THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD AND UNIFORMITARIANISM
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
Planetary Sciences: Geology and Astronomy
Astronomy is concerned with the assembly of matter into the galaxies, stars and planets often emphasizing timing and organization.
Planets are assemblages of material in time and space. Geology is concerned with this aspect of astronomy. In many ways, astronomy informs geology and vice versa (Geology- concerned with this planet but can be applied to other planets (like the moon) with observations)
Both rely heavily on the scientific method.
The Science of Geology: 2 Types
Geology is the science that pursues an understanding of planet Earth.
Physical Geology: examines Earth materials and seeks to understand the many processes that operate on our planet.
Historical Geology: seeks an understanding of the origin of Earth and its development through time.
Entire solar system is 4.6 billion years old (Earth formed with solar system)
Some Principles of Geology
→Earth Science “Zeroth” Law: Uniformitarianism (The natural processes we observe shaping Earth today)
→Layer Cake Geology (Strata) (Each layer is history
→Stratigraphic succession (Layers stack on top of each other)
Marker Horizons (Thin distinctive layer that stands out because of its color/ texture/ composition, and it is from the same timeline; acts like a timestamp)
→Placing events/strata into a relative age sequence (figuring out what came out first)
→Assess what processes may have operated in the past.
The Development of Geology
The nature of Earth has been a focus of study for centuries.
→Catastrophism: Earth’s landscapes were shaped primarily by catastrophes (like floods, volcanic eruptions, or meteor strikes)
→Uniformitarianism: the physical, chemical, and biological laws that operate today have operated through the geologic past (looks at gradual processes)
The Development of Geology 2
The magnitude of geologic time involves millions and billions of years
Earth is 4.6 billion years old.
An appreciation for the magnitude of geologic time is important because many processes are gradual.
Moon
The moon is gradually moving away.
It came from Earth since it has the same isotopic elements as Earth.
Allowed for crust to be recycled and tectonic movement; if moon didn’t separate then the crust would’ve been too thick and no recycling would occur.
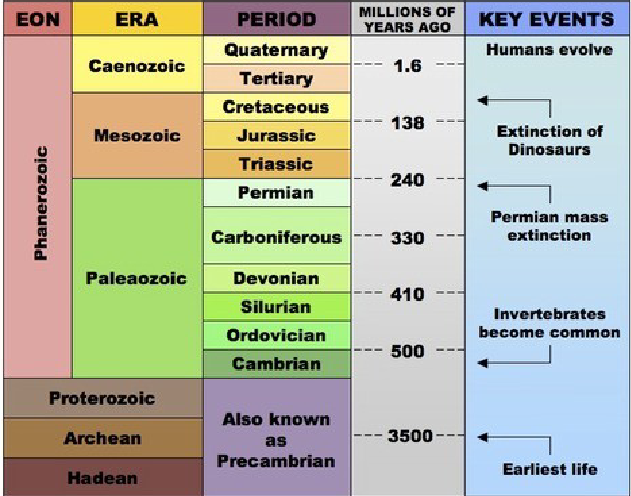
The Geologic Time Scale
STARTING WITH OLDER EONS:
The Hadean, Archean, and Proterozoic are about 3.5 million years, so they take up the MAJORITY of the timeline.
PRECAMBRIAN PERIOD
→Hadean (OLDEST): Super-hot (“Hades”)
→Archean: “Old”
→Proterozoic: Primitive lifeforms; soft/simple organisms (worms/ jellyfish)
→Phanerozoic (EON; With animals and dinos; it seems like the majority, but it isn’t)
→Paleaozoic: “Ancient Zoo”; Mass extinction with aquatic life because aquatic life dominated during the time.
→Mesozoic: “Middle Zoo” Age of Reptiles
→Caenozoic: “Recent Zoo” Age of Mammals
Zeroth Law of Thermodynamics
If A and C are each in thermal equilibrium with B, then A is also in thermal equilibrium with C.
If T(A) = T(B)
And T(B) = T(C)
Then T(A) = T(C)
Heat flow hot → cold.
If 2 things are out of balance, they’ll come into balance.
Uniformitarianism or Actualism