Organic Chemistry
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
67 Terms
alkenes test/result
-reacts with Br2(aq) immediately (addition reaction)
alkenes go colourless in bromine water
addition of halogens=test for double bonds
crude oil
a mixture of hydrocarbons
alkanes test/reactions
alkanes react with Br2 (aq) in presence of uv light (goes colourless)
undergoes substitution reaction
functional group
part of an organic molecle responsible for it’s chemical reaction
alkene general formular and functional group
CnH2n
C=C
molecular formular
exact number of atoms
empirical formula
simplest ratio
displayed formula
shows all atoms and all bonds
organic compound
a compound that is carbon based
why do we crack alkanes
smaller alkanes used for fuel = high demand
breaking long chains meets our needs and gives alkenes
conditions for cracking
600-700oC
Alumina/silica
steps of fractional distillation
crude oil heated until it vaporises
mixture of gases enter column
top hotter, bottom cooler
gases rise, cool and condense at boiling point
tapped off at height
small molecules collected at the top, long at the bottom
fractions
(rlly good kids deserve fancy biscuits)
refinery gases
gasoline
kerosene
diesel
fuel oil
bitumen
isomers
2 compounds that have the same molecular formular but a different displayed formular
hydrocarbon
a compound made of hydrogen and carbon only
saturated
contains only single C-C bonds
unsaturated
contains 1+ C=C double bonds
what is released when burning hydrocarbons
COMPLETE
CO2 - greenhouse gases
INCOMPLETE
C particulates - respiratory issues, global dimming
Sulfur dioxide from impurities - acid rain, ph in lakes, limestone
nitrogen oxides (car engines) - acid rain (catalytic converters
homologous series
compounds with…
same general formula
similar chemical properties
a trend in physical properties
differ by CH2
substitution reactions
swapping of one atom for another atom (or groups)
ALKANES
Addition reaction
adding a substance to another
2 substances —> 1 substance
ALKENES
longer chains are…
darker colour
very viscous
higher boiling point
non flammable (smokey flame)
alkane general formula + functional group
CnH2n+2
saturated
smaller chains are
lighter colour
non viscous
lower boiling point
flammable (burns with clean flame)
general formula
can be applied to whole homologus series
structural formula
gives us imformation on how atoms are arranged
Refinery gases used for
heating + cooking in homes
gasoline used for
petrol for cars
kerosene used for
jet fuel
diesel oil used for
trucks/lorries
fuel oil used for
big ships/ tankers
industrial heating
bitumen used for
road surfaces
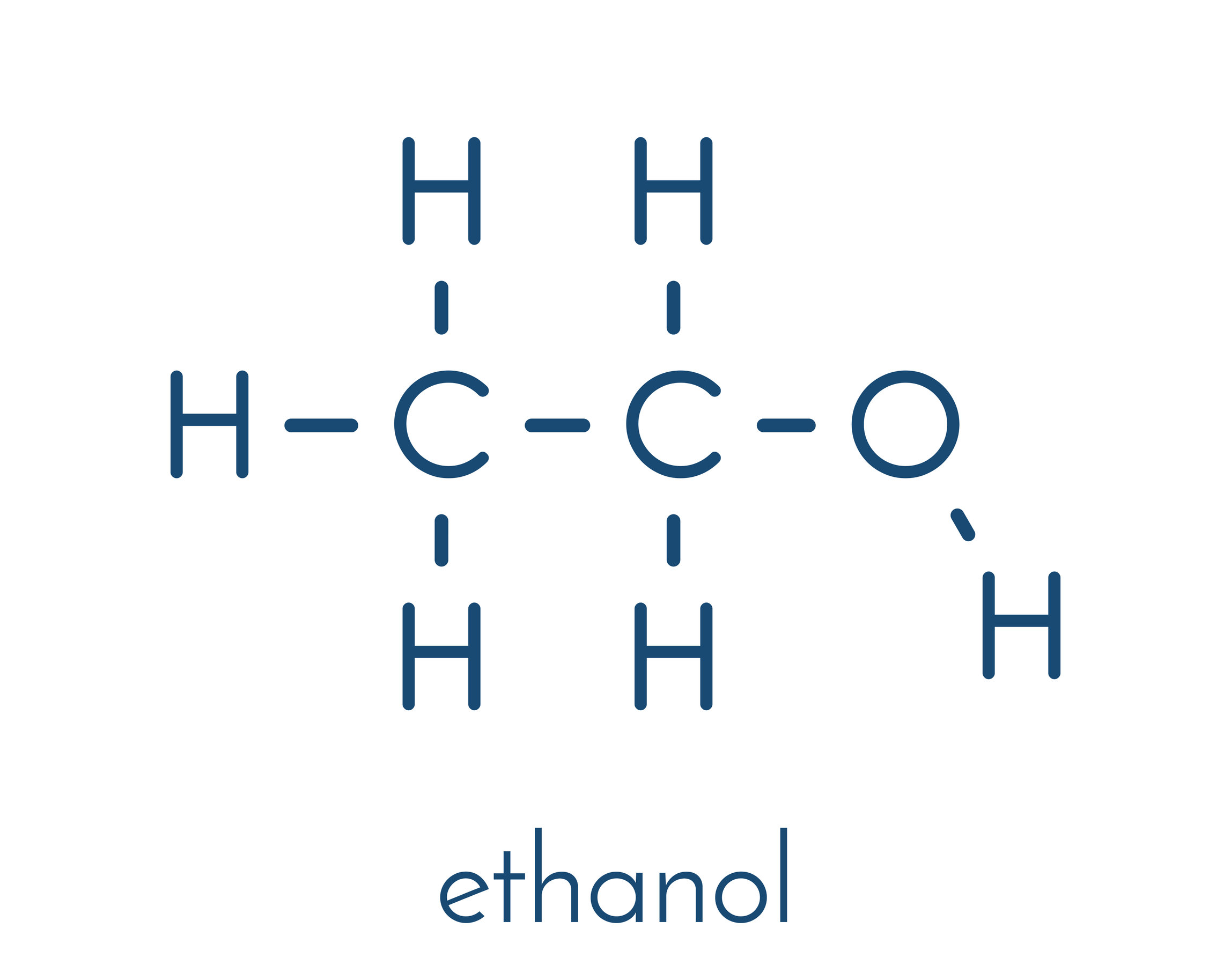
alcohol functional group
-O-H
structure of ethanol (add more c for others)
use of alohol
fuels
solvents (perfumes + aftershaves), dissolves solutes that can’t be dissolved in water
ethanol in alcoholic drinks (fermentation)
fermentation of carbohydrates conditions
approx temp = 30
pressure = normal
catalyst - enzymes in yeast
ABSENCE OF AIR
conditiond for reaction of ethene with steam
temp = 300
pressure = 60-70 atm
catalyst = phosphoric acid
fermentation raw material + type
sugar cane, renewable
ethene with steam raw material + type
crude oil, finite
fermentation type of process, speed, purity
batch
slow
impure
ethene with steam type of process, speed, purity
continuous
fast
pure
functional group of carboxylic acid
-COOH
functional group of esters
-COO-
2 ways to oxidise alcohols
burning in air
microbial oxidation
word equation ethanol burning in air
ethanol + oxygen —> carbon dioxide + water
microbial oxidation word equation
Ethanol + oxygen —> ethanoic acid + water
structure methanoic acid (add more c for others)
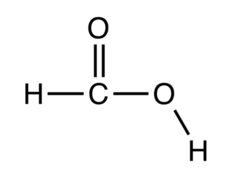
carboxylic acids are ____ acids
weak
what is a strong acid?
all the molecules break down to form H+ ions when added to water
what is a weak acid?
only a small fraction of the molecules break down to form H+ ions when added to water
Acid + carbonate —->
(+observations)
salt + carbon dioxide + water
fizzes gently
oxidation of alcohols leads to
carboxylic acids
Acid + metal —→
salt+ hydrogen
fizzes gently
vinegar is
an aqeous solution containing ethanoic acid
how are esters formed
carboxylic acid reacts with alcohol in presence of sulfuric acid catalyst
what is a polymer
a long chain molecule made by lots of smaller molecules joined together
how to molecules containing C=C bond form polymers
what type of reaction?
C=C bonds join together to form a chain (polymer) no other products are made
addition polymerisation reaction
3 examples of addition polymers and uses
polyetherne - plastic bags
poly tetrafluoroethene - teflon surfaces, non stick kitchenware.
poly chloroethene - water pipes
what is a repeating unit of a polymer
smallest structure with, joined together, forms a polymer
repeating unit of addition polymers
change double bond to single, extend single bonds on either end
what is a condensation polymer
polymer made in condensation polymerisation
molecules join together, also release small molecule (H2O or HCl, etc)
polyesters
polyamides
what are biodegradable polyesters called
biopolyesters
how to draw caboxylic acid and alcohol reaction
remove O-H from carboxylic acid
remove H from alcohol
but them togehter
name alcohol first ( bit with no double bond)
-yl -anoate
are esters volatile
yes
problems disposing of addition polymers
inert, strong C-C bonds, can’t biodegrade = landfill
toxic gases when burnt
2 things in a condensation polymer
dicarboxylic acid and diol
oxidising agent for alcohols + colour change
potassium dichromate in sulfuric acid
orange → green