CH 6) BONE TISSUE
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
-supports body
-facilitates movement
-protects organs
-rbc production
-stores and releases minerals and fat
function of the skeletal system (5)
hematopoiesis
-formation of blood cells
-carried out by red bone marrow
-active in childhood
-converts to yellow during adulthood
long bone
bones that are longer than they are wide
-humerus, femur, metacarpals, metatarsals
examples of long bone
flat bone
thin and curved bone; serves as a point of attachment for muscles and protects internal organs
-cranial, sternum, scapula, ribs
examples of flat bone
short bone
cube-shaped bone that is approximately equal in length, width, and thickness; provides limited motion
-carpals and tarsals
examples of short bones
irregular bone
bone of complex shape; protects internal organs from compressive forces
-vertebra, pelvis
examples of irregular bones
sesamoid bone
small, round bone embedded in a tendon; protects the tendon from compressive forces
-patella
example of a sesamoid bone
sutural bones (wormian bones)
irregular bones formed between cranial bones as sutures fuse; unique to every person
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage covering the joint surface at the epiphyses
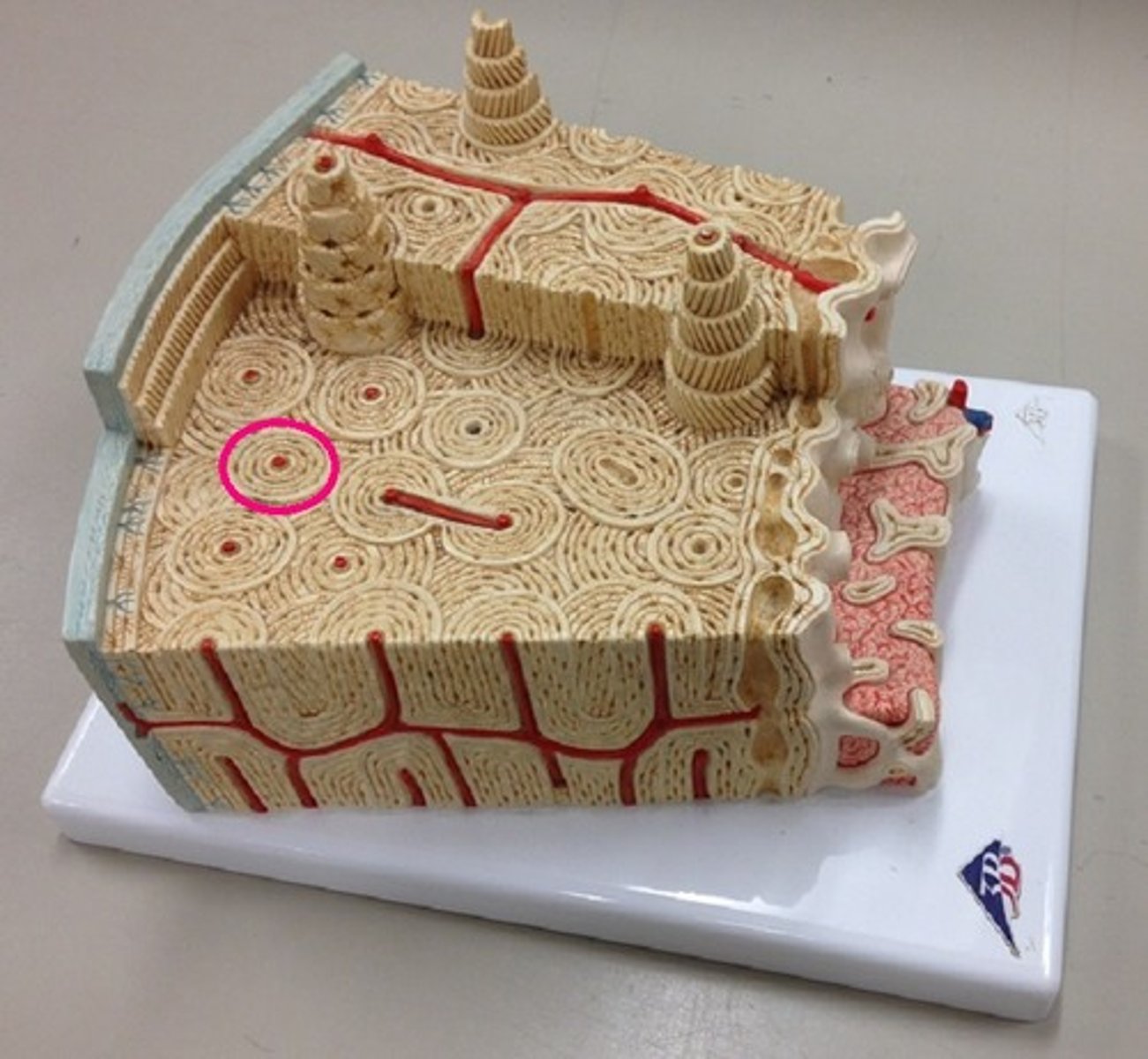
compact bone
bone tissue forming the walls of the diaphysis and the bony coverings of spongy bone
diaphysis
shaft of the long bone
endosteum
a connective tissue membrane lining the medullary cavity
epiphysis
enlarged proximal and distal ends of a long bone
epiphyseal line
part of the bone that replaces the epiphyseal growth plate
head
rounded epiphysis
medullary cavity
space within the diaphysis
neck
bony connection between the head and diaphysis of the long bone. The anatomical neck occurs with the epiphyseal line, where the surgical neck occurs at the junction of the epiphysis to the diaphysis where a joint replacement would be made.
periosteum
a dense connective tissue membrane covering the external bone surface
red marrow
red blood cell forming tissue that fills the spaces of spongy bone tissue
spongy bone
bone tissue filling the epiphyses and lining the medullary cavity
yellow marrow
a fatty material occupying the medullary cavity
sandwhich of compact, spongy, and compact bone
anatomy of a flat bone
proximal epiphyses, flat bones, irregular bones
where is red marrow found in an adult? (3)
osteoblasts
bone-forming cells, builds bone by secreting collagen and calcium salts
osetocytes
mature bone cells, maintains bone;
live in lacuna
osteoclasts
bone cells that break down bone matrix
osteogenic cell
bone stem cell (oligopotent)
osteoid
organic bone matrix secreted by osteoblasts;
rich in collagen
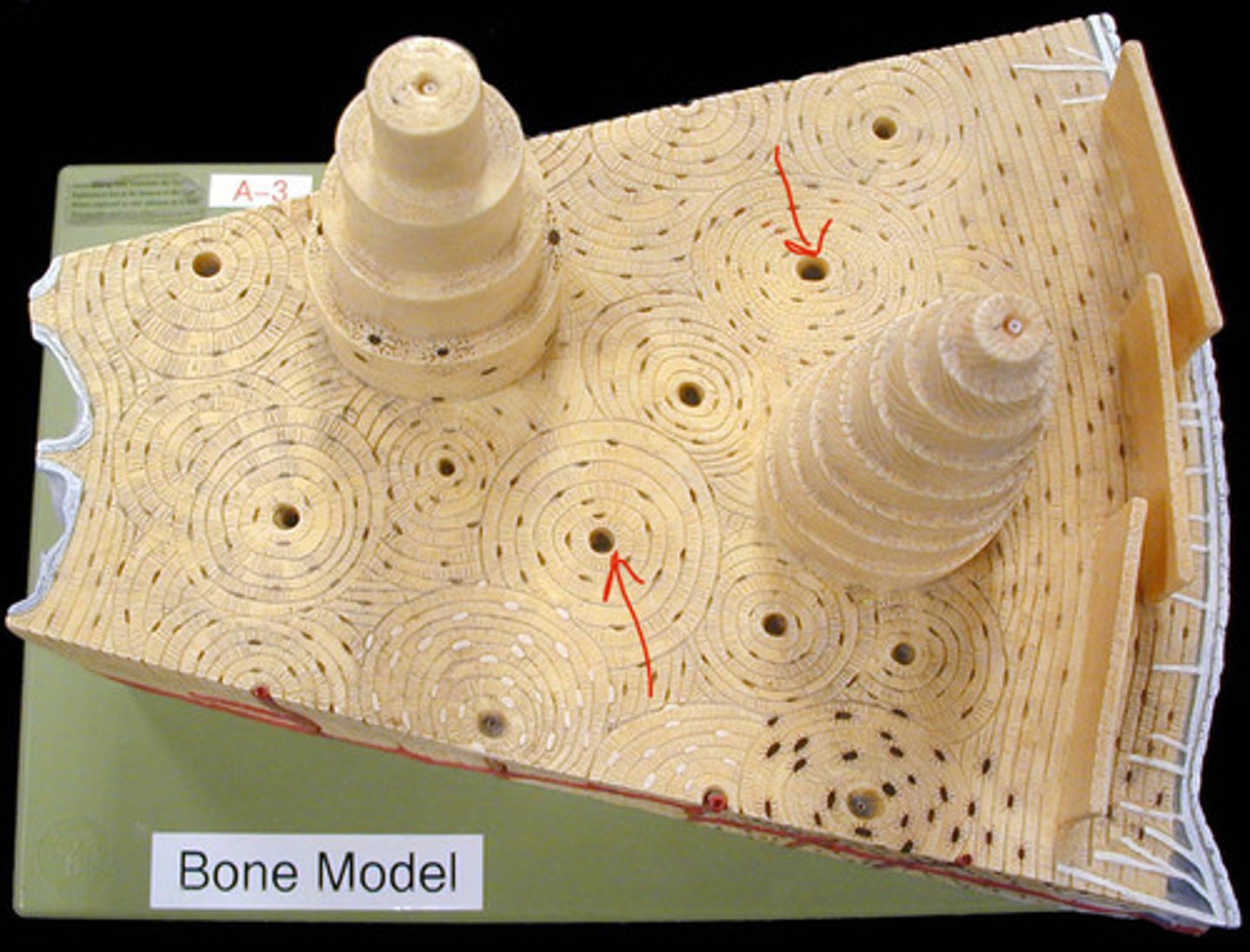
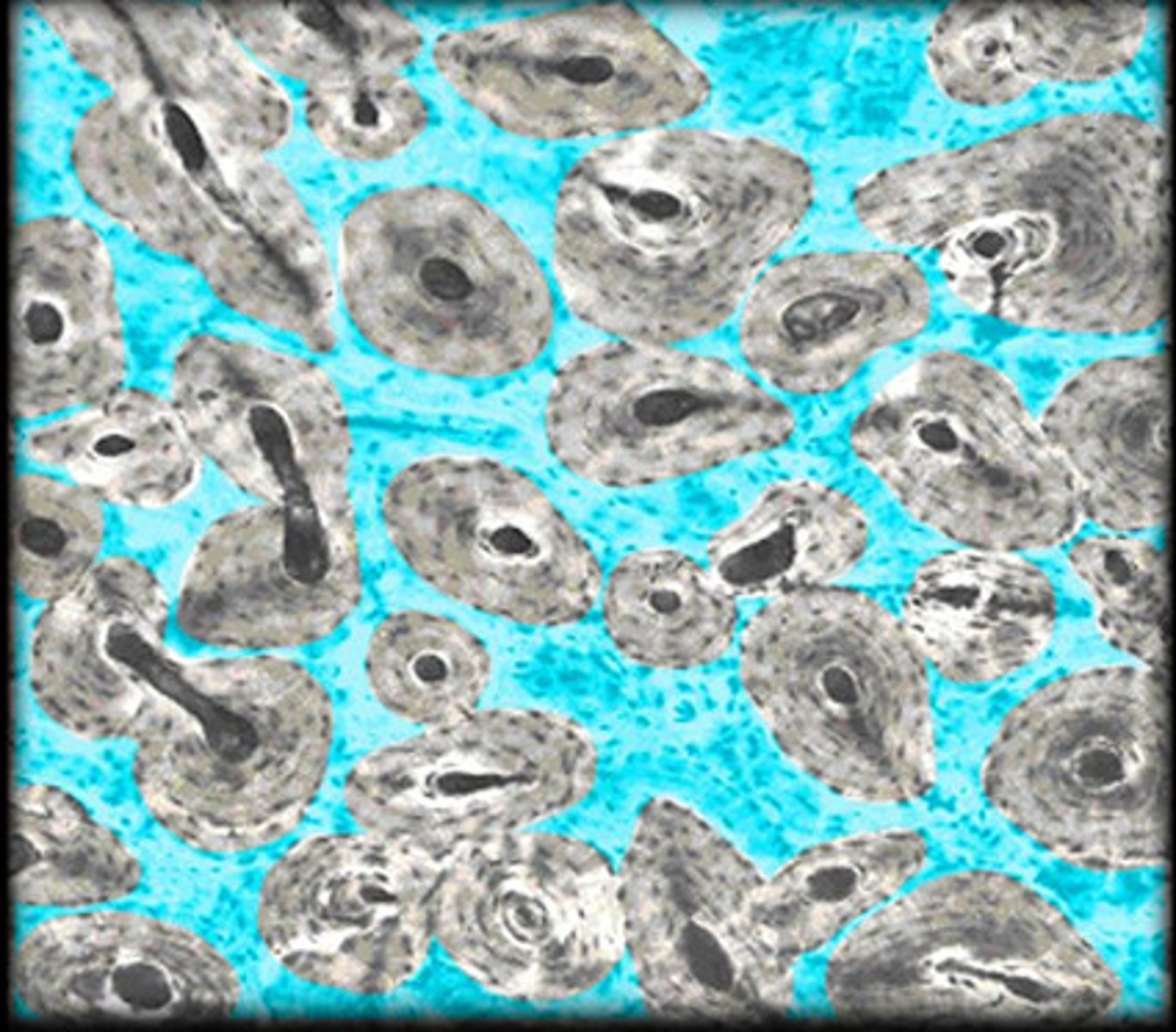
osteons
structural unit of compact bone;
cylindrical structure

concentric lamellae
circular layers of bony matrix around a central canal
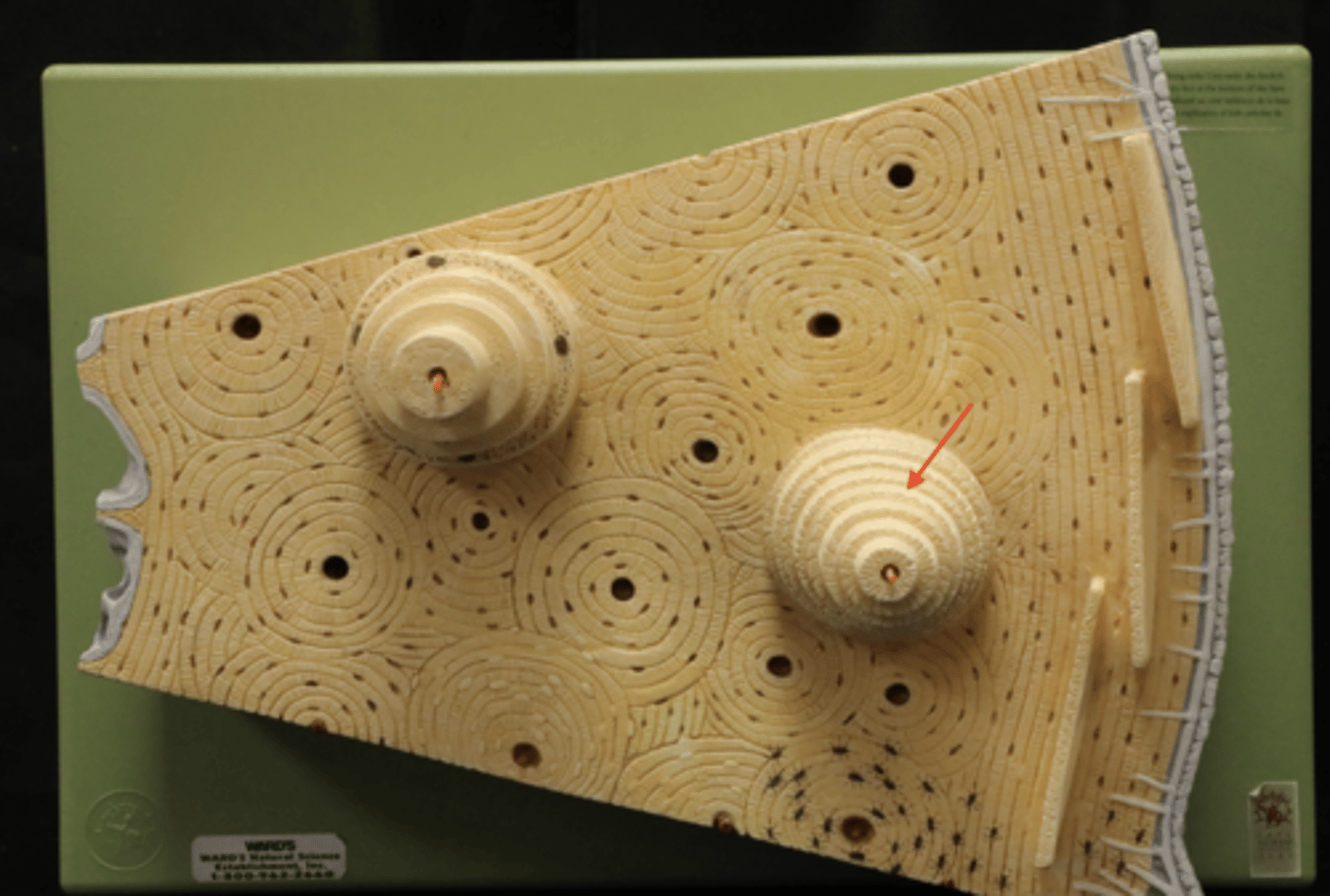
central canal of osteon
contains blood vessels and nerves of the osteon
perforating canals
run horizontal, supplies central canal with outside vessels and nerves
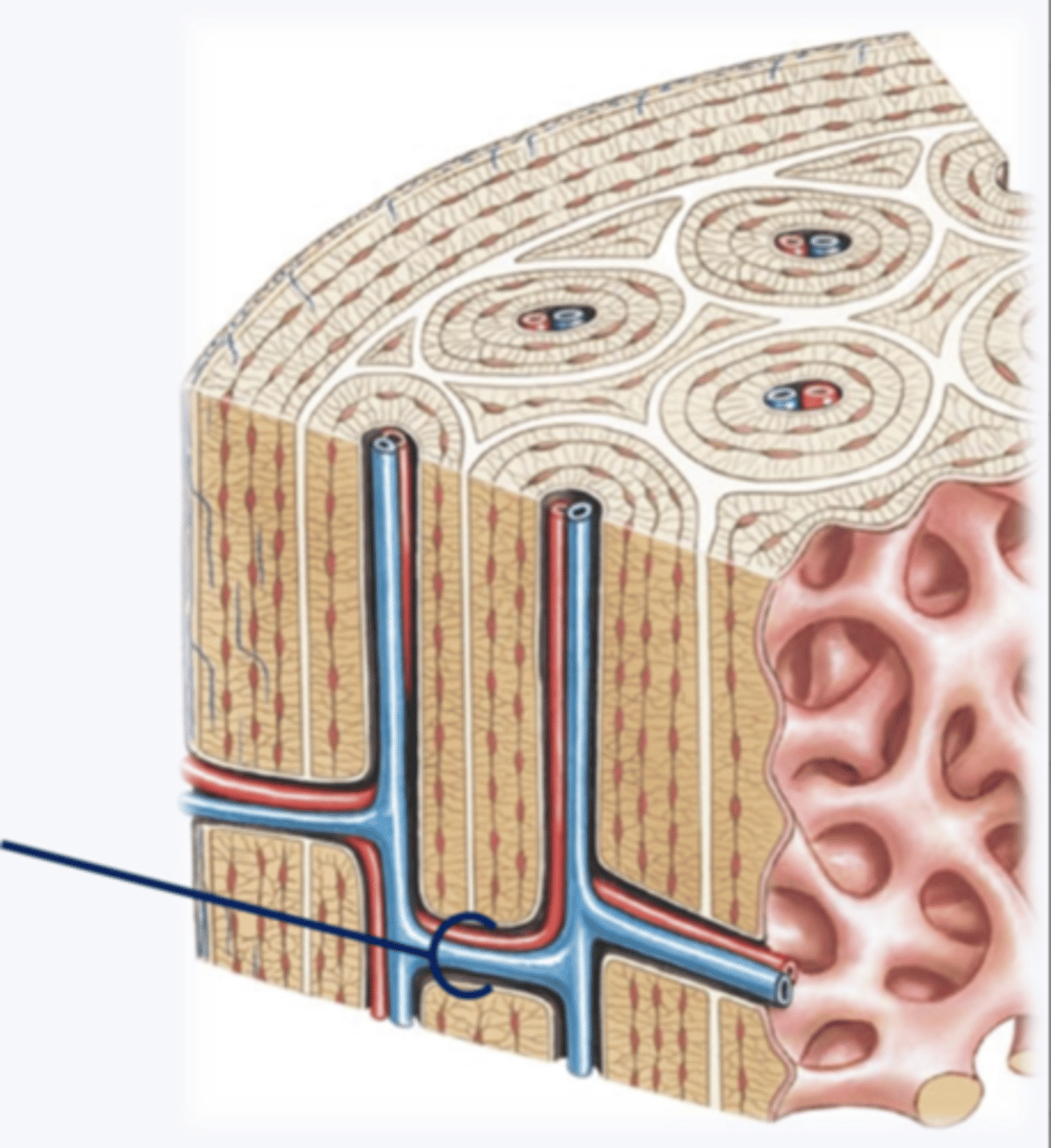
interstitial lamellae
lay between osteons
circumferential lamellae
beneath periosteum,
covers entire circumference
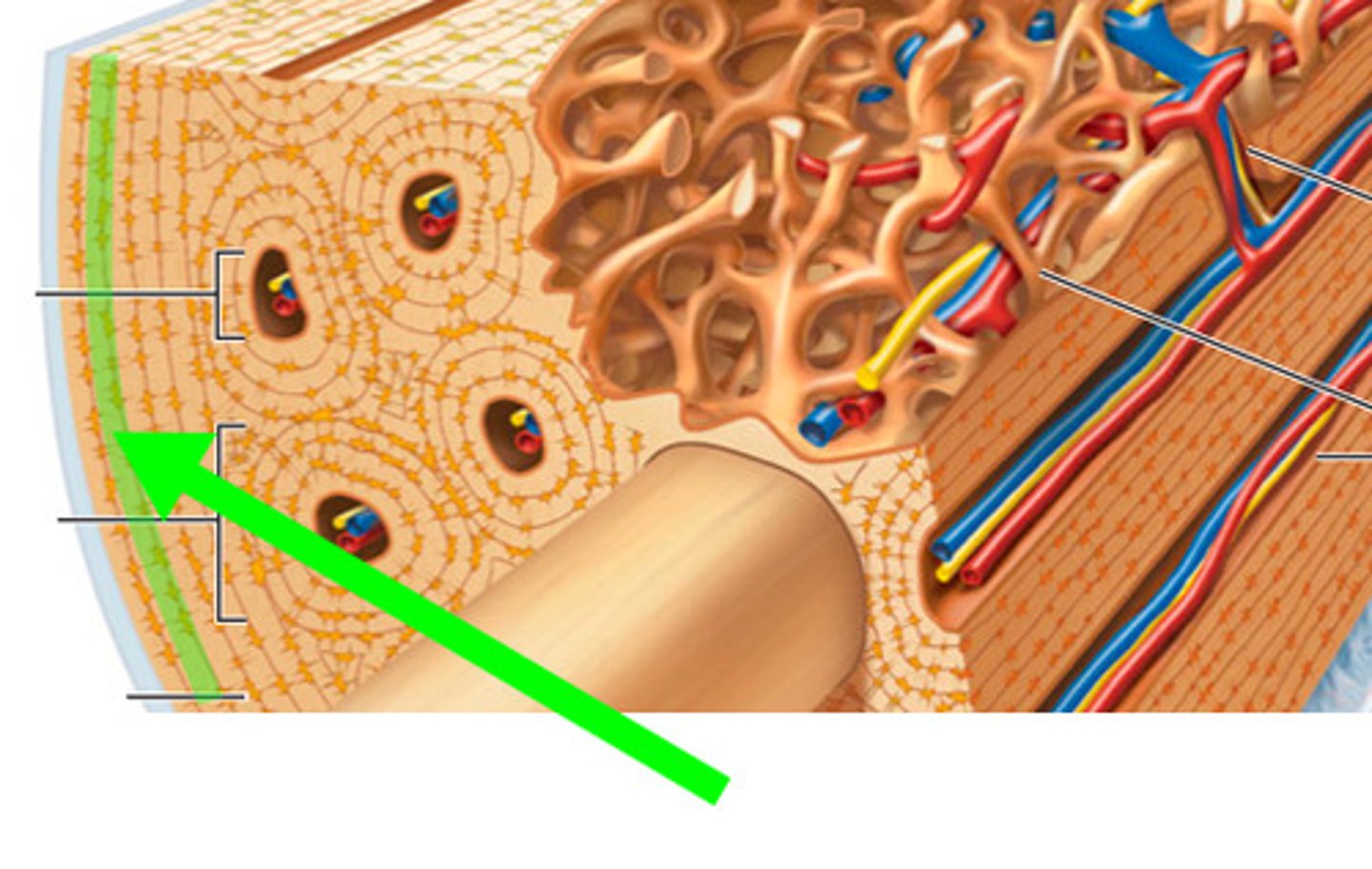
lacuna
small cavities in bone that contain osteocytes
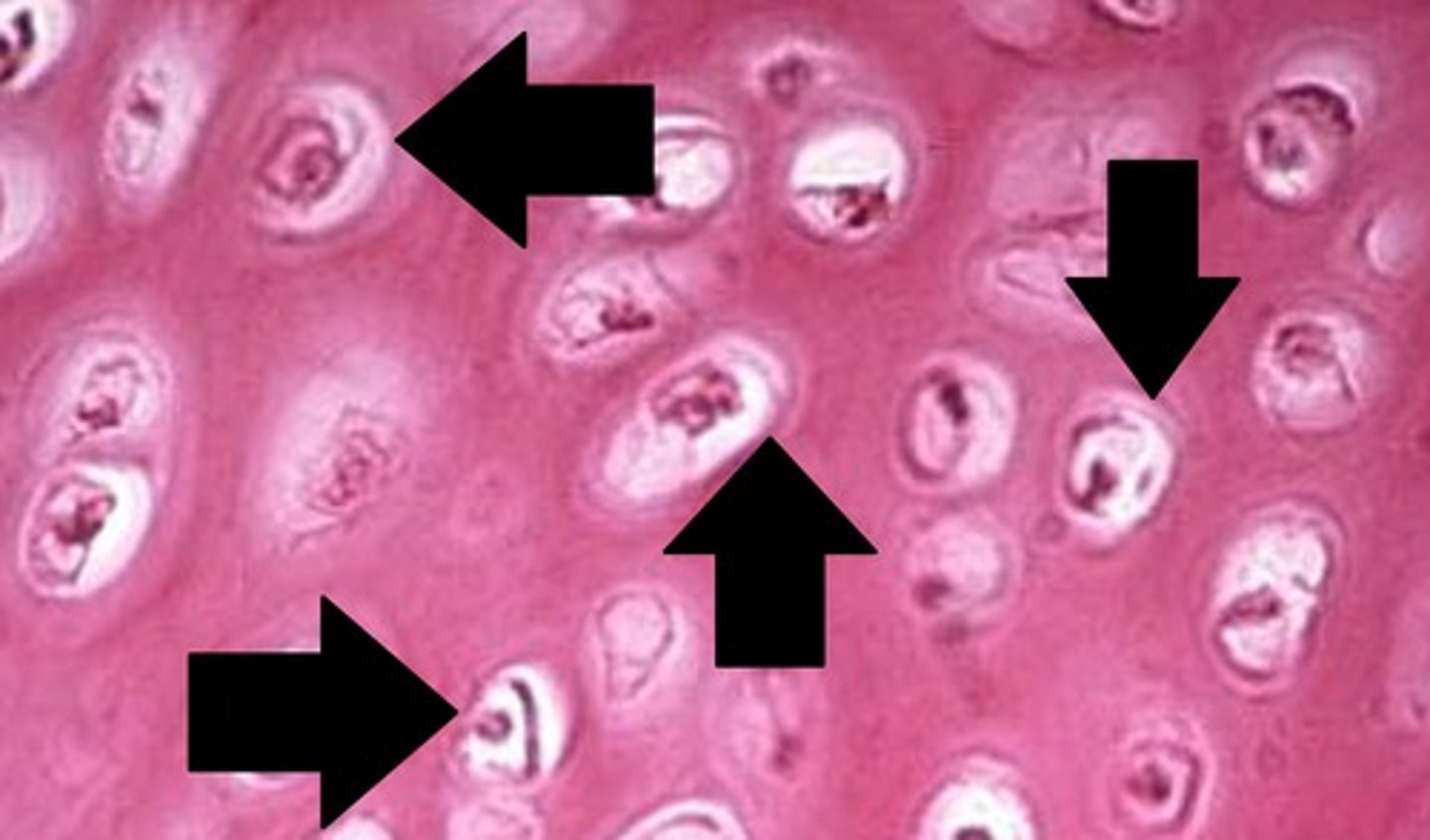
-no osteons
-arranged in lattice-like spicules, light weight
-houses bone marrow
-contains lacuna and osteocytes
characteristics of spongy bone
osteogenesis
process of bone formation
ossification
process of adding hard calcium salts to harden bone
intramembranous ossification
ossification in the membrane
develops from mesenchymal cells
-FLAT BONES develop this way
1. mesenchymal cells differentiate into capillaries and osteogenic cells
2. osteoblasts begin building bone at ossification centers, secretes osteoid
3. osteoid calcifies and bone hardens
4. osteoblasts become osteocytes
5. crowded blood vessels condense into red marrow
process of intramembranous ossification
endochondral ossification
ossification of hyaline cartilage
LONG BONES develop this way
1. mesenchymal cells differentiate into chondroblasts
2. hyaline calcifies at ossification centers
-chondrocytes stop cartilage production
-chondrocytes produce ALKALINE PHOSPHATES
-alk phos brings calcium to area
3. area calcifies and chondrocytes die
4. blood vessels infiltrate and enlarge cavity
-brings osteoblasts
-dead cartilage is remodeled into bone
5. perichondrium becomes periosteum
-bone collar forms under periosteum
-primary ossification center develops in diaphysis
6. chondrocytes and cartilage grow at ends of bone
AFTER BIRTH
7. secondary ossification center develops in epiphysis
8. cartilage remains at epiphyseal plate and joint
process of endochondral ossification
(good luck lol)
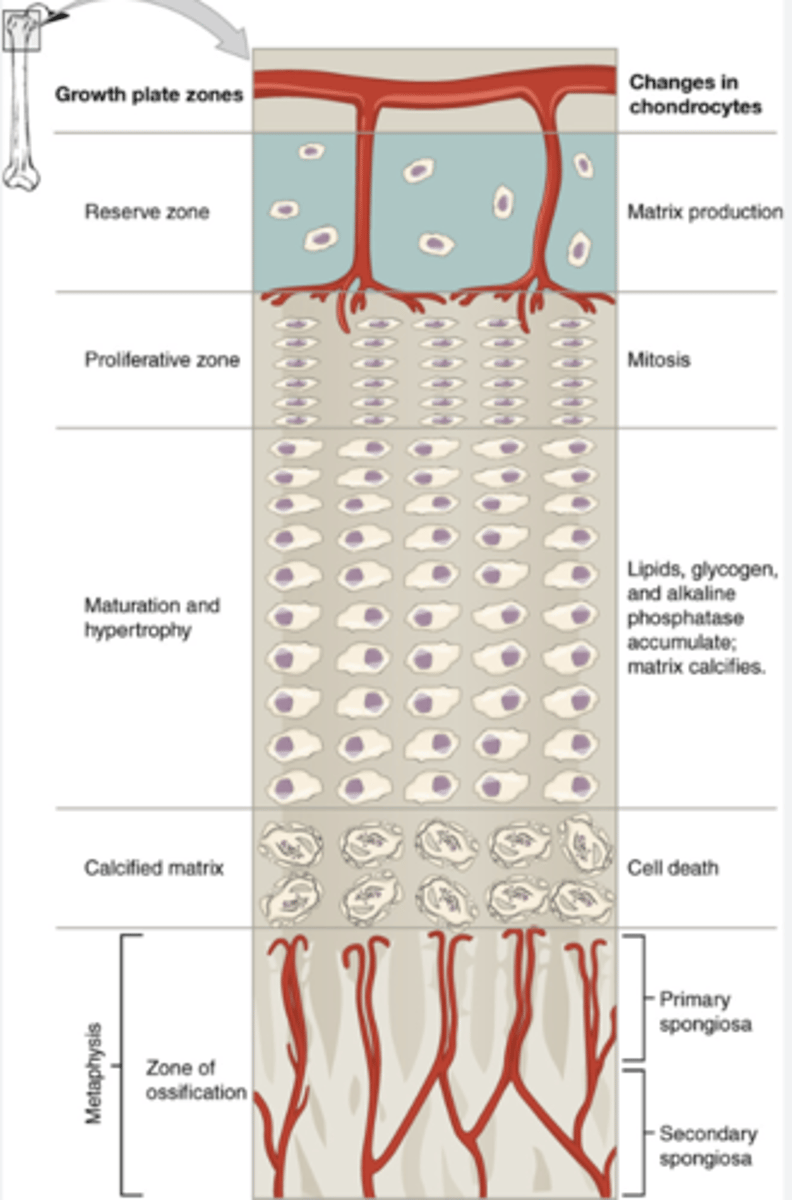
reserve zone of epiphyseal plate
anchors plate to epiphysis (cartilage)
proliferative zone of epiphyseal plate
chondrocytes replicate, growth plate cartilage grows
maturation/hypertrophy zone
chondrocytes grow and age, secretes cartilage that will soon be replaced with bone
calcification zone of epiphyseal plate
matrix becomes calcified, chondrocytes die
capillaries and osteoblasts invade and lay down osteoid
zone of ossification
(last region) consists of calcified chondrocytes and osteoblasts,
anchors plate to diaphysis
hi! study this diagram or else
wolff's law
bone responds and adapts to forces by reinforcing areas of demand (creates projections and markings)
"use it or lose it"
osteophytes
aka bone spurs
degenerative bone growths due to improper body mechanics
osteogenesis imperfecta
"brittle bone disease"
mutation that causes lack of collagen
fracture
broken bone
transverse fracture
fracture straight across long axis
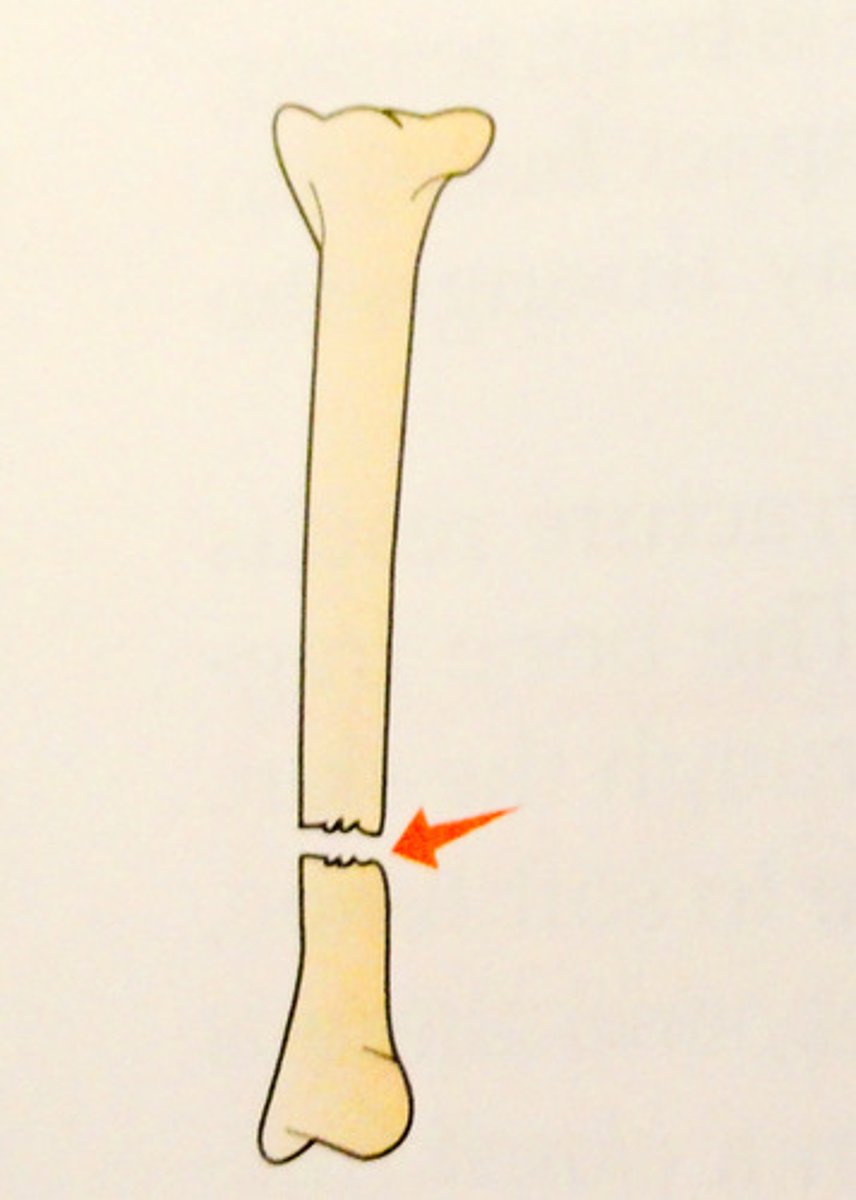
oblique fracture
fracture at an angle to the bone
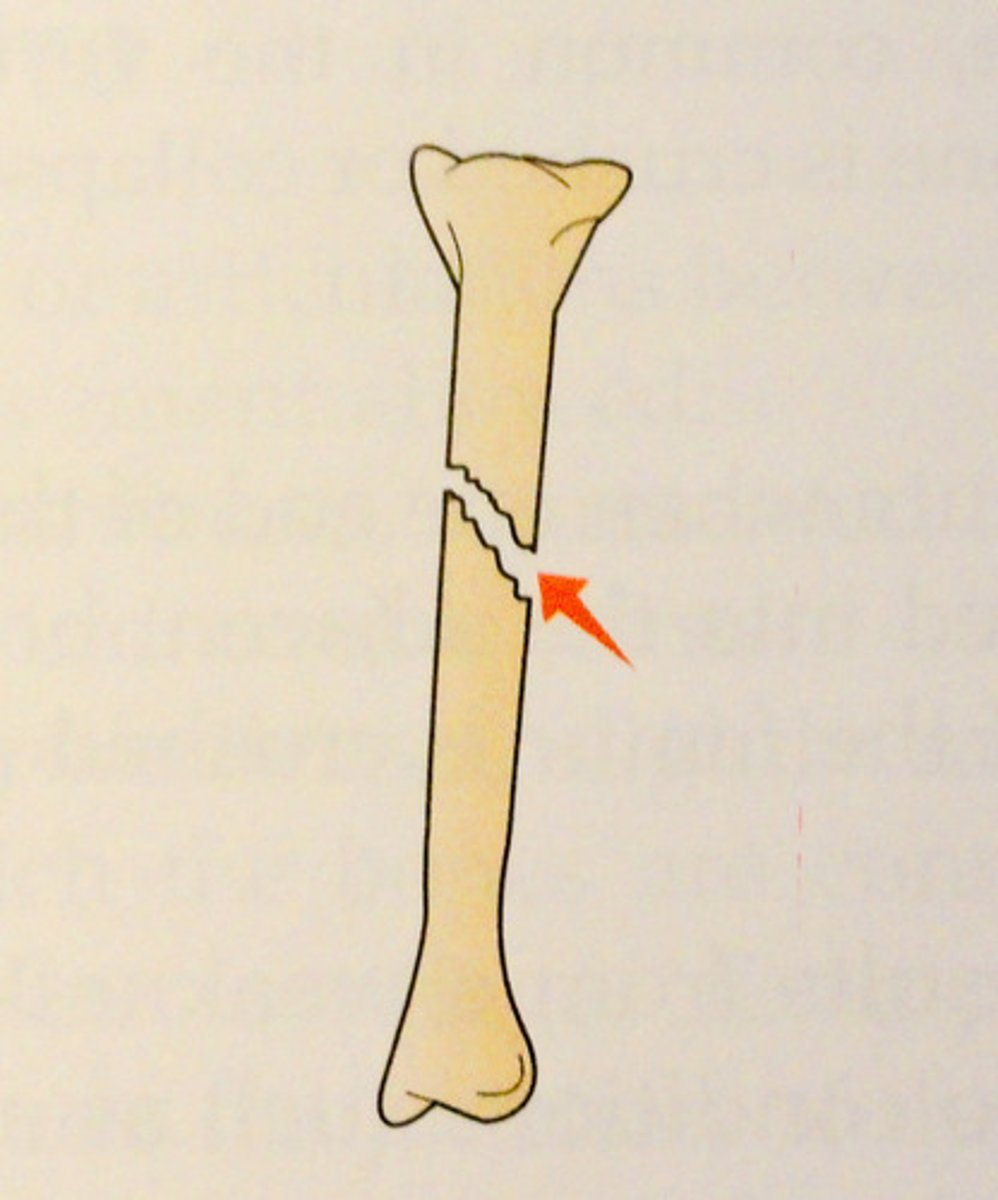
spiral fracture
a fracture in which the bone has been twisted apart
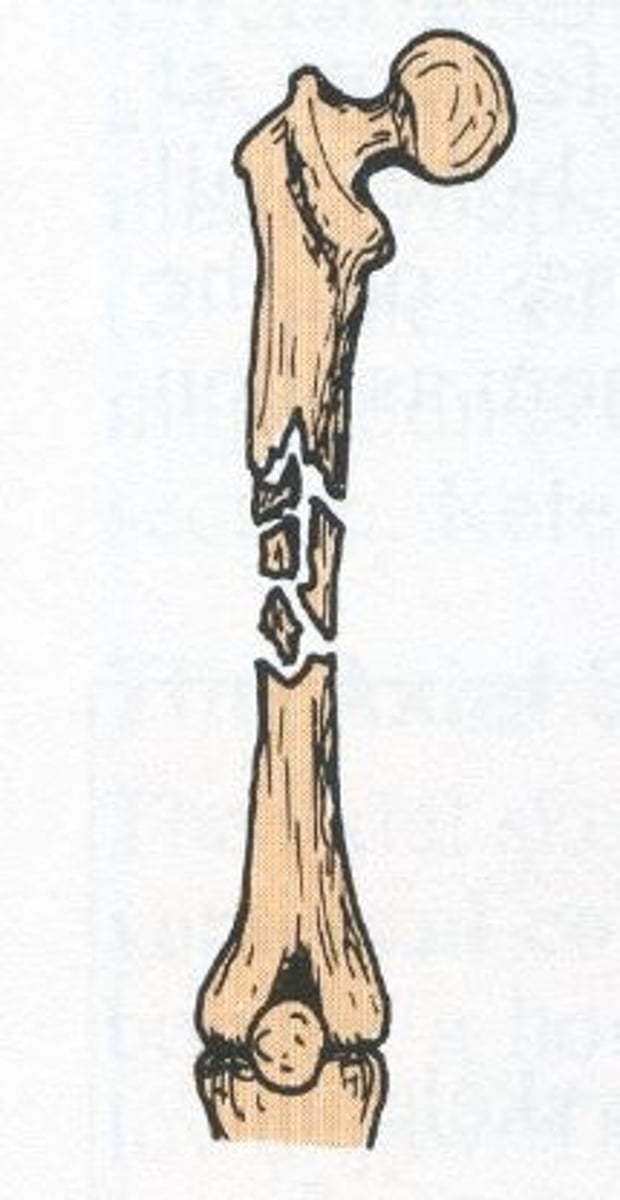
comminuted fracture
bone breaks into many fragments
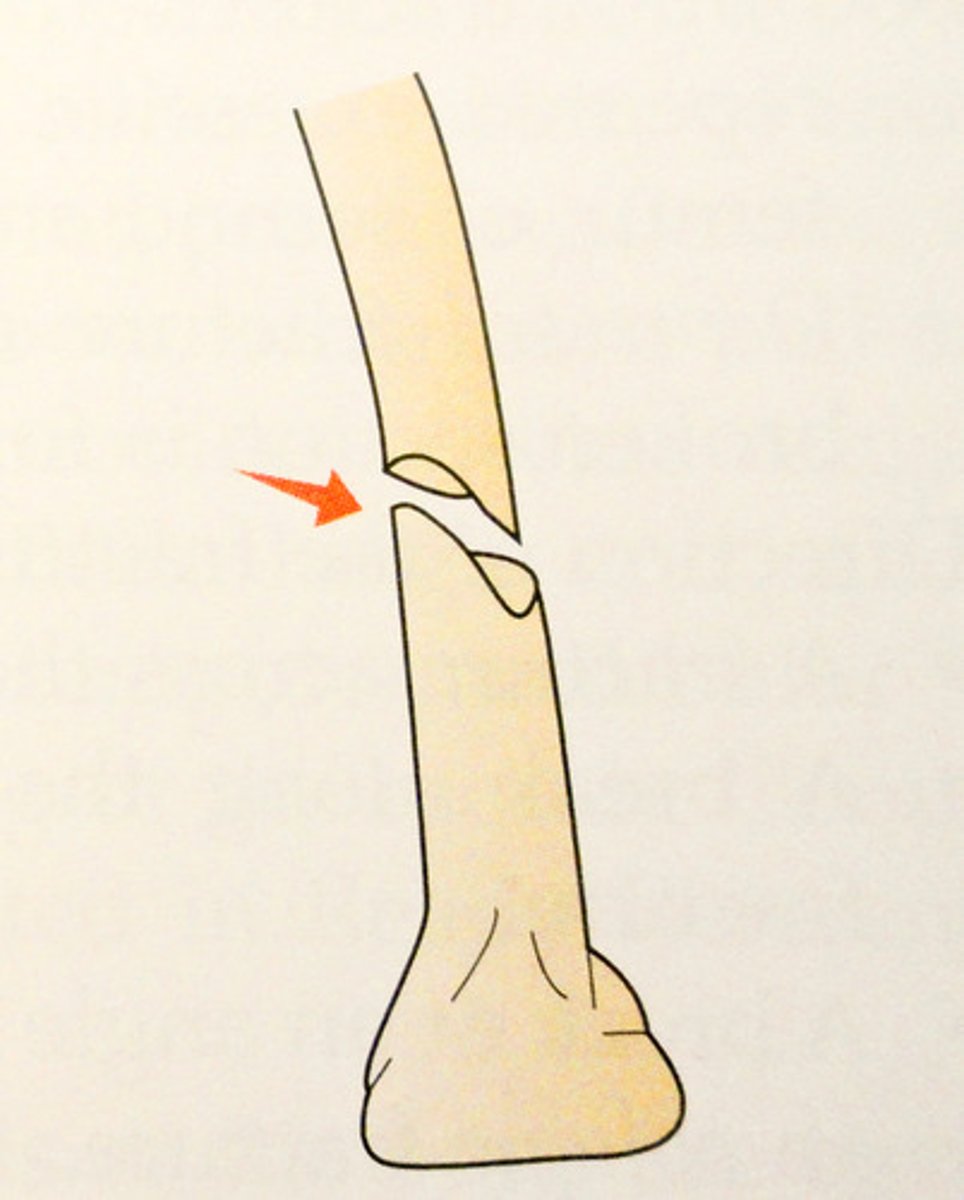
impacted fracture
ends drive into one another, result of compression
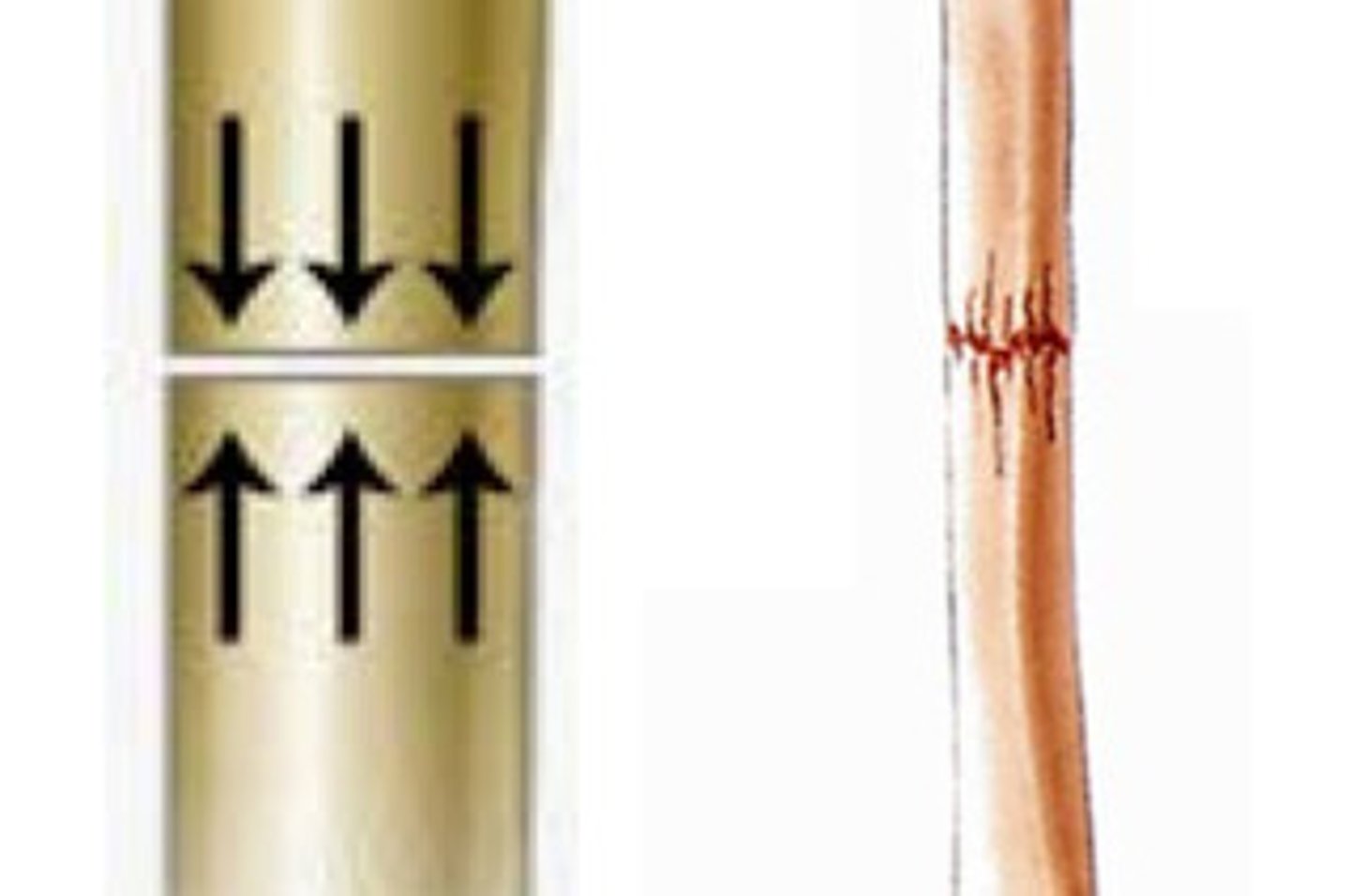
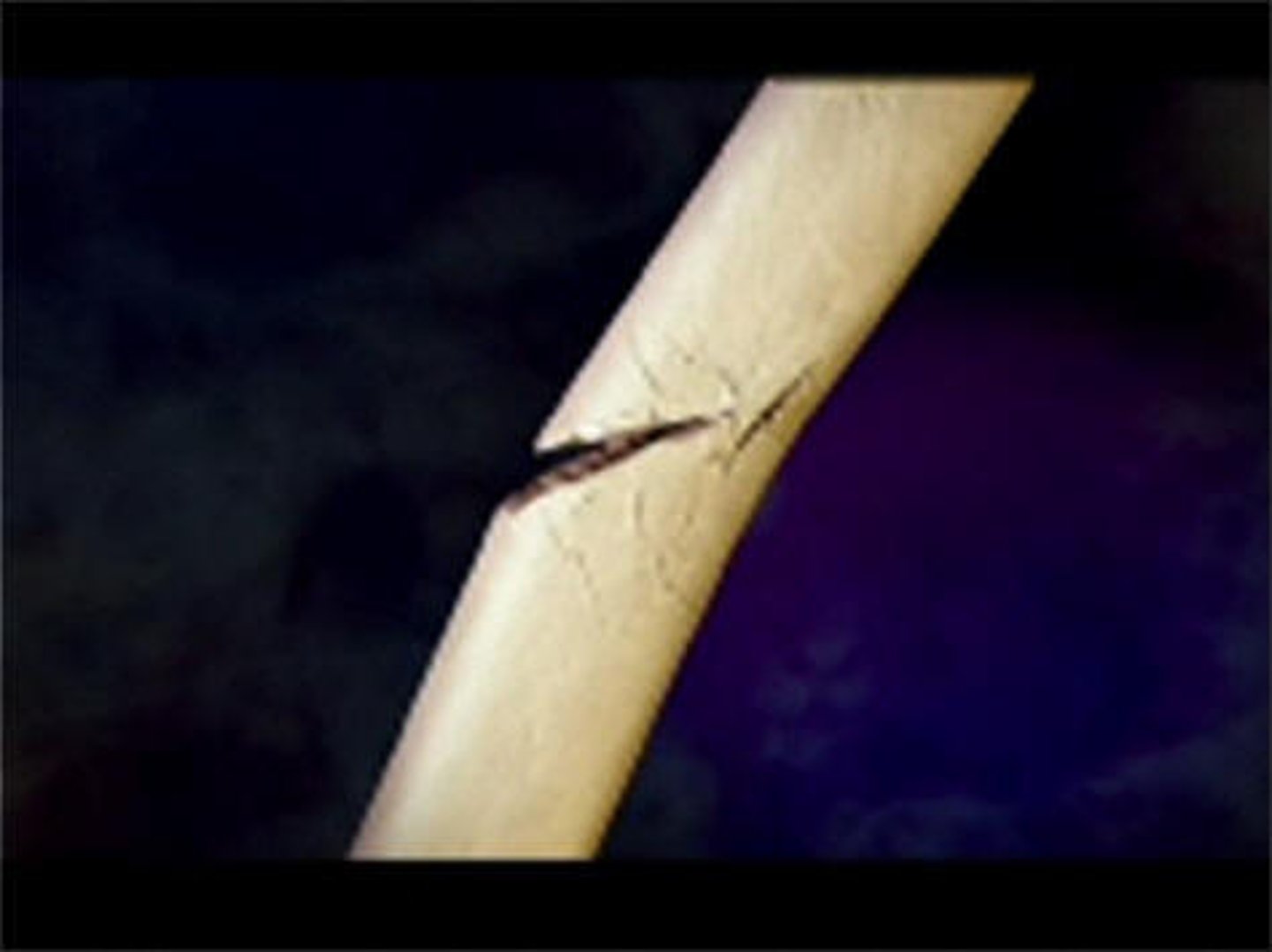
greenstick fracture
bending and incomplete break of a bone; most often seen in children

open (compound) fracture
broken bone penetrates through the skin
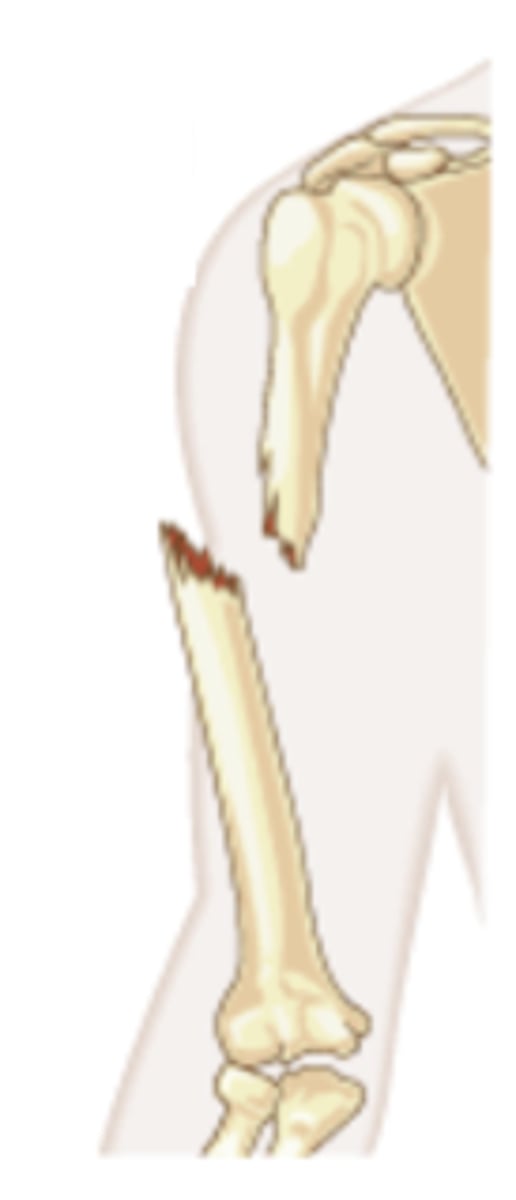
closed (simple) fracture
break that does not penetrate the skin
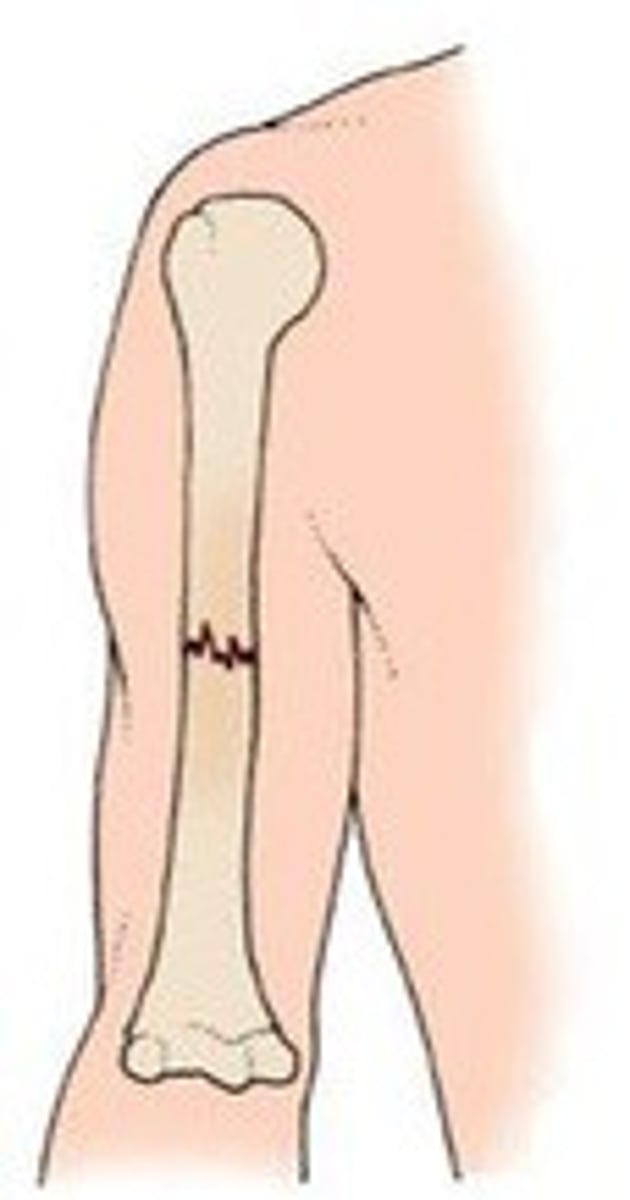
bone bruise
inner trabecular is fractured,
requires long healing process
osteoporosis
condition that causes loss of bone density
1. fracture hematoma (bone bleeds and clots)
2. callus formation
3. osteoclasts reabsorb dead bones, osteoblasts ossifies callus
4. cartilage of calli is replaced by trabecular
process of bone repair
calcium
essential for
-bone/tooth development
-heart rate and contractions
-nerve impulse
-blood clotting
-hardening bone
vitamin k
needed for calcium absorption