marketing
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
117 Terms
three ways to be wrong
ignore the problem
false positive: Type 1 error
false negative: Type 2 error
false positive: type 1 error
calling a bad opportunity good
results in waste of resources due to misunderstanding
false negative: type 2 error
Passing up a good opportunity
leaving an opportunity on the table because we cant see its good
often escapes the notice of others
more damaging than other issues
false positive type 1 example
when a credit card compnay issues a notice that a trqansaction has occured that doesnt fit the ordinary pattern
rather risk pbother the person than accepting a fraud theft opposed to accepting the more money they make
rational format
priorizite wich errors are least costly
Decision making process
define the problem
decide to fix it
do everything to fix it
identify the probelm
why are we doing this
whats the purpose
how will we achieve sucess
why am i failing
how can i fix it
scientific method
ongoing process:
make obervation
think of intresting questions
formulate hypothesis
develop testable predictions
gather data to test predictions
5 redifine alter expand regect hypthes go back to 5
develop general theories
scientific method book
theory
sampling
measurment
experimental design
data colelction
pattern discovery
implementation
evaluation
sampling
base of triangle
can i generalize from this?
who knows the awnswer?
do my responders represent everyone properly?
equal chance of selection?
measurement
second from bottom
have i measured the important things?
valid truthful, reliable repeatable, useful?
how good are my measures?
experimental design
3rd from bottom
can we attribute the different result to a different treatment?
did a cause b?
data collection
4th from bottom
uniabsed?
yeilds data responsive to my problem?
pattern discovery
5th from bottom
analysis fit the data colelcted?
provides actionable results?
answers our question?
implementation
6th from bottom
bad in practice=bad in game
who will this work on?
can we replicate the lab settong?
explantion=prediction?
evalution
top of pyramid
how accurate was our prediction?
cause and effect correct?
what else was impacted?
how to imporove next time?
SMED PIE bottoms up
sampling
measurment
experimental design
data collection
pattern discovery
implementation
evaluation
what we use in smed pie
sampling
measurment
data colelction
pattern data discover
evalution
what do current graduate lacks
critical thinking skills
attention to deatail
communication
writing skills
ownership
thinking critically: objective analysis and evalution of an issue in order to form a judgement
open midness
respect evidence and reasoning
cognitive flexibility: condisder different perspective
not stuck on one position
skepticism
clarity and precision
false equivalency
A logical fallacy that wrongly assumes two things are equal or comparable, even though they have significant differences. It disregards the nuances and context that make them distinct, leading to flawed reasoning and faulty arguments.
logical fallacies
innocent and wrong v lie with stats
disprove ur agrument
either illegitimate arguments or irrelevant points, and are often identified because they lack evidence that supports their claim.
ecological fallacy
inferences about the nature of individuals are deduced from inferences about the group to which those individuals belong
sampling of a popultion lets a few speak for many
ecological fallacy example
one of the business professors was busted form embesselment thefore alll busineess ppl are snakes
gamblers fallacy
believing that unrelated occurrences are dependent upon each other
mistaken belief that previous outcomes in a random event can influence future outcomes.
gamblers fallacy example
thinking that if a coin has landed on heads multiple times in a row, it is more likely to land on tails in the next flip. In reality, each coin flip is independent and has a 50% chance of landing on either heads or tails, regardless of previous outcomes.
umpires calling a pitch a ball after a lot of consecutive strike
strawman
misrepented somes argument to make it easier to attack
easier to present yout own position as beign resonable
exaggerating, misrepreeitn or lying about somones argument
ad hominem
attack oppents charecter or personal traits in attempt to undermine their argument
casting doubt on their charector to discreditut their argument
personal incredulity
because you found something difficult to understan or are unaware of how it work you made out like its not true
loaded question
you asks a question that had presumption built into it so that it couldnt be anwsered without apearing guilty
recipient of is compelled to defend themselves and may apear flustered or taken aback
black or white
you present two alternative states as the only possibilities when in fact more possibities exist
false dilema
black or white example
You're either with us or against us." This fallacy oversimplifies a complex issue by excluding any other potential positions or perspectives. It fails to acknowledge the possibility of a nuanced or moderate stance.
red herring
something that misleads or distract from a relevent or importanrt question
red herring example
when a politician is asked about their stance on a controversial topic and instead of answering the question, they start talking about an unrelated topic to divert attention.
errors in logic dont beleive these
when will i ever use stats
80% of a good solution is good enoguh
things will never get that bad
there are no great choices so i will sit out
all these are exuses to stop thinking
sequential decisions errors
mistakes or inaccuracies that occur when making a series of decisions in a specific order or sequence. These errors can arise due to various factors such as cognitive biases, lack of information, flawed decision-making processes, or external influences. It is important to identify and minimize sequential decision errors to improve the overall effectiveness and efficiency of decision-making processes.
sequential decisions errors example
One example is the "gambler's fallacy." This occurs when an individual believes that previous outcomes in a random process will influence future outcomes, even though each event is independent and unrelated. For instance, if someone repeatedly loses in a game of chance, they may mistakenly believe that their chances of winning increase with each subsequent attempt. However, in reality, the outcome of each event remains statistically independent, and past results do not affect future probabilities.
derivatives
combination of computing power and intellectual prohress led to the creation of whole new markets in finacial future and options made quanitative analysis as opposed to gut feel the respecrable way to go about making bets on the market
moneyball
inefficiency caused by sloppy data(opportunity)
questions the meaning of bb stats(conventional wisdom
define the goal- identify the problem(dependent variable)
know the true value of perfomance(solve an old problem in new way)
extract the element of luck(reduce error & optimize)
old school baseball biz
focus on the best selling product
create value(solve a problem better)
emphasize customer satisfaction
make financial available(remove barries)
ever improving target marketing(reduce error)
marketing goal of trucks
create awarness sed prospects to website
channels of trucks
all digital
google searcg
auto trader
trade association
facebook post and ads
sucess of trucks
clickes
likes
reviews
conversaions
cost/sale by chanel
chenels cost/sale trucks
customers-look alike-distribute-click through
optimizing facebooks tarfeting
customers
look alaike(indiviual purchale model aggregated to zip)
distribute(who how selceted
click thoguh(decreas cost)
score card modeling
give value to certain charecteristics
individual (direct marketing) targeting
customers:
some more desirble than others
profit
advocates
ltv
we control and optimize
look alike:
who didnt respond
we control and optimize
distribute
we control and optimize
conversion ourchase profit ect
lifted trucks problem solving:
increase marginal targeting control(opportunity)
question click based metrics as campaign drivers(conventional wisdom)
question the congruence of favebook goals with ours(dependent variable)
know the true value of a prospect potential (solve an old problem in a new way)
suck less(reduce error and optimize)
optimize by reducin error systematically
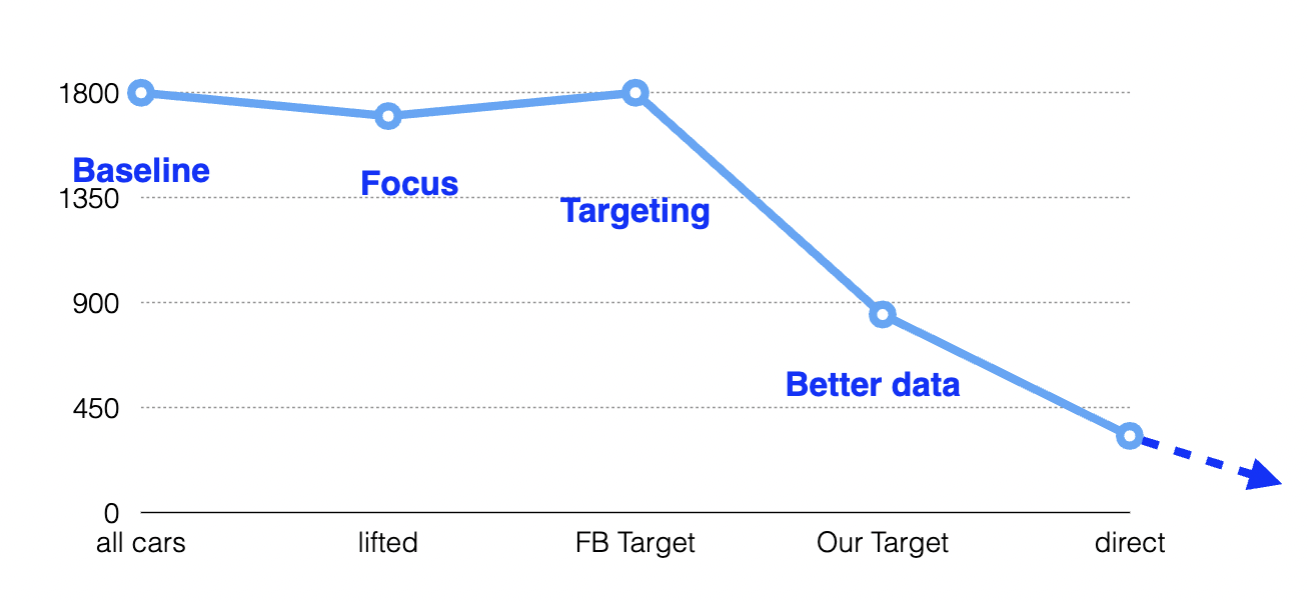
whats the business case
reduction of error optimizes marketing
innovation: what is it really
a new solution or perspective to an old problem
marketing optimization
systematic approach scientific method
measurment craft long
descibe its charector, psycology, history, power, grace, glory, consistency, sacrafice, courage, succes, falure, frustration, bad luck, ambition, overeaching, diabline
multi dimensional nuanced
measurment craft
collection and desgin of data
planning is 95% of success
B=f(e,p)
behavior is a function of our enviroment and our predispositions
Qualitative data
not so concerened with scaled or numberic data but a directional sense for our topic
quantitative
assinging values to aspects that cause/effect the phenomenon
when to use qualitative reasearch:
lack specific theory
arent sure how to form a construct
jsut starting to explore why people do what they do(explain
even what is it they do(describe)
how to conduct qualitative reaserch:
in-depth interview: explore the topic in a free rangign loosely structure format
focus groups: gather smalll groups of relevant consumers to react tpo specific questions still exploratory and intructive of qualitive design
observational unobstritopn npt asking questions but searcing in hwat wre can see
measurment craft: direct survey or interview
in peson
by mail
online
phones
in groups
measurment craft: inderect observed without interaction
secondary data
Anonymous
indirect methods: content analysis
social meadia:
indexing words patterns
keyword serch
linking content(meaning substence
to text streams
thematic analysis
indirect methods: Secondary data analysis
can be compiled from several sources to from a uique database
can be mered modeled from survey or other primary data
allows re analysis of the same research question over time
hight content data
doesnt have to be complex
just structured and relevent
correlation answer
as A changes so does B in whcih direction and by how much
regression answers
how much variance in B does A explain
qualitative research help us form an initial theory
what are the questions we need to ask to validate or refute
how can we sneak up on ourt topic without bias to the responder
how ca we creatively explore the concepts involved
measurement craft: TOP
theory → operationalize→ constructs
theory
getting on base is more important to a good season than defensive skill
operationalize
what are the observable(operational aspects of a theoretical concept
theory → operationalize→ constructs in practice
getting on base is more impontant to a good szn than defensive skill
get on base:hits,walks,hbp
good szn:make plaoffs, more wins than loss,95+ wins
defensive skill:errors made,double plays stikeouts
constructs
measured attempts to capute a concept
OPERATIONALIZE examples in practice
emotional ads have a greater effect than those stressing economic befinifts
what can we observe to construct each of these concepts
operationally how can we measure each one
are there differnt ways to measure each aspect
construc are operationalized by questions
how do we coneive the phenonmenon?
nominal- balcka nd white, categories
is it measurable at a higher mroe detailed level?
we can always reduce a measurment but we can never expand it
levels of measurment,worst to best
nominal
ordinal
interval
ratio
nominal
attributes are only name
weakest
ex. did u run in the race? yes or no?
ordinal
attributes can be prdered
ex. what placed did u come in the race
interval
distance is meaningful
ex. time between first and second place and other positions
ratio
absolute zero
likert scales def
psychometric scale commonly used in surveys and questionnaires to measure attitudes or opinions. It consists of a series of statements or items that respondents rate on a scale, typically ranging from "strongly agree" to "strongly disagree." The responses are then assigned numerical values, allowing for quantitative analysis of the data. provide a structured way to assess subjective constructs and are widely used in social sciences, market research, and other fields to gather and analyze data on people's attitudes, beliefs, and perceptions.
likert scales
easy to respond to
several uni dimensional measure froma batter
odd or even scaling with or without midpoint
often attitudinal or belief based
allows us to discover suprose associations: things we didnt know were related
the shallows blah
unified theoru of the univerus
brain cells look like trees
neaural plasticity
ability of neural networks in the brain to change through growth and reorganization when the brain rewired to function in som way from how it previously functioned
our fear: makign both kinds of errors
false positives: wirign unhelpful circuits
false engative: bot wiring more helpful circuits
distractions
someones good/necessecary
sleep on it- let subconscious figure things out
social psucological complications
lack of nature time limits evolutionary development
online develops qualitatively differnt relationships
opportunity cost
increased suspicion
incresed deception
anti scoial
revoeralbel
smart phones destoy a generation
physcially safer than ever
lesss drinking and also driving
less social
less sex
working less
homebodies, less time with friends
distraction on purpose
addicted
fomo
unhappy
depressed
less indipented
minds consume with a medium
t→o→c for social media
develop theory we can test
any truth to it
are the authors right
are they misisng things
is there more to the sotry
is social media waning
12%
young AMERICANS CANT FIND work
critical thinking/problem solving: why its importnat
how all orgs are able to function properly
intead of giving up they find a new way to fix the problem
you dont have to know everything
have multuple solutions
critical thinking/problem solving: how to get it
supposed to be taught during college
college hower often teach to be right than to learn
internships, volunteer campus orgs all help u gain this skill
attention to detail: why its important
second most popylar skill grads lack
shows u take the time to ensure every job u do is complete nearly perfectly and u took time to do so
obsevsional and dedication
attention to detail:how to get it
dont only focus on the big picture
deliver quality work even on uniportant stuff
high quality work
communication:why its important
3rd on the list
very important to have
listeing
figureing out what tyoe is needed for the situation
50% of language is non verbal
recnlty grads lack body language and use more emojies
communication: how to get it
talk more with ppl outside ur generation, you dont know
take notes on how they respond
what vocab do they use
builds rapport with coworkers
writing skills: why its importnatn
4th on the list
need to know how to make a point and make it well
basic grmmar and written etiquette
writing skills: how to get it
read more essays, emails,
expose yuorself to good writing
be aware of your audience
ownership: why its importnant
5th on th elist
tied with leadership
take responispitu
you have to initiate
dependable and trustworhty
hold youself accountable
reflection of work ethic
ownership: how to get it
in college with group projects
start a project