Digestive System
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms

Esophagus
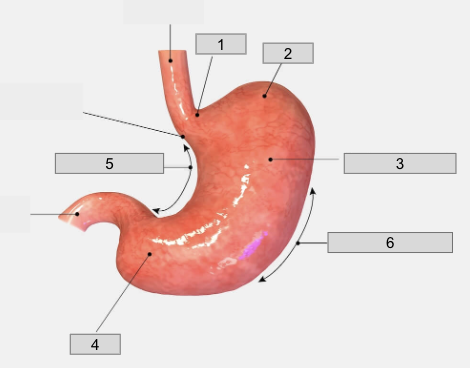
1
Cardiac region

2
Fundus
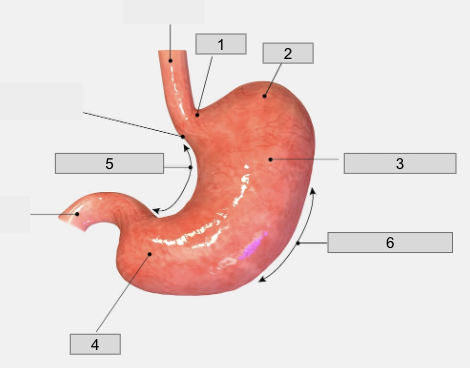
3
Body
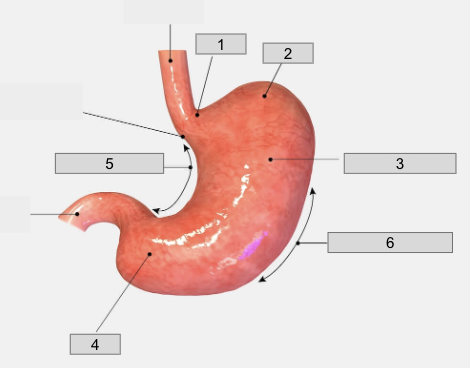
4
Pyloris
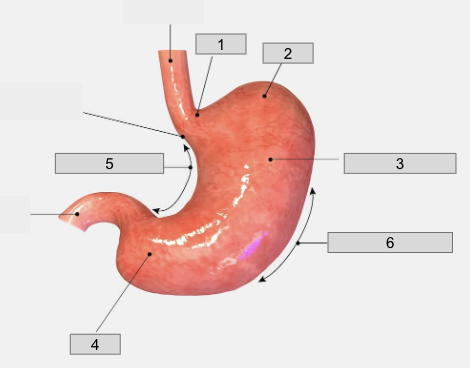
5
Lesser curvature

6
Greater curvature
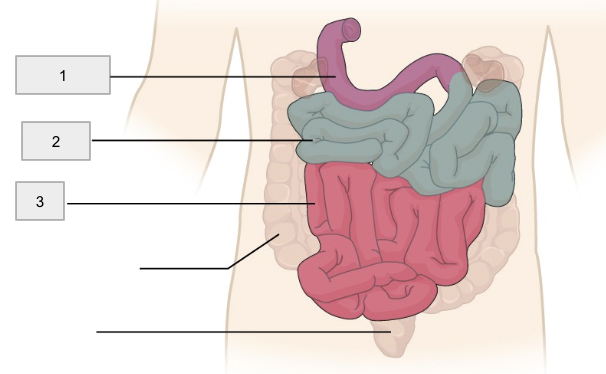
1
Duodenum
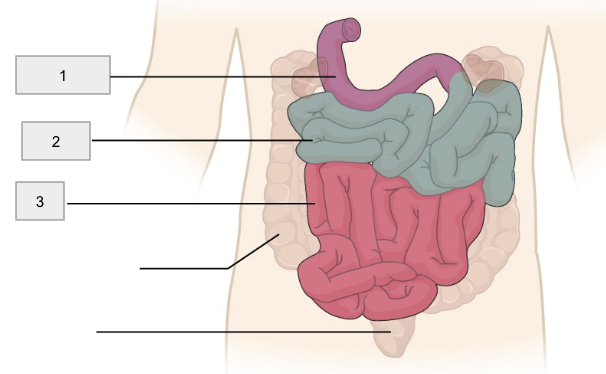
2
Jejunum
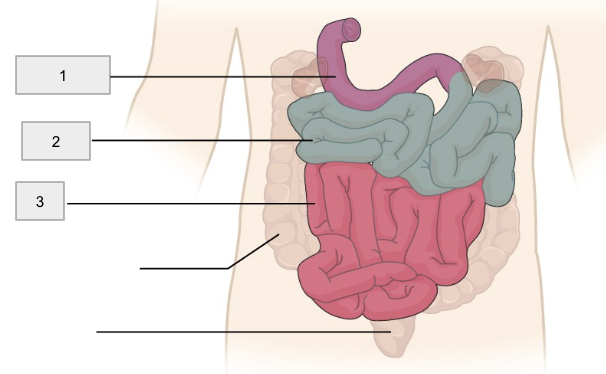
3
Ileum
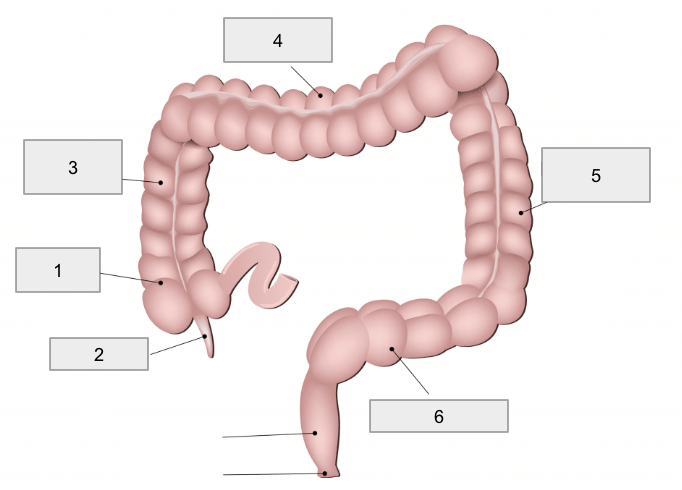
1
Cecum
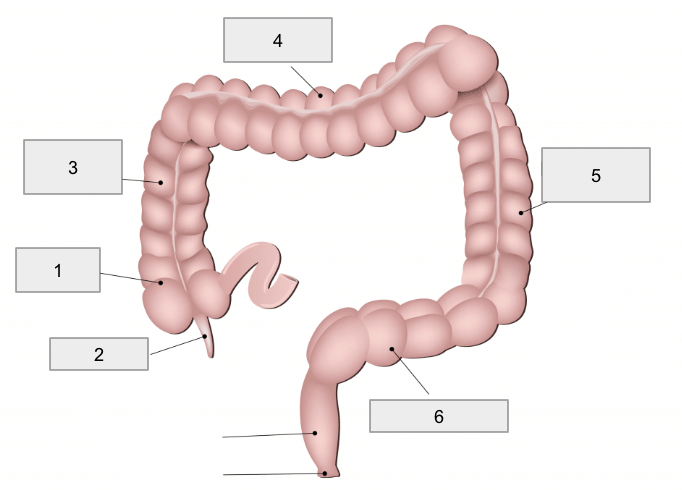
2
Appendix
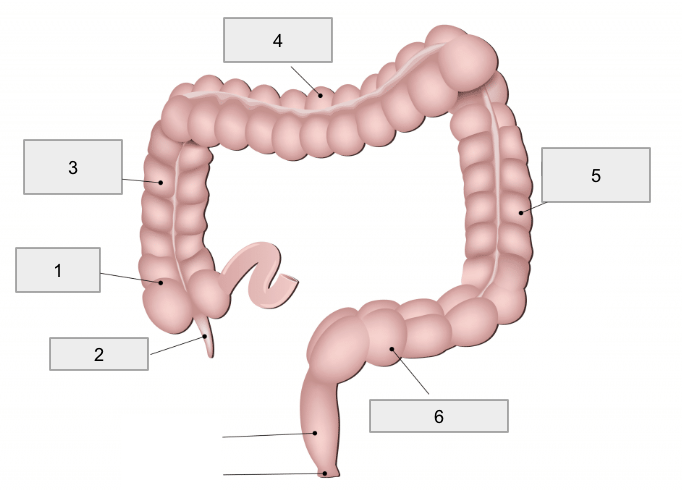
3
Ascending colon
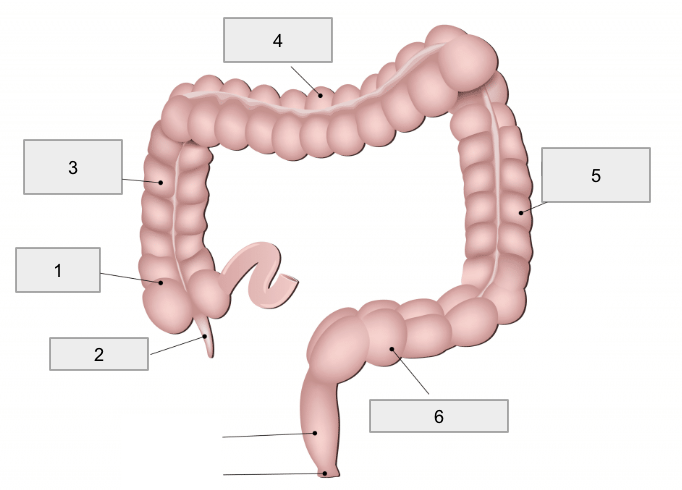
4
Transverse colon
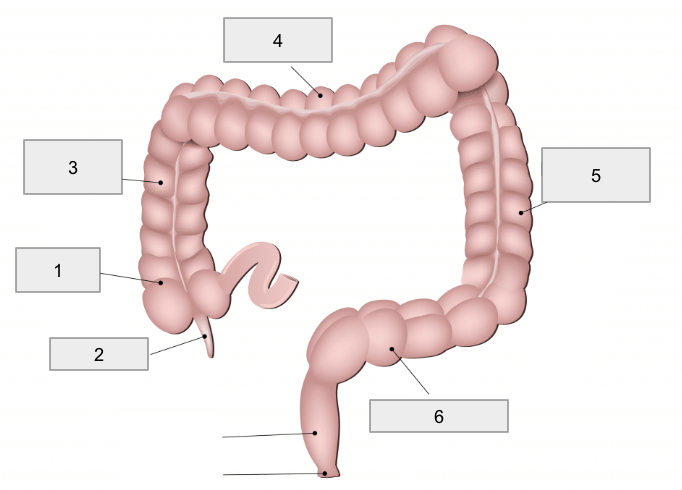
5
Descending colon
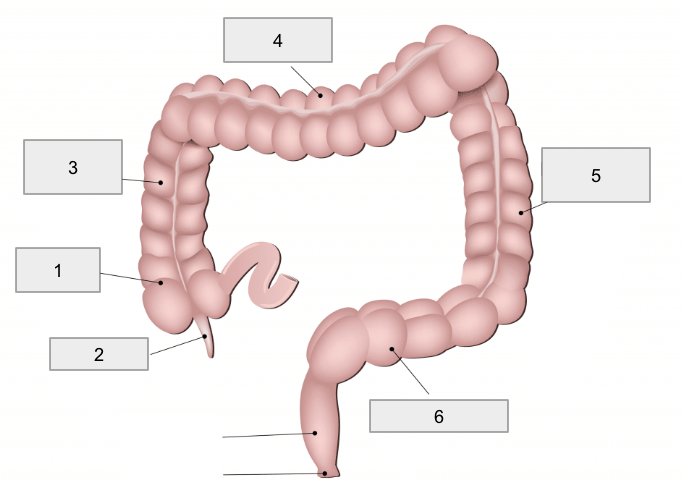
6
Sigmoid colon

1
Right Lobe
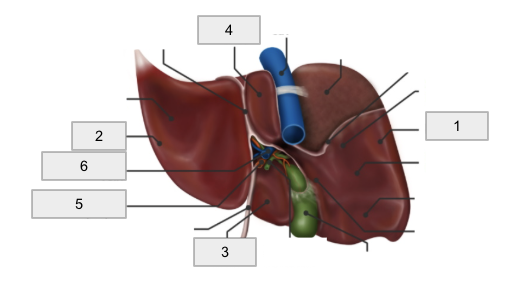
2
Left lobe
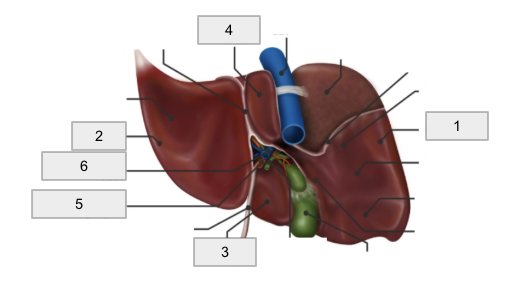
3
Quadrate lobe
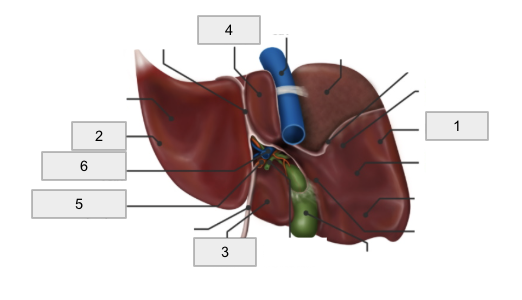
4
Caudate lobe
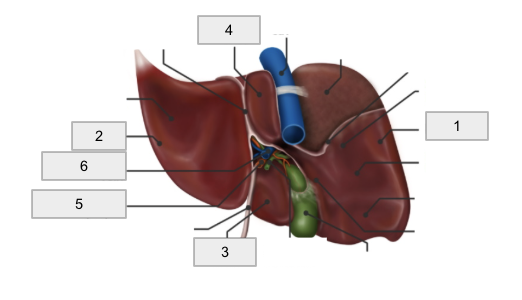
5
Hepatic artery

6
Hepatic portal vein

Porta hepatis
Falciform ligament
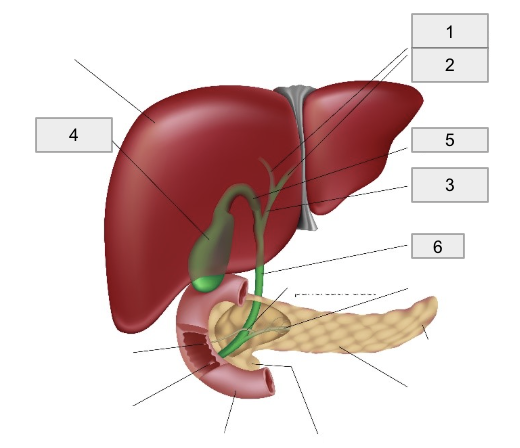
1
Right hepatic duct
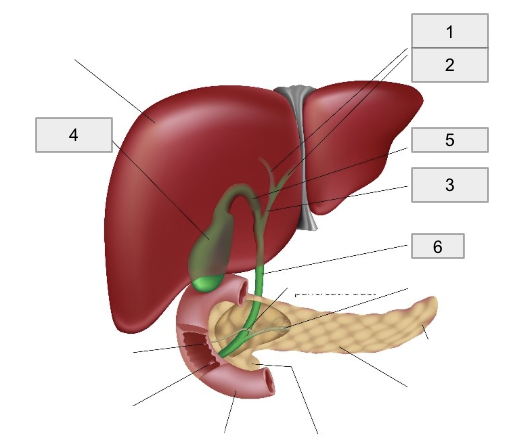
2
Left hepatic duct

3
Common hepatic duct

4
Gall bladder
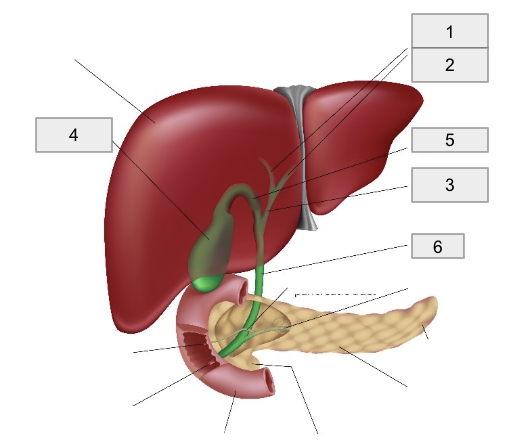
5
Cystic Duct
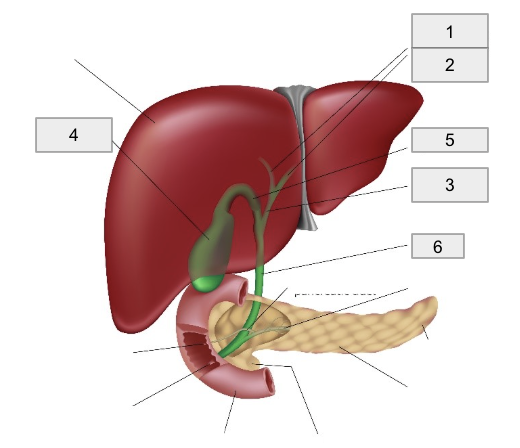
6
Common bile duct
Pancreas
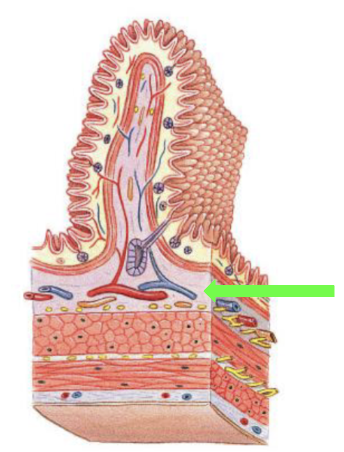
Submucosa
Areolar tissue surrounding the muscularis mucosa
Contents: blood vessels, lymphatics, exocrine glands, and submucosal plexus
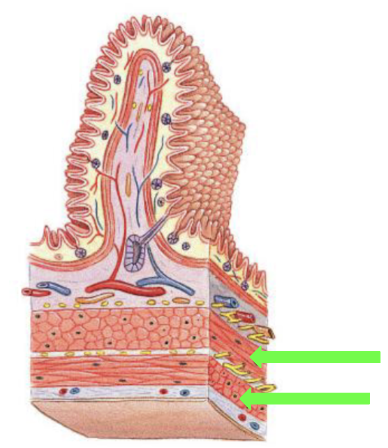
Muscularis Externa
Made up of Circumferentially oriented and Longitudinally oriented fibers
Circumferentially oriented
Smooth muscle fibers (inner layer)
Churning the contents in the digestive tract
Longitudinally oriented
Smooth muscle fibers (outer layer)
Runs down the tract
Peristalsis
Movement of Digestive Materials
Muscle cells are arranged in sheets or layers, and are
electrically connected to adjacent muscles by gap junctions.Contractions spread in a wave through the tissue in response
to motor neuron activation, chemicals, hormones, stretching,
and pacesetter cells.Pacesetter cells trigger muscle contraction patterns
(peristalsis and segmentation) that facilitate the propulsion
and mixing of contents along the digestive tract.
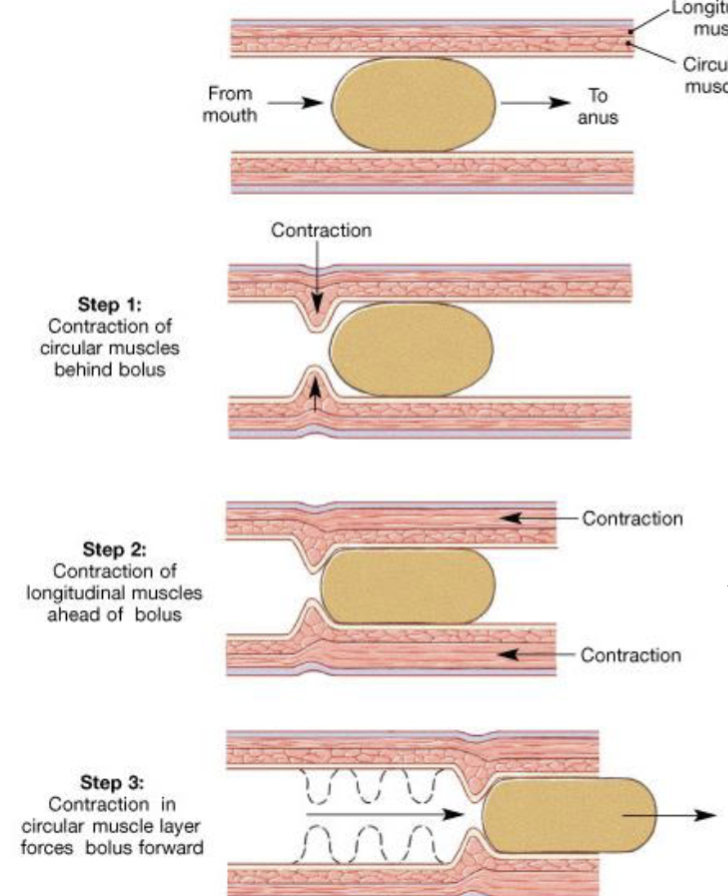
Peristalsis
Process whereby wavelike contractions of the muscularis externa propel a bolus along the digestive tract. It requires the coordinated actions of the circular and longitudinal muscles.
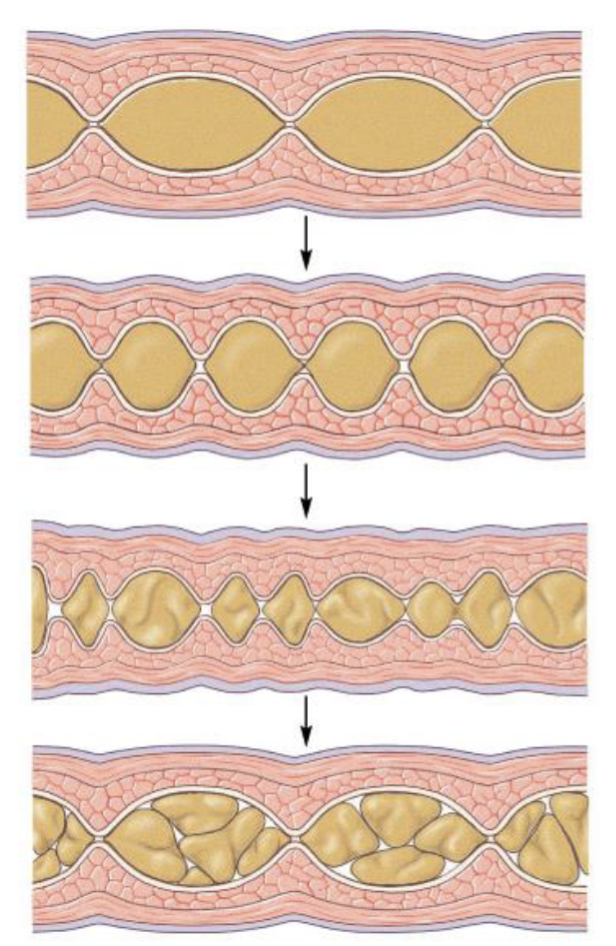
Segmentation
Process in which contractions of the circular layer of the muscularis externa churn and mix the contents of the digestive tract. No net movement
Peritoneal Cavity Organization
Parietal peritoneum: lines the inner surface of the body wall
Visceral peritoneum/serosa: outer lining of digestive tract
Mesenteries: fused, double sheets of peritoneal membrane
Mesenteries examples
Lesser omentum: between stomach and liver
Greater omentum: “fatty apron” that hangs anteriorly and inferiorly from the stomach
Mesentery proper: suspends and wraps most of the small intestine
Mesocolon: the mesentery that suspends and wraps part of the large intetsine
Mesenteries
Provide an access route for blood vessels, nerves, and lymph to & from tract
Stabilize the relative positions of the organs within the peritoneal cavity
Intraperitoneal organs
Organs are covered by visceral peritoneum and suspended by mesentery from the body wall. Ex: stomach - out in the cavity
Retroperitoneal organs
Mesentery has fused with the posterior abdominal wall. The organs lie posterior to (retro) the peritoneal cavity. Ex: pancreas - anchored to the wall
Oral Cavity accessory organs
Tongue
Teeth
Salivary glands
Buccal Phase of swallowing
Compression of bolus against hard palate; elevation of soft palate, retraction of tongue
Pharyngeal Phase of swallowing
Bolus contacts posterior pharyngeal wall; elevation of larynx; folding of epiglottis backward
Esophageal Phase of swallowing
Opening of upper esophageal sphincter, peristalsis; opening of lower esophageal sphincter
Esophagus
Flat muscular tube that transports foods and liquids to the stomach
Rugae
Longitudinal folds in the mucosa of the stomach wall that permit the expansion of the gastric lumen
Small Intestine
20ft tube that functions in the enzymatic digestion and absorption of water, organic substrates, vitamins, and ions
Duodenum
(the “mixing bowl”) receives chyme from stomach and digestive enzymes from pancreas and liver. Contains the pylorric sphincter
Jejunum
Bulk of chemicals and nutrients, absorption takes place here
Ileum
Controls flow of material into the large intestine via the ileocecal valve
The mixing bowl
The duodenum receives chyme from the stomach and mixes it with digestive enzymes from the following organs
Liver: bile from the liver empties into the duodenum via the common bile duct
Pancreas: digestive enzymes from the pancreas (pancreatic juice) enter the duodenum through the main pancreatic duct
Absorptive Structures of the Small Intestines
Plica circulares
Villi
Microvilli: These structures function to increase the surface area of the inner intestinal wall
Movement of material through the large intestine
Slow passage of material via peristaltic activity and Haustral Churning
Periodic mass movements of fecal matter via powerful peristaltic contractions
Distension of recal wall stimulate conscious urge to defecate
Internal anal sphincter
Involuntary smooth muscle that relaxes in response to rectal wall distension
External anal sphincter
Voluntary skeletal muscle whose relaxation allows for defecations
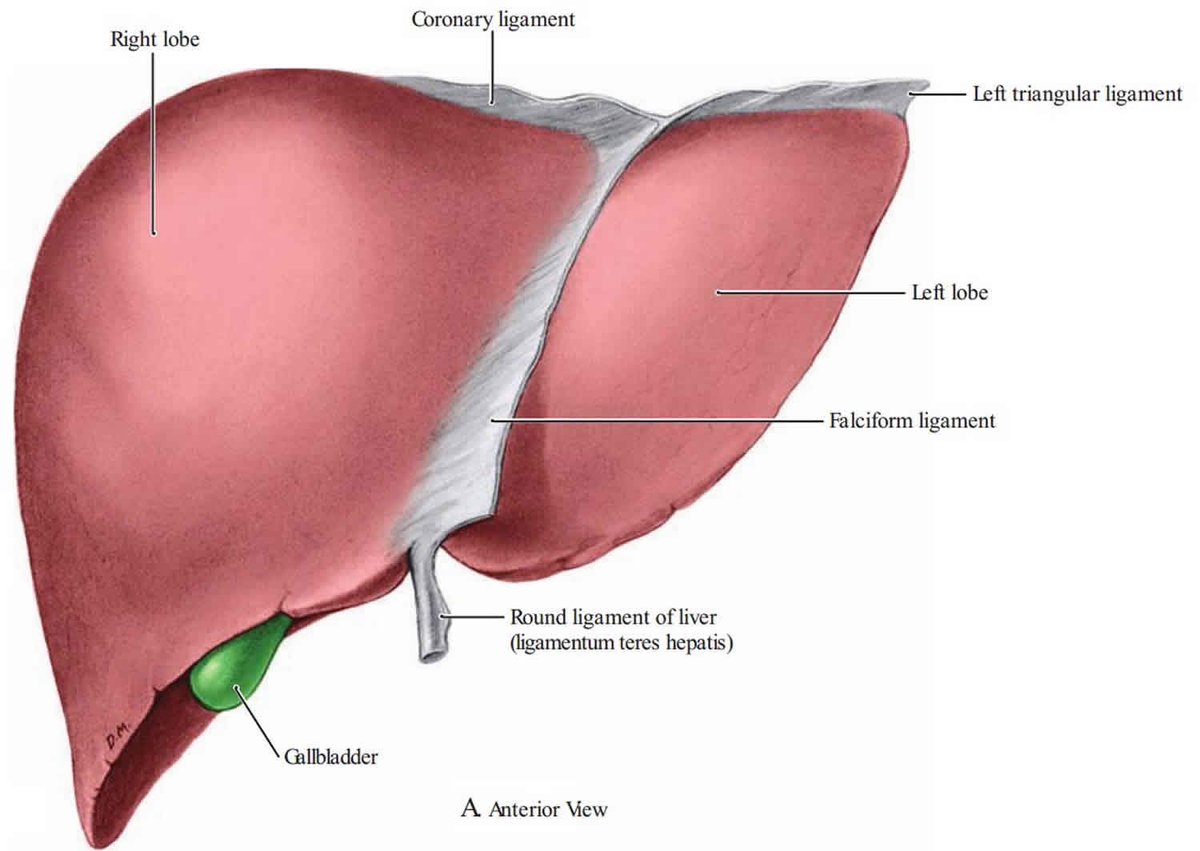
The Liver
Largest visceral organ
Perform 200+ functions related to:
Metabolic regulation: extraction and storage of nutrients from the blood; detoxification of harmful materials; storage of fat-soluble vitamins
Hematological regulation: blood reservoir and filter; removal of damaged blood cell/debris; synthesis of plasma proteins
Bile production
Bile Production and Pathway
Bile is produced in the liver and drained by right and left hepatic ducts into the common hepatic duct
Bile flows from the common hepatic duct through the cystic duct into the gallbladder for storage and concentration
When a fatty meal is eaten, bile is expelled from the gallbladder through the cystic duct into the common bile duct
The common bile duct empties bile into the duodenum to facilitate the breakdown of lipids into fatty acids suitable for absorption
Hepatic Portal System
Normal blood flow: Aorta artery - capillary bed - vena cava veins - heart
Portal system blood flow: Aorta artery - capillary bed in small and large intestines - Hepatic Portal vein - capillary bed in Liver - Inferior vena cava vein - heart
Most of the blood from the digestive tract is drained by the hepatic portal system. Blood flowing in veins from the digestive organs drains into hepatic portal vein.
The hepatic portal vein drains blood into the liver, where it is filtered by specialized capillary beds (sinusoids). The modified/filtered blood then flows through the hepatic vein and into the inferior vena cava to the heart.
Blood Supply to the Digestive System
3 unpaired branches of the abdominal aorta provide blood supply to the digestive system: Celiac Trunk, Superior Mesenteric artery, and Inferior mesenteric artery
Celiac Trunk
Stomach, liver, gallbladder, pancreas, spleen, and a part of the duodenum
Superior Mesenteric artery
Most of the duodenum, jejunum, ileum, cecum, appendix, ascending colon, and first ½ of transverse colon
Inferior Mesenteric artery
Second ½ of transverse colon, descending colon, sigmoid colon, and a part of the rectum