GCSE AQA Geography- RIVERS -Physical Landscapes of the UK
1/90
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
91 Terms
What is a tribuatary?
A small stream or river that flows into the main river channel
What is a Confluence?
When two or more rivers meet
What is a watershed?
High ground that surrounds a drainage basin. The boundary fo a river basin
What is a source?
The start of a river
What is a mouth?
The end of a river
Define velocity
The speed at which water is moving through the channel. Measured in (m/s)
Define Gradient
The change in the slope of the river bed as it passes from source to mouth.
Define channel width
The distance from one bank to the other
Define channel depth
The distance from the surface of the water to the channel bed.
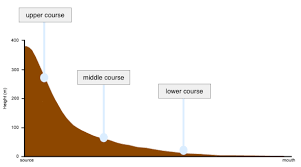
What is the name of this type of diagram?
A Long Profile of a River
What happens to the Channel Width and Depth as you travel downstream? Why?
It increases because vertical and lateral erosion occurs.
What happens to the velocity as you travel downstream? Why?
It increases as the friction between the water and the bed and banks decreases.
What happens to the discharge as you travel downstream? Why?
It increases as multiple rivers meet at tribuatories.
Define discharge
The amount of water passing a given point in a given time in a river.
How do you calculate discharge?
Velocity x Volume
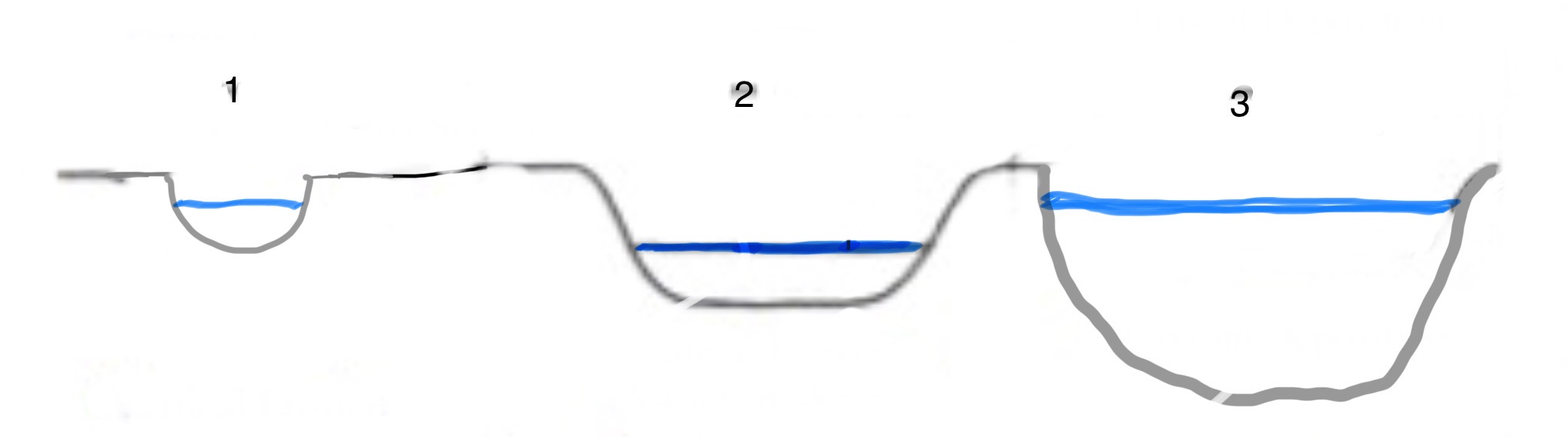
What part of the river’s course is 1?
The Upper Course
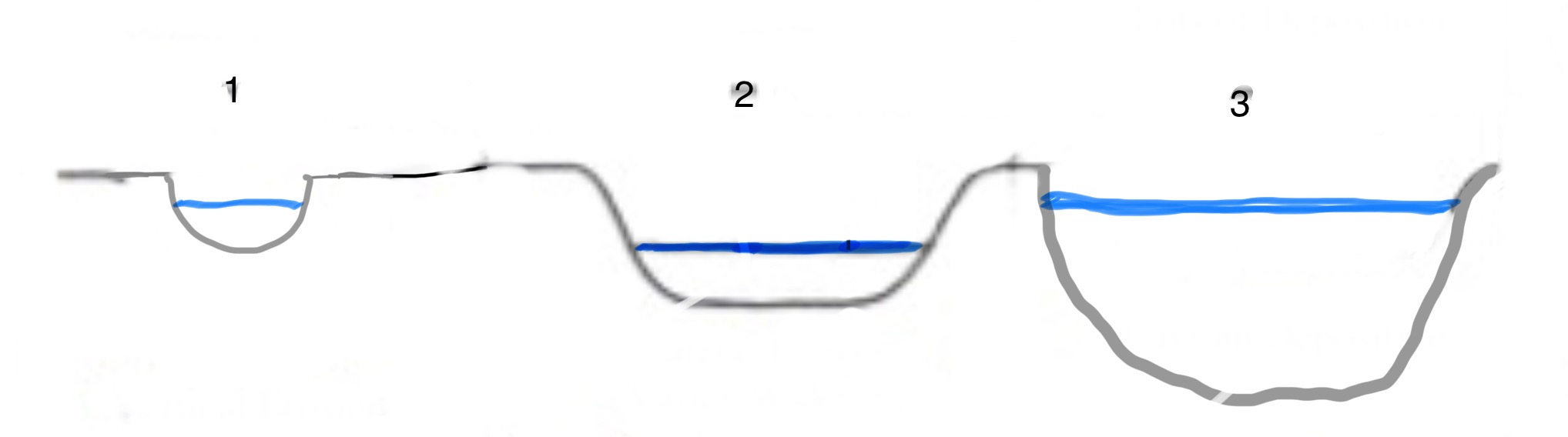
What part of the river’s course is number 2?
the middle course
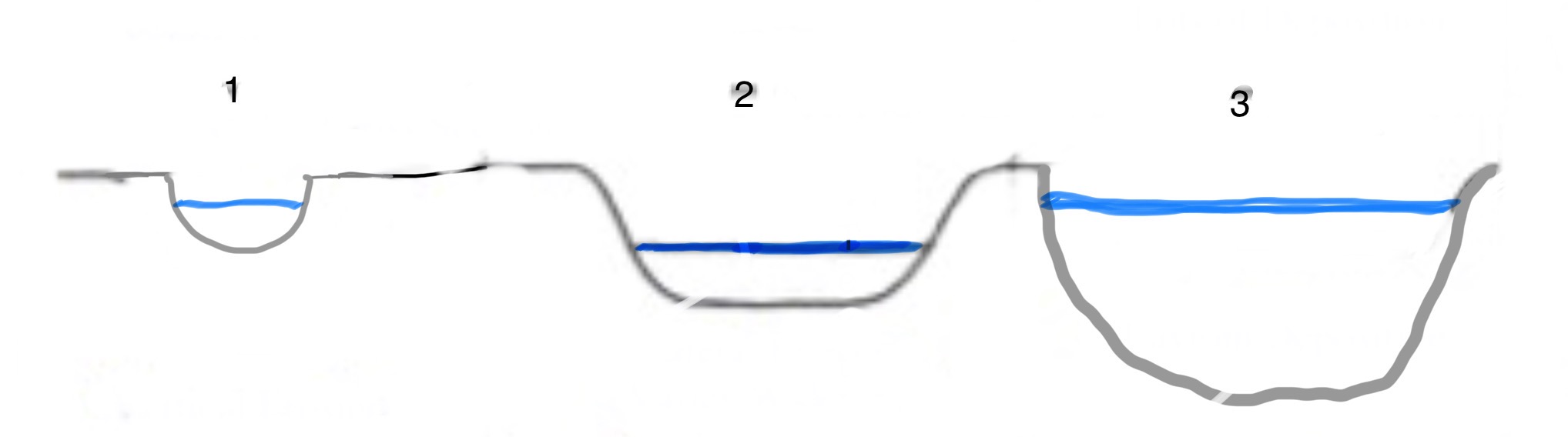
What part of the river’s course is number 3?
The Lower Course
Describe the Upper Course’s channel
Shallow and Narrow
What direction of erosion happens at the Upper Course?
Vertical erosion
What type of erosion happens at the Upper Course?
Hydraulic action, attrition and abrasion
What types of transportation happen in the Upper Course?
Traction and Saltation at high flow. Deposition of large material
Describe the channel in the middle course
Wider and deeper than the upper course
Describe the direction of erosion in the middle course
Some vertical erosion but mostly lateral erosion
What type of erosion becomes less important in the middle course?
Hydraulic Action
What is the main type of transportation present in the middle course? Are there any other types less prevalent?
Suspension is the main type. Saltation and Traction are still present.
What type of transport is more obvious in the middle course than the upper?
Deposition
Describe the channel of the Lower Course
The Widest and Deepest Channel
How much erosion is in the lower course? What direction does take place a little bit?
Very Little. Lateral erosion still occurs.
What is the dominant type of transportation in the lower course?
Suspension
What are the 6 types of erosion that occur in a river?
Hydraulic action, abrasion, attrition, solution, vertical erosion and lateral erosion.
Define solution (a type of fluvial erosion)
This is when river water dissolves some types of rocks.
Define vertical erosion
Erosion that makes the river channel deeper
Define Lateral erosion
Erosion that makes a river wider.
Name the four types of transportation that can happen in a river.
Solution, suspension, saltation and traction
When are the energy levels of a river usually at their highest?
In the Upper Course nearest to the source.
What is the relation between a river’s energy and the ability to transport sediment?
More energy = bigger particles able to be transported
Why do rivers deposit sediment? Give an example of when such conditions would take place.
When a river looses energy. For example, after a flood or when a river enters shallow water.
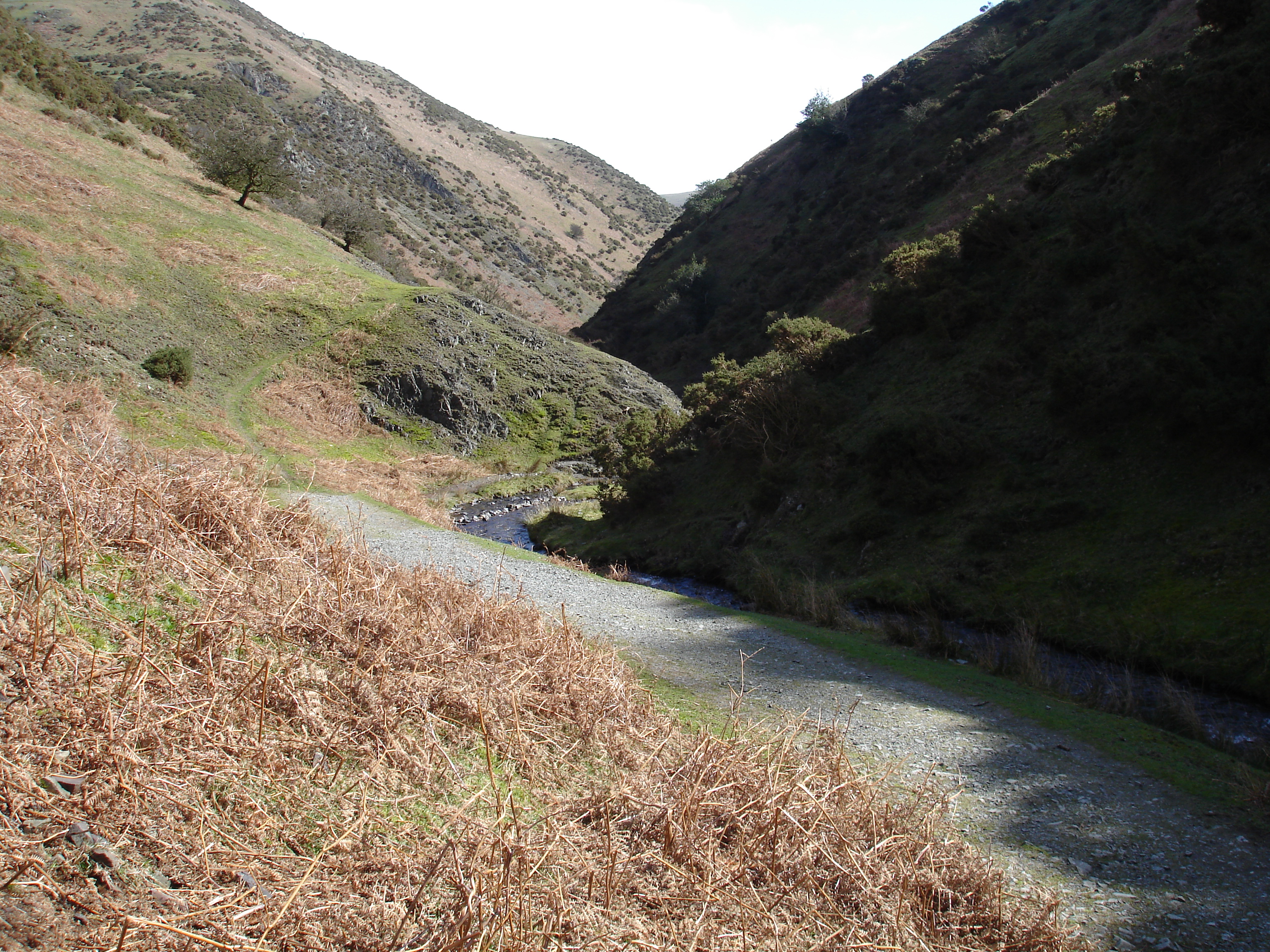

Identify these two river landforms
Interlocking Spurs and V Shaped Valleys
Where would you find interlocking spurs and/or V shaped valleys?
In the Upper course
Why do interlocking Spurs form?
As in the upper course there is more vertical erosion. If there are areas of hard rock which are harder to erode, the river will ben around it.
Why do V Shaped Valleys form?
The steep gradient of the upper course causes vertical erosion using hydraulic action, abrasion and solution
The valley sides are then exposed to freeze thaw which loosens the rock and steepens the valley/
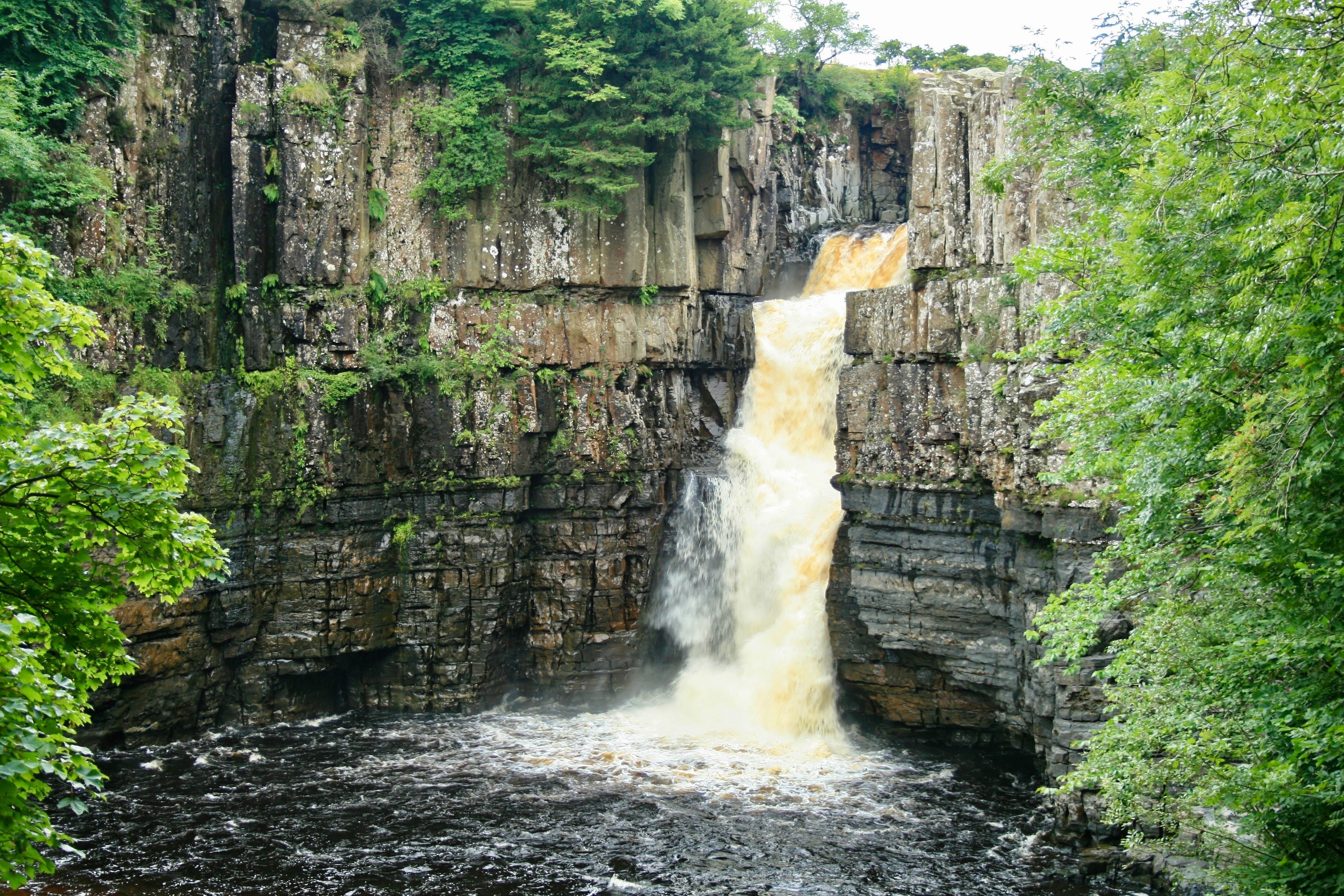

What is the name of this landform on the river Tees?
Waterfall
Where do waterfalls and gorges form?
In the Upper Course
Give the 6 Stages of a waterfall and gorge forming.
A river crosses a band of less resistant rock
The less resistant rock is eroded faster creating a step (by Hydraulic Action and Abrasion)
The force of the falling water creates a plunge pool at its base
The Plunge pool enlarges undercutting the cap rock
The cap rock collapses, enlarging the plunge pool by abrasion
The waterfall retreats forming a gorge

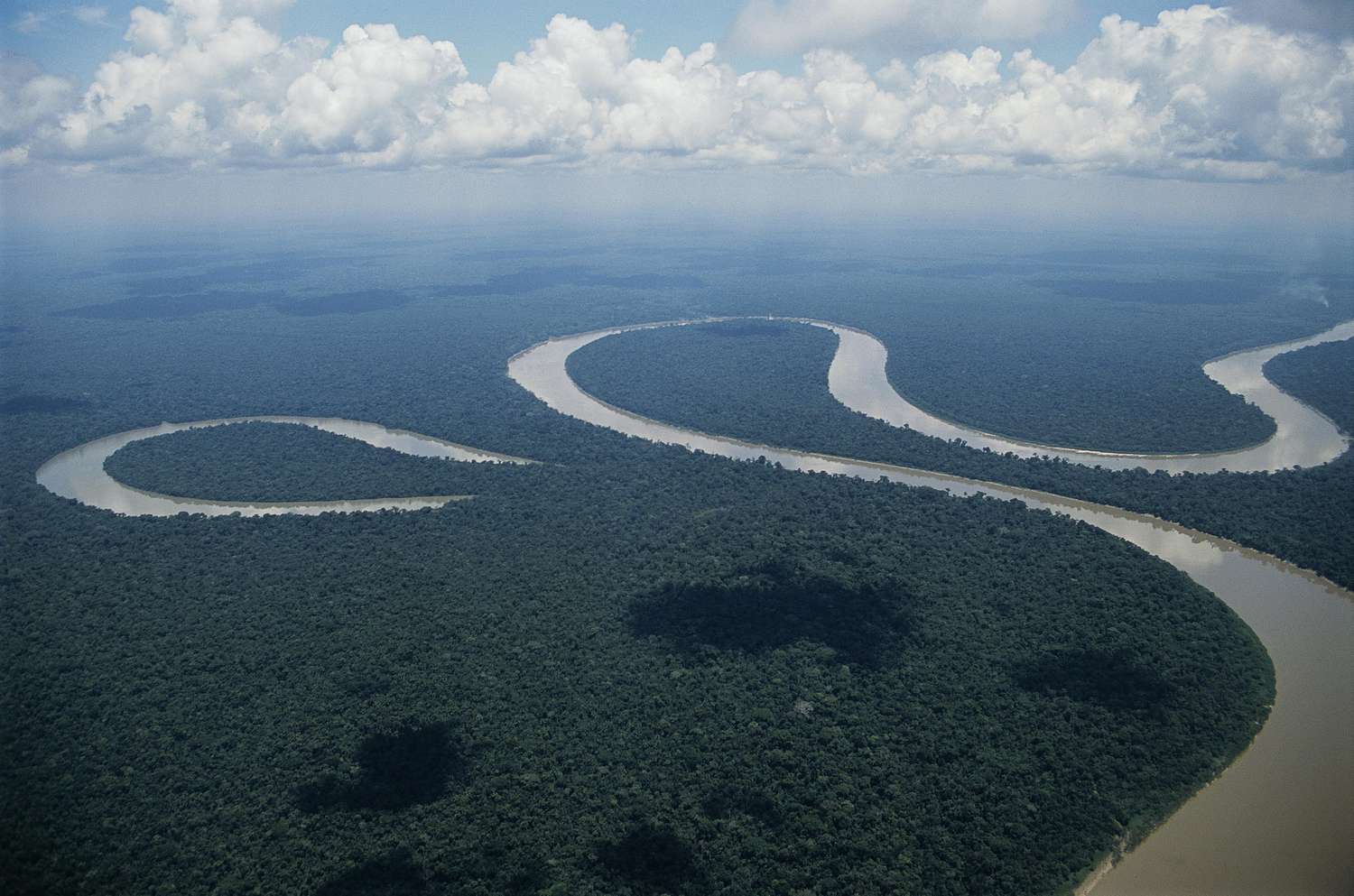
What is the name of this river landform on the river tees?
Meanders
Name the 4 stages of a meander forming
fast flowing water on the outside of the bank causes erosion through abrasion and hydraulic action
This makes the outside bend deeper and wider forming a river cliff
On the inside bend, the energy is much reduced so deposition occurs forming a slip off slope
Eventually this forms a meander.
What type of cross section does a meander have?
an asymmetrical cross section.

What river land form is this?
Ox bow lake
Describe the 5 steps of an ox bow lake forming.
The river has a meander which is eroding laterally on the outside bends
The neck of the meander is narrowed
Often due to a flood the river will cut through the neck
The river continues on this straighter path.
Deposition leads to the meander being cut-off forming an ox bow lake
Describe the conditions needed for a Levee to form.
The river is on a floodplain with a low gradient and is mainly depositing.
Name the three steps which create a levee
The river floods, depositing silt onto the river bank. Between floods the silt builds up on the river bed. This creates levees.
What are levees?
Naturally raised river banks found on either or both sides of the floodplain.
What do levees protect against?
Flooding
Describe the soil of the floodplain which makes it good for agriculture.
It is fertile as it is rich in alluvium.

What is this a picture of?
Levees
What is an estuary?
An estuary is the tidal part of a river, where the channel widens as it reaches the sea.
How did estuaries form?
Sea levels rose after the ice age, and low lying valley sides either side of the river were flooded forming an estuary
Within an estuary, when is sediment deposited?
When fresh and salt water meet and during rising tide.
What are three physical reasons for increased flood risk?
Precipitation, Geology and Steep slopes
How does geology increase flood risk?
Impermeable rocks encourage water to flow straight into river channels, essentially creating surface run off.
What are three human reasons for increased flood risk?
Urbanisation, Deforestation and Agriculture
How does urbanisation affect flood risk?
By creating impermeable surfaces, water moves quickly due to surface run off and via drains and sewers
How does deforestation affect flood risk?
Trees act as interception, storing water on leaves and branches and within the roots. When removed lots more water is flowing.
How does agriculture affect flood risk?
Water can flow very quickly across ploughed fields and soil left less permeable due to being exposed and unused.
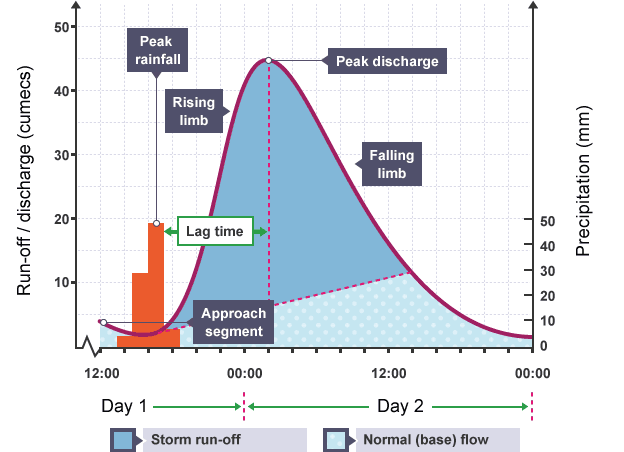
What is the name of this type of graph?
A Hydrograph
What is a hydrograph?
A graph that plots river discharge after a storm
How is rainfall shown on a hydrograph?
Shown as a bar graph in mm.
How is discharge shown on a hydrograph?
Show as a line graph in m/s
What is basin lag time on a hydrograph?
Time difference between the peal of the rain storm and the peak of the flow of the river.
How does basin size affect the shape of a hydrograph?
Small Basins often lead to a quicker water transfer compared to large basins.
How does drainage density affect the shape of a hydrograph?
A high density speeds up the water transfer compared to low density.
What are the 4 types of hard engineering for river management?
Dams and Reservoirs, Channel Deepening and Straightening, Artificial Embankments and Flood Relief Channels
What are dams and reservoirs?
A dam is a large barrier which causes valleys to flood behind and creates an artificial lake known as a reservoir.
What are three downsides of dams and reservoirs?
Social- can displace families
Economic- they are expensive
Environmental- Building could trigger landslides
What are three benefits of damns and reservoirs?
Social- Source of drinking water
Economic- boosts tourism
Environmental- can promote new habitats
What are three downsides to channel deepening and straightening?
Social- flooding risk is increased in some areas
Economic- Expensive
Environmental- endangers animals and destroys habitats
What are three benefits to channel deepening and straightening?
Social- reduces flood risk in some areas
Economic- gives home owners confidence to invest in their property
Environmental- There are none ):
What are three downsides to artificial embankments?
Social- river is not easily accessible for activities
Economic- Constant monitoring and repairs
Environmental- Unattractive
What are three benefits of artificial embankments?
Social- walking routes provided
Economic- relatively cheap
Environmental- habitats provided for riverbank animals
What are three downsides to flood relief channels?
Social- settlements downstream at higher risk of flooding
Economic- Expensive
Environmental- habitats disturbed
What are three benefits to flood relief channels?
Social- Removes the risk of flooding
Economic- value of homes increased
Environmental- If Artificial reed beds and grass covers concrete sides- habitats provided
What are the four types of soft engineering for river management?
Flood warnings and preparation, flood plain zoning, planting trees and river restoration
What are three benefits of flood plain zoning?
Social- risk of flooding is reduced due to no impermeable surfaces built
Economic- low cost, only administration costs
Environmental- Important green spaces provided
What are three downsides to flood plain zoning?
Social- worsening the housing shortage in the UK
Economic- housing prices increase due to scarcity of houses
Environmental- increased building on other greenfield sites to compensate
What are two benefits of flood warnings and preparation?
Social- can make people feel more secure and in control
Economic- very cheap
What are two downsides to flood warnings and preparation?
Only effective if people listen and take action, and the clear up operation can be distressing
What are three benefits to planting trees as river management?
Social- Reduces the risk of flooding by reducing surface run off
Economic- Inexpensive
Environmental- creates habitats and increases biodiversity, as well as taking in CO2
What are two downsides of planting trees as river management?
Changed appearances and loss of grazing land
What are three benefits of river restoration?
Social- decreases risk of flooding by increasing water storage areas
Economic- Increases tourism as it is aesthetically pleasing
Environmental- creates new wetland habitat, increasing biodiversity.
What are two downsides to river restoration?
Social- not always the most effective or practical
Economic- initial costs are high