Biomedical Science - Unit 1 DNA
1/29
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
30 Terms
James Watson and Francis Crick
Discovered that DNA was double helix
Nucleotide
Building block of DNA
Nucleotide Bases
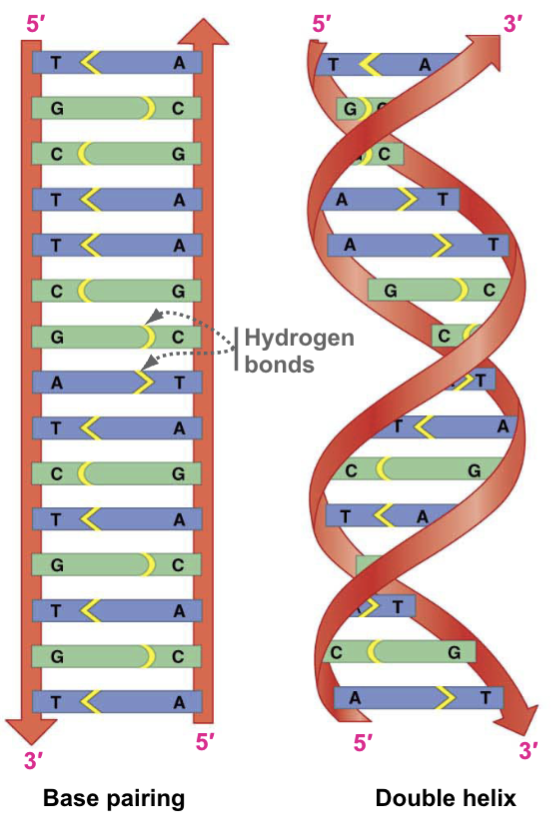
Fundamental building blocks of DNA and RNA. They include adenine, guanine, cytosine, and thymine. A pairs with T and C pairs with G, and hydrogen bonds form in between them.
Sugar Phosphate Backbones
Structural framework of DNA and RNA molecules. Forms sides of DNA doble helix
Purine-purine
Not enough space in double helix
Pyrimidine-pyrimidine
Too much space in double helix
Purine-pyrimdine
Just right space in double helix
Antiparallel
In a double stranded DNA, backbones must run in this direction
X-Ray Crystallography
Determines position of atom in molecule
Schematic Diagrams of DNA Structure
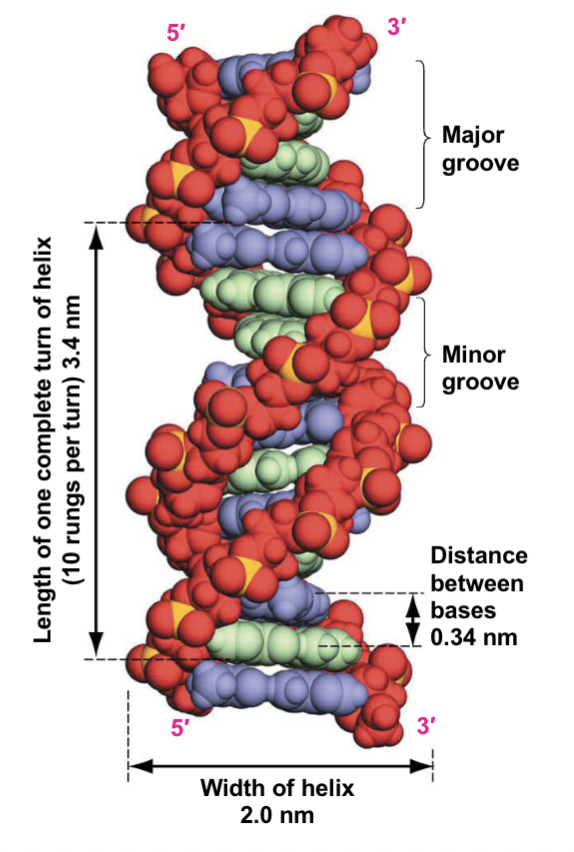
Space-filling Model of DNA Double Helix
Non-covalent Interactions
Interactions between any 2 molecules or between different groups of the same molecule that don’t involve covalent sharing of electrons. Allows molecules to attract to each other. Examples: hydrogen bonds (permanent dipole), ionic, and hydrophobic effect
Induced Dipole
Non-polar bonds; bunch of electrons orbiting around. Creates a weak dipole (ripple effect). Temporary shift of electrons in a molecule or atom that creates a temporary dipole, only lasts a fraction of a second because they even out. Occurs in O2, N2, CH4. Examples: interactions between noble gases (e.g., He–He) or non-polar hydrocarbons.
Permanent Dipole
Polar bonds; one positive, one negative pole. Unequal sharing of electrons in a covalent bond due to differences in electronegativity. Occurs in HCl, H₂O, NH₃. One atom pulls electrons more strongly than the other, making one side partially negative (δ⁻) and the other partially positive (δ⁺). Examples: Water molecules attract each other through dipole-dipole interactions.
Ionic Bonds
Permanent dipole can induce a dipole in another molecule. Complete transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal, forming oppositely charged ions. Occurs in NaCl, MgO, CaF₂. Strongest type of bond. Example: Sodium chloride (Na⁺Cl⁻), held together by strong electrostatic attraction.
How Mutations Occur
When sequence of the DNA basis is changed
Polymorphic Traits
Trait that appears commonly in two or more different forms
George Mendel
Worked on how genes are passed down through one generation to the next through his pea experiment. (Genetic determinant for wrinkled genes = recessive, for round seeds = dominant). Found 3:1 dominant to recessive
Parental Cross (P)
First cross
Fillial (Fl)
Offspring
Genes
Segments of four types of nucleotides in a segment of DNA
Traits
Controlled by genes
Two
How many alleles does each individual carry for each gene
Genotype
Combination of alleles found in an individual
Principle of Independent Assortment
Alleles of different genes are transmitted independently of each other
Pedigrees
Used to examine inheritance of normal traits (or disease traits) in families
Segregation
Separation of two alleles (50 50 chance you’ll get either of them)
DNA
Molecule that stores instructions for building proteins
Transcription
The process by which a gene’s DNA sequence is copied into messenger RNA (mRNA).
Translation
The process by which the mRNA sequence is used to build a protein (a chain of amino acids) in the ribosmoe