Physio Exam 4
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/145
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:33 PM on 4/3/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
146 Terms
1
New cards
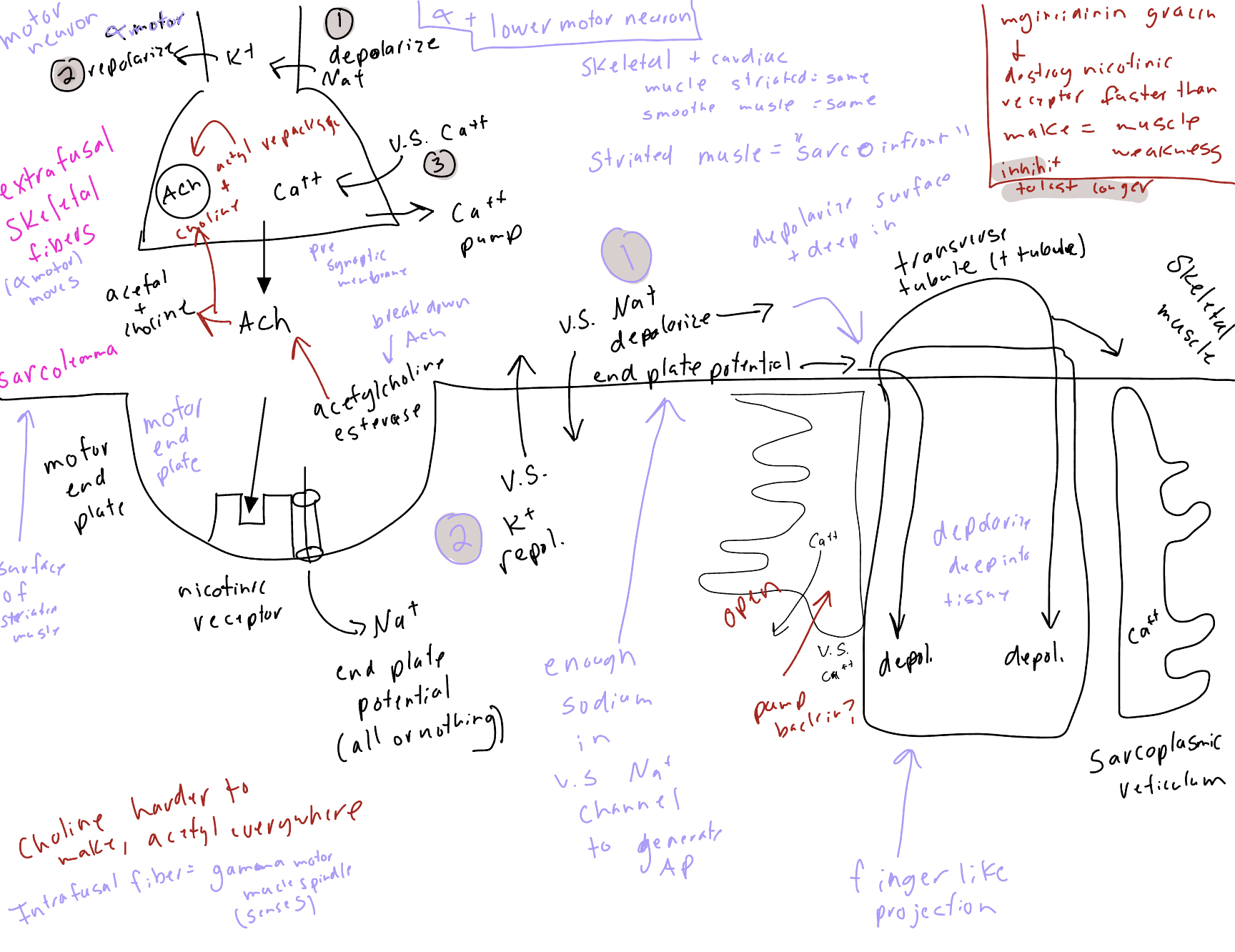
draw striated muscles with receptors
2
New cards
choline vs. acetyl
choline is harder to make, acetyl is everywhere
3
New cards
sarcolema
surface of striated muscle
4
New cards
acetylcholine esterase
break down ACH
5
New cards
what does striated muscle mean
sarco in front
6
New cards
myincidinin gracin
destroys nicotinic receptors, faster than making, muscle weakness
\
inhibit to last longer
\
inhibit to last longer
7
New cards
Thin filament vs thick filament
Thin = actin
Thick= myosin 2X thicker
Thick= myosin 2X thicker
8
New cards
3 parts of troponin hinge
TnC, TnT, TnI
9
New cards
TnC
Calcium binding
10
New cards
TnT
Tropomyosin
11
New cards
TnI
Inhibit
12
New cards
Draw thin filament

13
New cards
How does tropomyosin work in thin filament
. Block actin + myosin from cross bridging
14
New cards
How to cross bridge w/ thin filament
Open gate (tropomyosin) w/ hinge ( troponin)
15
New cards
Draw thick filament

16
New cards
Steps of thick filament
ATP → ADP + p extra energy sets trap
Myosin binds to actin (cross bridge, set trap)
ATP binds to myosin, myosin change shape, breaks actin-myosin crossbridge
troponin bound by Catt around, ca+ must be around to restart
\
\
\
Myosin binds to actin (cross bridge, set trap)
ATP binds to myosin, myosin change shape, breaks actin-myosin crossbridge
troponin bound by Catt around, ca+ must be around to restart
\
\
\
17
New cards
Sliding filament theory

18
New cards
Riga-mortis
When you die, don't make ATP, ATP releases myosin headi can't release cross bridge, stuck in position
19
New cards
Muscle formation
Rods align, head of myosin stick outwards thin filaments pulled together
20
New cards
Sacromere meaning
Muscle body
21
New cards
Draw sarcomere
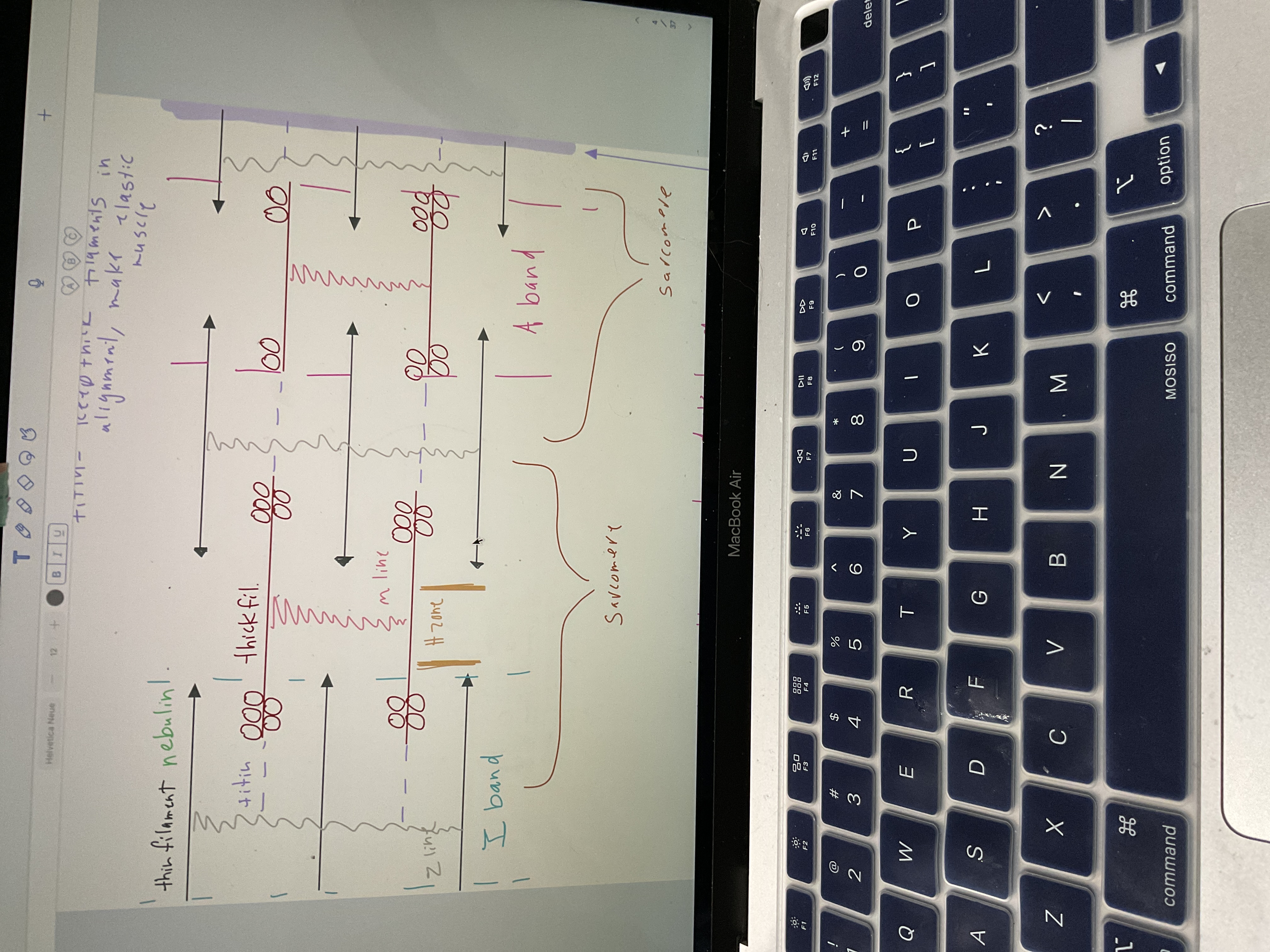
22
New cards
Nebulin
Protein, make sure filaments straight + same length
23
New cards
Titin
Keep thick filaments in alignment, make elastic muscle
24
New cards
A band
Thick thin over lap = dark band
25
New cards
I band
Thin, light
26
New cards
H zone
Sunny spot, middle of dark band
27
New cards
Z line to z line
Sarcomere
28
New cards
Striated
Alter dark + light band
29
New cards
Row of sarco meres
Myofibrils
30
New cards
Does muscles in body know their limitations?
Yes
31
New cards
Draw Anaerobic and aerobic

32
New cards
Anaerobic pathway

33
New cards
Aerobic pathway

34
New cards
Twitch
One release of acetal choline (1/10 second)
35
New cards
Isometric
Same length
36
New cards
ISOtonic
Same tension
37
New cards
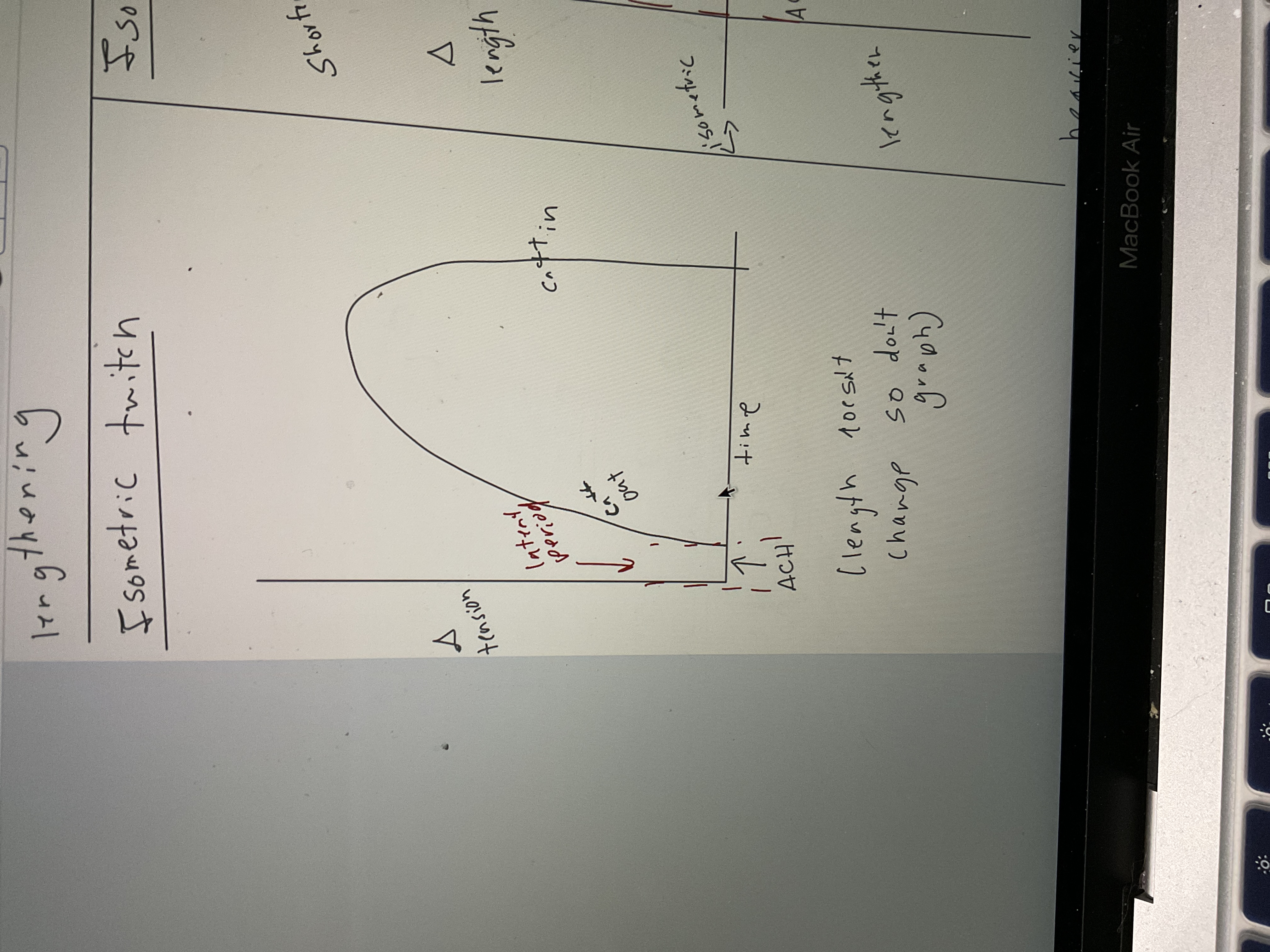
Draw Isometric twitch
38
New cards
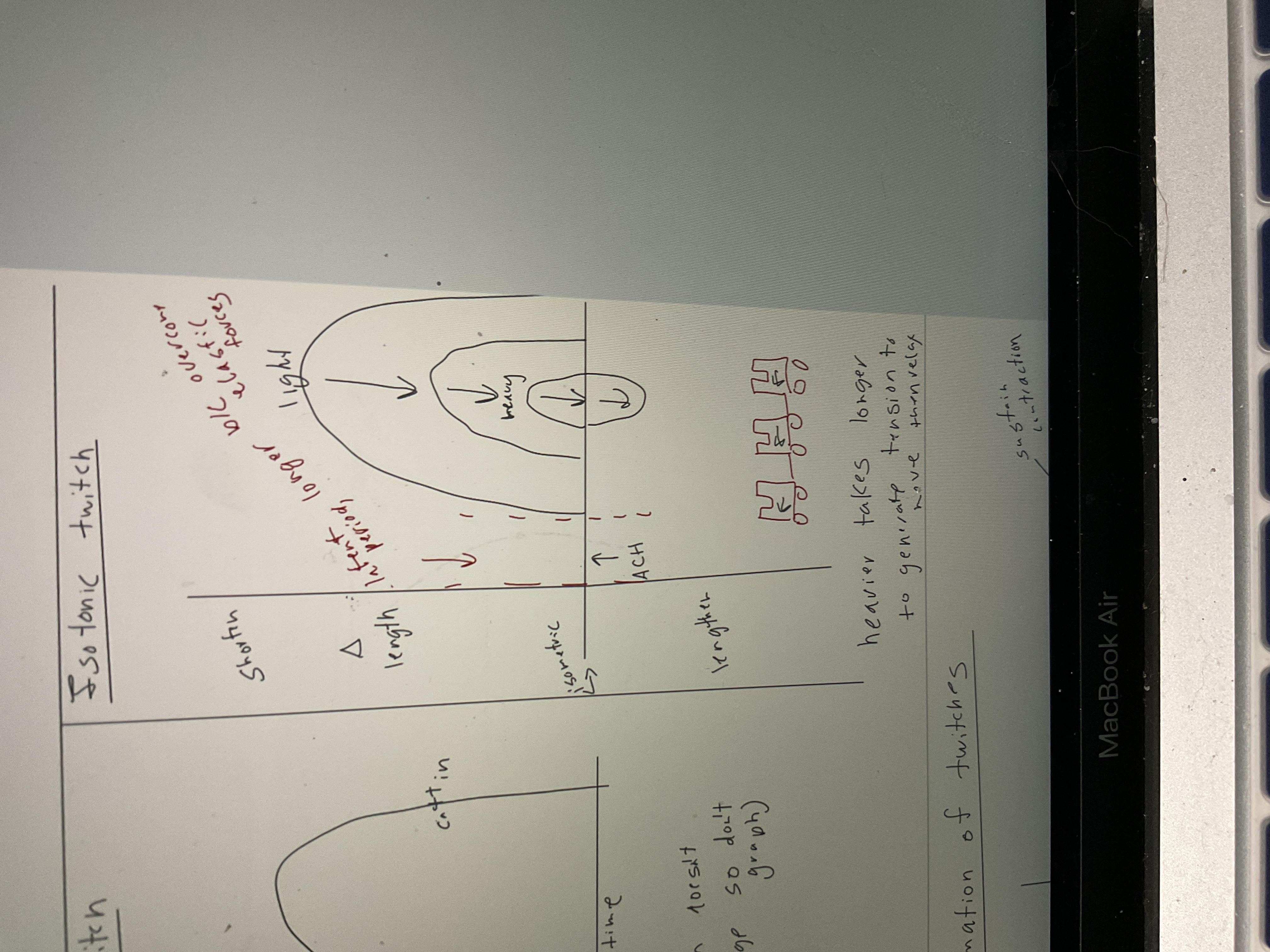
Draw isotonic twitch
39
New cards
Draw summation of twitches
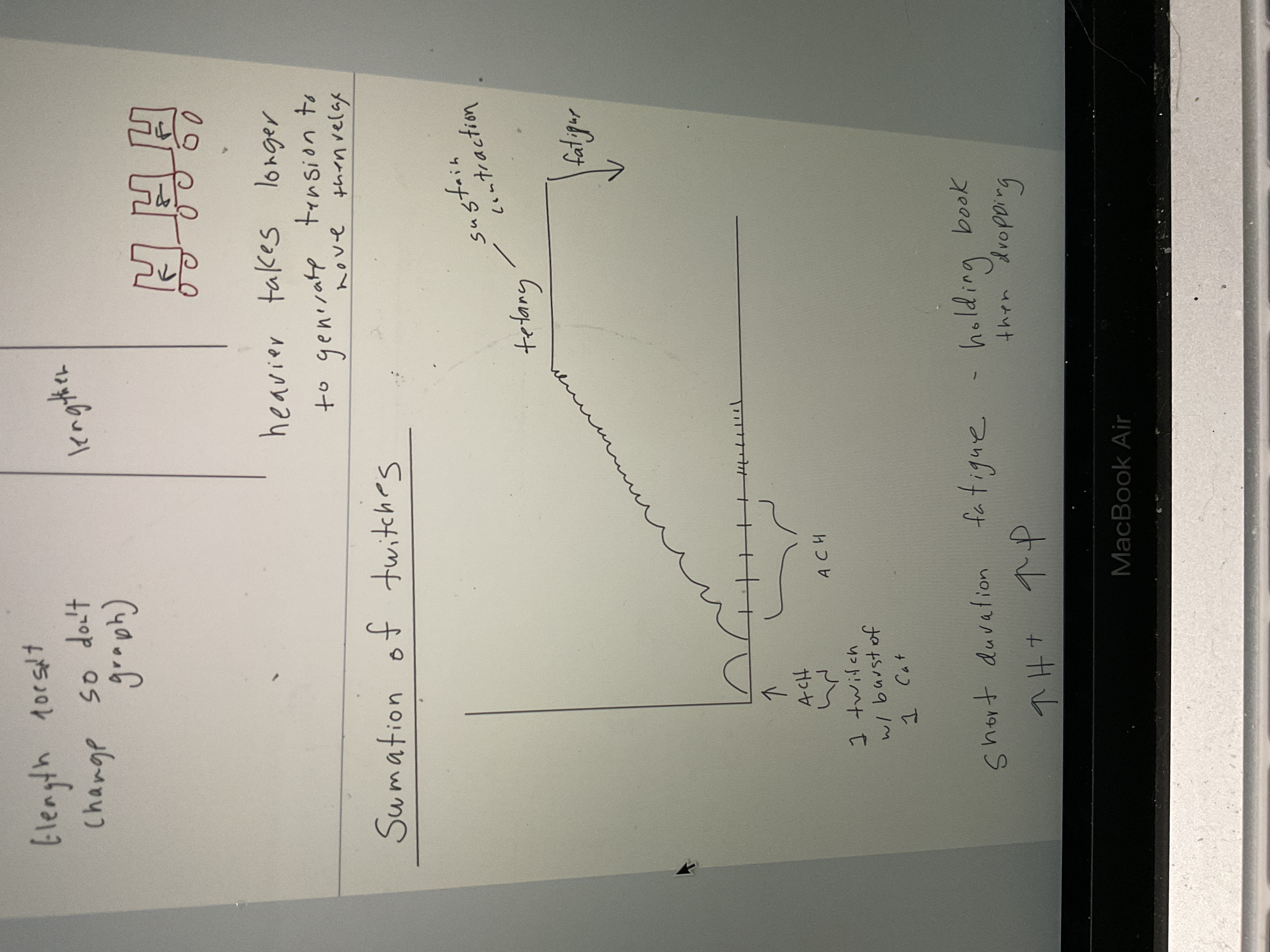
40
New cards
Short duration fatigue
Increase H and increase P, holding book then dropping, anaerobic
41
New cards
Long duration fatigue
Decrease glycogen
42
New cards
Draw muscle optimal length chart
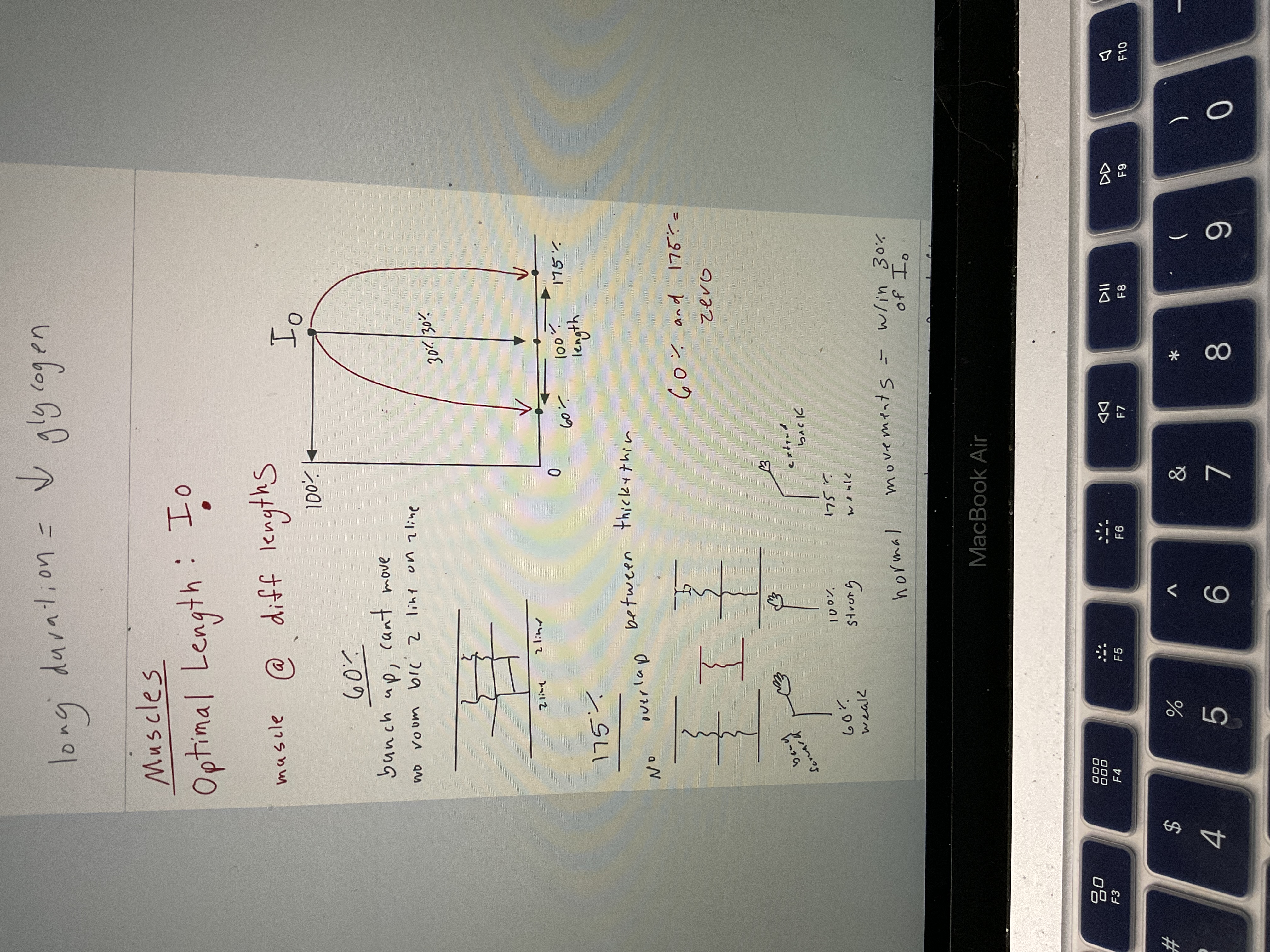
43
New cards
60% muscle length
Can't move b/c no room, Z line on Z line, bunch up
44
New cards
175% muscle length
No overlap between thick + thin filaments
45
New cards
Normal muscle usage %
Within 30% of 100%
46
New cards
Motor unit, alpha motor
Extra fusal fibers
1 motor to how many being used
1 motor to how many being used
47
New cards
Draw muscle type chart, source, myoglobin, diameter, depolarization, recruitment, fatigue
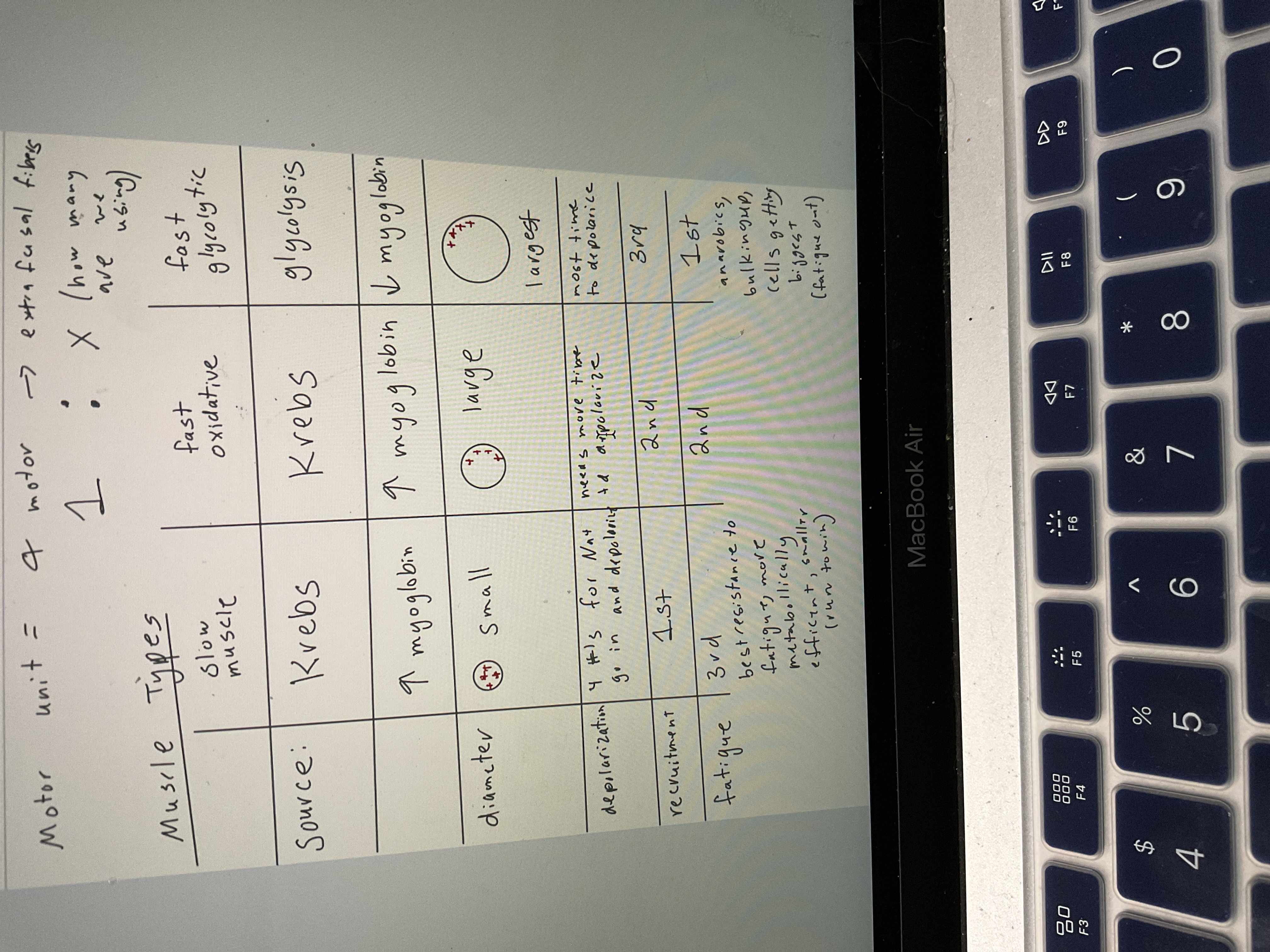
48
New cards
Draw smooth muscle cells
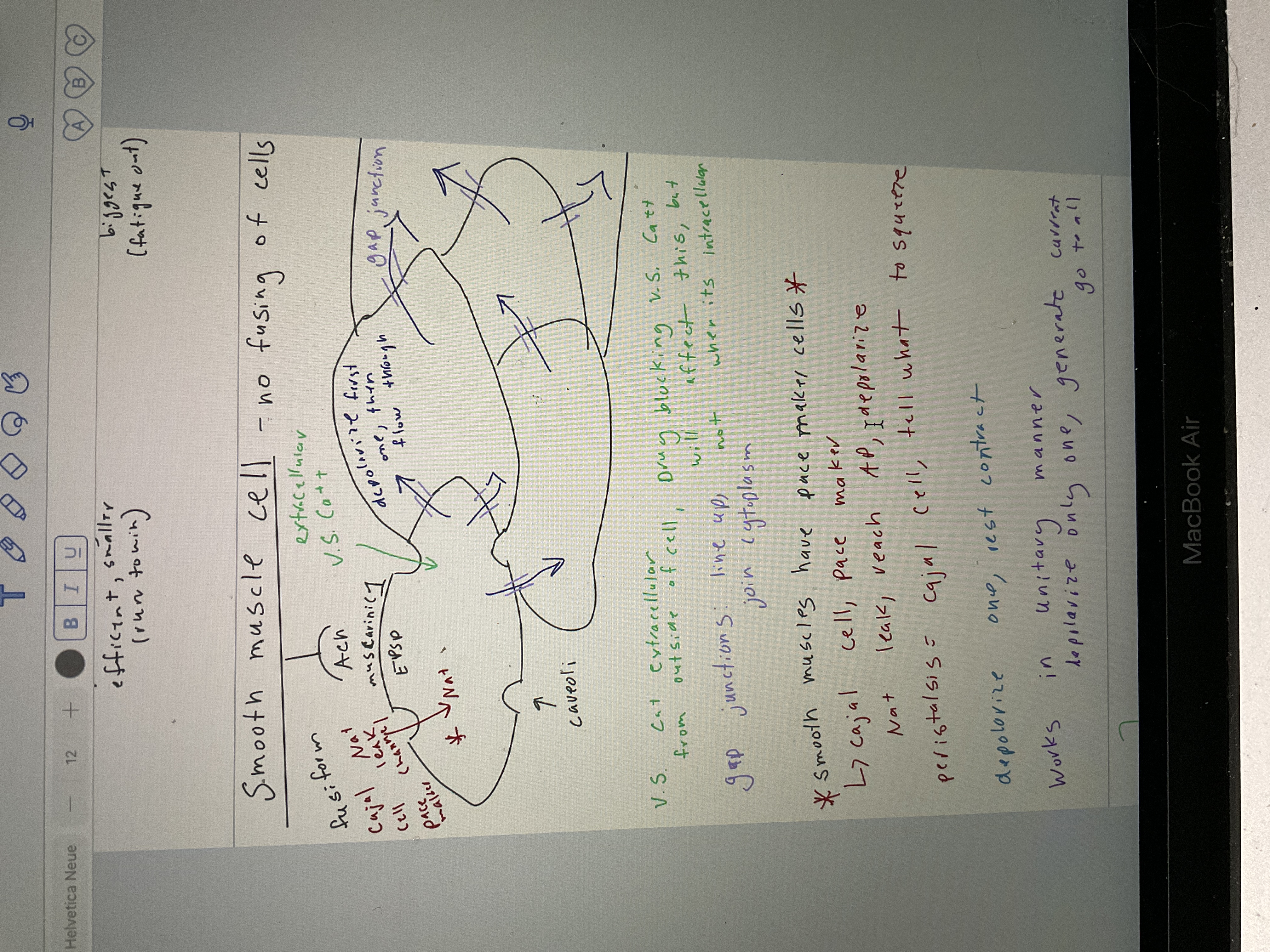
49
New cards
Pace maker cell in smooth muscle
Cajal cell, na+ leak I reach action potential, de polarize
Peristalsis, tells what to squeeze
Peristalsis, tells what to squeeze
50
New cards
Smooth cell function
Unitary manner, de polarice one cell generate current go through all
51
New cards
Smooth muscle latch mechanism (draw)
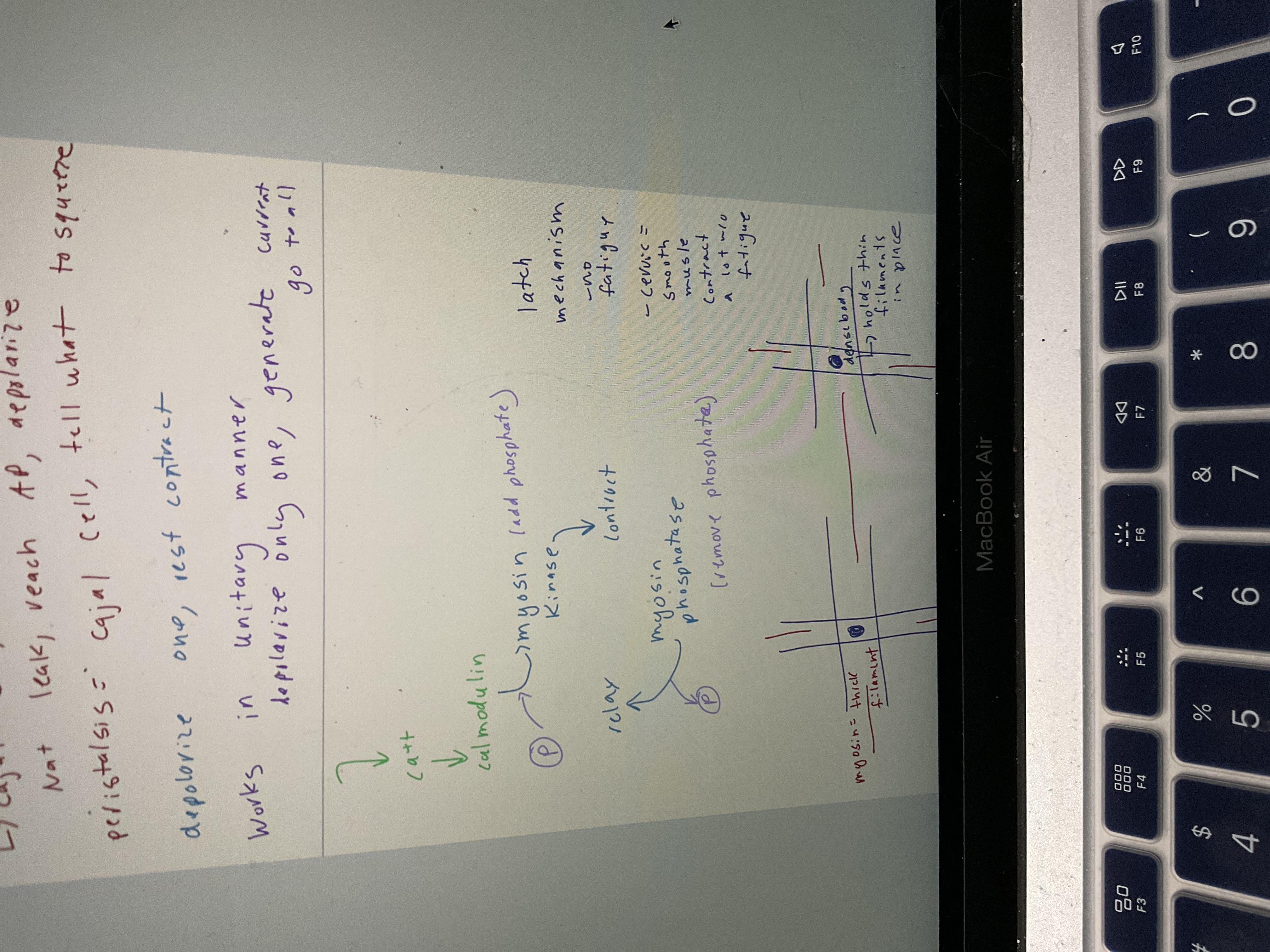
52
New cards
Draw smooth muscle filaments
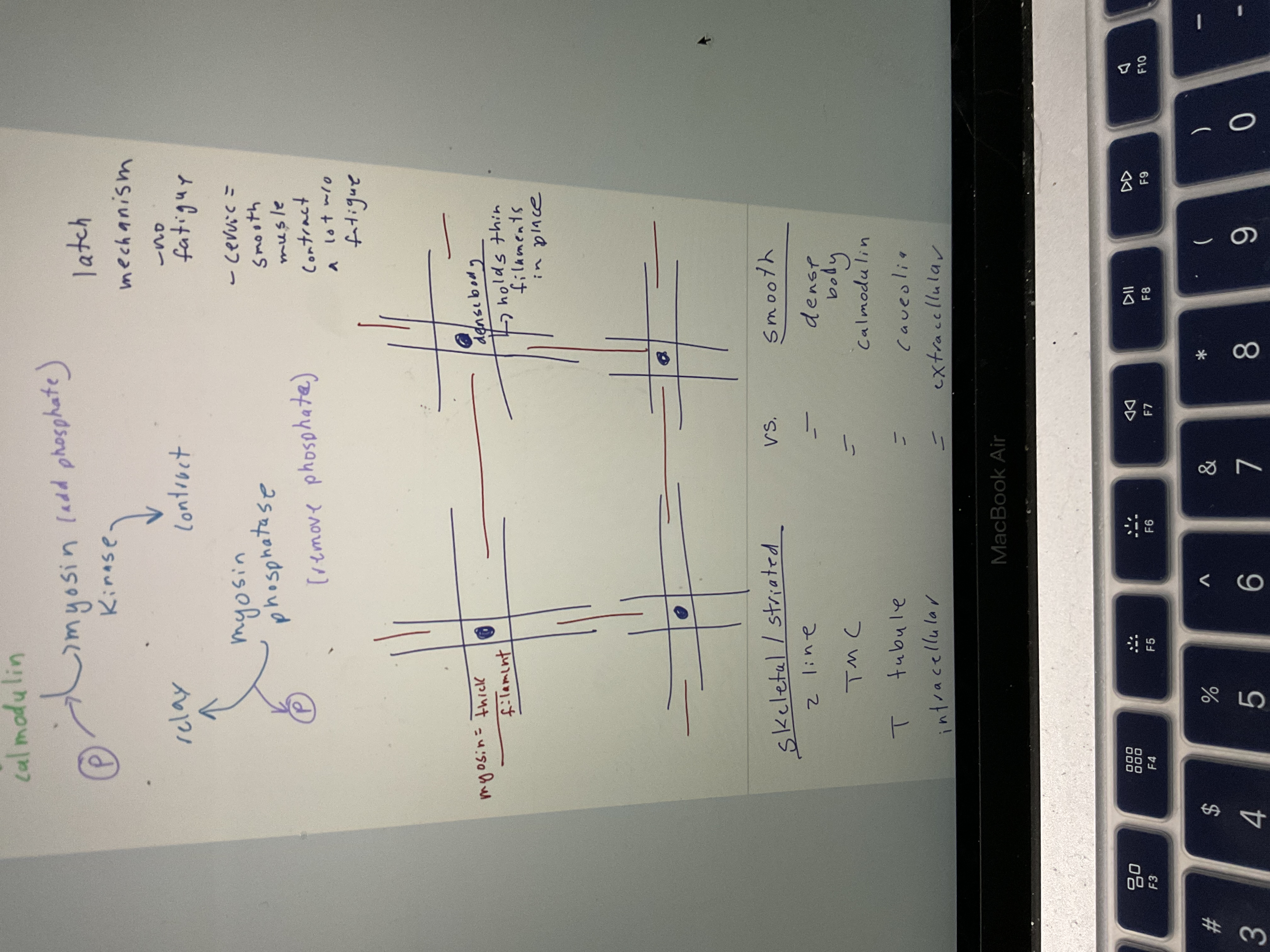
53
New cards
Skeletal/ striated V's smooth chart
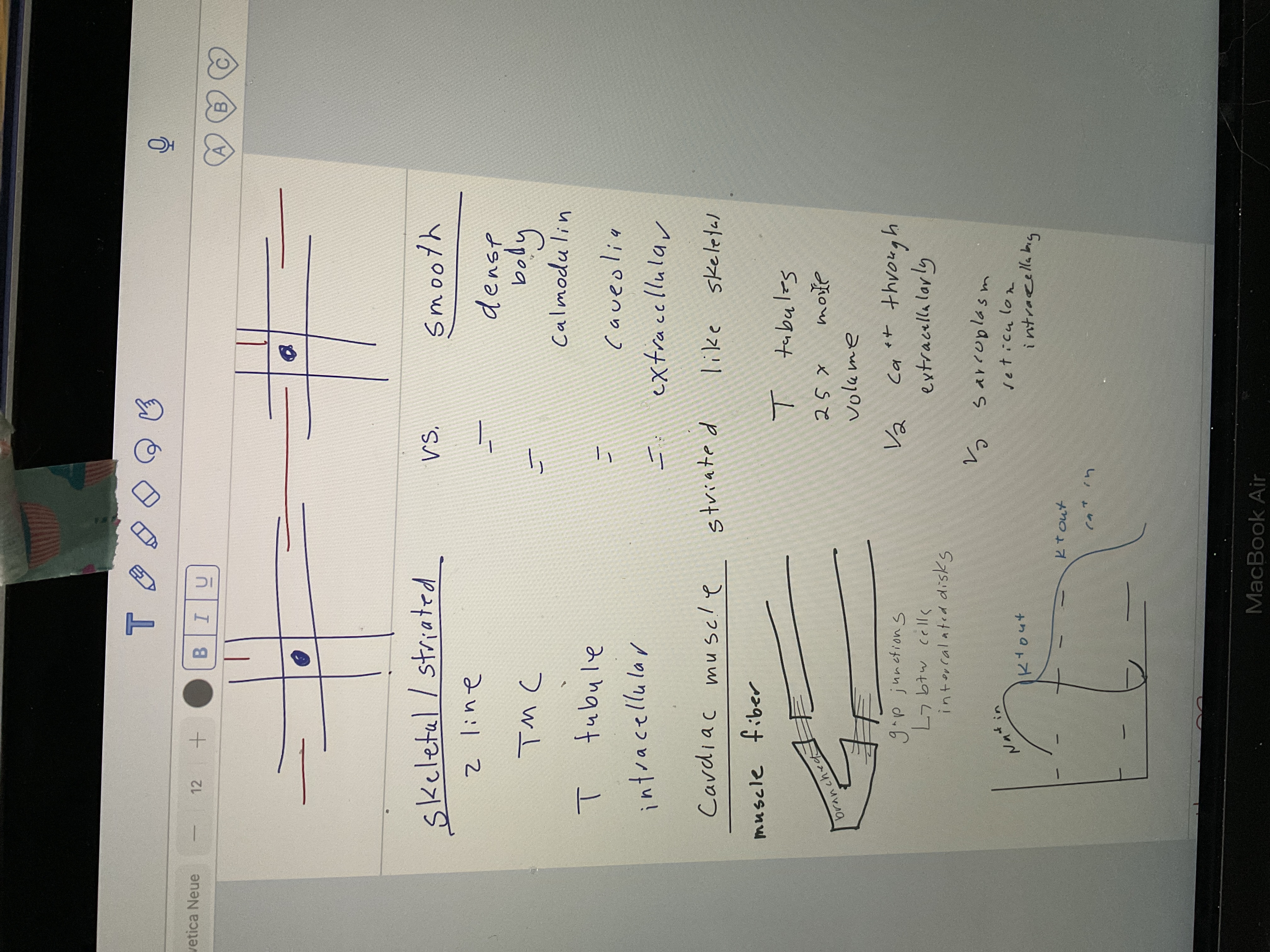
54
New cards
Cardiac muscle, t tubules, calcium
striated, t tubules 25x more volume, 1/2 Catt through extracellularly, 1/2 sarcoplasm reticulum intracellulary
55
New cards
Draw cardiac muscle fibers
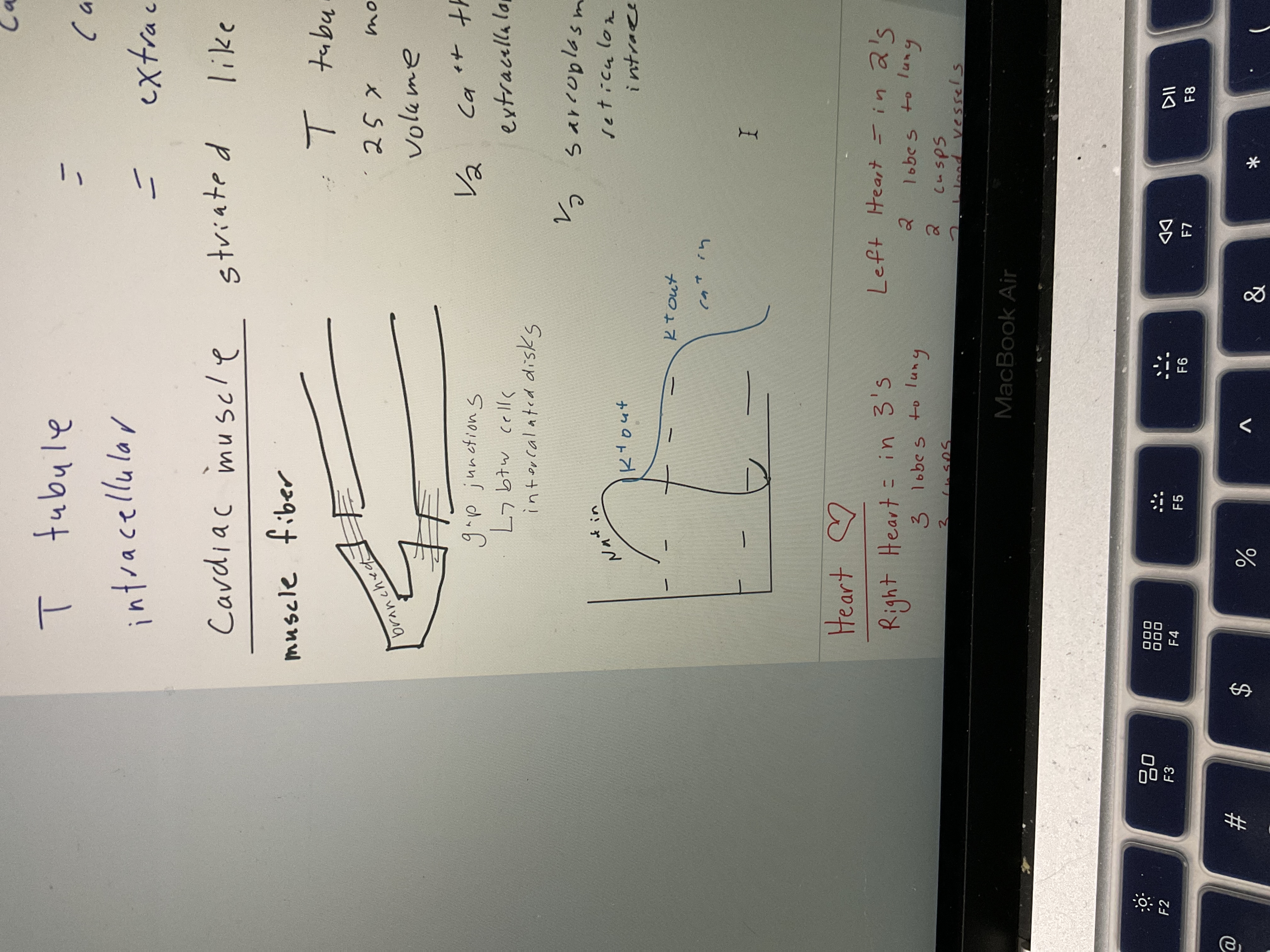
56
New cards
Right V's left heart
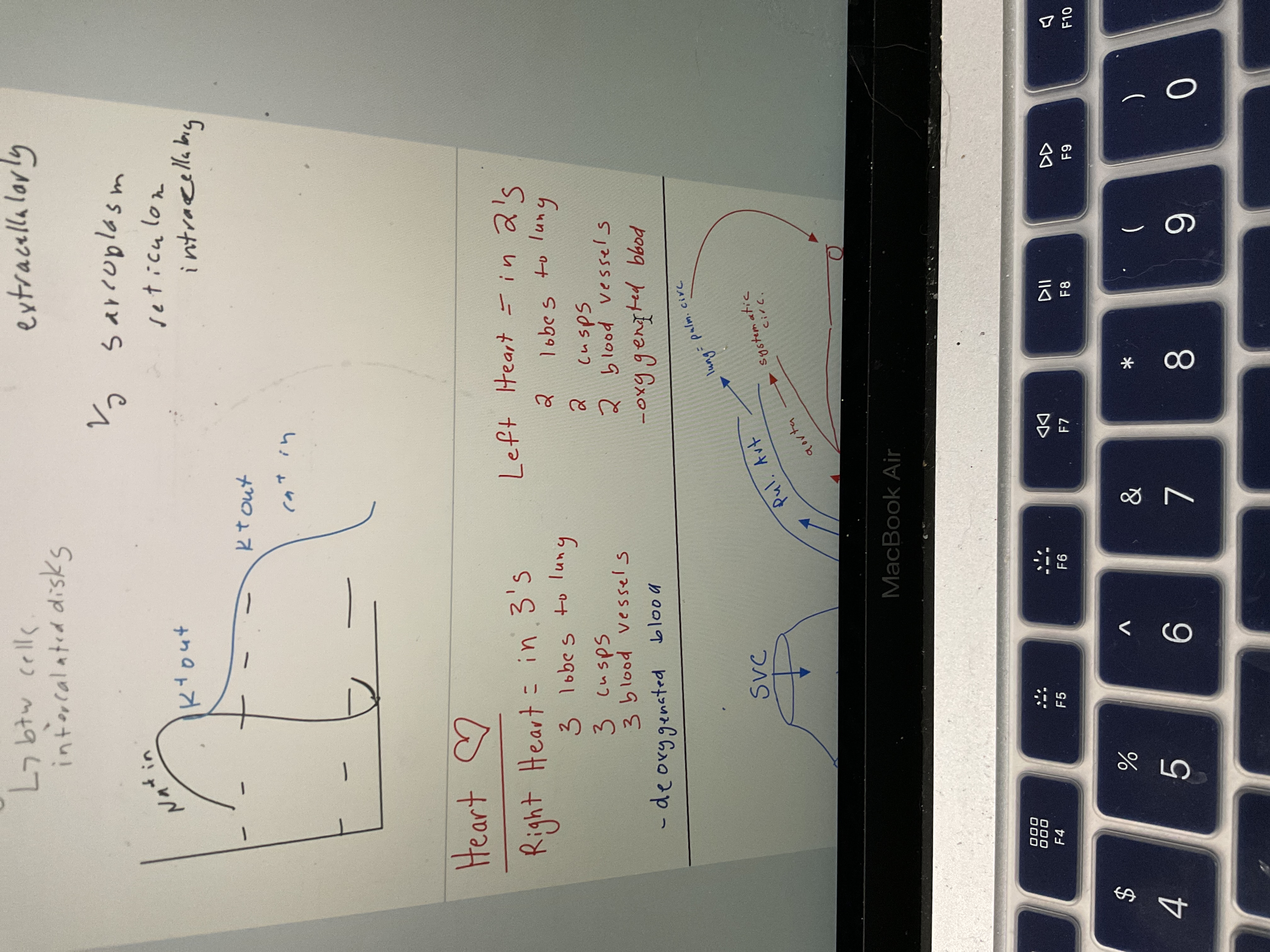
57
New cards
Draw heart
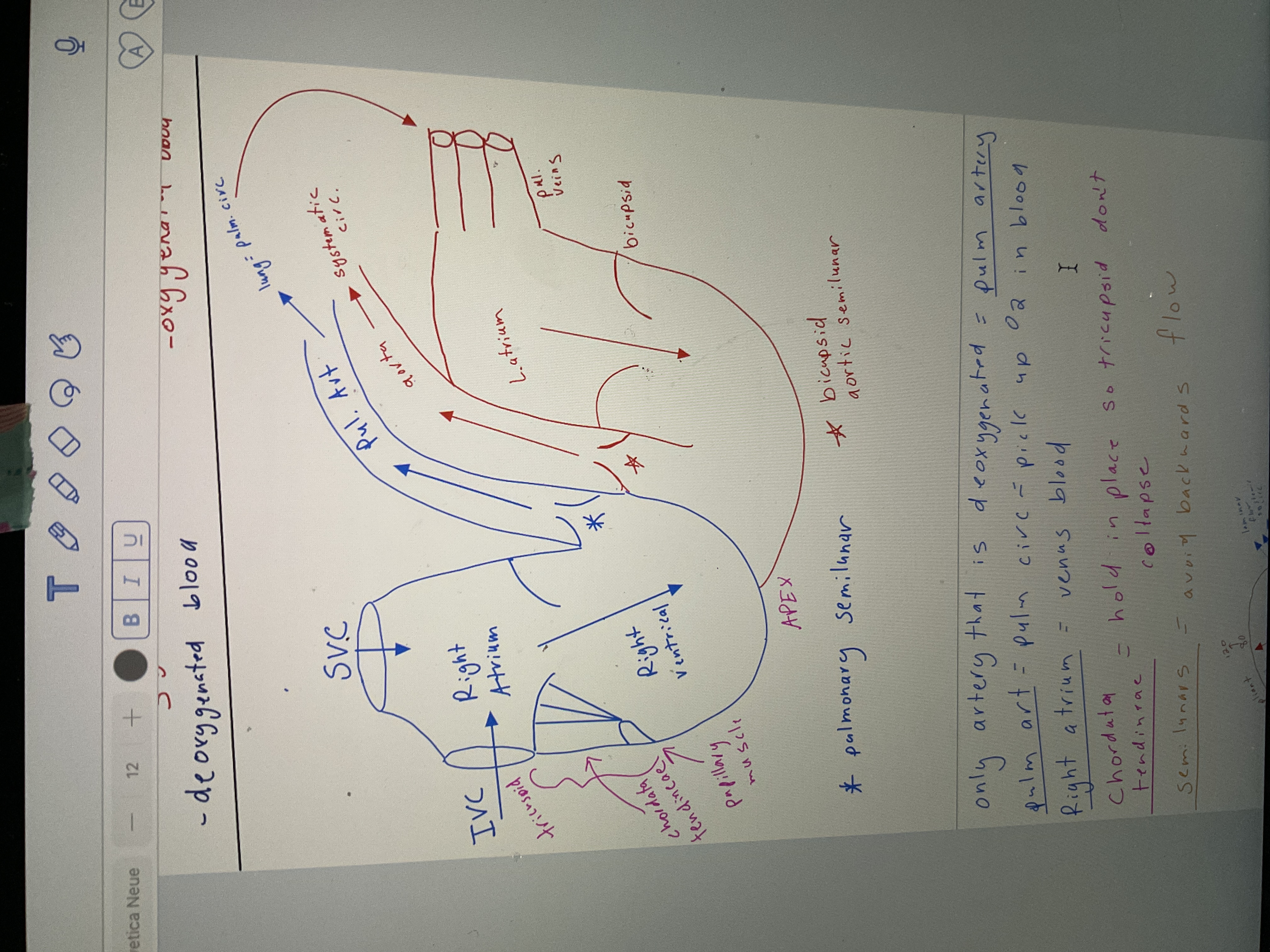
58
New cards
Only artery that is deoxygenated
Pulmonary artery
59
New cards
Pulmonary artery
Pulmonary circulation, pick up o2 in blood
60
New cards
Right Atrium
Venus blood
61
New cards
Chordata tendinae function
Hold in places so tricuspid don't collapse
62
New cards
Semilunar valves
. avoid backwards flow
63
New cards
Blood pressure

64
New cards
Draw aorta w/ blood flowing out
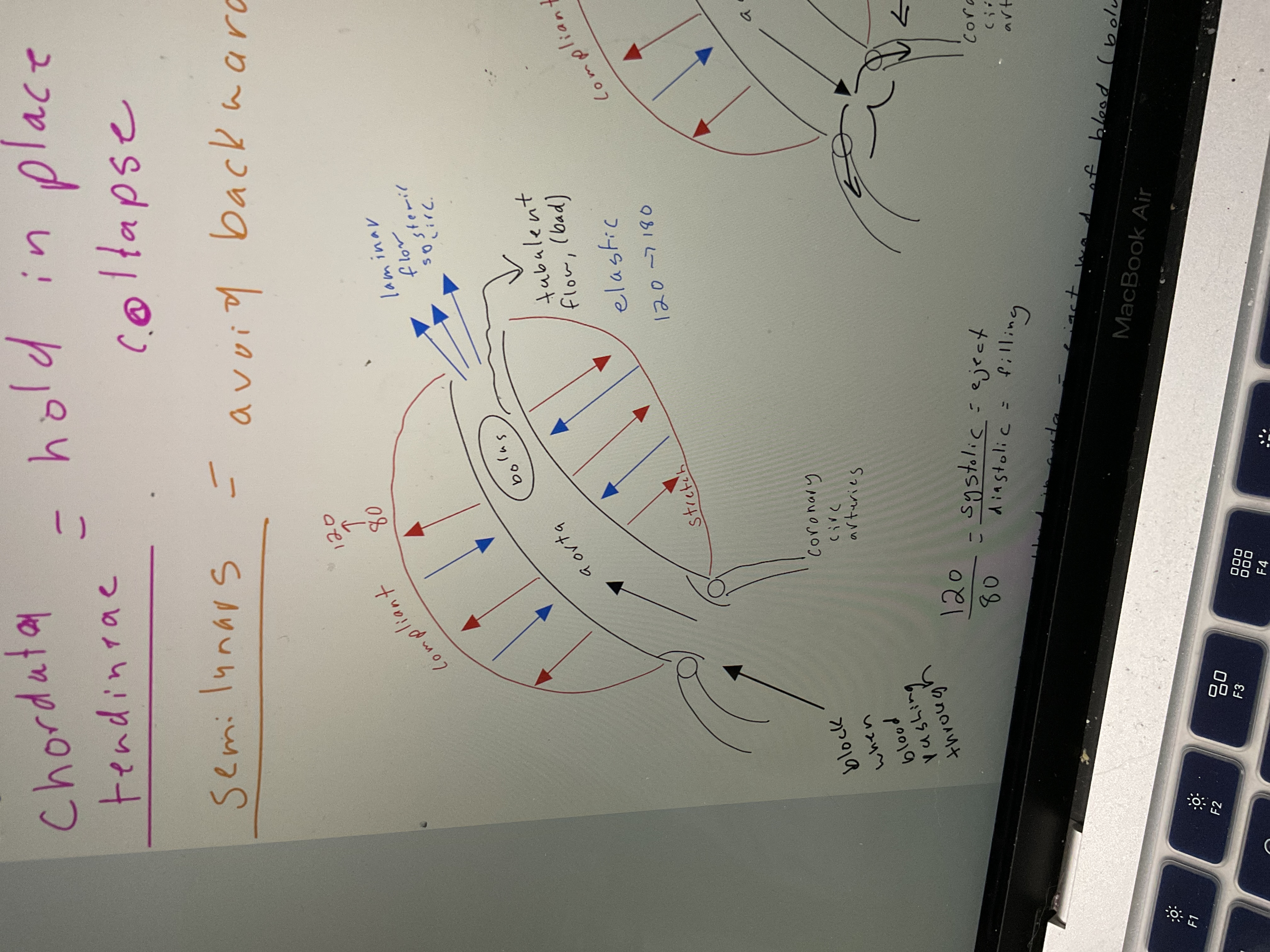
65
New cards
Draw aorta w/ blood flowing backwards
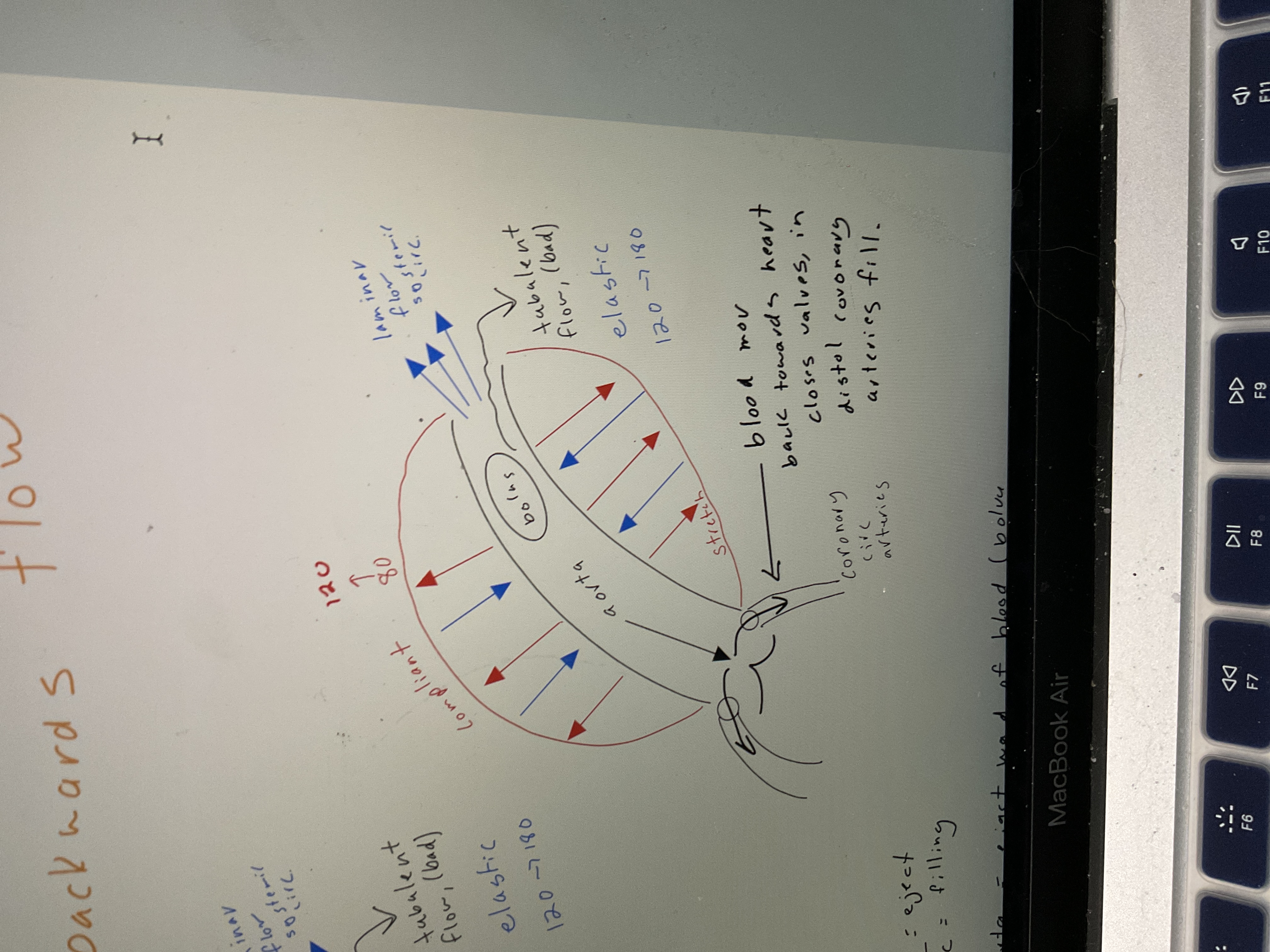
66
New cards
bolus
Turbulent flow eject blood into aorta, eject wad of blood
67
New cards
Draw heart w/ layers
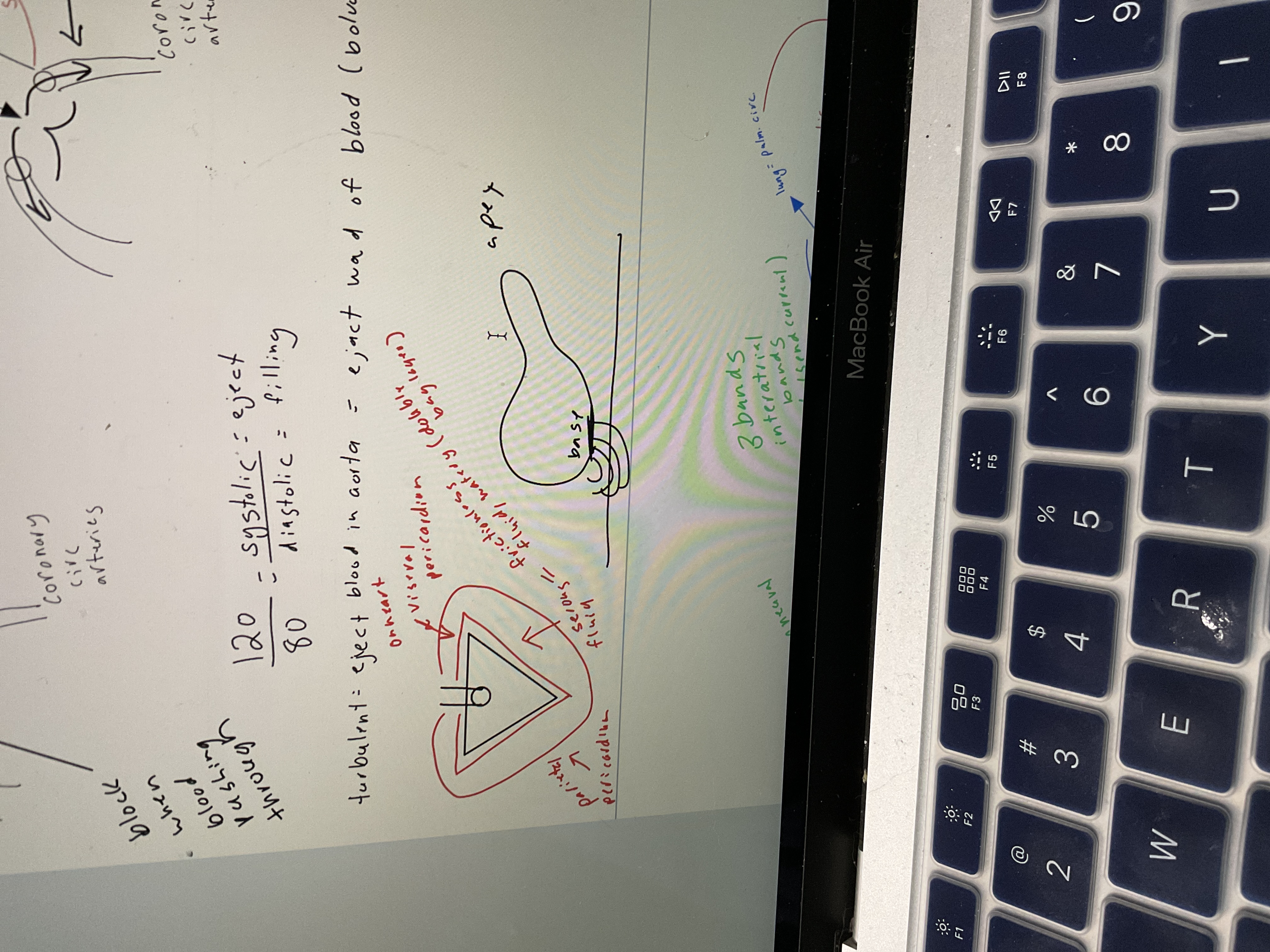
68
New cards
Draw heart w/ bands and cell layer
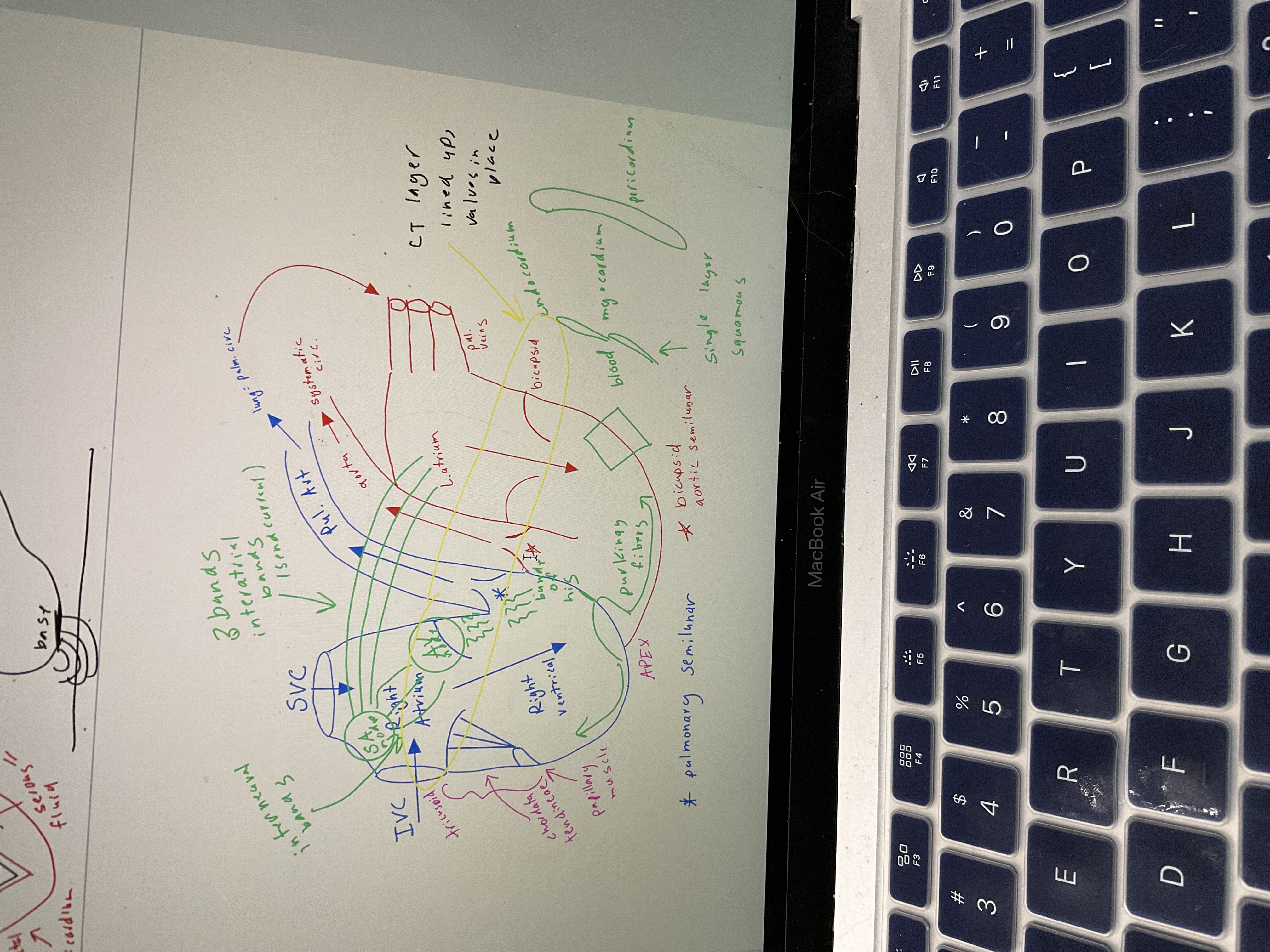
69
New cards
Draw EKG on man and Einthomis triangle
‘
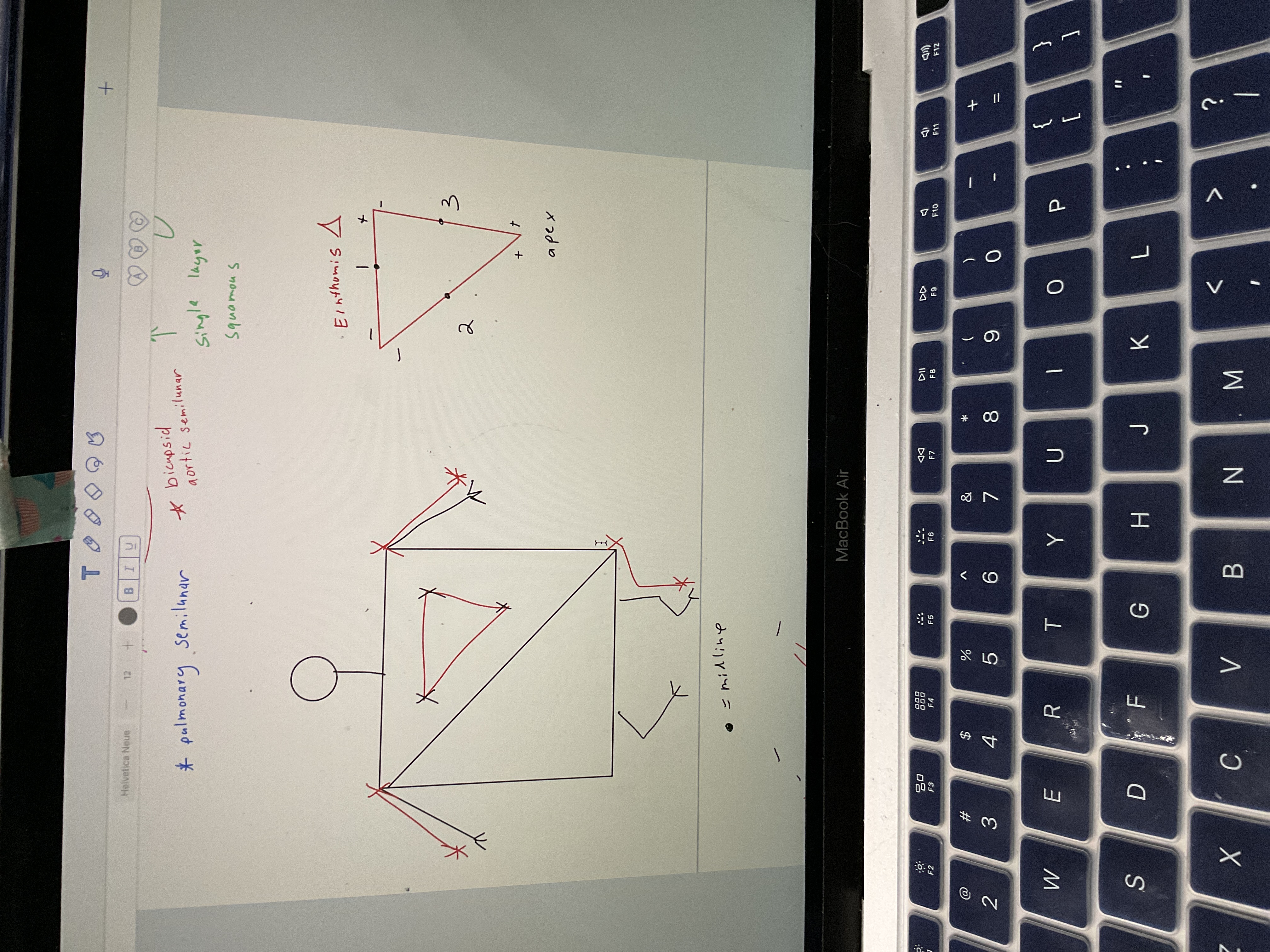
70
New cards
Draw EKG circle
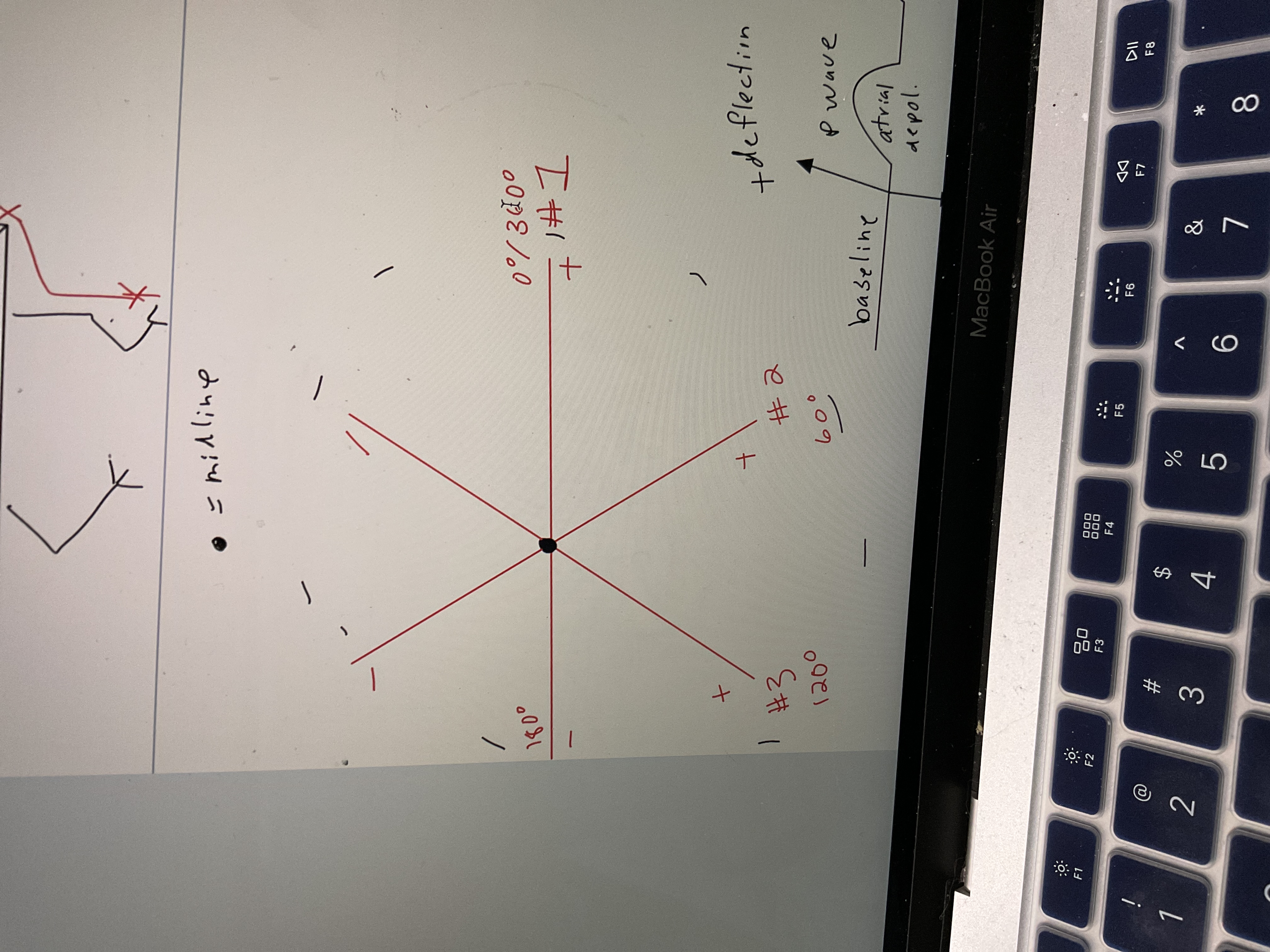
71
New cards
Draw different waves

72
New cards
Draw simple heart w/bands
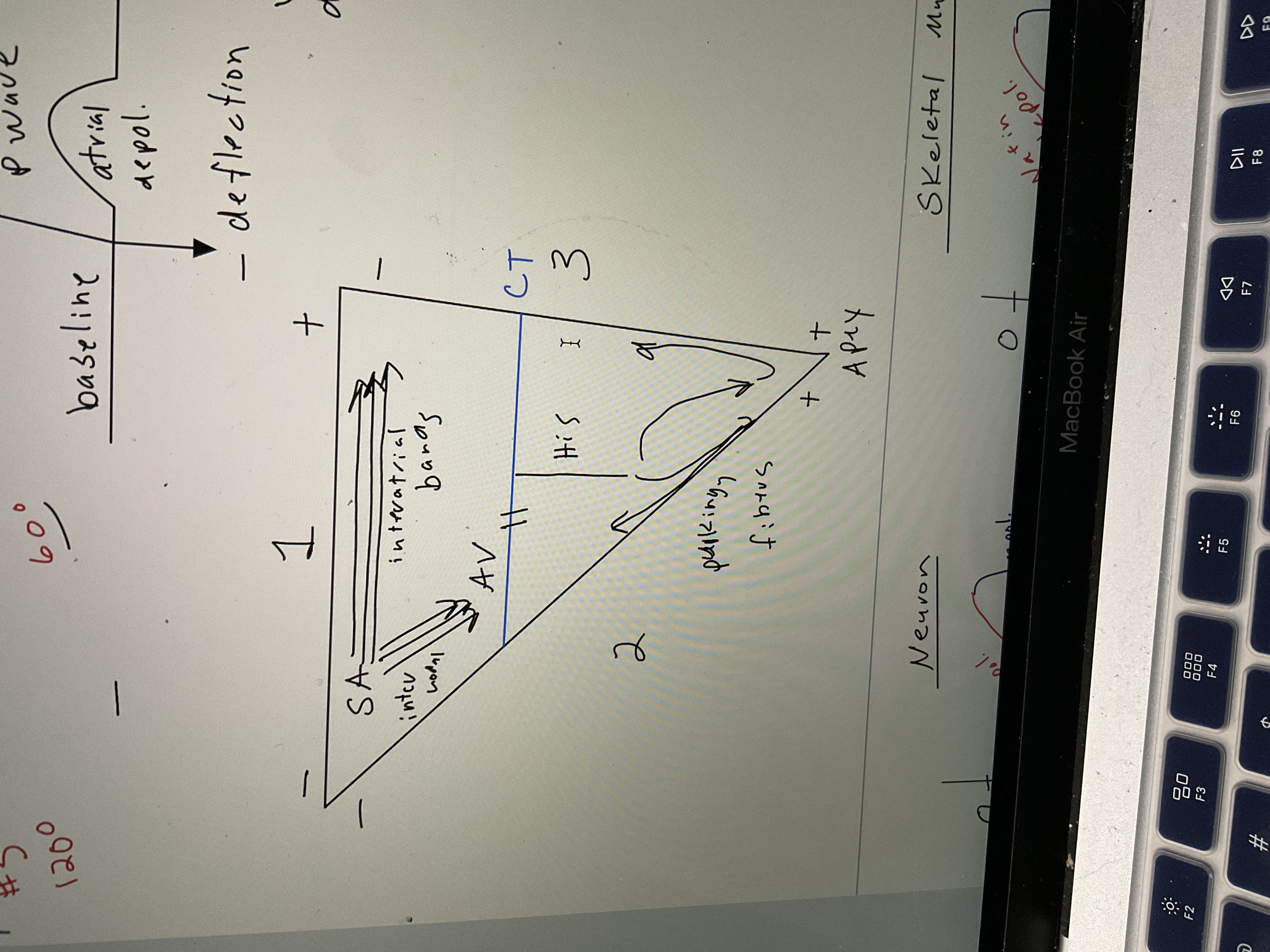
73
New cards
Draw neuron AP chart
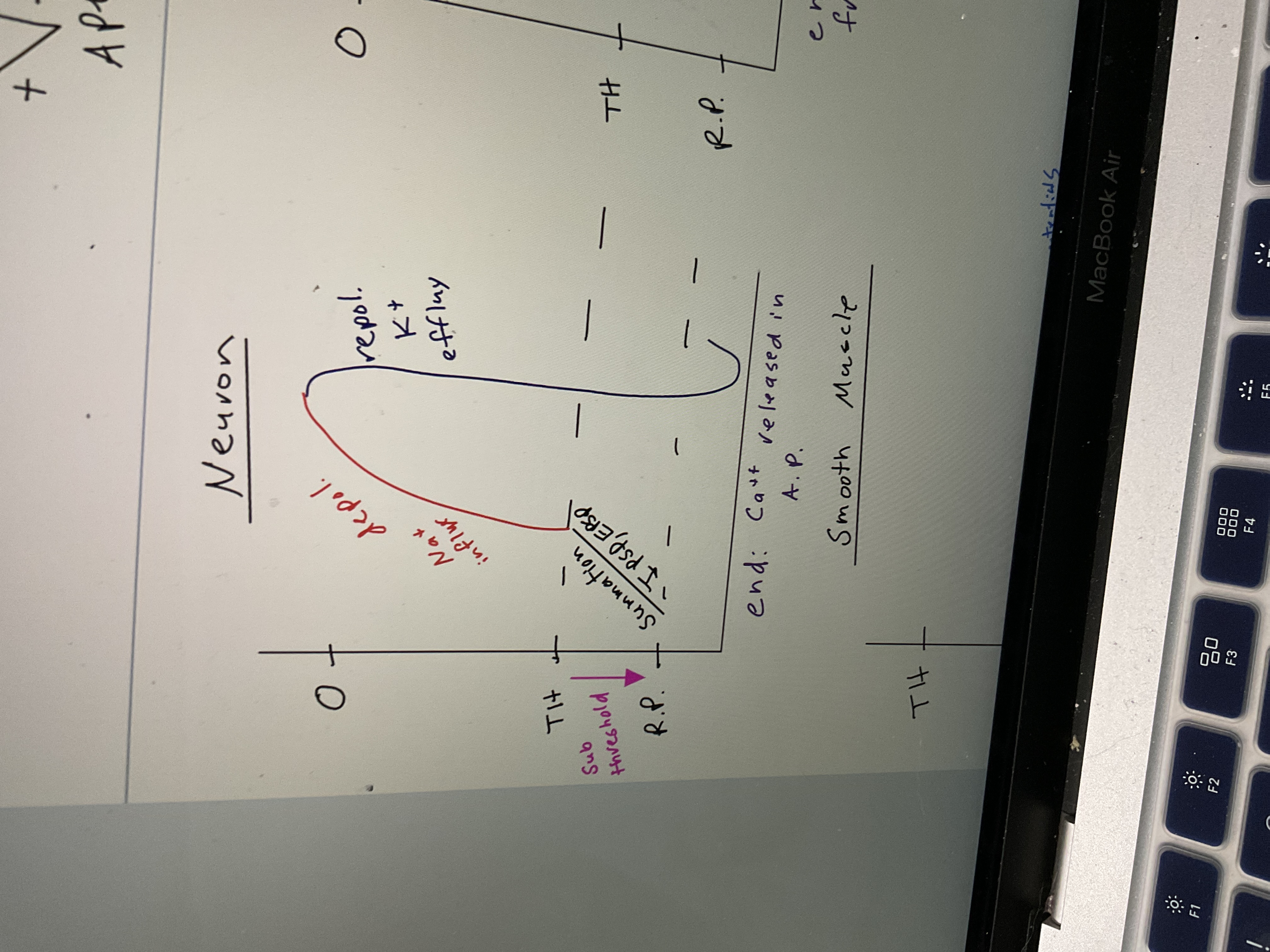
74
New cards
Draw skeletal muscle AP chart
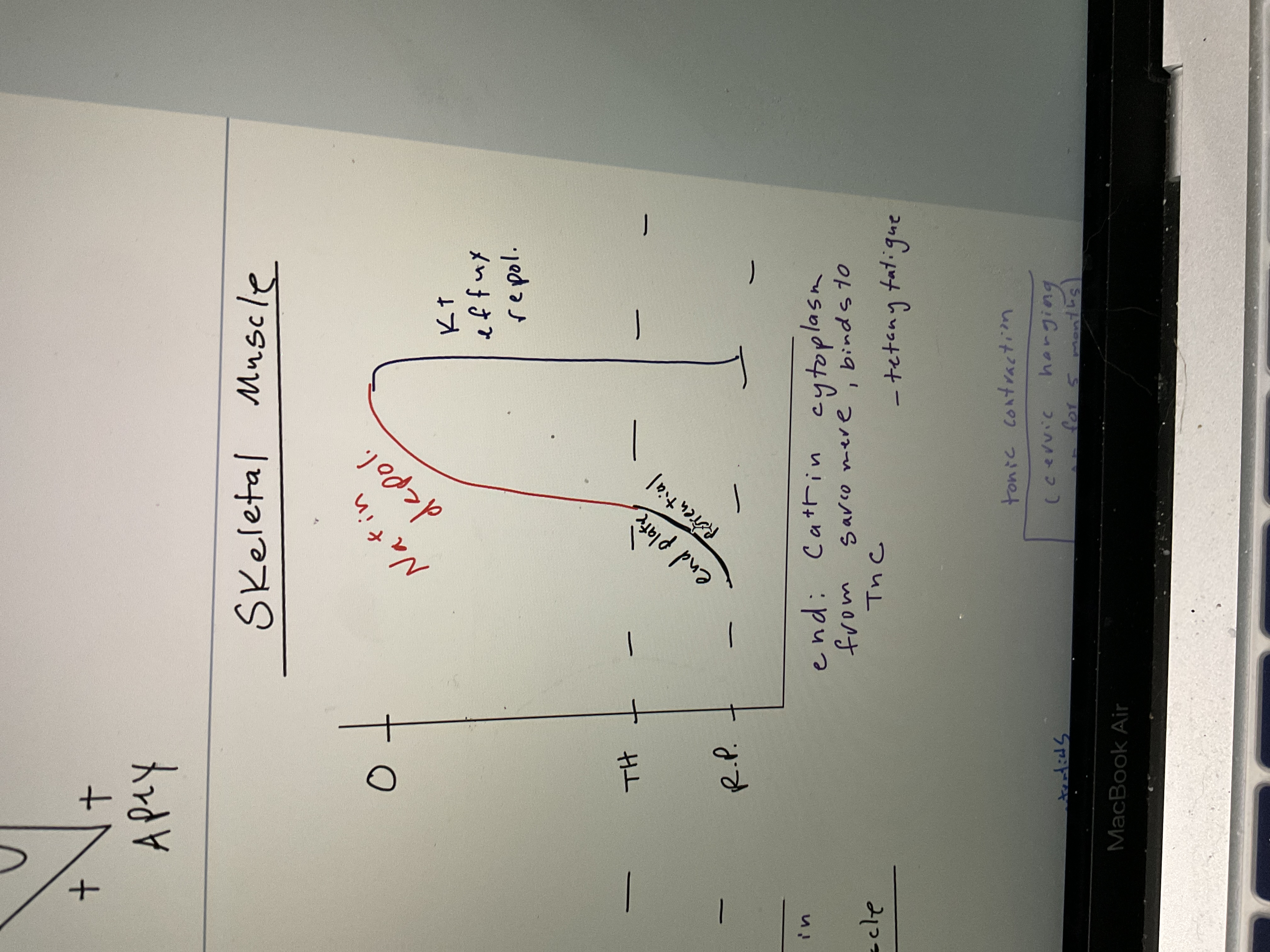
75
New cards
Draw Smooth muscle AP chart
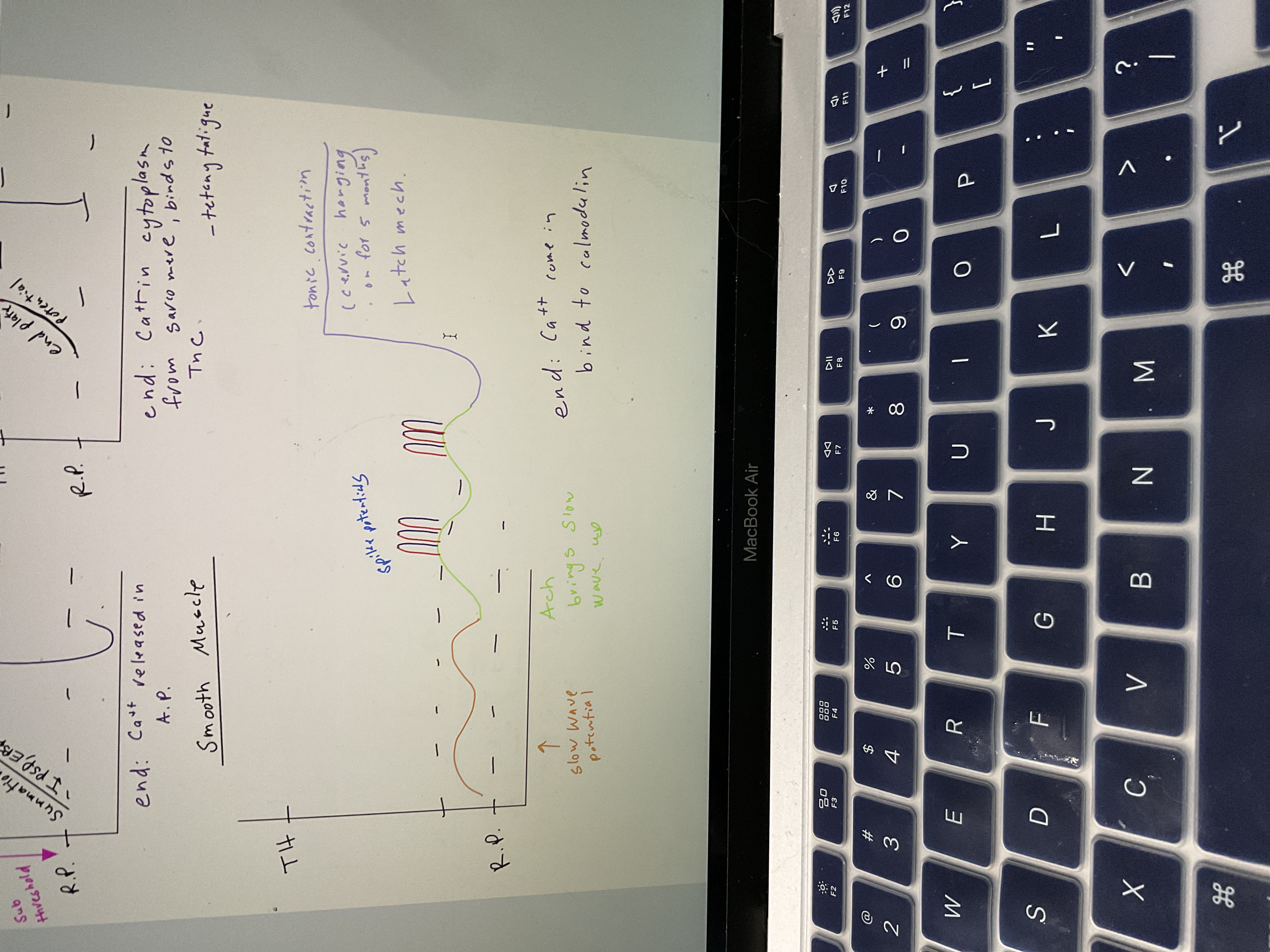
76
New cards
Draw cardiac muscle AP chart
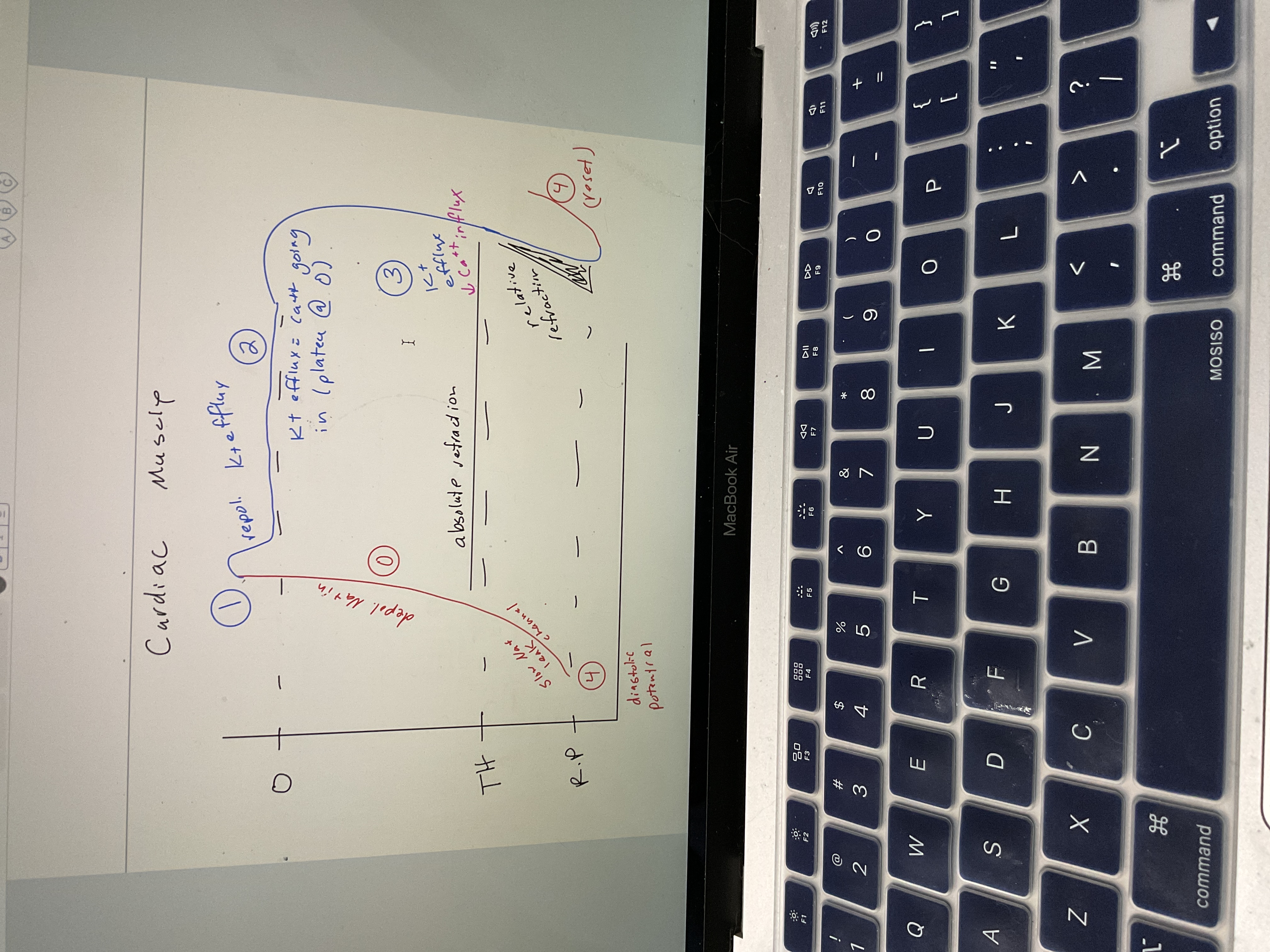
77
New cards
What is heart in most of time?
Absolute refraction, heart can’t go into tetany bc can’t sum ventricular refraction
78
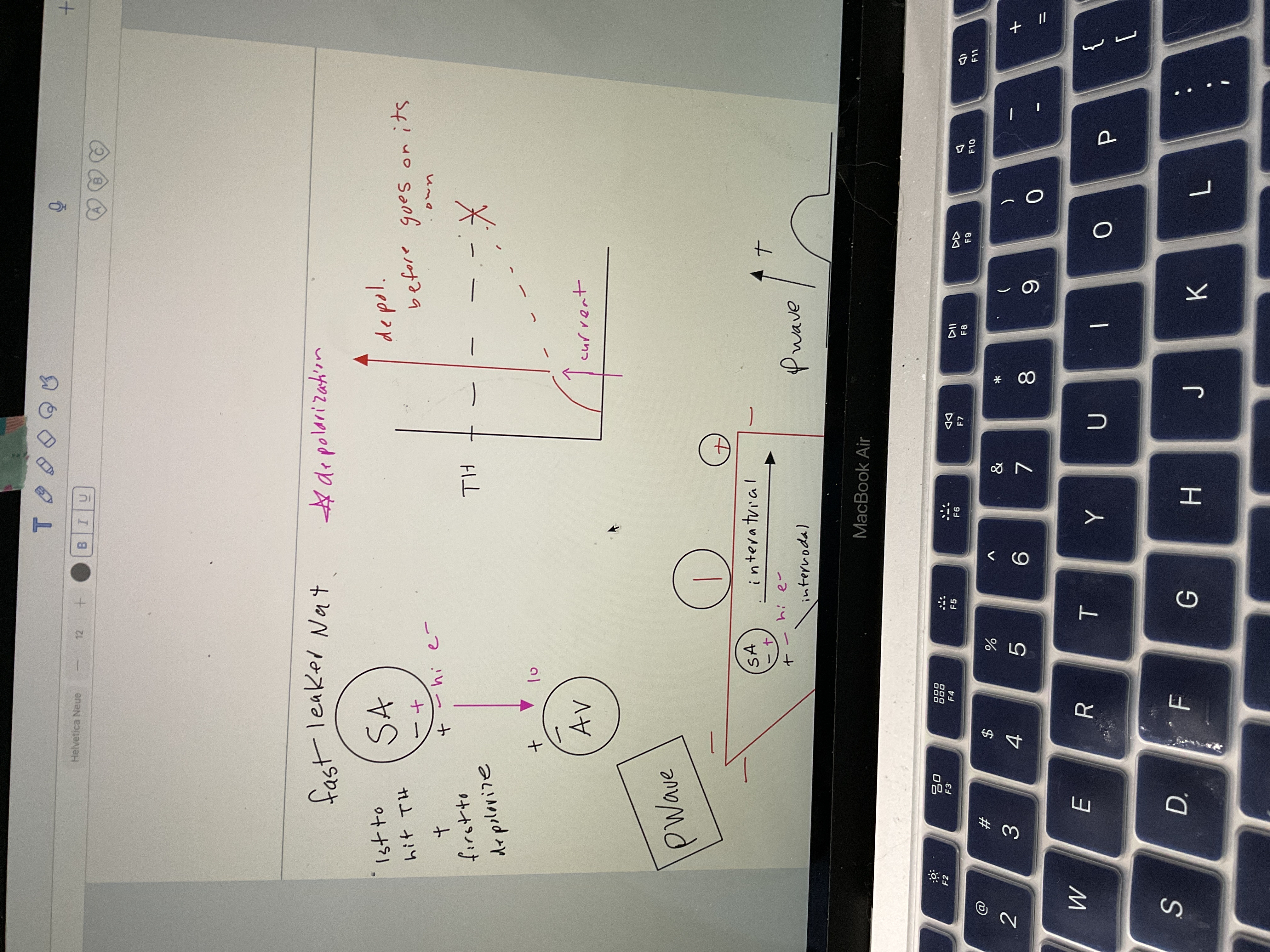
New cards
What is a fast leaker of na+
Sa node, 1st to hit threshold and depolarize
79
New cards
Draw depolarization of SA node
80
New cards
Draw P wave
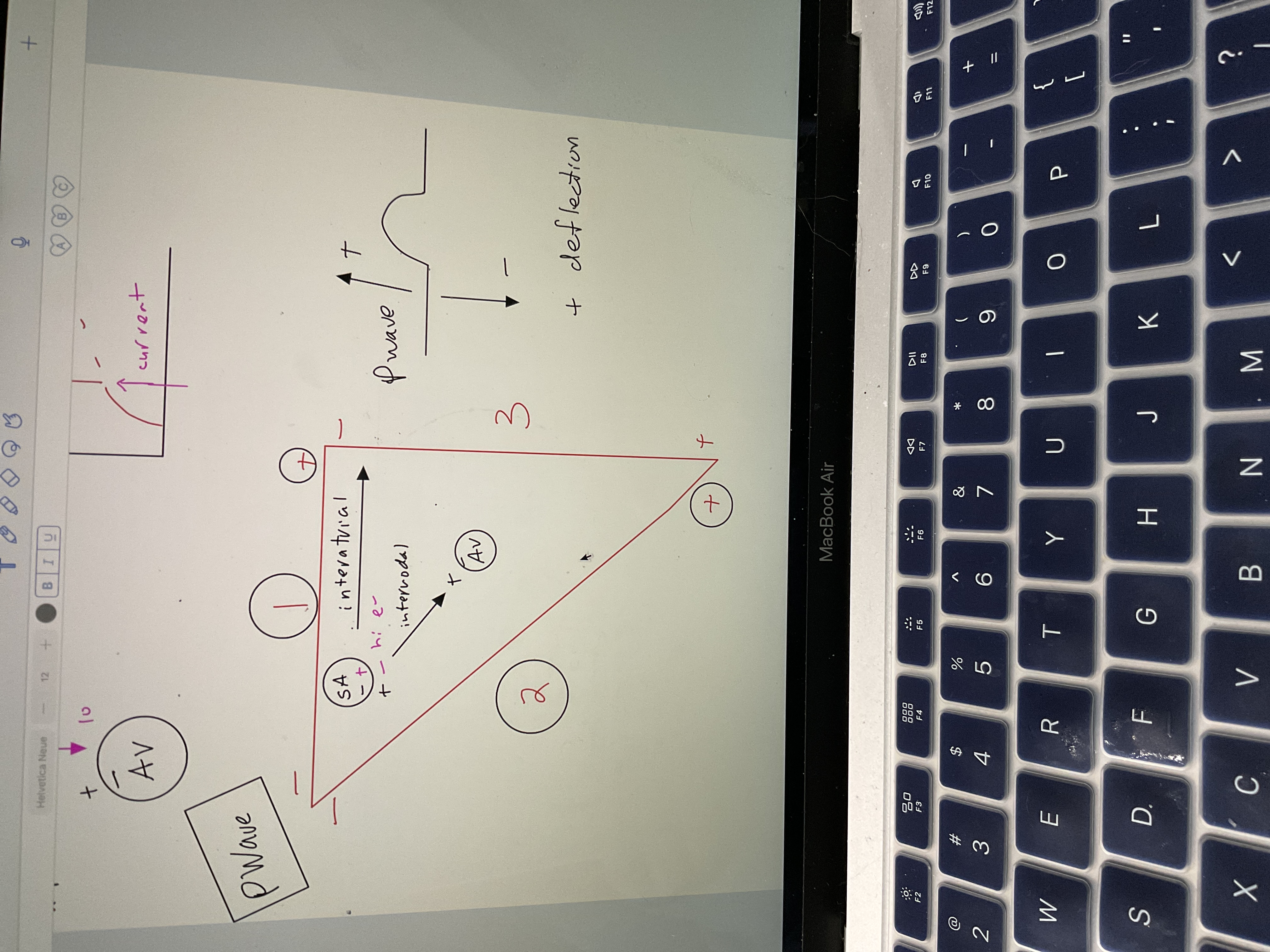
81
New cards
Draw QRS Wave
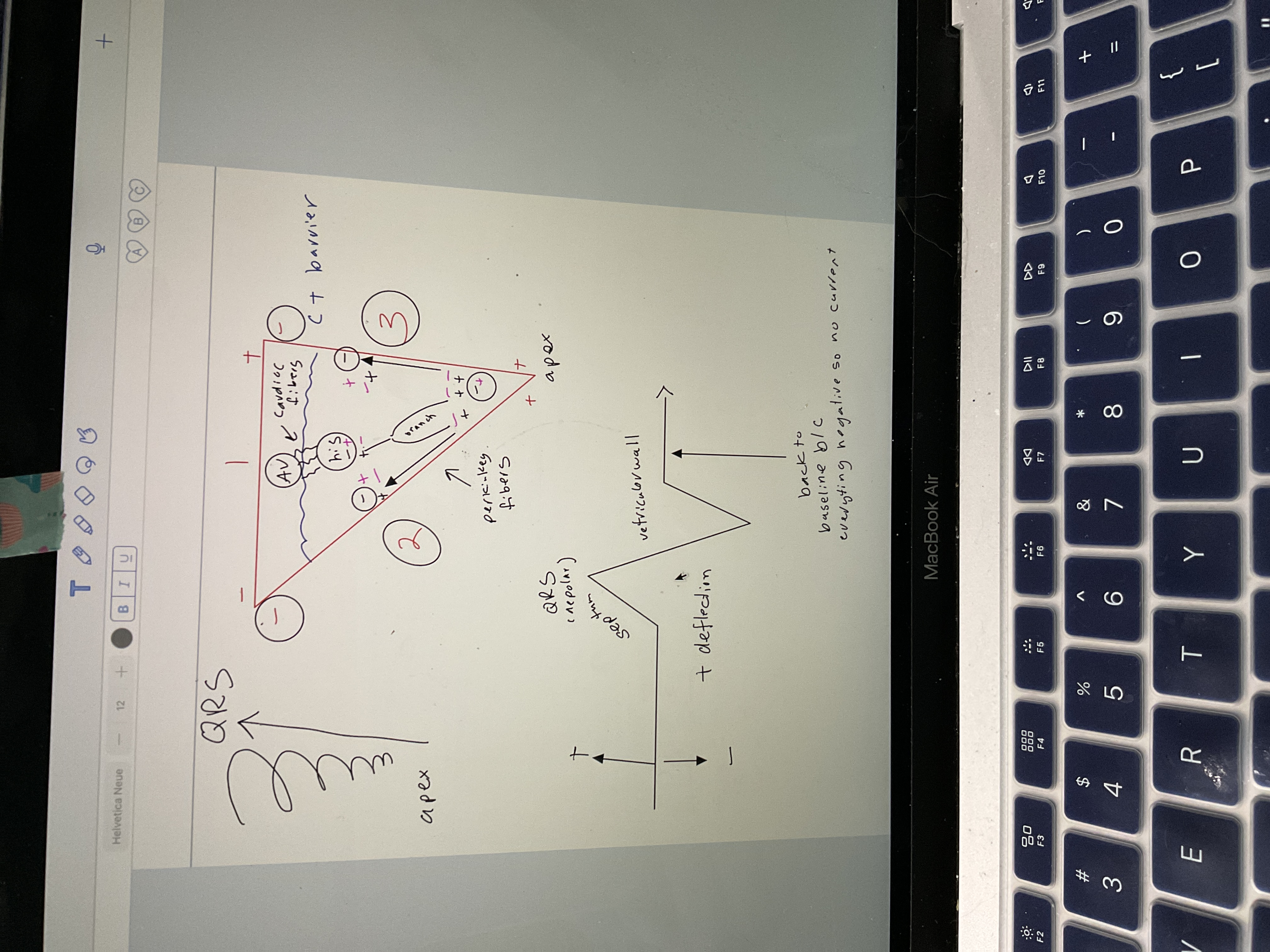
82
New cards
Draw t wave
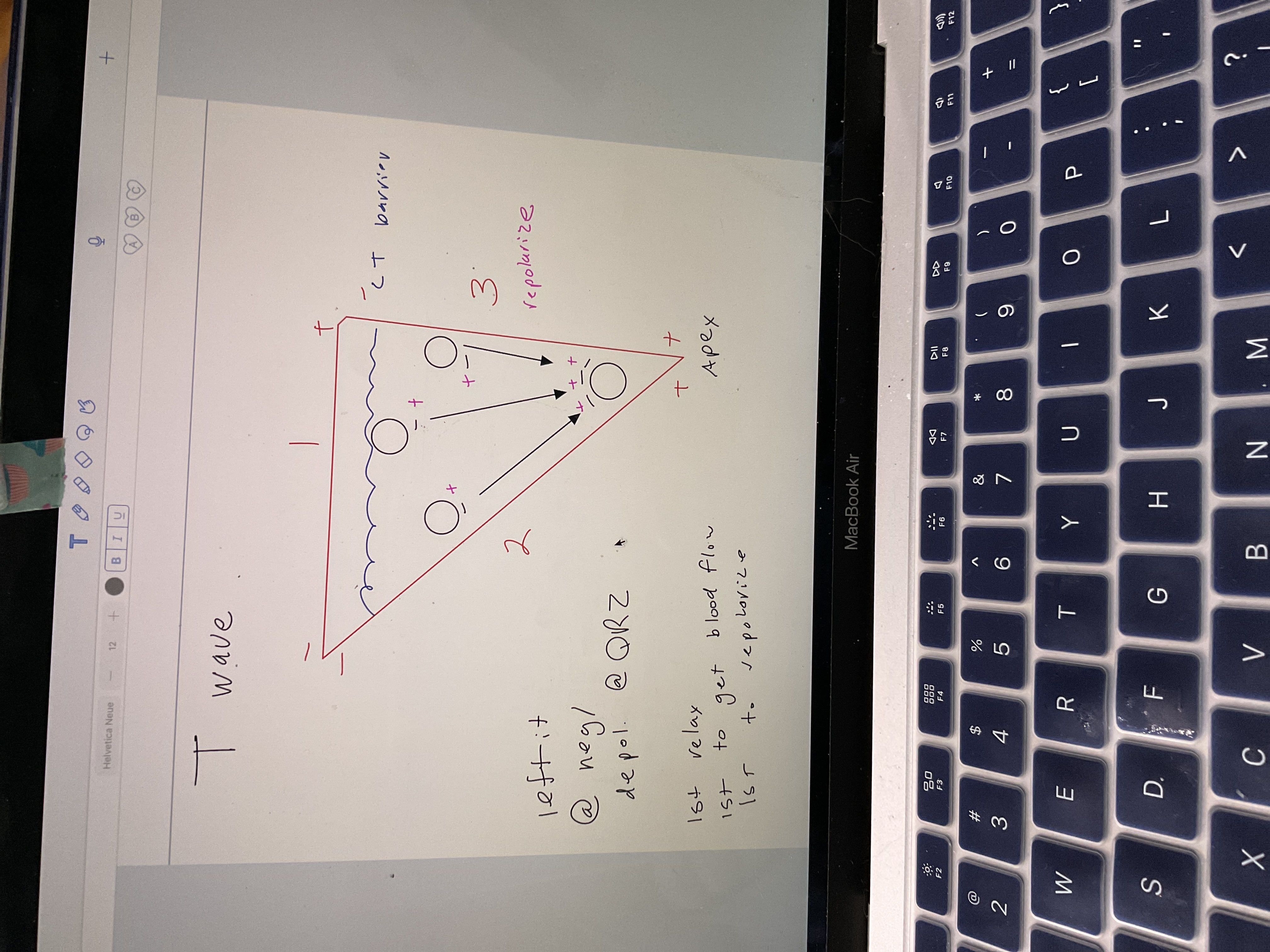
83
New cards
Absolute refraction in heart = tetany, explain
No tetany prevents ventricles from summing twitches up
84
New cards
Draw ventricular filling
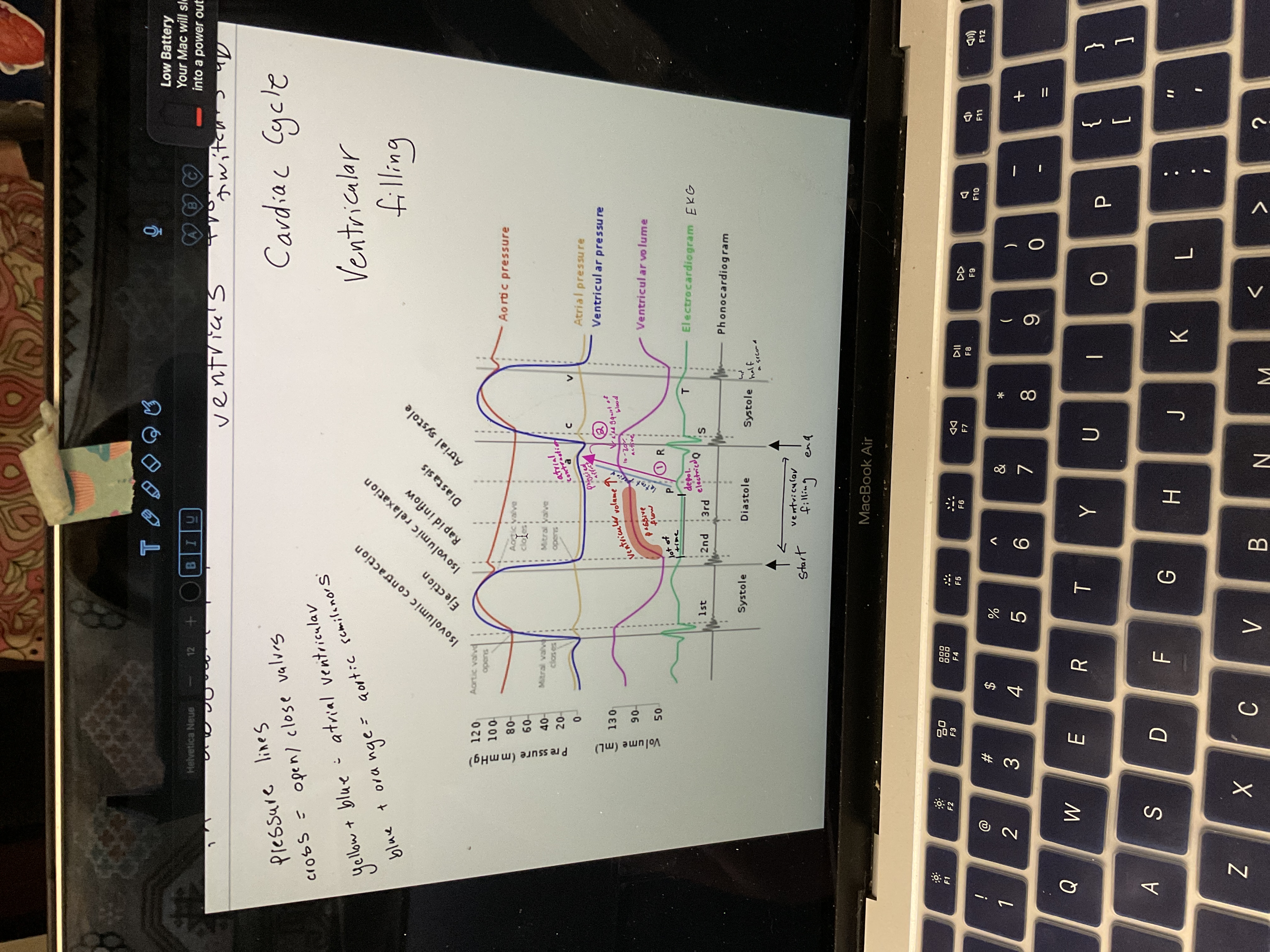
85
New cards
Draw ventricular relaxation
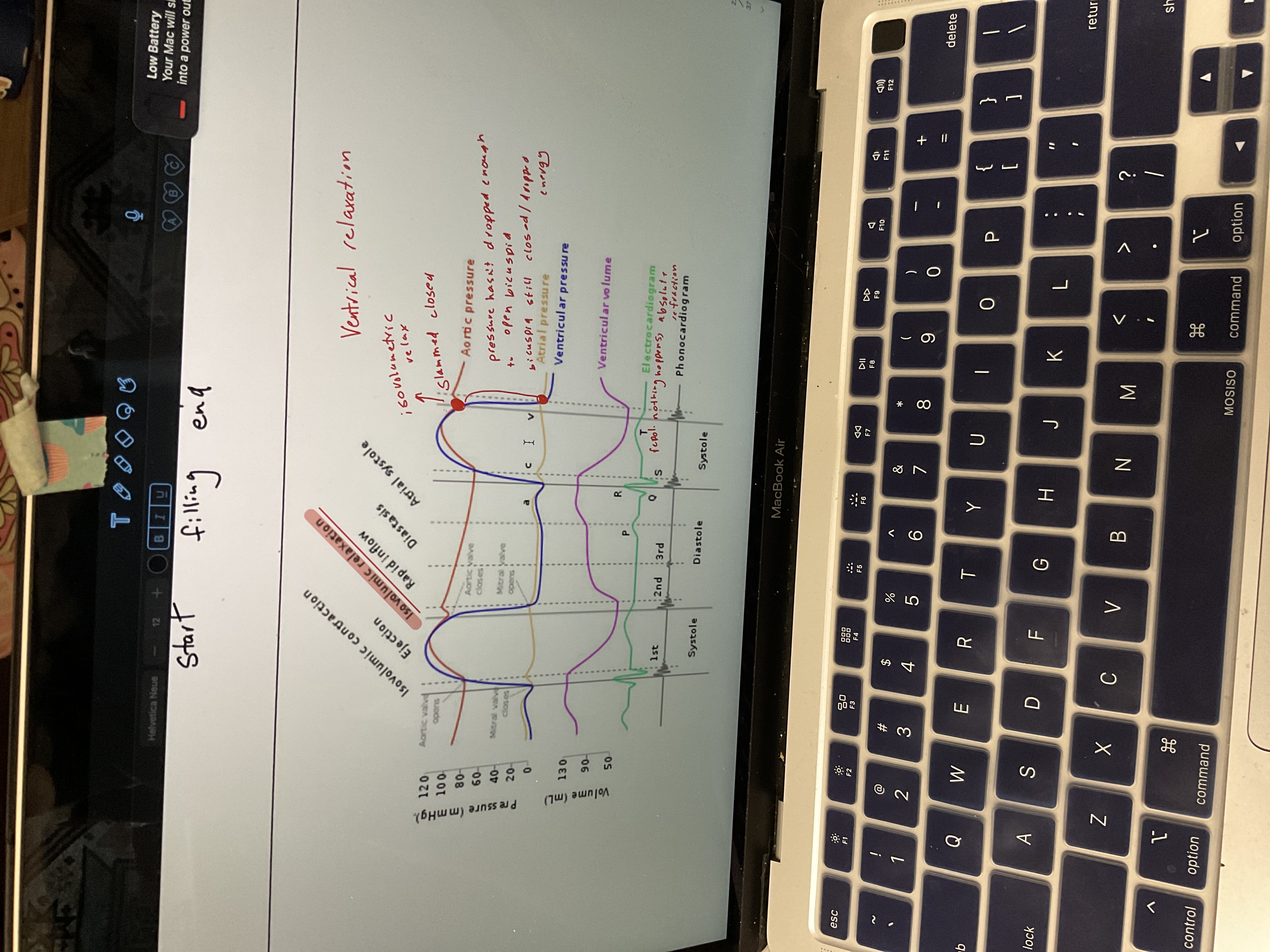
86
New cards
Draw ventricular ejection
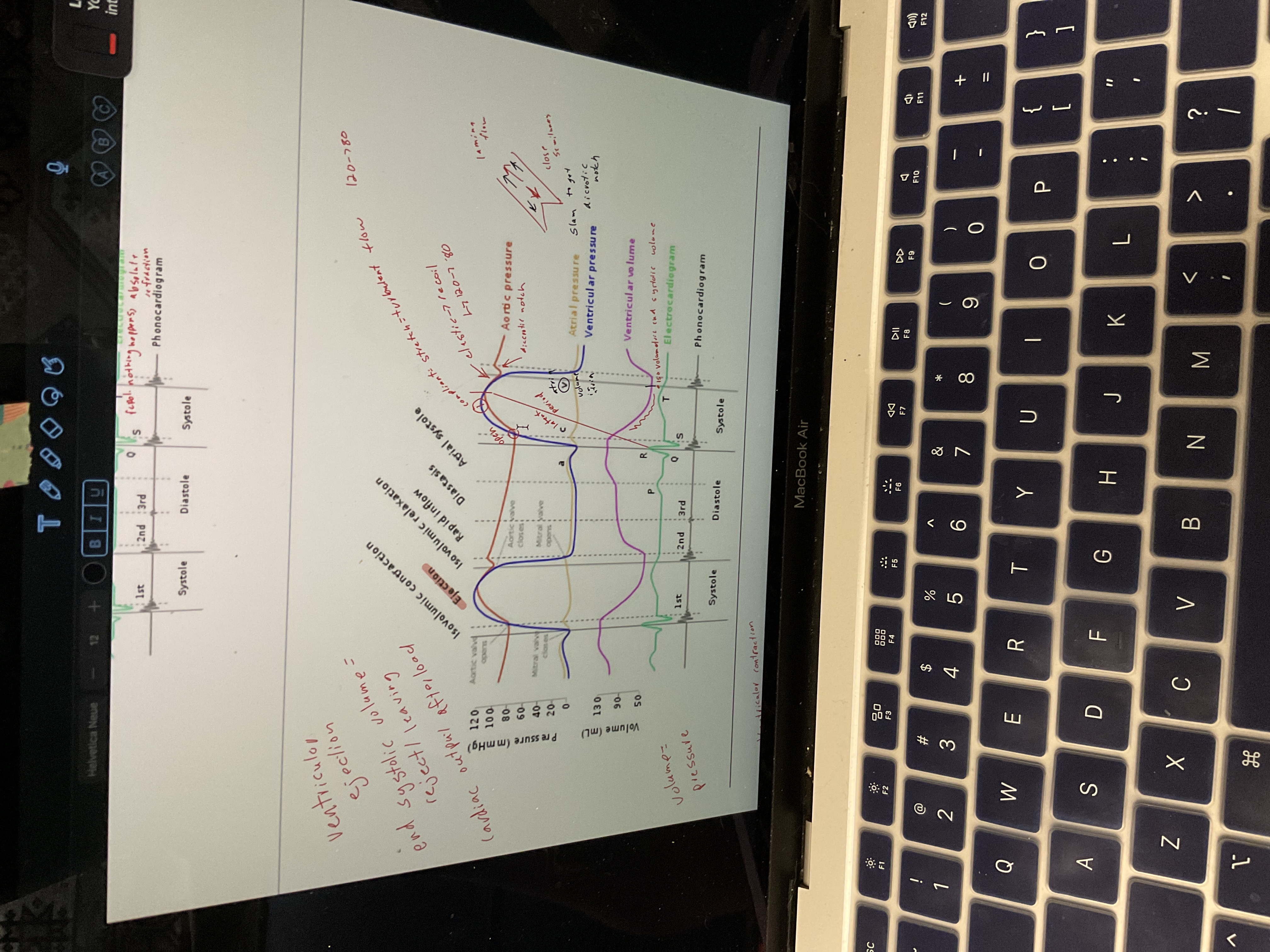
87
New cards
Draw ventricular contraction
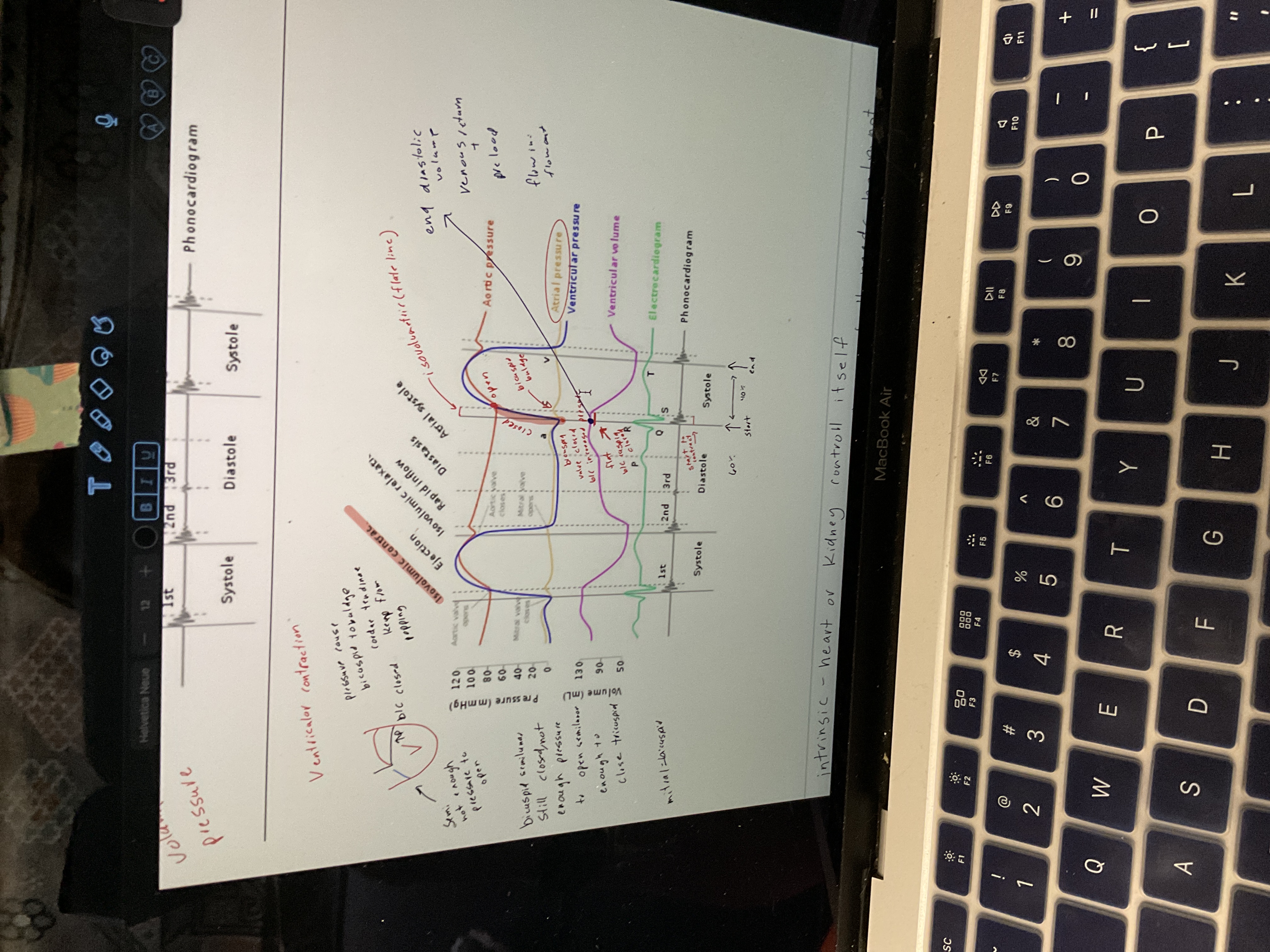
88
New cards
Intrinsic
Heart or kidney control itself
89
New cards
Extrinsic
Hormone, autonomic helps control need help not by itself
90
New cards
Draw law of heart chart
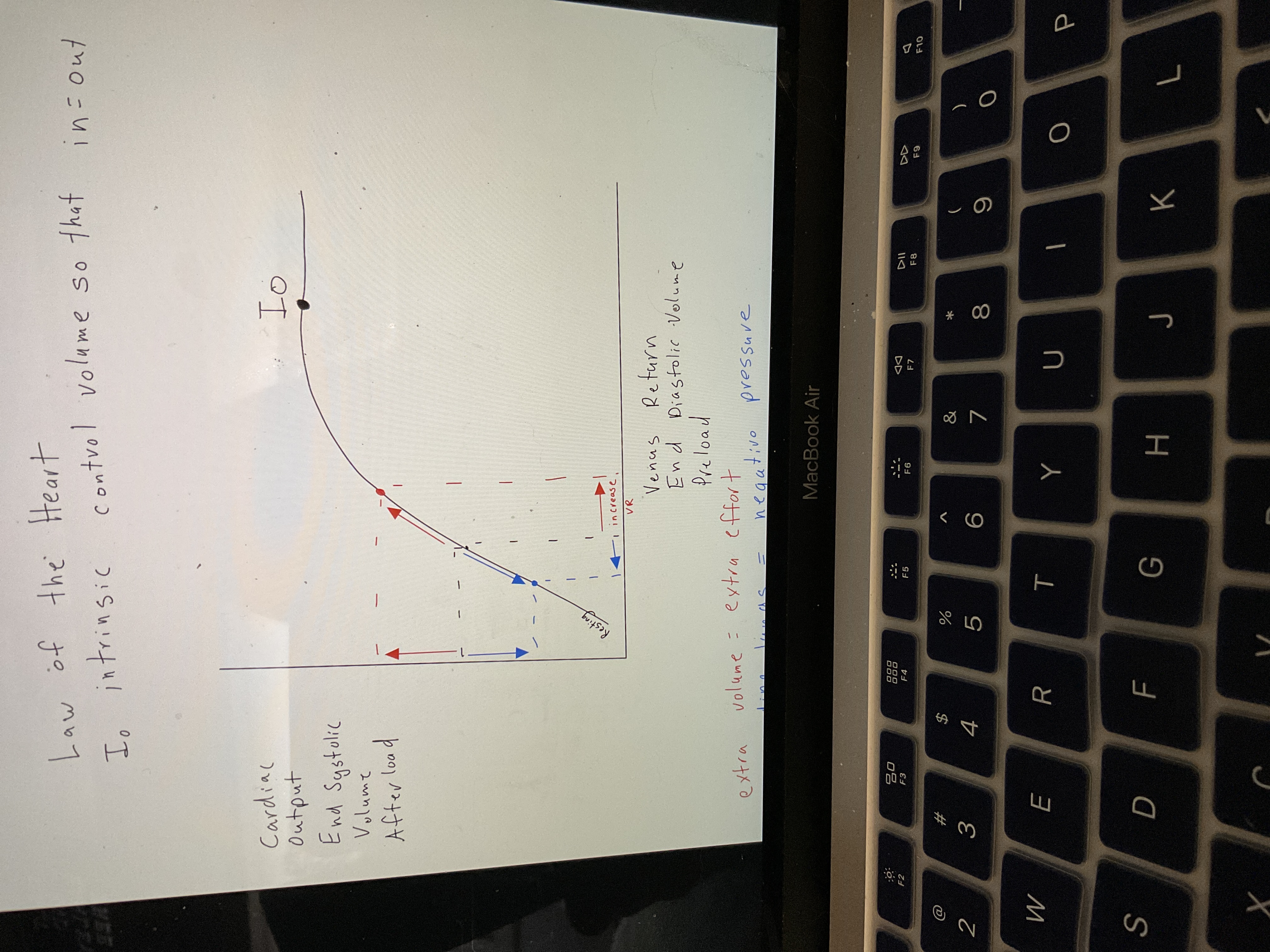
91
New cards
What does intrinsic control
Volume in = volume out
92
New cards
? What does extra volume mean
Extra effort
93
New cards
Surrounding lung pressure
Negative
94
New cards
What happens when you go from standing → laying
500 ml of fluid to thorax
95
New cards
Shunt
Move around
96
New cards
What controls bp
Autonomic nervous system
97
New cards
What controlls blood flow
Metabolism
98
New cards
Draw blood flow
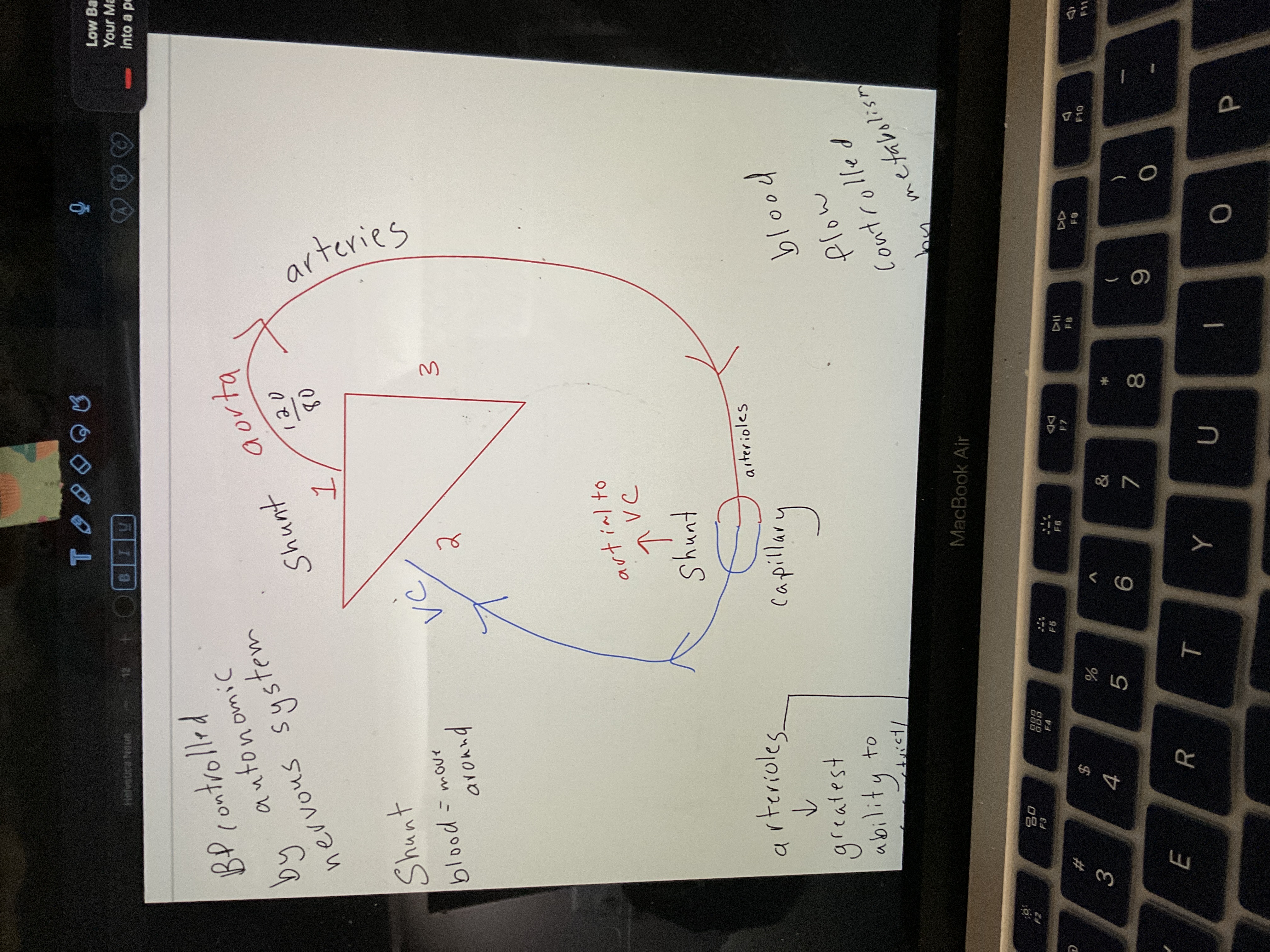
99
New cards
What has most resistance/ total resistance
Arterioles → greatest ability to vasoconstrictor vasodiate
100
New cards
Ohms law applied to blood flow
Volts= current x resistance
V= I x R
Delta p = I (blood flow) x R
V= I x R
Delta p = I (blood flow) x R