Biogeography, Climate, and Ecosystems: Key Concepts for Organism Distribution
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
What is biogeography?
The study of the geographic distribution of living organisms and the abiotic factors that affect their distribution.
What factors influence where a species is found on Earth?
Climate (rainfall and precipitation) and evolution.
What is the difference between climate and weather?
Climate refers to the average weather conditions in a region, while weather describes the local conditions at a specific time.
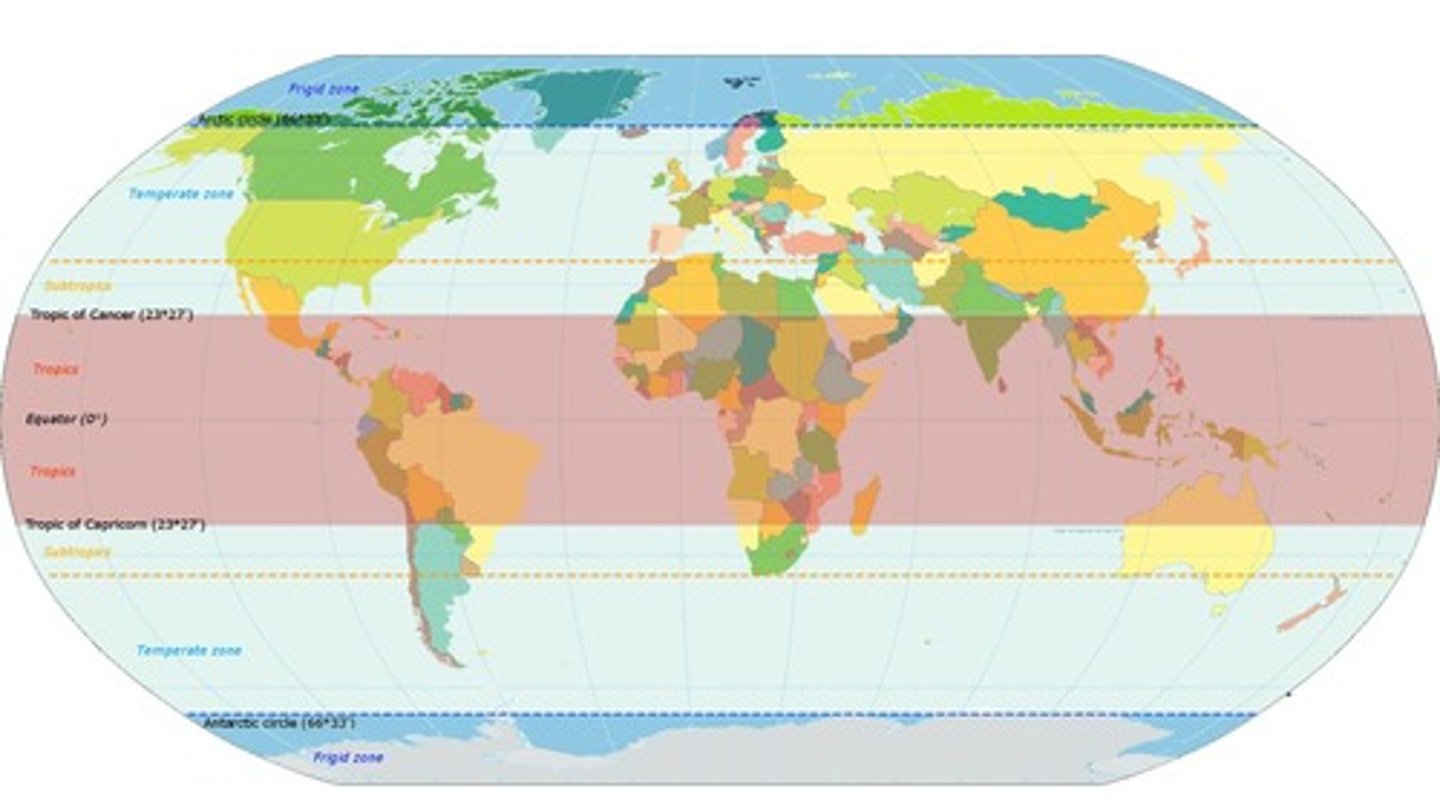
What are the main components that influence climate in a region?
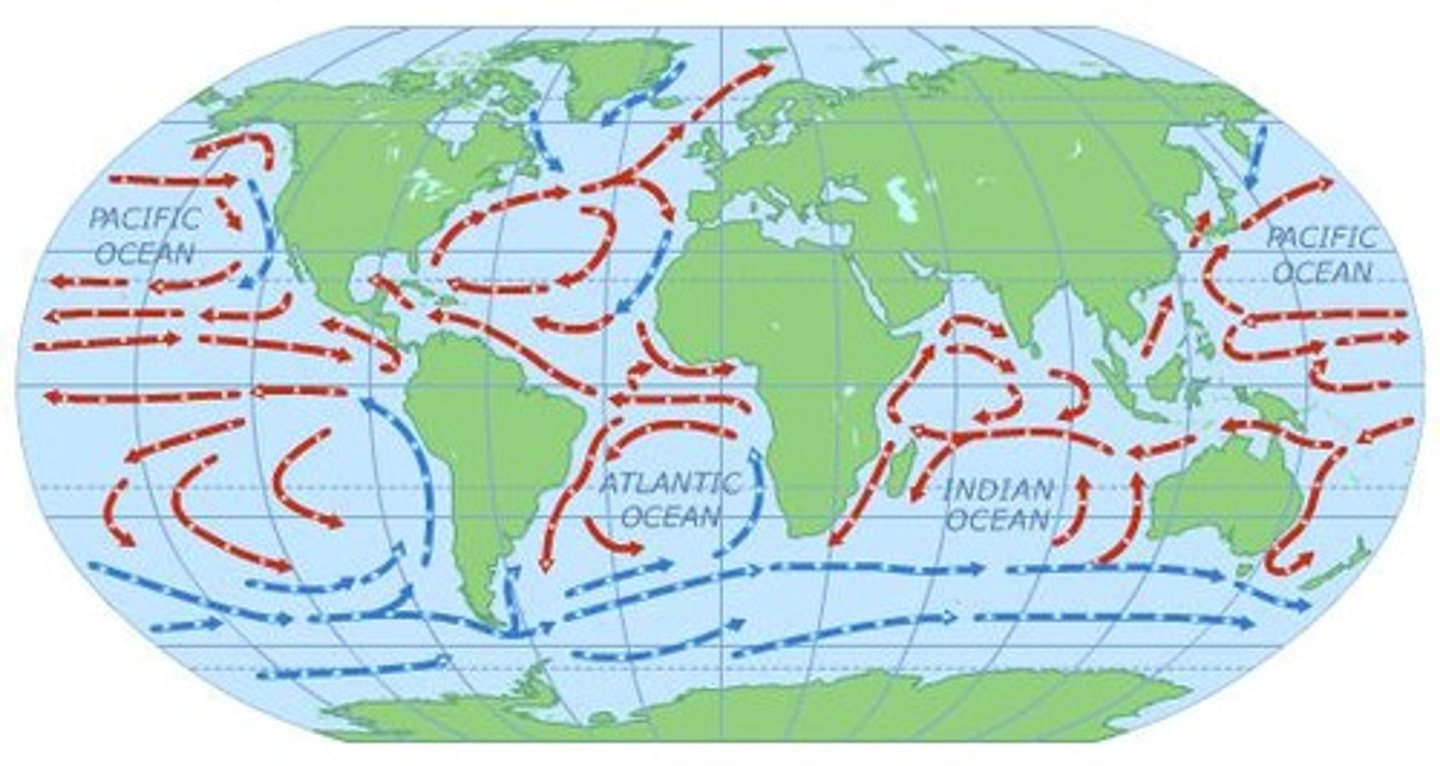
Latitude, day length, nearby water, elevation, topography, and global ocean circulation.
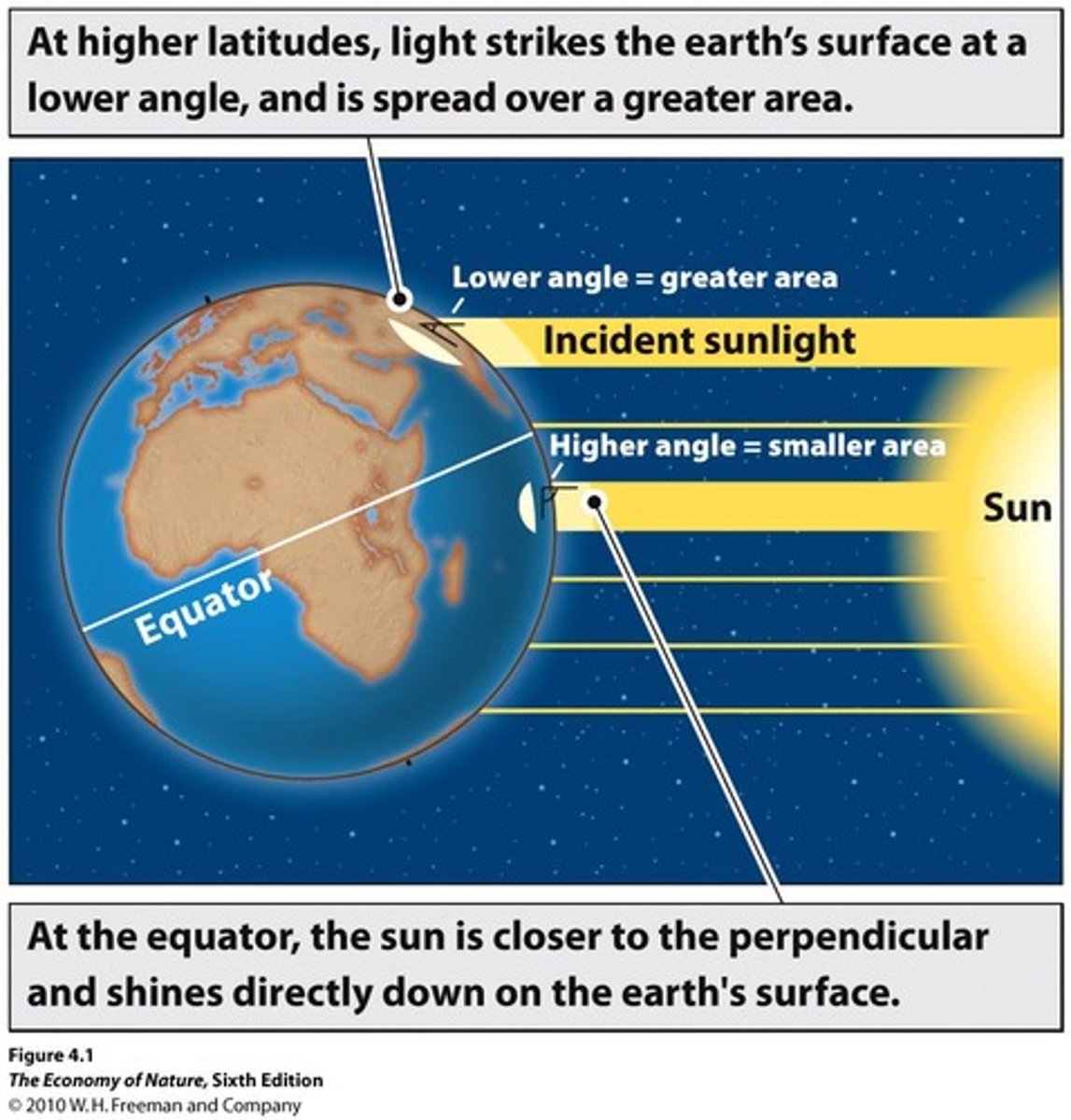
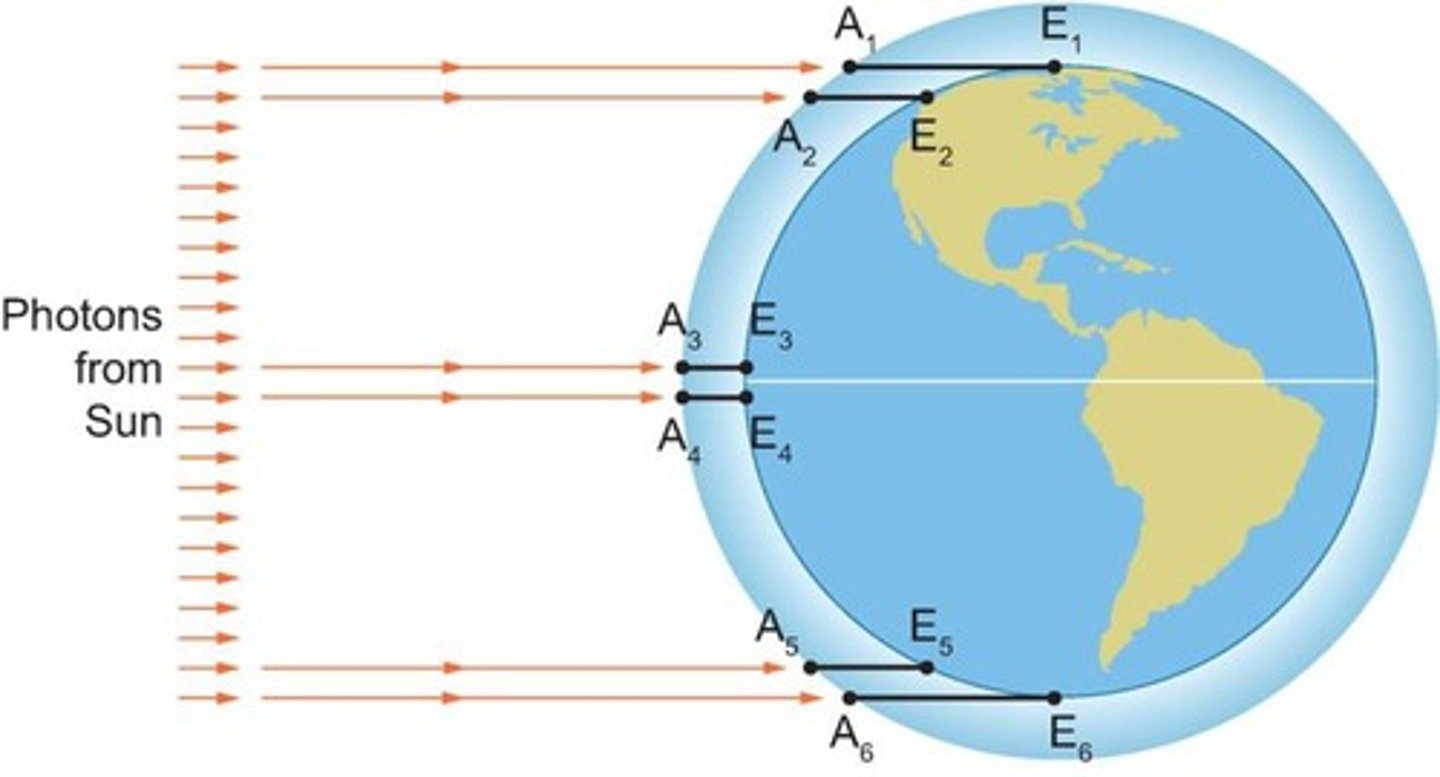
How does latitude affect temperature?
Less energy from the sun is received at higher latitudes, while more energy is received around the equator.
How does Earth's tilt influence temperature and seasons?
When tilted away from the sun, regions receive less energy (winter); when tilted towards the sun, they receive more energy (summer).
What factors influence precipitation?
Winds, topography (presence of mountains), seasons, and the amount of energy from the sun.
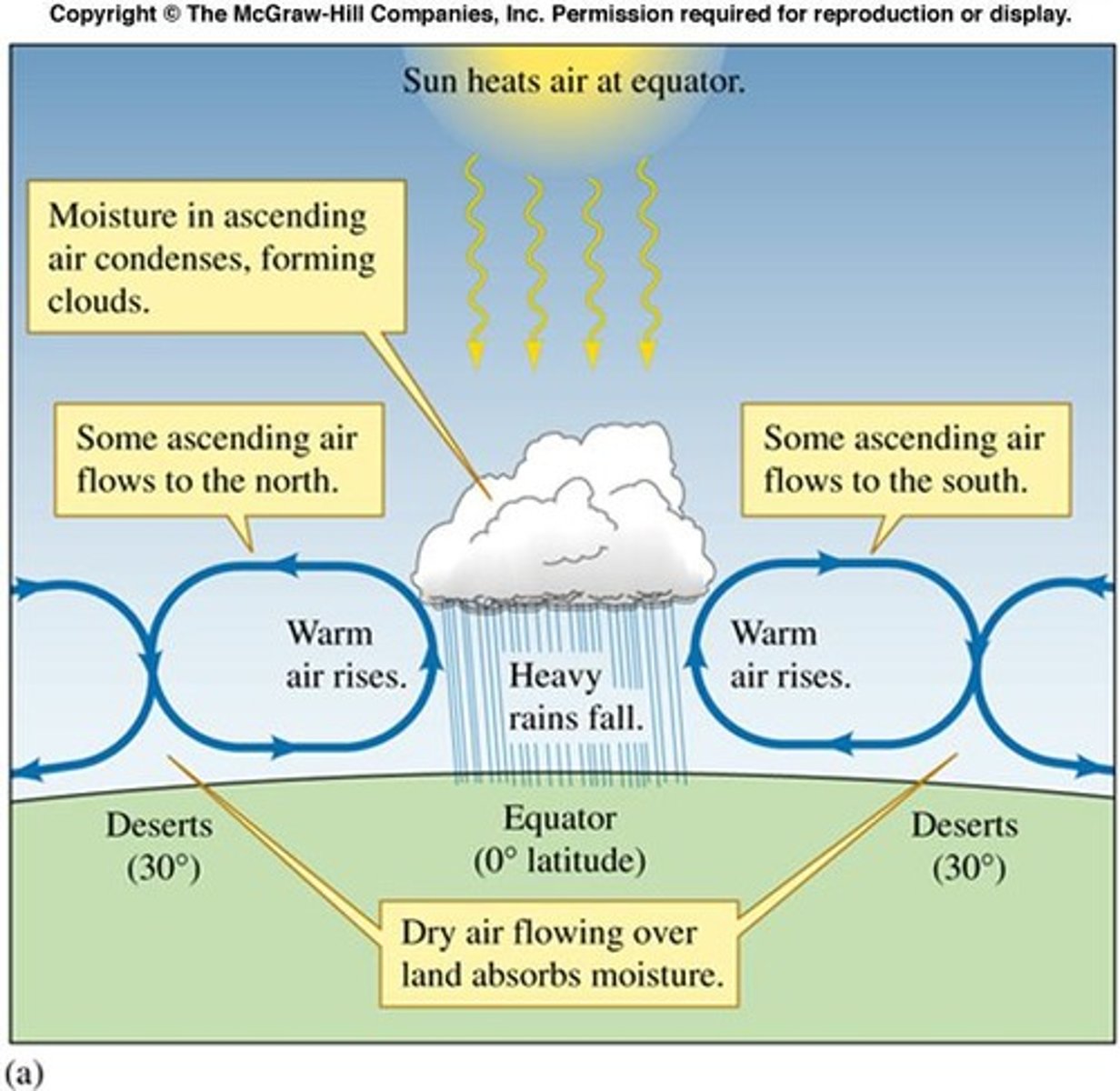
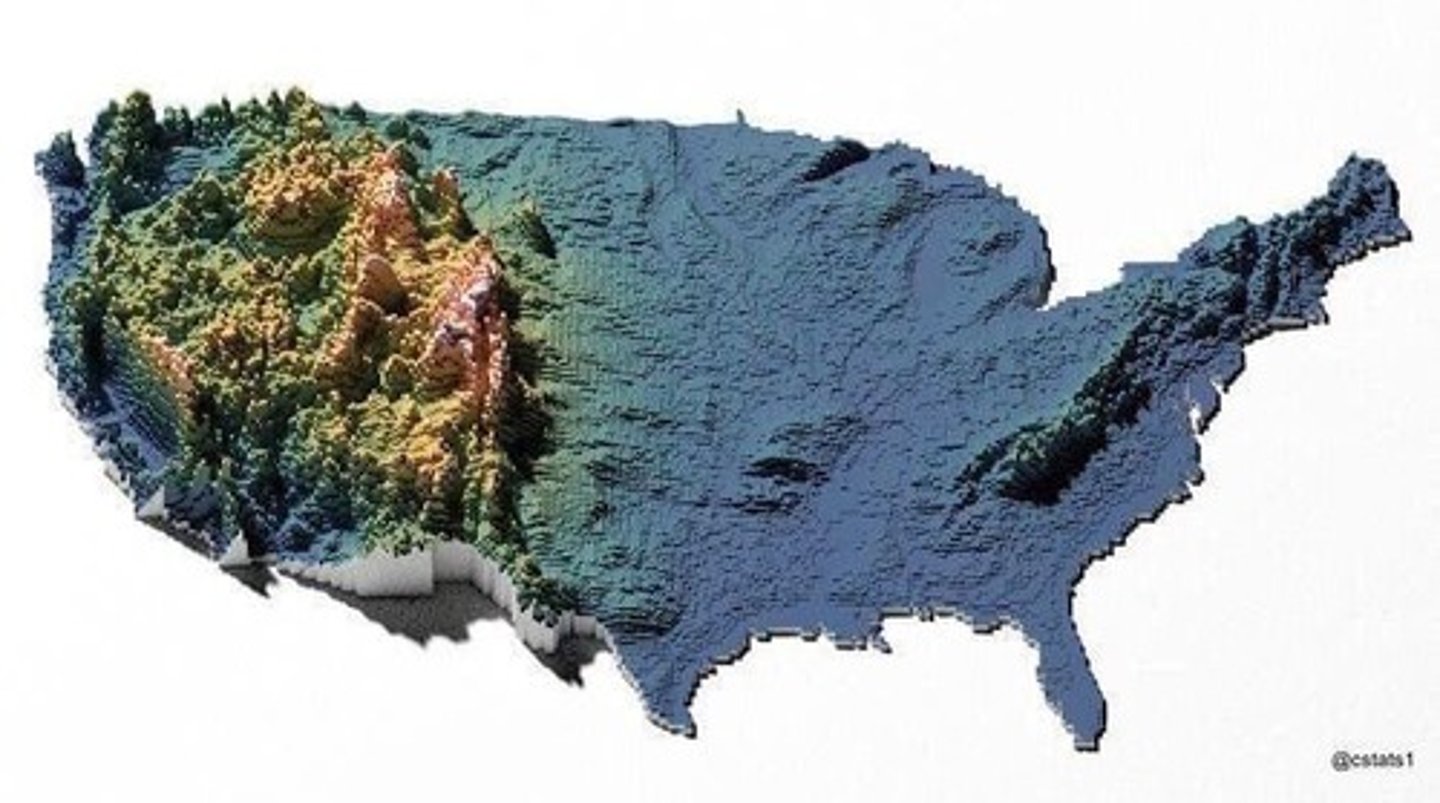
What is the Rain Shadow Effect?
A phenomenon where prevailing winds and topography affect precipitation, leading to dry areas on the leeward side of mountains.

Why is humidity higher in rainforests?
Dense tree canopies block wind, rainfall, and sunlight, while moisture is retained in the soil.

What causes the East Coast of the US to be more humid than the West Coast?
The East Coast has no rain shadow effect due to lower elevation and receives warmer winds from the Gulf Stream.
What is global warming?
The increase in global average annual temperature, primarily caused by increased greenhouse gases from burning fossil fuels.
What does climate change refer to?
Long-term changes and shifts in climatic conditions (temperature and precipitation) on a global scale.
What are some impacts of climate change?
Sea-level rise, intensification of storms, and intensification of droughts.
How can climate change impact biogeography?
It can lead to habitat change, movement of organisms, and endangerment or extinction of species.
What is an ecosystem?
A community of living organisms and their interactions with the abiotic components of their environment.
What are biomes?
Large ecological areas on the Earth's surface, classified by climate, plants, and animals.
What is nutrient cycling in ecosystems?
The movement and exchange of organic and inorganic matter back into the production of living matter.
What role does precipitation play in climate?
It is a key factor that influences the moisture availability in a region, affecting both climate and ecosystems.
How does topography affect climate?
It can influence wind patterns, precipitation distribution, and temperature variations across a region.
What is the significance of the equator in climate?
The equator receives a large amount of solar energy year-round, leading to consistently warm temperatures and high precipitation.