Dental Anatomy Part 2
1/108
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
109 Terms
Lobes
Primary growth centers/separate divisions that come together to form a tooth
On molars, what can lobes come together to form?
Cusps
All teeth are formed from how many lobes?
4-5
Mamelons
3 bulges on the incisal edge of newly erupted central incisors
3 rounded protuberances
Mamelons form from...
3 labial lobes
Perikymata
Small wave like ripples of enamel on newly erupted permanent teeth
Is perikymata seen on primary or permanent teeth?
permanent newly erupted
Cervical ridge
Bulge in the gingival third of the facial surface of an Anatomic crown
Where are cervical ridges found?
Mesiobuccal cusp of mandibular second molars
Common cervical ridge location
MB cusp of mandibular second molars
Crown depressions
Fossae
Pits
Primary grooves (developmental grooves)
Secondary grooves (supplemental grooves)
Analogy:
Mountain peak = cusp tip
Mountain ridge = cusp ridge
Valley = occlusal sulcus
Dried river bed = groove
Where river beds converge and there is a possible depression = fossa
Fossae
A rounded depression on the crown surface of a teeth
Occlusal surfaces of posterior teeth typically have how many deeper fossae?
2 or more
3 cusped pre-molars and most molars have how many fossae?
3
Mesial, central, distal
Incisors have a broad, shallow fossa where?
On the lingual side
Pit
A small depressed area where grooves join
A pit is where _________ join
grooves
Where are pits located?
Deepest part of the fossa
Occlusal sulcus
The broad V-shaped depression or valley on the occlusal surface of each posterior teeth running mesiodistally between the buccal and lingual cusps
Developmental (primary) groove
A groove that represents the coalescence of the lobes of the crown of the tooth
3 cusped premolars and most molars have how many fossae?
3
2 cusped premolars have how many fossae?
2
Central grooves are positioned...
Mesiodistally
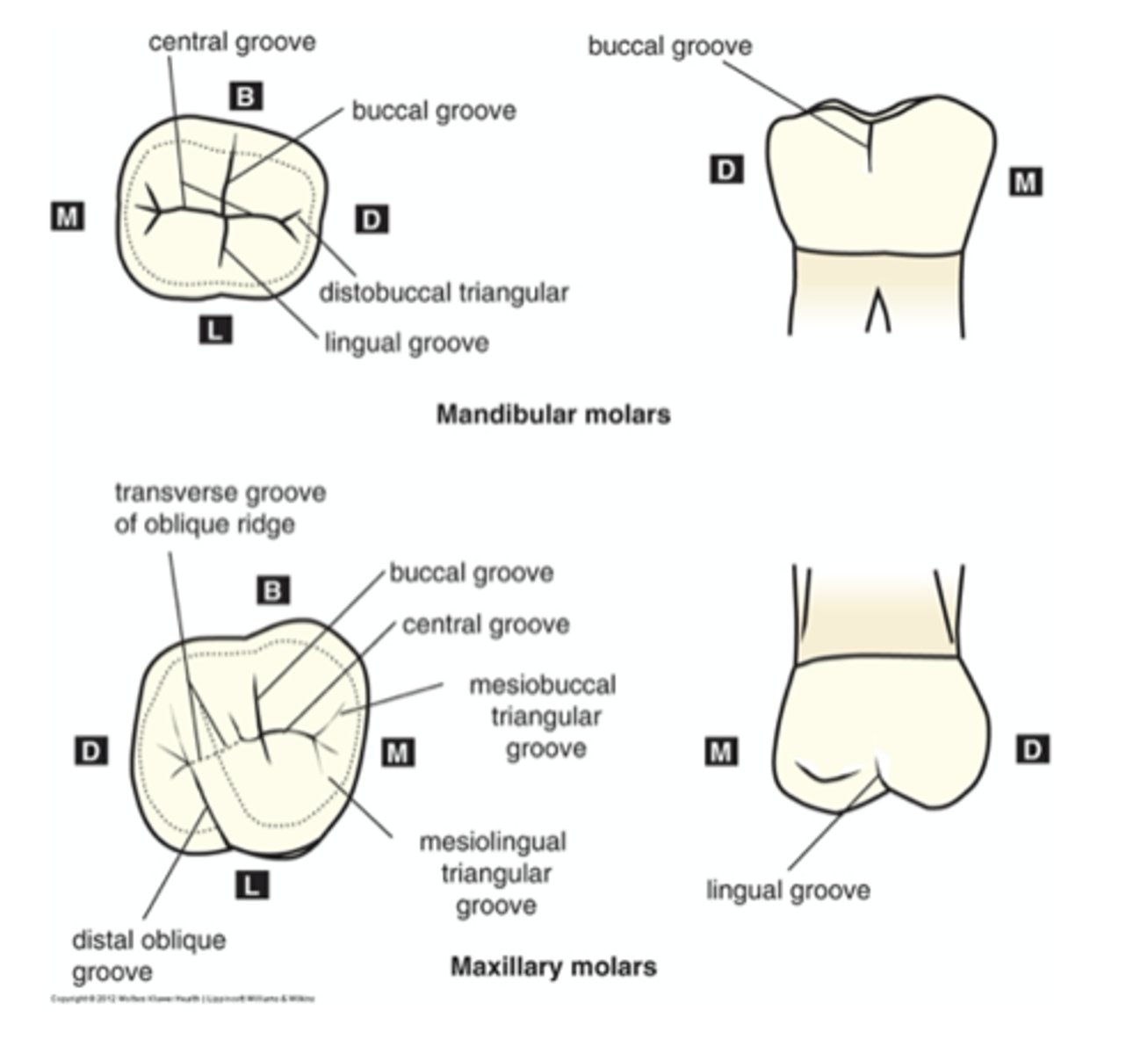
How are major grooves named?
For the surface or line angle they "aim" towards
Other names for major grooves
Developmental/primary groove
Fossa developmental groove
located at ends of central groove and named for corner of tooth toward which they aim
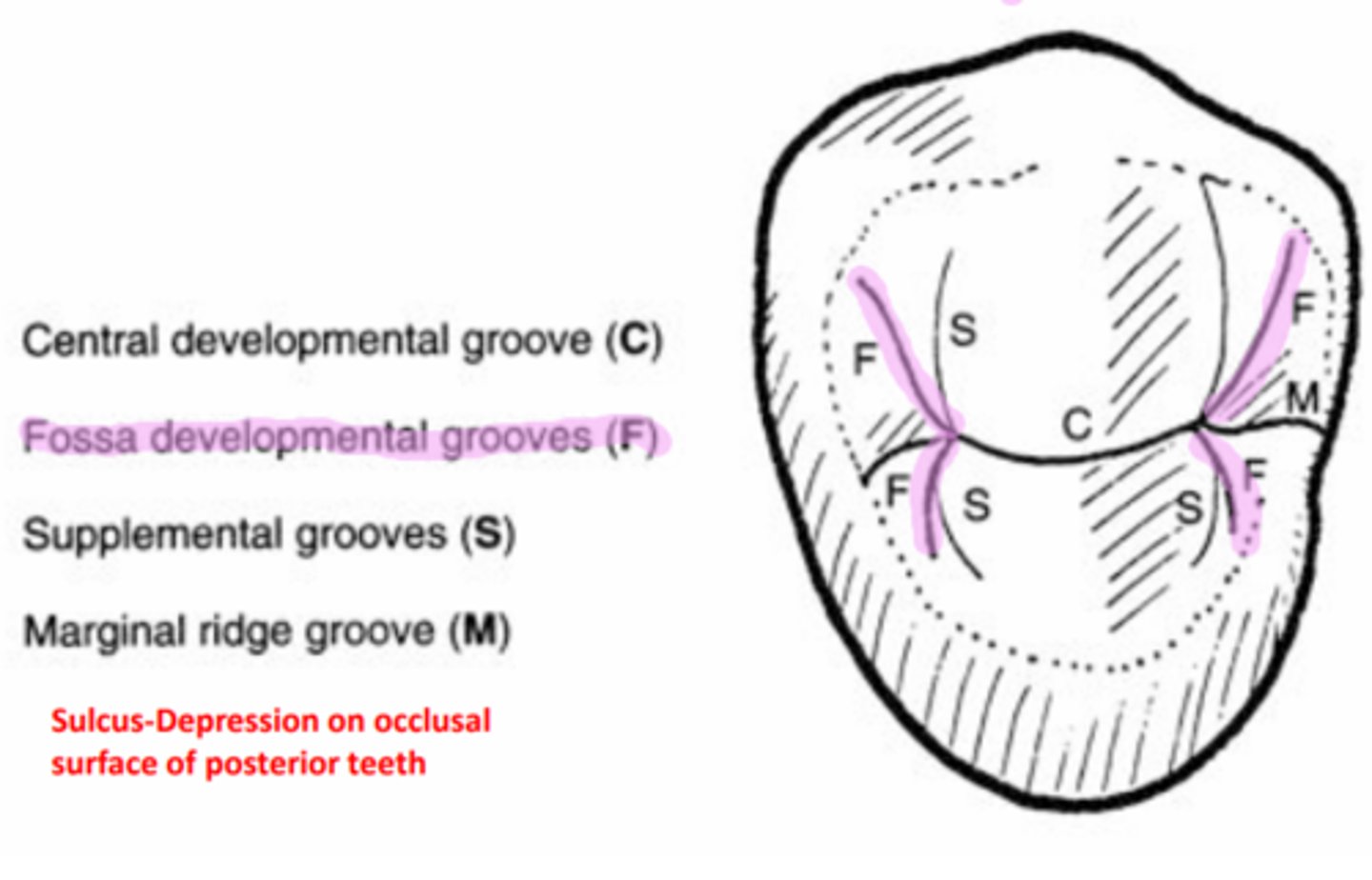
Supplemental (secondary) groove
An auxiliary groove that branches from a developmental groove
How do supplemental grooves differ from primary grooves?
They generally are not as deep as primary grooves
Where are supplemental grooves located?
Branching from primary grooves
Secondary grooves are not related to...
Coalescence of tooth lobes
Where are oblique ridges found?
only on maxillary molars
Examples of secondary grooves
triangular grooves, marginal grooves
Embrasure
spaces present when two adjacent teeth contact each other
4 types of embrasure
Gingival (cervical), incisal/occlusal, facial, lingual
Lingual embrasure is ____________ than facial embrasure
Larger
The gingival embrasure is also called the
interproximal space that is filled with gingiva
Proximal contact area
The area where each tooth touches the adjacent tooth
As a general rule, contacts move more ______________ from anterior to posterior
Cervically
Anterior contacts are centered...
Faciolingually
Posterior contacts are located towards...
The Buccal of center faciolingually
Proximal contact areas move more ______________ positioned as you move distally from the midline
Gingivally
Proximal contact areas are centered ___________ at the midline (8,9,24,25) when viewed from the incisal
Faciolingually
Proximal contact areas are ____________ to the center of posterior teeth when viewed from the occlusal
Buccal
When viewed from the incisal, proximal contact areas are near...
The middle of the tooth Faciolingually
Overall, a distal contact area will be slightly more _________ than the mesial contact area of a given tooth
Lingual
When looking at the teeth facially, what embrasure spaces are you seeing?
Gingival embrasure and incisal/occlusal embrasure
When looking at the teeth incisally, what embrasure spaces are you seeing?
Lingual embrasure and facial/buccal embrasure
Is lingual or facial embrasure larger?
Lingual
What embrasure is often quite small?
Incisal or occlusal embrasure
Is occlusal/incisal embrasure smaller or larger than gingival embrasure?
Smaller
Interproximal space
Space between adjacent teeth
When dividing teeth into thirds horizontally (looking at the tooth facially) what are the thirds?
Cervical third, middle third, incisal/occlusal third
When dividing teeth into thirds vertically (looking at the tooth mesially or distally) what are the thirds?
Lingual third, middle third, facial/buccal third
Height of contour
Where the biggest bump is on the tooth
Height of contour is also called
crest of curvature
Where is the biggest bulk/size present on posterior teeth?
Buccal area
Ideal heights of contour lead to
Gingival health
What does food stimulate when the person chews?
The gingiva, promoting health
On adjacent teeth, the amount of curvature of the CEJ is typically...
The same
The depth of curvature of CEJ is greatest on the...
Central incisors and decreases posteriorly
Curvature of the CEJ is toward the ____________ on facial and lingual
Apex
Curvature of the CEJ is toward the _______________ on mesial and distal
Incisal and occlusal
The amount of curvature of the cervical line is normally greater on what surface?
Mesial
Periodontium
Consists of the bone and soft tissues that surround and support the teeth
Mineralized tissues of periodontium
alveolar bone
alveolus
lamina dura
Alveolar bone
portion of the maxilla and mandible that surrounds the tooth roots
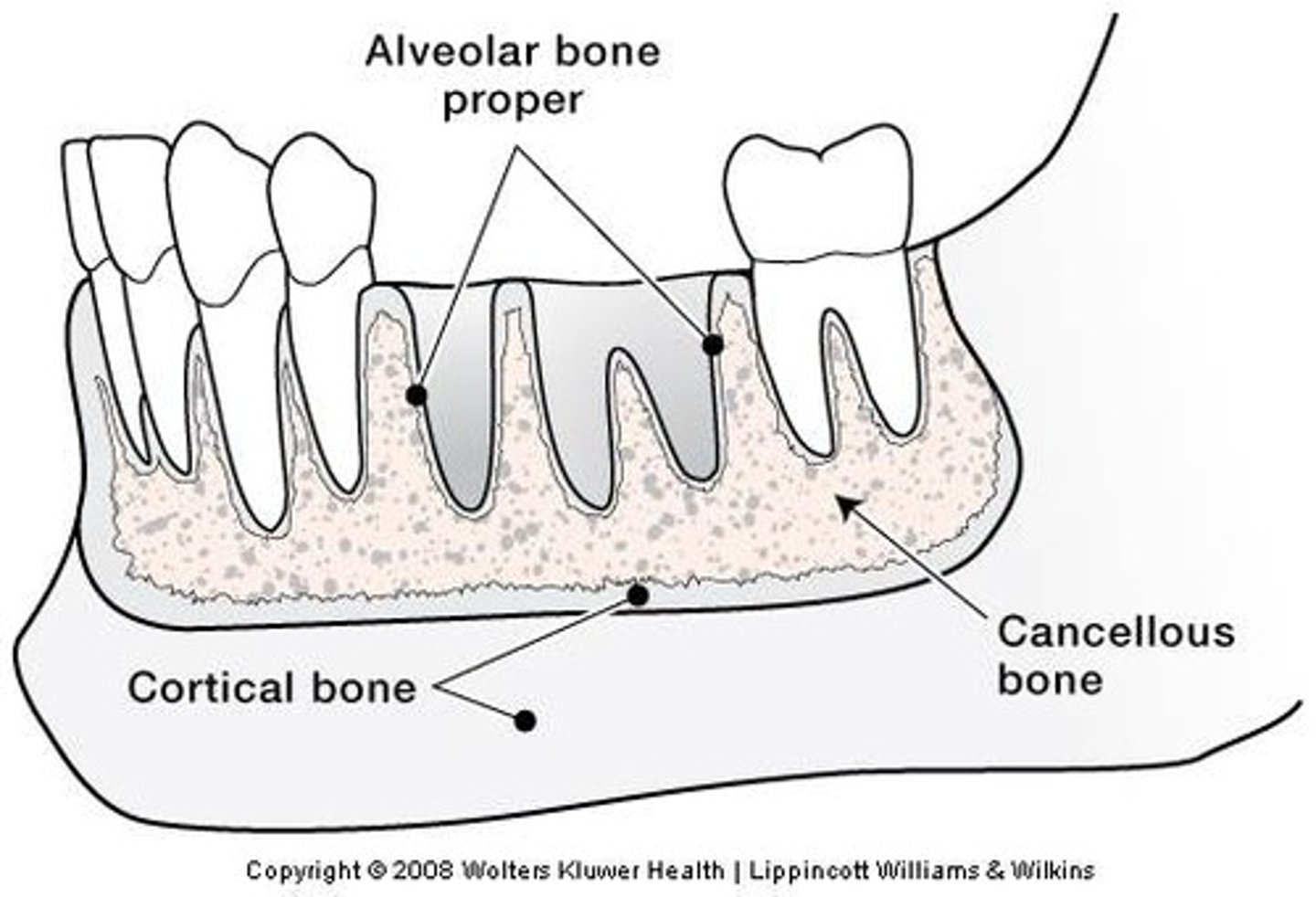
Alveolus
The tooth socket within the bone
Periodontal ligament
ligament surrounding the teeth that supports and attaches them to alveoli bony surface
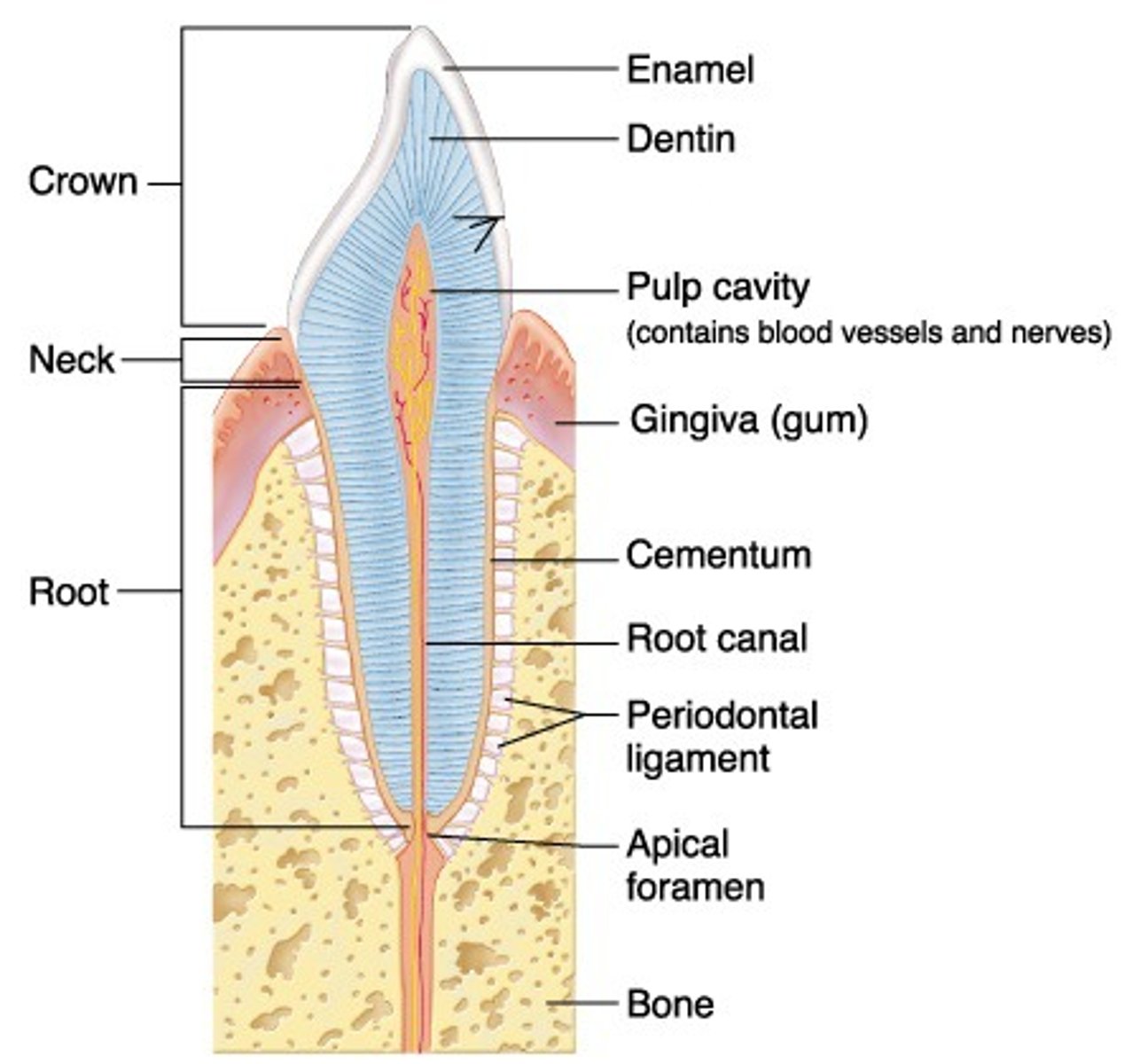
How many alveoli are present if 32 teeth are present?
32
Lamina dura
Thin layer of compact bone that lines each alveolus
Soft tissues of peridontium
gums
periodontal ligament
Gingiva
Gums
Gingiva is soft tissue that covers...
Alveolar bone
Attached gingiva
Tissue attached to bone
Free gingiva
Tissue not attached to bone
Parts of free gingiva
marginal gingiva and interdental papilla
Interdental papilla
Sharp, pointed projection of gingiva between the teeth
Marginal gingiva
Gingiva at the gingival margin of each tooth
Is the free gingival groove always visible?
no
Gingival sulcus
Space between free gingiva and tooth surface
Periodontal ligament contains...
Nerve endings
Periodontal Ligament fibers attach to the ____________ and ______________
cementum and lamina dura
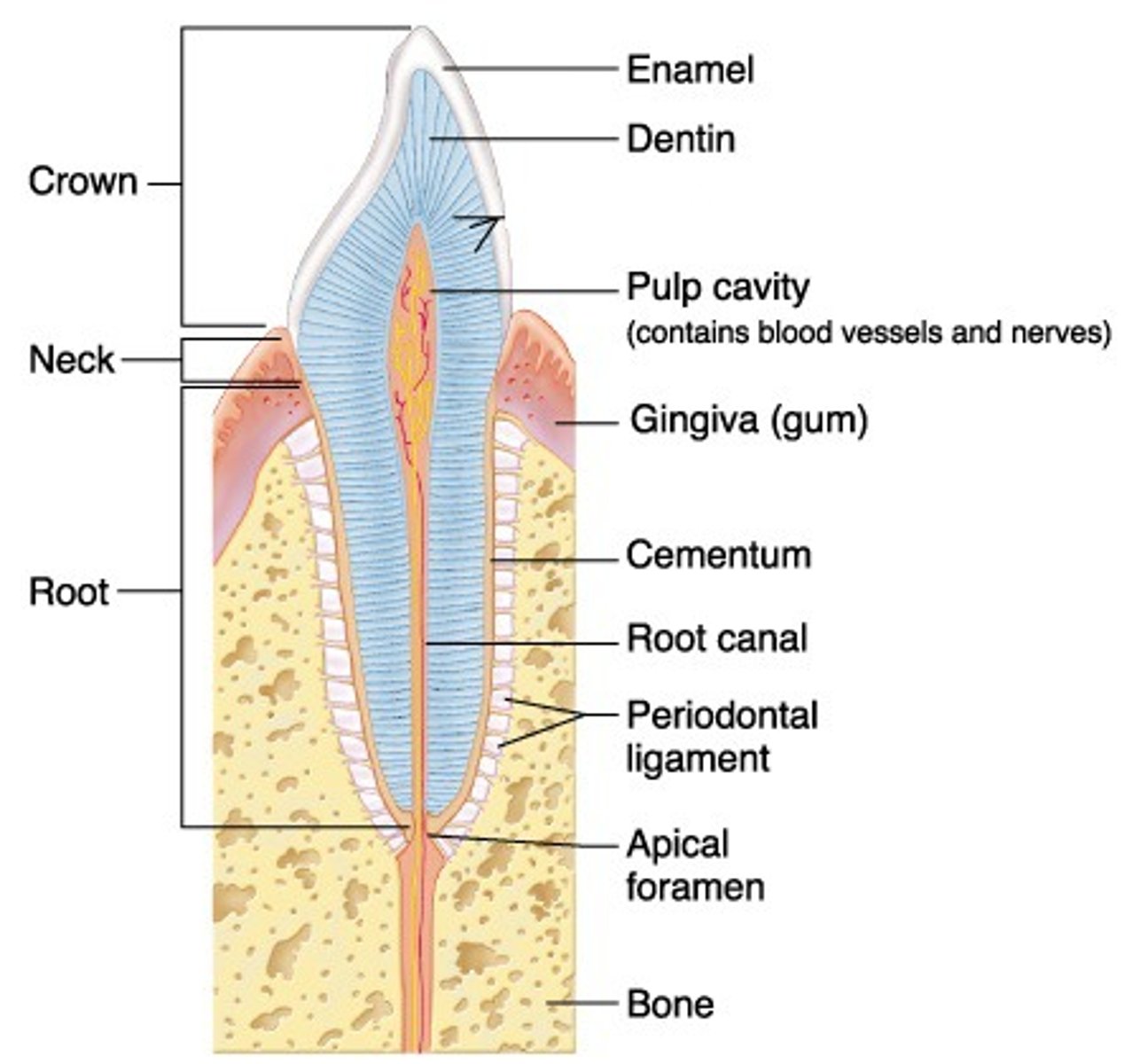
How short are PDL fibers?
~0.2 mm
Function of the PDL
attachment and support, allows for some movement. like a trampoline
The zone between the _________ and _________________ is free gingiva covering the sulcus
gingival groove and gingival margin
Alveolar mucosa
thin, loosely attached mucosa covering the alveolar bone
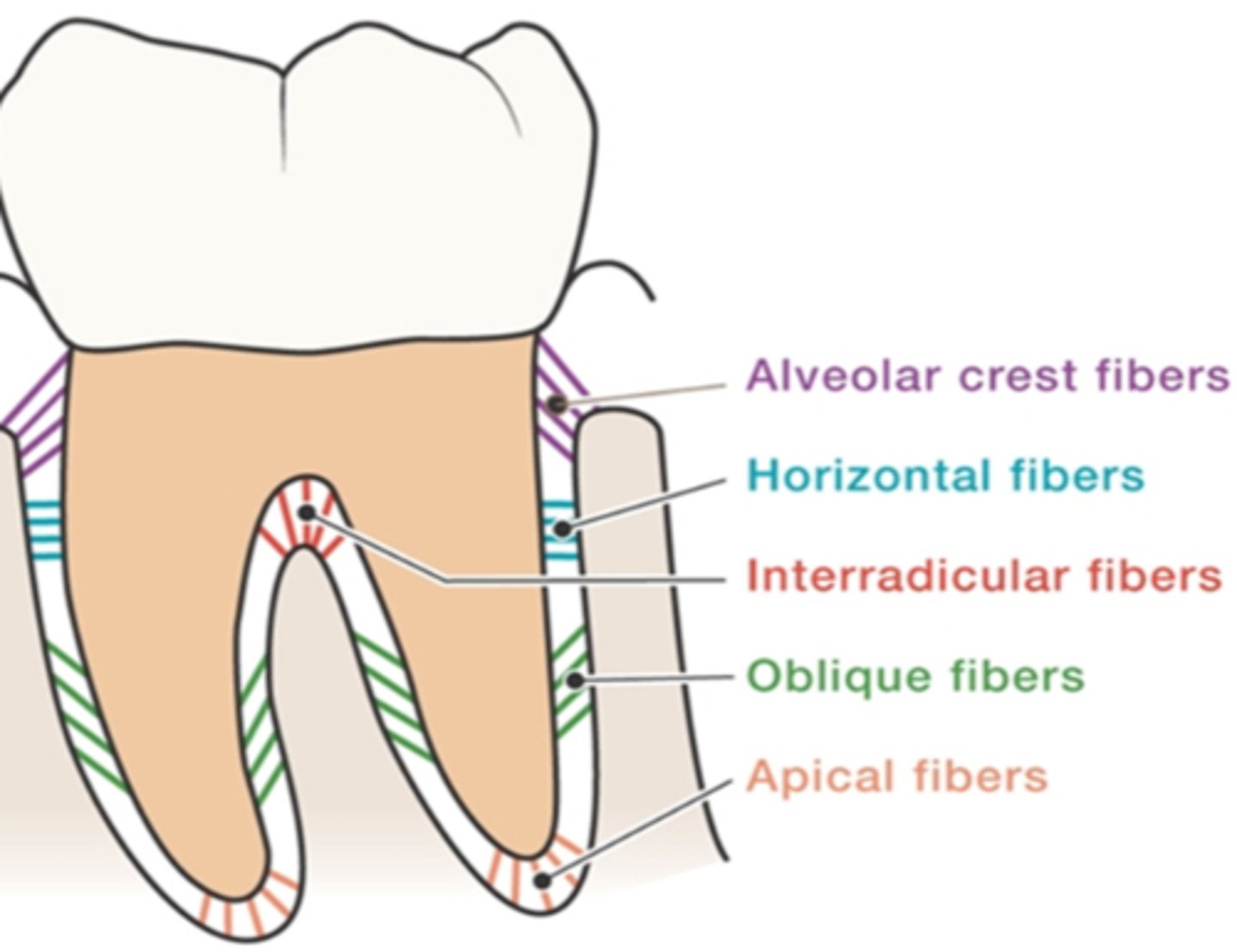
Alveolar crest fibers
located at the cementoenamel junction assists with the retention of the tooth in its socket and protects the deeper fibers
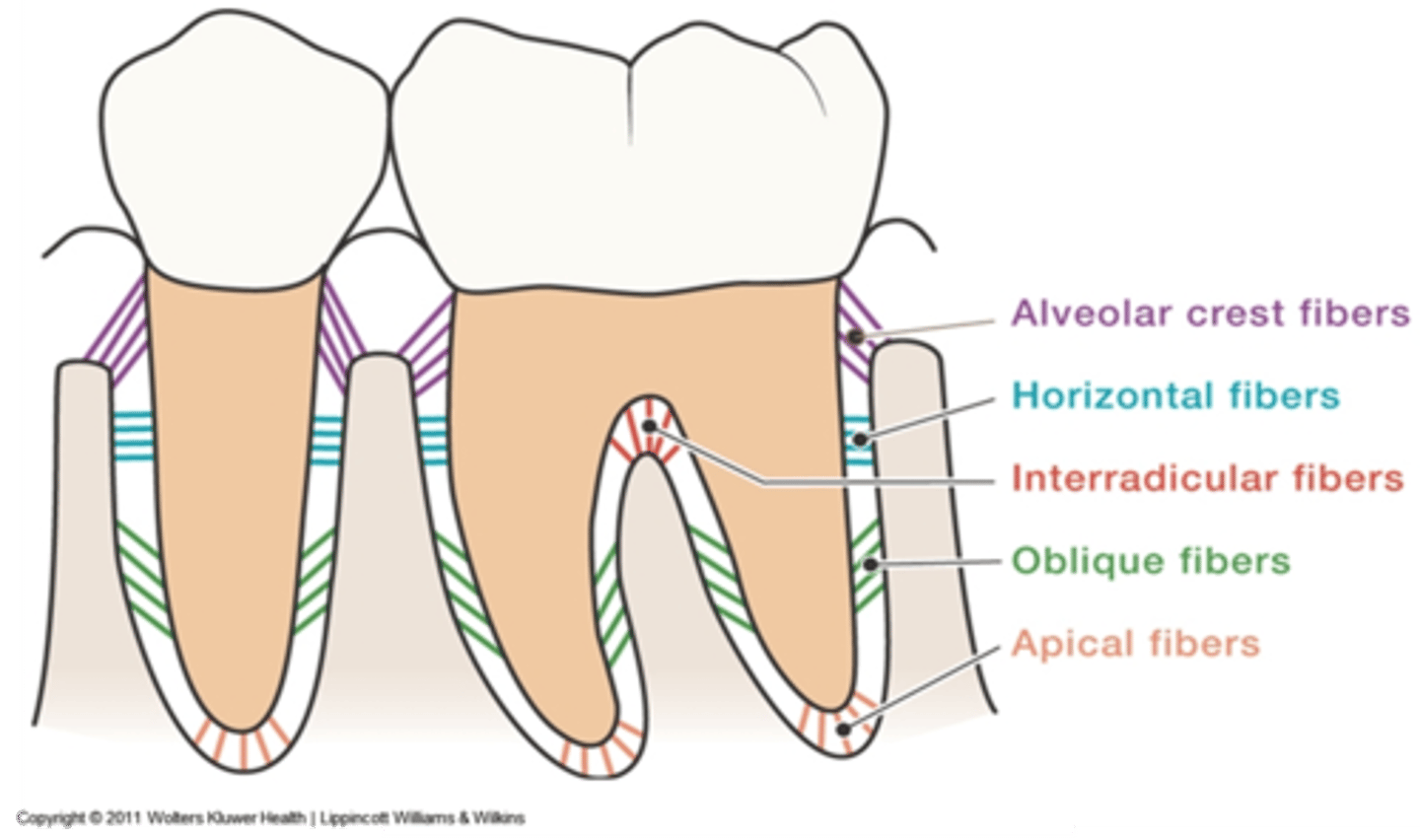
Oblique fibers
from the root above the apical fibers obliquely toward the occlusal to resist vertical and unexpected strong forces
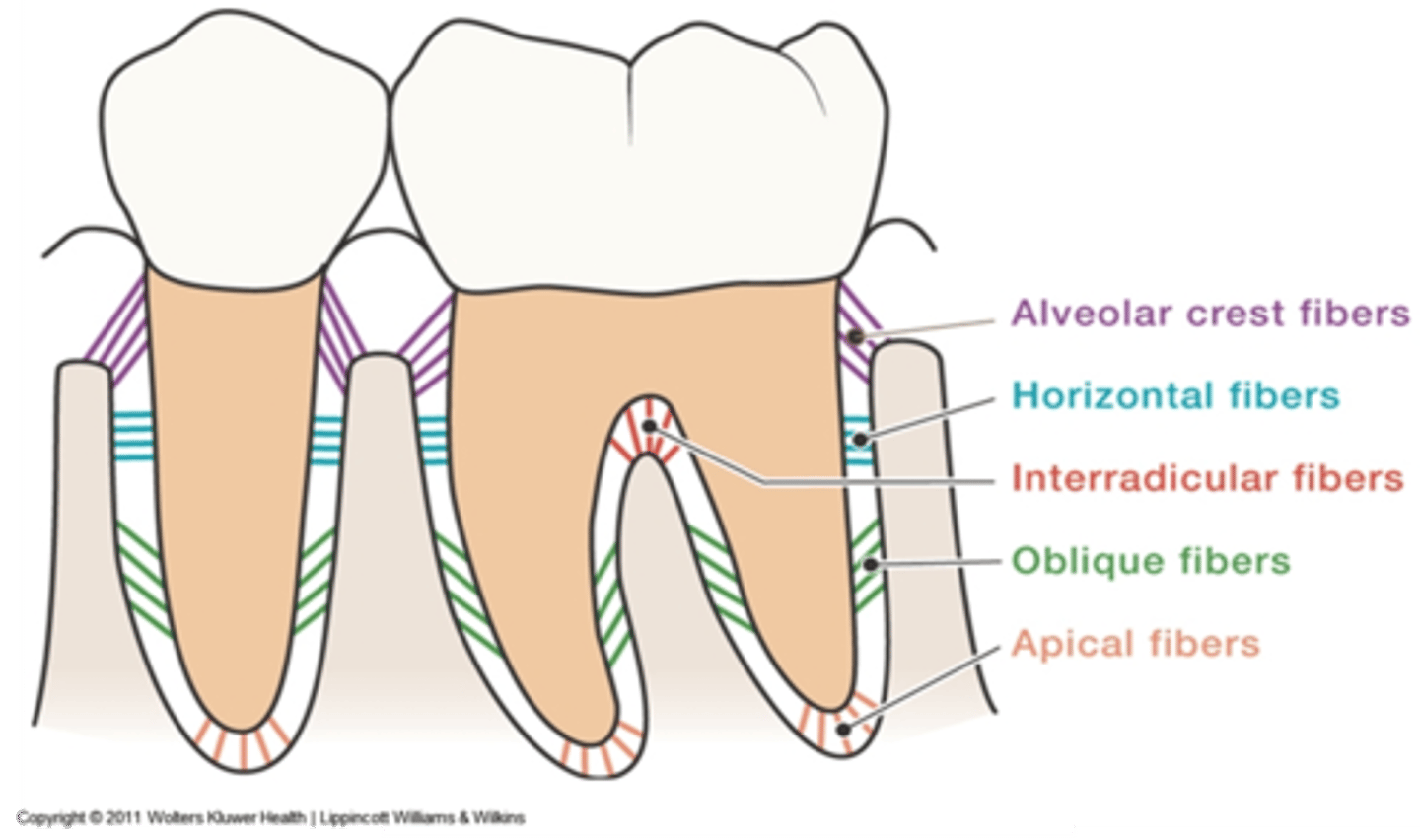
Transseptal fibers
from the cervical area of one tooth across to an adjacent tooth (on the mesial or distal only) to provide resistance to separation of teeth
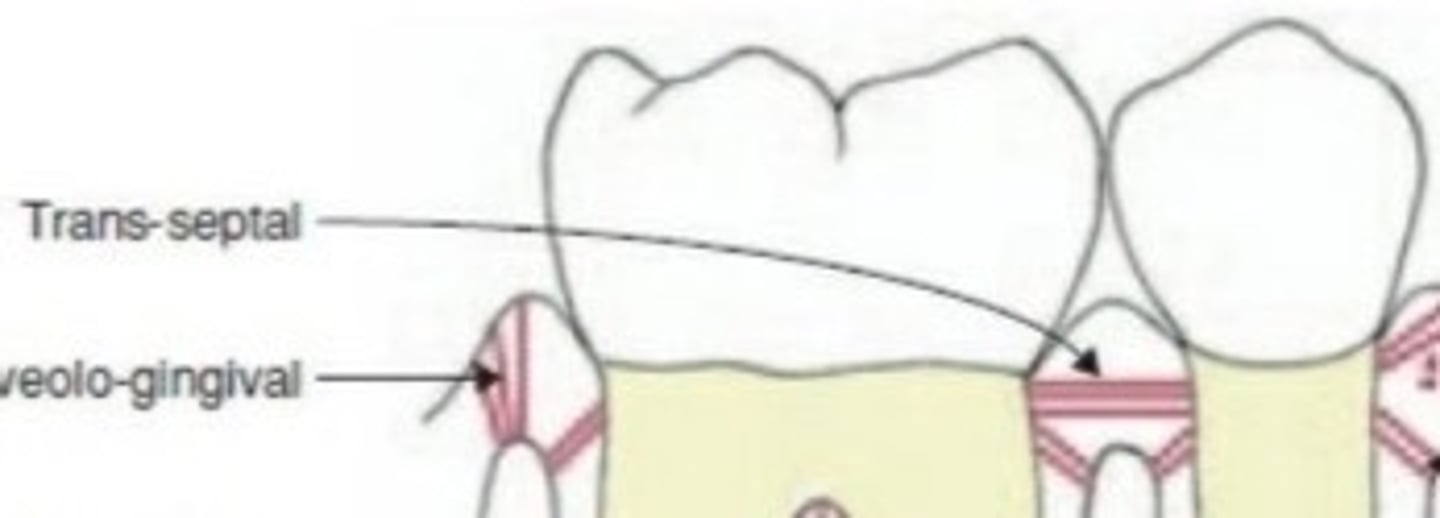
Horizontal fibers
from the cementum in the middle of each root to adjacent alveolar bone to resist tipping of the tooth
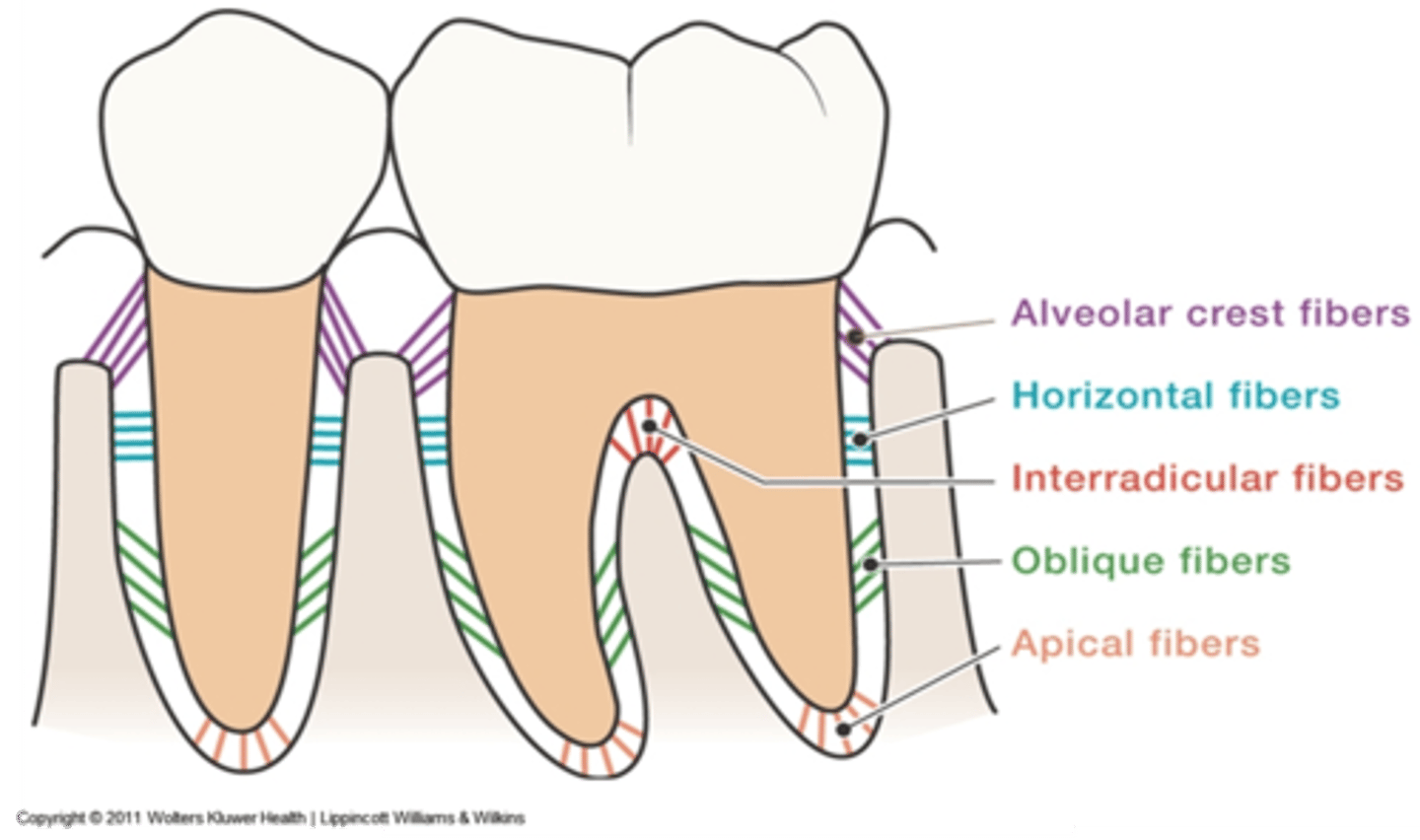
Interradicular fibers
from cementum between the roots of multirooted teeth to the adjacent bone to resist vertical and lateral forces
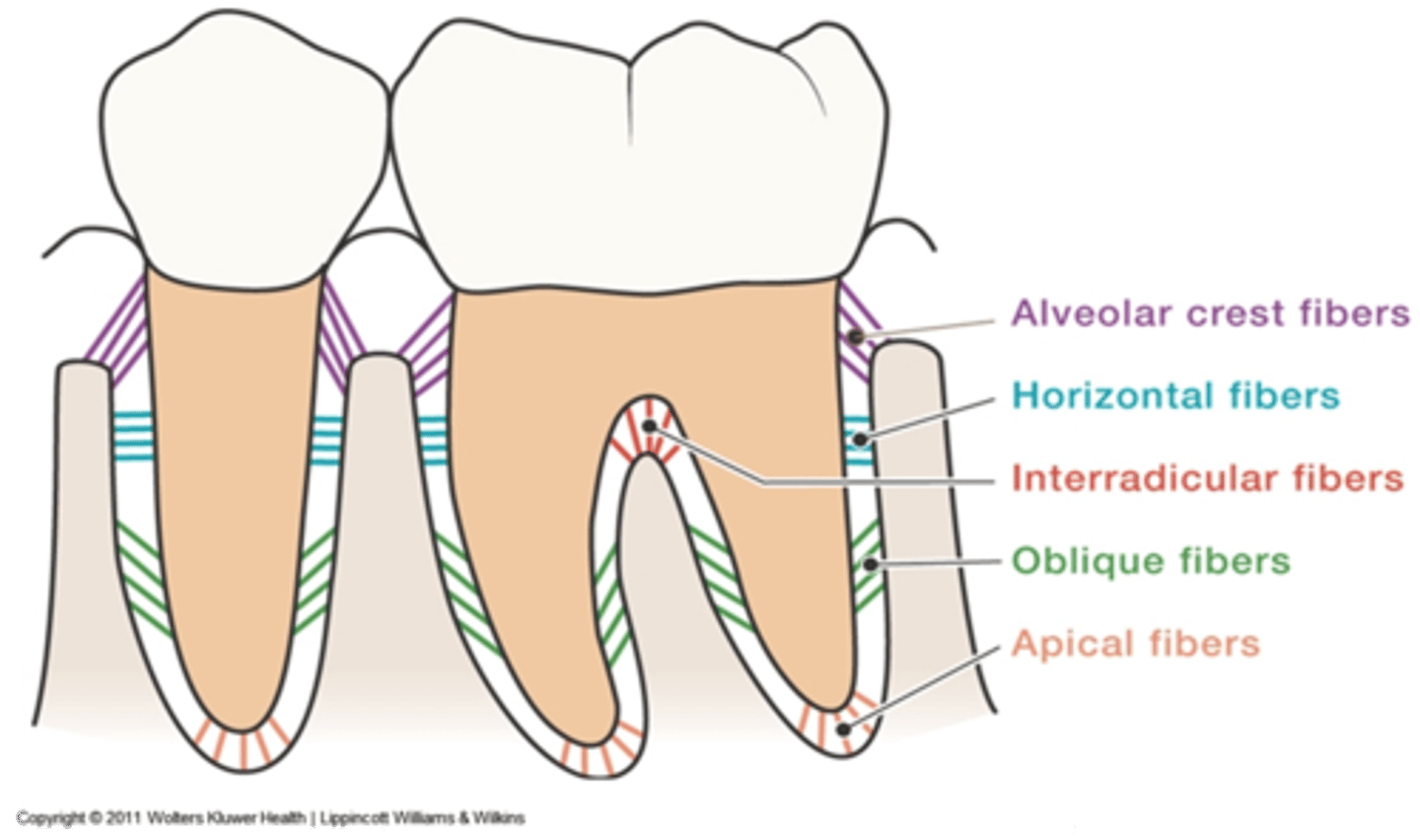
Apical fibers
from the root apex to adjacent surrounding bone to resist vertical forces
Proper contours of facial and lingual heights of contour direct food...
away from the gingiva
Undercontoured and overcontoured heights of contour lead to
gingival inflammation
Flat contours of facial and lingual lead to
abrasion of the gingiva by food impaction into the gingiva
Bulky contours of facial and lingual lead to
lack of stimulation by food
Overcontoured=
too bulky
Undercontoured=
too flat
The free gingival groove and the mucogingival junction are the boundaries of the
attached gingiva