33 - Metabolism of ammonia – generation, toxicity, ammonia detoxification: reductive amination of alpha-ketoglutarate, glutamine synthesis, role of ammoniagenesis in kidney. Urea cycle – regulation, metabolic disorders. Glucose-alanine cycle.
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
sections
production
ammonia detoxification
location
urea cycle
glutamine synthesis
role of liver + muscle
oral box
production
derives from metabolism of AAs
transamination + deamination produces ammonia
ammonia detoxification
Ammonia si weak toxic base so needs to be detoxified/eliminated from body
done by circulation in liver to convert to urea
Toxic to CNS as reacts with alpha-KG to make glutamate
Depleted levels of alpha-KG leads to impairment of TCA
Location
liver → urea cycle
Brain → hepatic encephalopathy
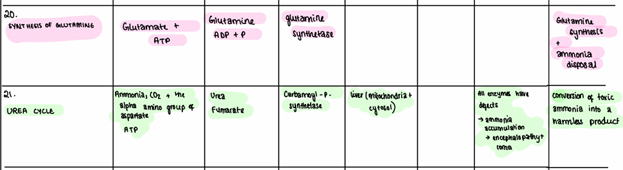
urea cycle
requires glutamate dehydrogenase reaction
Uses NAD/NADP to release nitrogen as ammonia
glutamine synthesis
fixes ammonia or glutamate and is catalysed by glutamine synthase
ammonia detoxified by ammoniagenesis:
by kidney as response to alkalosis
more bicarbonate secreted = lower glutamine metabolism + ammonia excretion
NH4+ produced in proximal tubules
role of liver + muscle
free AAs, alanine + glutamine are released from muscle into circulation
Alanine extracted by liver
glutamine → gut + kidney
glutamine is source of ammonia for excretion by kidney
oral box