AP Psychology Cram Packet - Key Concepts and Theories
1/525
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
526 Terms
Inferential Statistics
Analyzes data to draw conclusions beyond sample.
Hypothesis
Tentative explanation that can be tested.
Placebo Effect
Behavior change due to belief in treatment.
Double-Blind Study
Neither participant nor experimenter knows conditions.
Single-Blind Study
Only participant is unaware of conditions.
Falsifiable
Can be supported or rejected through evidence.
Operational Definition
Precise definition allowing replication of study.
Statistical Significance
Results unlikely due to chance, p<.05 indicates significance.
Effect Size
Indicates practical significance of data findings.
Ethical Guidelines
Standards ensuring participant rights and safety.
Informed Consent
Participants must agree to participate knowingly.
Confidentiality
Participants' identities must remain private.
Population
Entire group research findings apply to.
Sample
Specific individuals chosen for study participation.
Random Assignment
Participants assigned randomly to groups for fairness.
Confound
Unintended variable affecting study results.
Naturalistic Observation
Observing subjects in their natural environment.
Case Study
In-depth analysis of a single individual.
Surveys
Data collection method using self-reported responses.
Random Sample
Participants selected randomly from the population.
Meta-Analysis
Combines results from multiple studies for insights.
Descriptive Statistics
Summarizes data characteristics through measures.
Measures of Central Tendency
Mean, median, and mode describe data center.
Sampling Bias
Sample not representative of the population.
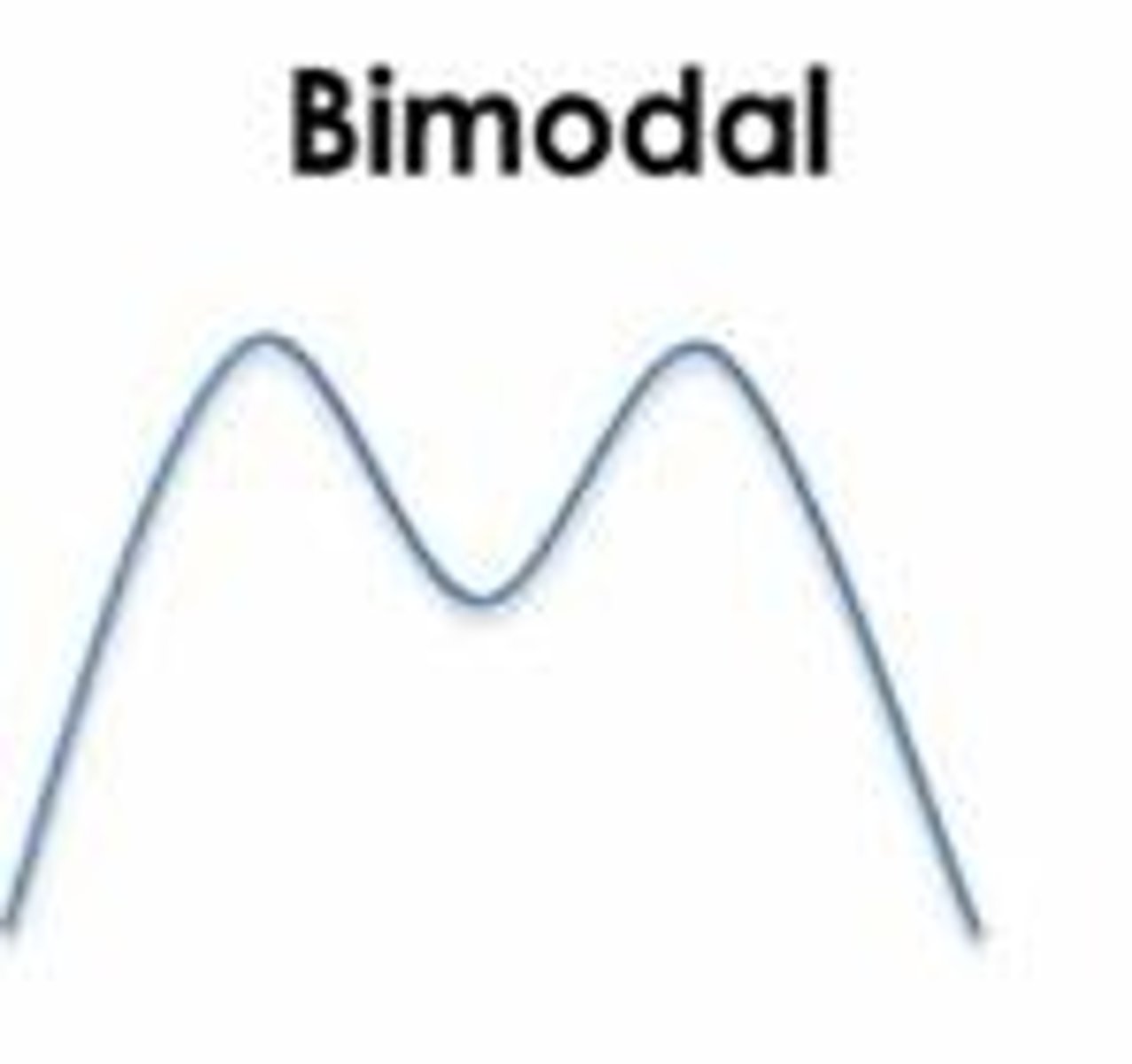
Bimodal Distribution
Data set with two modes or most frequent values.
Cultural norms
Behaviors of a group influencing research outcomes.
Experimenter bias
Researcher expectations affecting study results.
Participant bias
Participants' expectations influencing study outcomes.
Independent Variable
Manipulated factor to observe effects.
Dependent Variable
Measured outcome dependent on independent variable.
Experimental Group
Group receiving treatment in an experiment.
Control Group
Baseline group receiving no treatment.
Confirmation bias
Favoring information that supports existing beliefs.
Hindsight bias
Believing one predicted an outcome after it occurs.
Overconfidence
Exaggerated belief in one's knowledge or abilities.
Hawthorne effect
Behavior change when individuals are observed.
Skew
Distribution distortion caused by outliers.
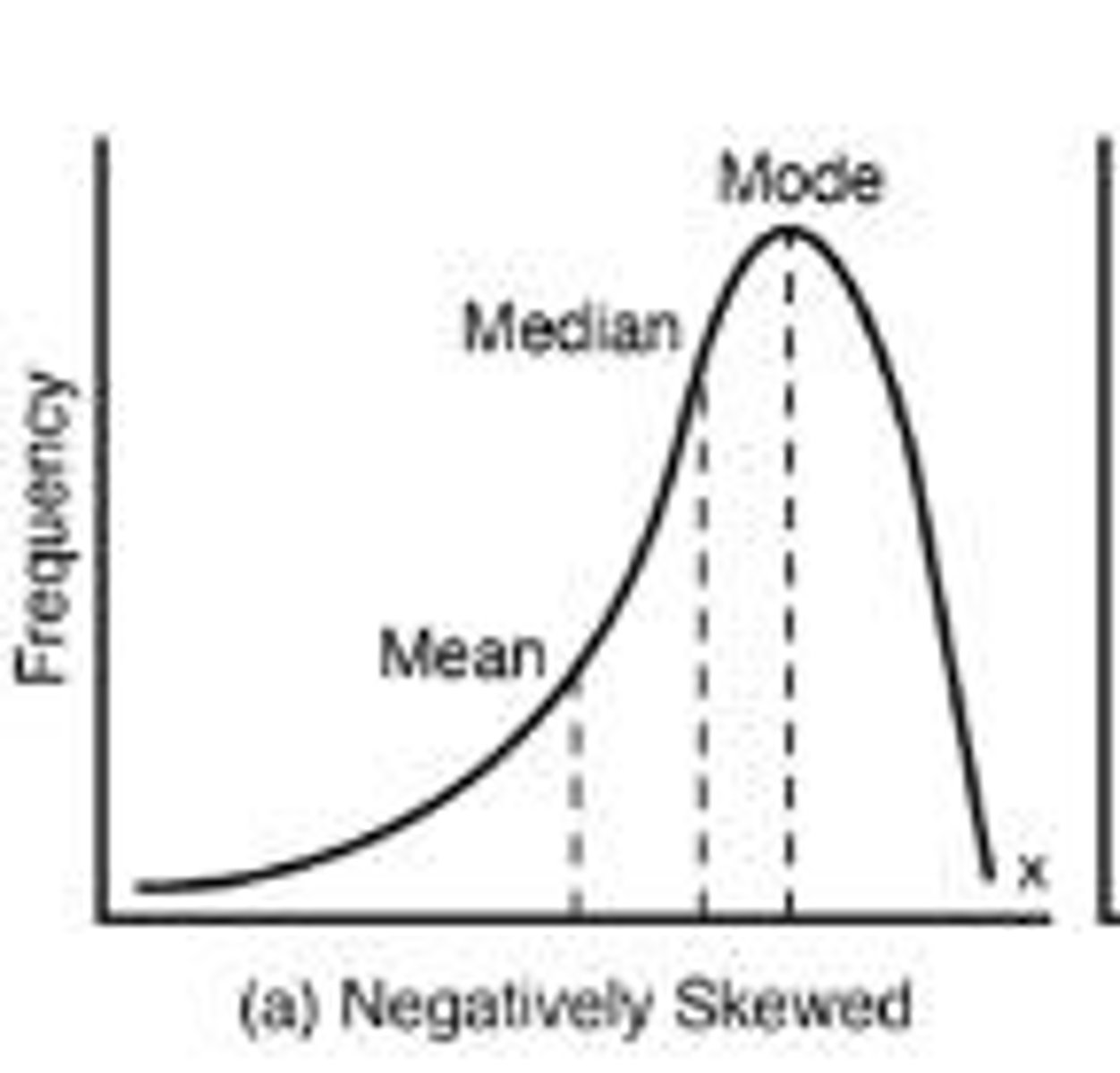
Negative skew
Mean is less than median; tail on left.
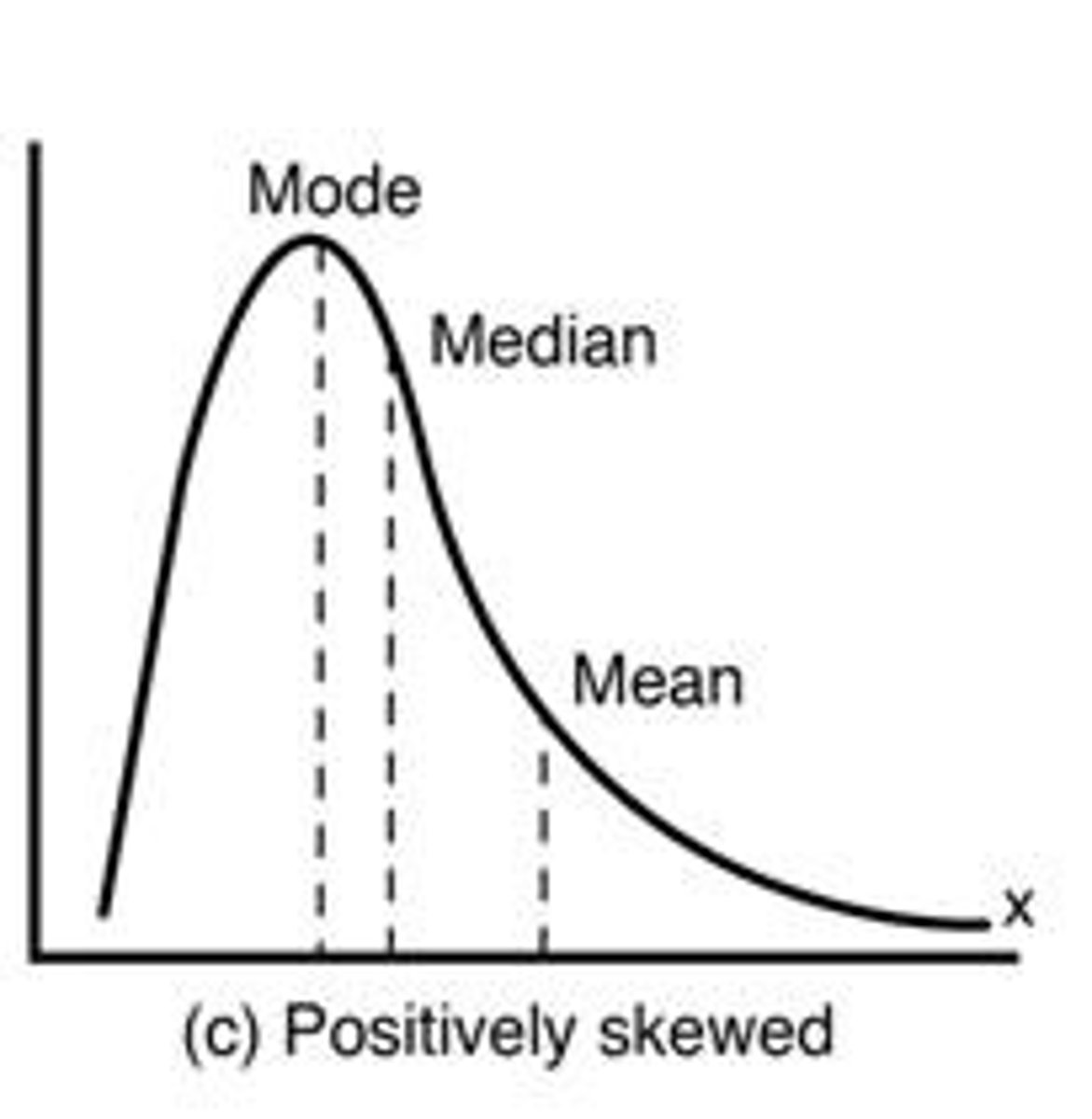
Positive skew
Mean is greater than median; tail on right.
Range
Difference between highest and lowest values.
Standard deviation
Average distance of scores from the mean.
Action Potential
Electrical charge traveling down a neuron's axon.
Resting potential
Neuron's stable charge at -70mV.
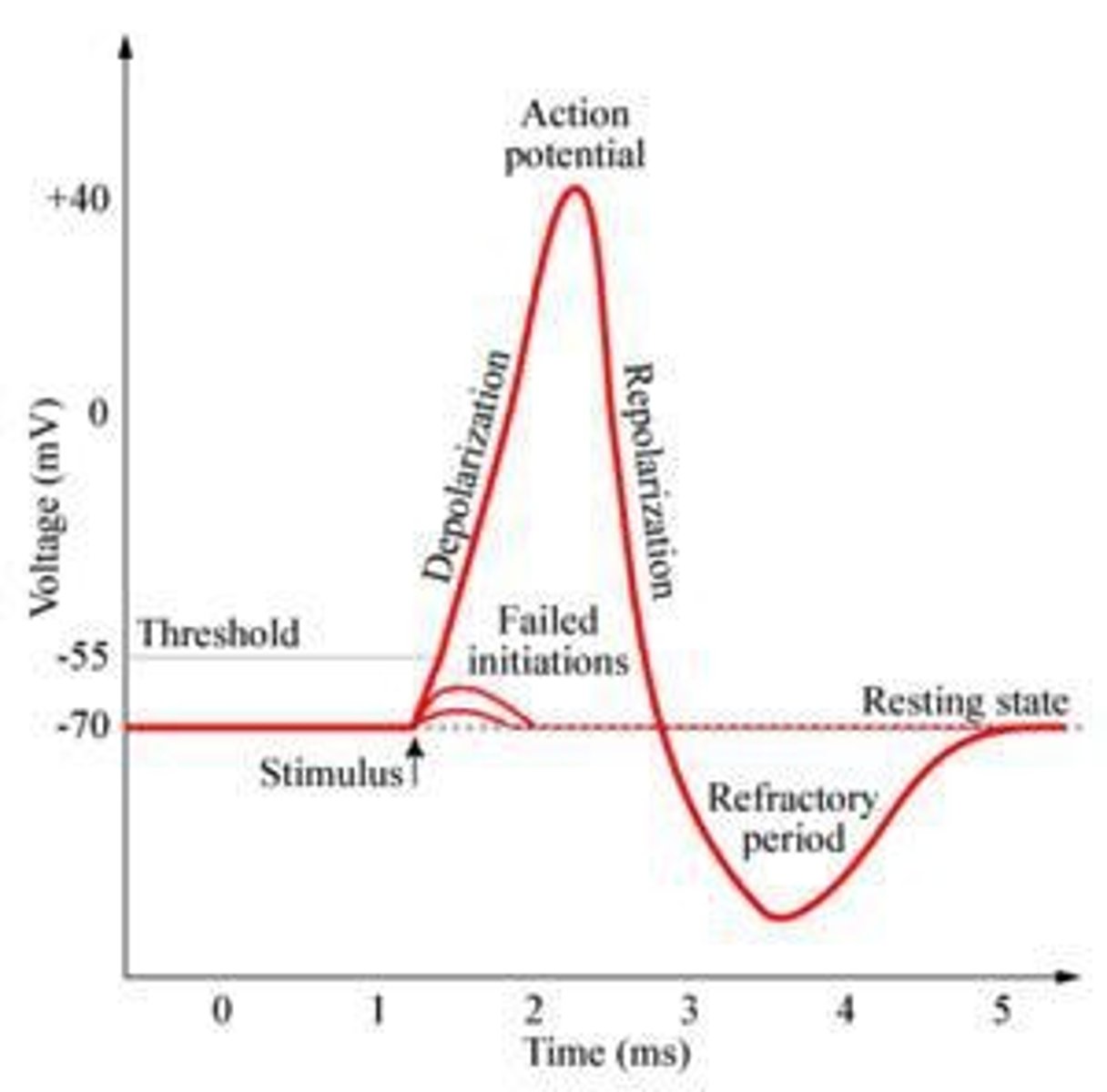
Depolarization
Neuronal charge shift from negative to positive.
Threshold of depolarization
Minimum stimulus strength to trigger action potential.
All or nothing principle
Neuron fires fully or not at all.
Psychoactive drugs
Substances affecting mental processes and behavior.
Depressants
Drugs that reduce nervous system activity.
Stimulants
Drugs that increase nervous system activity.
Hallucinogens
Substances causing altered perceptions and hallucinations.
Opioids
Pain-relieving drugs that act as endorphin agonists.
Tolerance
Needing more of a drug for the same effect.
Addiction
Compulsive need to use a substance to avoid withdrawal.
Withdrawal
Symptoms occurring after sudden cessation of drug use.
Cerebellum
Brain region for movement and balance.
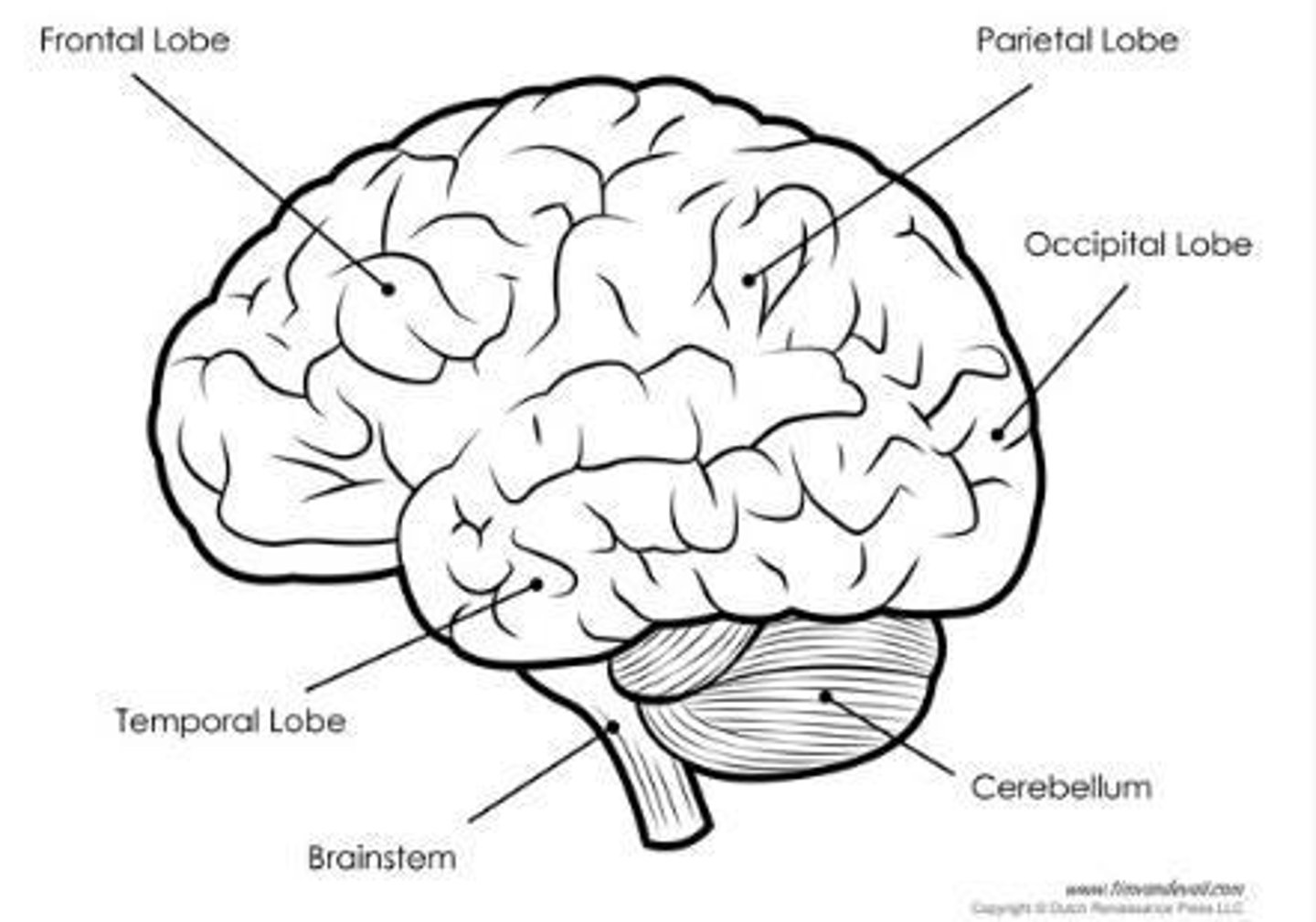
Brainstem
Controls vital functions like heart rate and breathing.
Reticular activating system
Regulates alertness and sleep-wake cycles.
Cerebral Cortex
Outer brain layer for higher-order functions.
Limbic System
Brain region involved in emotions and memory.
Somatic NS
Controls voluntary movements and sensory information.
Autonomic NS
Regulates involuntary bodily functions.
Sympathetic NS
Activates fight or flight response.
Twin/Adoption Studies
Research comparing genetic and environmental influences.
Excitatory neurotransmitter
Increases action potentials in other neurons.
Inhibitory neurotransmitter
Decreases action potentials in other neurons.
GABA
Major inhibitory neurotransmitter in the brain.
Glutamate
Major excitatory neurotransmitter, activates neurons.
Dopamine
Involved in reward and short-term pleasure.
Serotonin
Regulates mood and long-term emotional stability.
Acetylcholine (ACh)
Important for memory and muscle movement.
Norepinephrine
Involved in sympathetic nervous system responses.
Hypothalamus
Regulates reward, pleasure, and homeostasis.
Thalamus
Relay center for sensory information.
Pituitary gland
Interacts with the endocrine system for hormone release.
Parasympathetic nervous system
Controls rest and digest functions.
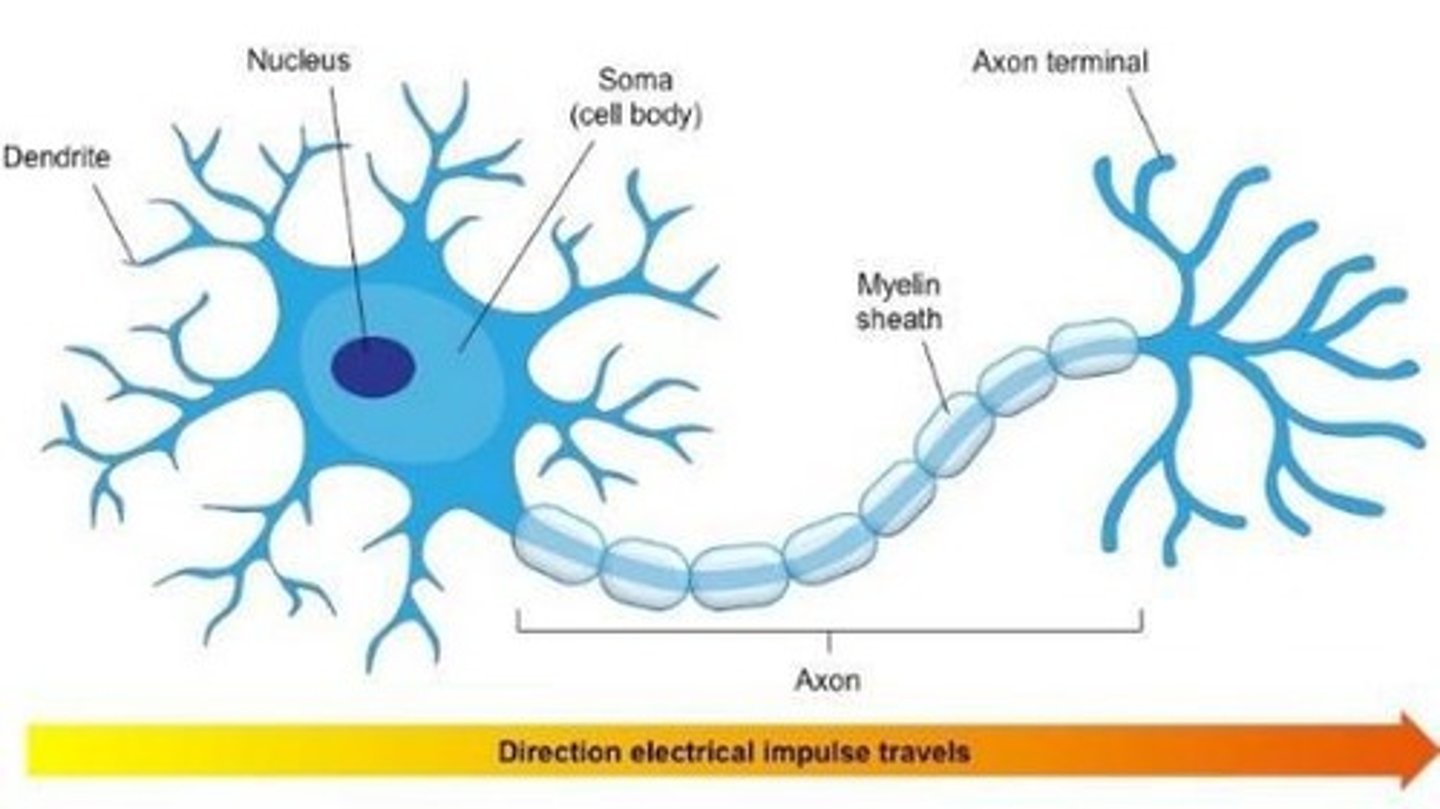
Neuron
Basic cell of the nervous system.
Endorphins
Natural pain relievers produced by the body.
Substance P
Neurotransmitter involved in pain regulation.
Dendrites
Receive incoming neurotransmitters from other neurons.
Axon
Pathway for action potentials to travel.
Myelin Sheath
Insulates axon, speeding up action potential.
Synapse
Gap between two communicating neurons.
Sensory Neurons
Receive sensory signals and send to brain.
Occipital Lobe
Brain region responsible for vision processing.
Frontal Lobe
Involved in decision making and personality.
Motor Neurons
Transmit signals from brain to muscles.
Interneurons
Connect sensory and motor neurons in the CNS.
Somatosensory Cortex
Processes touch and sensation information.
Oxytocin
Hormone associated with love and bonding.
Adrenaline
Hormone that triggers fight or flight response.
Leptin
Hormone that signals fullness to the brain.
Ghrelin
Hormone that stimulates hunger and appetite.
Melatonin
Hormone regulating sleep-wake cycles.
Agonist
Drug that mimics neurotransmitter action.
Antagonist
Drug that blocks neurotransmitter action.
Reuptake
Process of neurotransmitter recycling in neurons.
Reflex Arc
Pathway for immediate reflex actions.
Glia
Support cells providing nutrients to neurons.
Circadian Rhythms
24-hour biological clock regulating sleep patterns.
Corpus Callosum
Connects left and right brain hemispheres.