Unit 1 All Together + General Ques
1/201
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
202 Terms
Bacterial cells are prokaryotic, in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell, bacterial cells would;
Be smaller
In eukaryotes, mitochondria are the organelles primarily involved in
The production of ATP
You would expect a cell with an extensive Golgi apparatus to
Secrete a lot of protein
What is the correct order in which organelles function to make and secrete an enzyme?
Nucleus, rough endoplasmic reticulum, golgi body & vesicle
Some substances can move through the plasma membrane. The membrane is said to be
Partially permeable
Carbon dioxide can also move freely through the plasma membrane by the process of
Diffusion
In cell replication, the correct order of events is
Dna replication, mitosis, cytokinesis
Endosymbiosis
A term used to describe two organisms living together with one inside the other
Membrane bound
Structures such as organelles found in eukaryotic cells, which are enclosed by a lipid bilayer
Organelle
A sub-cellular (contained within a cell) structure that has one or more specific jobs to preform in the cell
Formula for surface area
2lw+2lh+2hw
LxWxH
Formula for volume
Single Membrane
An organelle with only one membrane communicate with external medium eg. Vacuole, lysosome, golgi apparatus & endoplasmic reticulum
Double Membrane
Organelles with two membranes have cytoplasm in the inner compartment eg. Nucleus, mitochondria & chloroplast
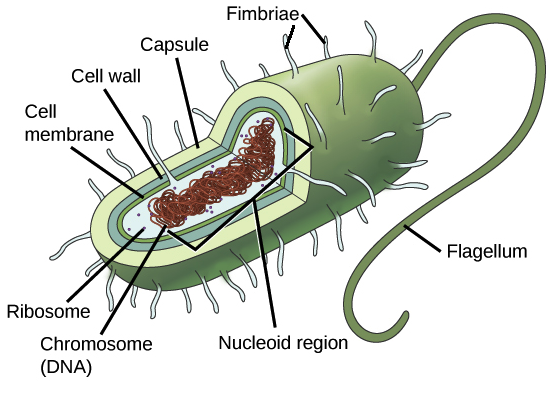
Prokaryotic cells
Cells lacking a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, typically smaller and simpler than eukaryotic cells. Examples include bacteria and archaea, produces asexually
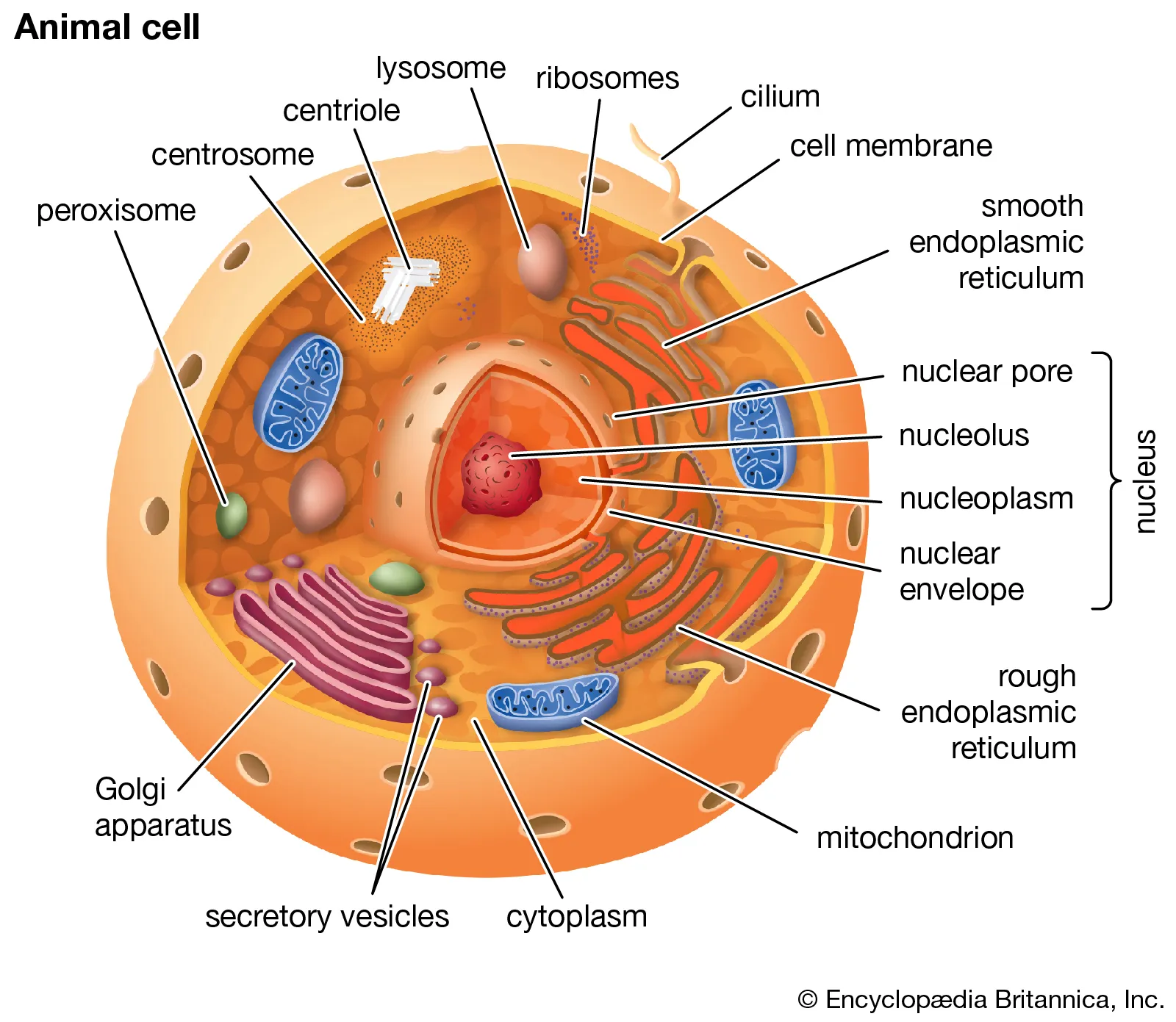
Eukaryotic cells
Cells with a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles, generally larger and more complex than prokaryotic cells. Examples include animal and plant cells, produces sexually
Cytoplasm
The gel-like substance inside the cell membrane that contains organelles and is the site of many metabolic processes
Cytosol
The fluid component of the cytoplasm, excluding organelles and other solid structures, where many cellular processes occur
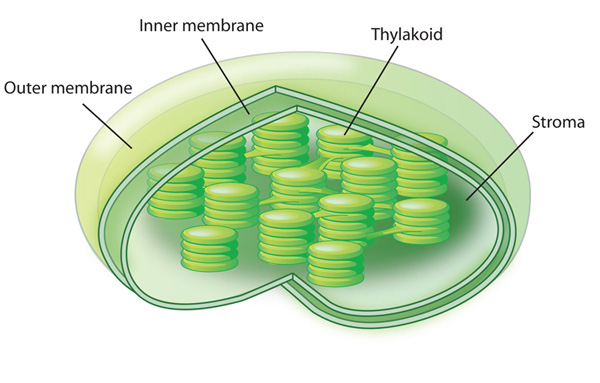
Chloroplast
A green organelle in plant cells that conducts photosynthesis by converting sunlight (photosynthesis) into chemical energy in the form of glucose
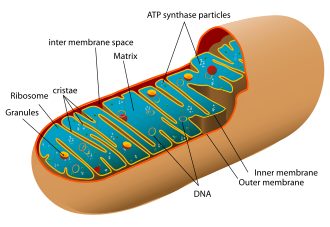
Mitochondria
Organelles known as the powerhouses of the cell, responsible for producing ATP through cellular respiration
Cellular Respiration
The biochemical process by which cells convert glucose and oxygen into energy (ATP), releasing carbon dioxide and water as byproducts, C₆H₁₂O₆ + 6O₂ → 6CO₂ + 6H₂O + ATP
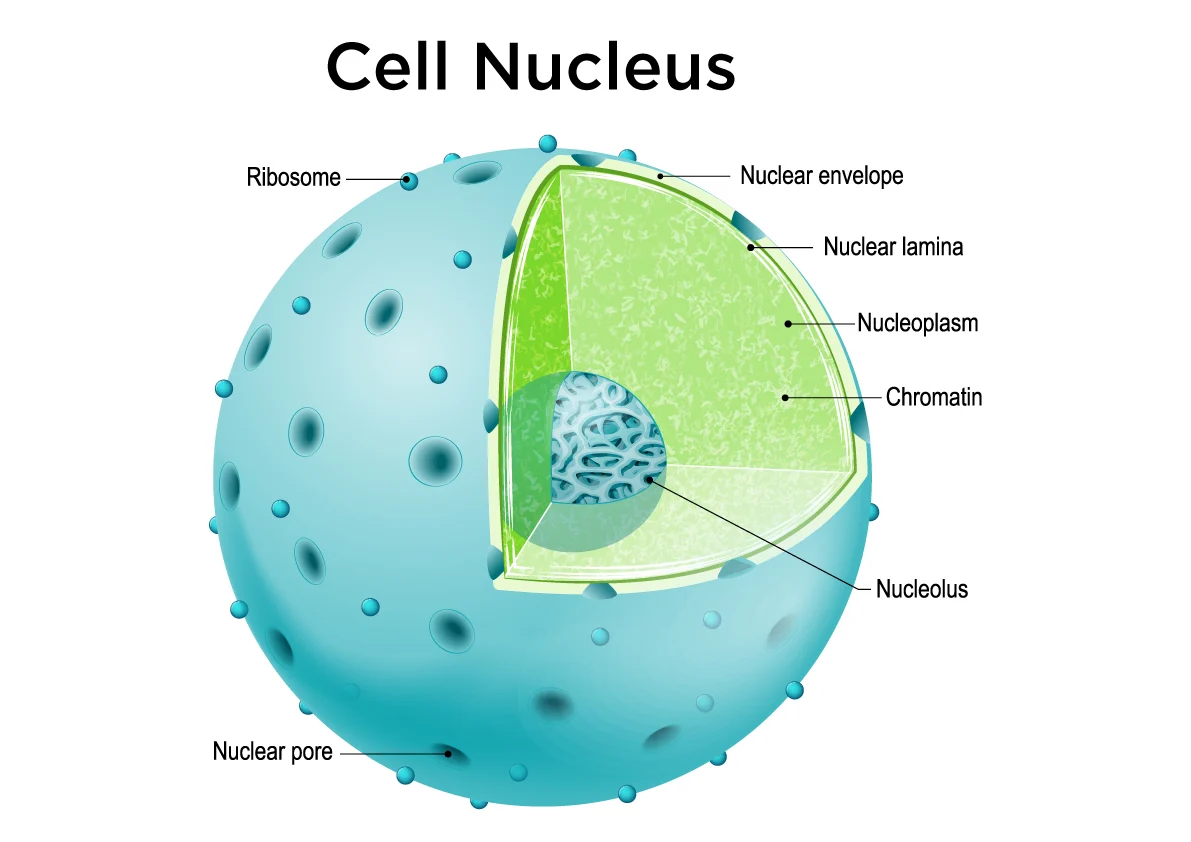
Nucleus
The organelle that houses the cell's genetic material (DNA) and coordinates activities such as growth, metabolism, and reproduction
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum covered with ribosomes, involved in protein synthesis and processing

Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
A type of endoplasmic reticulum that is not covered with ribosomes, involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification
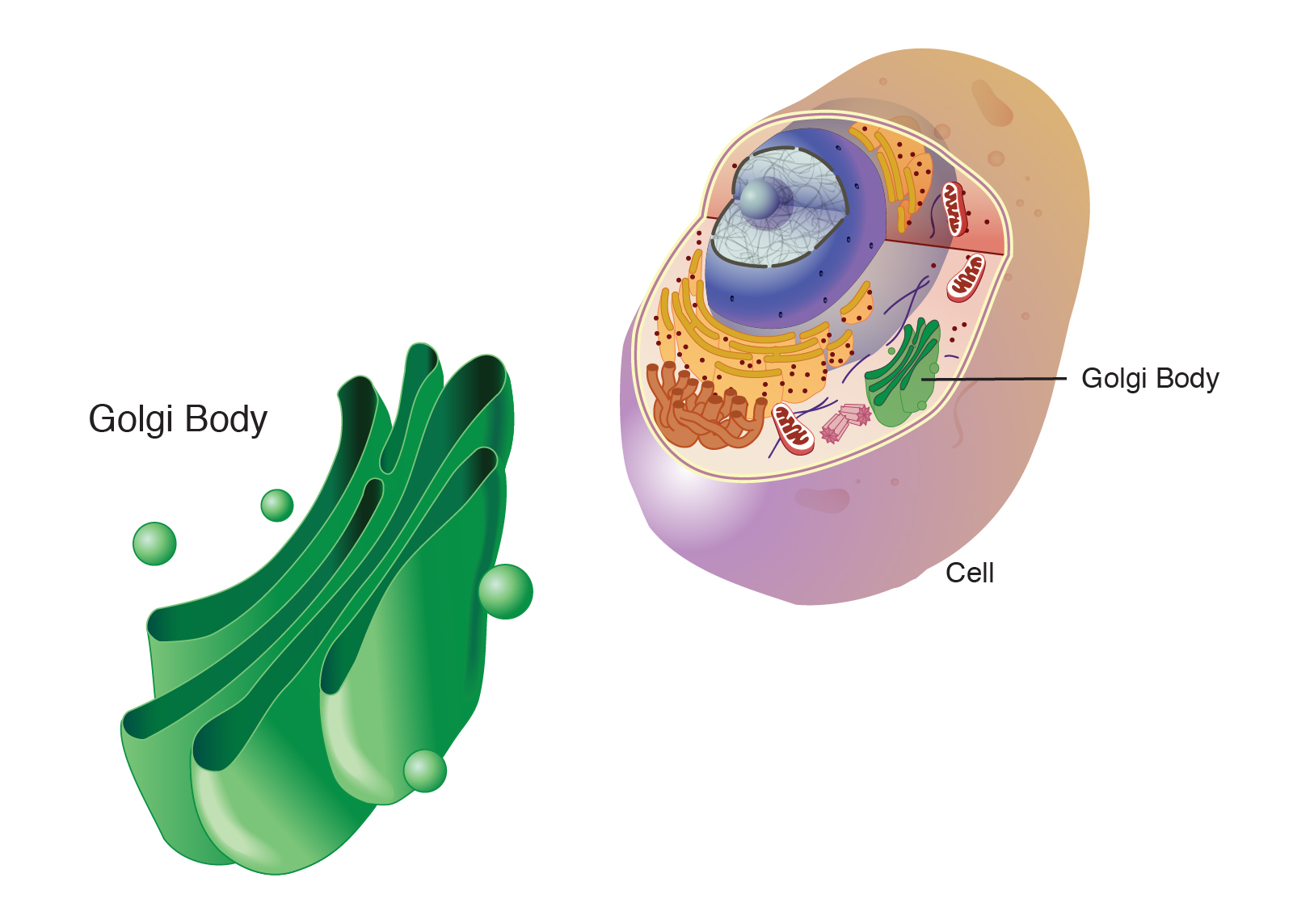
Golgi apparatus
An organelle that modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for secretion or delivery to other organelles
Protein
A large, complex molecule made up of amino acids, playing vital roles in the structure, function, and regulation of the body's tissues and organ
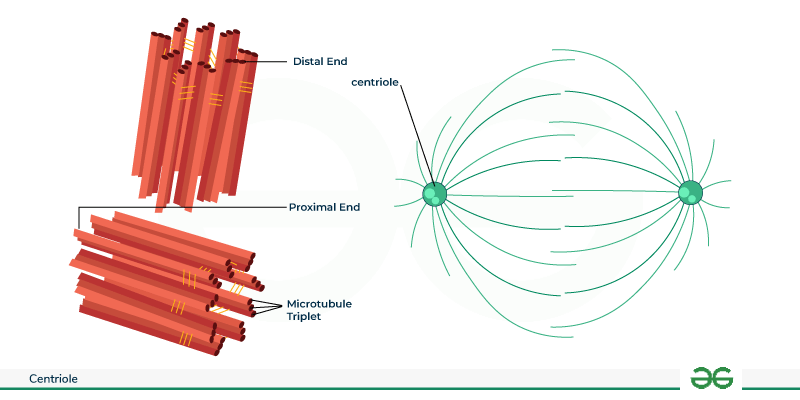
Centrioles
Cylindrical structures involved in cell division and the formation of spindle fibers, help ensure the correct chromosomes are available to each daughter cell upon division
Peroxism/peroxisome
Break down fatty acids to be used for forming membranes & as a fuel for respiration, looks like half a coconut
Equilibrium
When equal numbers of a specific molecule are on either side of the plasma membrane
Plasma membrane
A biological membrane that separates and protects the interior of a cell from the external environment, regulating what enters and exits the cell
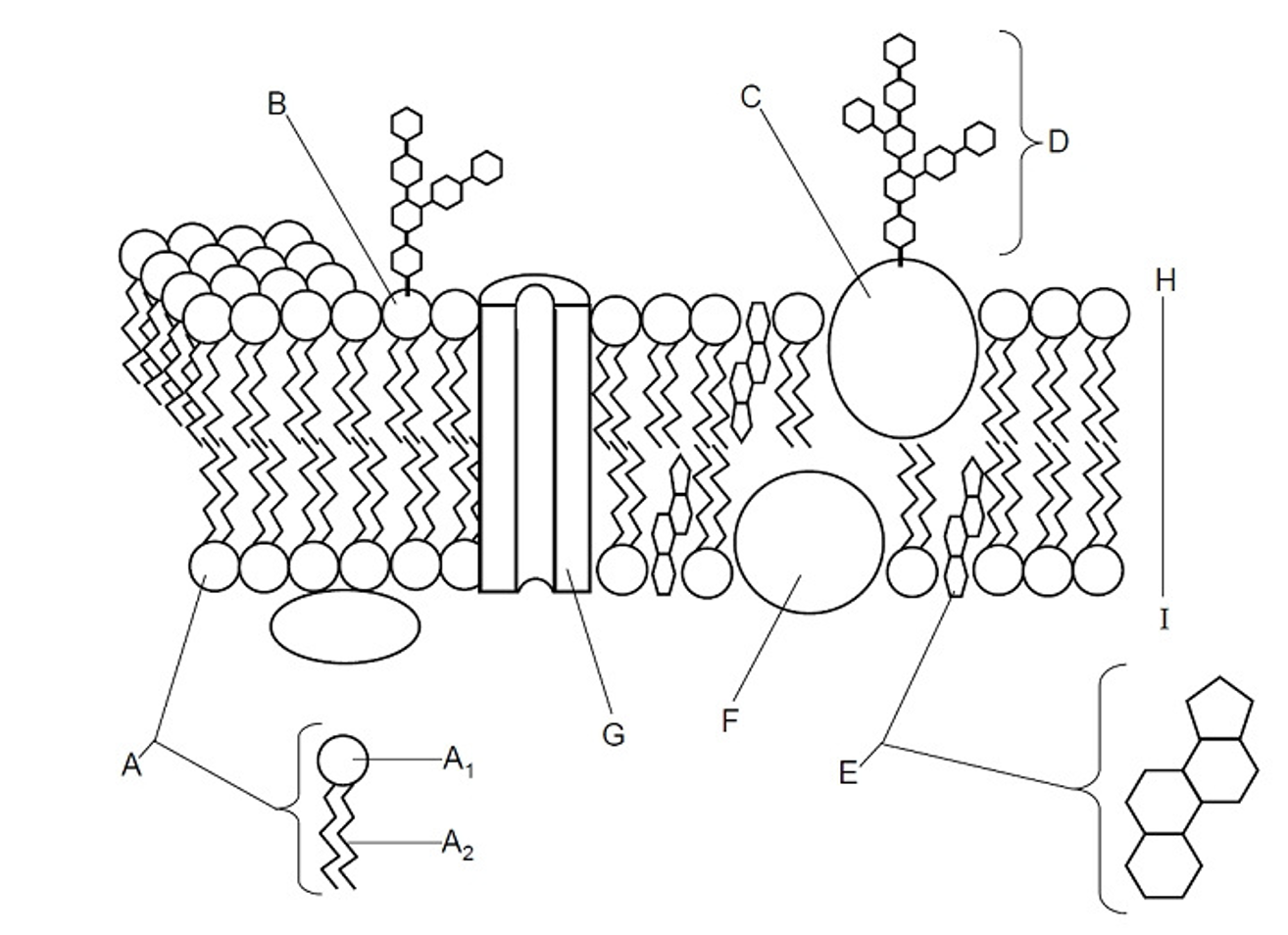
Fluid
Describes the liquid nature of the membrane, it can move freely because of the cholesterol
Mosaic
Describes the composition of the membrane being made up of thousands of lipids and proteins
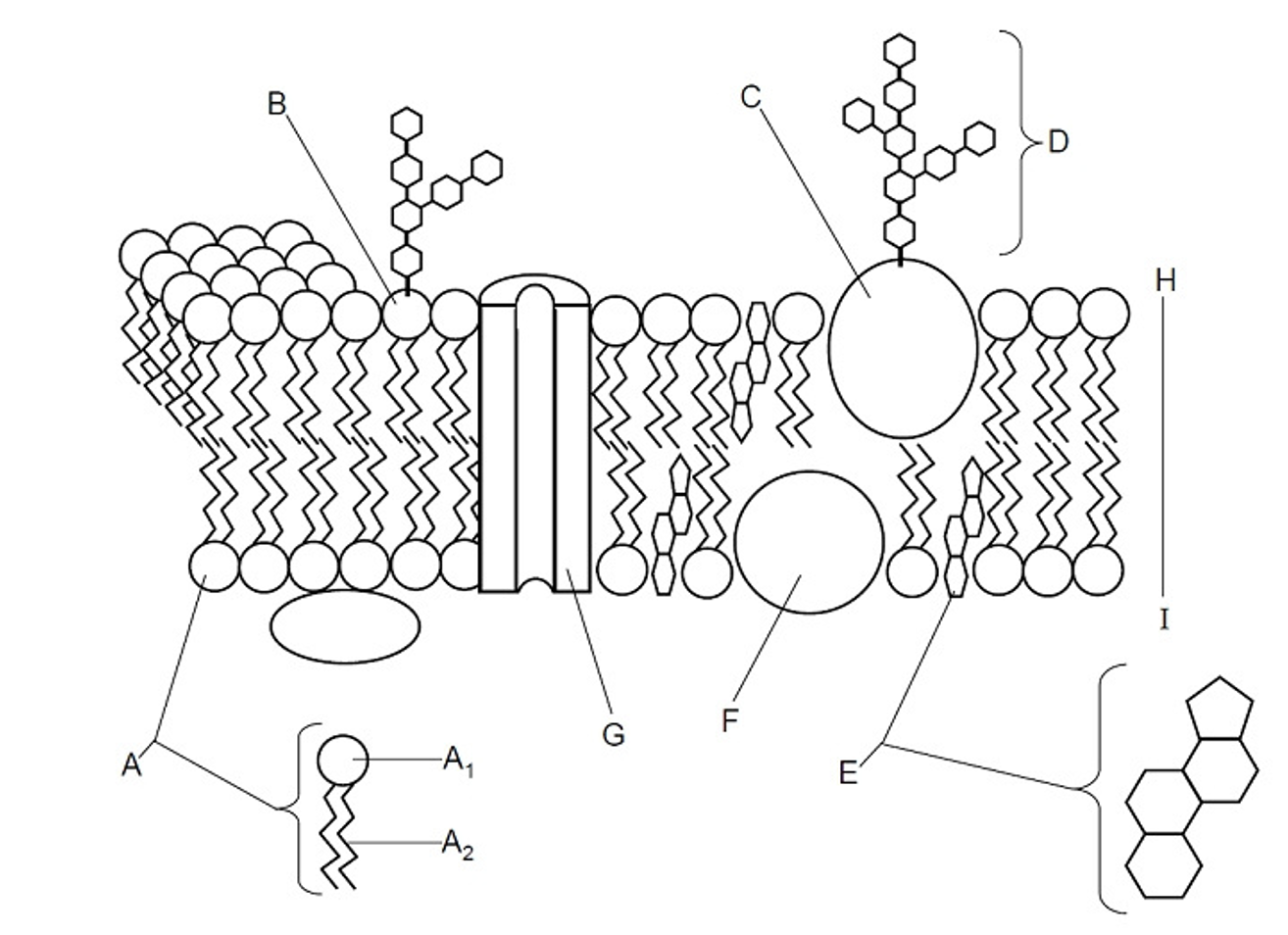
Phosphate head
(A) The hydrophilic ‘water loving’ part of a phospholipid that interacts with water, making it essential for forming the plasma membrane

Fatty acid tail
(A) The hydrophobic ‘water fearing’ part of a phospholipid that repels water and helps form the lipid bilayer of the plasma membrane
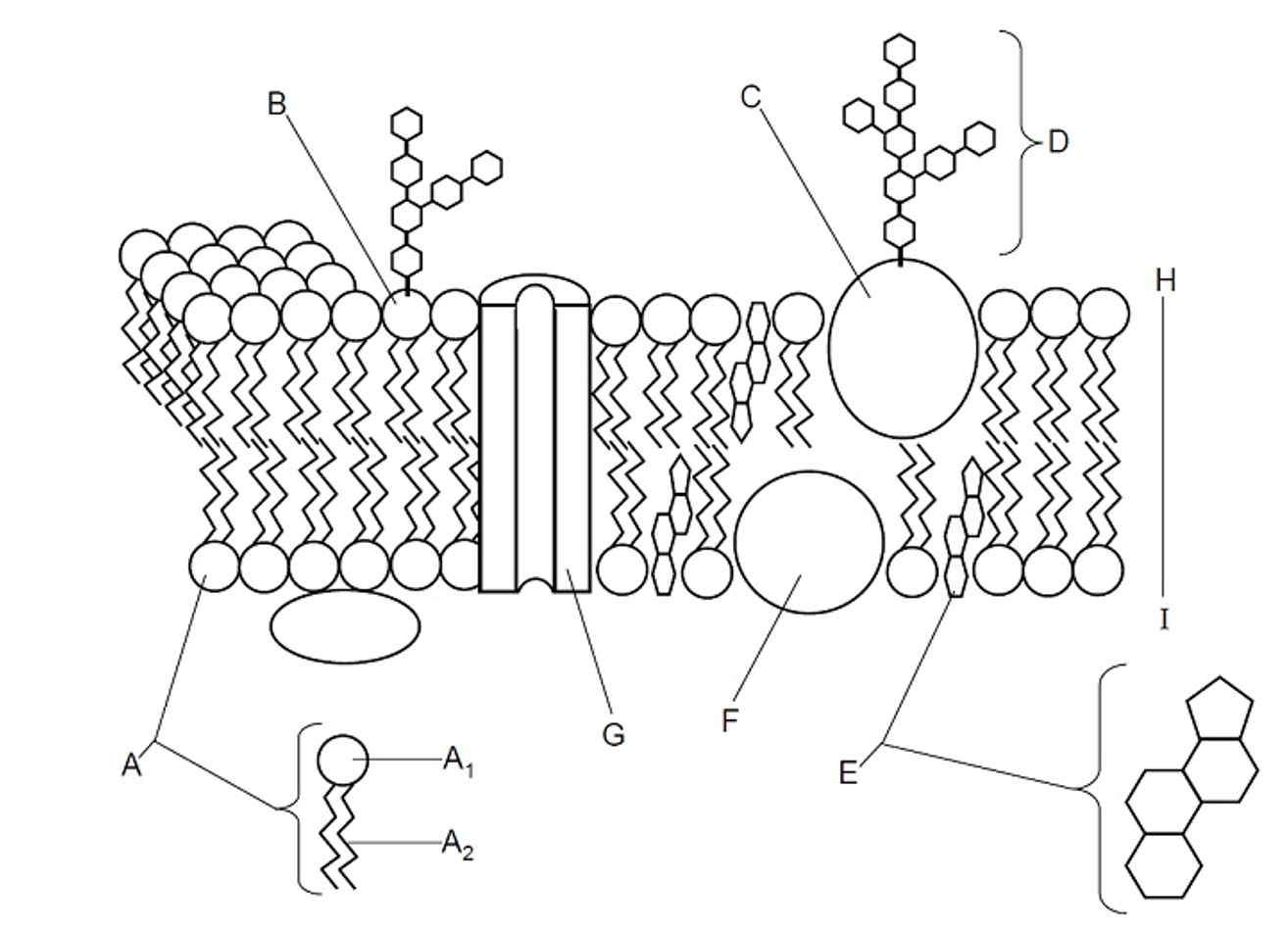
Glycolipid
(B) A lipid with a carbohydrate attached, contributing to cell recognition and the maintenance of the cell membrane, acts as receptors for messenger molecules, LIPID OF THE PM
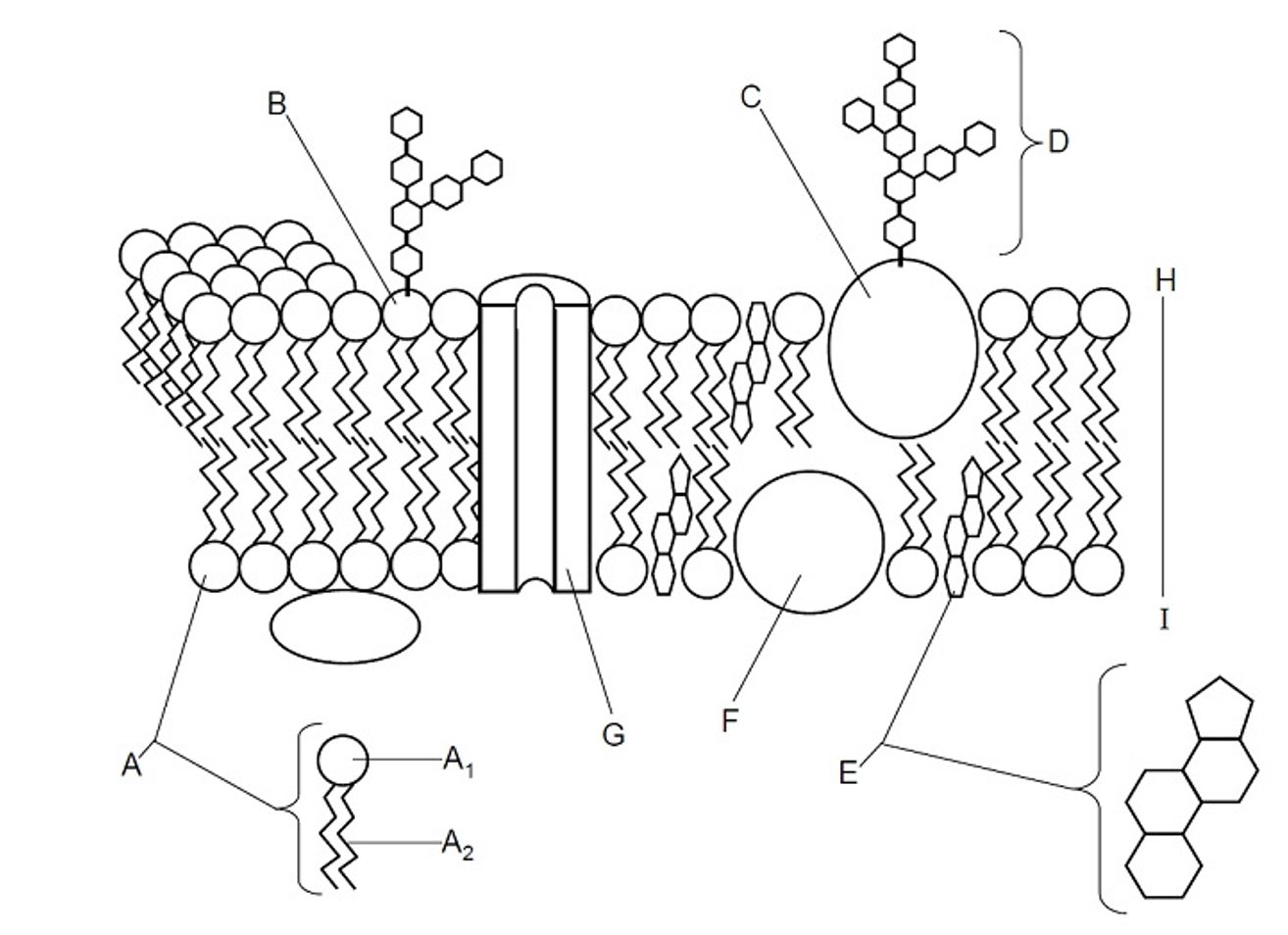
Glycoprotein
(C) A protein with a carbohydrate group attached, playing a key role in cell recognition, signaling, and maintaining the structure of the cell membrane, PROTEIN OF THE PM
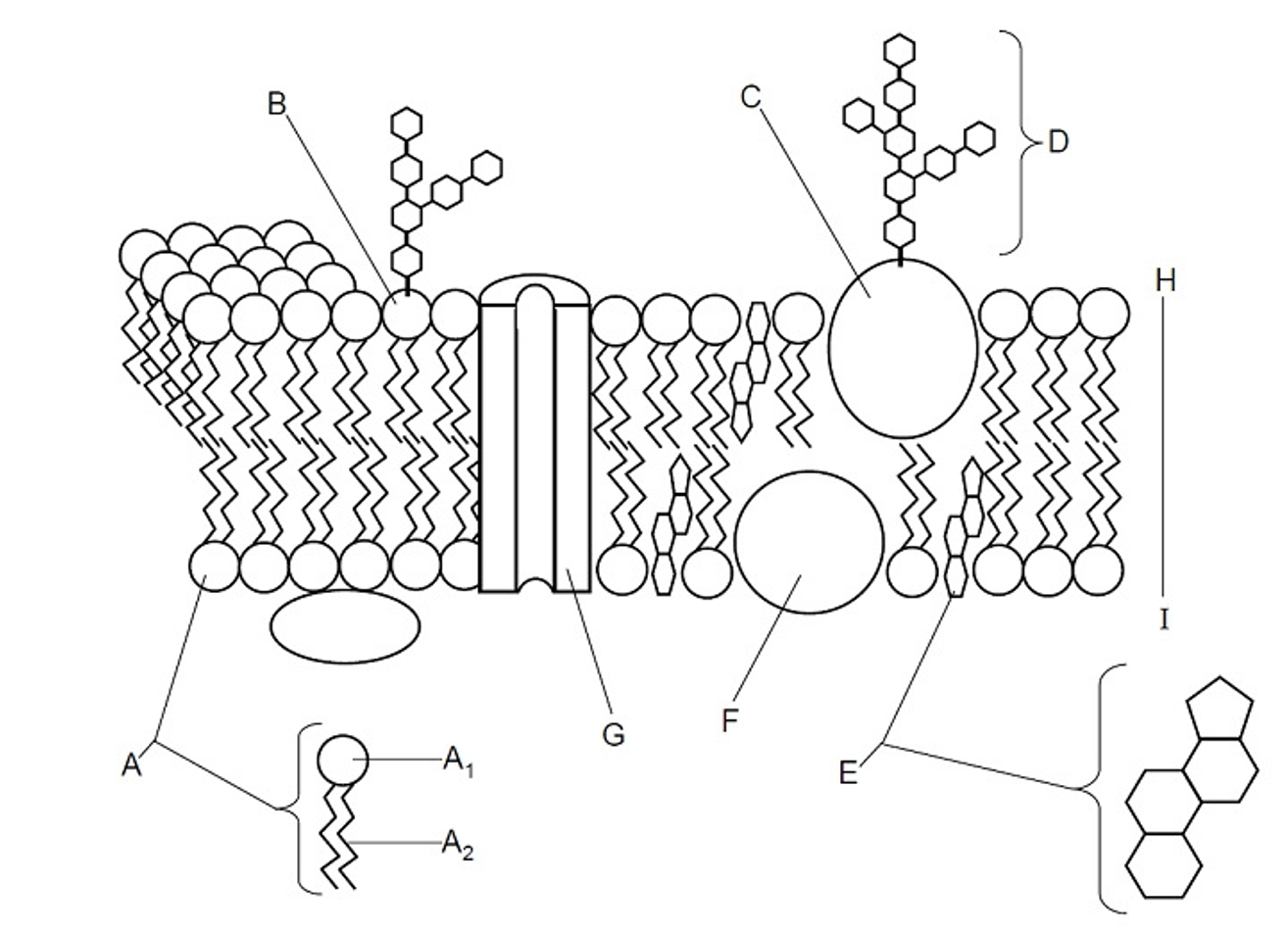
Cholesterol
(E) A type of lipid that is found in the cell membrane, playing a crucial role in maintaining membrane fluidity and stability, steroid molecule
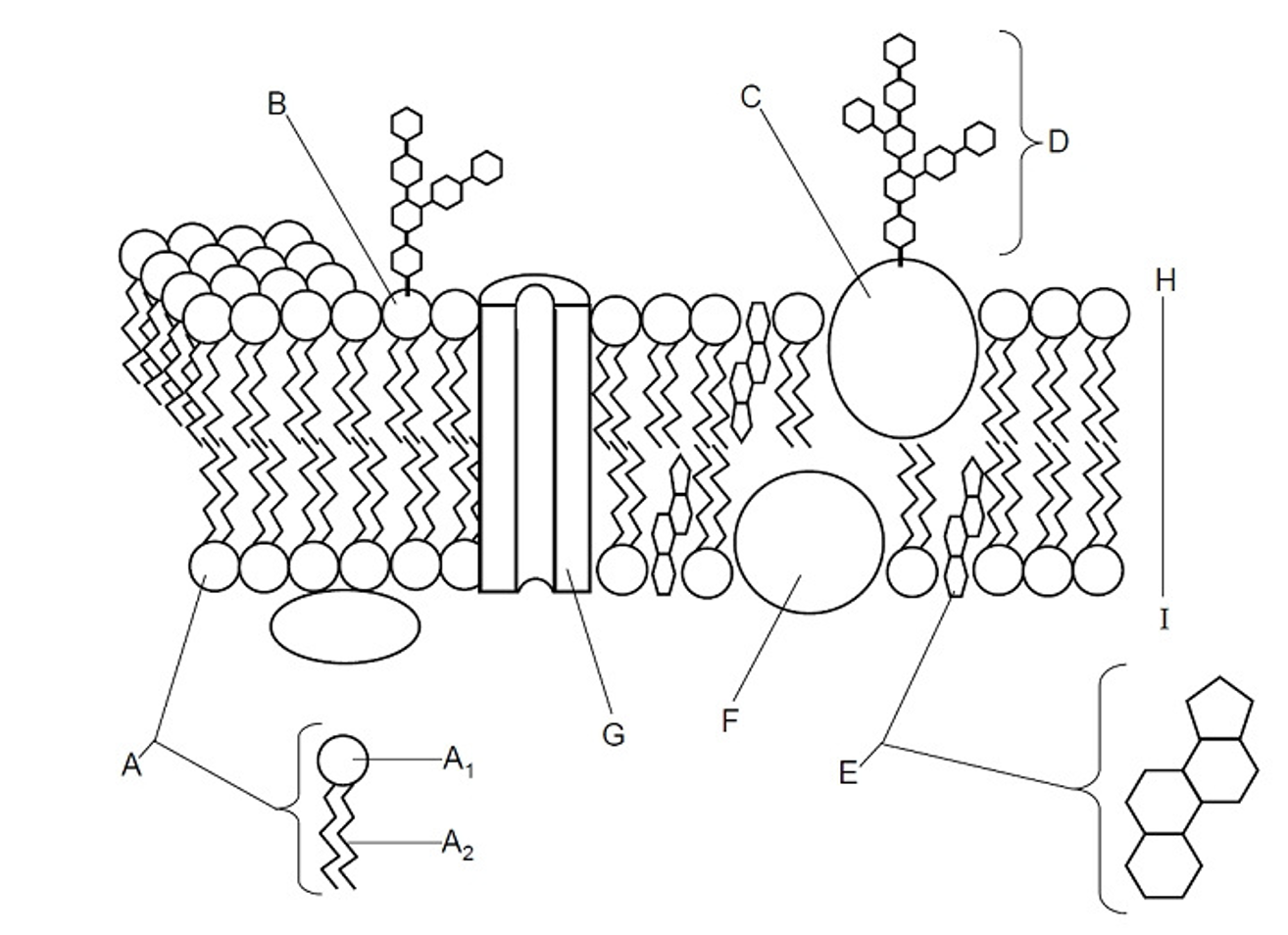
Lipid
Hydrophobic molecules for energy storage, membrane structure, and signalling
Peripheral protein
(F) Offers support, communication, enzymes & molecule transfer in the cell
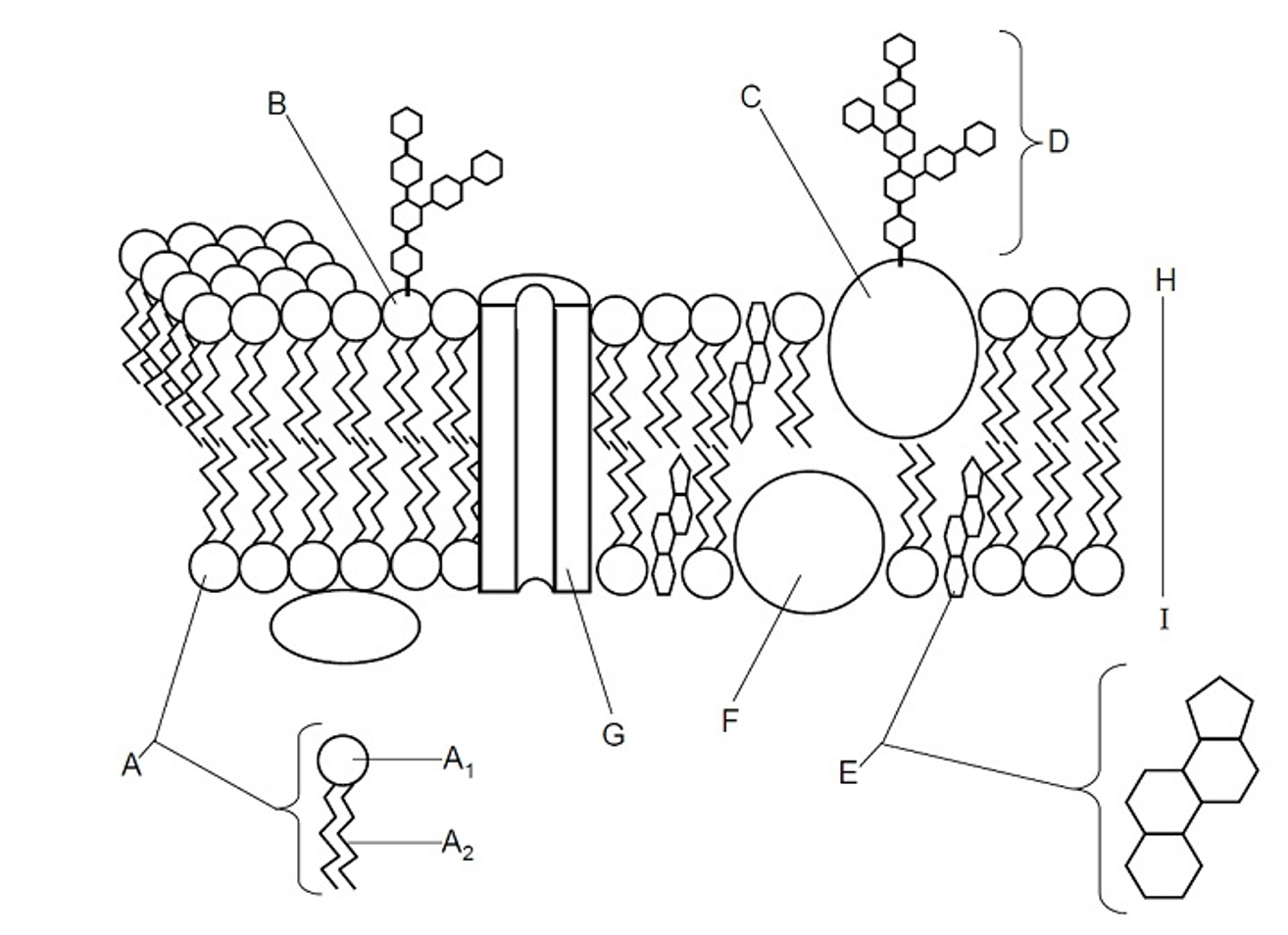
Integral protein
(G) Embedded with the bilayer, involved in transporting large molecules across the membrane
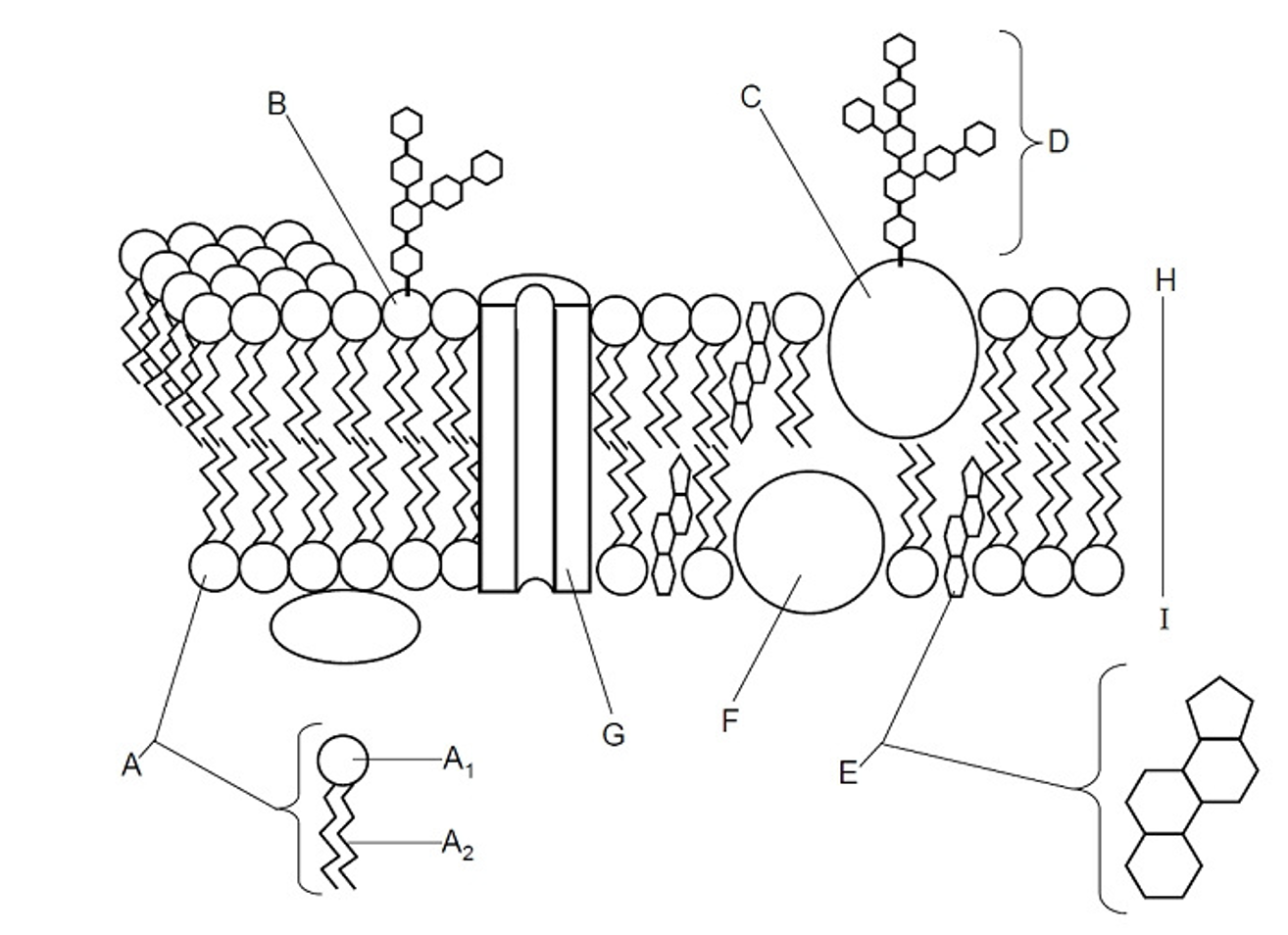
Bilayer
(H) The two layers in between the plasma membrane
What are the three main ways for passive transport?
Simple diffusion, facilitated diffusion & osmosis
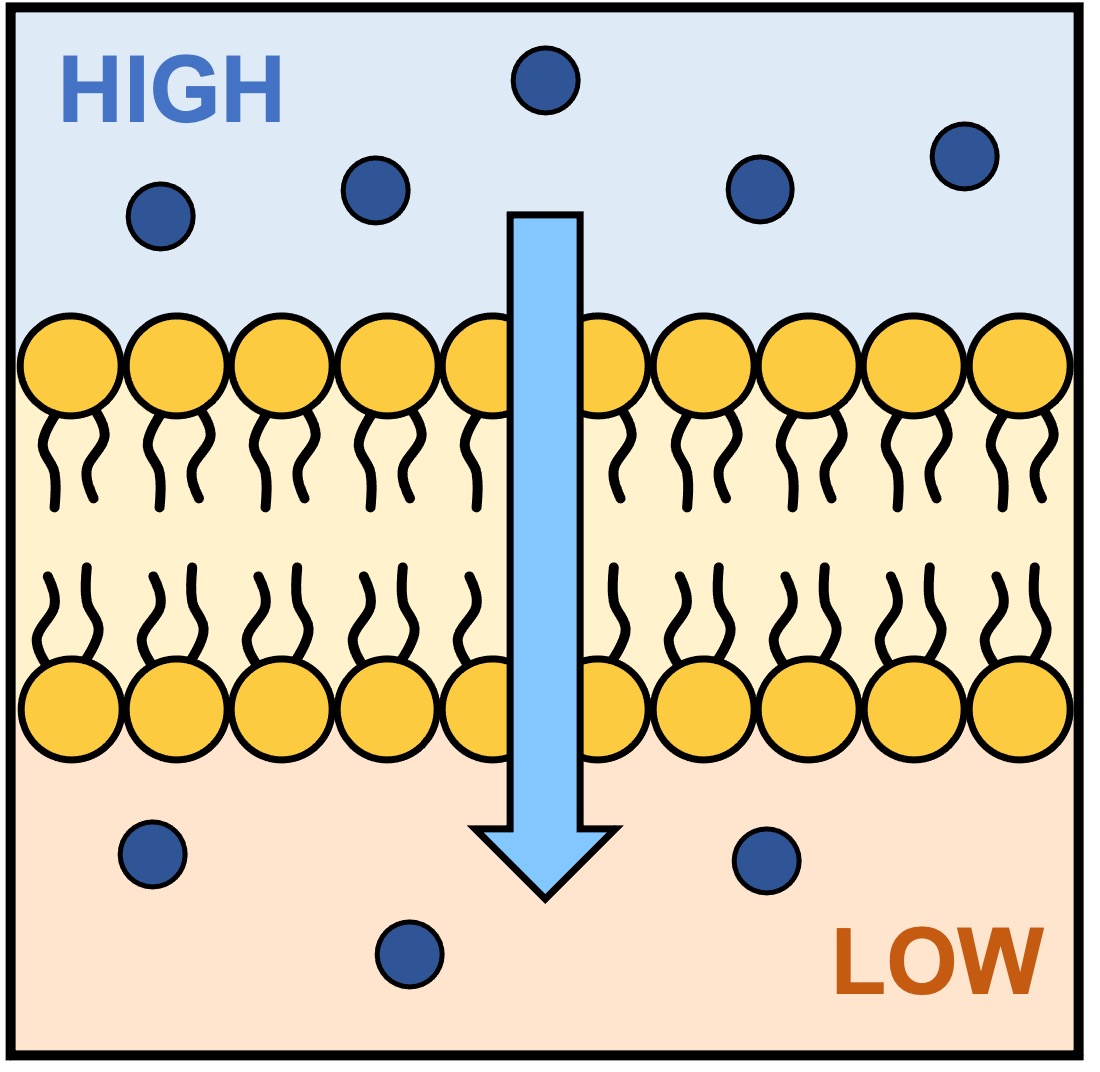
Simple diffusion
Passive movement of substances across the plasma membrane - movement of small or lipophilic molecules without the need for energy or transport proteins
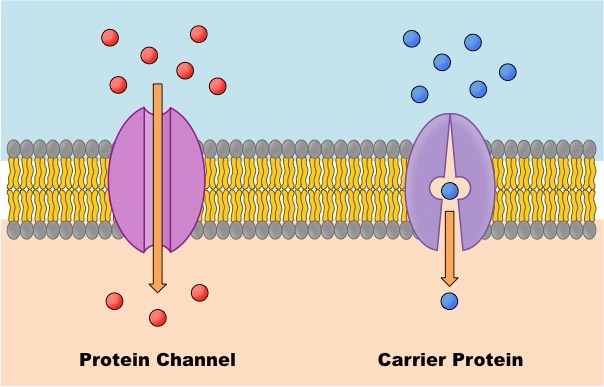
Facilitated diffusion
Molecules diffuse across the plasma membrane with assistance from membrane proteins such as channels and carriers - movement of large or charged molecules via membrane proteins eg: ions, sucrose etc
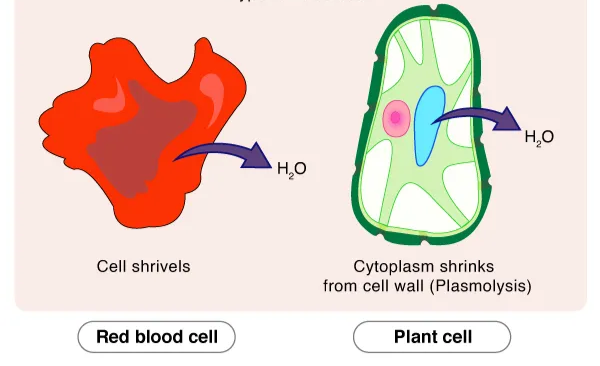
Osmosis
The diffusion of water molecules from a lower solute to a higher solute concentration across a partially permeable membrane (PM) - movement of water molecules (dependent on solute concentration)
What are the three types of osmosis?
Hypertonic, isotonic & hypotonic
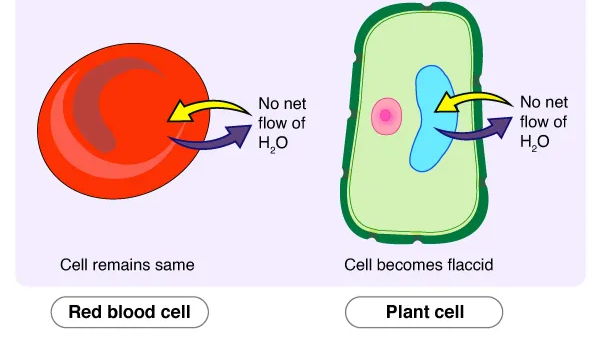
Isotonic
Having the same solute concentration as the other solution - No net movement
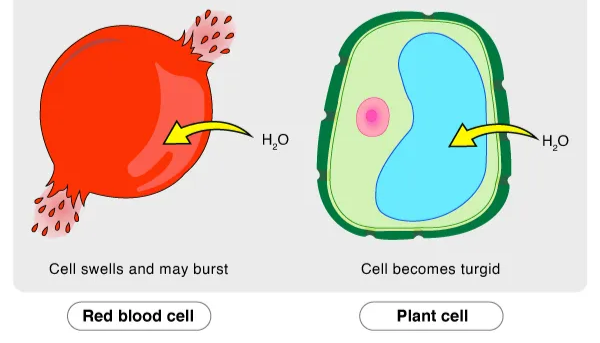
Hypotonic
Having a lower solute concentration relative to the other solution - Water will rush in (making the lower solute grow bigger)
Hypertonic
Having a higher solute relative to the other solution - Water will rush out (making higher solute grow smaller)
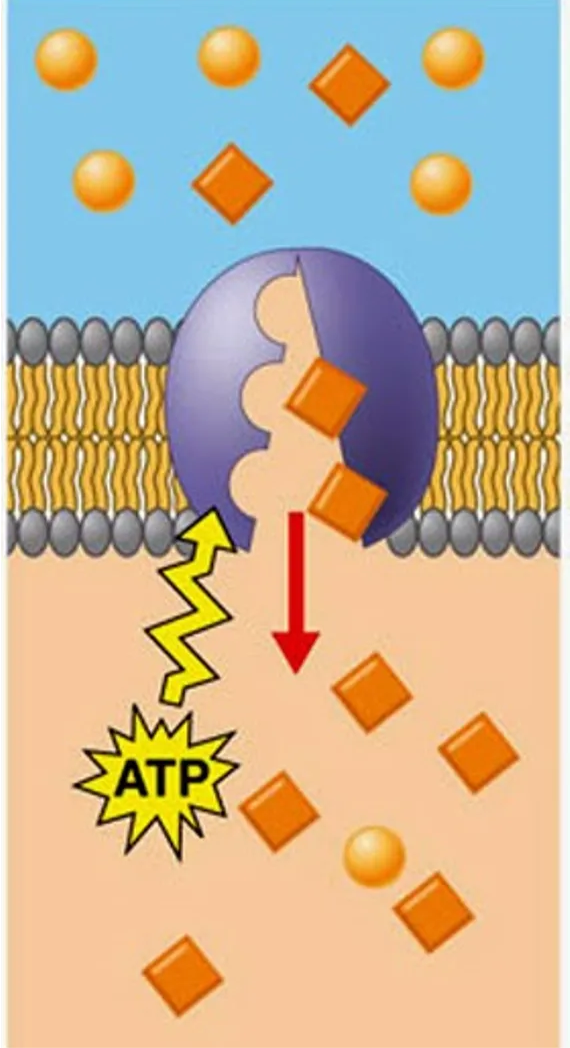
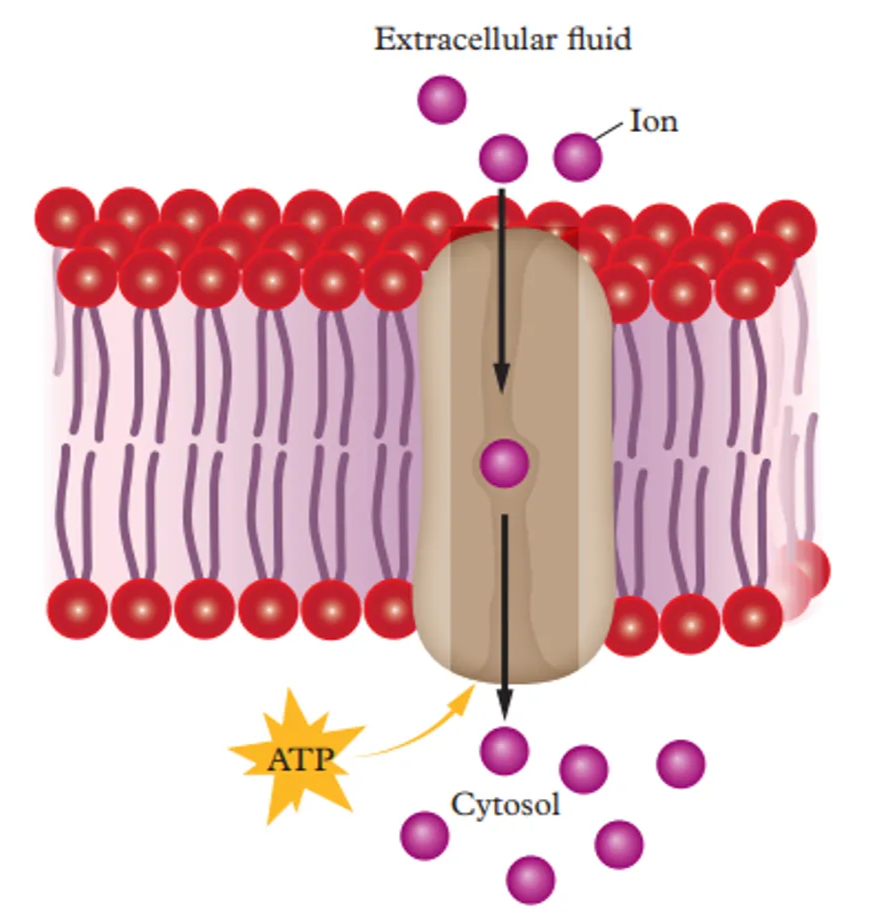
Active Transport
The process of moving substances across the plasma membrane against the concentration gradient, needs input of ATP for this task
What are the three main ways of active transport?
Protein pumps, endocytosis & exocytosis
Protein pumps
The pump uses the energy from ATP to move the substances across the plasma membrane. In this process, the pump (proteins) changes shape
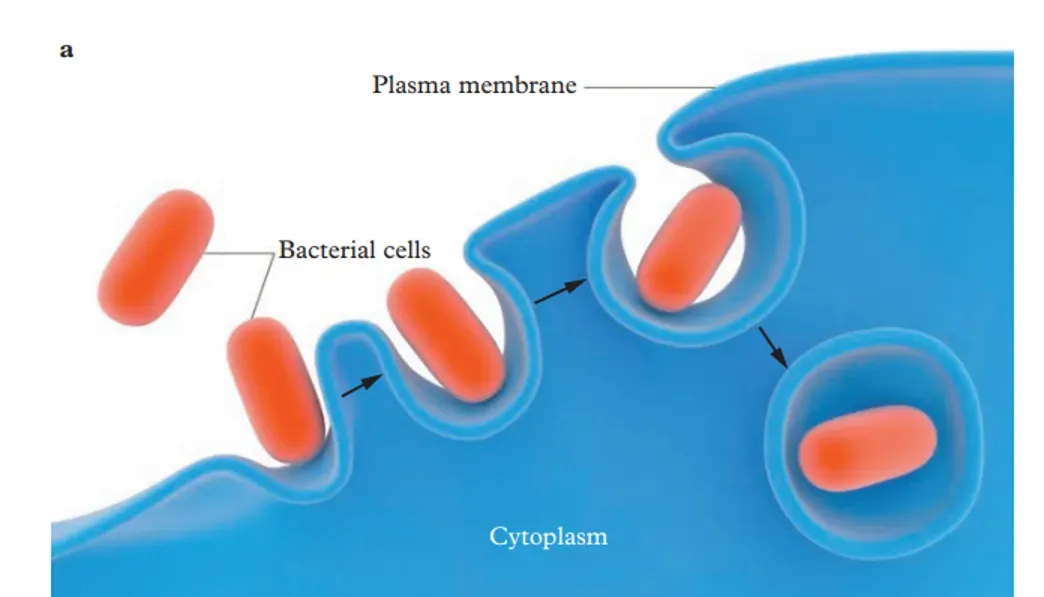
Endocytosis
The active transport of macromolecules into the cell via vesicle formation, part of the PM engulfs (surrounds) the large substance, the large substance and PM is then pinches off and forms a vesicle, which is then moved into the cell
Phagocytosis
If the bulk substance is a solid = (to eat), a process where a cell engulfs and digests large particles, like bacteria or cellular debris, using its own membrane
Pinocytosis
If the bulk substance is a liquid = (to drink) a type of endocytosis where a cell takes in extracellular fluid and dissolved substances by engulfing them in small vesicles
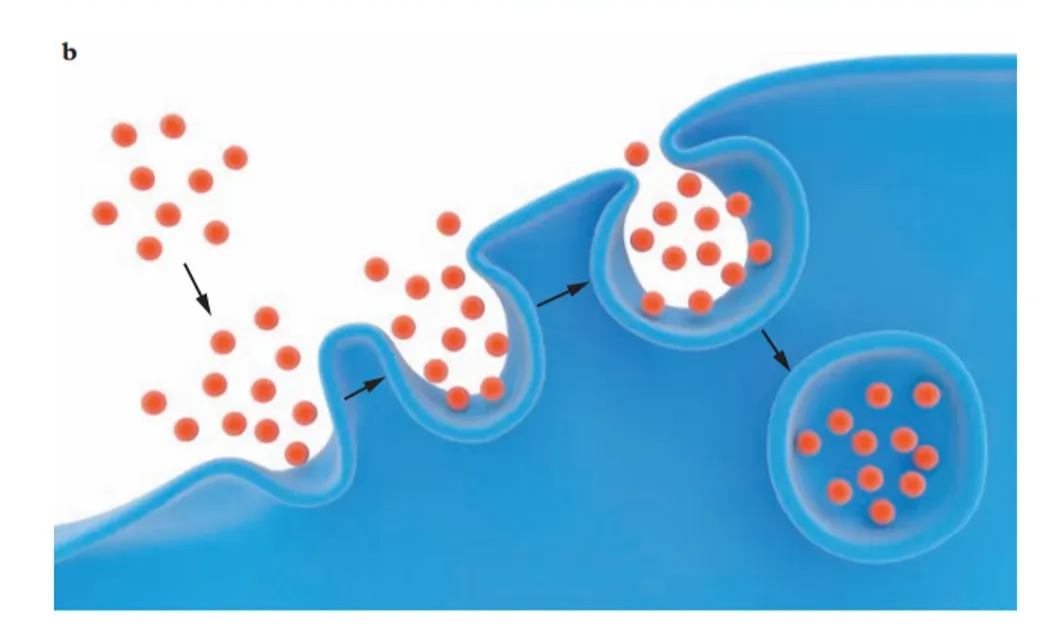
Exocytosis
The active transport of macromolecules out of the cell by a vesicle fusing with the plasma membrane, Vesicle formed within the cell, fuses with the PM and then is released out of the cell, This process is utilised when the Golgi apparatus exports proteins and other materials out of the cell
Binary fission
A form of asexual reproduction in which the parent cells splits into two equal sized daughter cells
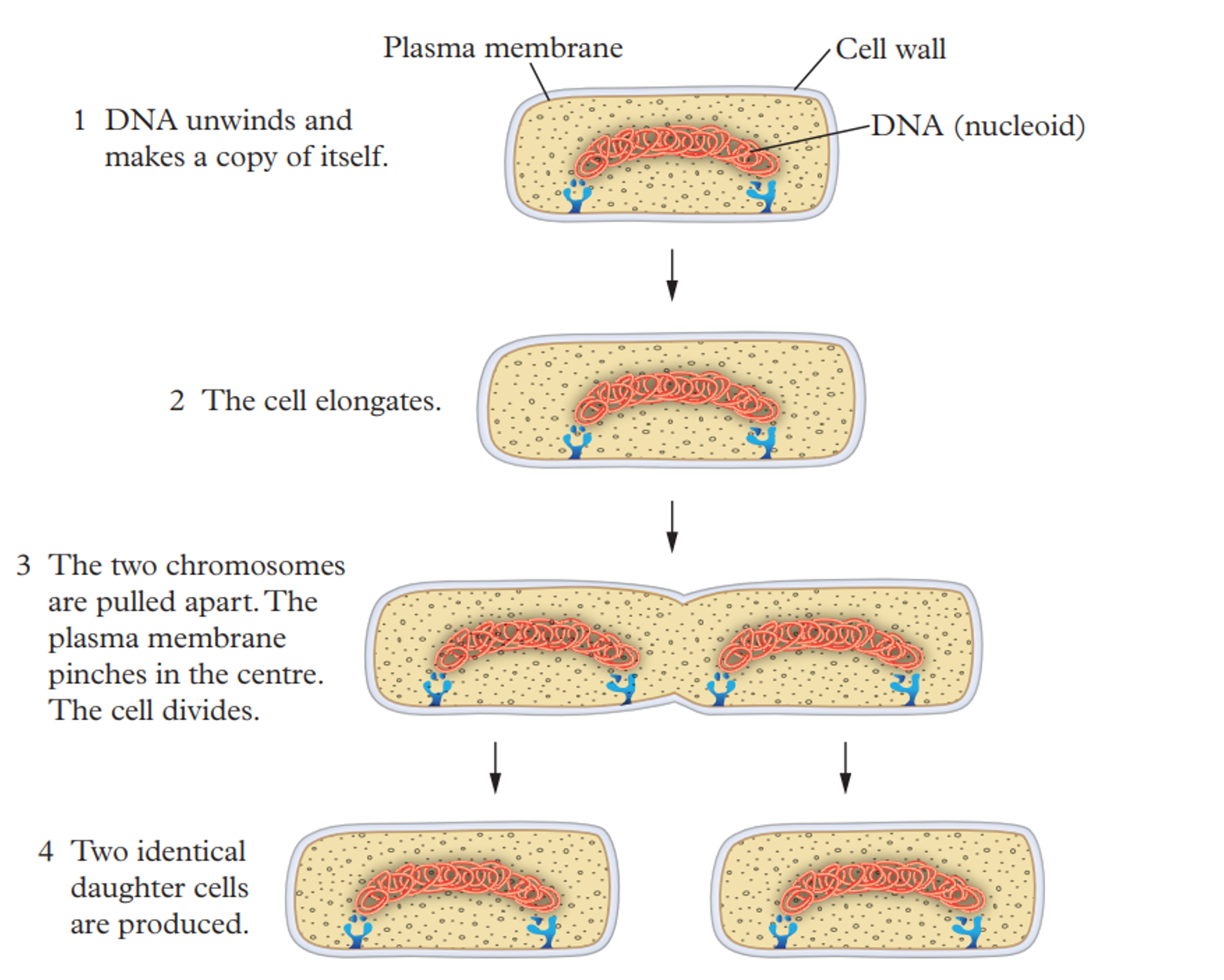
1st stage of binary fission
A single DNA molecule unwinds and is replicated and attaches to the membrane
2nd stage of binary fission
The cell membrane grows and doubles in size
3rd stage of binary fission
The two chromosomes are pulled apart. The plasma membrane pinches in the centre
4th stage of binary fission
Two identical daughter cells are produced
Asexual reproduction
A type of reproduction where a single parent produces without the fusion of gametes (sperm and egg)
Advantages of asexual reproduction
Only 1 cell is required to make 2 cells
It is a rapid process
Disadvantages of asexual reproduction
The daughter cells are genetically identical
The species is more susceptible to environmental changes
What cells would use binary fission?
Prokaryotic cells
Eukaryotic cells
What cells would use mitosis?
Cell Cycle (Mitosis)
The process of a cell growing, dividing and dying, The organised division of the nucleus
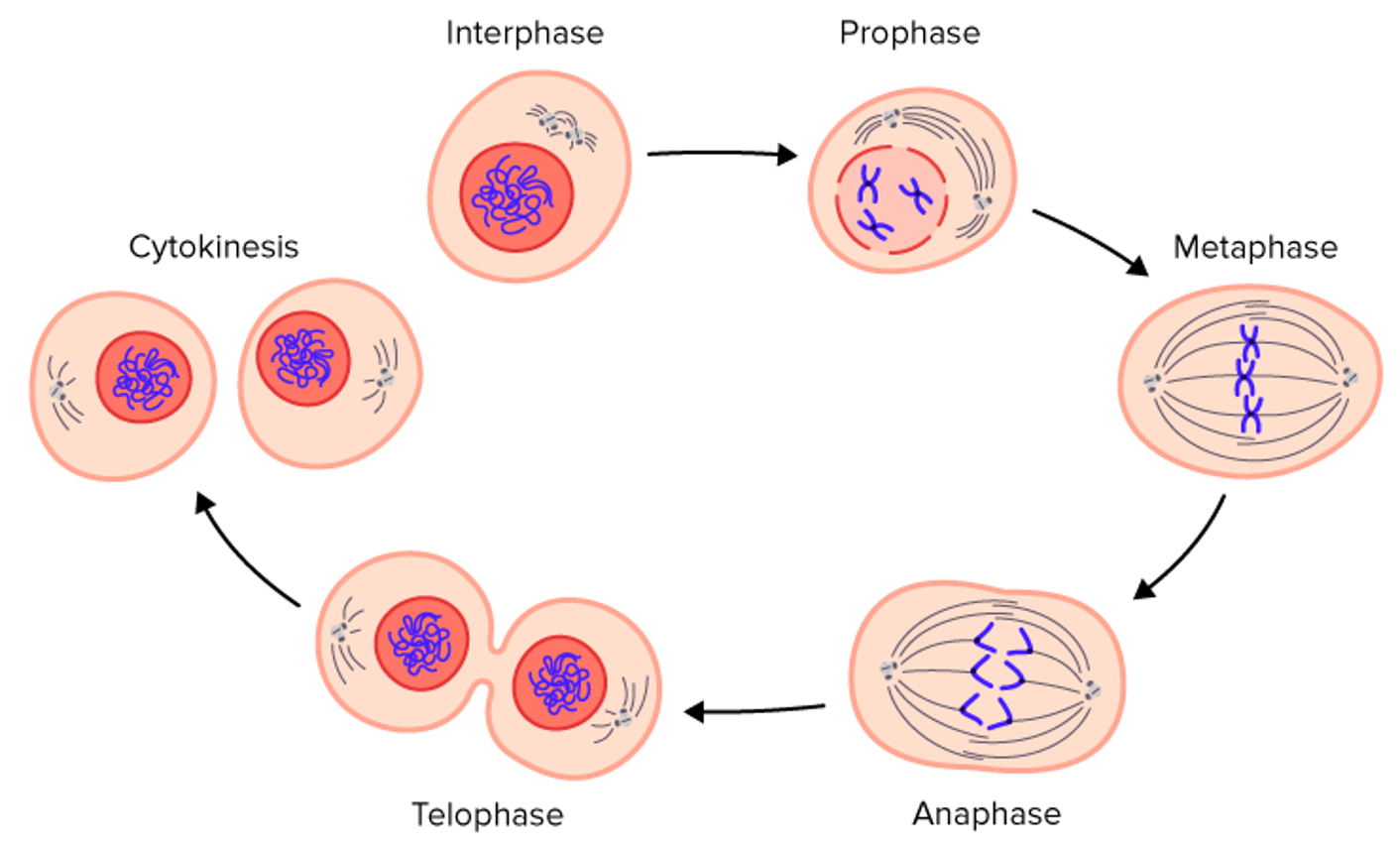
Interphase
The phase cells exist in majority of the time when they are not dividing
G1 Phase
The longest phase of the cell cycle. During this phase, the cell becomes larger and synthesises proteins and organelles
S Phase
The cell replicates it’s DNA by copying each strand of chromatin
G2 Phase
The cell grows rapidly for the start of mitosis
Checkpoint
Exist at various stages of the cell cycle to guard against damaged cells replicating
G1 checkpoint
Cells assesses the health of it’s organelles
G0 checkpoint
Cells exit further replication if it is not fit to continue
G2 checkpoint
Cells assesses if the DNA strands have replicated correctly before proceeding
Prophase
Replicated DNA coils into chromosomes
Metaphase
Chromosomes move to the centre of the cell
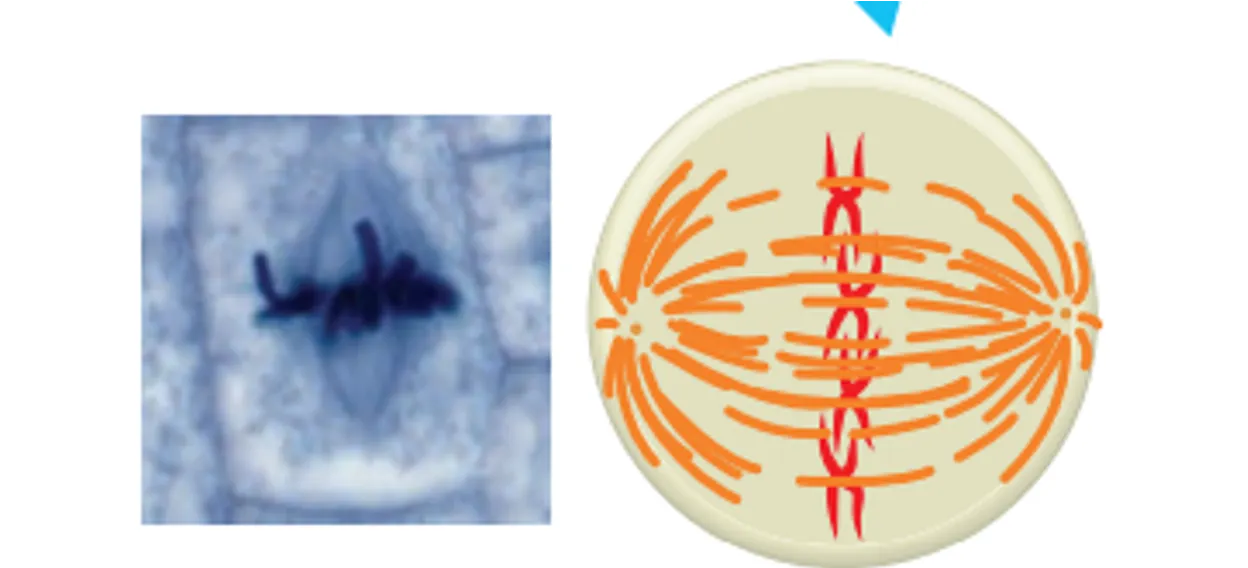
Anaphase
Chromosomes seperate at the centromere and move to the opposite sides of the cell
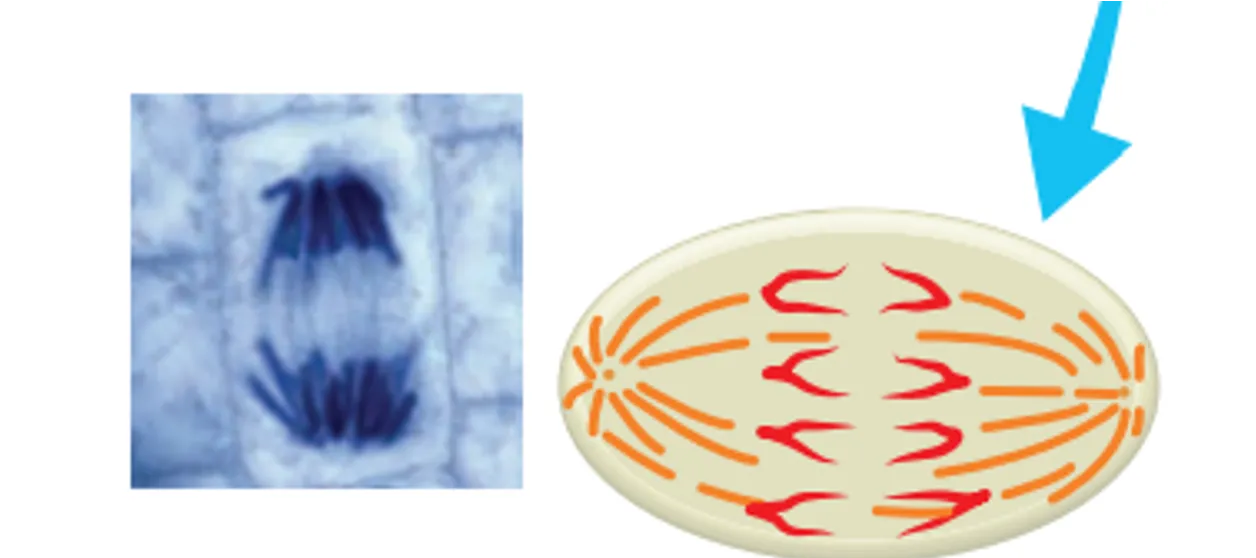
Telophase
The chromosomes begin to unravel and a new nuclear membrane forms around the DNA at seperate ends of the cells
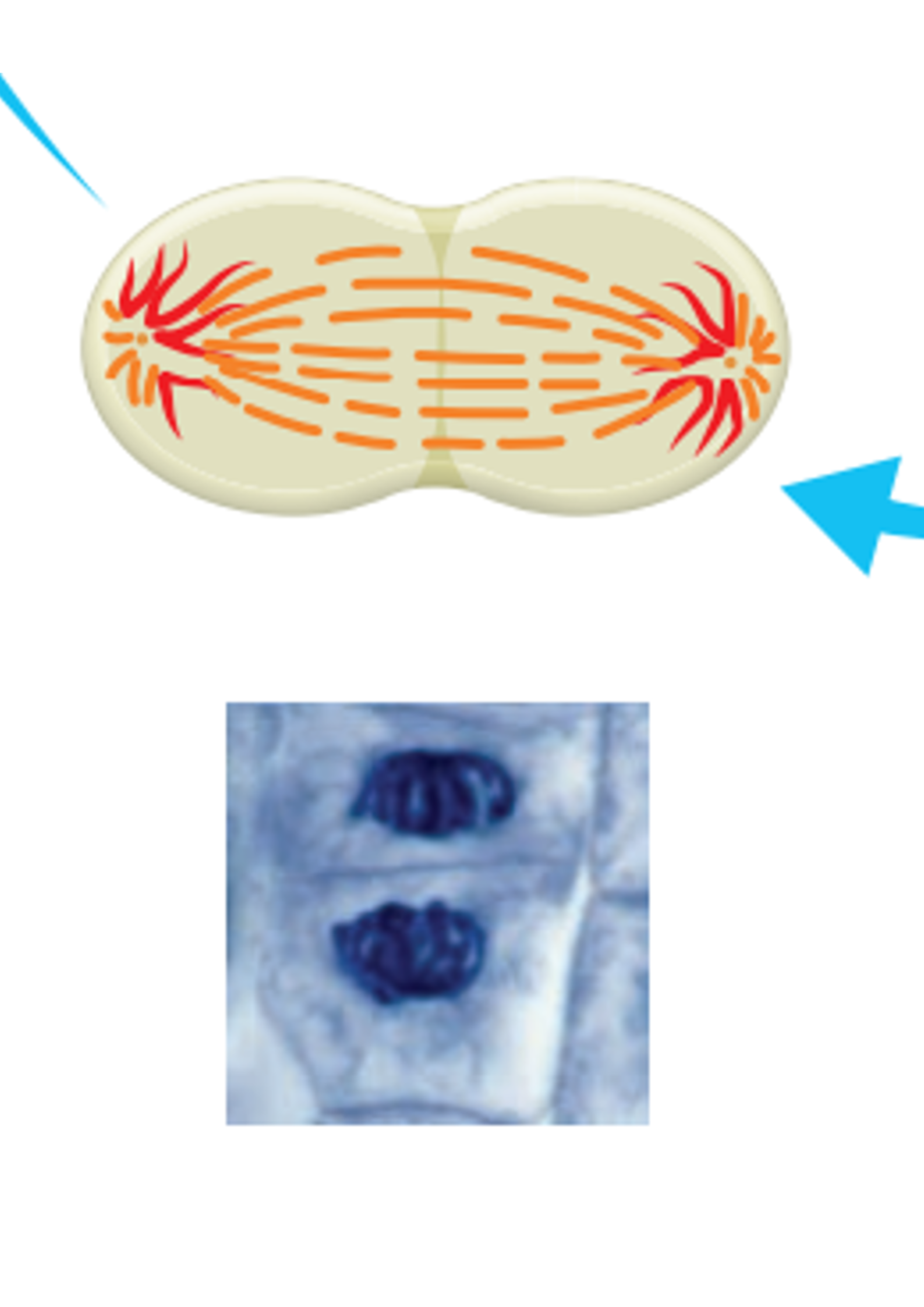
Cytokinesis
The end of mitosis where the cell splits to form two identical daughter cells
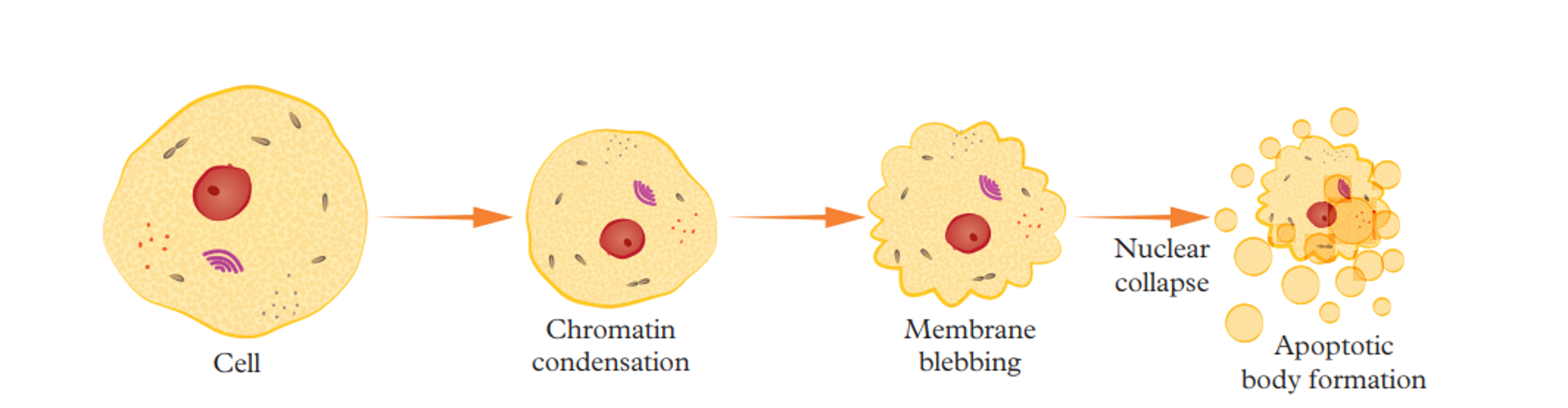
Apoptosis
Naturally programmed cell death
Intrinsic pathway
A biochemical pathway occuring completely within a cell that triggers apoptosis, Internal signals (stress from inside the cell)
DNA damage
Lack of growth factors
Oxidative stress
Cell injury or aging
Extrinsic pathway
Apoptosis initiated by an external signal binding to a death receptor. External signals (coming from outside the cell)
Binding of a death ligand (e.g., FasL, TNF) to a death receptor (e.g., Fas, TNFR) on the cell membrane.
1st stage of apoptosis
A series of enzymes called caspases are activated and start to break down the cytoskeleton of the cell
2nd stage of apoptosis
The cell starts to shrink
3rd stage of apoptosis
DNA is broken down
4th stage of apoptosis
The cell membrane forms into small bulges called blebs
5th stage of apoptosis
The blebs break off from the cell to form apoptopic bodies
Necrosis
Unplanned cell death as a result of injury to the cell
Cell bursts and spills contents
Causes inflammation in the body
Cancer
A disease caused when cells divide uncontrollably and spread into surrounding tissues
Mutagen
Any agent that causes permanent damage to the DNA of a cell
Stem cells
A cell that is capable of forming different cell types
Embryonic stem cells
Cells found in an embryo that can become any type of specialised cell and endlessly reproduce
These are found in the embryo
They can become any specialised cell in the body
Adult stem cells
Cells that can reproduce themselves or produce daughter cells that can become more than one cell type
Totipotent stem cells
An undifferentiated cell that can later differentiate into any type of cell
These can differentiate into any cell in the organism
They are only found in early cells of the embryo, from the zygote
They can be come “totally anything”
Pluripotent stem cells
A stem cell that can differentiate into any cell type within a broad group
These stem cells can differentiate into most of the cells in multicellular organisms, except placenta cells
Can become “pretty much anything”
Multipotent stem cells
A stem cell that can only differentiate into a limited number of closely related cells
They have limited ability to produce different cell types, eg. the stem cells in bone marrow can produce red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets, but they cannot produce other types of cells
Unipotent stem cells
A stem cell that can only form one cell type
These are the most common type of stem cells in the human body
These type of cells can only be used for the regenerated as a stem cell
They are “unique”
What is the correct order for hierarchy of cell potency
Totipotent, pluripotent, multipotent & unipotent
What is the correct order for hierarchy of organisation
Organism, systems, organs, tissues & specialised cells