APHG Map projections
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
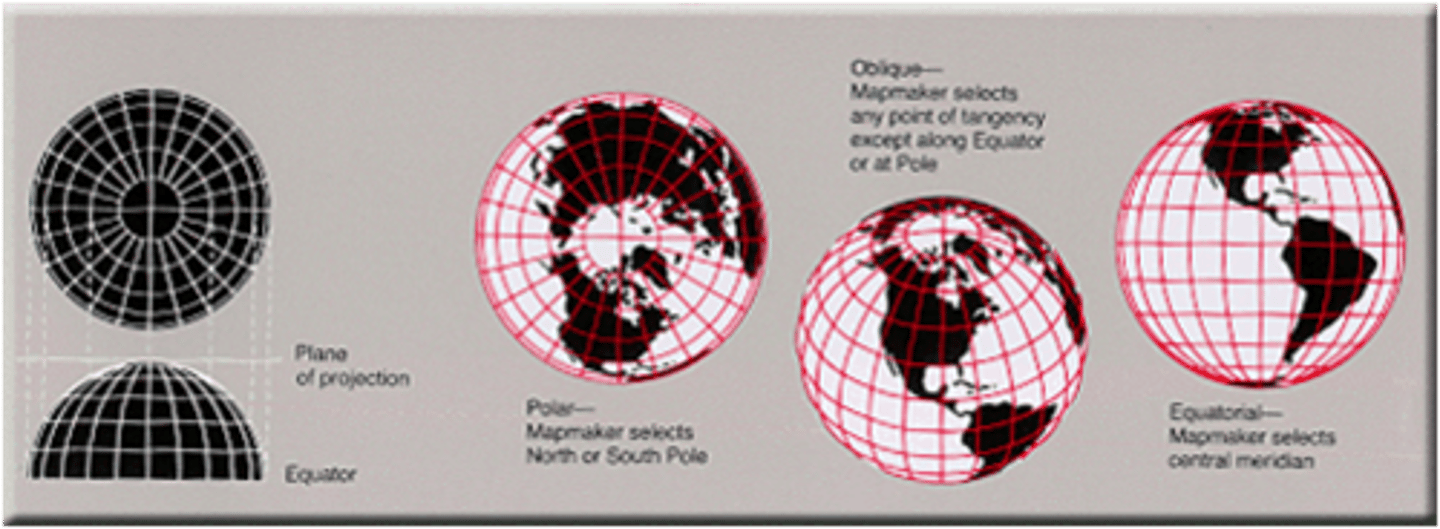
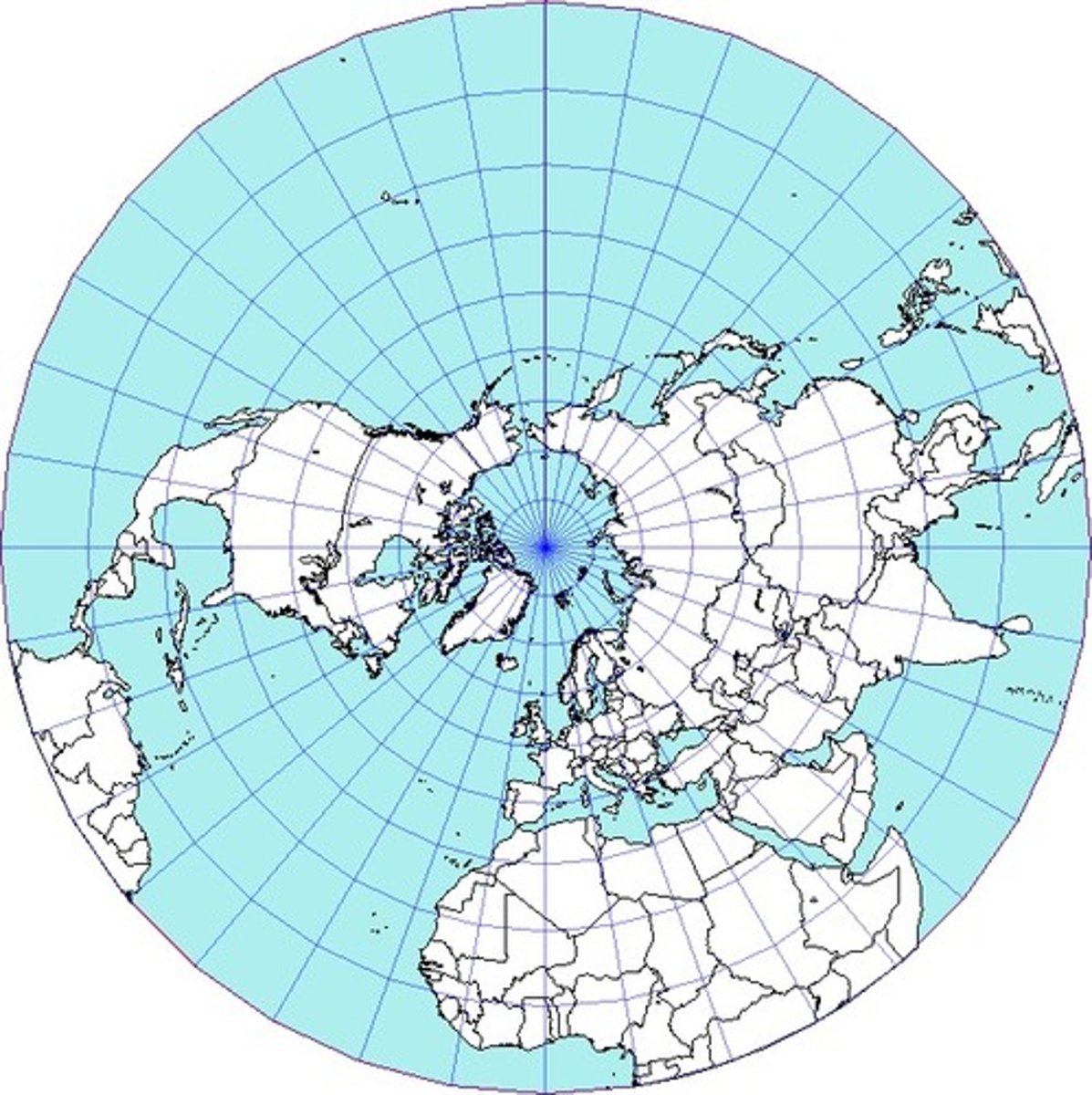
Polar Map
A circular map with chosen central point where distances and shapes are usually distorted away from center, drawn to show Arctic & Antarctic areas
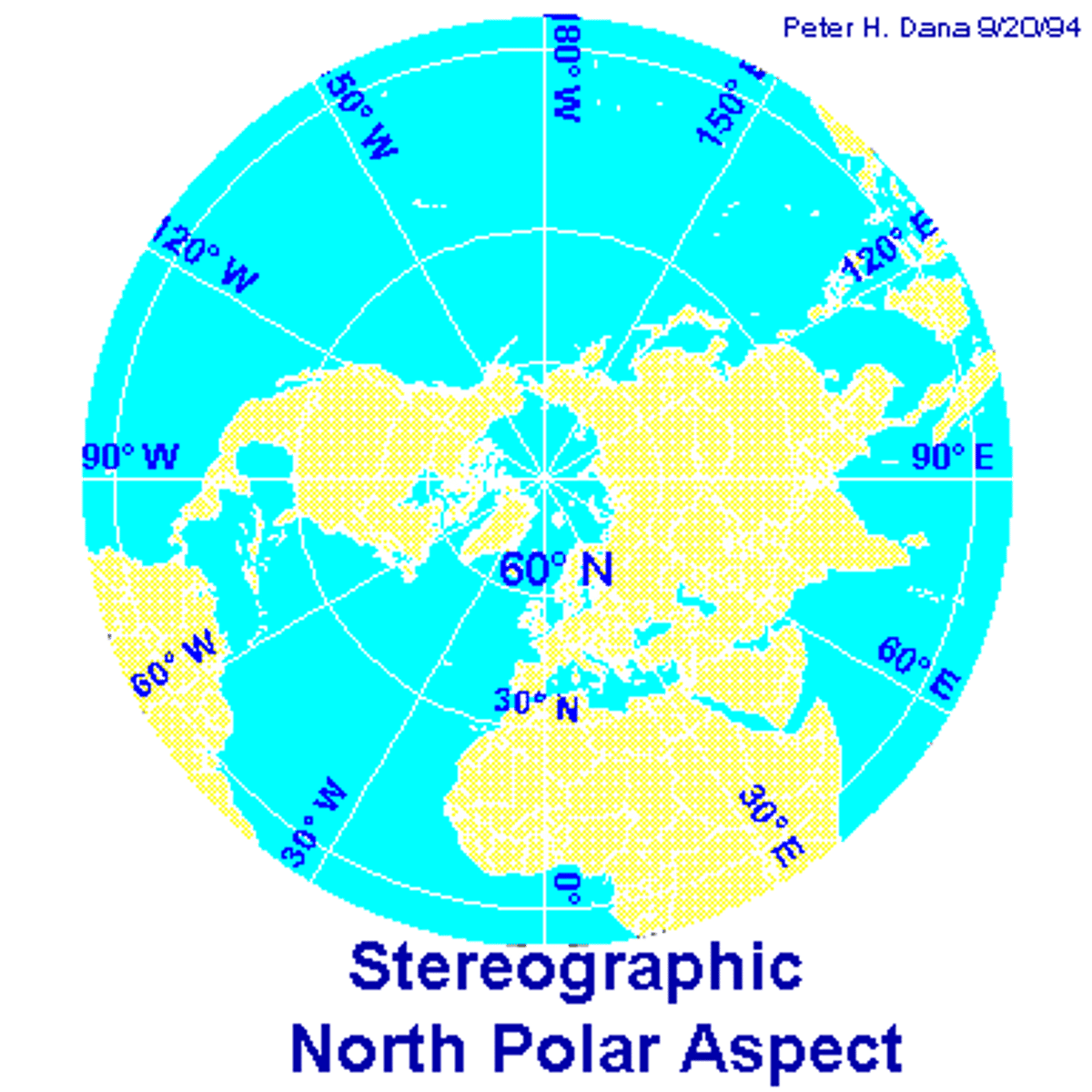
Azimuthal Projection
A map projection that shows true directions from a single point, creating a 'realistic' view of earth as seen from space.
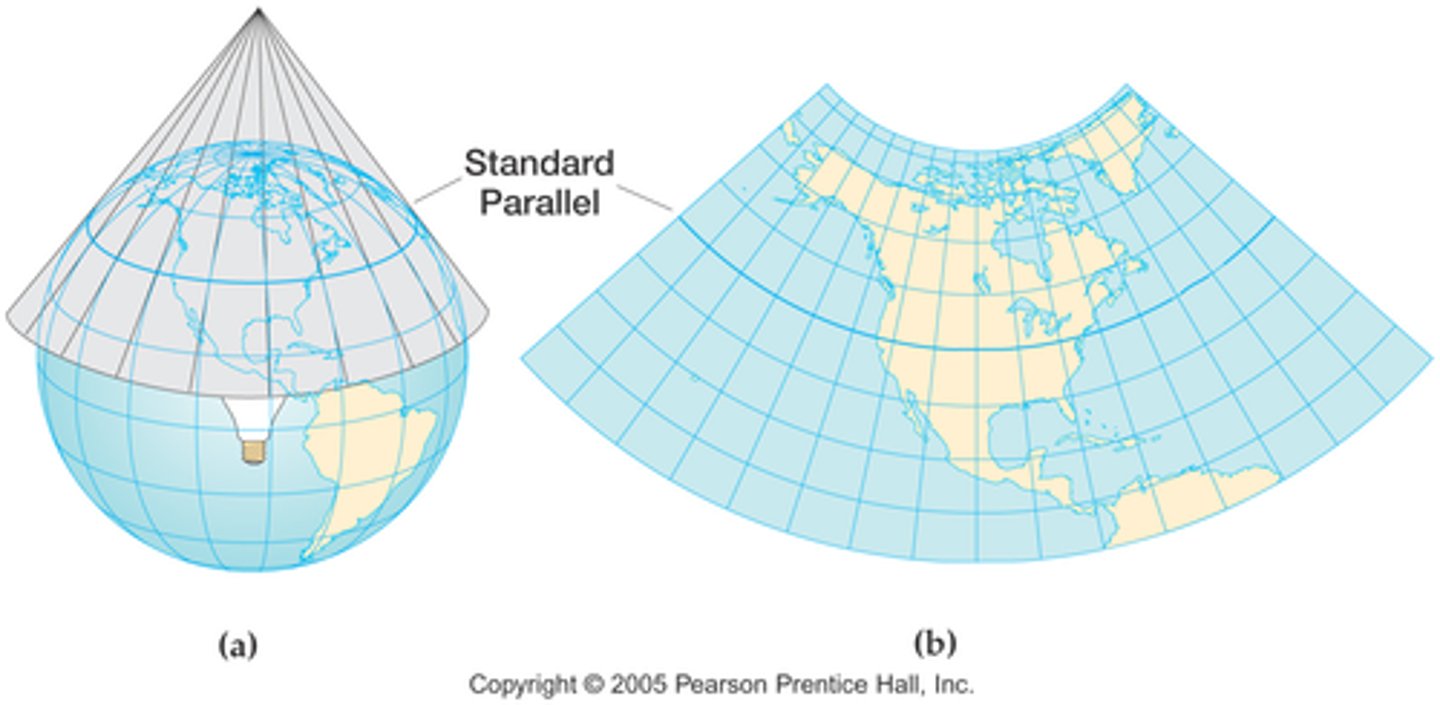
Conic Projection
A map projection that shows the earth's surface in the form of a cone, in which meridians are perpendicular to every parallel and every parallel is a concentric circle.
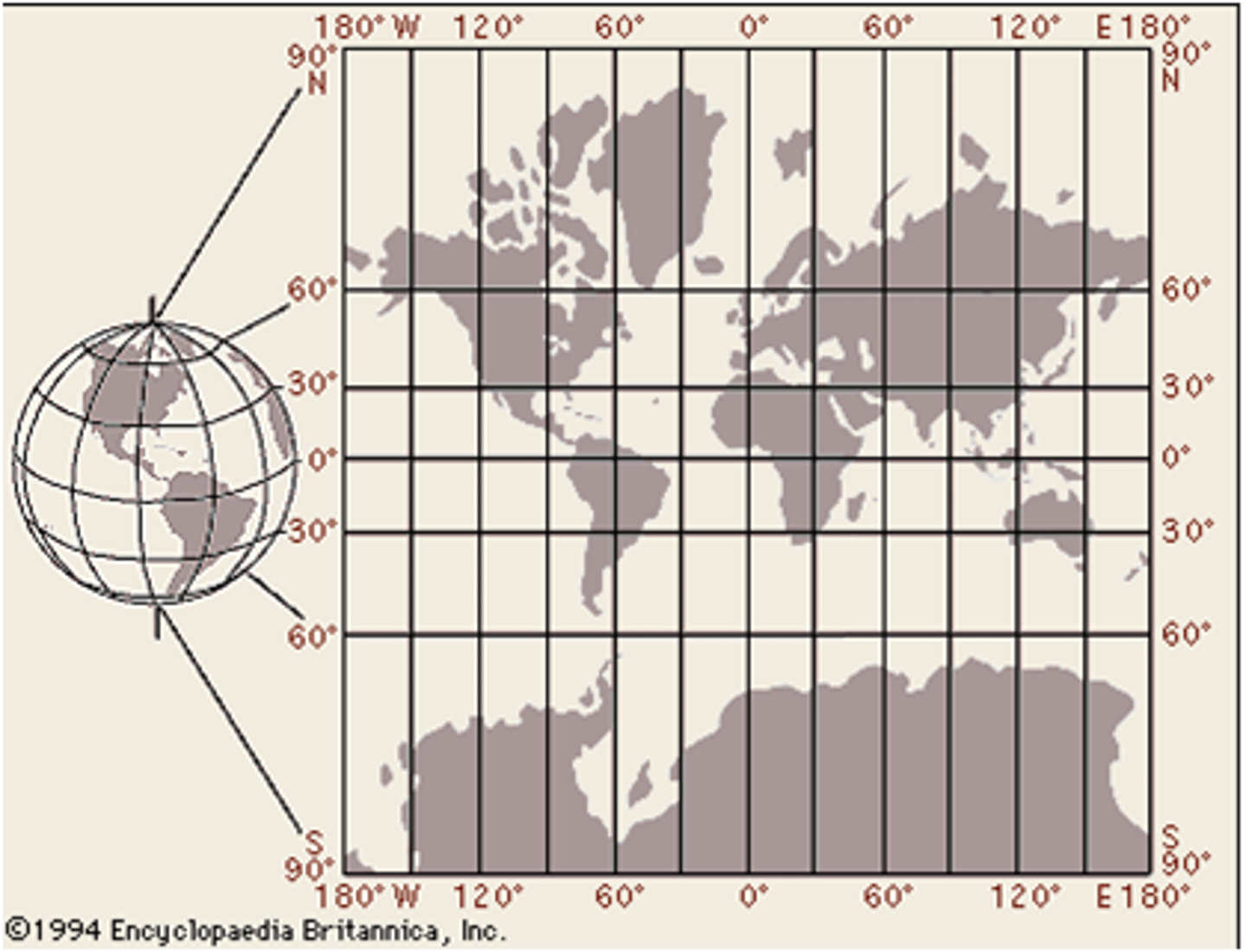
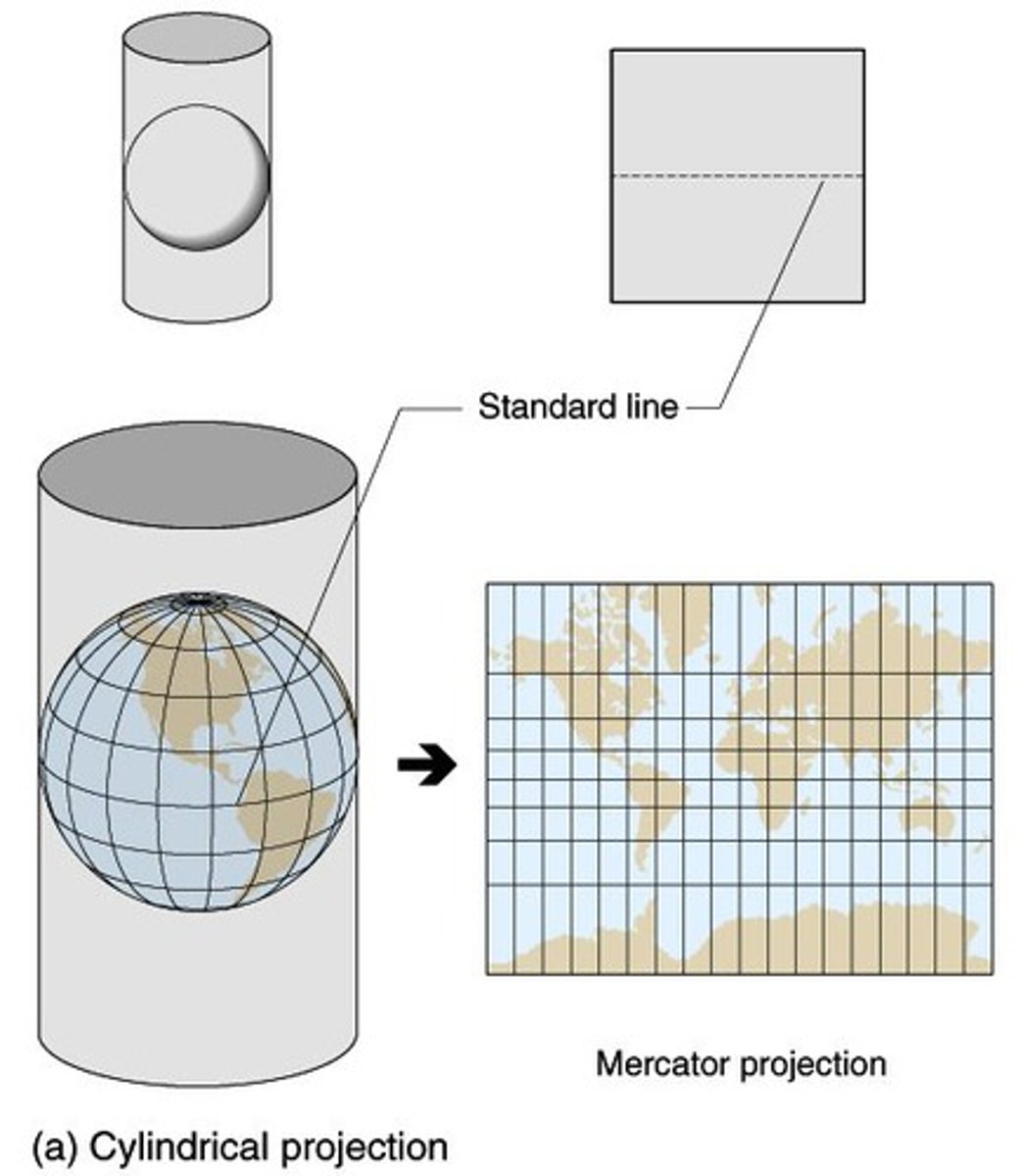
Cylindrical Projection
A map projection that shows the earth's surface in the form of a cylinder, in which meridians and parallels are straight lines.
Equal Area Projection
A map projection in which the relative sizes of land masses are proportional to actual landmasses while the rest of the map may be distorted (such as the north and south poles).
Conformal Projection
A map projection in which shape is preserved in small areas.
Compromise Projection
A projection that does not have equal area, conformal, or equidistant characteristics, but rather seeks to minimize and balance distortion overall.
Equidistant Projection
A map projection in which the distances between one or two points and every other point on the map differ from the corresponding distances on the sphere by only a constant scaling factor.
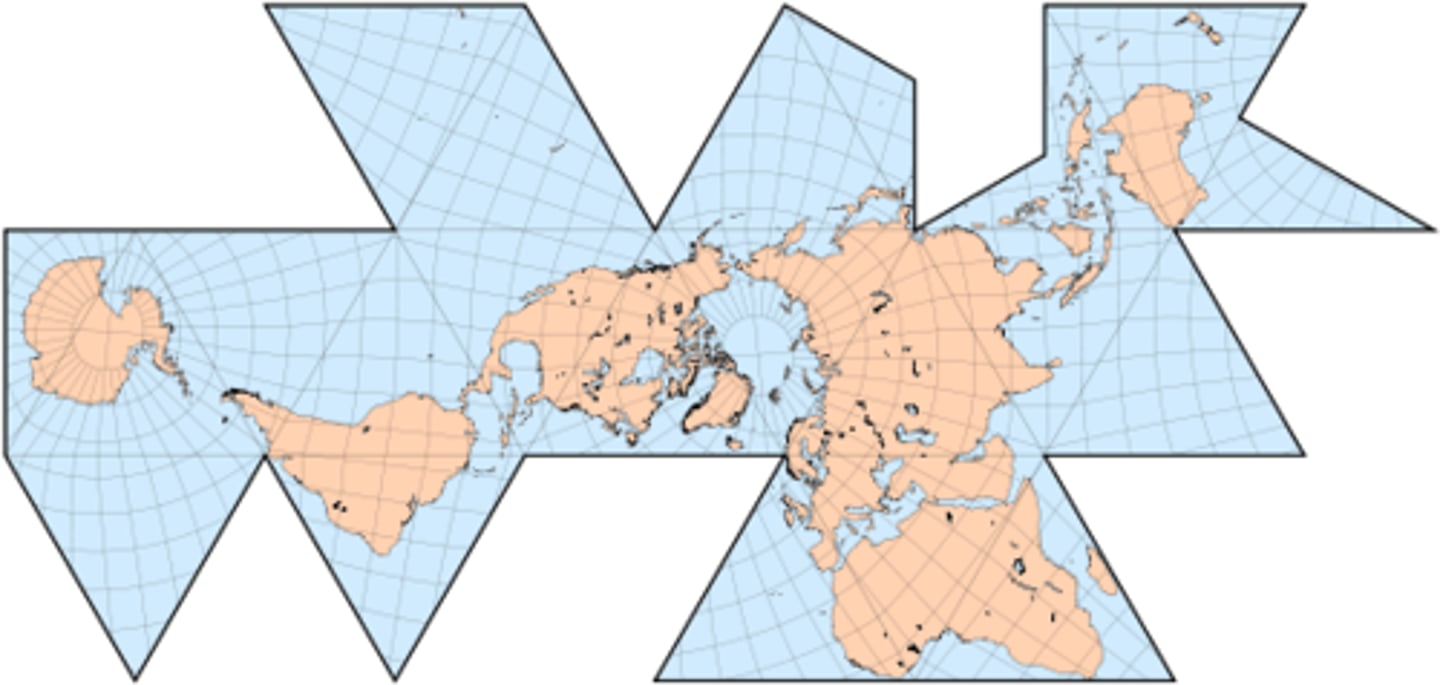
Fuller Projection
A type of map projection that maintains the accurate size and shape of landmasses but completely rearranges direction such that the four cardinal directions - north, south, east, and west - no longer have any meaning.
Goode's Projection
An equal area projection of the world, distorting ocean areas in order to minimize the distortion of the continents.
Lambert's Conformal Projection
A map projection most useful for aeronautical navigation in which latitude lines are unequally spaced arcs that are portions of concentric circles and longitude lines are radii.
Mercator Projection
A conformal cylindrical map projection that is particularly useful for navigation since it maintains accurate direction, though it is famous for its area distortion that makes landmasses at the poles appear oversized.
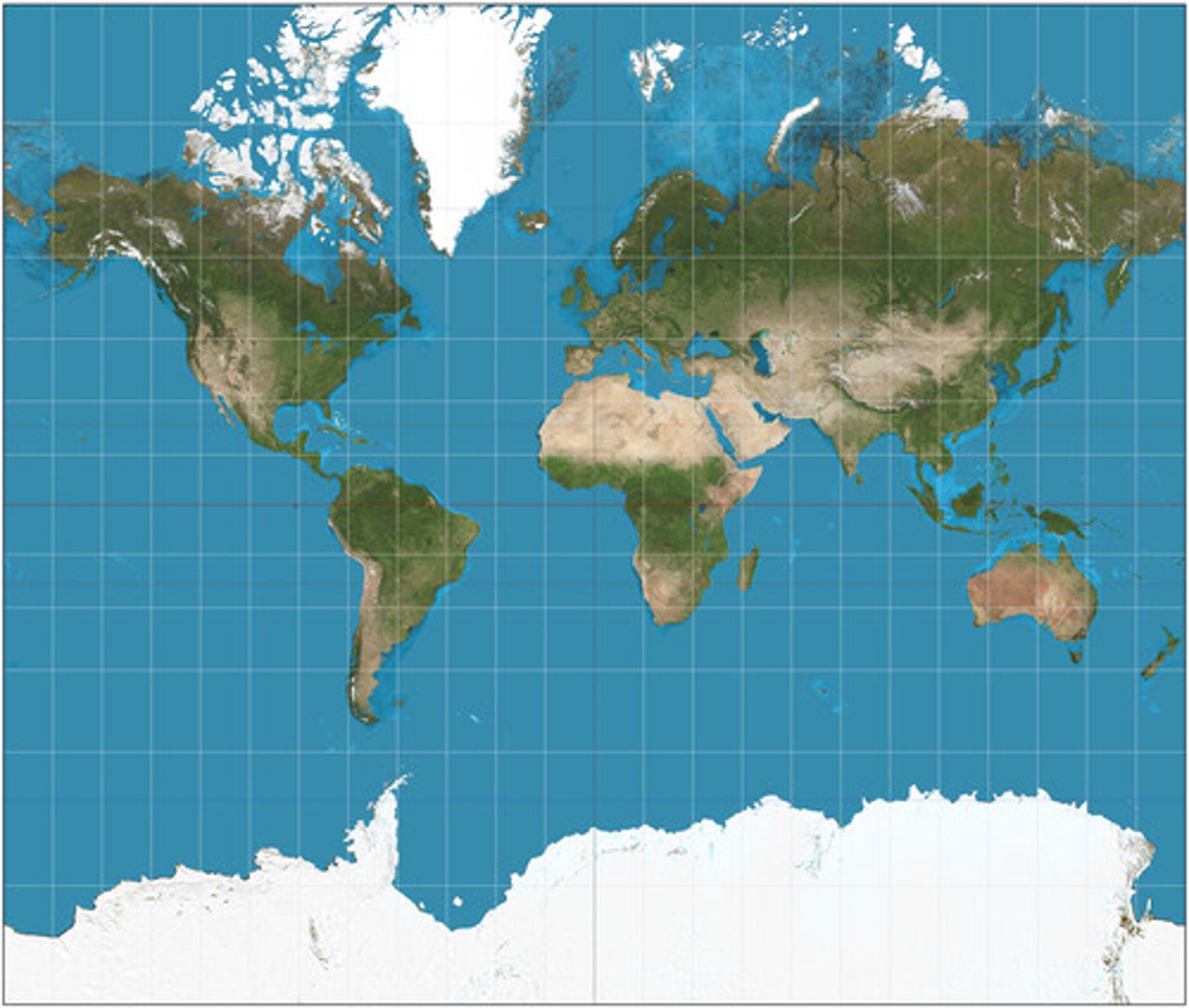
Miller Equidistant Projection
A cylindrical map projection in which shapes and areas are distorted, directions are only true at the equator, though distance is accurately proportional throughout.
(Like a squished Mercator Map)
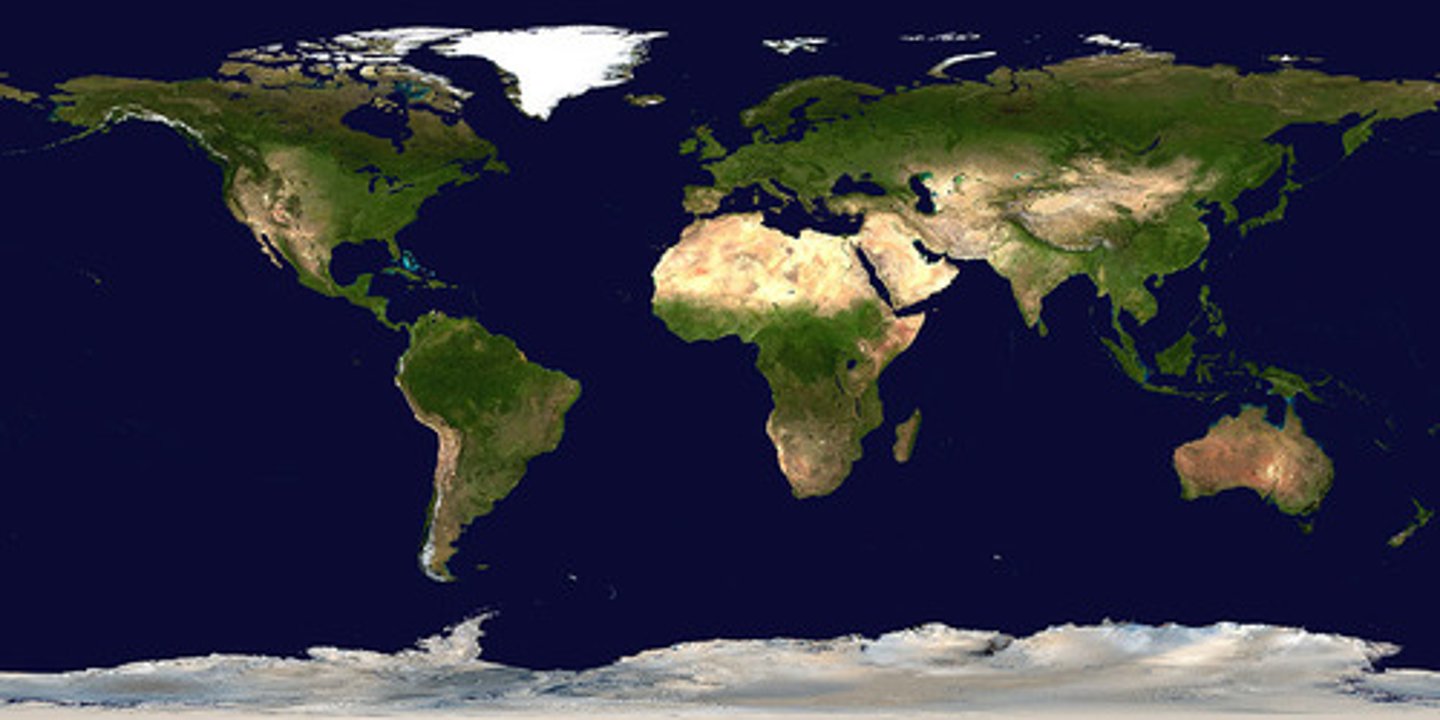
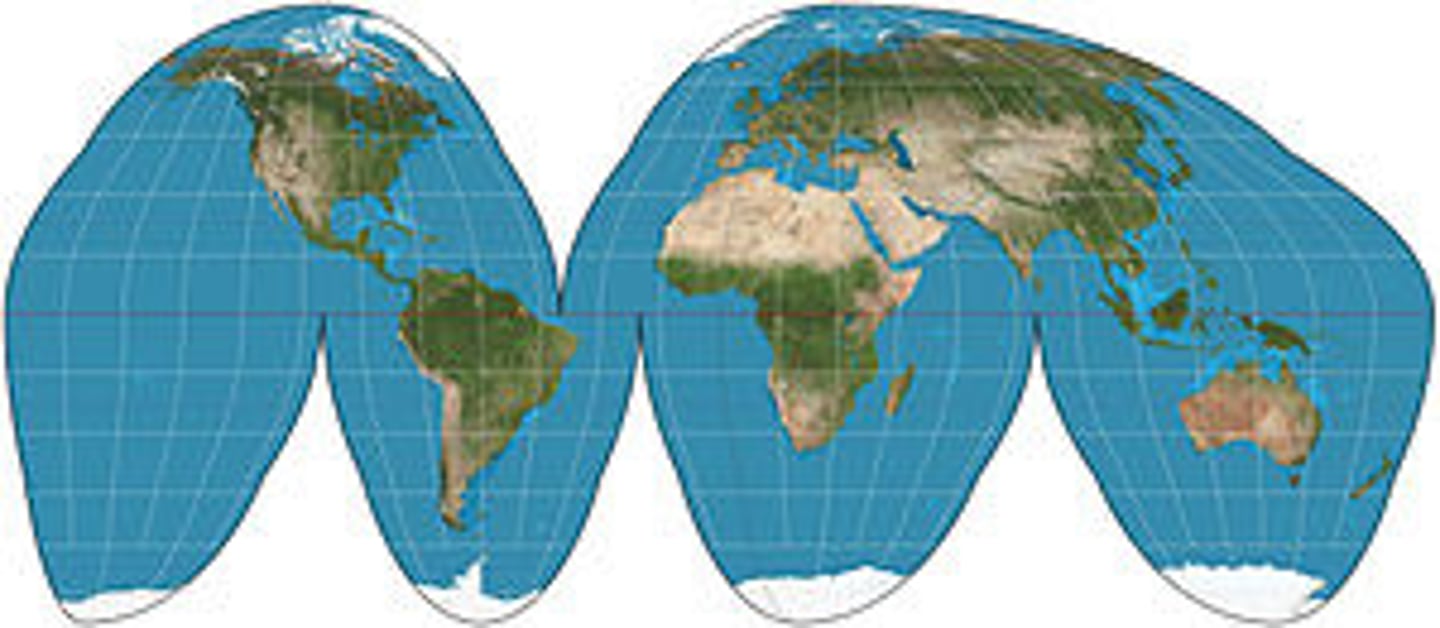
Mollweide Projection
An equal-area map projection that is an ellipse.
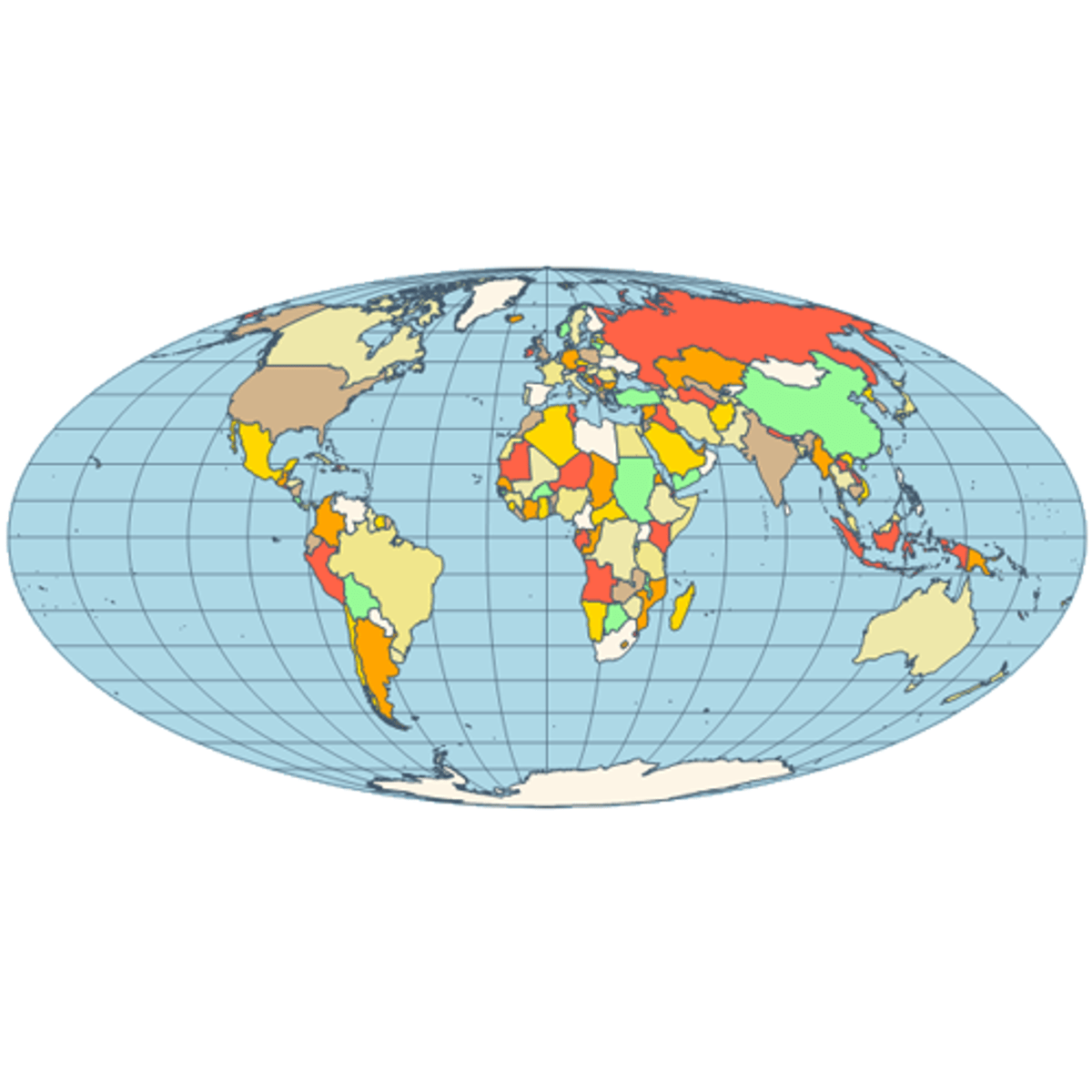
Peters Projection
An equal-area projection purposely centered on Africa in an attempt to treat all regions of Earth fairly.
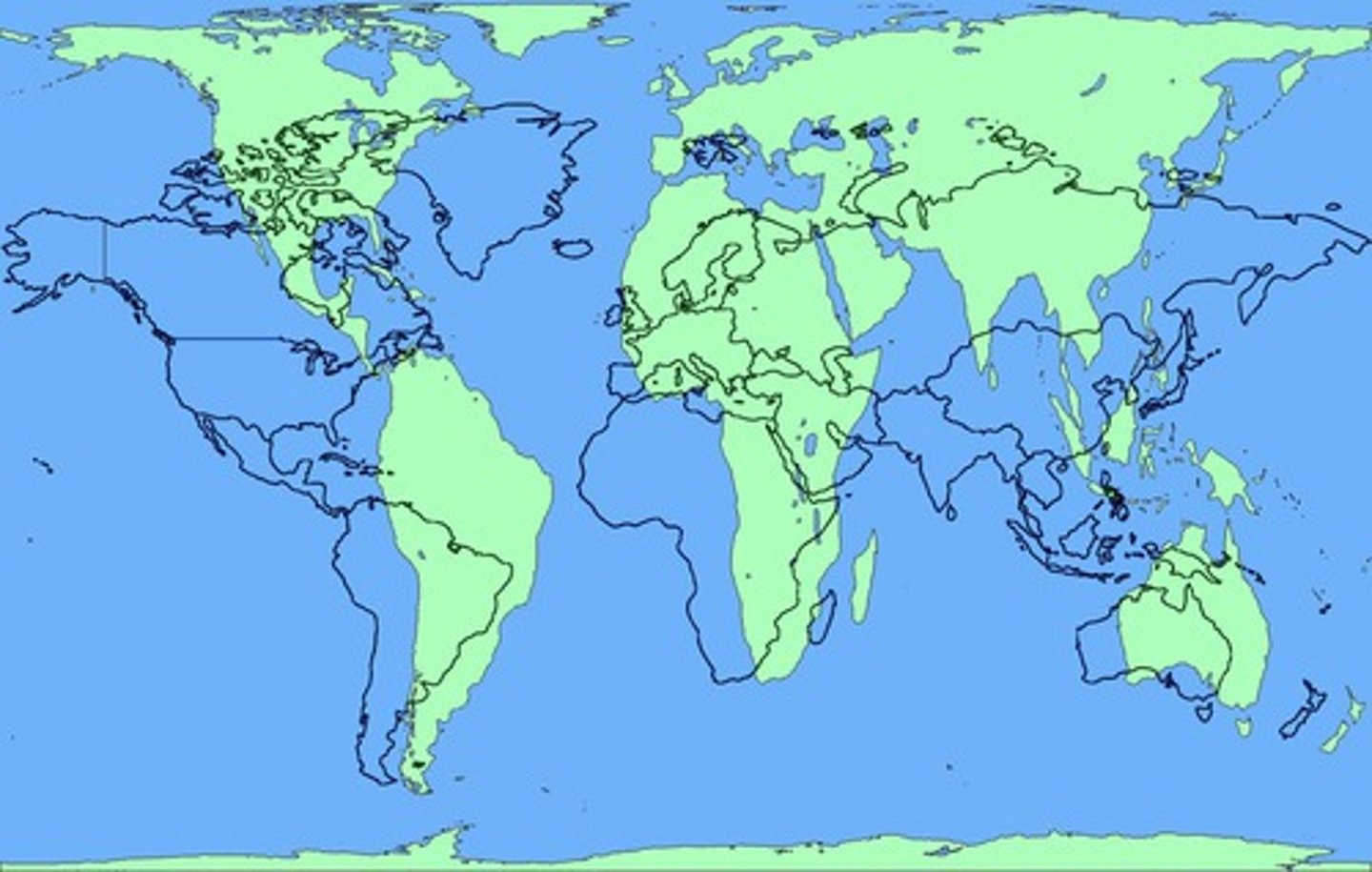
Robinson Projection
A pseudocylindrical compromise map projection that was adopted by the NGS in 1988.
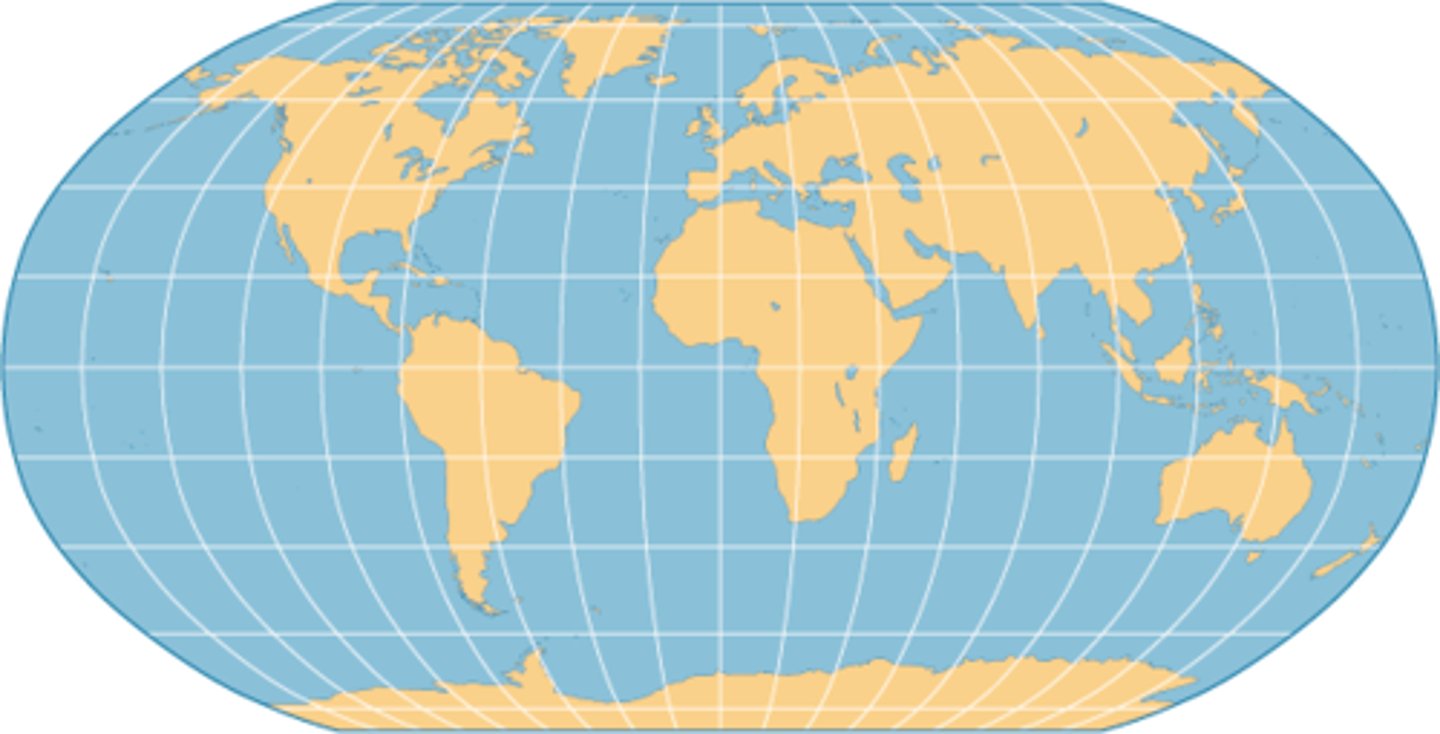
Winkel Tripel Projection
An azimuthal compromise map projection that was adopted by the NGS in 1998.
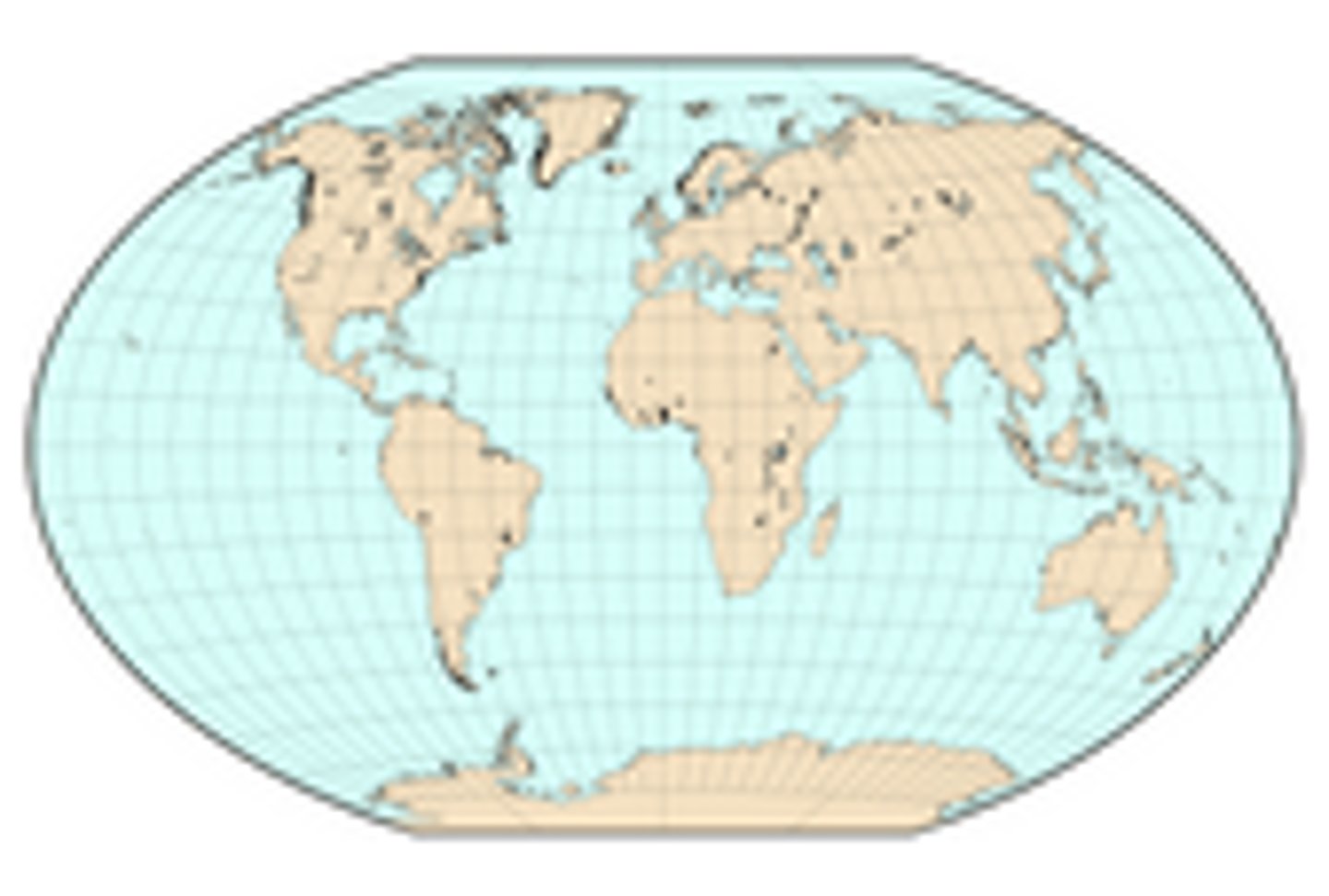
Map Projection
A mathematical method that involves transferring Earth's sphere onto a flat surface. This term can also be used to describe the type of map that results from the process of projecting. All map projections have distortions in area, direction, distance, or shape.