Unit 5A.8: MOUTH & PHARYNX Assessment | Eyes, Ears, Nose & Sinuses, Mouth & Pharynx, Neck
1/117
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
118 Terms
Lips
Teeth and gums
Buccal mucosa
Inspect and palpate the tongue
Inspect hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and uvula
Note odor.
Assess uvula.
Inspect Tonsils.
Test gag reflex.
9 Steps for Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Lips
First Step for Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Lips are smooth and moist without lesions or swelling
Normal Finding for 1. LIps
Circumoral Pallor
Cyanotic Lips
Reddish Lips
Edema
Abnormal findings for 1. Lips
Circumoral Pallor
Abnormal findings for 1. Lips
Pallor around the lips
Seen in anemia and shock

Anemia
Shock
What conditions cause circumoral pallor?
Bluish/Cyanotic Lips
Abnormal findings for 1. Lips
May result from cold or hypoxia
Oxygenation; cardiac arrest

Cold
Hypoxia
What conditions cause cyanotic lips?
Reddish Lips
Abnormal findings for 1. Lips
Seen in clients with ketoacidosis, carbon monoxide poisoning, COPD with polycythemia, liver problems
Ketoacidosis
Carbon Monoxide Poisoning
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) with polycythemia
What conditions cause Reddish Lips?
Edema/Swelling of the Lips
Abnormal findings for 1. Lips
Common in local or systemic allergic or anaphylactic reactions
Herpes Simplex Type 1
Cheilosis of the Lip
Carcinoma of the Lip
Leukoplakia (Ventral Surface)
Hair Leukoplakia (Lateral Surface)
Candida Albicans Infection (Thrush)
Smooth, reddish, shiny tongue without papillae due to Vitamin B12 deficiency
Black hairy tongue
Carcinoma od tongue
Cankersore
10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
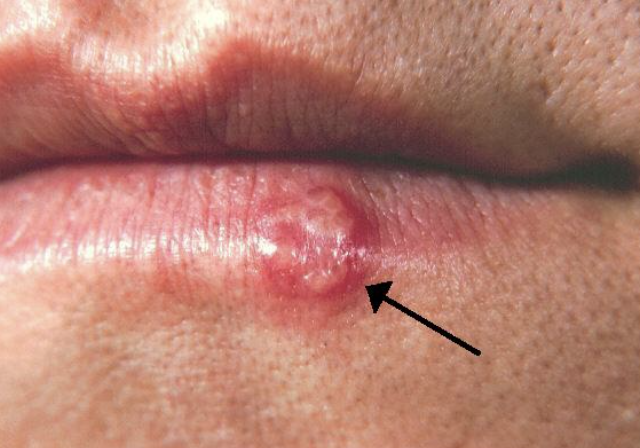
Herpes Simplex Type I
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Crust
Commonly known as oral herpes or cold sores
Viral infection that manifests as small, painful, fluid-filled blisters or ulcers, usually around the lips or mouth
Often recur, especially during stress, illness, or weakened immunity
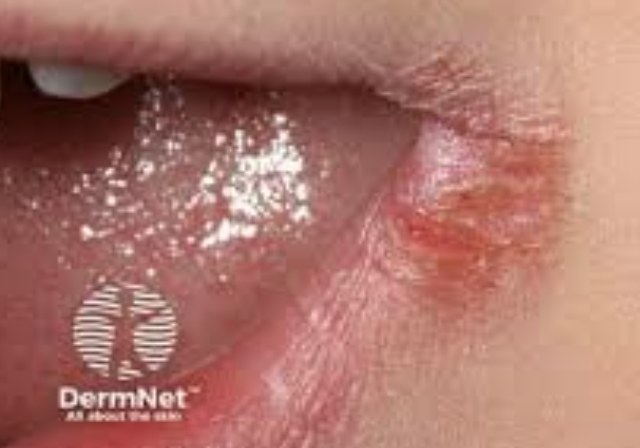
Cheilosis of the Lips/Angular Cheilitis
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Inflammatory condition that causes cracking, crusting, and scaling of the corners of the mouth
Painful, red, inflamed fissures or cracks at corners of the mouth
Can be caused by fungal or bacterial infections, vitamin deficiencies, (especially Vitamin B2 or riboflavin), or drooling
May also occur in people with poorly fitted dentures or those who frequently lick their lips

Vitamin B2
Riboflavin
Deficiencies in what vitamins may cause Cheilitis?
Fungal or bacterial infections
Vitamin B2 Deficiency
Riboflavin Deficiency
Drooling
Poorly fitted dentures
Frequent lip lickers
What is Cheilitis caused by?
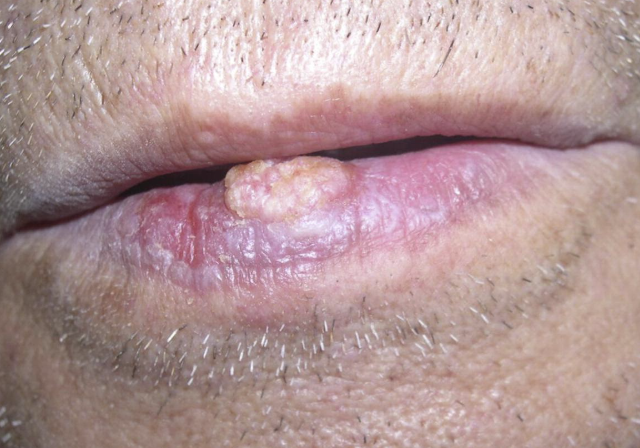
Carcinoma of the Lip
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Malignant tumor, typically a squamous cell carcinoma that develops on the lip, most commonly the lower lip
May appear as a persistent sore, ulcer, or lump that does not heal
Leukoplakia (Ventral Surface)
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Development of thickened, white patches on the mucous membranes of the mouth, particularly on the ventral (underside) surface of the tongue or inner cheeks
Patches cannot be scraped off and signal a pre-cancerous condition, especially individuals who smoke or use alcohol excessively
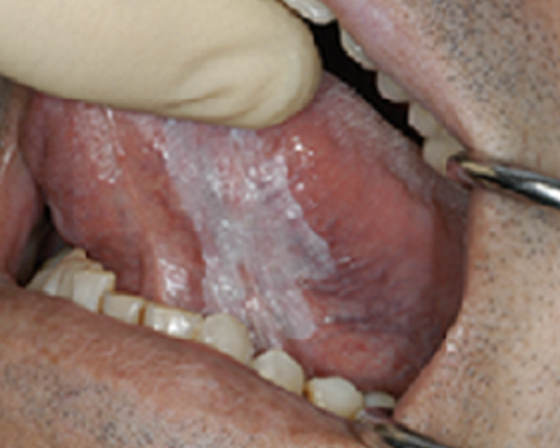
Those that smoke or use alcohol excessively.
What individuals usually have leukoplakia?
Hairy Leukoplakia
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Viral infection of the mouth often seen in individuals with compromised immune systems, particularly those with HIV/AIDS
Appears as white, hairy-looking patches on the lateral sides of the tongue
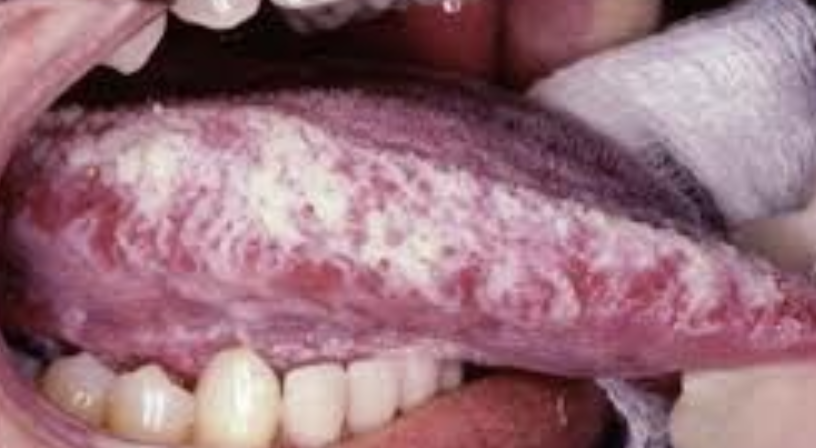
HIV/AIDS
What condition causes Hairy Leukoplakia?
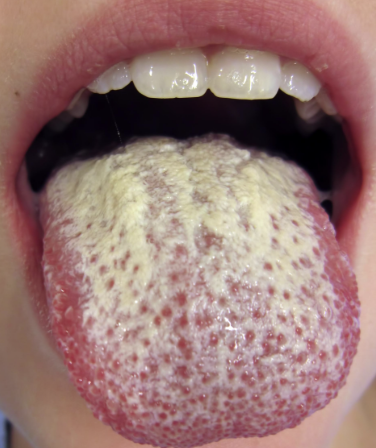
Candida Albicans
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Fungal infection caused by an overgrowth of Candida albicans in the mouth
Presents as creamy white, curd-like patches on the tongue, inner cheeks, gums, or throat, which may be painful or cause a burning sensation
patches can be scraped off, leaving a red or bleeding surface
Smooth, reddish, shiny tongue without papillae due to vitamin B12 deficiency
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Often indicative of glossitis caused by vitamin B12 deficiency
Results from atrophic glossitis, loss of tongue papillae, making tongue appear smooth and inflamed
Commonly associated with pernicious anemia and can cause a burning sensation or discomfort when eating
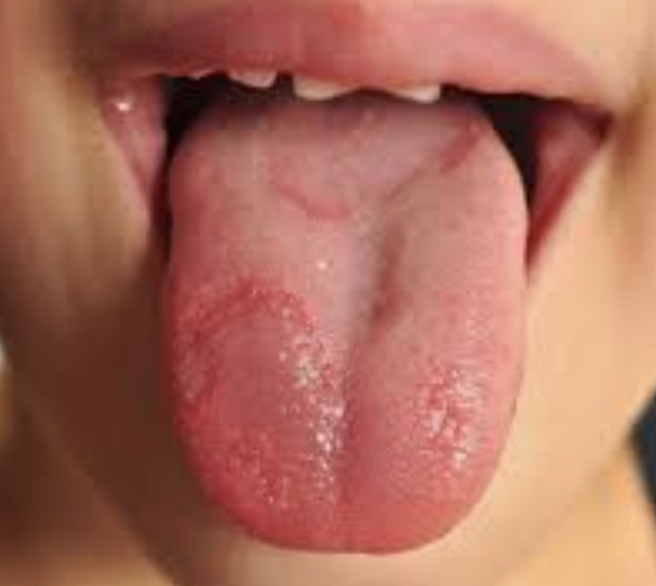
Vitamin B12
Deficiency in what vitamin causes a smooth, reddish, shiny tongue?
Black Hairy Tongue
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Papillae on surface of tongue become elongated and darkened, giving appearance of black hair
Caused by an overgrowth of bacteria or yeast, often due to poor oral hygiene, smoking, certain mediations (like antibiotics), or excessive use of mouthwashes
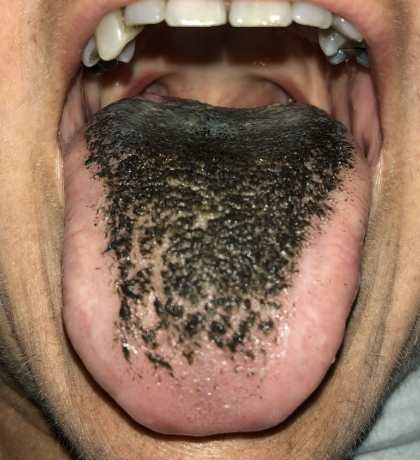
Poor oral hygiene
Smoking
Certain medications (like antibiotics)
Excessive mouthwash use
What may cause bacteria or yeast overgrowth that causes a Black Hairy Tongue?
Carcinoma of Tongue
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Usually squamous cell carcinoma
Type of oral cancer that manifests as a non-healing sore or lesion on the tongue
May appear as a red or white patch an ulcer, or a lump on the tongue’s surface
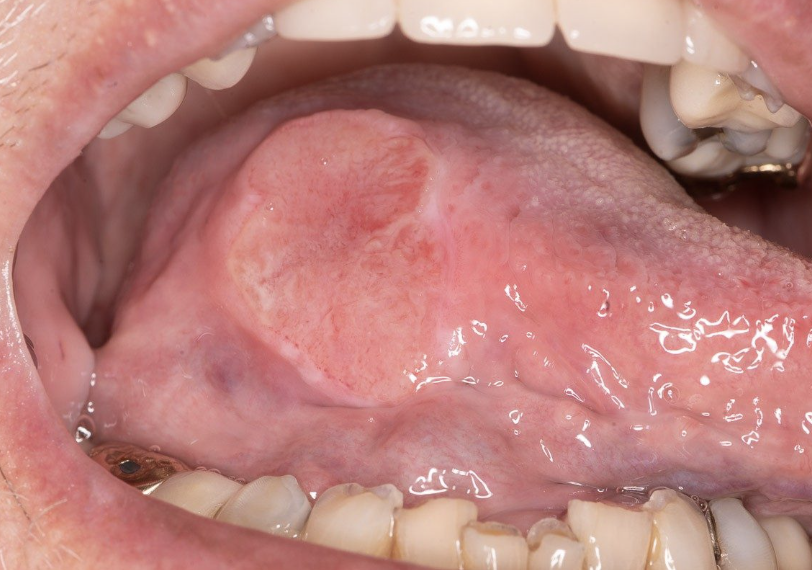
Cankersore
One of the 10 Common Abnormalities of the Mouth
Small, painful, round or oval ulcer that forms inside the mouth, typically on the inner cheeks, gums, or tongue
Ulcer has a white or yellowish center with a red, inflamed border
Triggers may include stress, minor mouth injuries, food allergies, and certain vitamin deficiencies
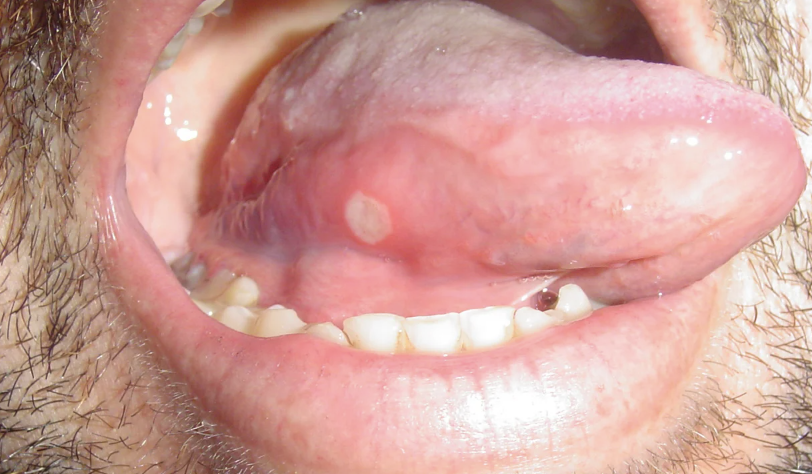
Teeth & Gums
Second Step of Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Ask client to open mouth. Note number of teeth, color, and condition.
Ask client to bite down and note alignment of lower and upper jaws.
Put on gloves and retract client’s lips and cheeks to check gums for color and consistency.
How to assess 2. Teeth & Gums?
32 pearly whitish teeth with smooth surfaces and edges
No decayed areas; no missing teeth
Gums are pink, moist, and firm with tight margins to the tooth. No lesions or masses.
Normal Findings for 2. Teeth & Gums
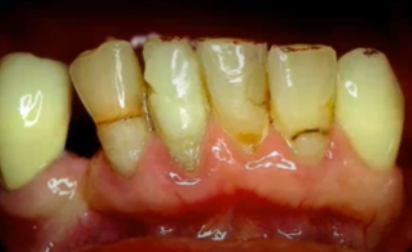
Yellow or Brownish Teeth
Caries
Missing Teeth
Chalky White Area
Malocclusion
Brown or yellow stains or white spots
Red, swollen gums
Receding Gums with loss of teeth
Hyperplasia
Bluish-Black or Grey-White Line
Abnormal findings for 2. Teeth & Gums
Malocclusion
Abnormal findings for 2. Teeth & Gums
Seen when upper and lower incisors protrude
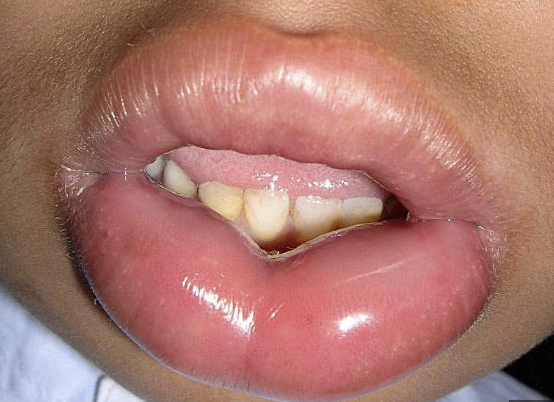
Red, Swollen Gums
Abnormal findings for 2. Teeth & Gums
Seen in gingivitis, scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency) and leukemia
Gingivitis
Scurvy (Vitamin C deficiency)
Leukemia
What cause red, swollen gums?
Hyperplasia
Abnormal findings for 2. Teeth & Gums
Enlarged reddened gums that may cover some of the normally exposed teeth
May be seen in pregnancy, puberty, leukemia, and use of some medications, such as phenytoin
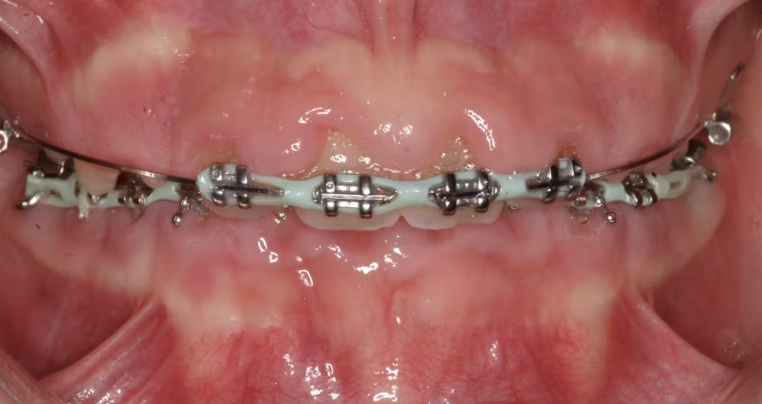
Pregnancy
Puberty
Leukemia
Medications (Phenytoin)
What may hyperplasia be seen in?
Periodontitis
Where are receding red gums with loss of teeth seen in?
Lead Poisoning
When are bluish-black or grey-white line along the gum line seen in?
Buccal Mucosa
Third Step of Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Use penlight and tongue depressor to retract lips and cheeks to check color and consistency
Note Stenson’s Ducts
How to assess 3. Buccal Mucosa?
Buccal mucosa should appear pink in light-skinned clients
Tissue is smooth and moist without lesions
Stenson’s ducts are visible with flow of saliva and with no redness, swelling, pain or moistness
Fordyce spots
Normal Findings for 3. Buccal Mucosa
Fordyce Spots
Normal Finding for 3. Buccal Mucosa
Yellowish-whitish raised spots
Normal ectopic sebaceous glands
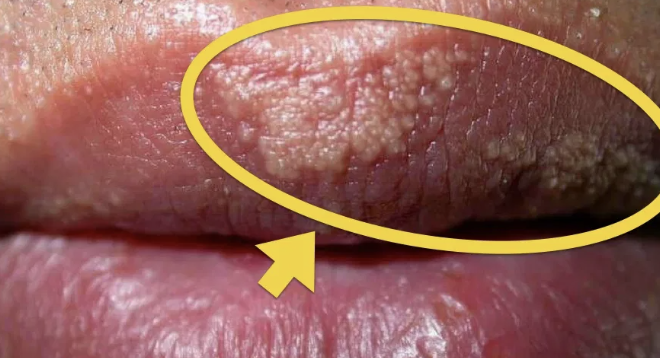
Leukoplakia
Abnormal Findings for 3. Buccal Mucosa
May be seen in chronic irritation and smoking
Precancerous lesion, whitish patch and painless
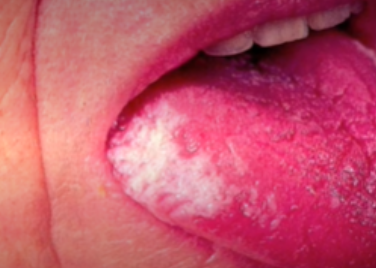
Yellow Brown Coating
Other than leukoplakia, what may be seen on smoker's tongues?
Inspect & palpate the tongue
Fourth Step of the Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Tongue pink, moist, moderate size with papillae present
No lesions
Normal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Deep longitudinal fissures
Black tongue
Smooth, reddish, shiny tongue
Enlarged tongue
Small tongue
Atrophied tongue
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Deep longitudinal fissures
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Seen in dehydration
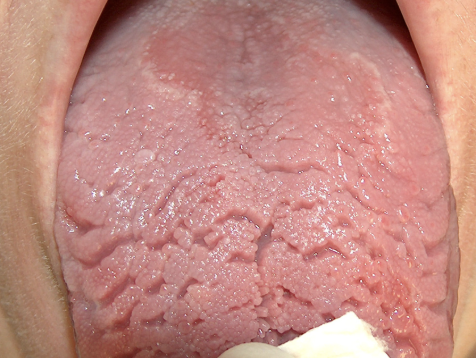
Dehydration
When are deep longitudinal fissures seen?
Black Tongue
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Indicative of bismuth (Pepto-Bismol) toxicity
Bismuth (Pepto-Bismol) toxicity
When is black tongue seen?
Enlarged Tongue
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Suggest hypothyroidism, acromegaly, or Down’s Syndrome, and angioneurotic edema of anaphylaxis
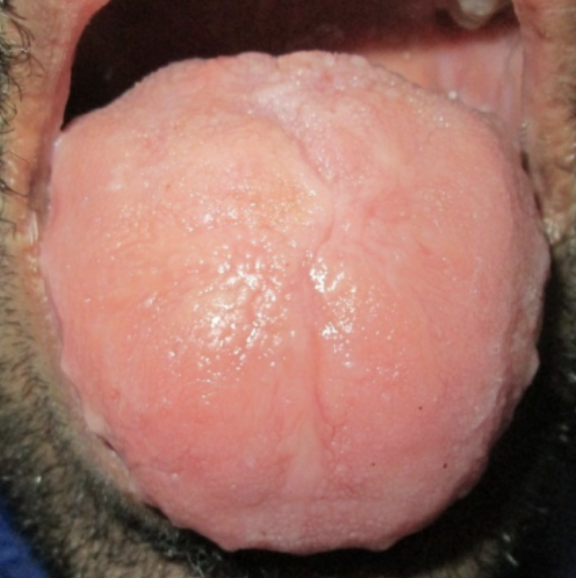
Niacin/Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Anemia
Antineoplastic Therapy
What does a smooth, reddish shiny tongue without papillae indicate?
Hypothyroidism
Acromegaly
Down’s Syndrome
Angioneurotic Edema of Anaphylaxis
What does an enlarged tongue suggest?
Small Tongue
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Suggests malnutrition
Malnutrition
What does a small tongue suggest?
Atrophied Tongue/Fasciculations
Abnormal Findings for 4. Inspect & palpate the tongue
Point to cranial nerve damage: Hypoglossal, CN 12
Hypoglossal, CN XI
Damage of what nerve does an atrophied tongue/fasciculations indicate?
Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Fifth Step for Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Hard palate is pale or whitish with firm, transverse rugae
Torus Palatinus
Soft palate pinkish, movable, spongy and smooth
Normal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Torus Palatinus
Normal Finding for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Bony protuberance in the midline of the hard palate
More often in females, Native Americans, and Asians
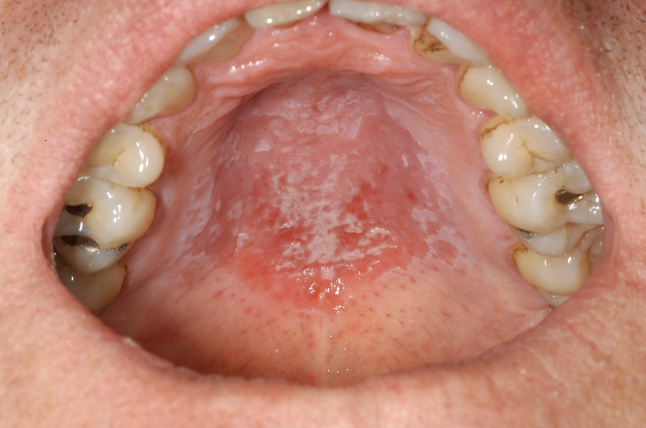
Thick white plaques on hard palate
Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Yellow Tint
Cleft Palate
Abnormal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Thick white plaques
Abnormal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Candidal infection
Karposi’s Sarcoma
Abnormal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Deep purple, raised, or flat lesions
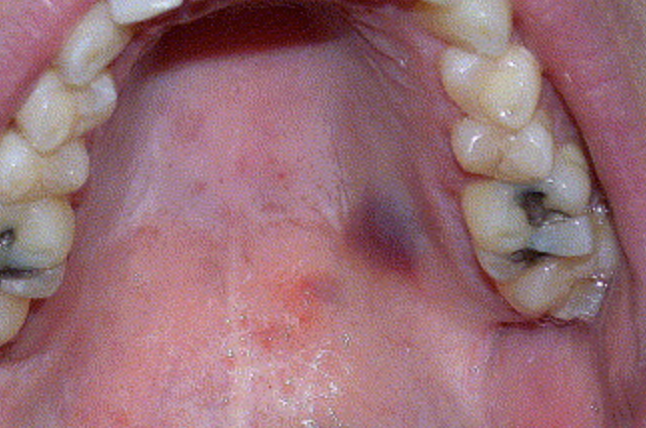
Yellow Tint
Abnormal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
May indicate jaundice since bilirubin adheres to elastic tissue (collagen)
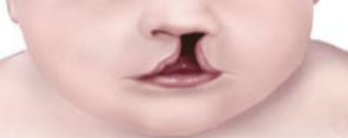
Cleft Lip/Palate
Abnormal Findings for 5. Hard (anterior) and soft (posterior) palates and width
Congenital
Opening in the hard palate
Note odor
Sixth Step of Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
No unusual or foul odor noted
Normal finding for 6. Note Odor
Fruity/Acetone Breath
Ammonia
Foul Odors
Fecal Breath Odor
Sulfur Odor (Fetor Hepaticus)
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Fruity/Acetone Breath
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Associated with diabetic ketoacidosis
Diabetic Ketoacidosis
What is a fruity/acetone breath indicative of?
Ammonia Odor
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Associated with Kidney Disease
Kidney Disease
What is an ammonia breath indicative of?
Foul Odors
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Indicate oral or respiratory infection, or tooth decay
Oral or respiratory infection
Tooth decay
What is a foul breath indicative of?
Fecal Breath Odor
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Occurs in bowel obstruction
Bowl Obstruction
What is a fecal breath indicative of?
Sulfur Odor (Fetor Hepaticus)
Abnormal findings for 6. Note Odor
Occurs in endstage liver disease
Enstage liver disease
What is a Sulfur Odor (Fetor Hepaticus) indicative of?
Uvula
Seventh Step of Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Apply tongue depressor to tongue and shine penlight into client’s wide-open mouth
Ask client to say “aaah” snd watch for uvula and soft palate to move
How to assess 7. Uvula?
No redness of or exudate form uvula or soft palate
Midline elevation of uvula and symmetric elevation of the soft palate
Bifid Uvula
Normal findings for 7. Uvula
Bifid Uvula
Normal findings for 7. Uvula
Common in Native Americans
Looks like uvula is split in two or partially severed
Asymmetric movement or loss after stroke
Palate fails to rise and uvula deviates to normal side
Abnormal findings for 7. Uvula
Cerebrovascular (Stroke)
When does asymmetric movement or loss of movement of the uvula occur?
Vagus CN X
Paralysis of what cranial nerve causes the palate to fail to rise and the uvula to deviate to the normal side?
Tonsils
Eighth Step for Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Tonsils pink and symmetric and may be enlarged to +1 for healthy clients
No exudate, swelling, or lesions
Normal Findings for 8. Tonsils
+1
Tonsil Grade
Tonsils occupy less than 25% of the oropharyngeal width
+2
Tonsil Grade
Tonsils occupy 26-50% of the oropharyngeal width
+3
Tonsil Grade
Tonsils occupy 51-75% of the oropharyngeal width
+4
Tonsil Grade
Tonsils occupy more than 75% of the oropharyngeal width
Gag reflex
Ninth Step of Mouth & Pharynx Assessment
Gag reflex intact
Normal Finding for 9. Gag Reflex
Glossopharyngeal (CN IX)
Vagus (CN X)
Lesions in what cranial nerves cause an absent gag reflex?
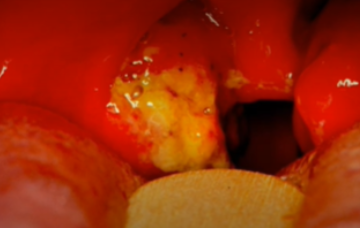
Aphthous Ulcer
Cankersore
Koplik Spots
Peculiar spots present on buccal mucosa, whitish spots and be scrapped off
Measles
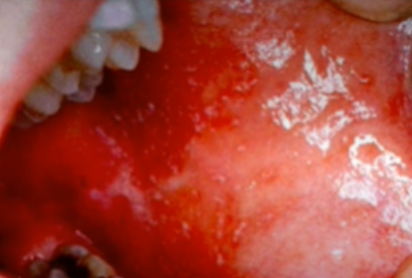
Receding Gums
Gums atrophy
Tonsillitis
Inflammation of tonsil (palatine) with yellowish exudate