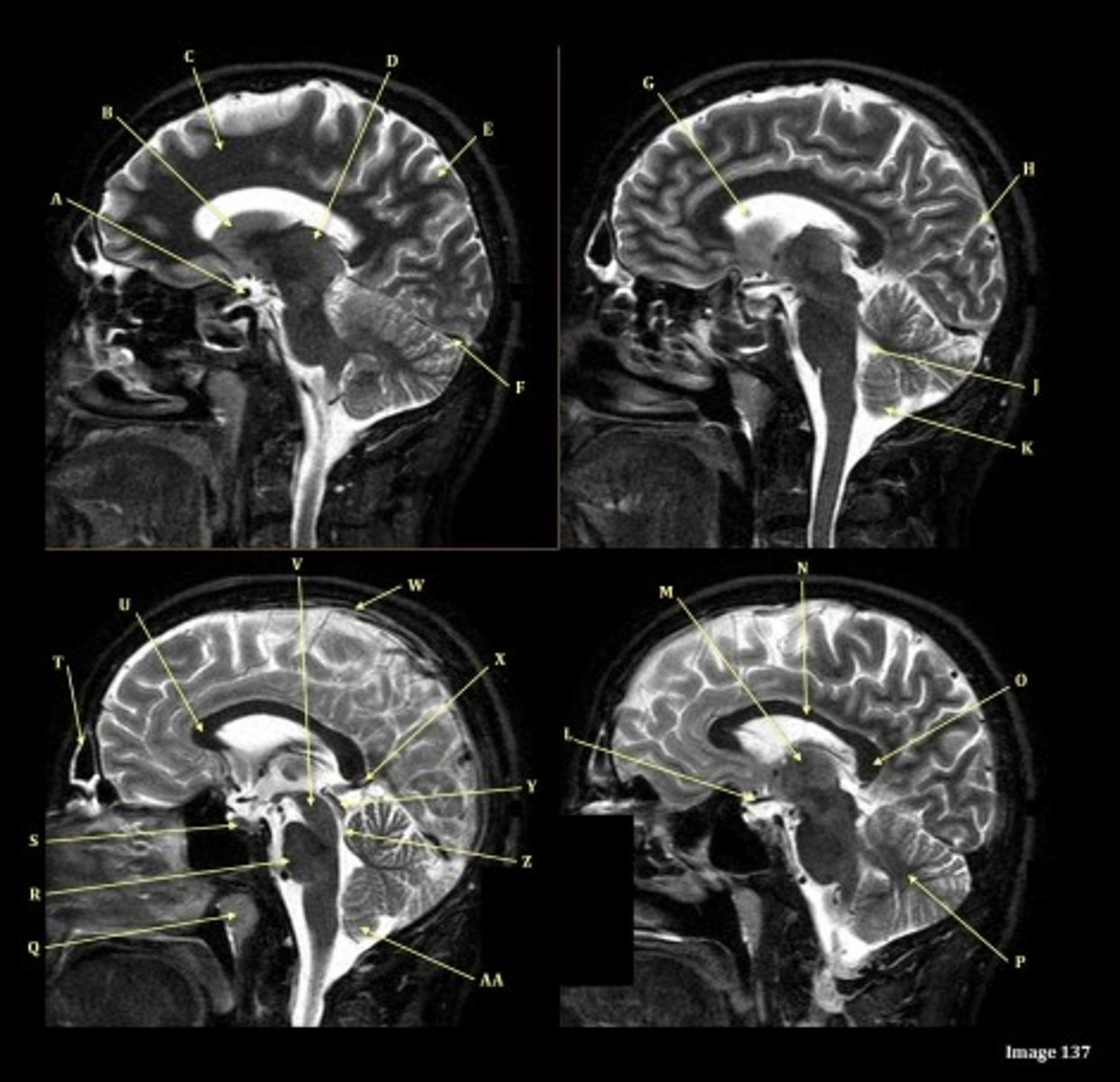
A
Internal carotid artery
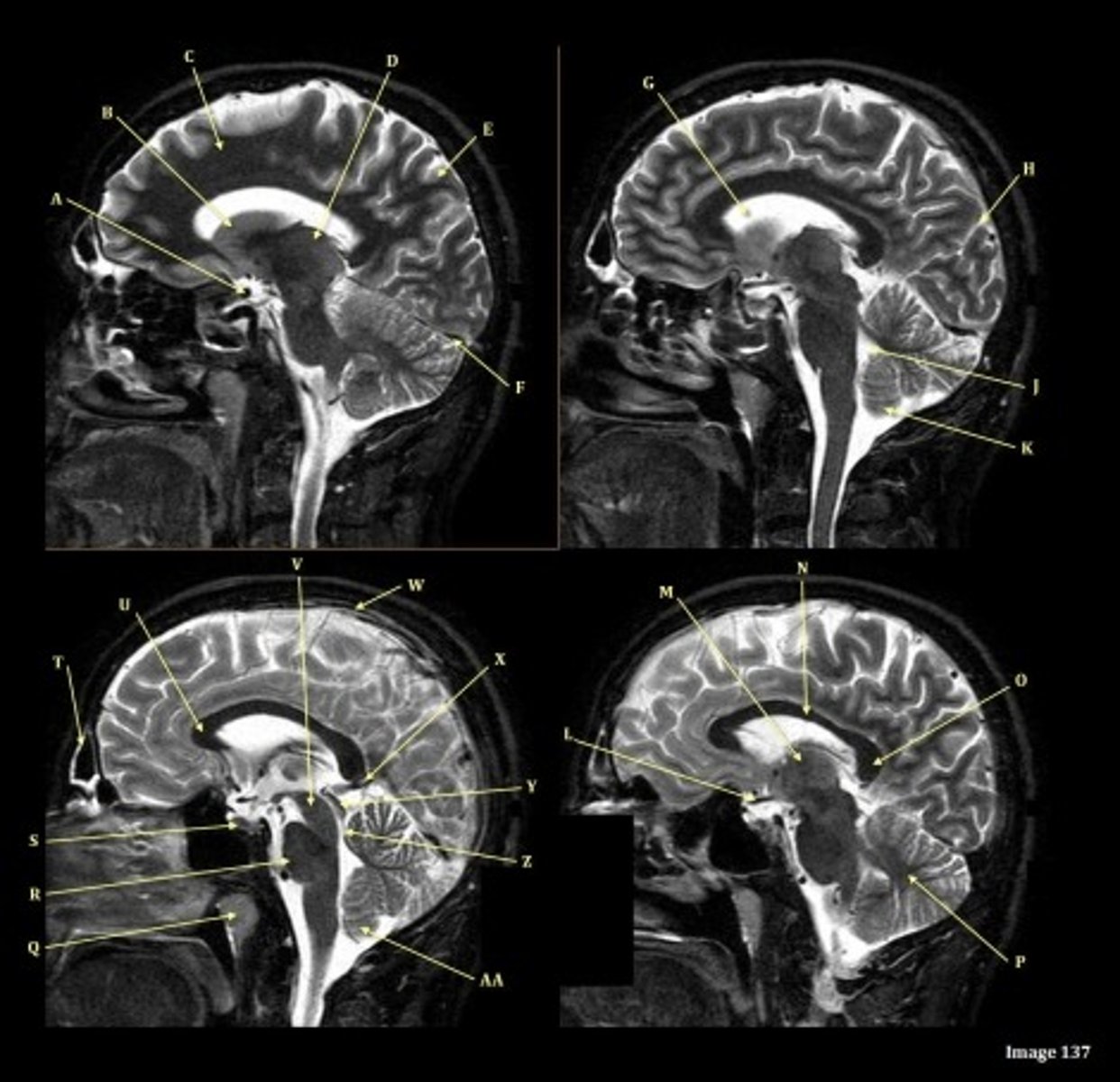
B
Caudate nucleus
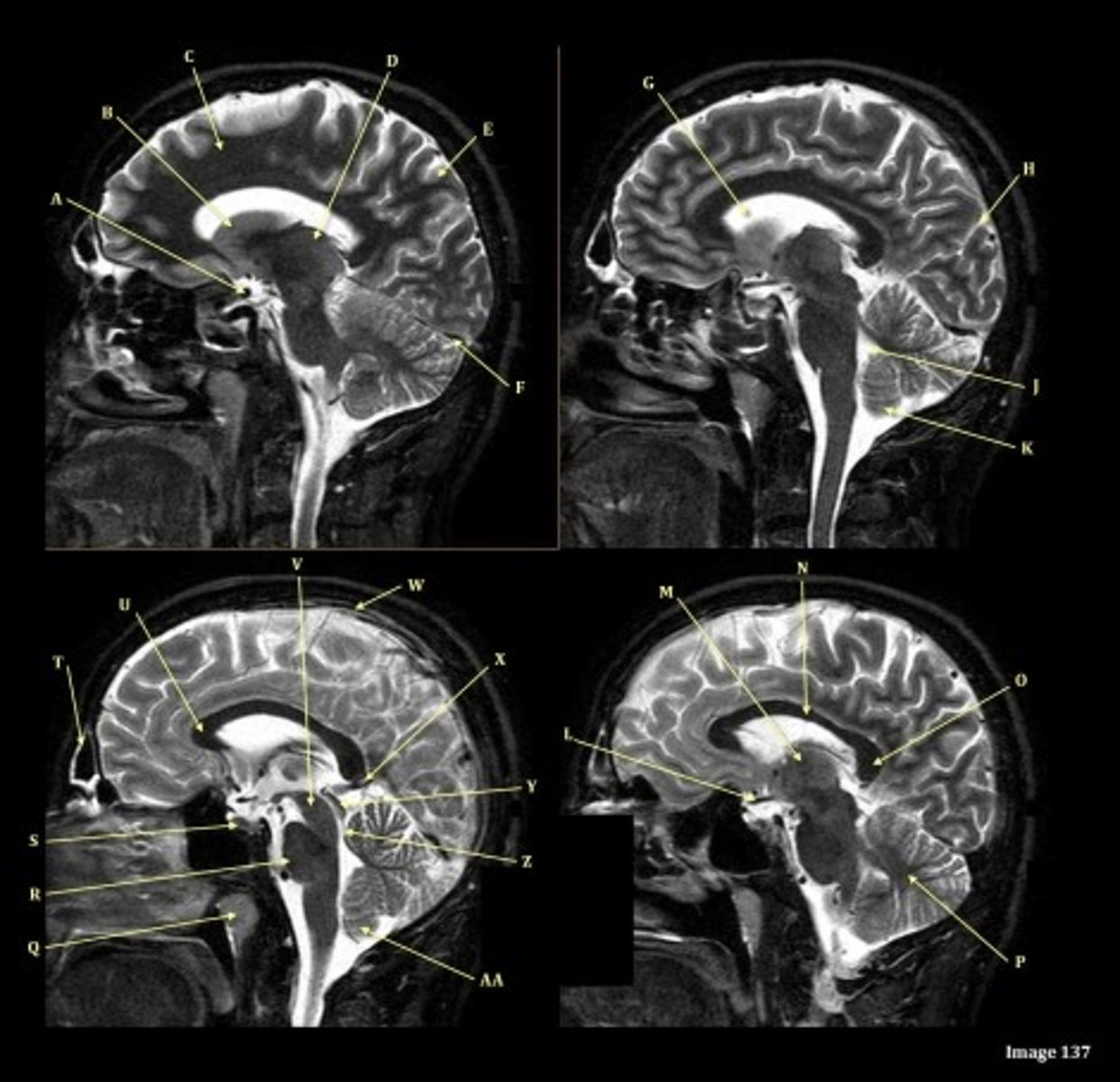
C
white matter
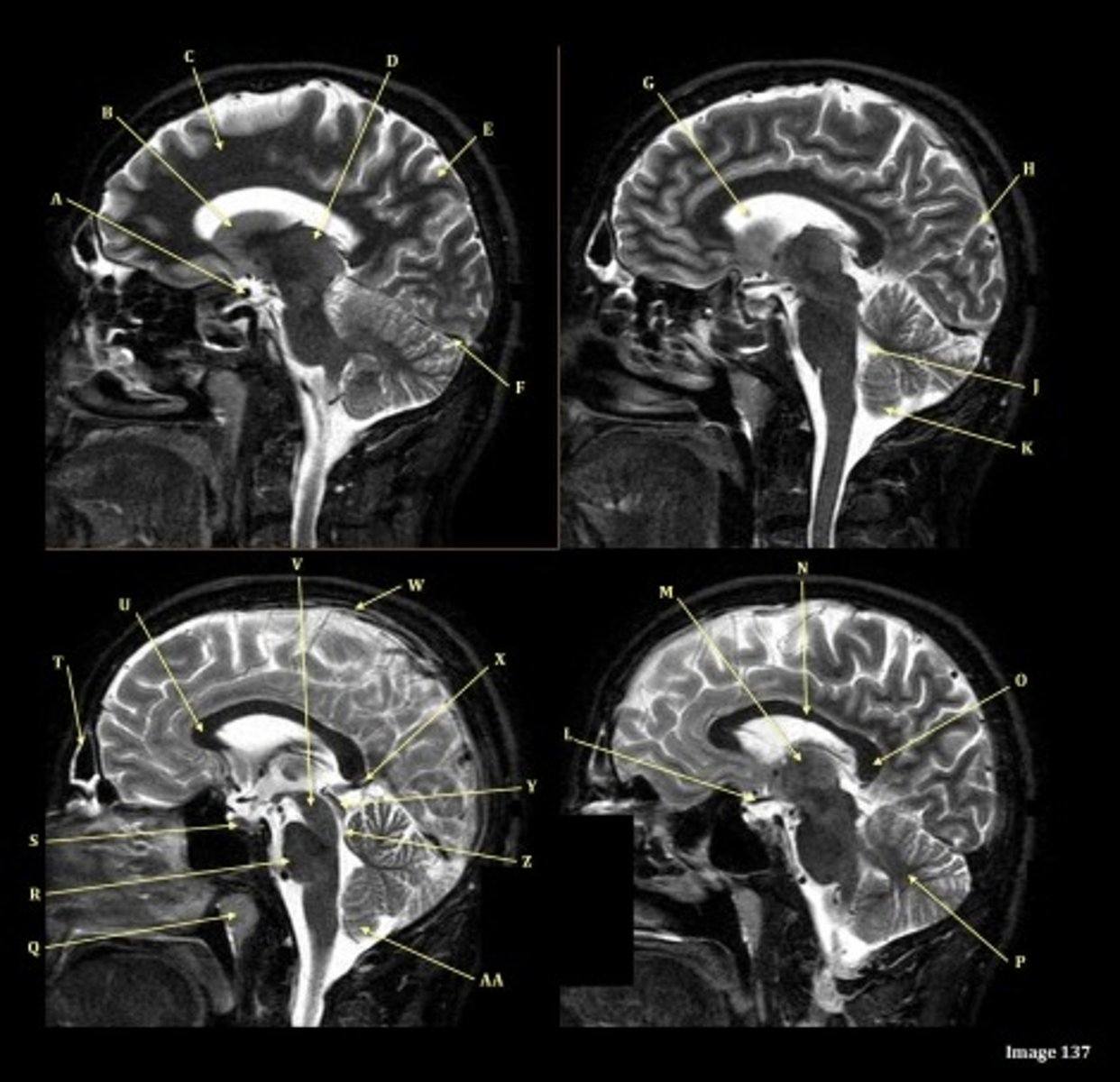
D
thalamus
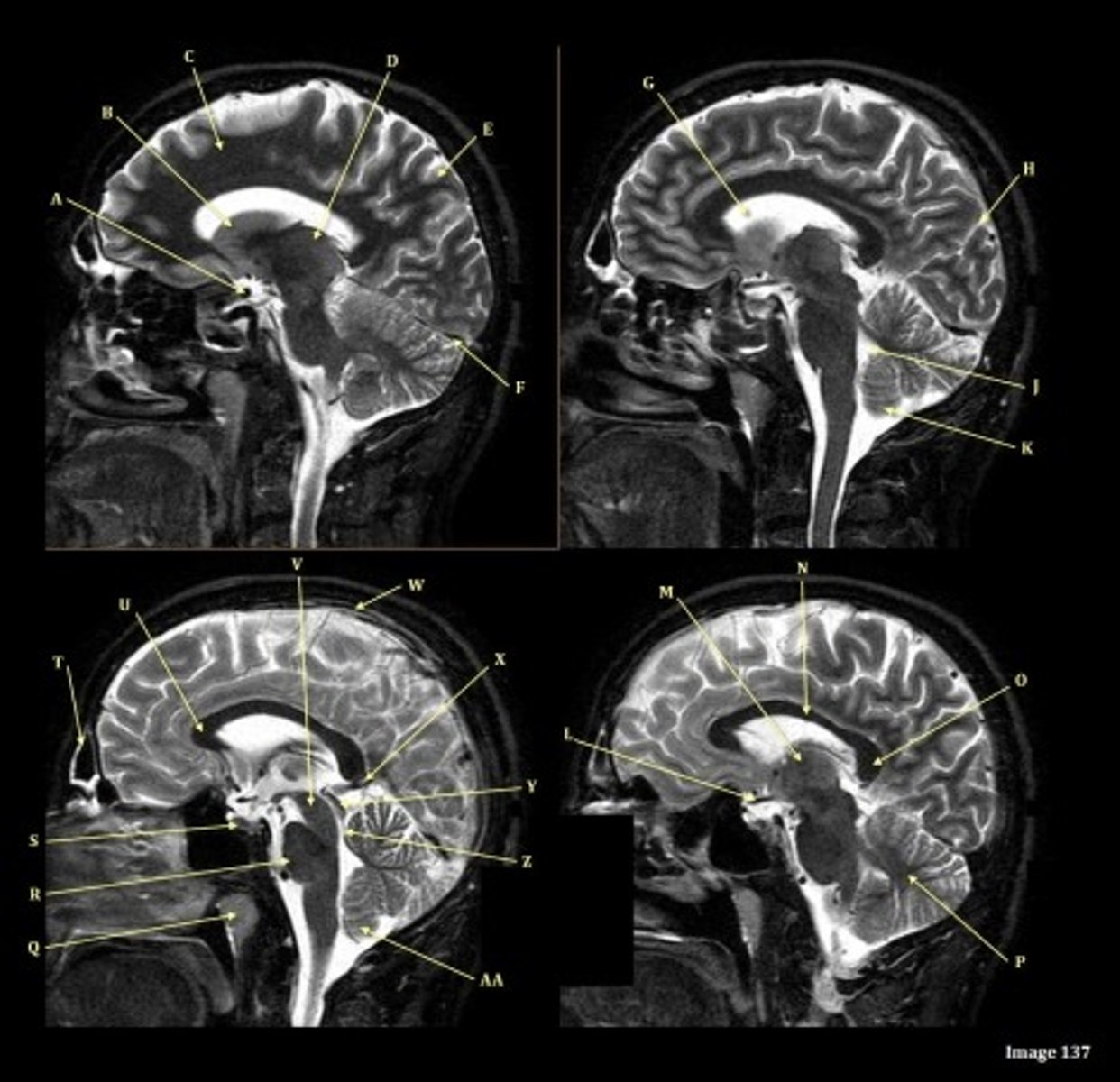
F
straight sinus
G
lateral ventricle
H
lateral sulcus
L
optic chiasm
O
Splenium of corpus callosum
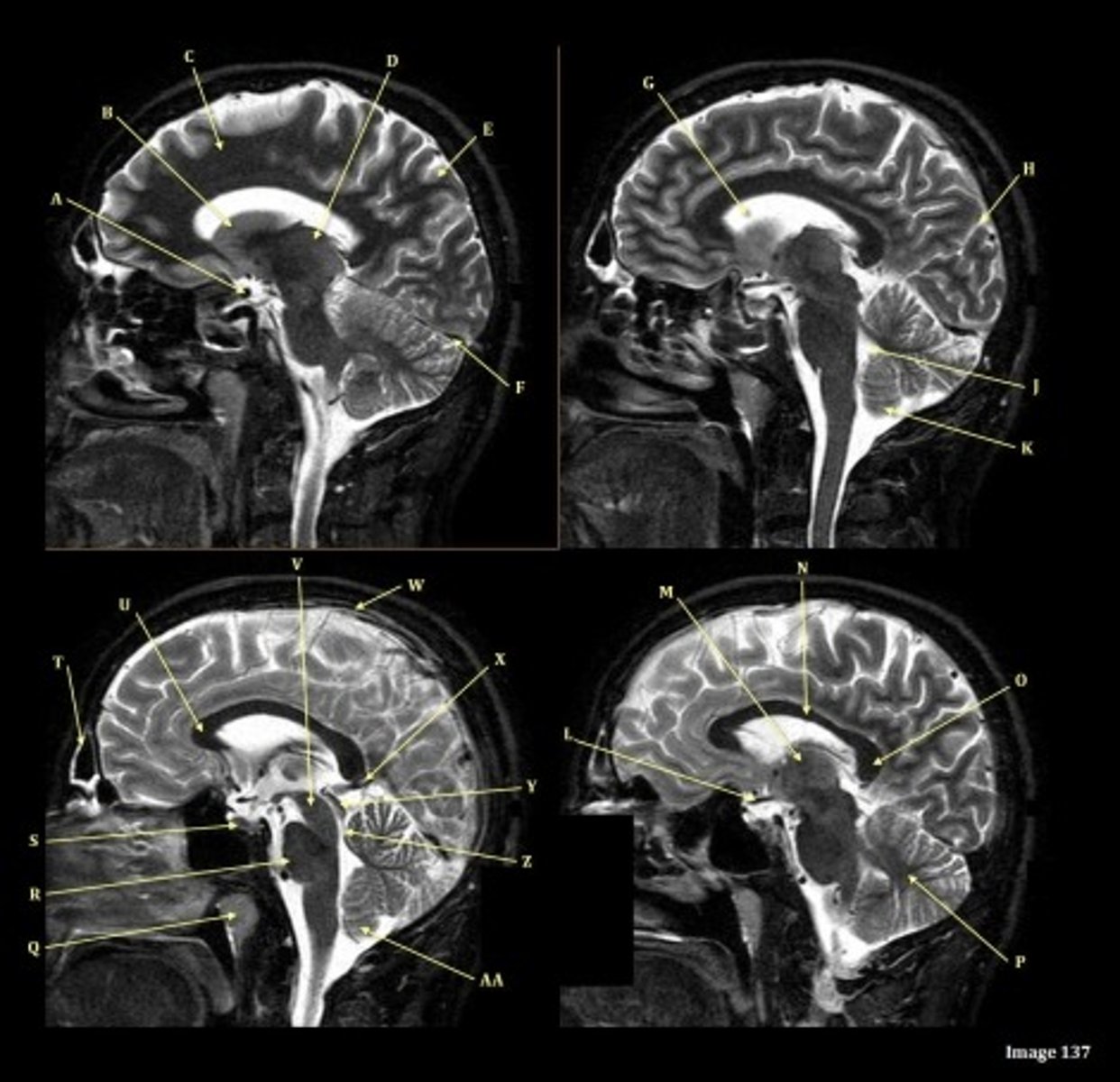
V
Cerebral peduncle
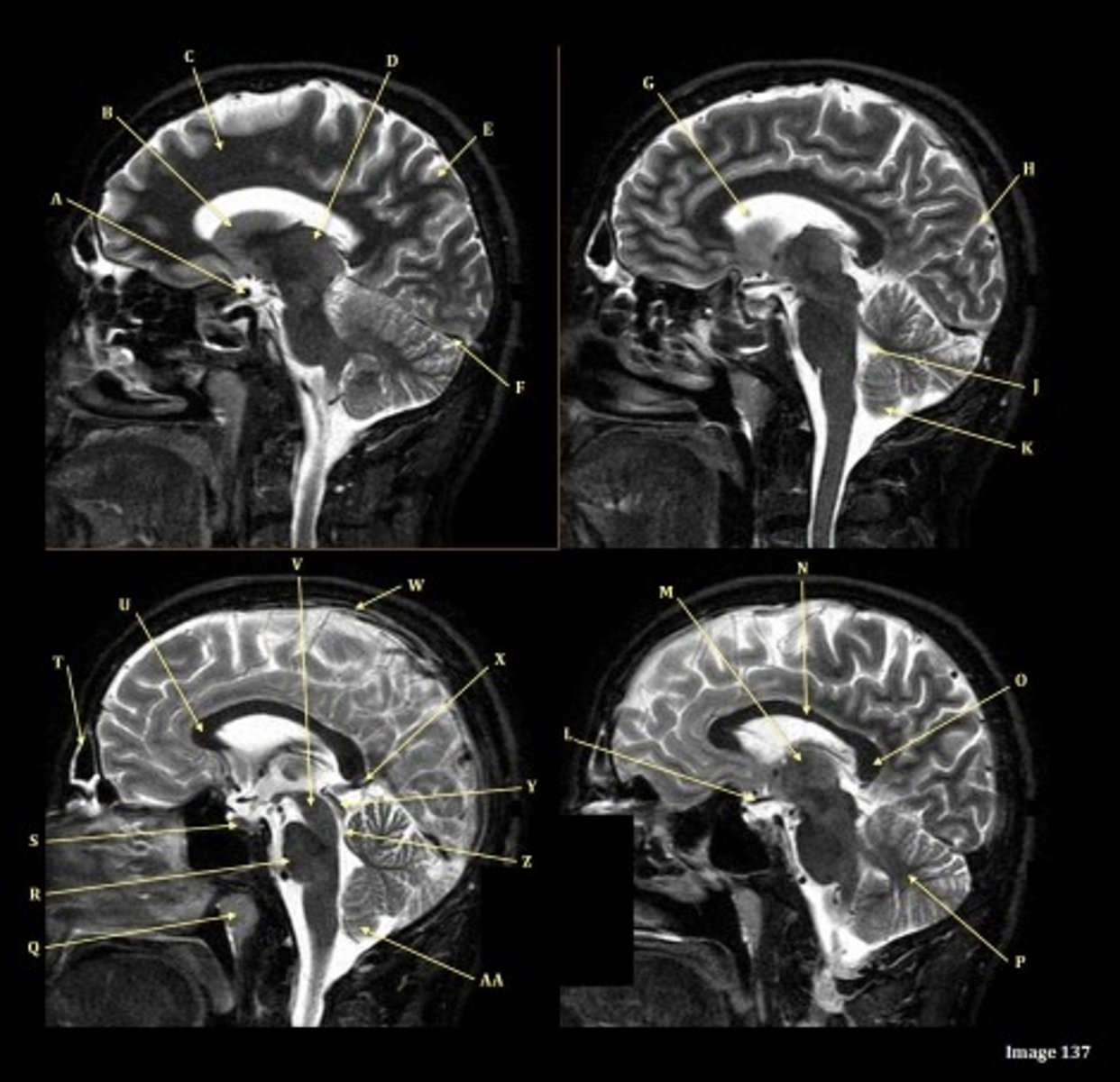
W
superior sagittal sinus
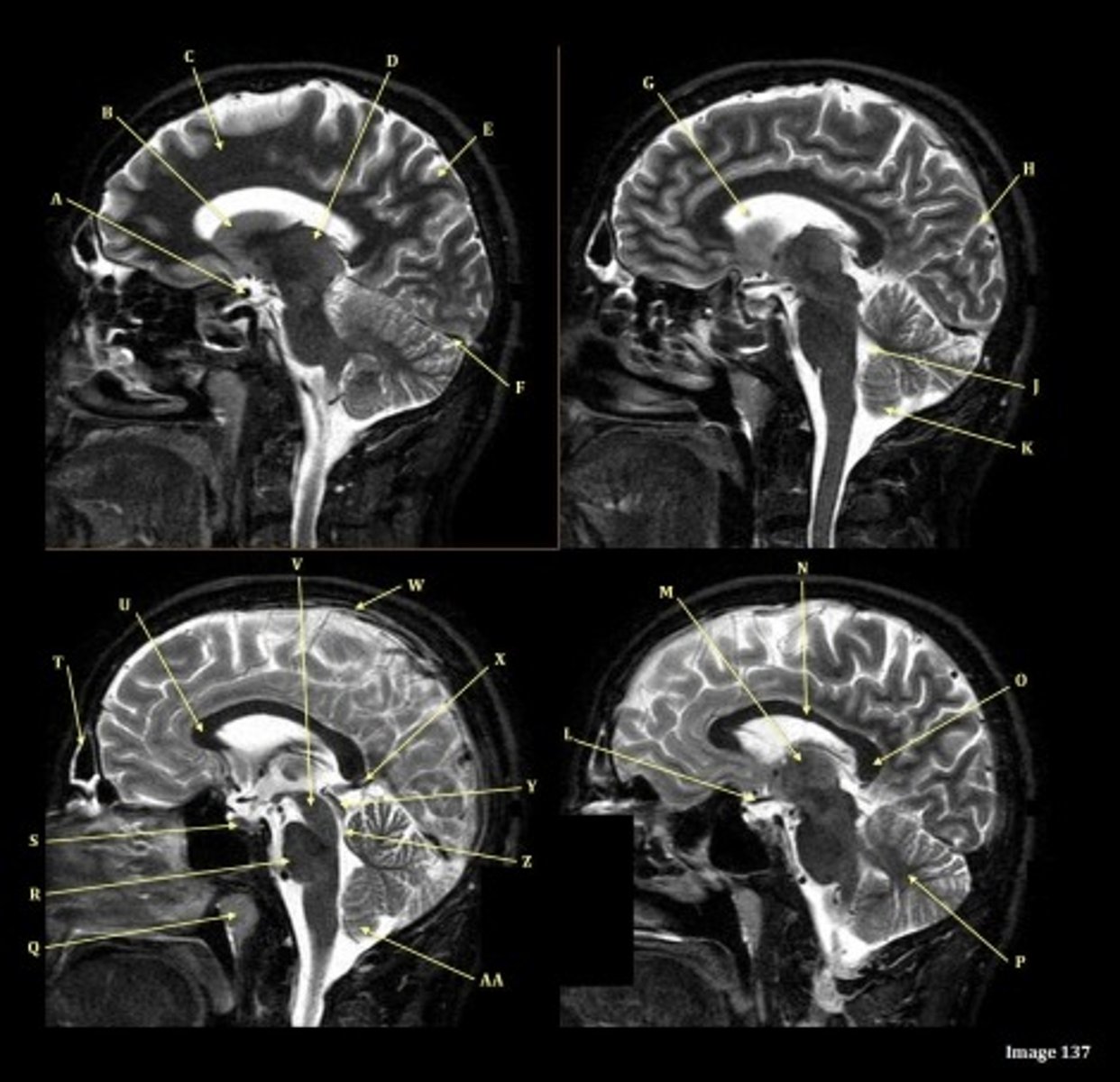
X
vein of galen
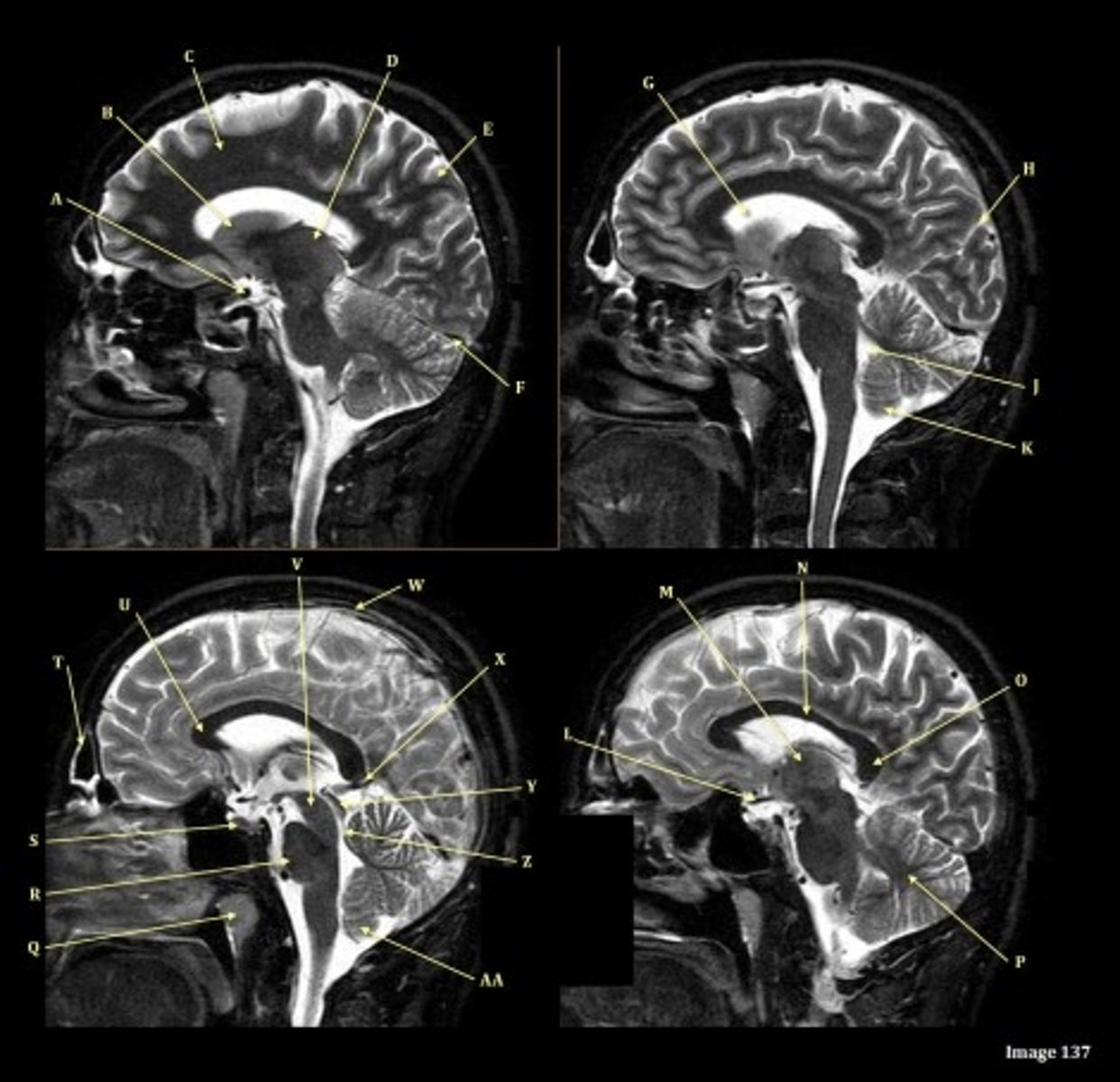
Y
Inferior colliculus of midbrain,
just inferior to pineal gland / superior to the cerebral aqueduct
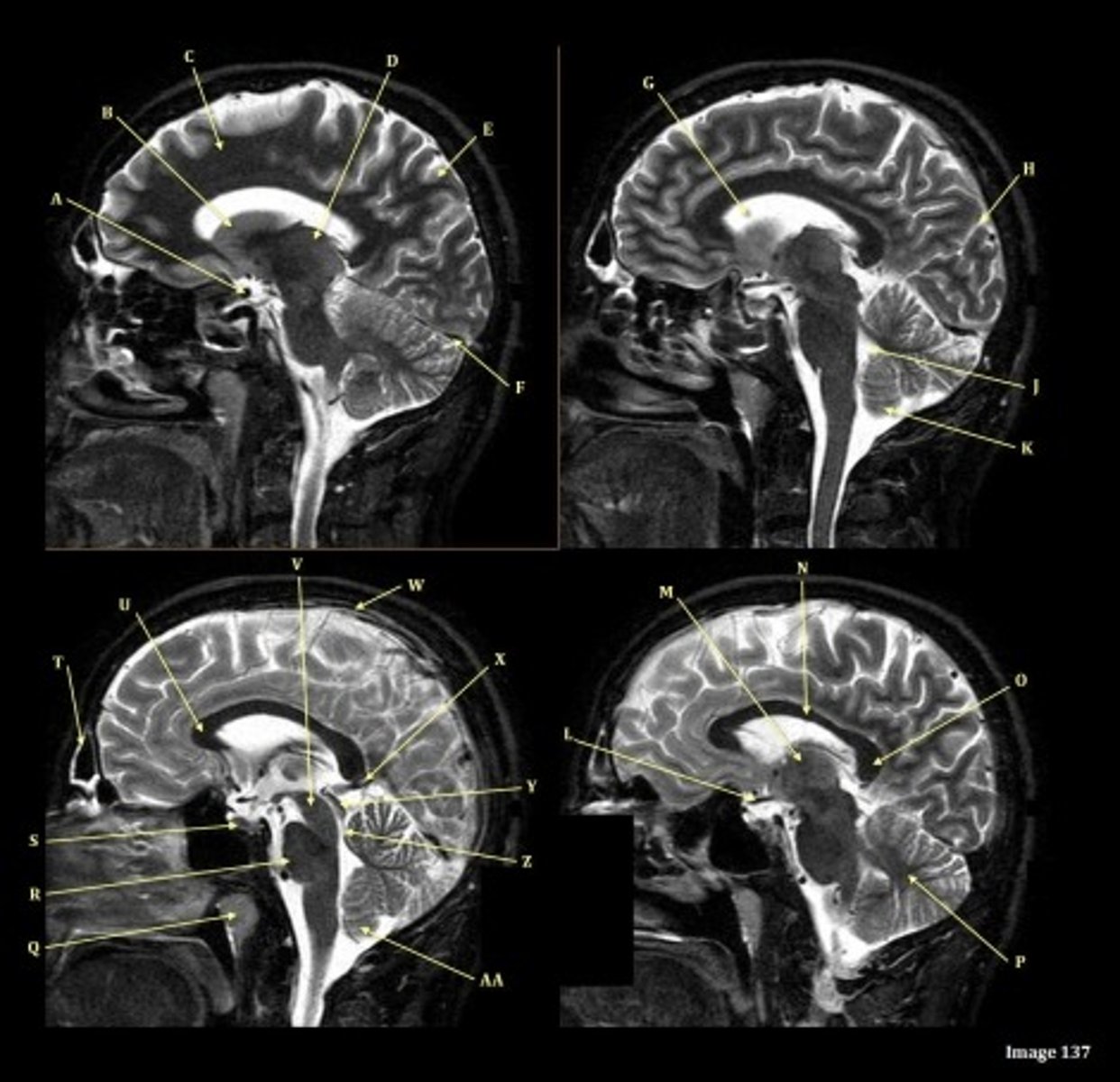
Letter N in Image 137 is pointing to what type of tissue?
White matter
The corpus callosum is the only white matter tissue structure found in the midline sagittal slice of the brain.
Which arteries join together to form the basilar artery?
vertebral arteries
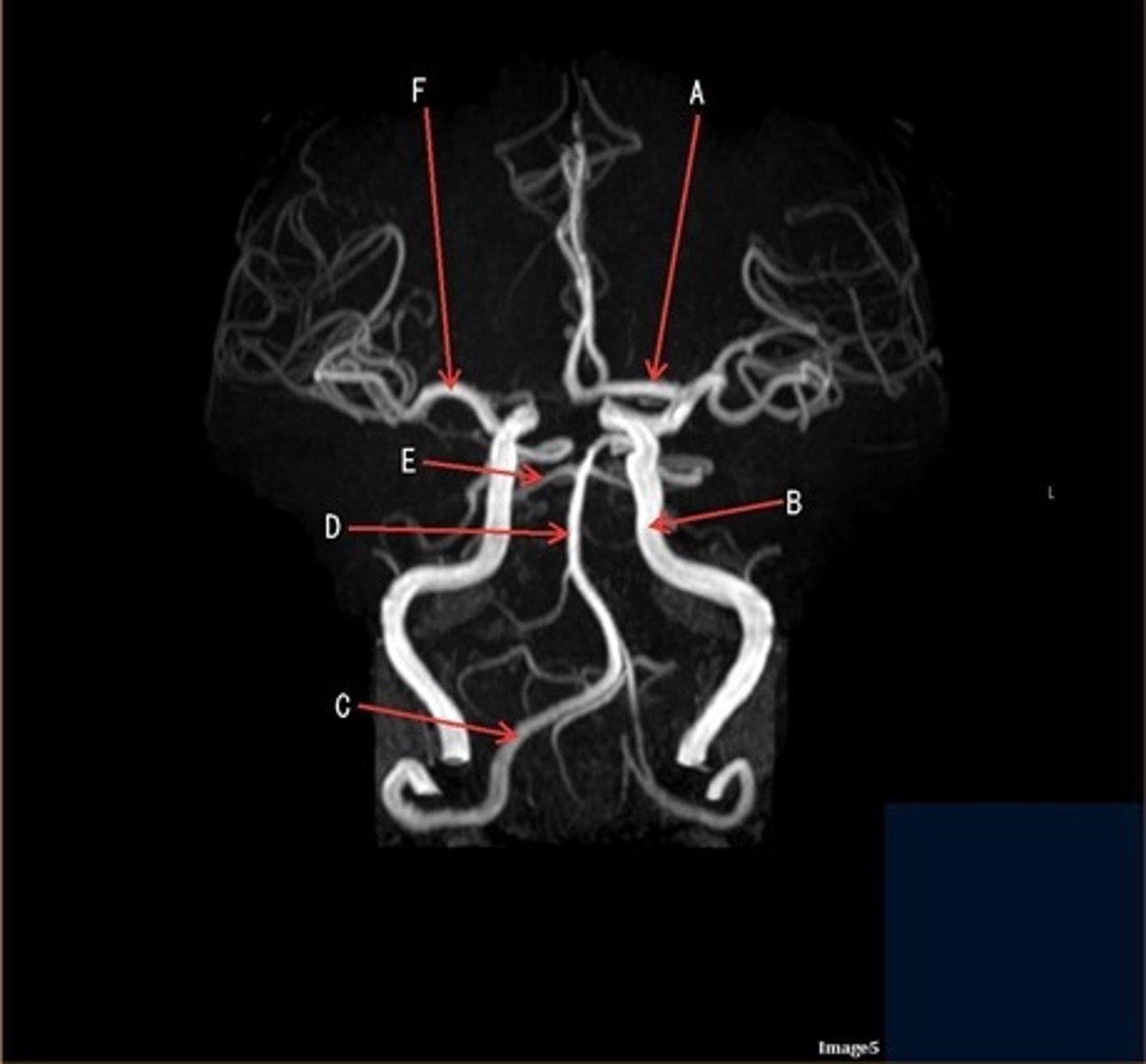
letter A
anterior cerebral artery
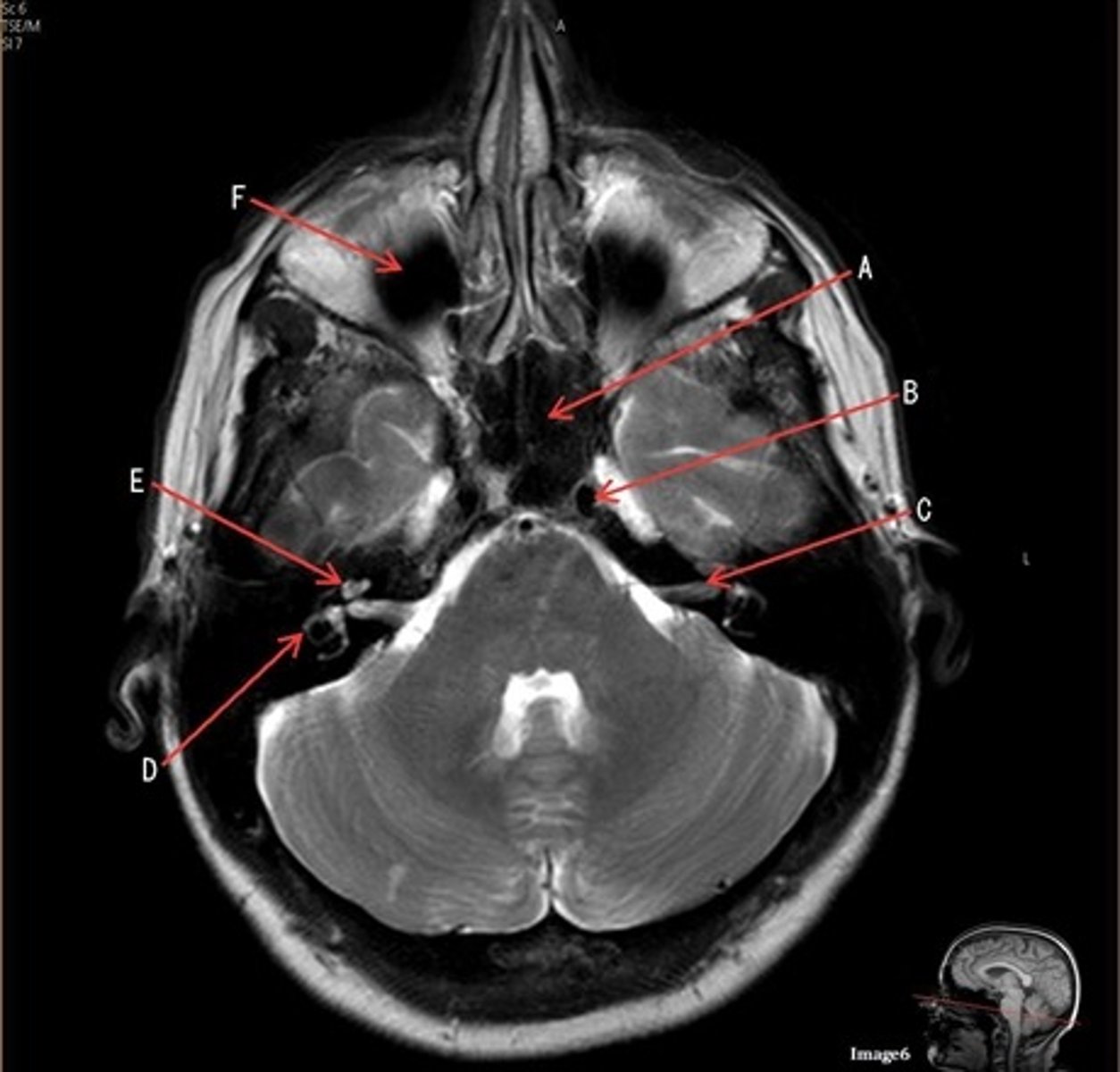
letter C
7th cranial nerve- facial
8th cranial nerve vestibulocochlear on other side (posterior) of semicircular canal
letter F
medulla oblongata
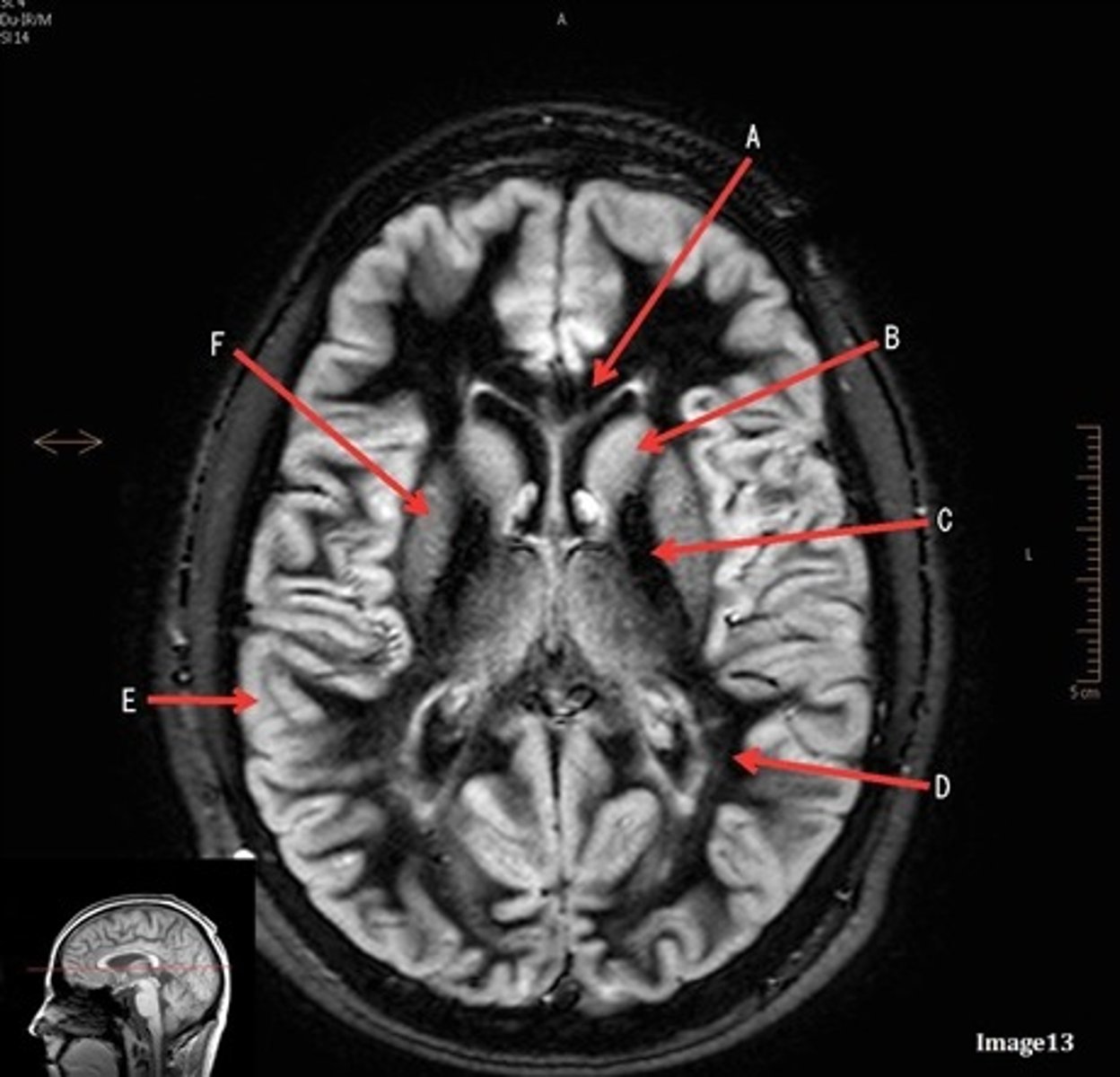
letter C
internal capsule
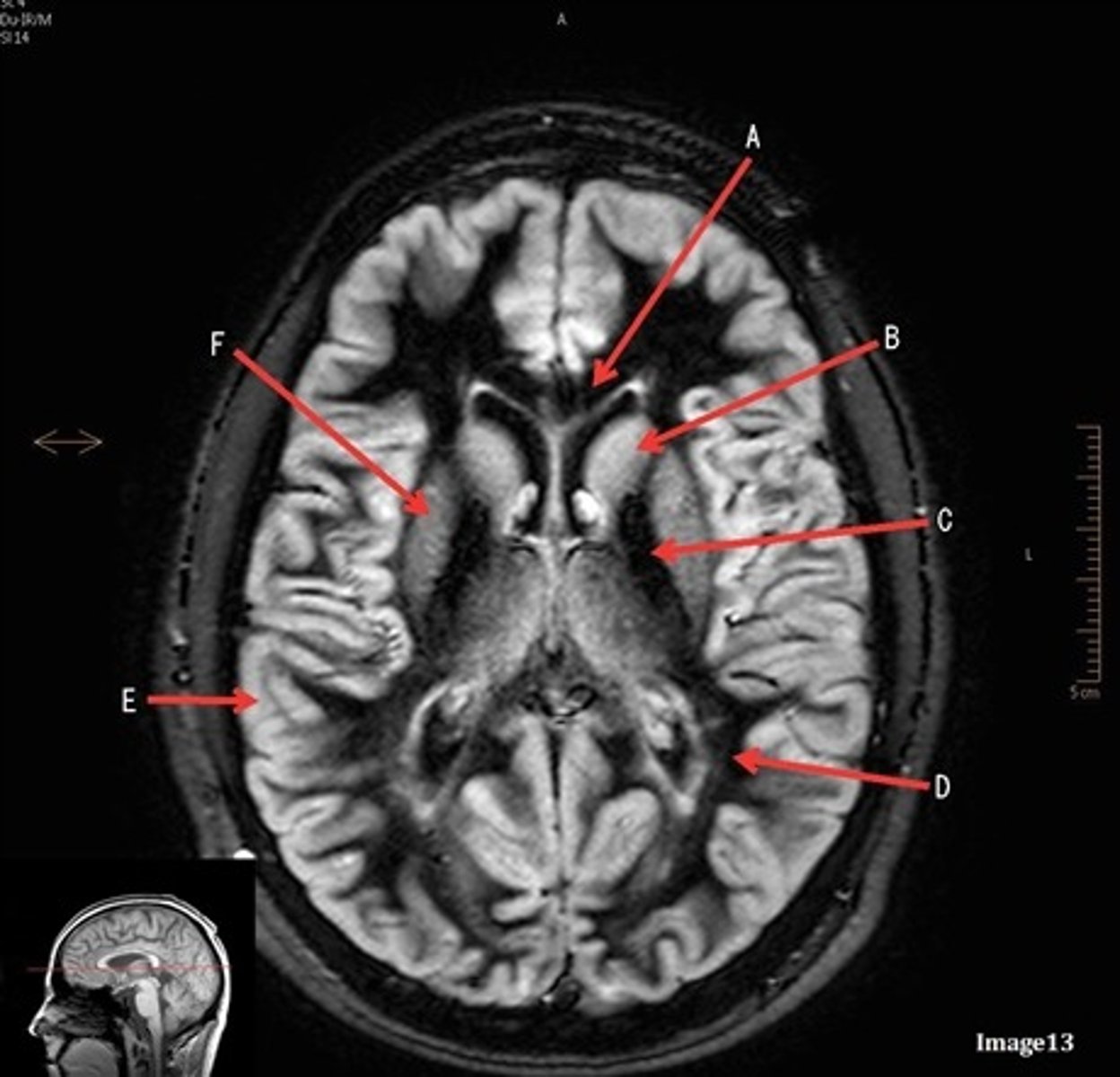
letter D
white matter
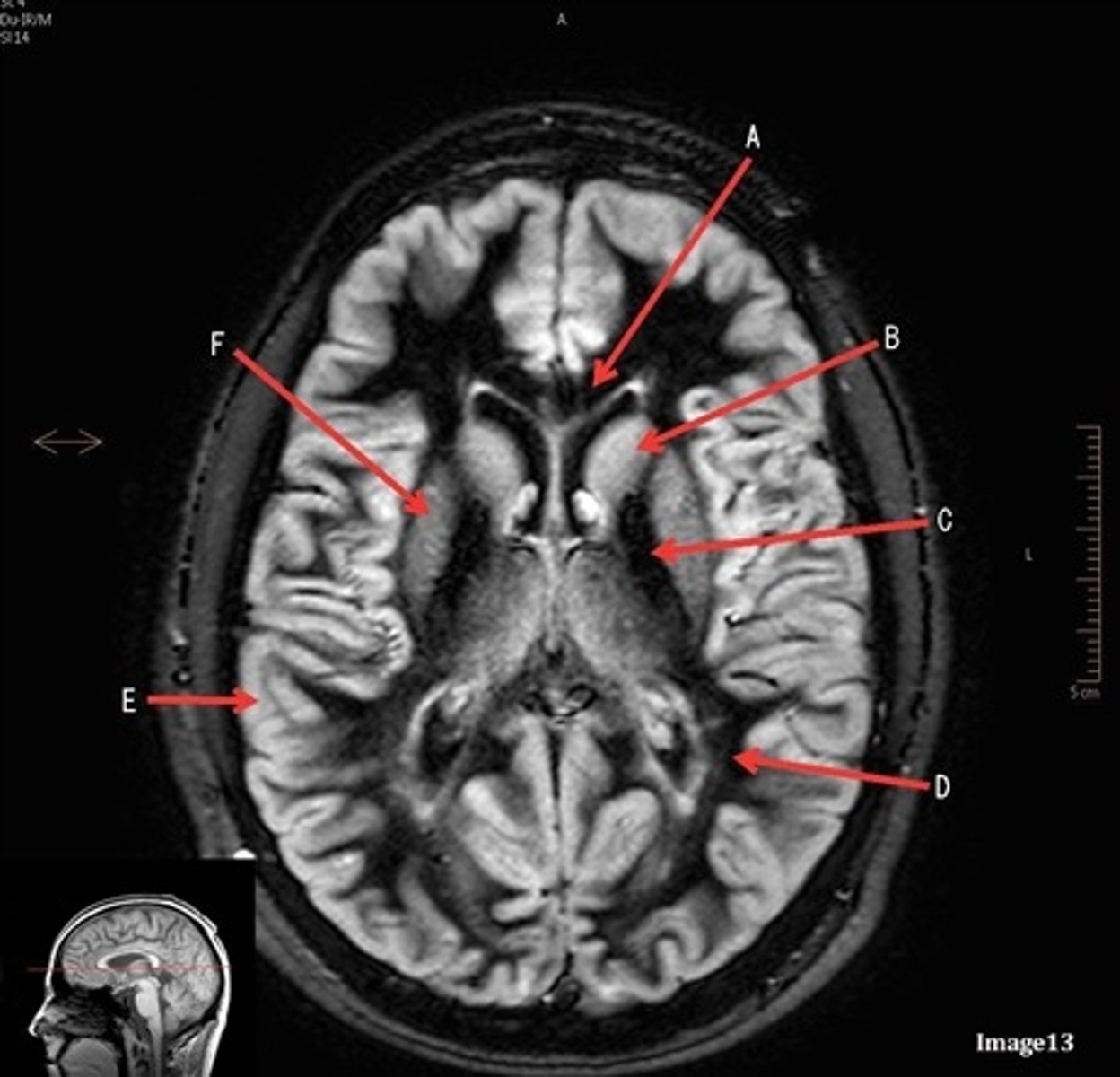
letter F
lentiform nucleus
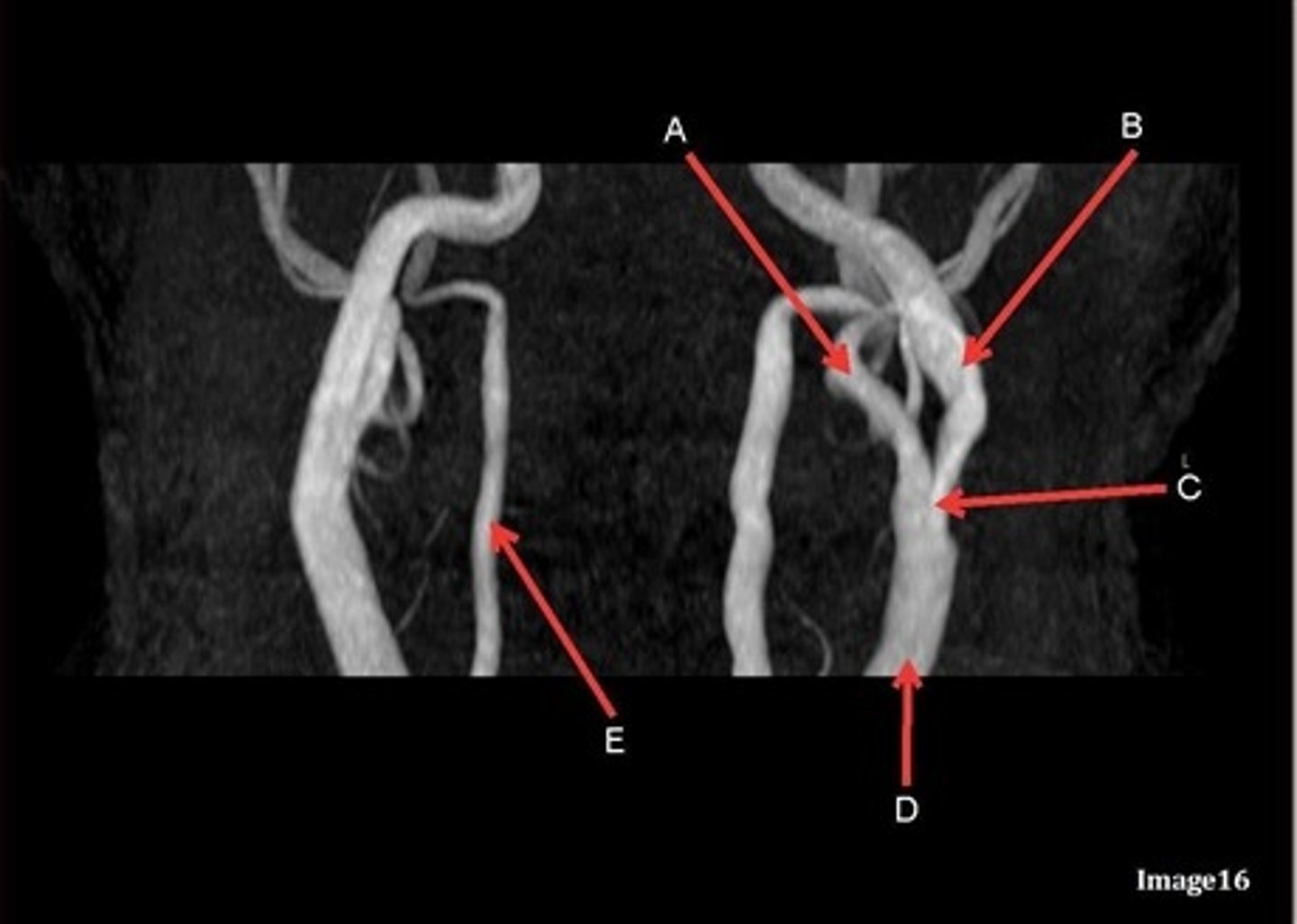
letter A responsible for blood supply to where
posterior brain
anterior brain
face
upper extremities
face
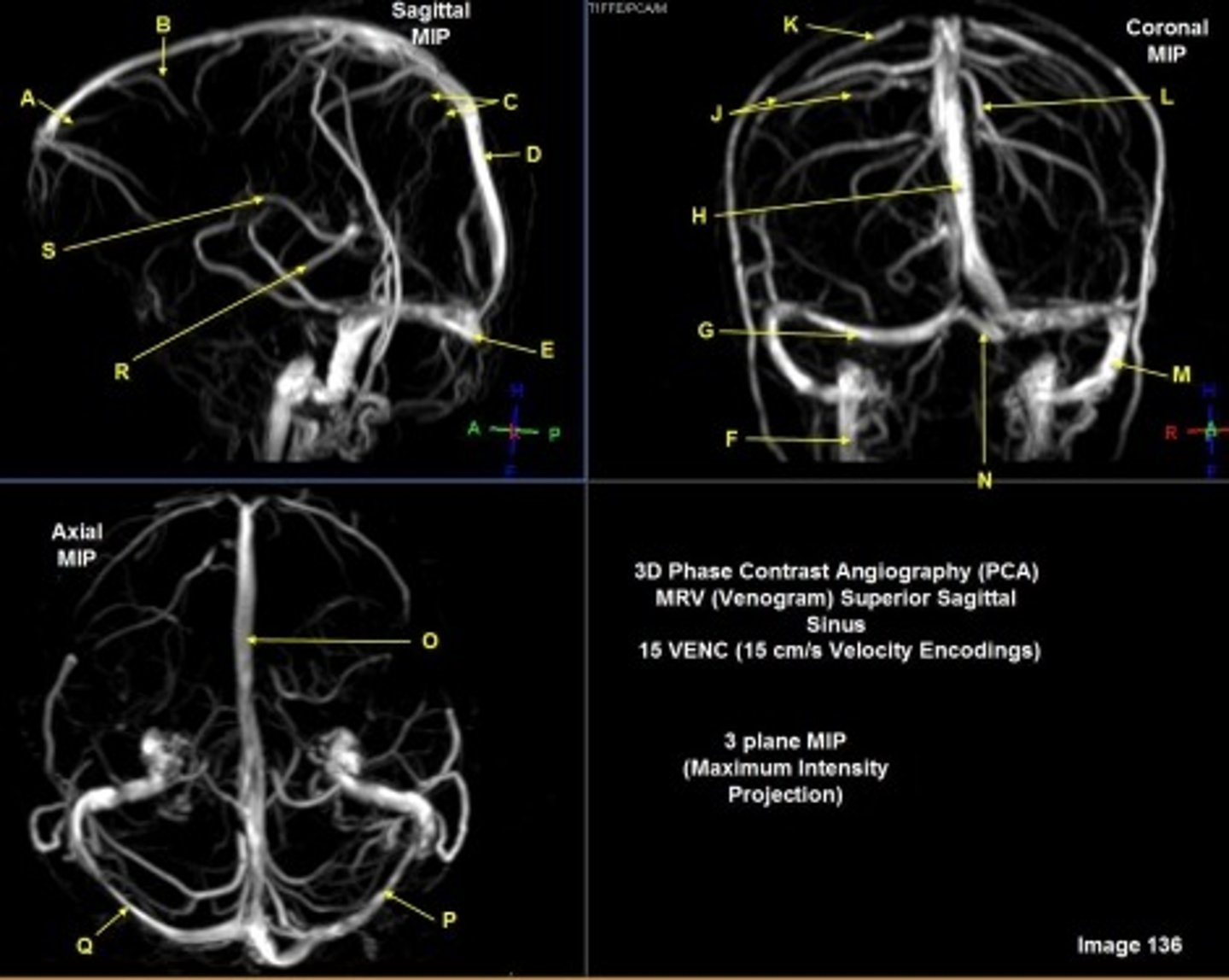
B
posterior frontal vein
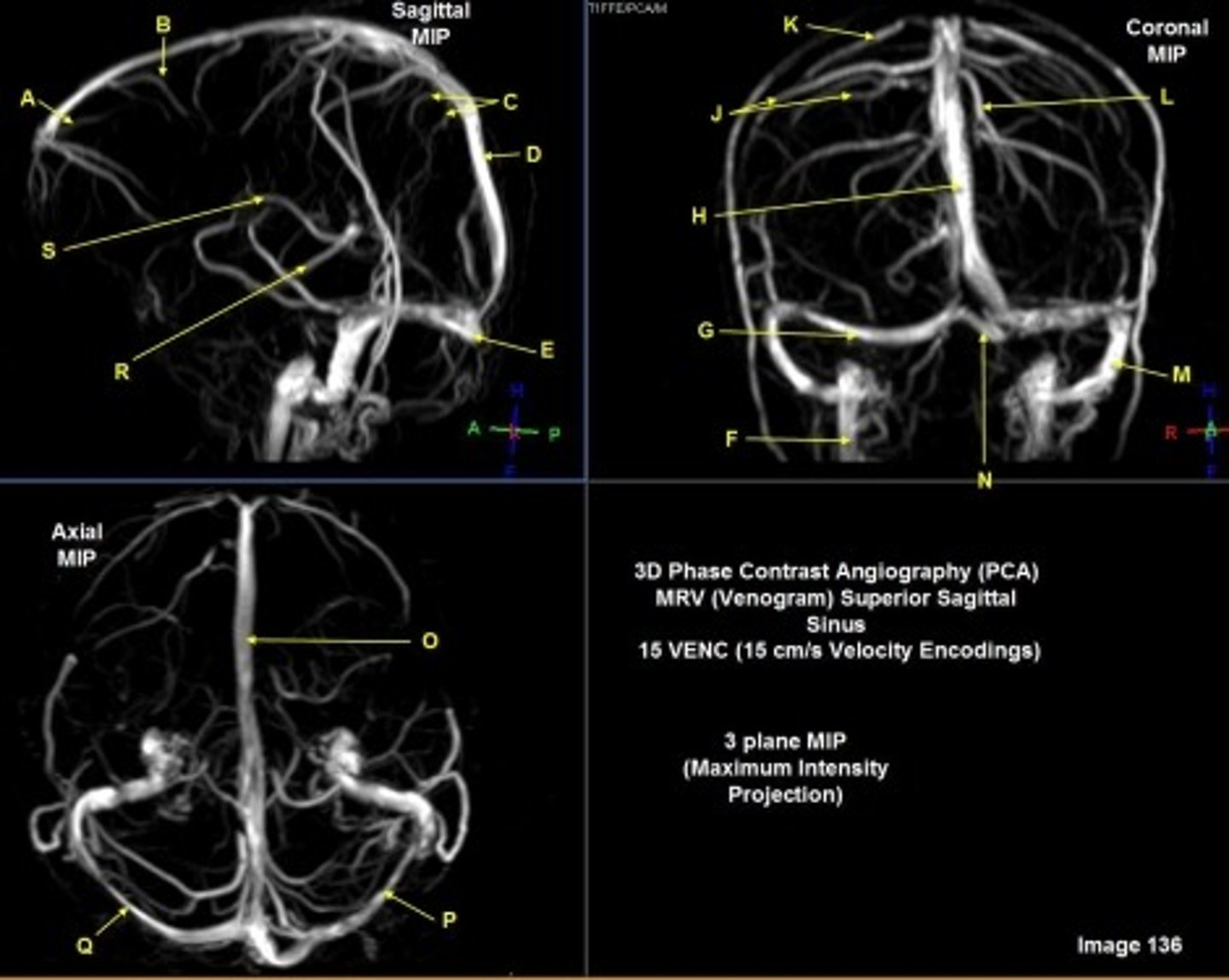
C
parietal veins
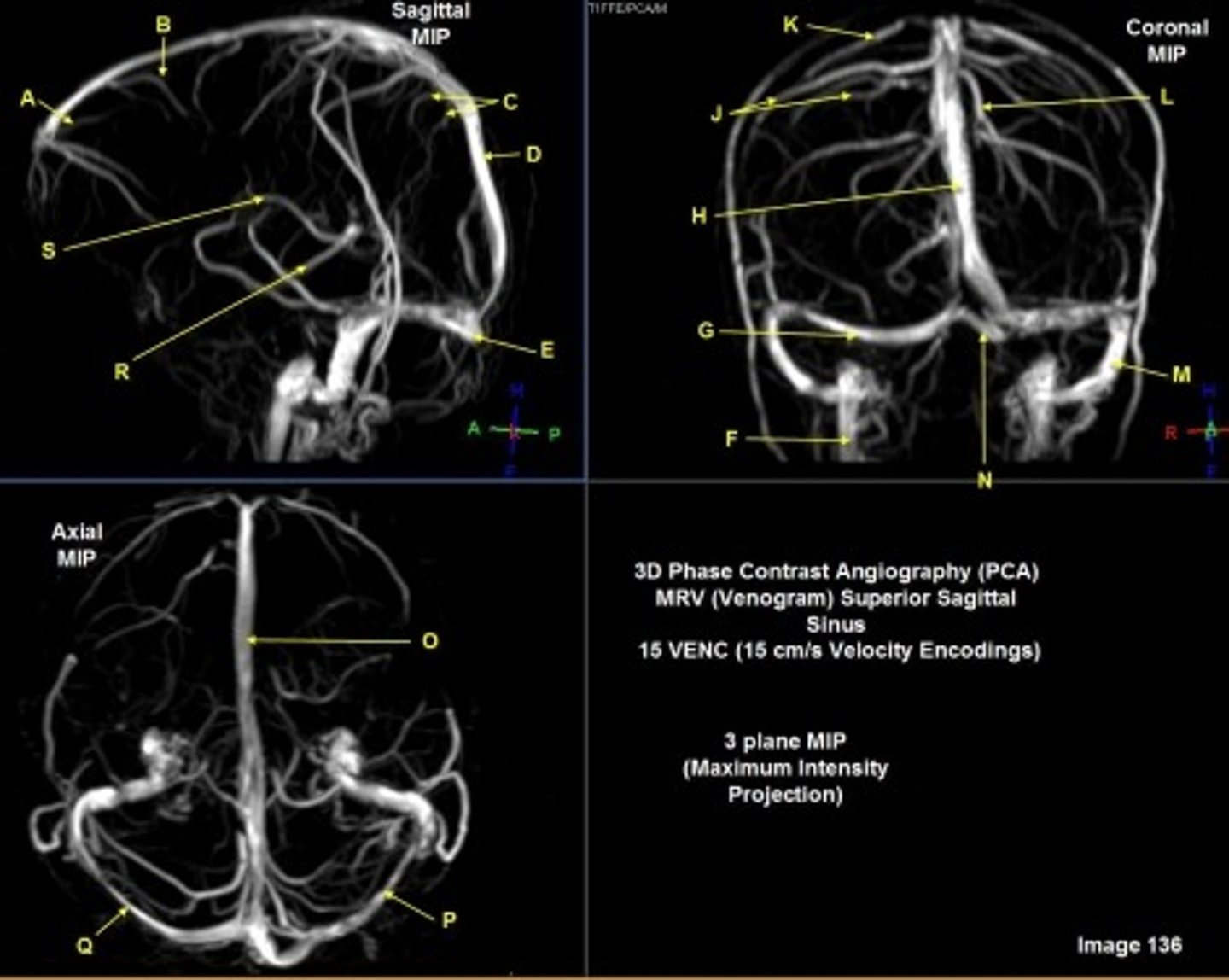
D
superior sagittal sinus
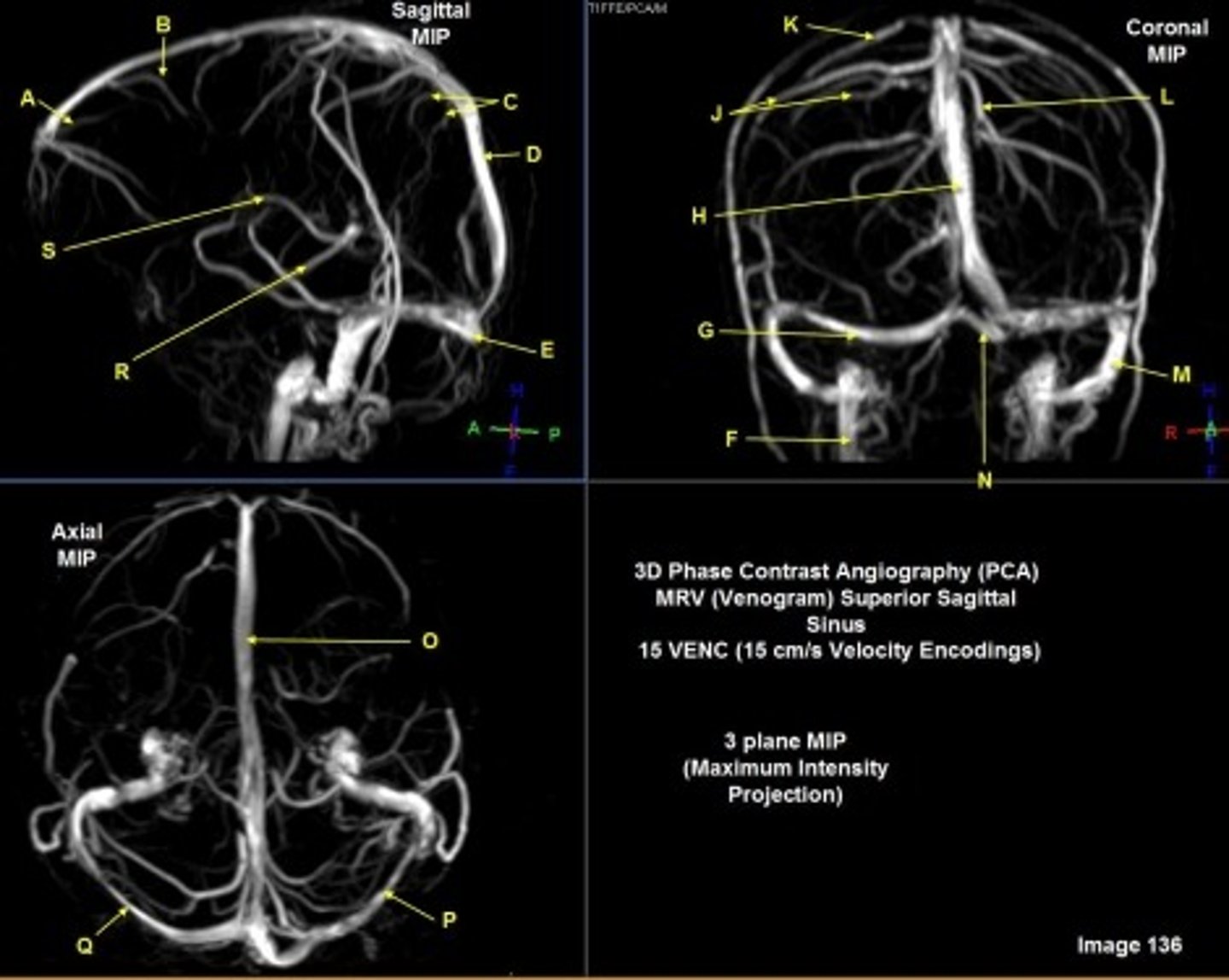
E
Torcular herophili
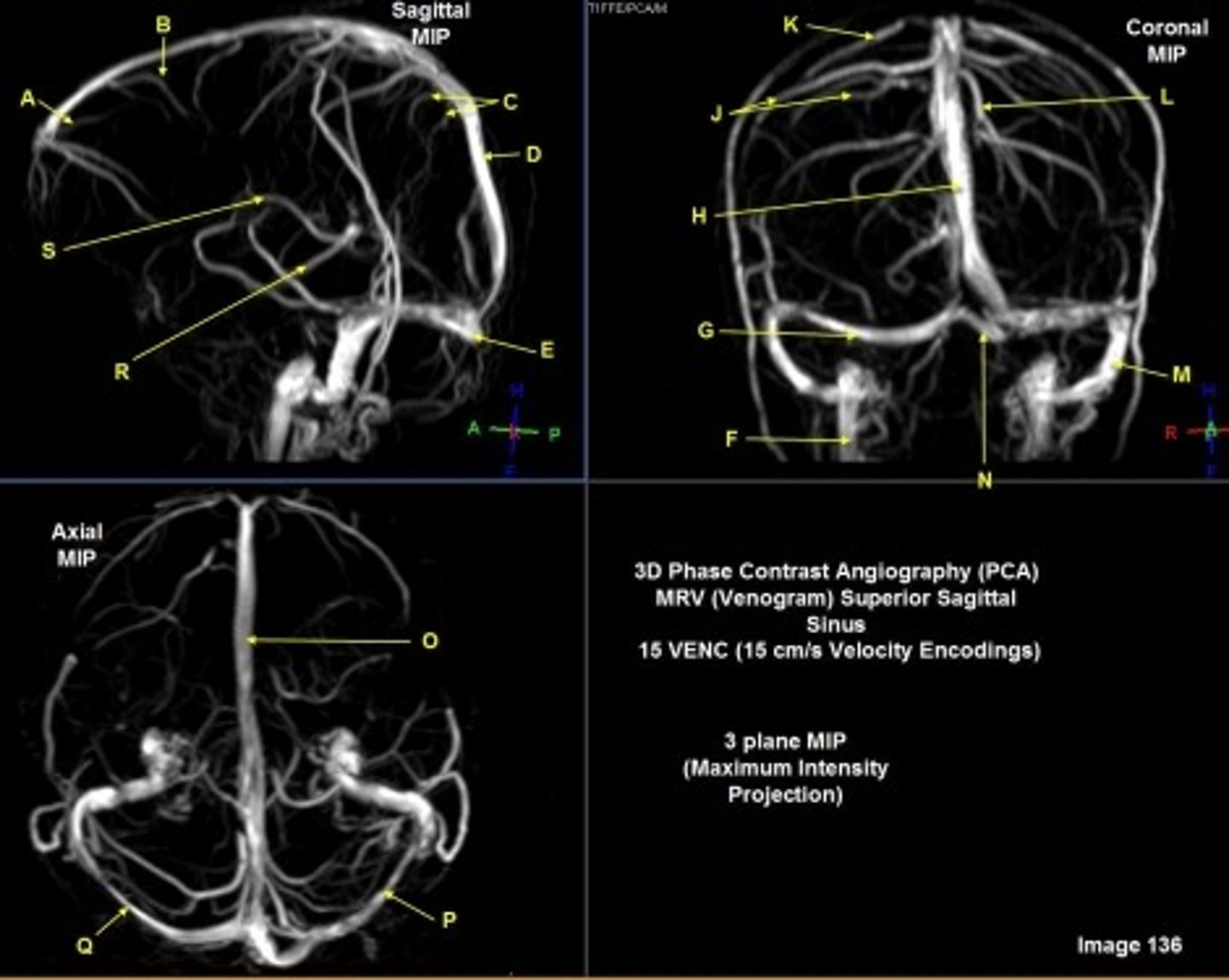
A
anterior frontal vein
G
right transverse sinus
L
left parietal veins
k
Vein of Trolard
m
left sigmoid sinus
N
torcular Herophili
o
superior sagittal sinus