ET&P adaptations to aerobic training
1/68
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
69 Terms
when do we see the greatest improvement occur with measuring aerobic capacity
greatest improvement occurs when test exercise duplicates training exercise
When training for specific aerobic activities, overload must:
1.Engage appropriate muscles required by activity
2.Provide exercise at a level sufficient to stress
cardiovascular system
how does overloading specific muscles with endurance training enhances perfromance and aerobic power how?
by facilitating O2 transport to and O2 use by trained muscles
greatest blood flow in active tissues with aerobic training and overload result from:
-Increased microcirculation
-More effective redistribution of cardiac output
-Combined effect of both factors
adaptations in muscles only occur how?
when specifically trained and become apparent in exercise that activates it
what percent did swim training improve VO2 max during vs running?
swimming → 11%
running → 1.5%
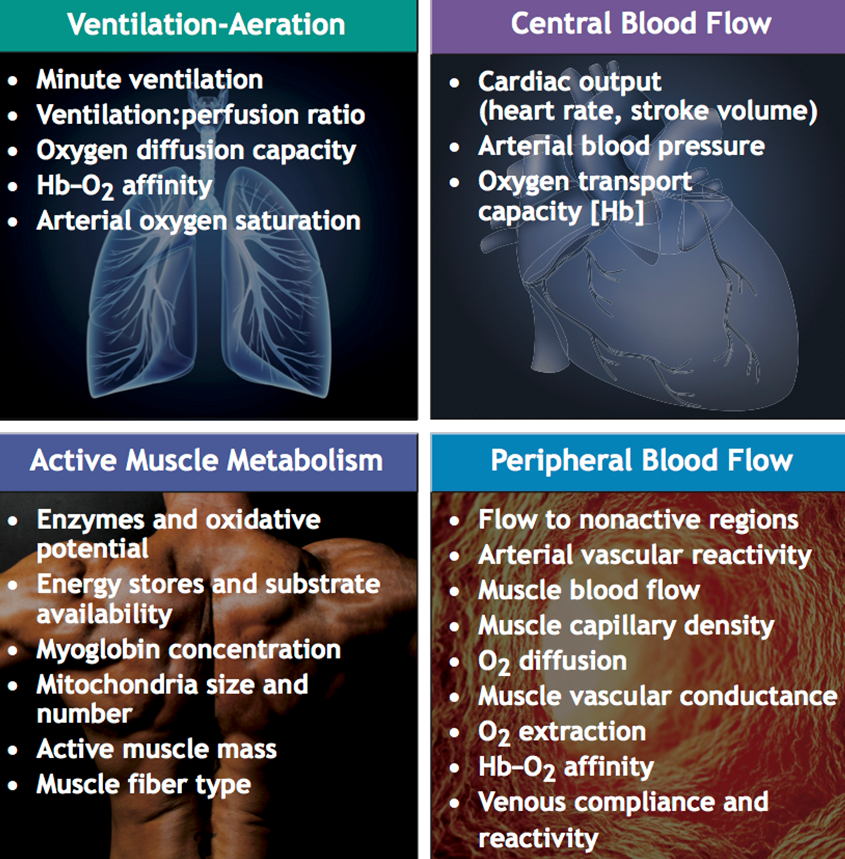
the four categories of diverse physiologic and metabolic factors related to O2 transport and use::
ventilation-aeration (lungs)
central blood flow (heart)
active muscle metabolism
peripheral blood flow → arms, legs, etc.
with training, are positive adaptations inepedent or dependent on race, gender, age, and health status?
independent
(metabolic adaptation) true or false, aerobic training improves capacity for respiratory control in skeletal muscle?
true
why/how does aerobic training improve respiratory control capacity in skeletal muscle?
-Endurance-trained skeletal muscle fibers contain larger and more numerous mitochondria than less active fibers
-Mitochondrial enzyme activity increases
by 50% (mito. is where ETC happens → ATP)
by how much does mitochondrial enzyme activity increase with aerobic training?
50%
reasons how aerobic training increases intramuscular fatty acid oxidation:
Greater blood flow within trained muscle
More fat-mobilizing and fat-metabolizing enzymes
Enhanced muscle mitochondrial respiratory capacity
Decreased catecholamine release for the
same absolute power output
know these
what happens with carb metabolism in aerobic training?
trained muscle exhibits enhanced capacity to oxidize carbs during maximal exercise
what does reduced carbs as fuel and increased fatty acid combustion in submaximal exercise result from?
decreased muscle glycogen use
reduced glucose production
reduced use of plasma-borne glucose
explain the muscle fiber type and size results from aerobic exercise:
enhanced metabolic adaptations in each muscle fiber type
all fibers maximize existing aerobic potential
endurance athletes have larger ST-fibers than FT-fibers in the same muscle
what kind of fiber type do endurance athletes have more of?
endurance athletes have larger ST-fibers than FT-fibers in the same muscle
do slow or fast twitch fibers have a high capacity to generate ATP?
slow
ST fibers with high capacity to generate ATP aerobically contain large quantities of what?
myoglobin
explain “athletes heart”
long-term aerobic training increases heart’s mass and volume with greater left-ventricular end-diastolic volumes during rest and exercise
LVH= left ventricular hypertrophy- long term adaptation
cardiac enlargement is characterized by what?
characterized by eccentric hypertrophy and concentric hypertrophy
endurance athletes average what percent larger heart volume than sedentary counterparts?
25%→ training duration affects cardiac size and structure
what is similar to heart size in illness vs from exercise? why?
disease induces considerable cardiac enlargement like exercise
with disease, typically increase in BP and hypertrophy of the LV
patholigic “hypertrophied” heart; enlarged, distended, functionally inadequate organ unable to deliver blood sufficient for resting requirements
exercise training in healthy imposes temporary myocardial stress so rest periods provide for recuperation
what does athlete’s heart not reoresent?
does not represent dysfunctional organ
→ rather demonstrates normal systolic and diastolic functions and superior fucntional capacity
what percent increase occurs in plasma volume after 3-6 aerobic training sessions?why?
12-20%
increases quickly bc of retained electrolytes and fluids do to hormonal changes
immediate, acute and chronic response
what does plasma volume increase enhance?
enhances circulatory reserve and increases end-diastolic volume, stroke volume, O2 transport, VO2max, and temp regulation during exercis
within how many weeks does expanded plasma volume return to detraining levels within?
1 week
what does training to do HR
decreases intrinsic firing rate of SA node pacemaker tissue
contributes to resting and submaximal exercise bradycardia in trained endurance athletes, or the previously sedentary who train aerobically
submaximal HR for standard exercises decreases by how many beats per minute with endurance training?why?
12-15
→smaller HR decrease for resting HR
→ reduction coincides with increased max stroke volume and cardiac output
endurance training causes SV to do what during rest and exercise regardless of age or gender?
increase
increase blood→ heart has to adapt→ increase volume to grow mass
factors that increase stroke volume:
increased internal LV volume and mass
reduced cardiac and arterial stiffness
increased diastolic filling time (decreased HR increases this)
improved intrinsic cardiac contractile function (more forceful contraction)
do endurance athletes heart exhibit larger or smaller SV during rest and exercise?
larger
when does the greatest SV increase during upright exercise for trained and untrained occur?
occurs in transition from rest to moderate exercise
max stroke volume occurs in SV between what percent of VO2max in untrained?
40-50%
for untrained, is there a large or small increase in SV during transition from rest to exercise?
small
for endurance athletes, HR and SV increase to increase what?
cardiac output→ how much blood can we push around the body
what is the most significant cardiovascular adaptation with aerobic training? why?
increase in max cardiac output
→ results directly from improved SV
in trained athletes, what kind of relationship does cardiac output and VO2 have throughout the major portion of exercise intensity?
linear relationship
a training-induced reduction in submaximal cardiac output reflects what factors?
more effective redistribution of blood flow
trained muscles enhanced capacity to generate ATP aerobically at a lower tissue Po2 (in mito.)
how does aerobic training effect O2? what does it increase? why/how?
increases quantity of O2 extracted from circulating blood
→ results from more effective cardiac output distribution to active muscles combined with enhanced capacity of trained muscle to extract and process available O2
increase amount of O2 in aterial blood
decrease amount of O2 in venous blood
why might someone have low cardiac output and lower muscle blood flow in submaximal exercise int training? maximal?
bc heart and blood is so effective, it doesn’t need to pump as hard
rapid trianing induced changes in vasoactive properties of alrge arteries and local resistance vessels within skeletal and cardiac muscle
muscle cell changes that enhance oxidative capacity
maximal;
larger maximal cardiac output
greater blood flow distribution to muscle from non-active areas
enlargment of cross-sectional areas of arteries (is muscle; carries blood away) and veins; 20% increase in capillarization muscle
what is your pulse?
blood being pushed
what vascular modifications occur regarding myocardial vlood flow?
increase in cross-sectional area of proximal coronary arteries, possible anterior proliferation and longitudinal growth, recruitment of collateral vessels, and increased capillary density
→ provides adequate perfusion for icnreased blood flow and energy demands
training increasses coronary blood flow and capillary exchange from;
→ structural remodeling to improve vascularizaion
→ more effective control of vascular resistance and blood distrubution within myocardium
how does regular aerobic training impact sustolic and disatolib BP during rest and submax exercise?
reduce
→ largest reduction occurs in systolic pressure, particulary in hypertensive subjects
how does endurance trianing impact blood lactate levels?
lowers blood lactate levels and extends exercise before OBLA during exercise of increasing intensity
endurance training lowers blood alctate levels and extends exercise before OBLA during exercise of increasing intensity by:
decreasing rate of lactate formation during ex.
increasing rate of lactate clearance during ex
combined effects of decreasing lactte formation and icnreasing alctate removal
what is the relationship in percent for HRmax and VO2 max?
increase in VO2 max %=increase in Oxgyen (the gap closes)
aerobic capacity improves if exercise intensity maintains HR between what percentof max? what body exercise?
55-70%
→ HR increase equals about 40-55 of VO2max
Karvonen method
(Vo2 amx)
HR threshold=HR rest + 0.60 (can be changed) (HRmax-HRrest)
what msut happen as we continue to train to achieve desired exercise HR?
exercise level must increase
not srressing heart=not training hard enough
look at slide34
HR max during swimming or performaing other upper-body exercises averages what percent higher or lower fro trained and uintrained than for running? why?
13 beats/min lower
less feed-forward stimulation from motor cortex to medulla during swimming
less feedback stimulation from smaller, active upper-body muscle mass in swimming
horizontal body position and cooling effect of water during swimming
what level of alctate threshold is most effective to exercise at? why?
at or slightly above
higher exercise levels produce greatest benefits
need to evaluate blood lactate/exercise intensity relationship (intensity adjusted as fitness improves)
what si the distinction between %HRmax and lactate threshold?
%HRmax method establishes level of exercise stress to overload central circulation
exercise intensity from lactate threshold reflects capacity of what?
reflects capacity of peripheral vasculature and active muscles to sustain steady-rate aerobic metabolism
blood lactate concentration goal for intensity marker
4mmol
is there a duration threshold per workout for optimal aerobic improvement? if so, what? if not, why?
no
→ if there is, it likely depends on interaction of four variables:
total work accomplished (volume)
exercise intensity
training frequency
initial fitness level
more frequent training produces beneficial effects when training at what kind of intensity?
lower intensity
for weight loss with exercise each session should last how long and how many kcals burned?
last minimum 60 mins
300 kcals or more
typical aerobic training programs take place how many days/week
3
is maintaing constancy for exercise intensity, duration, and frequency produce training response independent or dependent of training mode, provided exercise involves large muscle groups?
independent
how long does aerobic fitness improvements occur?
within several weeks
adaptive responses eventually level off as subjects approach genetically predisposed max
cardio adaptations occur with short-term ex. training in young men and women
does strenous exercise enhance level of fitness regardless of genetic background?
yes
what are limits for developing fitness capacity linked to with trainign and genes?
link to natural endowment
genotype dependency exists for much of one’s what?
one’s sensititvity in repsonding to max aerobic and anaerobic power training, including adaptations of msot muscles enxzymes
factors in formulating effective aerobic training;
cardiovascular overload must be intense enough to sufficiently overload SV and cardiac output
cardiovasular overload must occur from activation of sport-specific muscle groups to enhance local circulation and muscle’s metabolic machinery