Neck and Salivary Glands
1/95
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
96 Terms
A congenital diverticulum of the brachial cleft located directly below the angle of the mandible.
Brachial cleft cyst
Bulging of the eyeballs
Exophthalmos
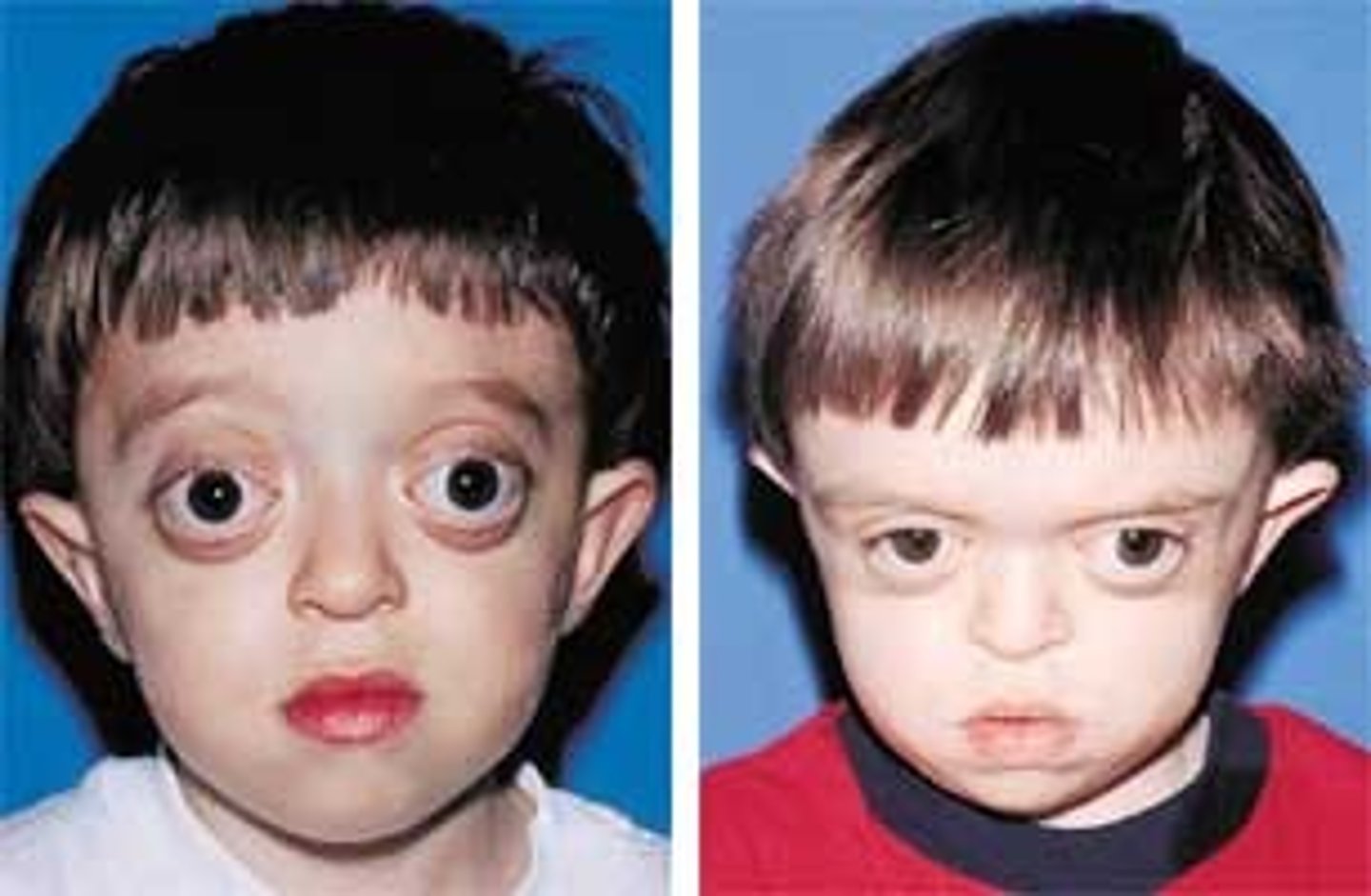
Exophthalmos (bulging of the eyeballs) is associated with _____.
Hyperthyroidism
Subacute thyroiditis secondary to a viral infection.
De Quervain syndrome
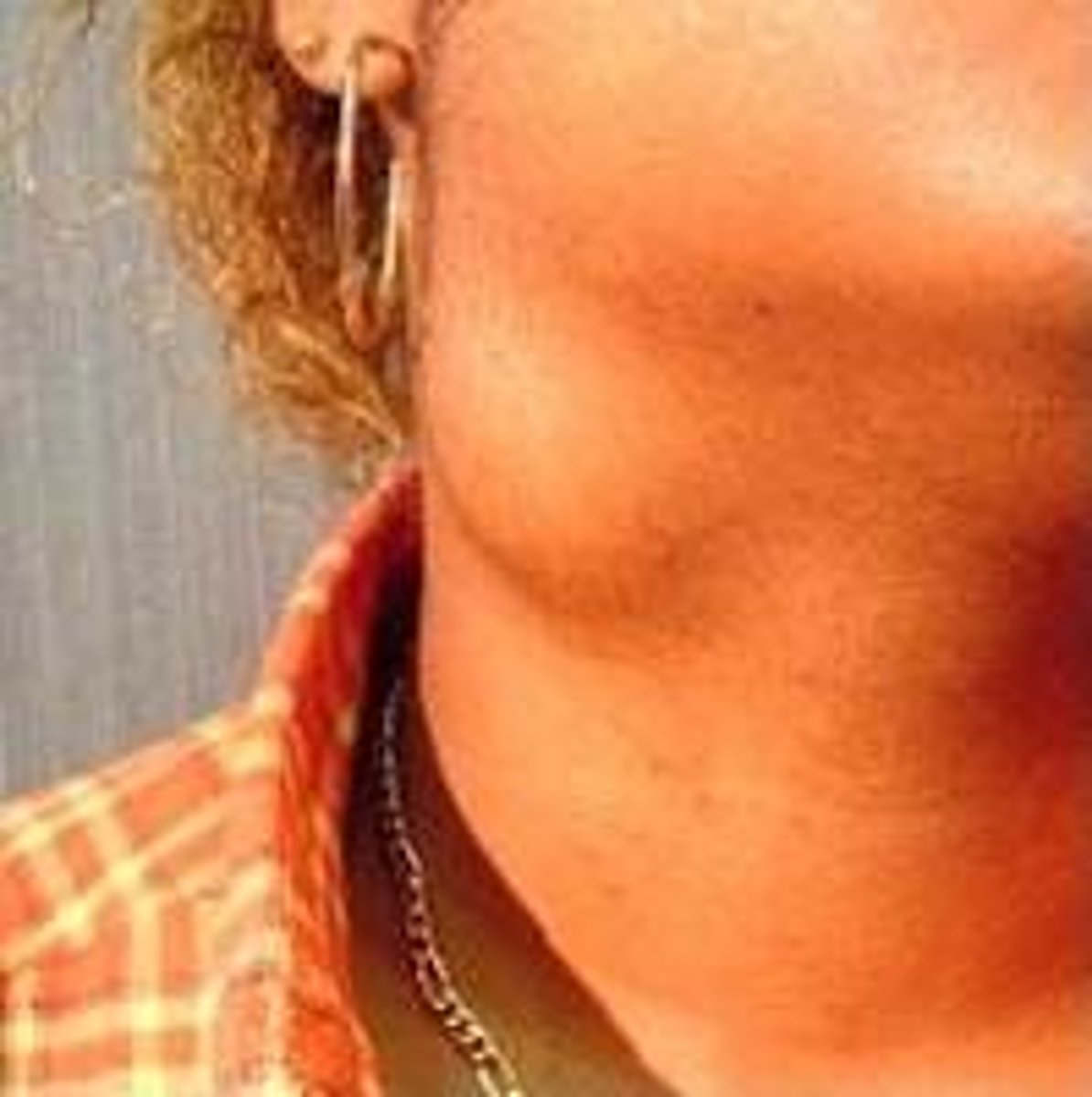
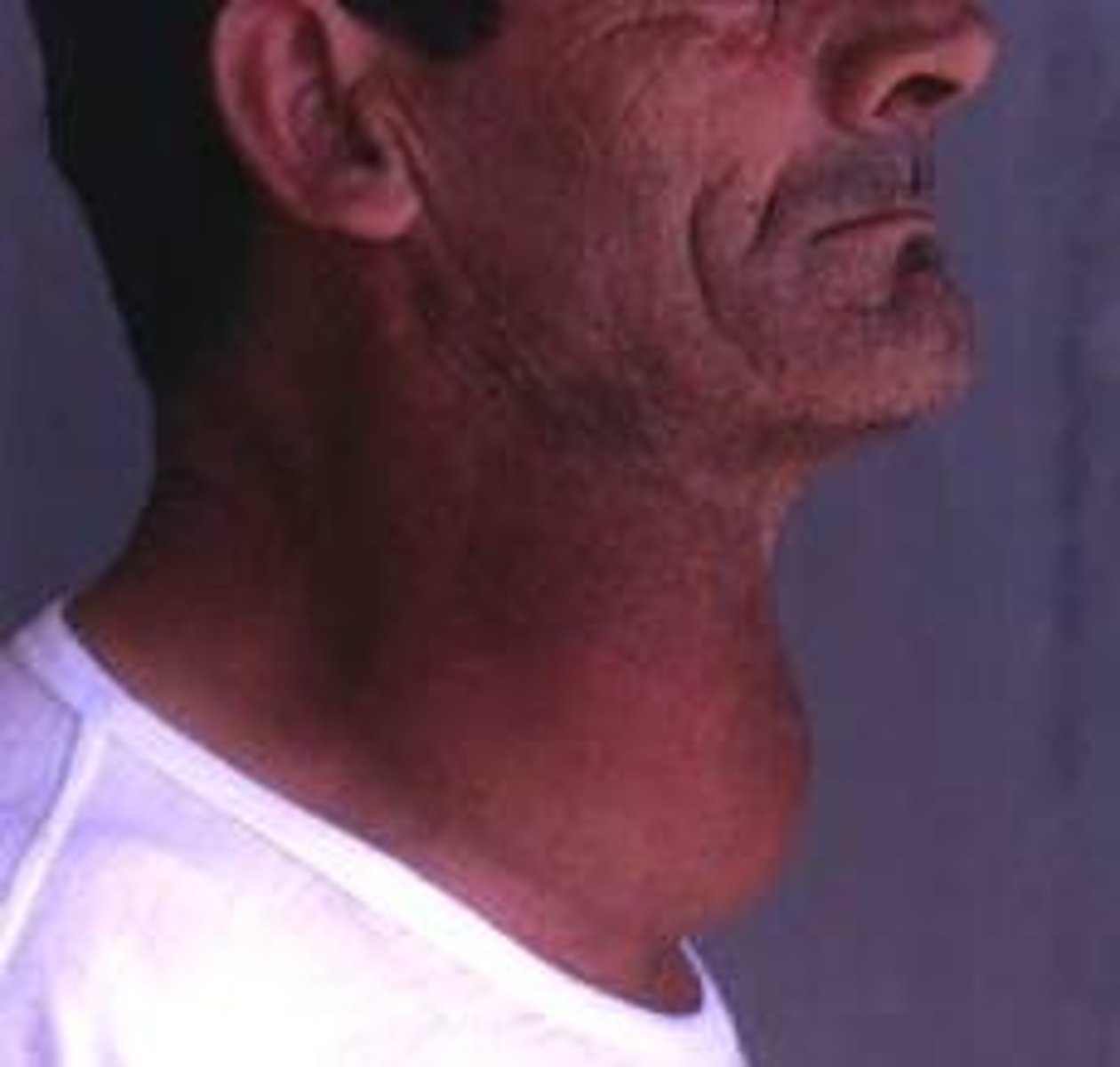
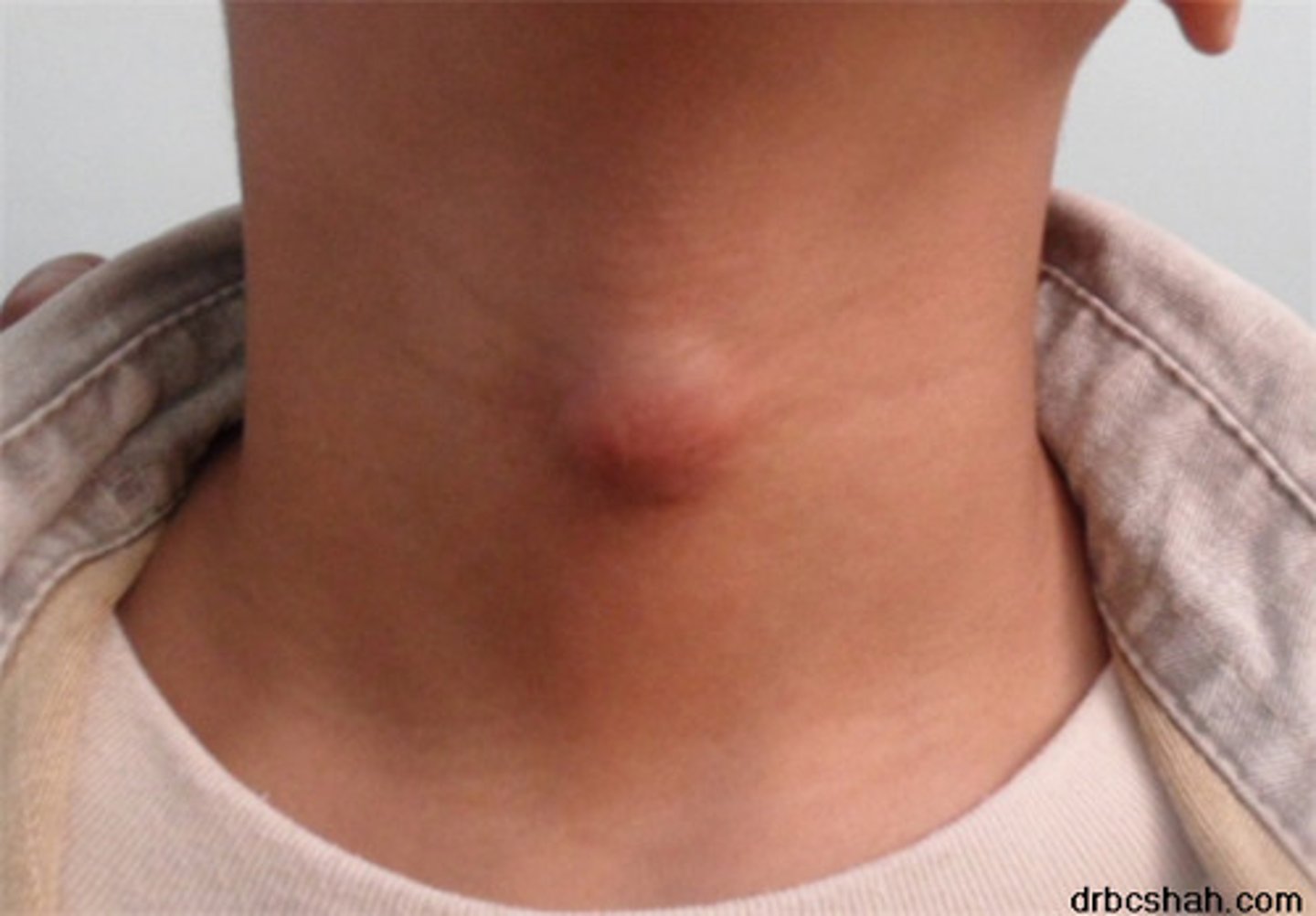
A pronounced swelling of the neck caused by an enlarged thyroid gland.
Goiter
A multisystemic autoimmune disorder characterized by pronounced hyperthyroidism; usually associated with an enlarged thyroid and exophthalmos.
Graves disease
A progressive autoimmune inflammatory disorder of the thyroid gland; most common cause of hypothyroidism; associated with an increased risk of developing a thyroid malignancy.
Hashimoto disease
What is the most common cause of thyroid enlargement in children and hypothyroidism in adults?
Hashimoto disease
An excessive amount of calcium in the blood; associated with hyperparathyroidism.
Hypercalcemia
Hypercalcemia is associated with ______.
Hyperparathyroidism
Excessive function of the parathyroid glands; may lead to osteoporosis and nephrolithiasis.
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperactivity of the thyroid gland; associated with Graves disease.
Hyperthyroidism
Graves disease is associated with _____thyroidism.
Hyperthyroidism
A deficiency of calcium in the blood; associated with hypoparathyroidism.
Hypocalcemia
Hypercalcemia is associated with _____.
Hypocalcemia is associated with _____.
Hyperparathyroidism
Hypoparathyroidism
A condition of insufficient secretion of the parathyroid glands; associated with hypocalcemia and primary parathyroid dysfunction.
Hypoparathyroidism
Decreased activity of the thyroid gland; associated with Hashimoto disease.
Hypothyroidism
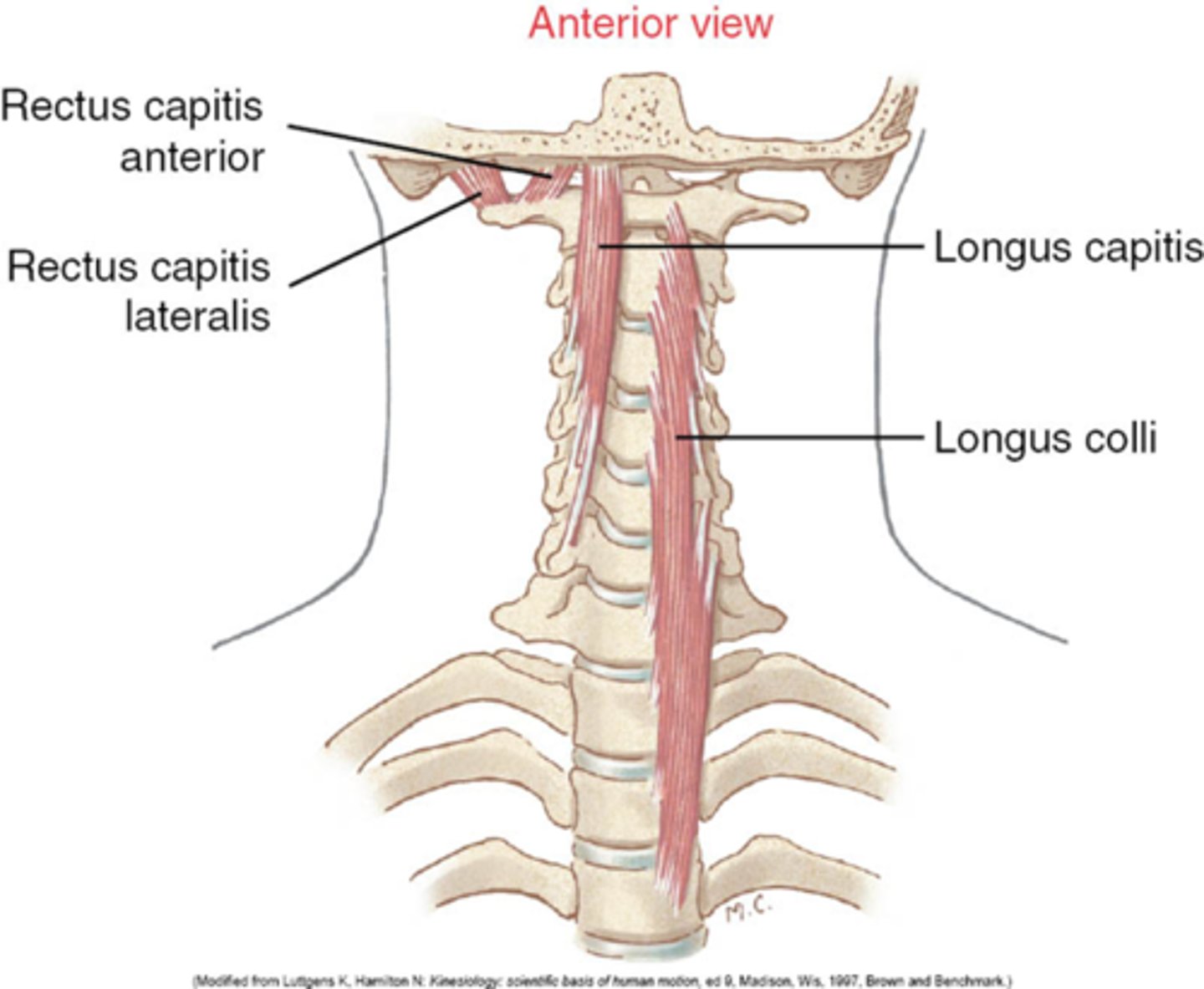
Neck muscles located on the anterior surface of the vertebral column, between the atlas and the 3rd thoracic vertebra; commonly associated with whiplash injuries.
Longus colli muscles
The most severe form of hypothyroidism; characterized by swelling of the hands, face, and feet; may lead to coma and death.
Myxoedema
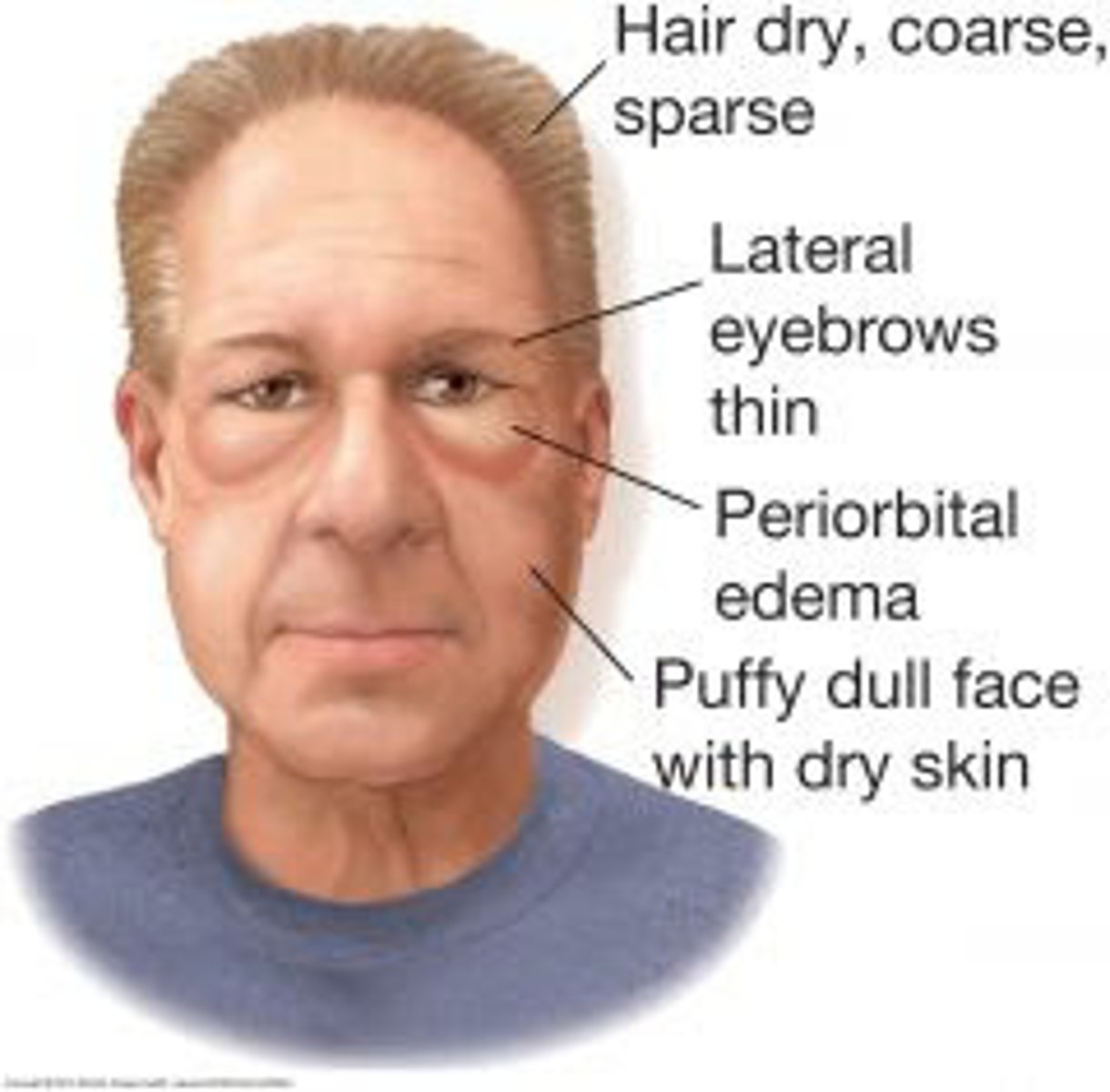
Myxoedema is characterized by swelling of the ____, ____, and ____.
Hands, face, and feet
Myxoedema is the most severe form of _____.
Hypothyroidism
A transient thyroiditis seen following pregnancy.
Postpartum thyroiditis
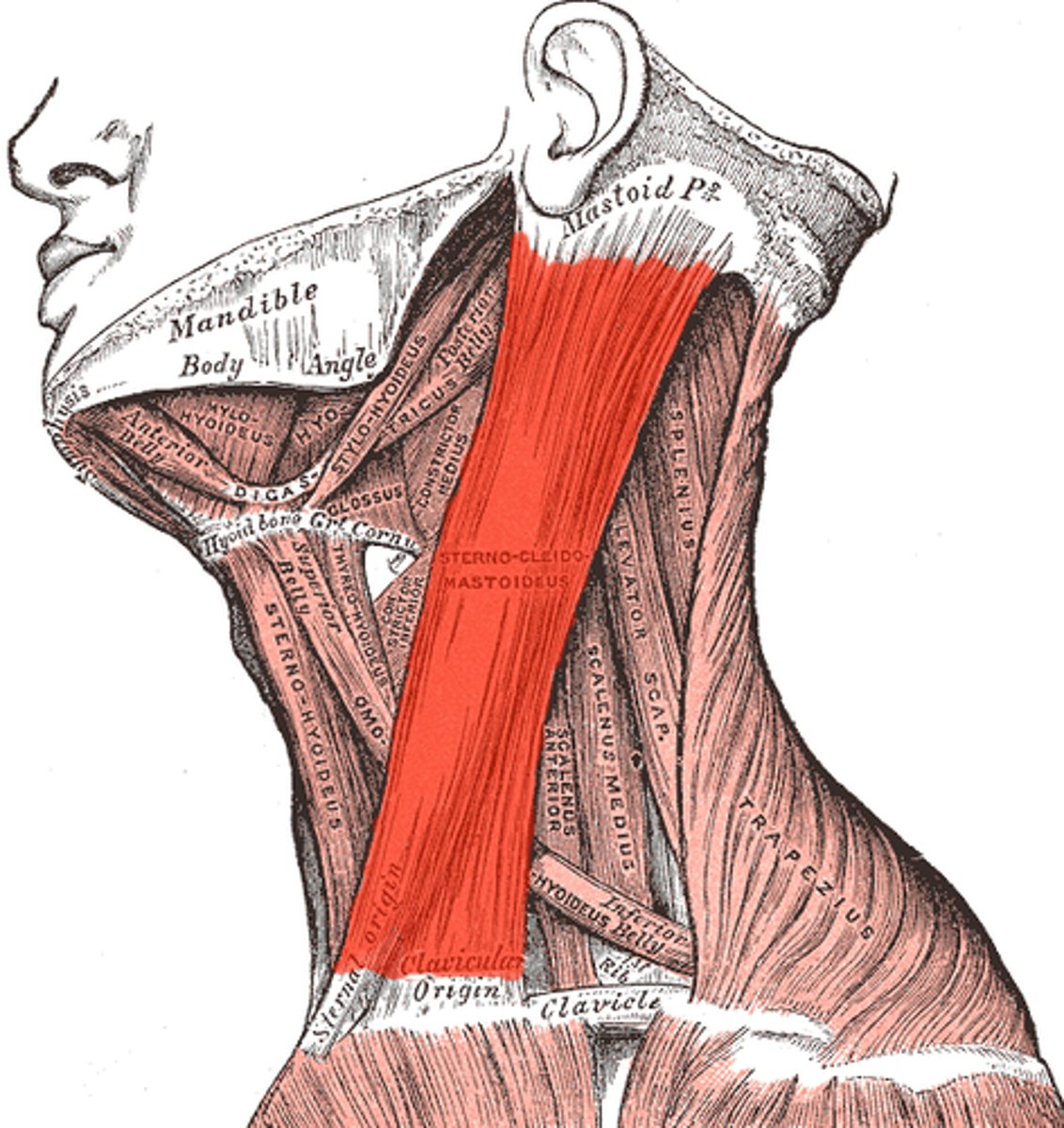
Lateral and superficial neck muscles that attach to the sternum, clavicle, and the mastoid process of the temporal bone; act to flex and rotate the head.
Sternocleidomastoid muscles
A group of long and flat muscles located anterior and lateral to each thyroid lobe; includes the sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and omohyoid muscles.
Strap muscles
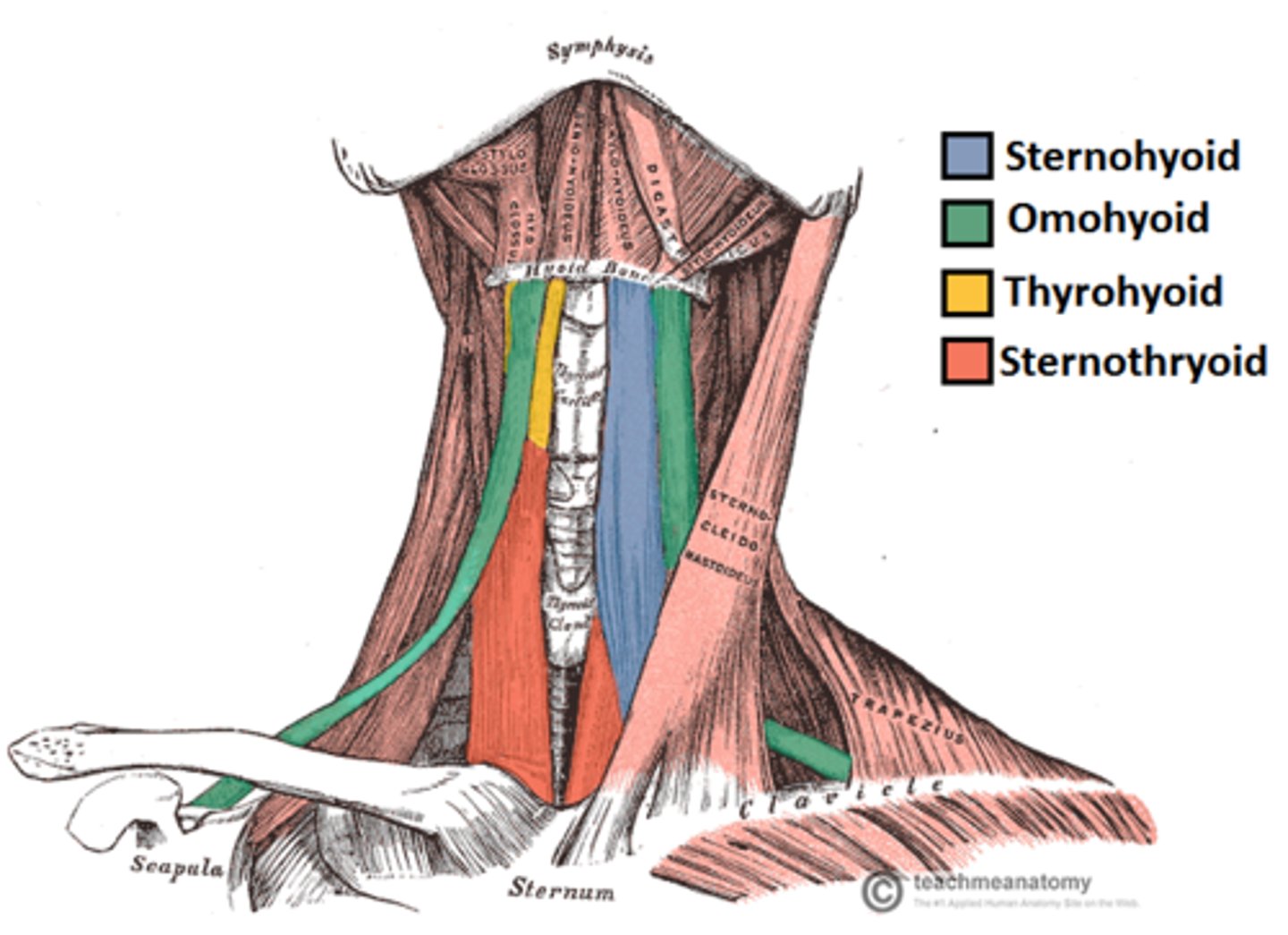
What are the 3 strap muscles?
Sternohyoid, sternothyroid, and omohyoid
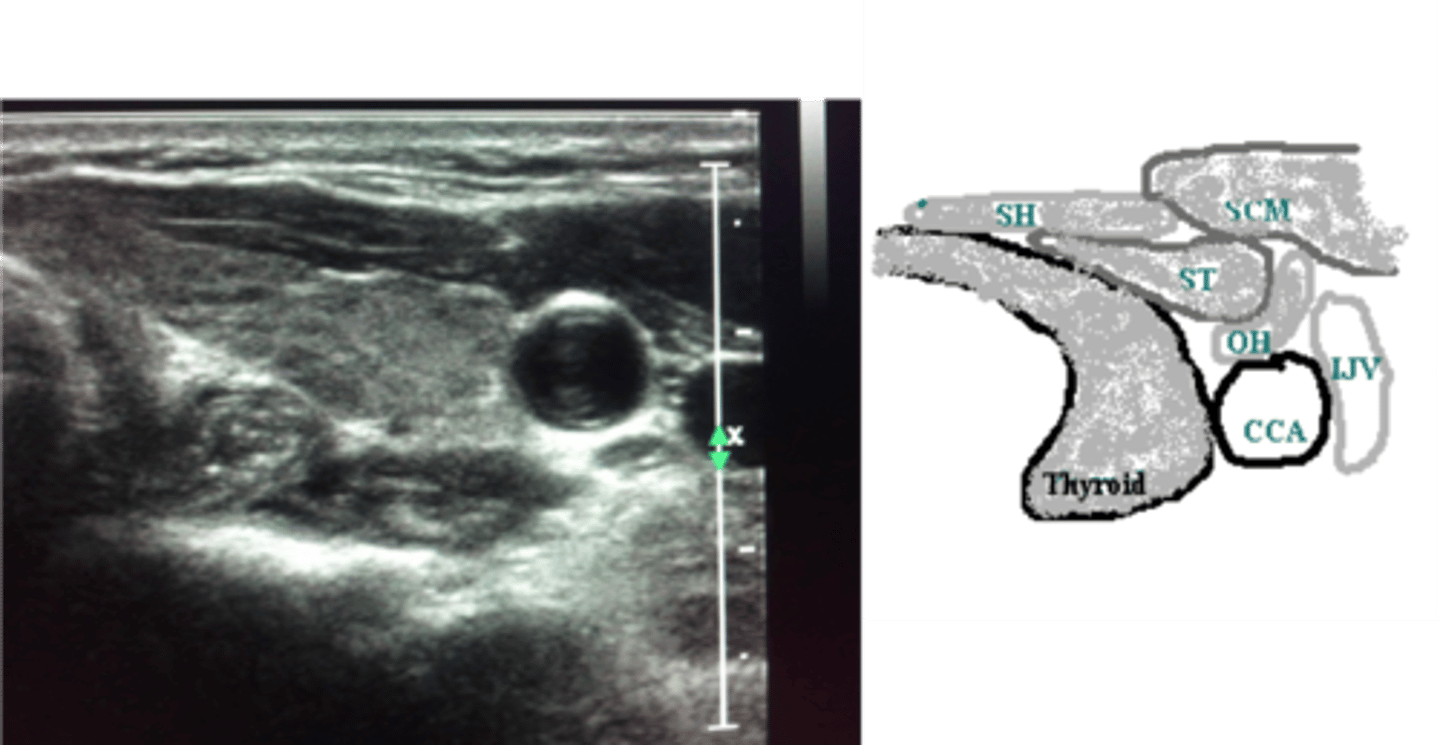
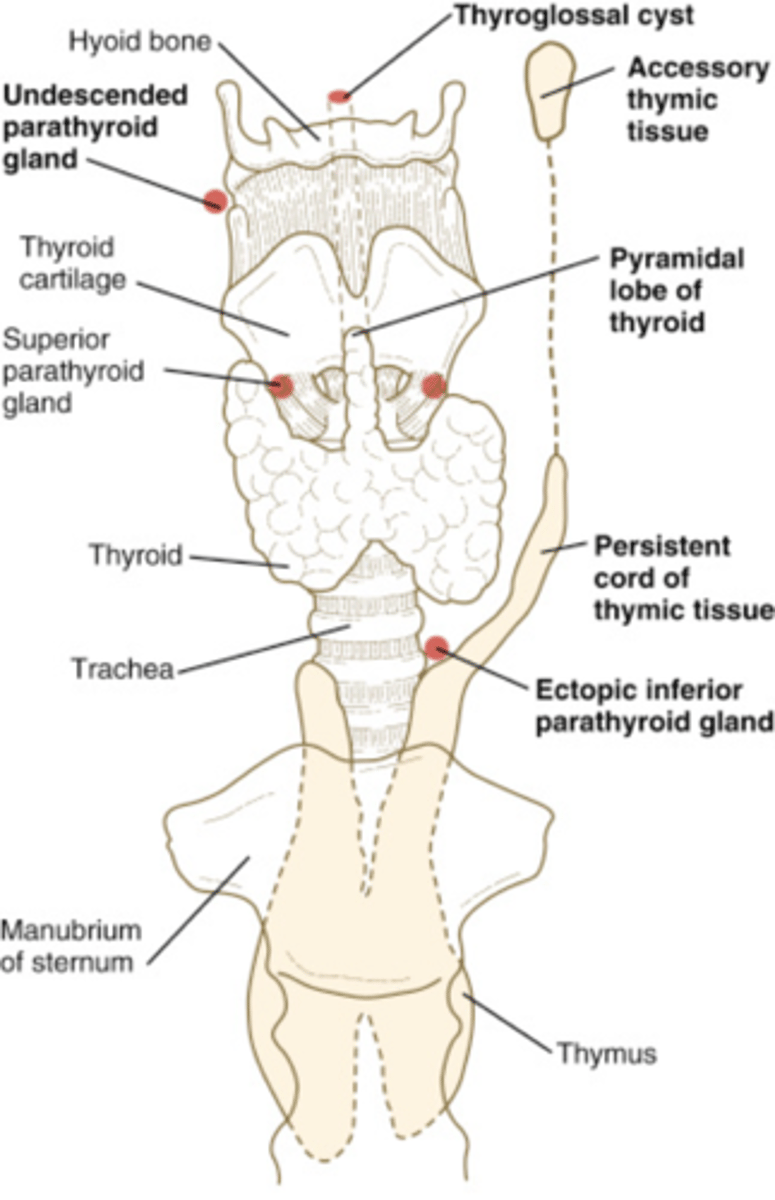
An embryonic remnant cyst located between the isthmus of the thyroid and the tongue.
Thyroglossal cyst
Function of the Thyroid Glands:
-Maintain body ____, ____, and ____
-_____ is processed to manufacture, store, and secrete hormones: ____, ____, and ____
-Secretion of thyroid hormones is primarily controlled by the _____ hormone produced by the _____
-Functions to control the _____
-Maintain body metabolism, growth, and development
-Iodine is processed to manufacture, store, and secrete hormones: thyroxine (T4), triiodothyronine (T3), and calcitonin
-Secretion of thyroid hormones is primarily controlled by the thyroid-stimulating hormone produced by the pituitary gland
-Functions to control the basil metabolic rate (BMR)
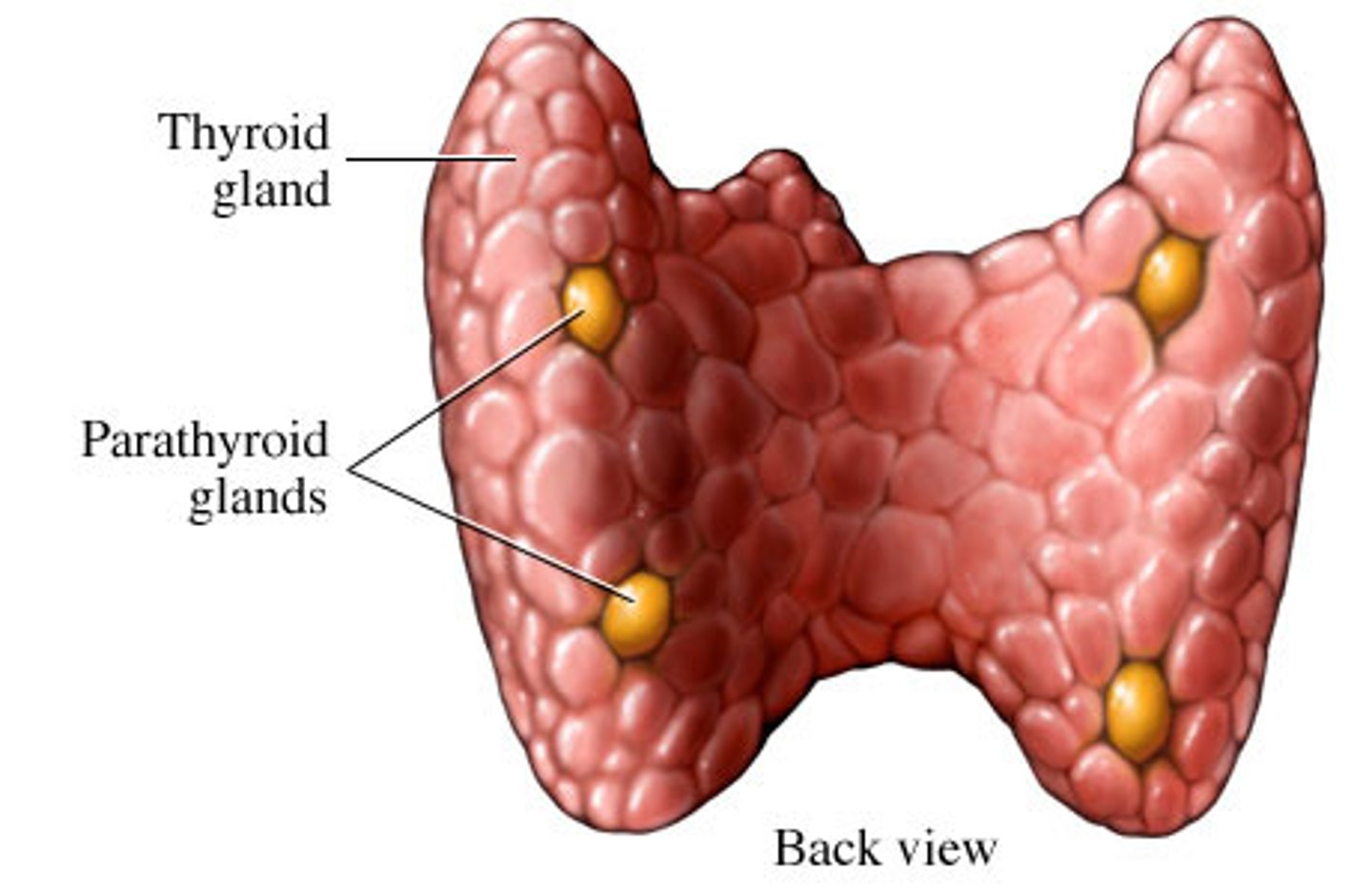
Function of the Parathyroid Glands:
-Maintain homeostasis of blood _____ concentrations
-Secretes _____
-Maintain homeostasis of blood calcium concentrations
-Secretes parathormone
Function of the Salivary Glands:
-_____ glands that secrete enzymes as saliva to aid in mouth _____, _____, maintain _____ integrity, and _____ activity
-Exocrine glands that secrete enzymes as saliva to aid in mouth lubrication, digestion, maintain tooth integrity, and antibacterial activity
Function of the Carotid Arteries:
-Supply blood to the _____ and _____
Head and neck
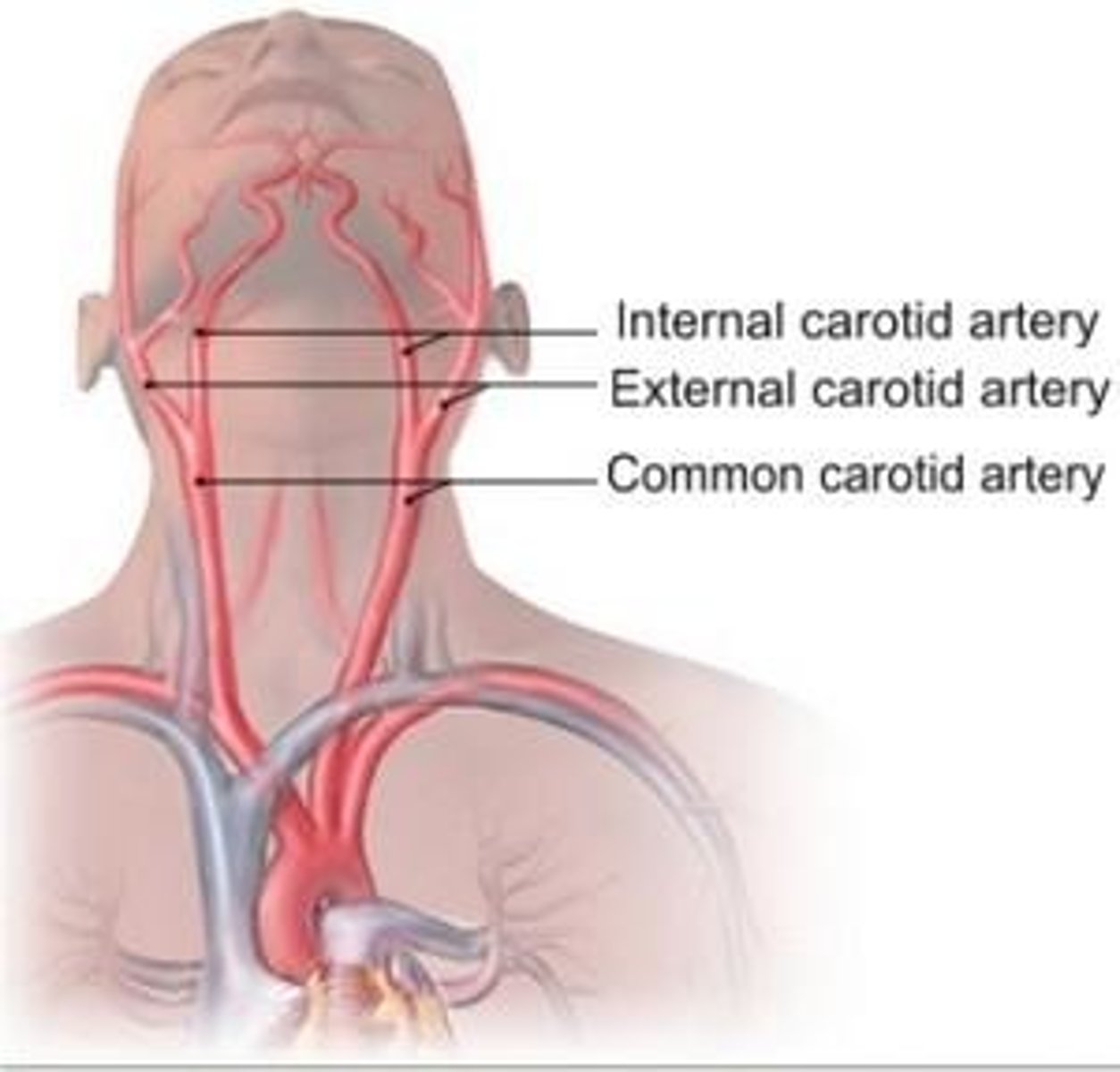
Function of the Jugular Veins:
-Drain blood from the _____ and _____
Head and neck
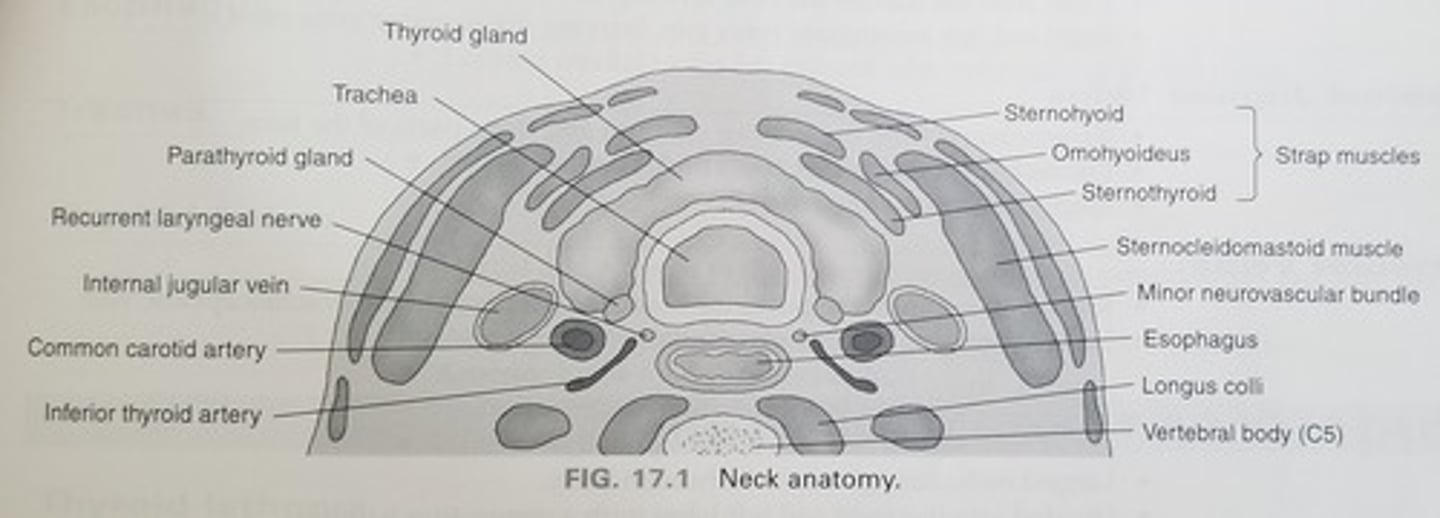
Muscles of the neck - Longus colli muscles:
-Located on the _____ surface of the vertebral column
-Lie adjacent to the ____ and _____ to the thyroid lobe and CCA
-May be mistaken for an enlarged _____
-Located on the anterior surface of the vertebral column
-Lie adjacent to the trachea and posterior to the thyroid lobe and CCA
-May be mistaken for an enlarged parathyroid gland
Muscles of the neck - Platysma Muscles:
-Superficial muscles located in the _____ neck
-Located _____ to the subcutaneous tissues
Lateral
Posterior
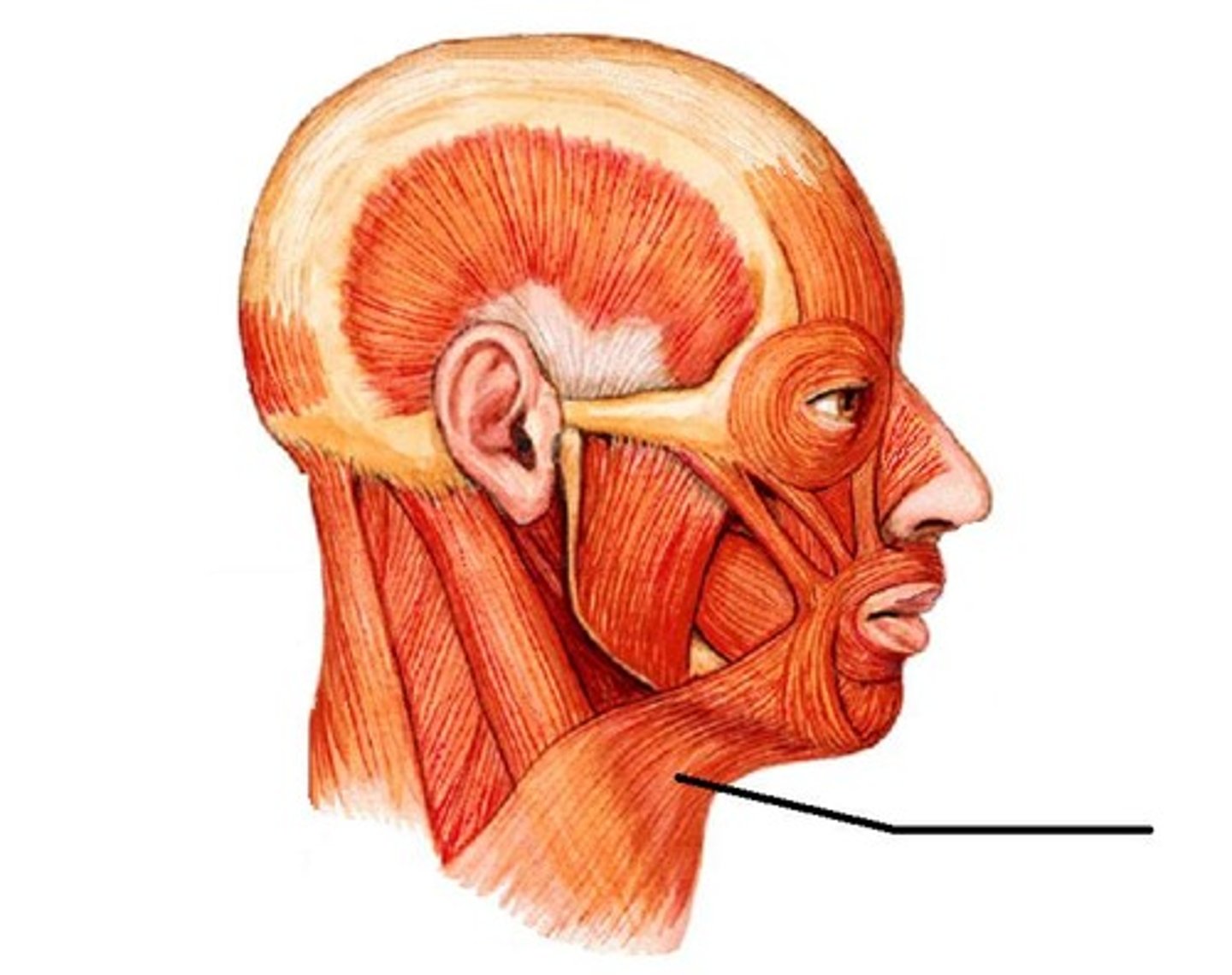
Muscles of the neck - Sternocleidomastoid Muscles:
-_____ and _____ neck muscles
-Located _____ to the thyroid lobes, sternohyoid muscle and sternothyroid muscle
-Lateral and superficial neck muscles
-Located lateral to the thyroid lobes, sternohyoid muscle and sternothyroid muscle
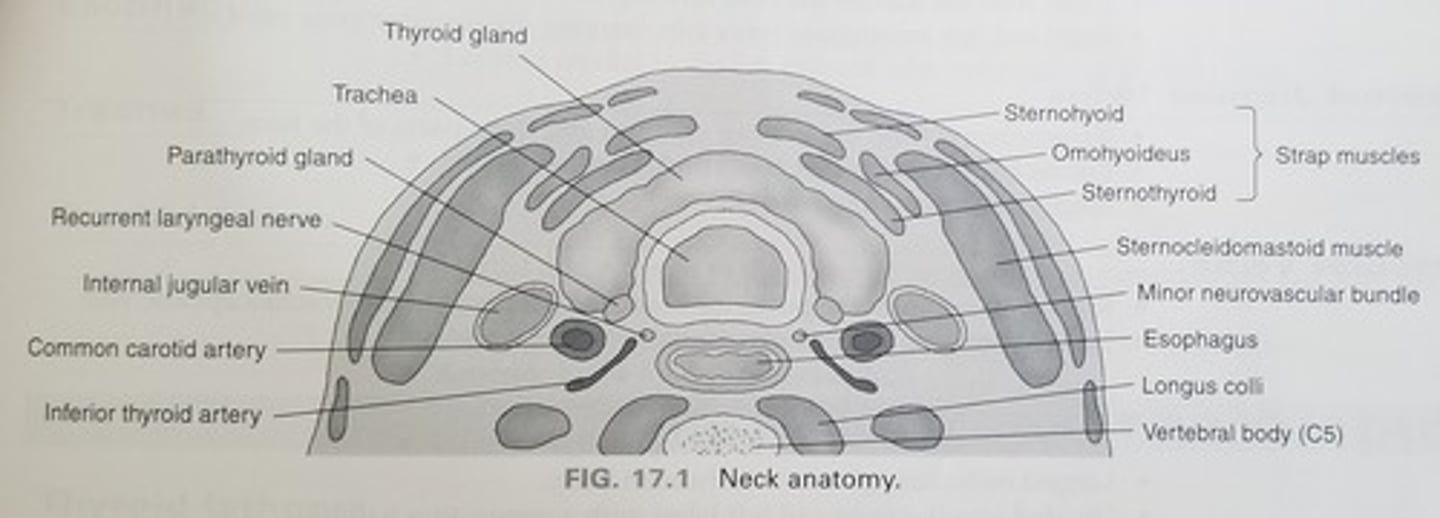
Muscles of the neck - Strap Muscles:
-A collective group of long flat neck muscles
-Located _____ and _____ to the thyroid gland
Include the:
-Sternothyroid - located directly _____ to the thyroid gland
-Omohyoid - located _____ to the sternothyroid muscles
-Sternohyoid - located _____ to the sternothyroid muscles
-A collective group of long flat neck muscles
-Located anterior and lateral to the thyroid gland
Include the:
-Sternothyroid - located directly superficial to the thyroid gland
-Omohyoid - located lateral to the sternothyroid muscles
-Sternohyoid - located anterior to the sternothyroid muscles
Common carotid arteries:
-Left originates from the _____
-Right arises from the _____
-Ascend the _____ aspect of the neck
-Lie _____ to the internal jugular vein and _____ to the thyroid lobe
-Course deep to the _____ muscles
-Typically, no _____
-Bifurcate into the _____ and _____ carotid arteries
-Left originates from the aortic arch
-Right arises from the innominate (brachiocephalic) artery
-Ascend the anterolateral aspect of the neck
-Lie medial to the internal jugular vein and lateral to the thyroid lobe
-Course deep to the sternocleidomastoid muscles
-Typically, no branches
-Bifurcate into the external and internal carotid arteries
External carotid arteries:
-Supplies the ____, ____, and ____ with blood
-Lies _____ and _____ to the ICA
-Multiple extracranial _____
-_____ is the first branch of the ECA
-Supplies the neck, scalp, and face with blood
-Lies anterior and medial to the ICA
-Multiple extracranial branches
-Superior thyroid artery is the first branch of the ECA
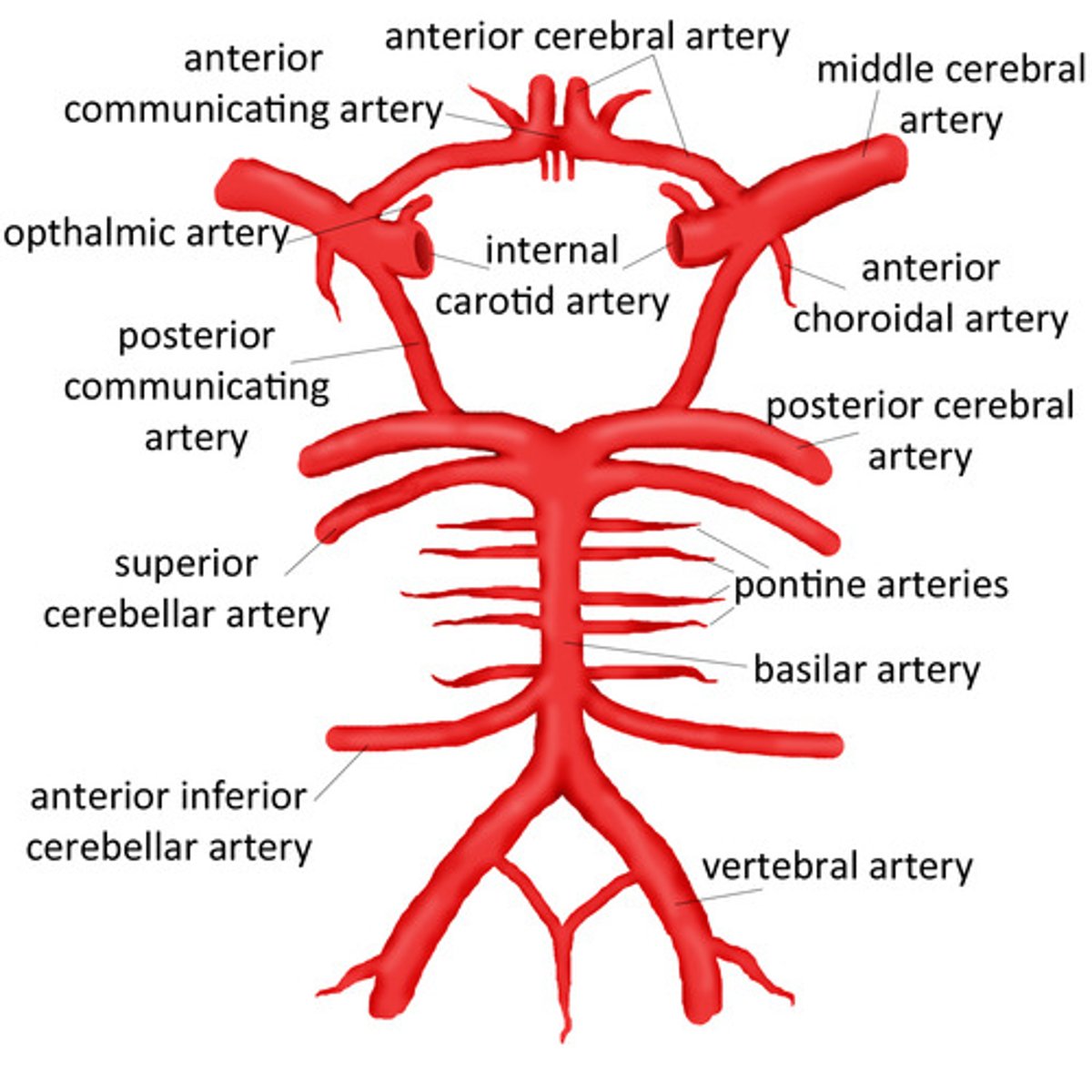
Internal carotid arteries:
-Main blood supply to the _____ and _____
-Lie _____ and _____ to the ECA
-Terminate at the _____
-No _____ branches
-_____ is the first branch of the ICA
-Main blood supply to the eyes and brain
-Lie posterior and lateral to the ECA
-Terminate at the circle of Willis
-No extracranial branches
-Ophthalmic artery is the first branch of the ICA
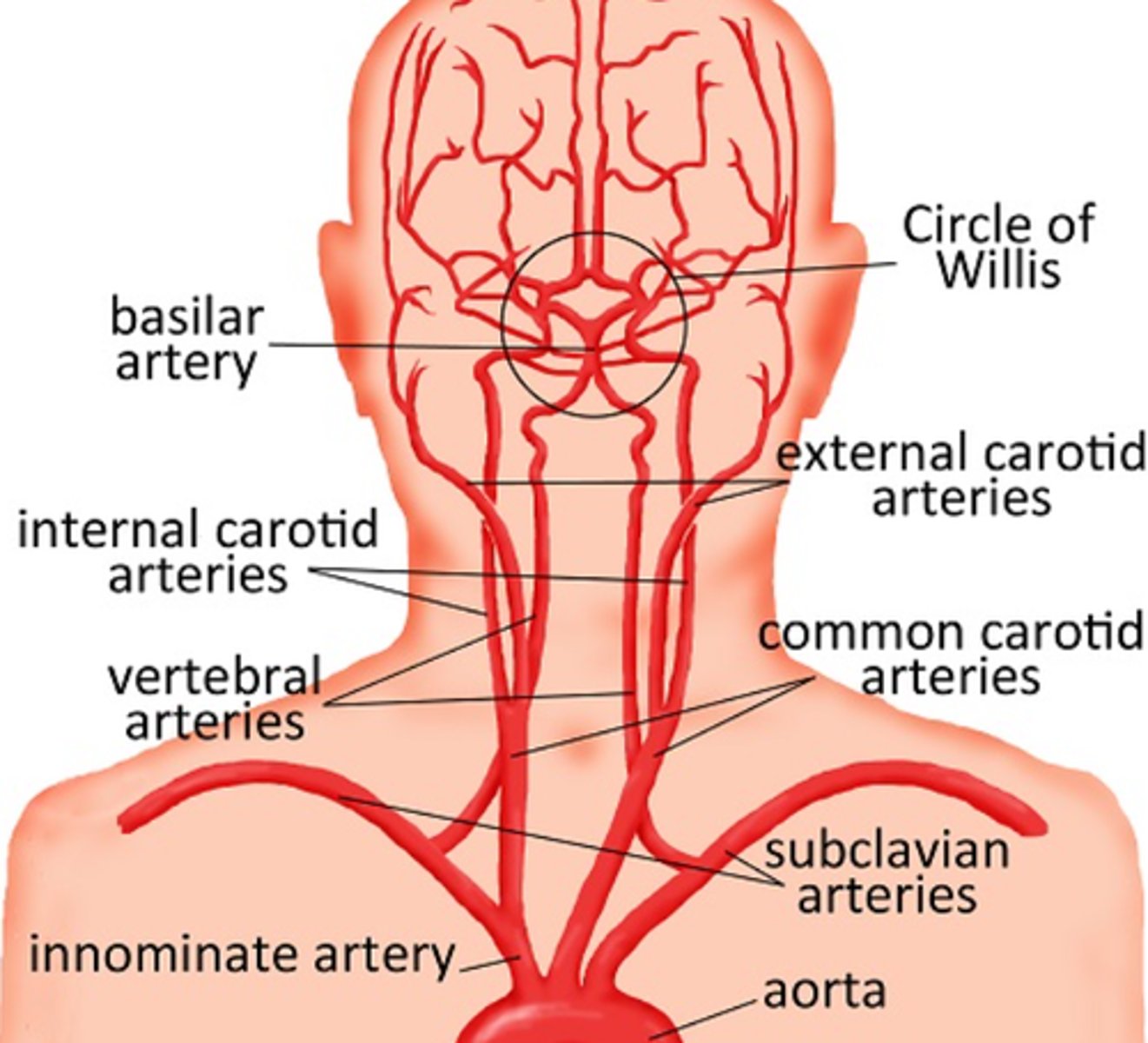
Vertebral arteries:
-Arise from the first segment of the _____
-Provide blood to the _____ brain
-Lie in the _____ neck, ascending through the _____ of the spine
-Left and right vertebral arteries join to form the _____ at the base of the skull
-Basilar artery terminates in the posterior aspect of the _____
-Multiple _____ branches
-Arise from the first segment of the subclavian artery
-Provide blood to the posterior brain
-Lie in the posterior neck, ascending through the transverse processes of the spine
-Left and right vertebral arteries join to form the basilar artery at the base of the skull
-Basilar artery terminates in the posterior aspect of the circle of Willis
-Multiple extracranial branches
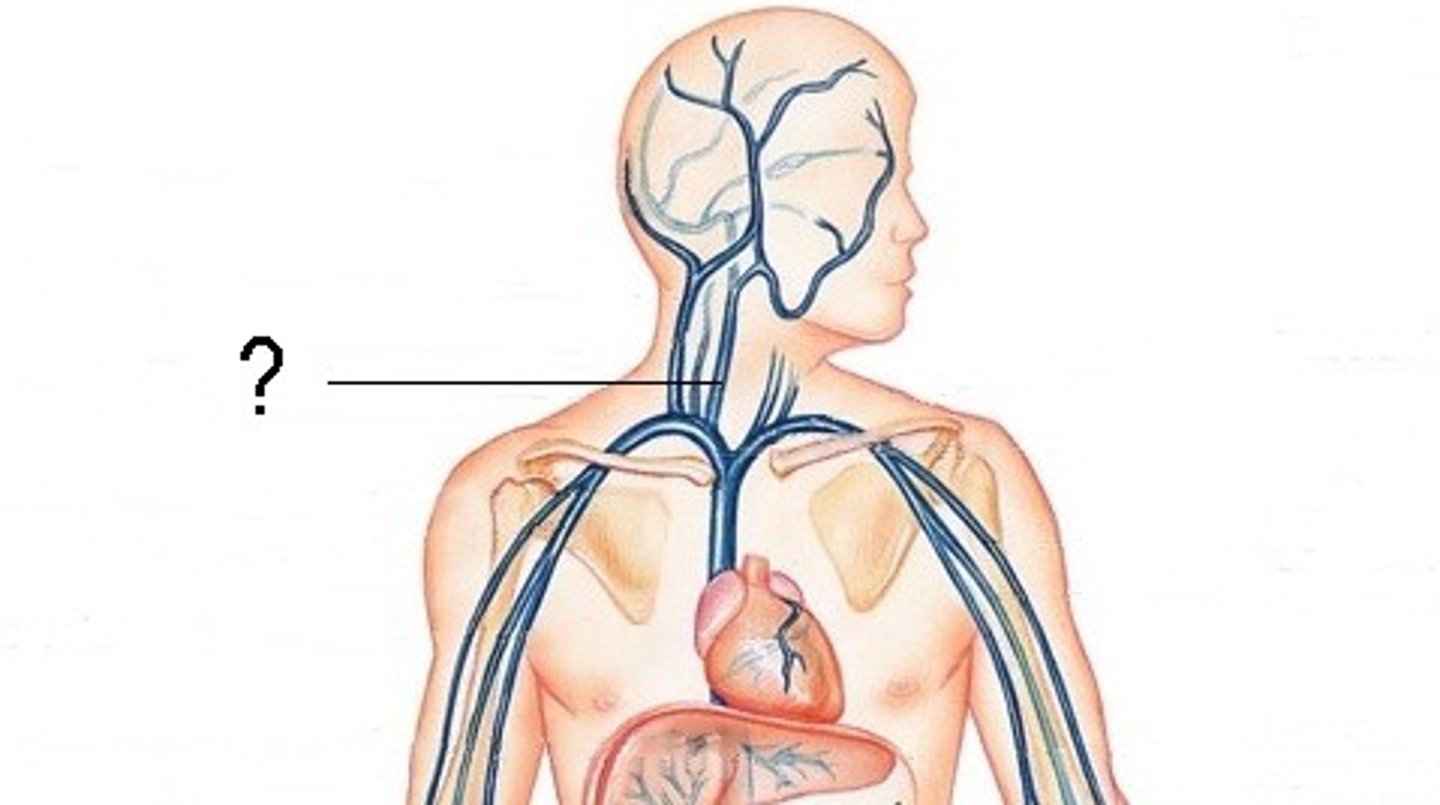
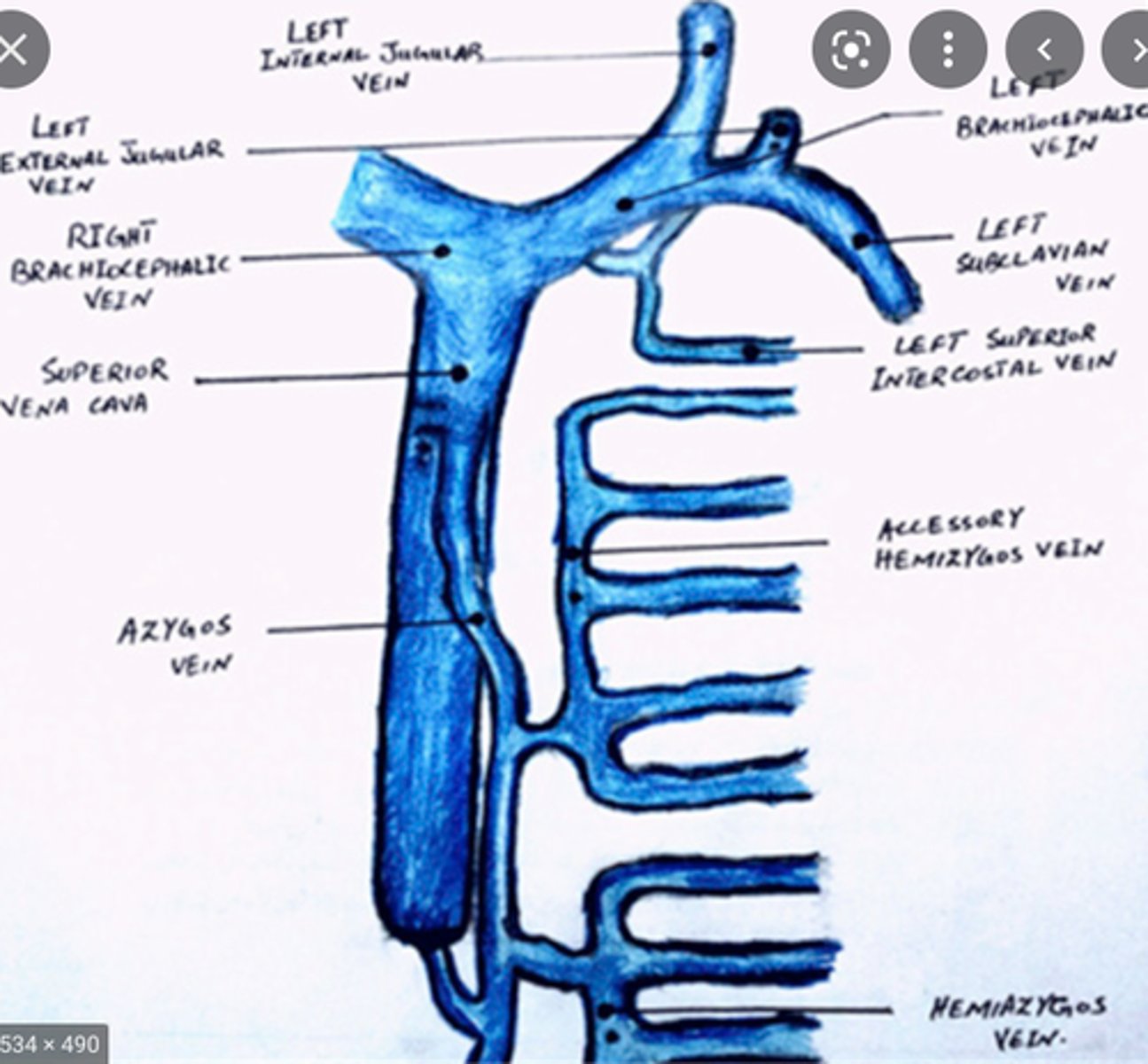
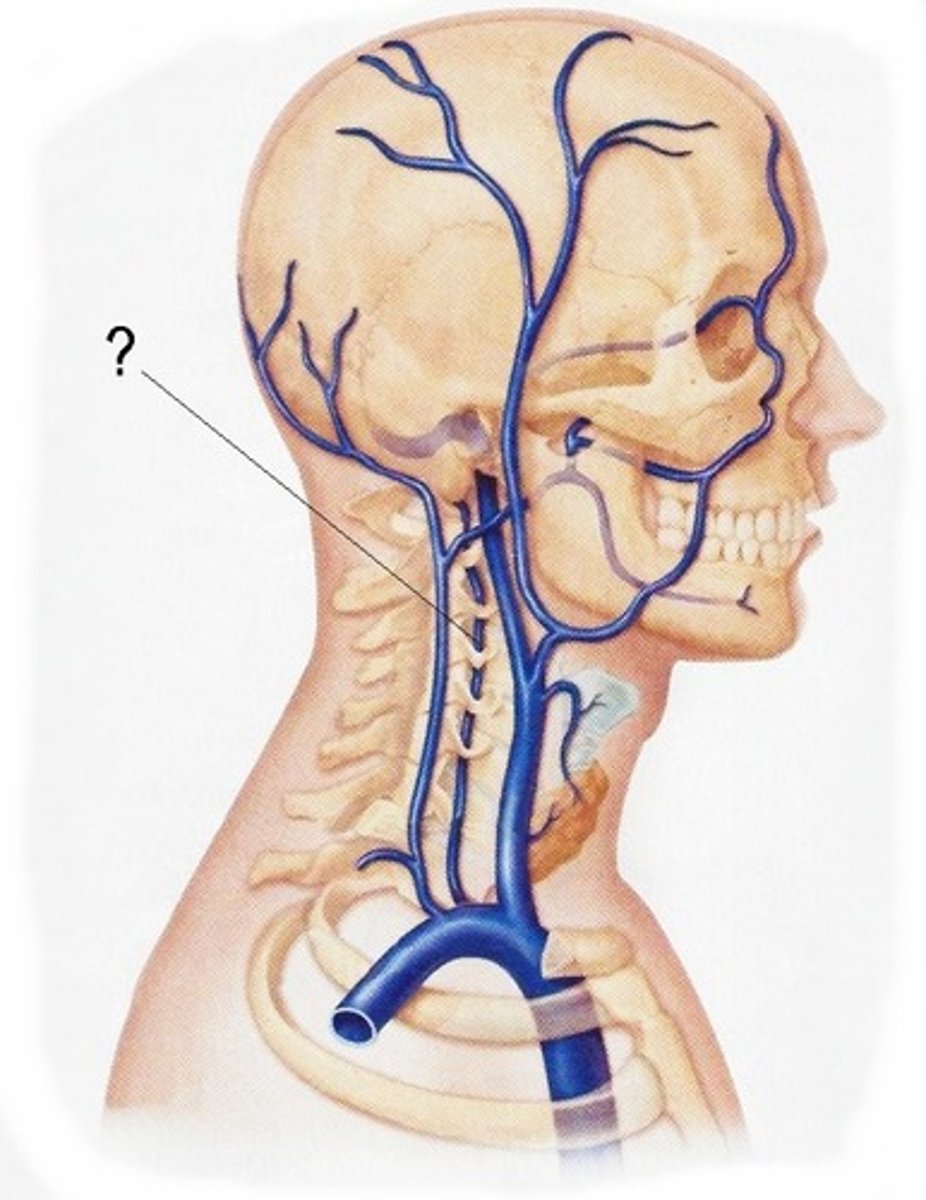
Internal Jugular Veins:
-Receive the major portion of blood from the _____,_____, and superficial parts of the _____
-Course ______ to the carotid artery
-Unite with the _____ vein, forming the _____ vein
-Right and left innominate veins join, forming the _____
-Receive the major portion of blood from the brain, neck, and superficial parts of the face
-Course lateral to the carotid artery
-Unite with the subclavian vein, forming the innominate (brachiocephalic) vein
-Right and left innominate veins join, forming the SVC
External Jugular Veins:
-Receive blood from the exterior _____ and _____ parts of the face
-Located in the superficial fascia of the _____ neck
-Empty into the _____
-Receive blood from the exterior cranium and deep parts of the face
-Located in the superficial fascia of the lateral neck
-Empty into the subclavian vein
Vertebral Veins:
-Receive blood from the _____ brain and empty into the _____ vein
-Located _____ to the corresponding vertebral artery
-Receive blood from the posterior brain and empty into the brachiocephalic vein
-Located anterior to the corresponding vertebral artery
What is the largest endocrine gland in the body?
Thyroid gland
Anatomy of the Thyroid Glands:
-Largest _____ gland in the human body
-Divided into the right and left lobes with a connecting _____
-_____ lobe is usually larger than the _____
-Isthmus connects the _____ third of the thyroid lobes
-Consists of follicles, connective tissue, nerves, lymphatics, and stroma
-Covered by two layers of _____
-Largest endocrine gland in the human body
-Divided into the right and left lobes with a connecting isthmus
-Right lobe is usually larger than the left
-Isthmus connects the lower third of the thyroid lobes
-Consists of follicles, connective tissue, nerves, lymphatics, and stroma
-Covered by two layers of connective tissue
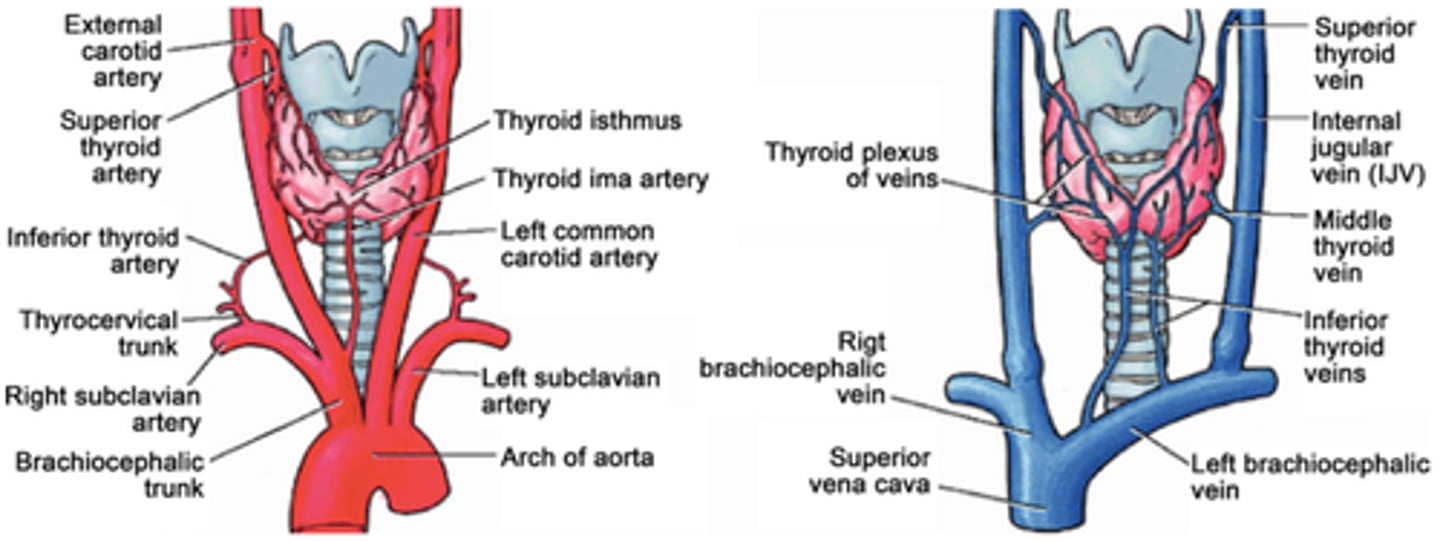
Vasculature of the Thyroid Glands:
-_____ arteries supply blood flow to the superior portion of the thyroid gland
-_____ arteries supply blood flow to the inferior portion of the thyroid gland
-Superior thyroid artery arises from the _____
-Inferior thyroid artery arises from the _____
-Superior, middle thyroid veins drain into the _____
-Inferior thyroid vein drains into the _____
-Superior thyroid arteries supply blood flow to the superior portion of the thyroid gland
-Inferior thyroid arteries supply blood flow to the inferior portion of the thyroid gland
-Superior thyroid artery arises from the ECA
-Inferior thyroid artery arises from the thyrocervical artery
-Superior, middle thyroid veins drain into the internal jugular vein
-Inferior thyroid vein drains into the innominate vein
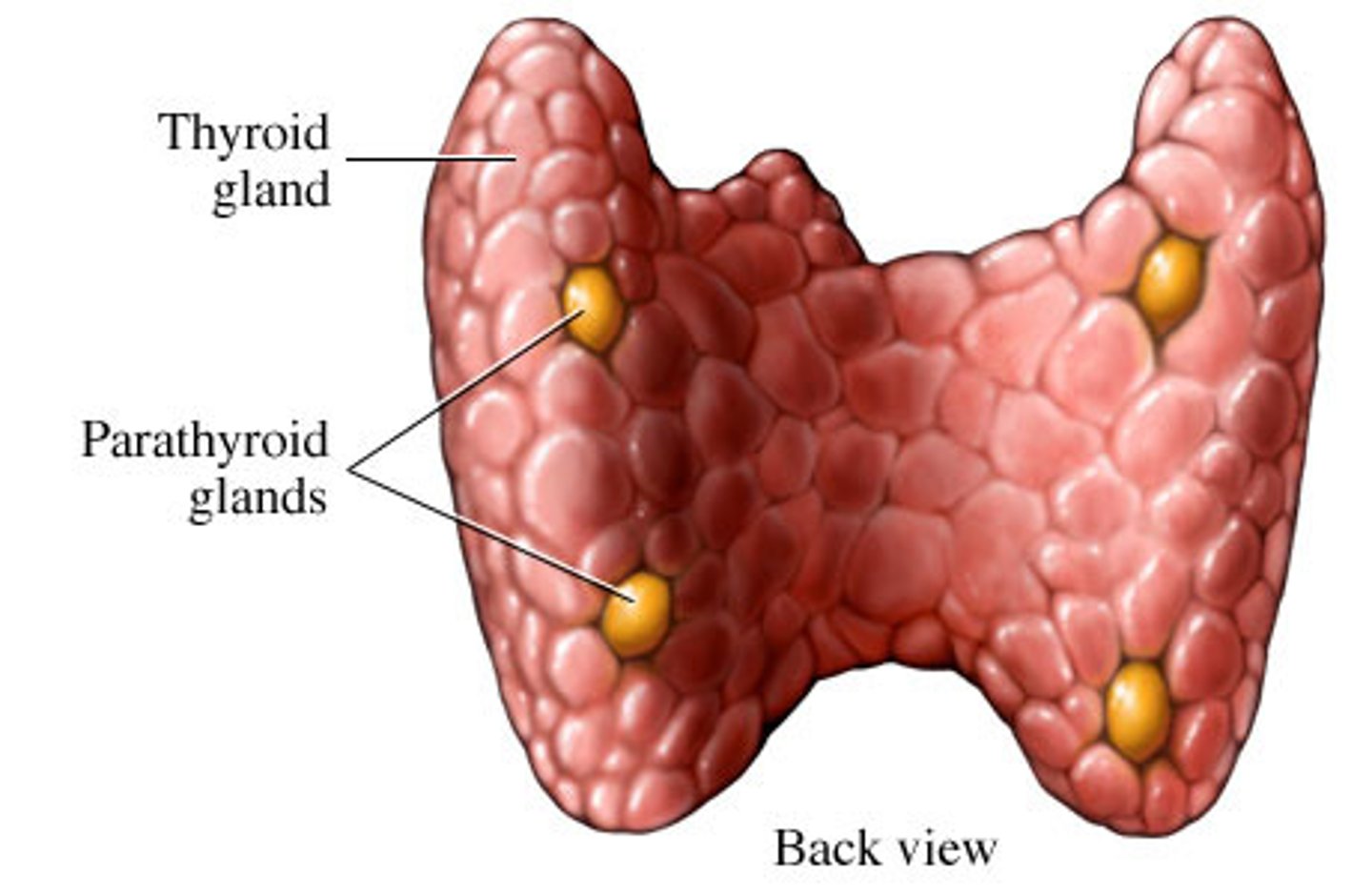
Parathyroid glands:
Two paired, bean-shaped glands located _____ to the thyroid gland
Posterior
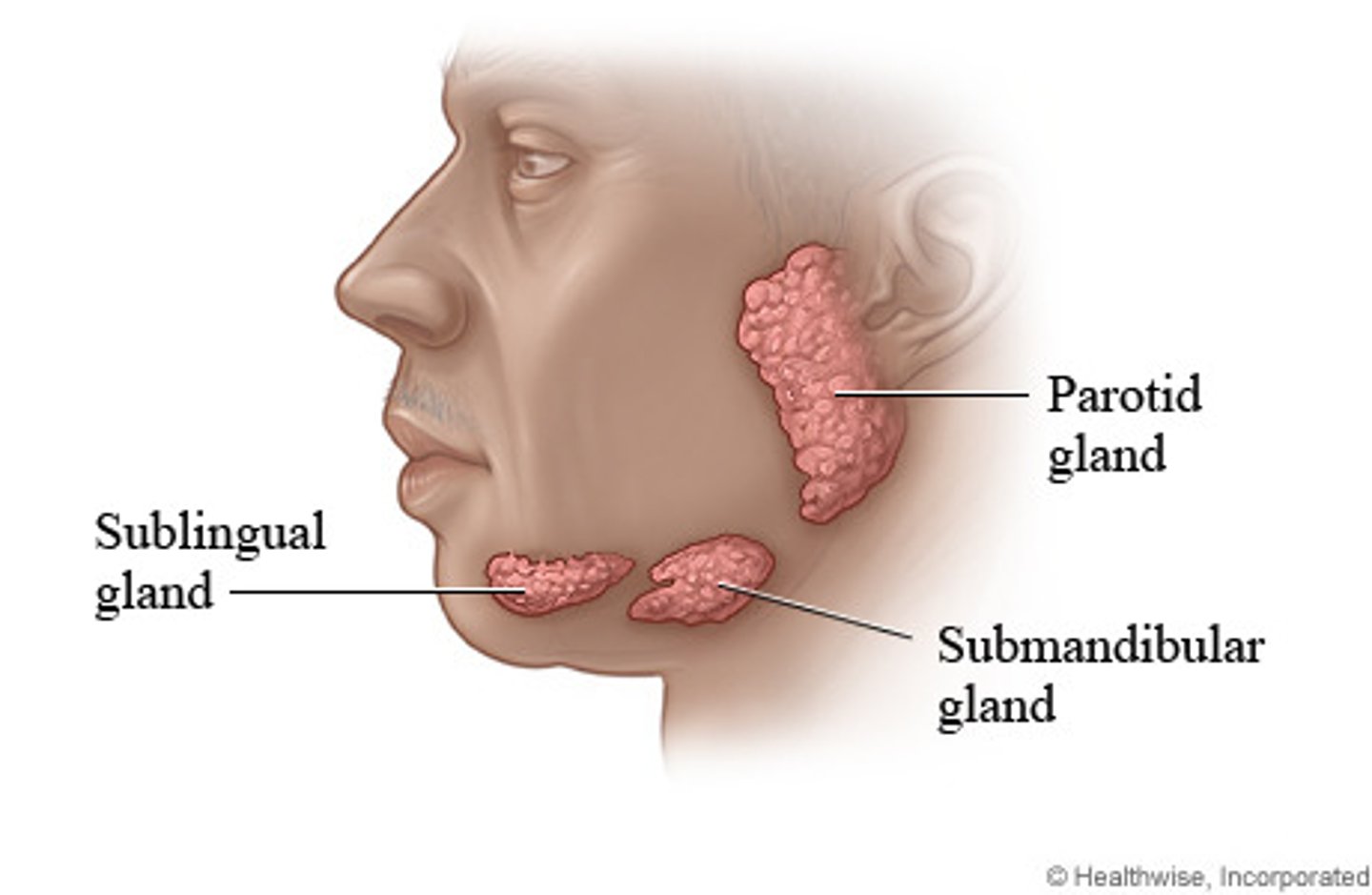
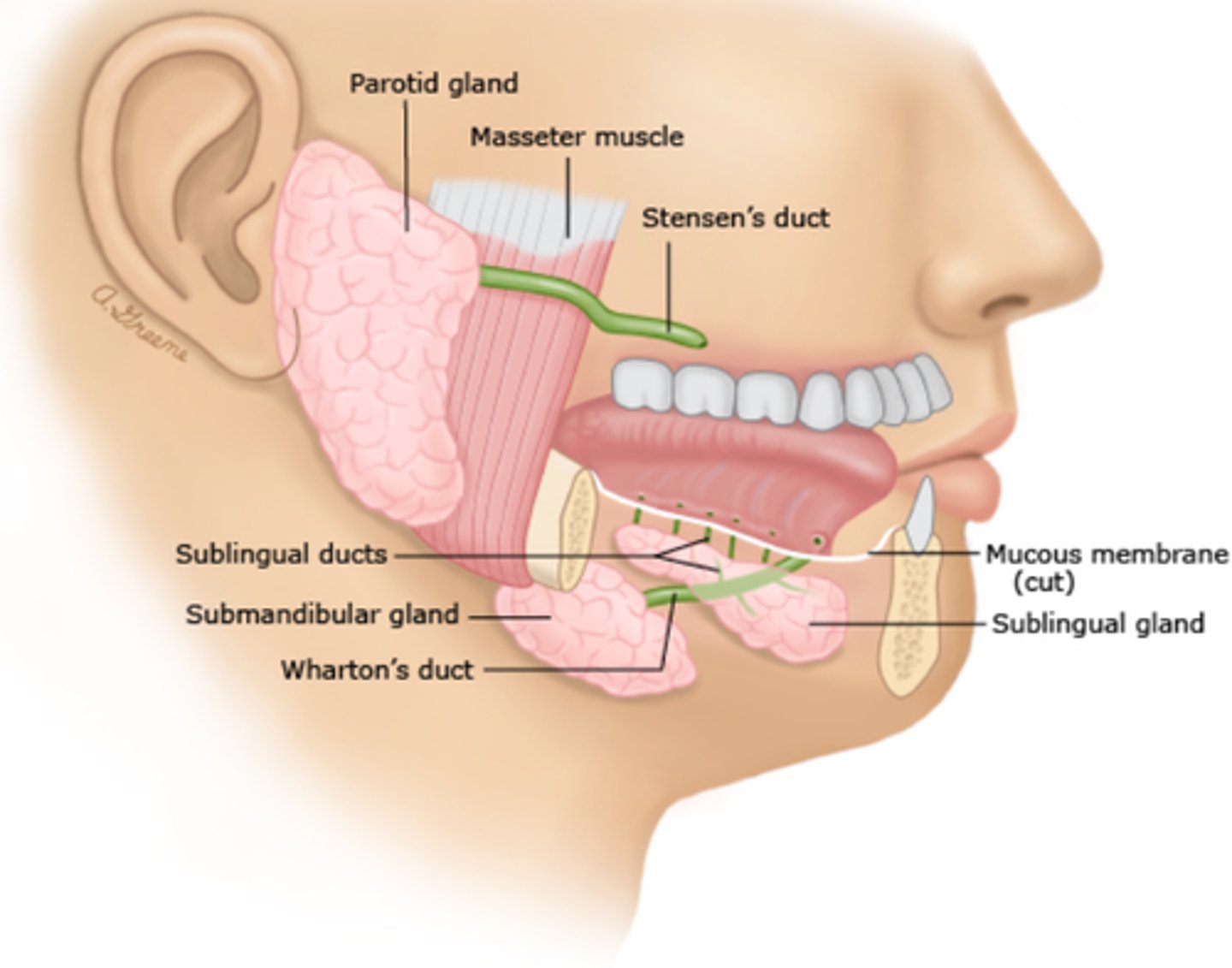
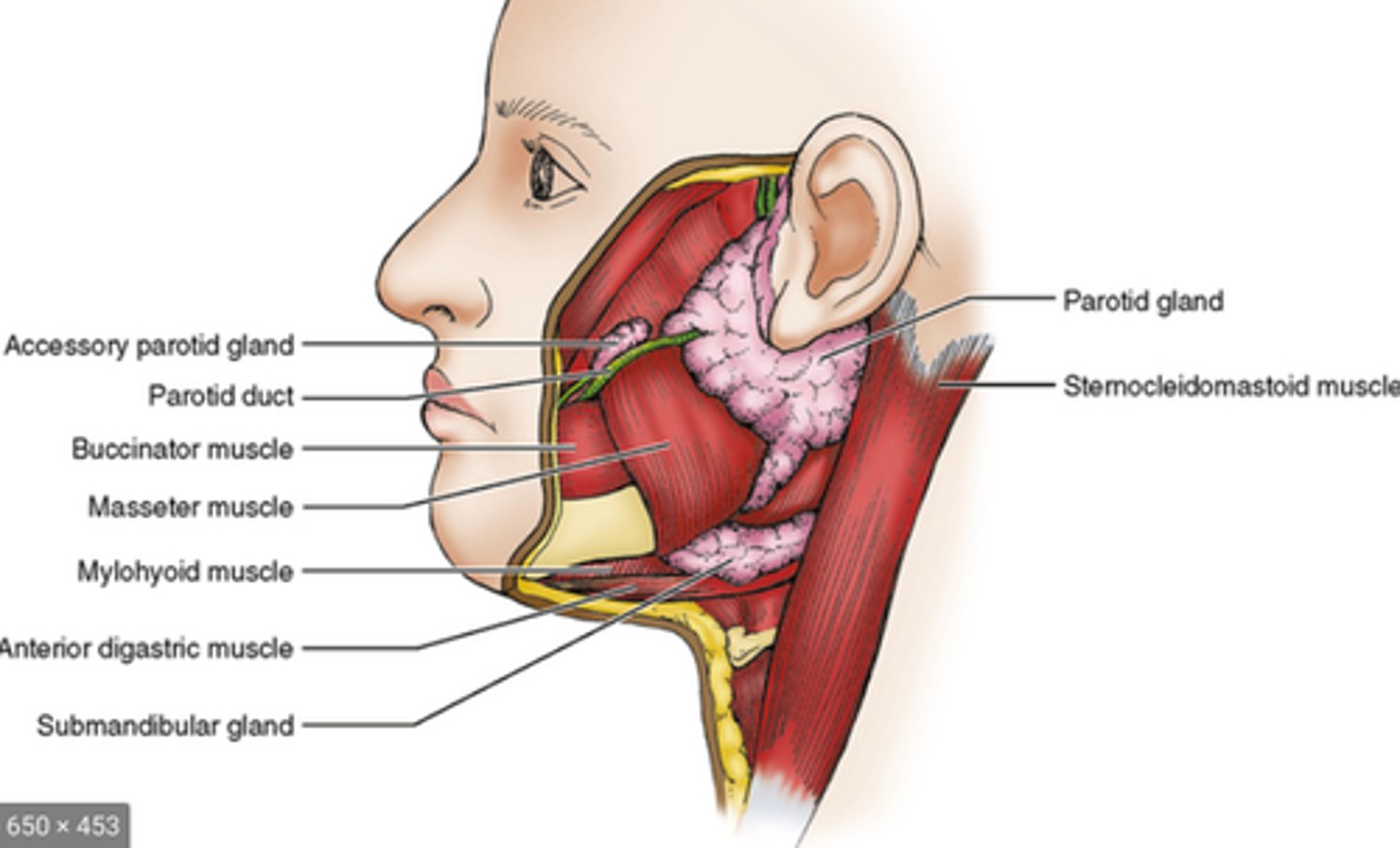
What are the 3 salivary glands?
Parotid
Submandibular
Sublingual
Salivary Glands:
-_____ glands divided into lobules with a hilum where branching blood vessels, ducts and nerves are present
Parotid gland
-_____ of the salivary glands
-Shaped like an _____
-Contains _____ duct (excretory duct)
-Only salivary gland that has intraparenchymal _____
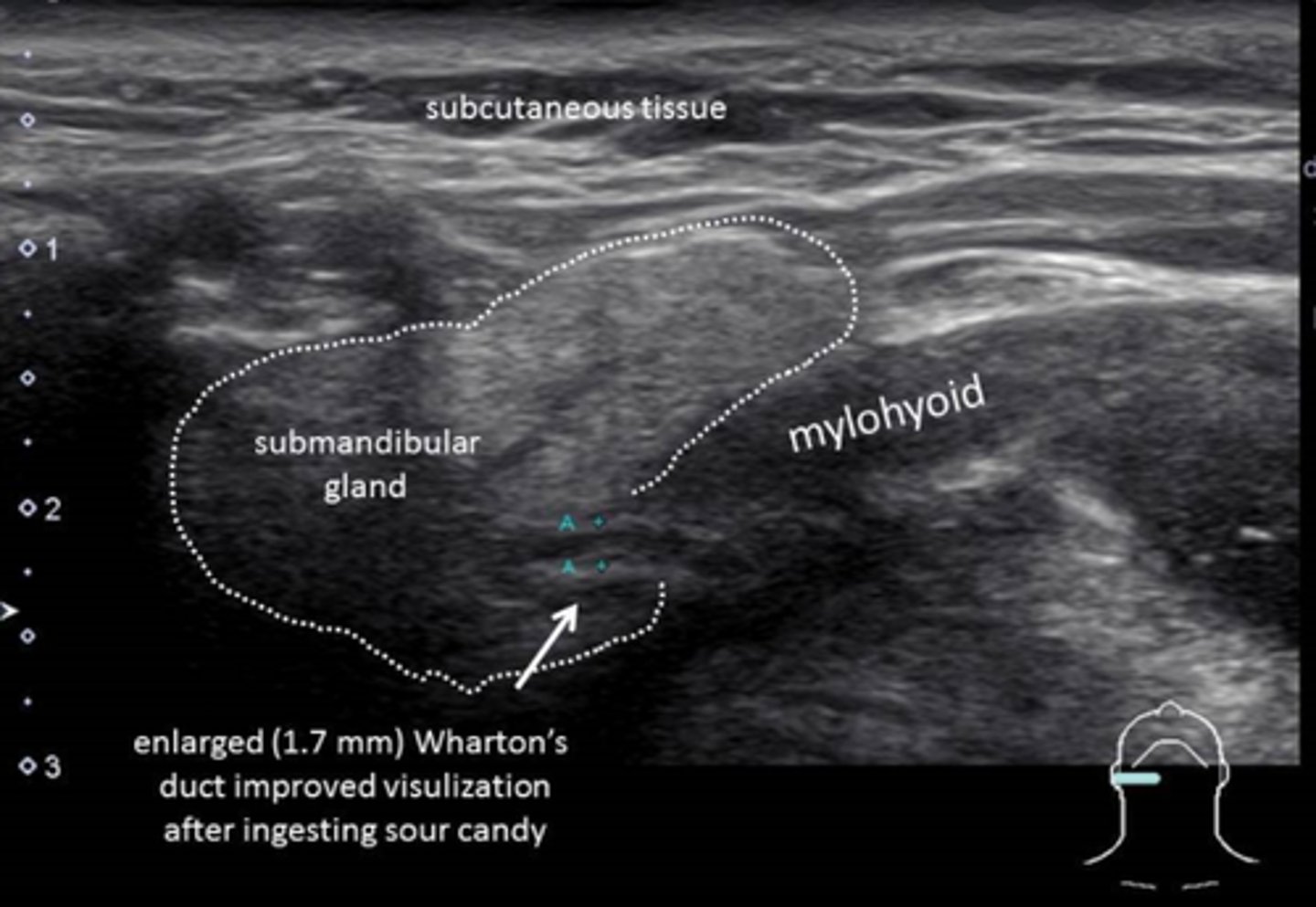
Submandibular gland
-Produce 70% of _____
-_____ in shape
-Contains _____ duct
-Glandular processes may connect the submandibular gland with the parotid and sublingual glands
Sublingual gland
-_____ and oval in shape
-Contains _____ excretory glands
-Exocrine glands divided into lobules with a hilum where branching blood vessels, ducts and nerves are present
Parotid gland
-Largest of the salivary glands
-Shaped like an inverted pyramid
-Contains Stenson's duct (excretory duct)
-Only salivary gland that has intraparenchymal lymph nodes
Submandibular gland
-Produce 70% of saliva
-Triangular in shape
-Contains Wharton's duct
-Glandular processes may connect the submandibular gland with the parotid and sublingual glands
Sublingual gland
-Small and oval in shape
-Contains 8-20 excretory glands
Location - Esophagus:
-Located _____ to the left thyroid lobe and _____ to the trachea
Medial
Posterior
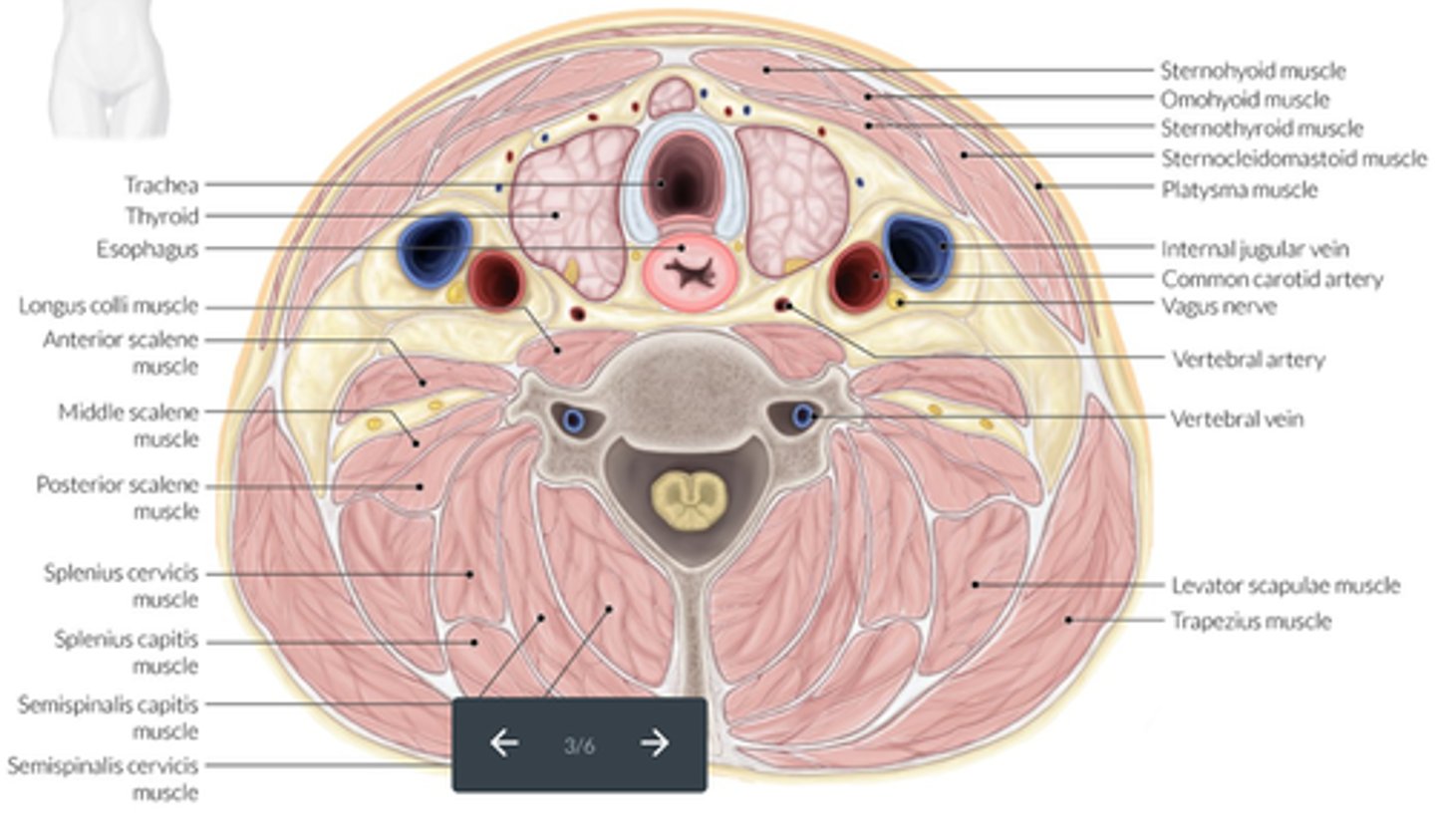
Location - Trachea:
-Forms the _____ border of the thyroid glands
Medial
Location - Thyroid Lobes:
-_____ and _____ to the corresponding CCA and IJV
-_____ and _____ to the SCM and strap muscles
-_____ to the longus colli muscle
-_____ to the trachea and esophagus
-_____ to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx
-Medial and anterior to the corresponding CCA and IJV
-Posterior and medial to the SCM and strap muscles
-Anterior to the longus colli muscle
-Anterolateral to the trachea and esophagus
-Inferior to the thyroid cartilage of the larynx
Location - Thyroid Isthmus:
-_____ to the trachea
-_____ and _____ to the CCA and IJV
-Anterior to the trachea
-Medial and anterior to the CCA and IJV
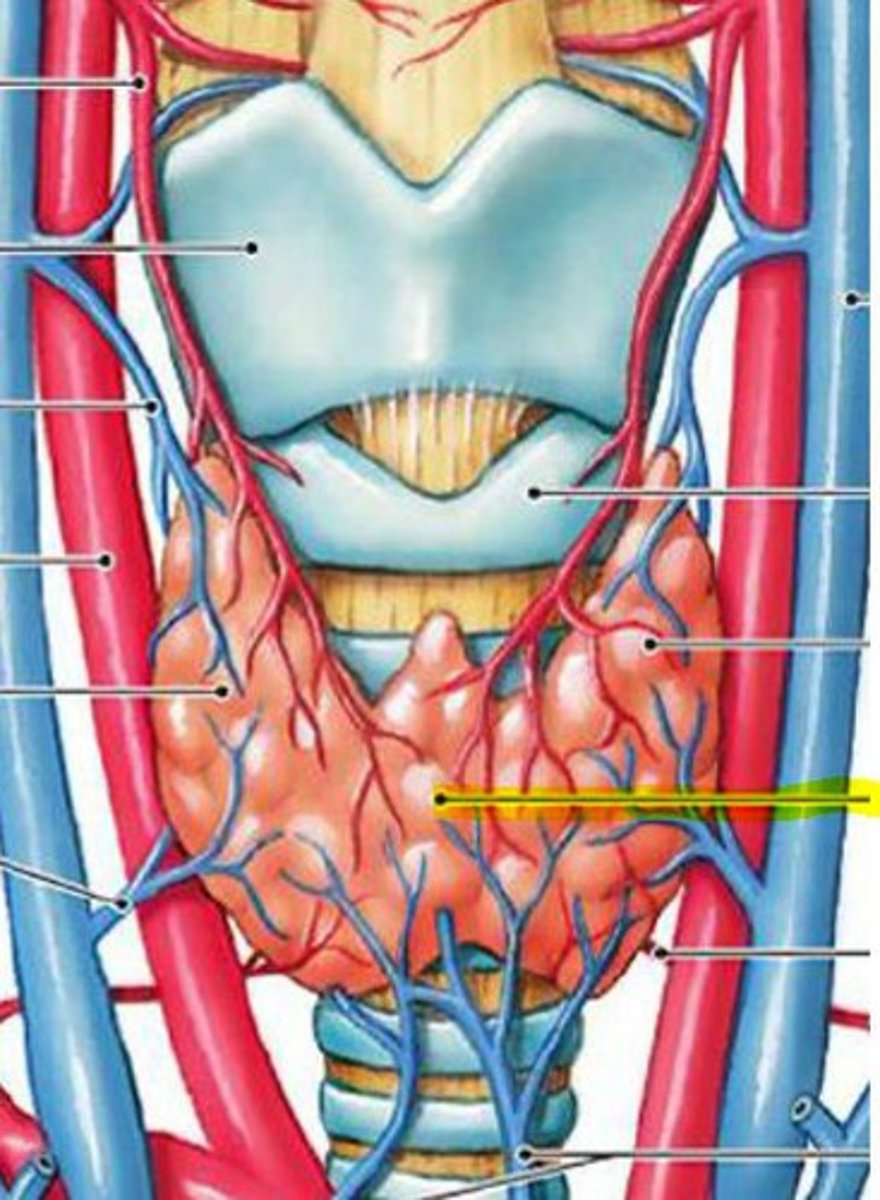
Location - Parathyroid Glands:
-_____ to the thyroid glands
-_____ to the longus colli muscles
-Posterior to the thyroid glands
-Anterior to the longus colli muscles
Location - Salivary Glands:
Parotid gland
-_____ to the ear near the ramus of the mandible
-_____ vein separates the superior and deep lobes of the gland
Submandibular gland
-Located beneath the anterior _____, inferior and lateral to the _____ muscle
Sublingual gland
-Located beneath the muscles of the _____, medial to the _____muscle and lateral to the _____ muscle
Parotid gland
-Anterior to the ear near the ramus of the mandible
-Retromandibular vein separates the superior and deep lobes of the gland
Submandibular gland
-Located beneath the anterior mandible, inferior and lateral to the mylohoid muscle
Sublingual gland
-Located beneath the muscles of the tongue, medial to the mylohoid muscle and lateral to the hypoglossal muscle
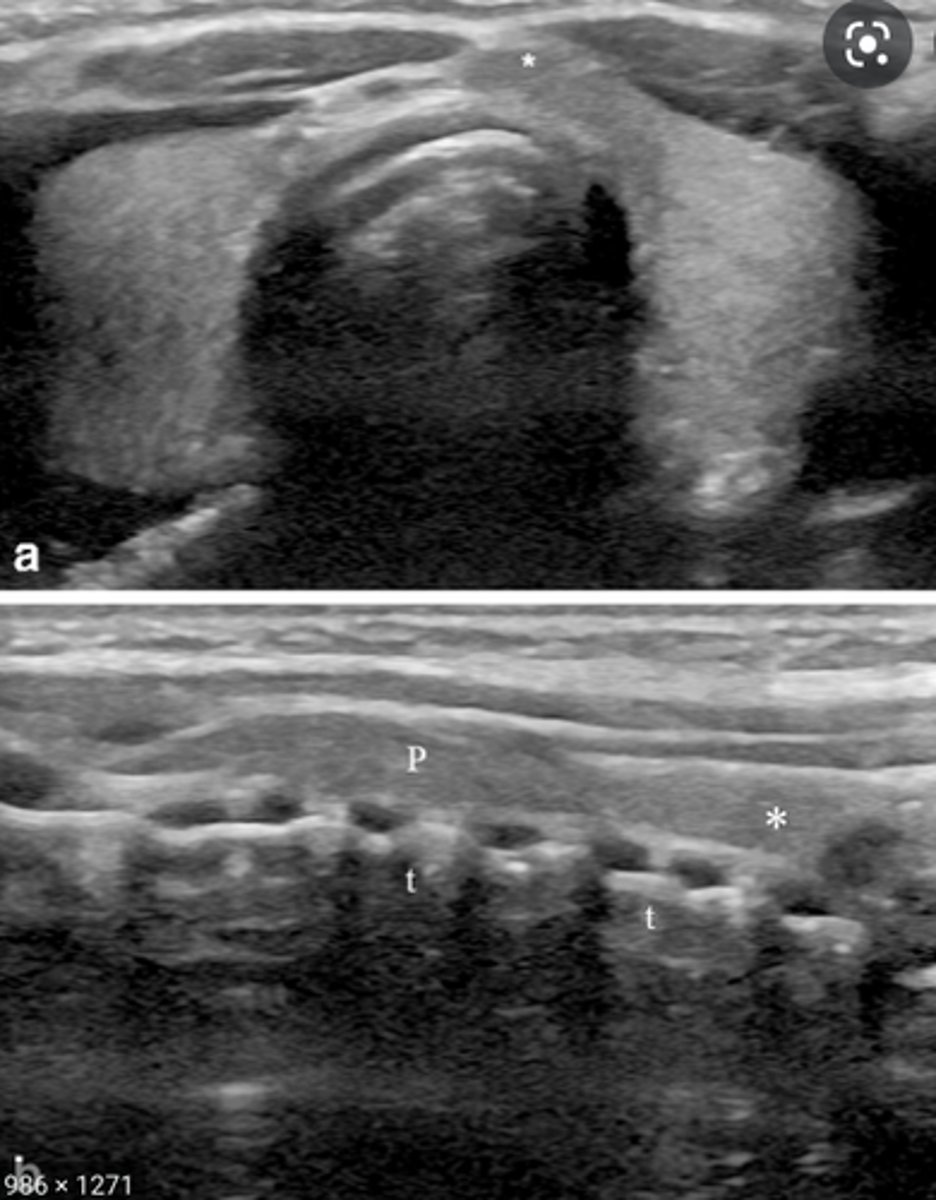
Congenital Anomalies - Pyramidal Lobe:
-Third lobe arising from the _____ portion of the _____
-Ascends to the level of the _____
-Appears in _____% of patients
-Begins to _____ in adulthood
-Appears _____echoic to the normal thyroid gland
-Third lobe arising from the superior portion of the isthmus
-Ascends to the level of the hyoid bone
-Appears in 10-40% of patients
-Begins to atrophy in adulthood
-Appears isoechoic to the normal thyroid gland
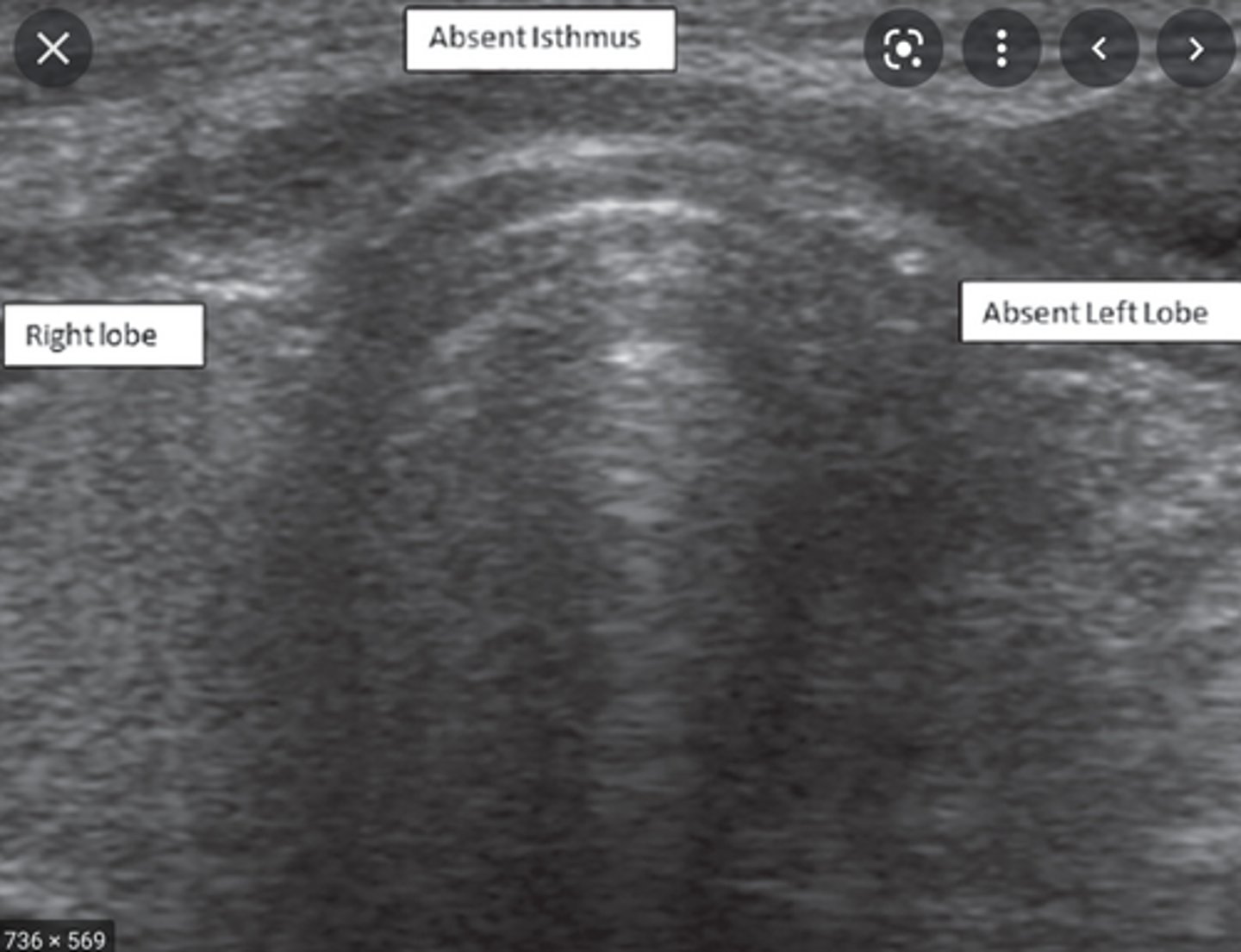
The following describes which congenital anomaly of the thyroid?:
-Thyroid consists of two distinct lobes
Absent Isthmus
Congenital Anomalies - Ectopic Parathyroid Gland Location:
-May be found near the _____ bifurcation or posterior to the _____
-May also be located retroesophageal, substernal, _____, or intrathyroid
-May be found near the carotid bifurcation or posterior to the carotid artery
-May also be located retroesophageal, substernal, submandibular, or intrathyroid
Size:
-Isthmus: ____ in height
-Thyroid glands (adult): ____ in length, ____ in height, and ____ in width
-Thyroid glands (pediatric): ____ in length, ____ in height, and ____ in width
-Isthmus: 0.2-0.6 cm in height
-Thyroid glands (adult): 4-6 cm in length, 1.3-1.8 cm in height, and 1.5-2 cm in width
-Thyroid glands (pediatric): 2-3 cm in length, 0.2-1.2 cm in height, and 1-1.5 cm in width
Size:
-Parathyroid glands: up to ____ in length, ____ in height, and ____ in width
-Parotid glands: up to ____ in length, and ____ in both height and width
-Submandibular glands: averages ____ in length
-Sublingual gland: up to ____ in length
-Parathyroid glands: up to 6 mm in length, 2 mm in height, and 4 mm in width
-Parotid glands: up to 7 cm in length, and 3.5 cm in both height and width
-Submandibular glands: averages 3.5 cm in length
-Sublingual gland: up to 2.5 cm in length
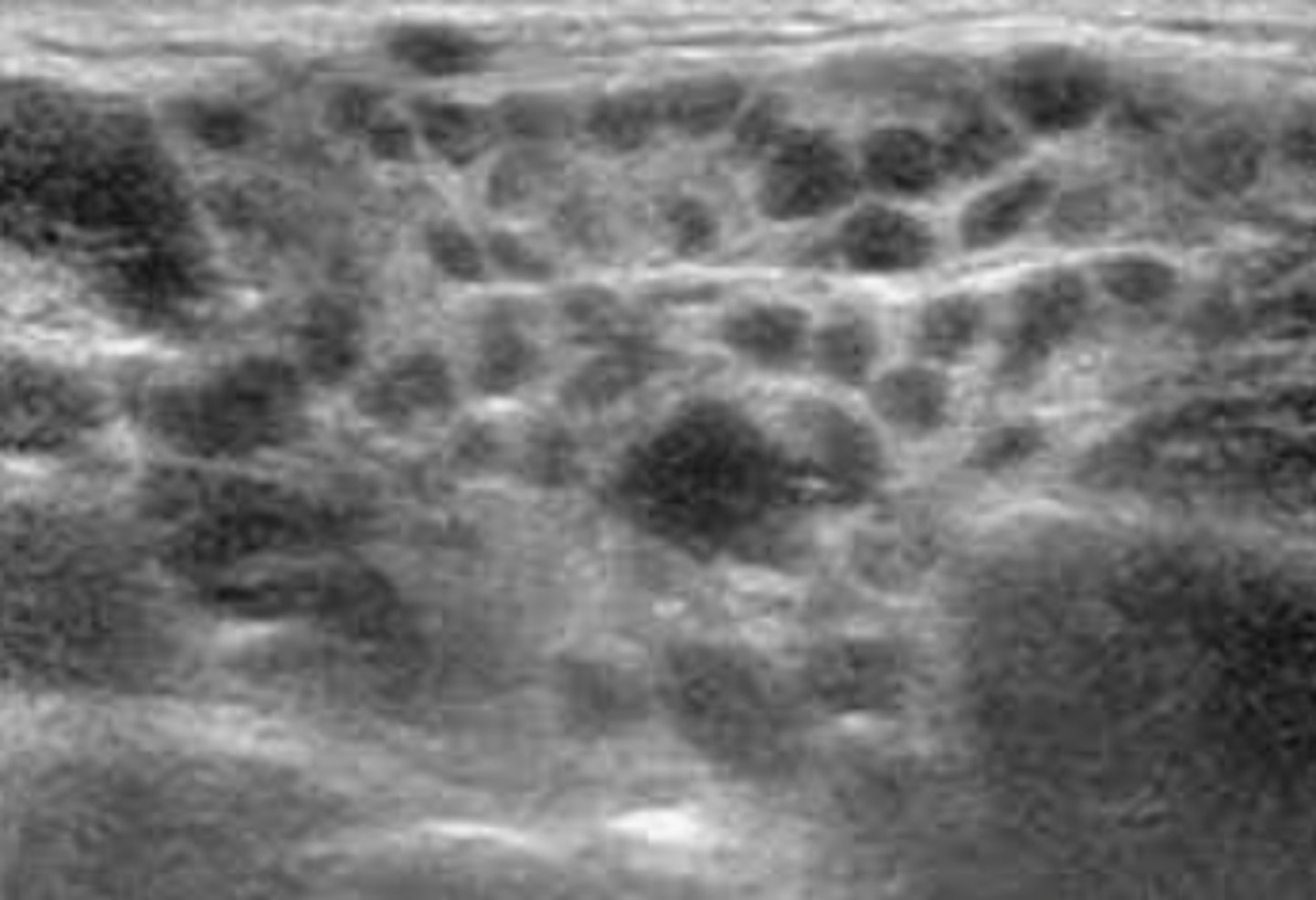
Sonographic Appearance:
-Thyroid lobes and isthmus appear as ____geneous solid structures demonstrating a medium-gray echo pattern with a surrounding thin ____echoic line
-Sternocleidomastoid muscle are _____ and oval in shape appearing ____echoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
-Strap muscles are _____ and ____echoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
-Longus colli muscles appear ____echoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
-Thyroid lobes and isthmus appear as homogeneous solid structures demonstrating a medium-gray echo pattern with a surrounding thin hyperechoic line
-Sternocleidomastoid muscle are large and oval in shape appearing hypoechoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
-Strap muscles are thin and hypoechoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
-Longus colli muscles appear hypoechoic compared with the normal thyroid gland
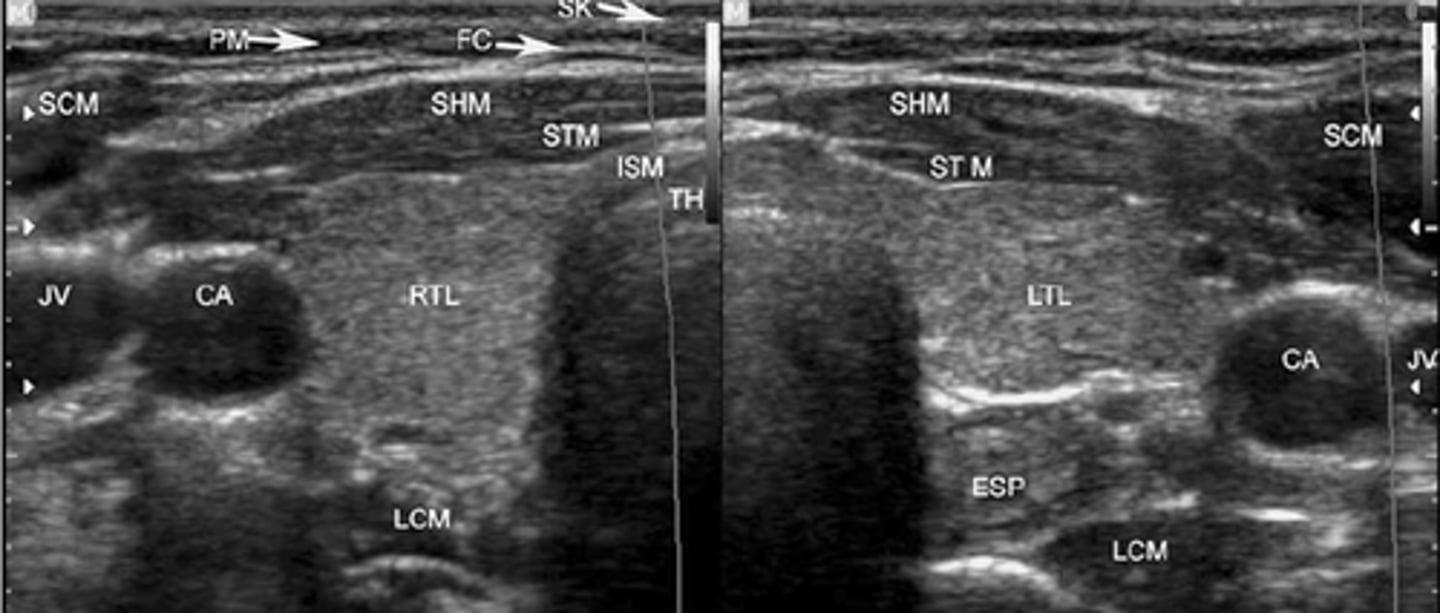
Sonographic Appearance:
-Parathyroid glands are flat, bean-shaped _____echoic structures located _____ and _____ to the thyroid lobes
-Salivary glands - ____geneous and ____echoic compared with the normal surrounding muscle. Degree of echogenicity depends on the amount of intraglandular _____ tissue
-Carotid arteries and jugular veins appear as ____echoic tubular structures demonstrating internal _____
-Parathyroid glands are flat, bean-shaped hypoechoic structures located posterior and medial to the thyroid lobes
-Salivary glands - homogeneous and hyperechoic compared with the normal surrounding muscle. Degree of echogenicity depends on the amount of intraglandular fatty tissue
-Carotid arteries and jugular veins appear as anechoic tubular structures demonstrating internal vascular flow
Thyroid Lab Values: Thyrotropin (TSH):
-Normal range _____ ng/mL
-_____ (TSH)
-Regulates thyroid hormone _____ and _____
-Secretion controlled by the ______
-Prolonged elevation is associated with _____ and _____
-Decrease in levels is the first indication of _____
-Normal range 3-42 ng/mL
-Thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH)
-Regulates thyroid hormone secretion and production
-Secretion controlled by the anterior pituitary gland
-Prolonged elevation is associated with hyperplasia and thyroid enlargement
-Decrease in levels is the first indication of thyroid gland failure
Thyroid Lab Values: Thyroxine (T4)
-Normal range _____ ug/dL
-Stimulates consumption of _____
-Secreted by the _____ cells of the thyroid
-Controlled by _____
-100-200 mg of _____ must be ingested per week for normal thyroxine production
-Decreases associated with _____ and _____
-Normal range 4.5-12.0 ug/dL
-Stimulates consumption of oxygen
-Secreted by the follicular cells of the thyroid
-Controlled by thyrotropin (TSH)
-100-200 mg of iodide must be ingested per week for normal thyroxine production
-Decreases associated with thyroid disease and nonfunctioning pituitary gland
Thyroid Lab Values: Triiodothyronine (T3)
-Normal range _____ ng/dL
-Regulates tissue _____
-Decreases associated with _____
-Normal range 70-190 ng/dL
-Regulates tissue metabolism
-Decreases associated with Hashimoto thyroiditis
Thyroid Lab Values: Calcitonin
-Normal range <_____ pg/mL
-Lowers _____ and _____ concentration in the blood
-Inhibits _____
-Secreted by the _____ cells (____-cells) of the thyroid gland
-Elevation associated with _____
-Decreases are associated with _____ or _____
-Normal range <100 pg/mL
-Lowers calcium and phosphorus concentration in the blood
-Inhibits bone resorption
-Secreted by the parafollicular cells (C-cells) of the thyroid gland
-Elevation associated with medullary thyroid carcinoma
-Decreases are associated with surgical removal or nonfunctioning thyroid glands
Parathyroid Lab Values: Parathormone (PTH)
-Normal range _____ pg/mL
-Regulates _____ metabolism in conjunction with calcitonin
-Released in response to low extracellular concentration of _____
-Elevation associated with _____
-Normal range 12-68 pg/mL
-Regulates calcium metabolism in conjunction with calcitonin
-Released in response to low extracellular concentration of free calcium
-Elevation associated with hyperparathyroidism
Parathyroid Lab Values: Calcium
-Normal range _____ mg/dL
-Aids in the _____ of _____ through the cell membranes
-Elevation associated with ____, ____, and ____
-Levels exceeding _____ mg/dL can be life-threatening
-Decreases are associated with _____ or _____ of the parathyroid glands
-Normal range 8.5-10.5 mg/dL
-Aids in the transportation of nutrients through the cell membranes
-Elevation associated with hyperparathyroidism, hyperthyroidism, and malignancy
-Levels exceeding 14.5 mg/dL can be life-threatening
-Decreases are associated with nonfunctioning or surgical removal of the parathyroid glands
Hyperthyroidism:
-_____ of the thyroid gland
-Symptoms include nervousness, _____, tremors, constant _____, weight _____, _____ intolerance, _____, increased _____, and _____
-Causes include toxic _____, _____ disease, and _____
-If untreated, may lead to _____
-Sonographic appearance - normal or _____ ____geneous ____vascular thyroid gland
-Hyperactivity of the thyroid gland
-Symptoms include nervousness, exophthalmos, tremors, constant hunger, weight loss, heat intolerance, palpitations, increased heart rate, and diarrhea
-Causes include toxic adenoma, Graves disease, and trophoblastic tumors
-If untreated, may lead to cardiac failure
-Sonographic appearance - normal or enlarged heterogeneous hypervascular thyroid gland
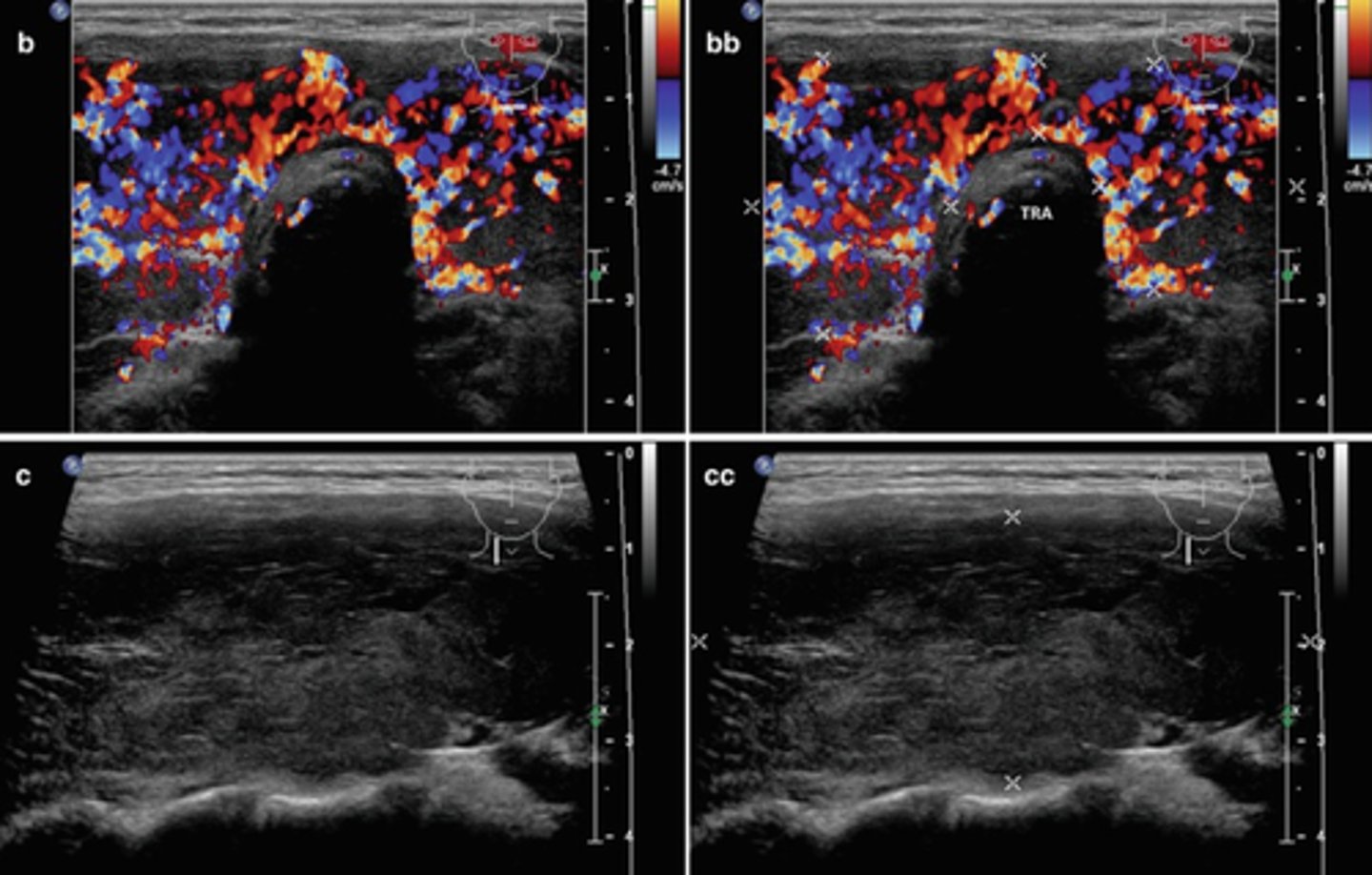
Hypothyroidism:
-Inadequate production of _____ and _____
-Symptoms include weight _____, _____ loss, mental and physical _____, skin _____, feeling _____, _____ cramps, _____, arthritis, _____ metabolic rate, and decreased _____
-Caused by _____ deficiency, chronic autoimmune _____, thyroid _____, and disease of the _____ or _____
-If untreated, may lead to ____, ____, or ____
-Sonographic appearance - _____, _____geneous irregular thyroid gland with possible _____
Hypothyroidism:
-Inadequate production of triiodothyronine (T3) and thyroxine (T4)
-Symptoms include weight gain, hair loss, mental and physical lethargy, skin dryness, feeling cold, muscle cramps, constipation, arthritis, slow metabolic rate, and decreased heart rate
-Caused by iodine deficiency, chronic autoimmune thyroiditis, thyroid hormone failure, and disease of the pituitary gland or hypothalamus
-If untreated, may lead to myxedema, coma, or death
-Sonographic appearance - enlarged, heterogeneous irregular thyroid gland with possible calcifications
What pathology does the following sonographic appearance describe?:
Normal or enlarged heterogeneous hypervascular thyroid gland
Hyperthyroidism
What pathology does the following sonographic appearance describe?:
Enlarged, heterogeneous irregular thyroid gland with possible calcifications
Hypothyroidism
Thyroid nodules:
___% are benign
___% are cysts
___% are malignant
60% are benign
20% are cysts
20% are malignant
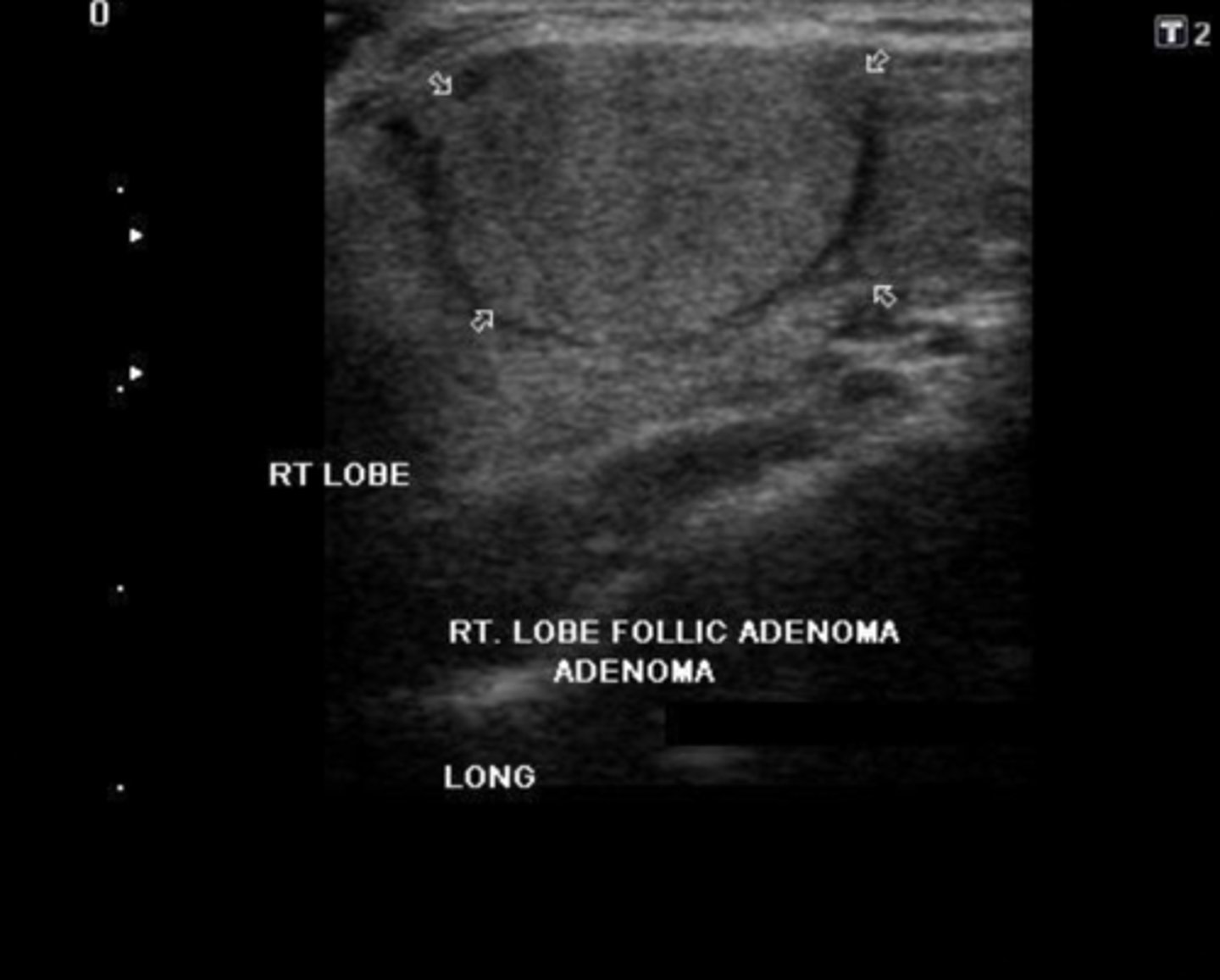
Benign Thyroid Neoplasms - Adenoma:
Etiology
-Composed of _____ tissue
-____ common thyroid neoplasm
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-_____
-_____ prevalence (7:1)
Sonographic findings
-Homogeneous _____ mass
-Prominent _____echoic peripheral halo
-_____ blood flow
-May degenerate and appear _____
-"_____" nodule on nuclear medicine scan
Etiology
-Composed of epithelial tissue
-Most common thyroid neoplasm
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Hyperthyroidism
-Female prevalence (7:1)
Sonographic findings
-Homogeneous echogenic mass
-Prominent hypoechoic peripheral halo
-Peripheral blood flow
-May degenerate and appear complex
-"Cold" nodule on nuclear medicine scan
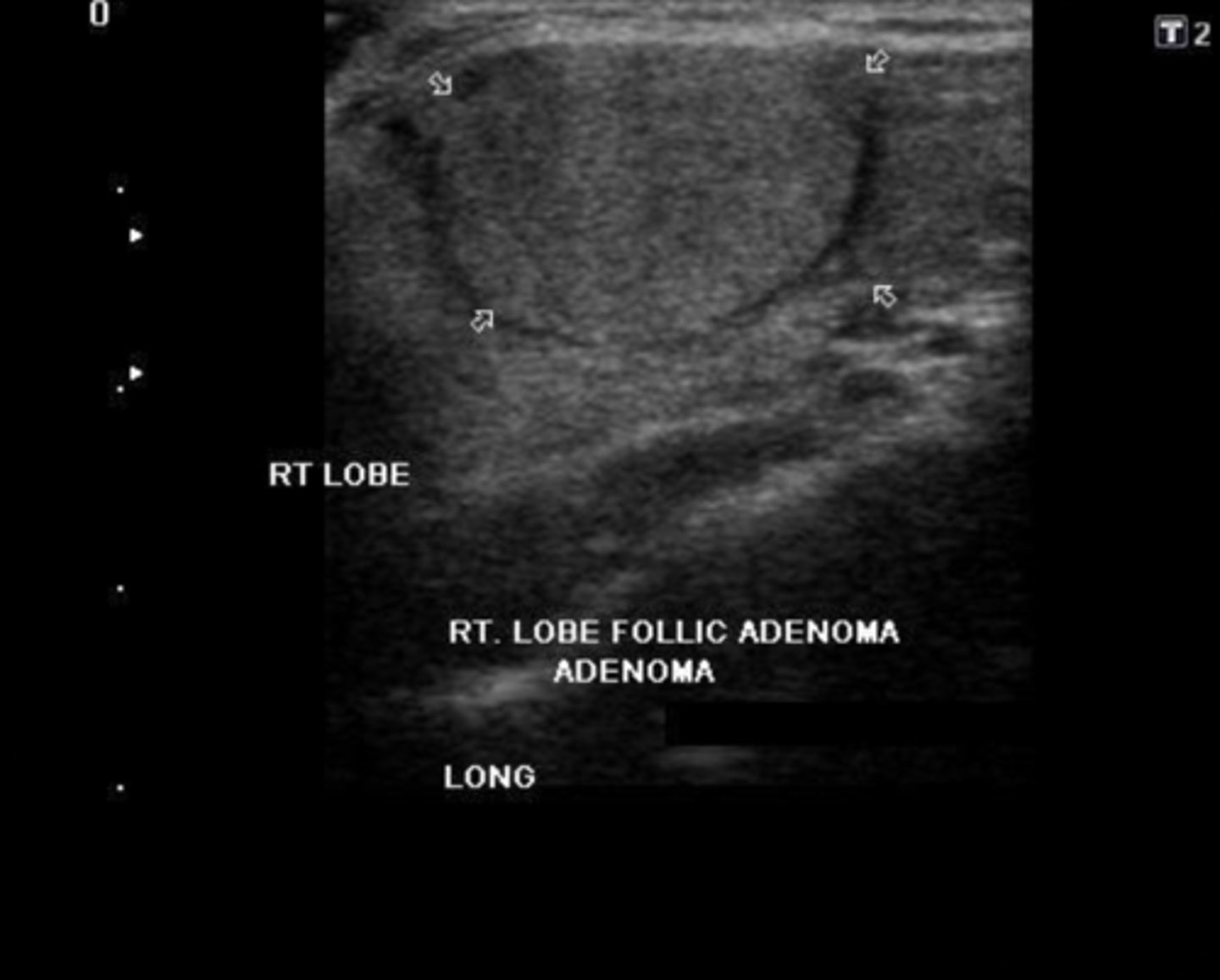
What is the most common thyroid neoplasm?
Adenoma
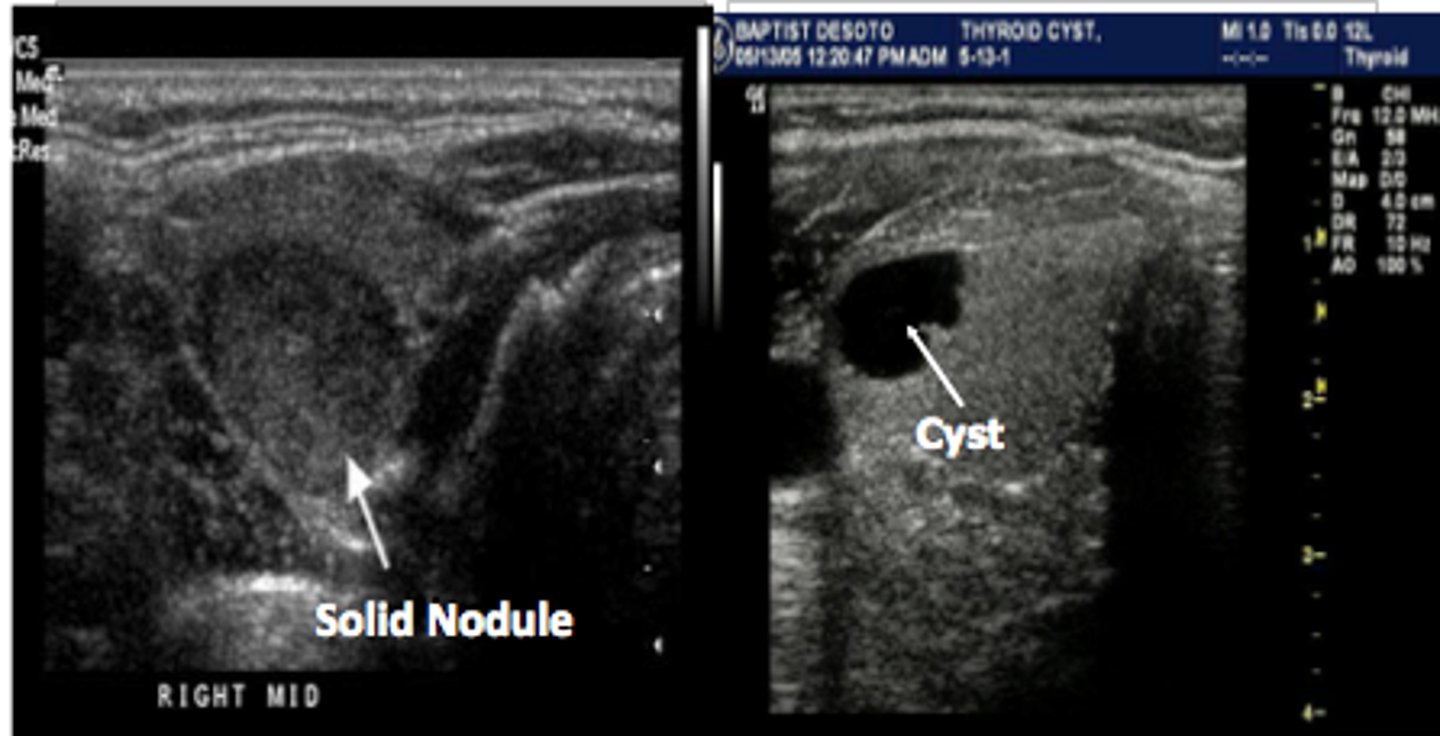
Benign Thyroid Neoplasms - Cyst:
10-15% of solitary thyroid nodules
Etiology
-_____ cyst
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-_____ neck mass
Sonographicfindings
-_____echoic mass
-_____ wall margins
-Posterior acoustic _____
-May demonstrate internal _____
Etiology
-Simple cyst
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Palpable neck mass
Sonographicfindings
-Anechoic mass
-Smooth wall margins
-Posterior acoustic enhancement
-May demonstrate internal debris
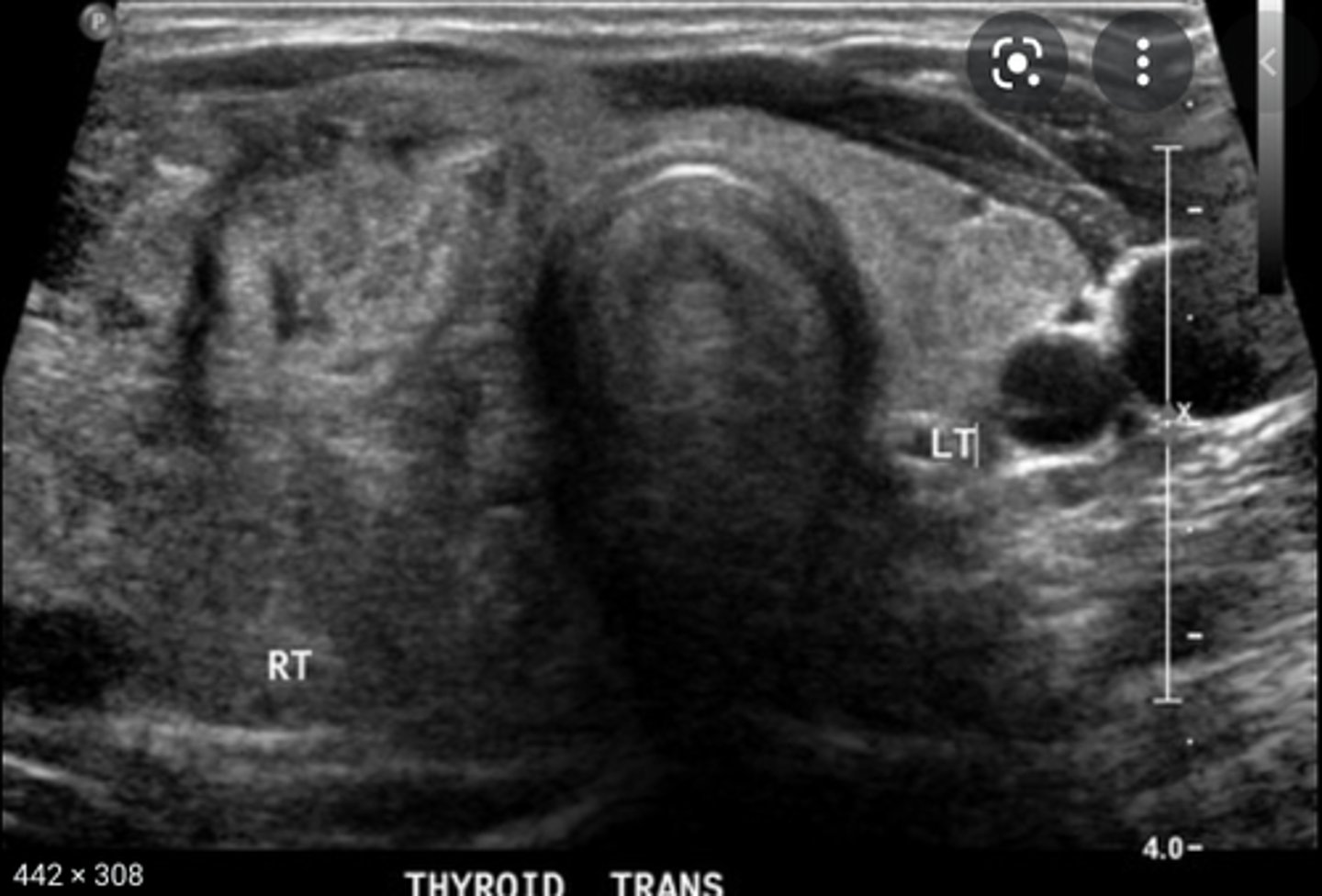
Benign Thyroid Neoplasms - Goiter:
Etiology
-_____ deficiency
-_____ deficiency
-_____ disease
-Thyroiditis
Clinical findings
-Palpable neck mass
-Dys____
-Dys____
-_____ or _____
Sonographic findings
-_____ thyroid lobe(s)
-Diffusely _____
-Areas of _____ degeneration
-May demonstrate _____
Etiology
-Thyroid hormone deficiency
-Iodine deficiency
-Graves' disease
-Thyroiditis
Clinical findings
-Palpable neck mass
-Dysphagia
-Dyspnea
-Hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged thyroid lobe(s)
-Diffusely heterogeneous
-Areas of cystic degeneration
-May demonstrate calcification(s)
Benign Thyroid Neoplasms - Hashimoto disease:
Etiology
-Chronic ____ ____ disease
Clinical findings
-Often _____
-_____thyroidism
-Leukocytosis
-Sore _____
-_____
Sonographic findings
-_____ _____echoic thyroid glands
-_____vascular parenchyma
Etiology
-Chronic lymphatic inflammatory disease
Clinical findings
-Often painless
-Hypothyroidism
-Leukocytosis
-Sore throat
-Fever
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged hypoechoic thyroid glands
-Hypervascular parenchyma
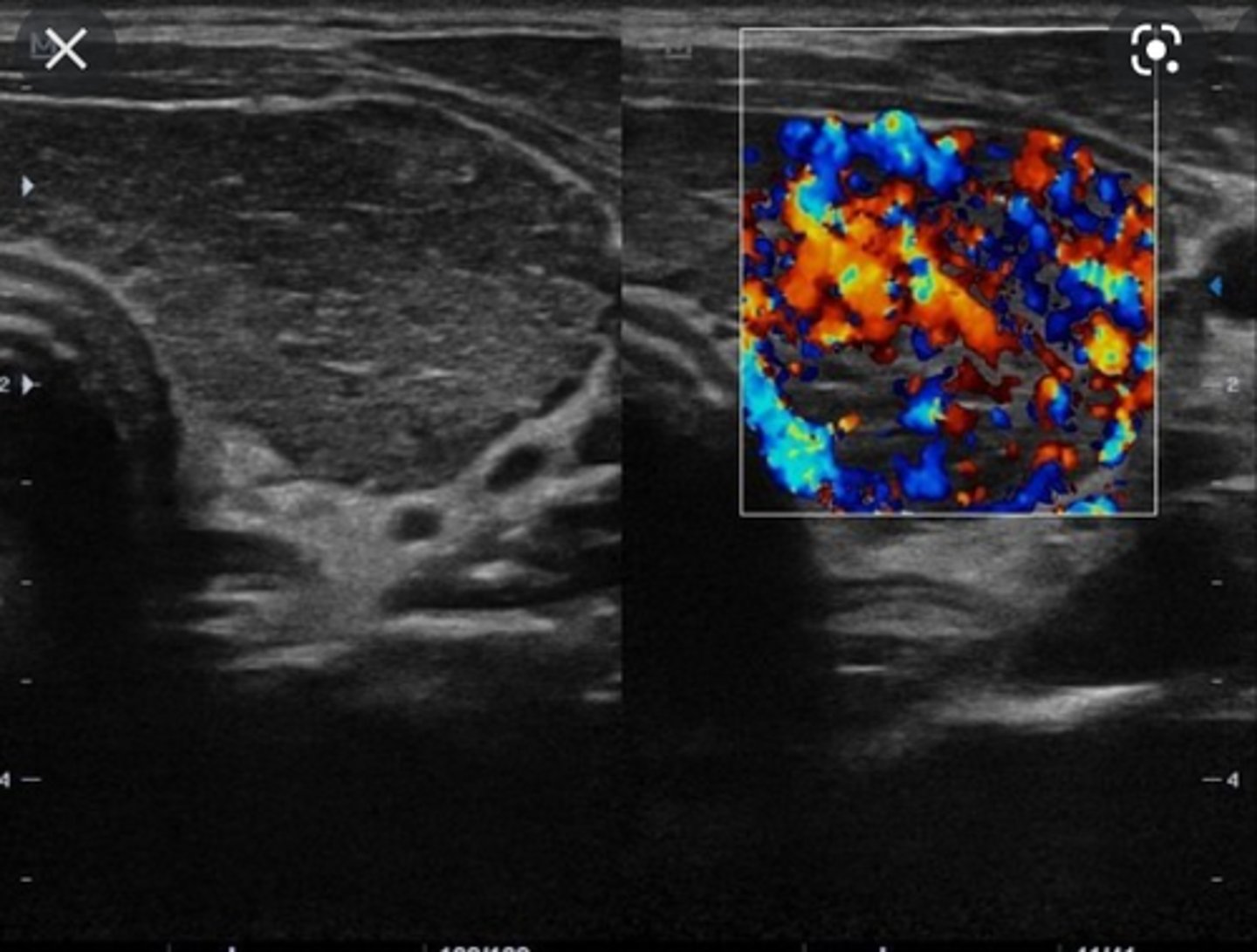
Benign Thyroid Neoplasms - Thyroiditis:
Etiology
-_____ disease
-_____ syndrome
-_____ infection
Clinical findings
-_____thyroidism followed by _____thyroidism
-_____
-Fever
-Leukocytosis
-_____ pain
-_____
Sonographic findings
-_____ ____echoic gland
-_____vascular perenchyma
-Discrete _____
Etiology
-Hashimoto disease
-De Quervain syndrome
-Viral infection
Clinical findings
-Hyperthyroidism followed by hypothyroidism
-Fatigue
-Fever
-Leukocytosis
-Neck pain
-Dysphagia
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged hypoechoic gland
-Hypervascular perenchyma
-Discrete nodules
Cysts of the Neck - Brachial cleft cyst:
Etiology
-Congenital _____ of the brachial cleft
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Palpable _____ neck mass
Sonographic findings
-Anechoic _____ neck mass
-Located directly below the angle of the _____
-Located _____ to the SCM muscle
-May demonstrate internal _____
Etiology
-Congenital diverticulum of the brachial cleft
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Palpable lateral neck mass
Sonographic findings
-Anechoic superficial neck mass
-Located directly below the angle of the mandible
-Located anterior to the SCM muscle
-May demonstrate internal debris
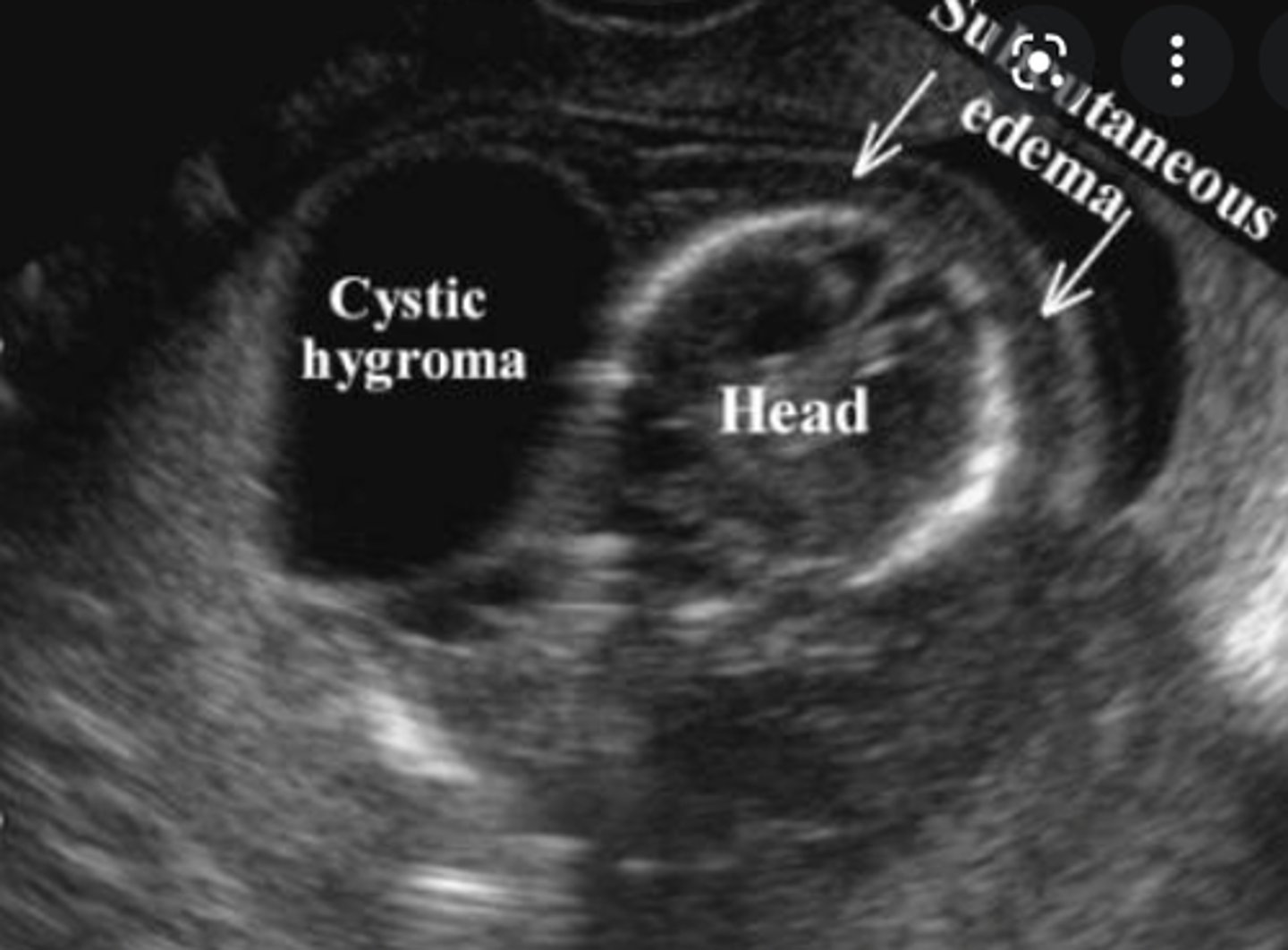
Cysts of the Neck - Cystic hygroma:
Etiology
-Inadequate drainage of lymph fluid into the _____
-Increased _____ from the epithelial lining
-Associated with _____ syndrome
Clinical findings
-Asymtpomatic
-_____ neck mass
Sonographic findings
-_____-walled, _____ cystic structure
Etiology
-Inadequate drainage of lymph fluid into the jugular vein
-Increased secretion from the epithelial lining
-Associated with Turners syndrome
Clinical findings
-Asymtpomatic
-Posterior neck mass
Sonographic findings
-Thin-walled, multilocular cystic structure
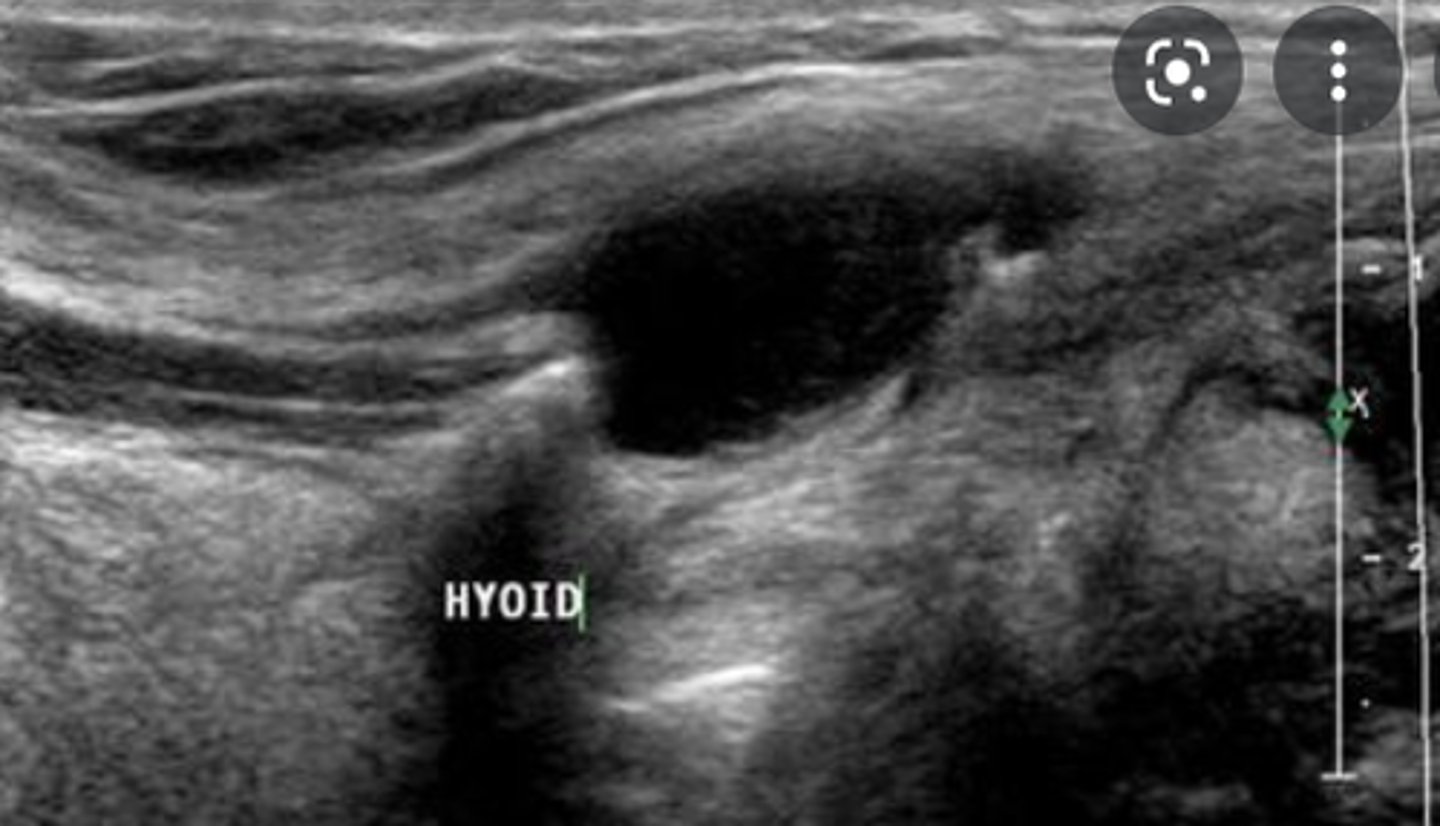
Cysts of the Neck - Thyroglossal cyst:
Etiology
-_____ remnant
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Palpable _____ _____ neck mass
Sonographic findings
-____echoic superficial neck mass
-Located between the _____ and the _____
-May demonstrate internal _____
-Document relationship to _____ (e.g., inferior)
Etiology
-Embryonic remnant
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Palpable superficial anterior neck mass
Sonographic findings
-Anechoic superficial neck mass
-Located between the tongue and the thyroid isthmus
-May demonstrate internal debris
-Document relationship to hyoid bone (e.g., inferior)
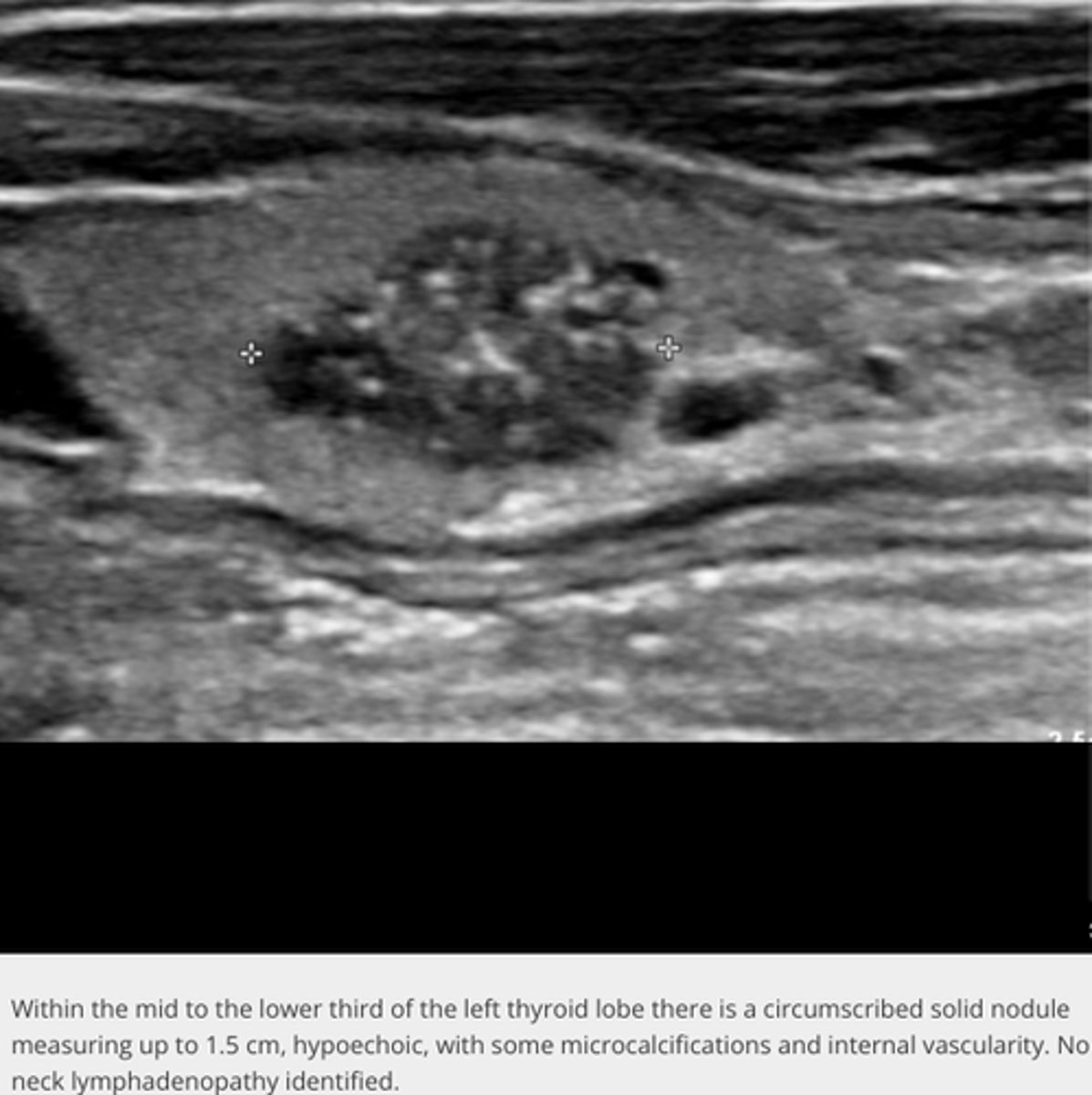
Malignant Thyroid Neoplasms - Carcinoma:
Etiology
-_____ (80%)
-_____ (5-15%)
-_____ (5%)
-_____ (2%)
Clinical findings
-Palpable _____ mass
-_____
-_____
-_____
-Neck pain
-Lymphadenopathy
Sonographic findings
-_____echoic mass
-_____ borders
-Thick _____ peripheral halo
-_____
-May degenerate
-Increase in _____ from previous exam
-_____ to cervical lymph nodes, lung, bone, and larynx
Etiology
-Papillary (80%)
-Follicular (5-15%)
-Medullary (5%)
-Anaplastic (2%)
Clinical findings
-Palpable neck mass
-Dysphagia
-Dyspnea
-Hoarseness
-Neck pain
-Lymphadenopathy
Sonographic findings
-Hypoechoic mass
-Irregular borders
-Thick incomplete peripheral halo
-Microcalcification(s)
-May degenerate
-Increase in size from previous exam
-Metastases to cervical lymph nodes, lung, bone, and larynx
Parathyroid Pathology - Hypercalcemia:
-Elevated _____ in the blood
-Symptoms include ____, ____, ____ pain, muscle pain and ____, ____ formation, ____, arthritis, weight ____, and bone ____
-Associated with ____parathyroidism, metastatic ____ tumor, ____ disease, and ____
-Extremely high levels may result in ____, ____, ____ failure, or ____
-Elevated calcium in the blood
-Symptoms include confusion, anorexia, abdominal pain, muscle pain and weakness, stone formation, gout, arthritis, weight loss, and bone demineralization
-Associated with hyperparathyroidism, metastatic bone tumor, Paget disease, and osteoporosis
-Extremely high levels may result in coma, shock, kidney failure, or death
Parathyroid Pathology - Hyperparathyroidism:
-Excessive function of the _____
-Most commonly caused by a _____ (80%)
-May lead to _____ and _____
-Elevated levels of ______
-Excessive function of the parathyroid glands
-Most commonly caused by a parathyroid adenoma (80%)
-May lead to osteoporosis and nephrolithiasis
-Elevated levels of parathormone
Parathyroid Pathology - Hypocalcemia:
-Deficiency of _____ in the blood
-Symptoms may include _____, _____ of the hands, feet, lips, and tongue; _____ cramps; _____; and fatigue
-Associated with _____, _____ failure, acute _____, and inadequate amount of _____ and _____
-Deficiency of calcium in the blood
-Symptoms may include cardiac arrhythmia, hyperparesthesia of the hands, feet, lips, and tongue; muscle cramps; anxiety; and fatigue
-Associated with hypoparathyroidism, kidney failure, acute pancreatitis, and inadequate amount of magnesium and protein
Parathyroid Pathology - Hypoparathyroidism:
-Insufficient function of the _____
-Associated with _____ and primary _____
-Insufficient function of the parathyroid glands
-Associated with hypocalcemia and primary parathyroid dysfunction
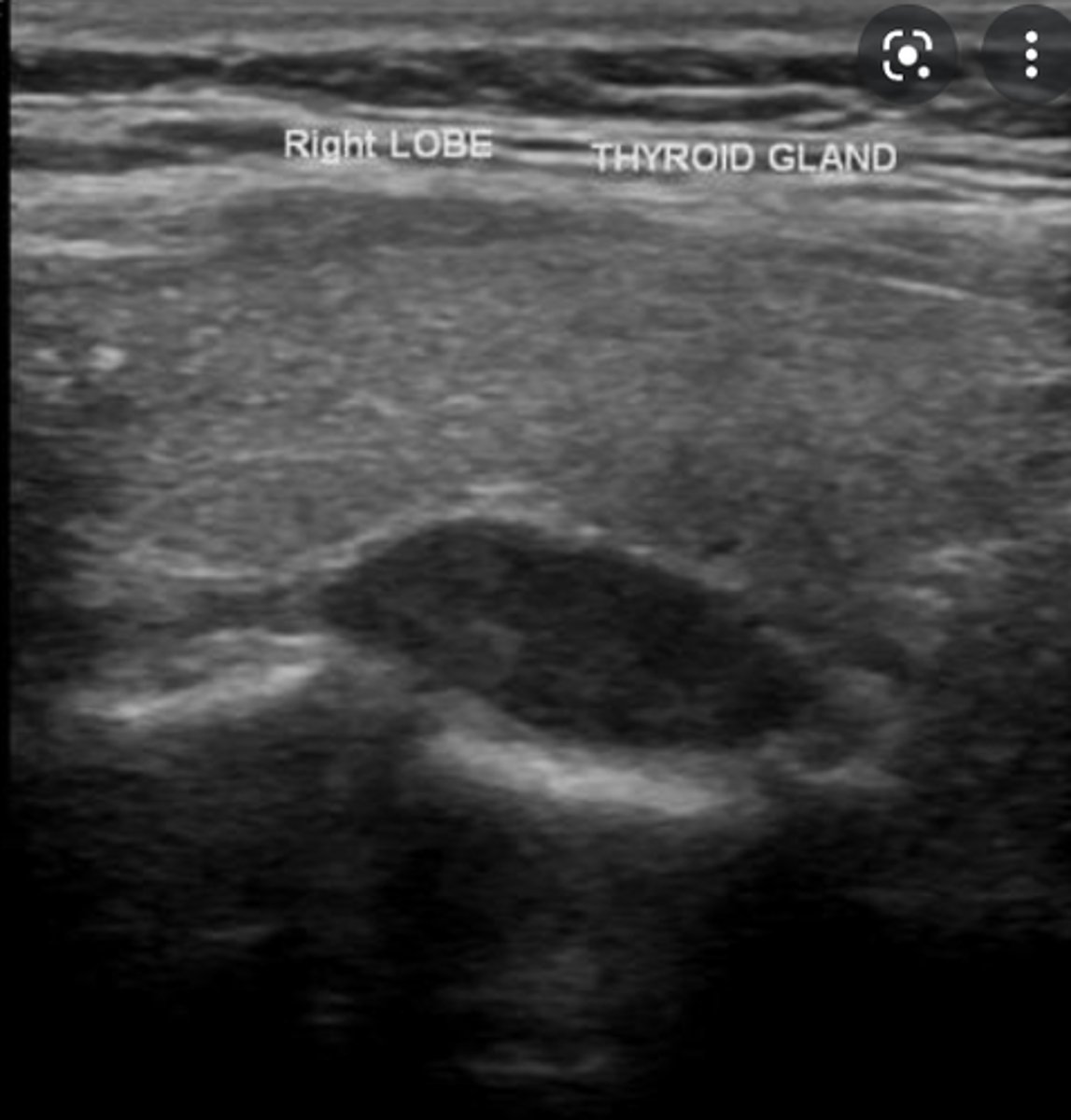
Parathyroid Pathology - Adenoma:
Etiology
-Exposure to _____
Clinical findings
-_____
-Decrease in serum _____
-Increase in _____
-Hypertension
-_____lithiasis
-_____lithiasis
-Pancreatitis
Sonographic findings
-_____echoic mass located _____ and _____ to the thyroid gland
-_____ in shape
-_____ vascular flow within larger lesions
Etiology
-Exposure to ionizing radiation
Clinical findings
-Hypercalcemia
-Decrease in serum phosphorus
-Increase in parathormone
-Hypertension
-Nephrolithiasis
-Cholelithiasis
-Pancreatitis
Sonographic findings
-Hypoechoic mass located posterior and medial to the thyroid gland
-Oval in shape
-Internal vascular flow within larger lesions
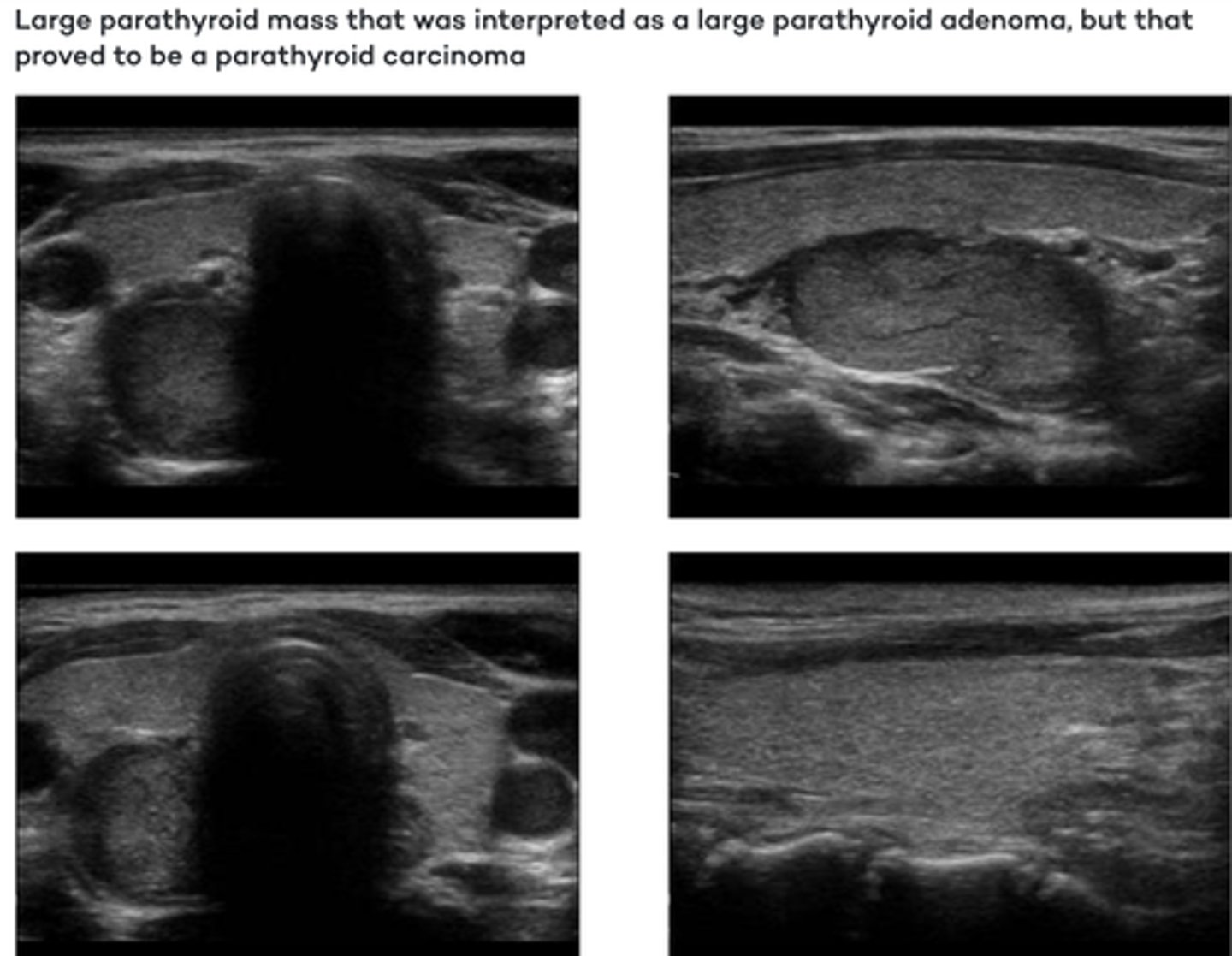
Parathyroid Pathology - Carcinoma:
Etiology
-_____ neoplasm
-_____-growing
-Tend to _____ surrounding tissues
Clinical findings
-_____
-Elevated _____ level
-_____ palpable neck mass
Sonographic findings
-_____echoic _____ mass
-Round or oval in shape
-_____ of sound (dense)
-_____vascular
Etiology
-Epithelial neoplasm
-Slow-growing
-Tend to infiltrate surrounding tissues
Clinical findings
-Hypercalcemia
-Elevated parathormone level
-Firm palpable neck mass
Sonographic findings
-Hypoechoic lobulated mass
-Round or oval in shape
-Attenuation of sound (dense)
-Hypervascular
Parathyroid Pathology - Cyst:
Etiology
-Uncommon
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-_____ prevalence
-_____ yrs of age
Sonographic findings
-_____echoic mass located _____ and ______ to the thyroid gland
-_____ wall margins
-Posterior acoustic _____
Etiology
-Uncommon
Clinical findings
-Asymptomatic
-Female prevalence
-60-70 yrs of age
Sonographic findings
-Anechoic mass located posterior and medial to the thyroid gland
-Smooth wall margins
-Posterior acoustic enhancement
What is the most common vascular mass in infants?
Hemangioma
Salivary Gland Pathology - Hemangioma:
Etiology
-Most common _____ mass in infants
-Usually located in the _____ gland (80%)
Clinical findings
-Painless
-_____, _____ growing mass
-May have _____ or _____ skin colouring
Sonographic findings
-_____geneous, _____echoic enlargement or mass
-_____vascular
-_____ circumscribed
-Usually located in the _____ gland (80%)
Etiology
-Most common vascular mass in infants
-Usually located in the parotid gland (80%)
Clinical findings
-Painless
-Compressible, slow growing mass
-May have red or blue skin colouring
Sonographic findings
-Heterogeneous, hypoechoic enlargement or mass
-Hypervascular
-Well circumscribed
-Usually located in the parotid gland (80%)
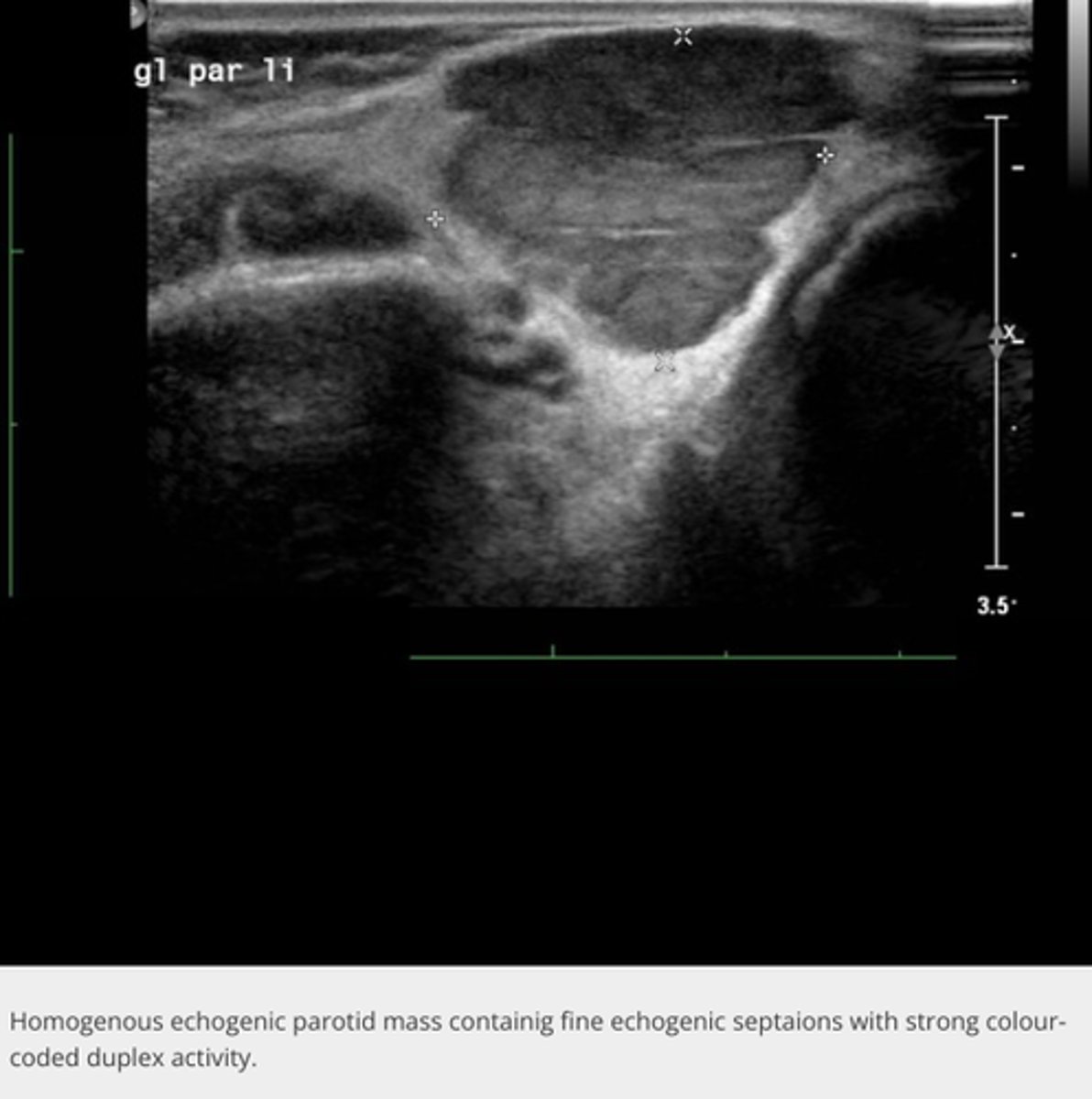
Salivary Gland Pathology - Parotitis:
Etiology
-Chronic _____ (salivary gland infection)
-Present _____ yrs of age
-More common in _____
Clinical findings
-Pain and swelling especially _____
Sonographic findings
-_____ _____geneous gland(s)
-Excretory duct(s) may be _____
-______ (presence of calculi in the salivary glands or ducts)
-_____ vascular flow
Etiology
-Chronic sialadenitis (salivary gland infection)
-Present 3-6 yrs of age
-More common in males
Clinical findings
-Pain and swelling especially postprandial
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged heterogeneous gland(s)
-Excretory duct(s) may be dilated
-Sialolithiasis (presence of calculi in the salivary glands or ducts)
-Normal vascular flow
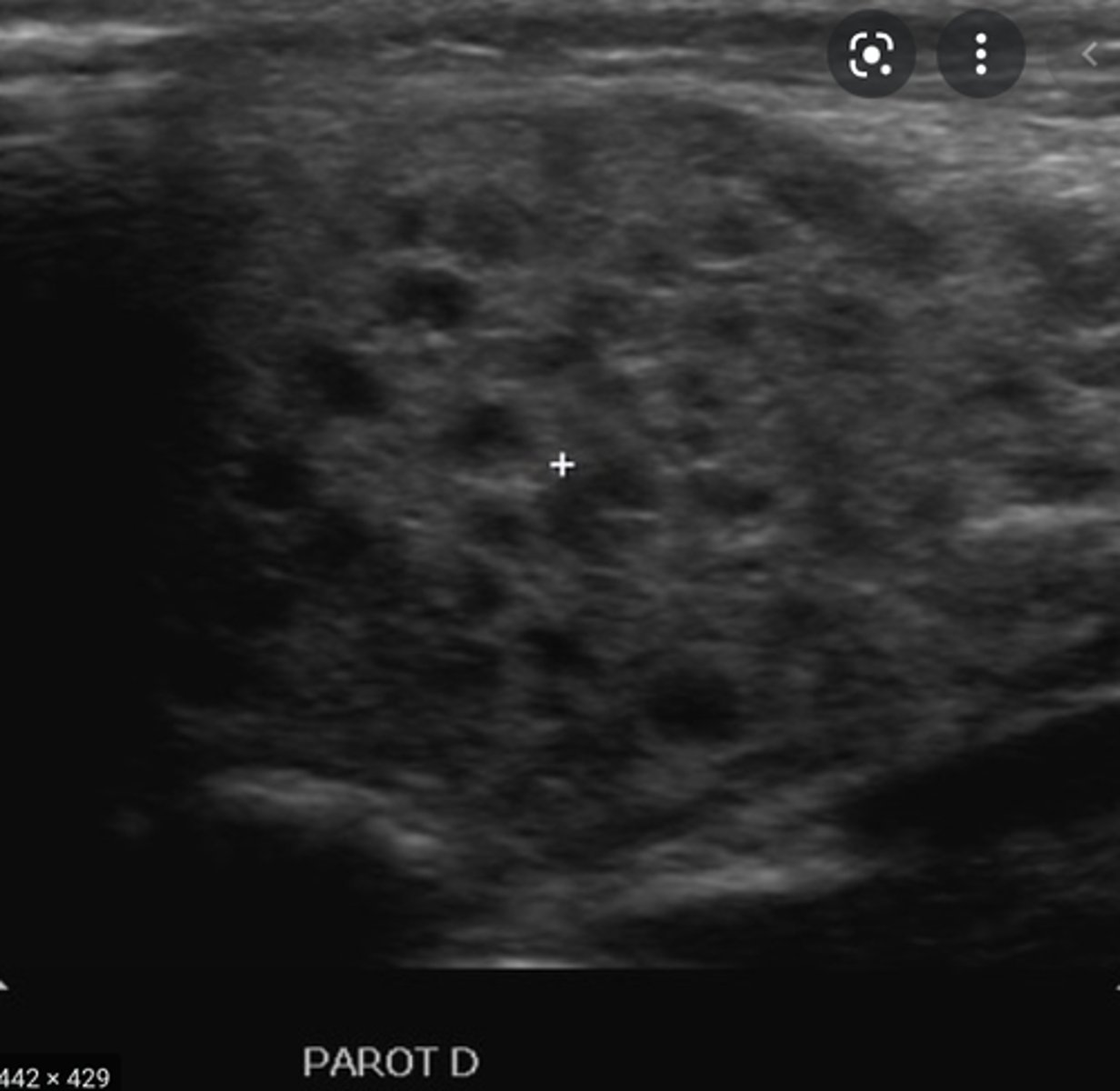
Salivary Gland Pathology - Sialadenitis:
Etiology
-Acute ____ or ____ infection
Clinical findings
-Painful swelling ___laterally
-Swelling during _____
-_____ pain
-_____ of skin
Sonographic findings
-_____, diffusely ____echoic gland
-_____ appearance
-_____vascular
-Cervical _____
Etiology
-Acute viral or bacterial infection
Clinical findings
-Painful swelling bilaterally
-Swelling during eating
-Postprandial pain
-Reddening of skin
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged, diffusely hypoechoic gland
-Complex appearance
-Hypervascular
-Cervical lymphadenopathy
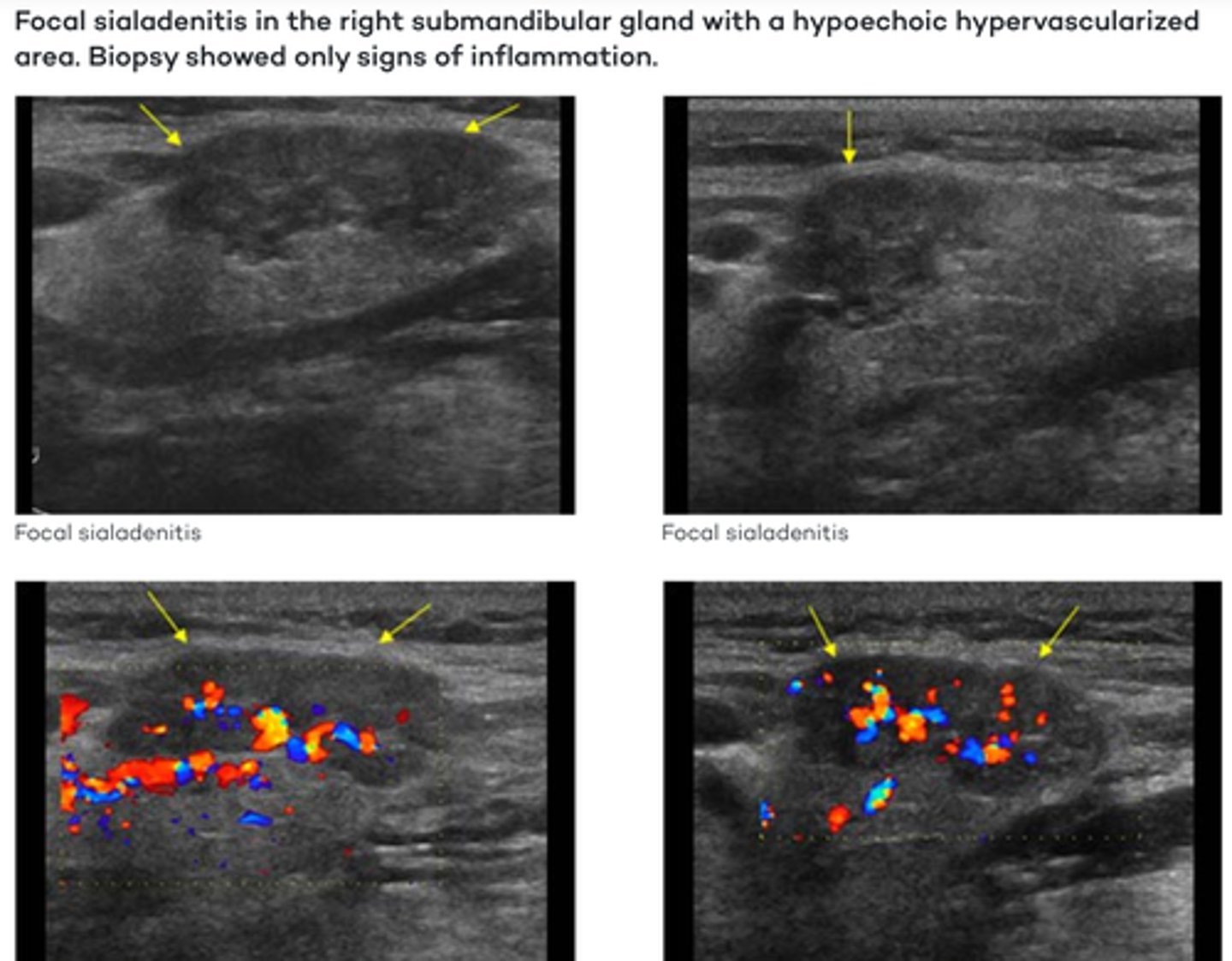
Salivary Gland Pathology - Sialolithiasis:
-_____ in 60-90% of cases
-_____ in 10-20% of cases
Etiology
-_____ in 50% of cases
Clinical findings
-Pain and swelling during _____
-_____ mass
Sonographic findings
-_____ or _____ echogenic focus(i)
-Posterior acoustic _____
-Submandibular in 60-90% of cases
-Parotid in 10-20% of cases
Etiology
-Infection in 50% of cases
Clinical findings
-Pain and swelling during eating
-Palpable mass
Sonographic findings
-Intraductal or intraglandular echogenic focus(i)
-Posterior acoustic shadowing
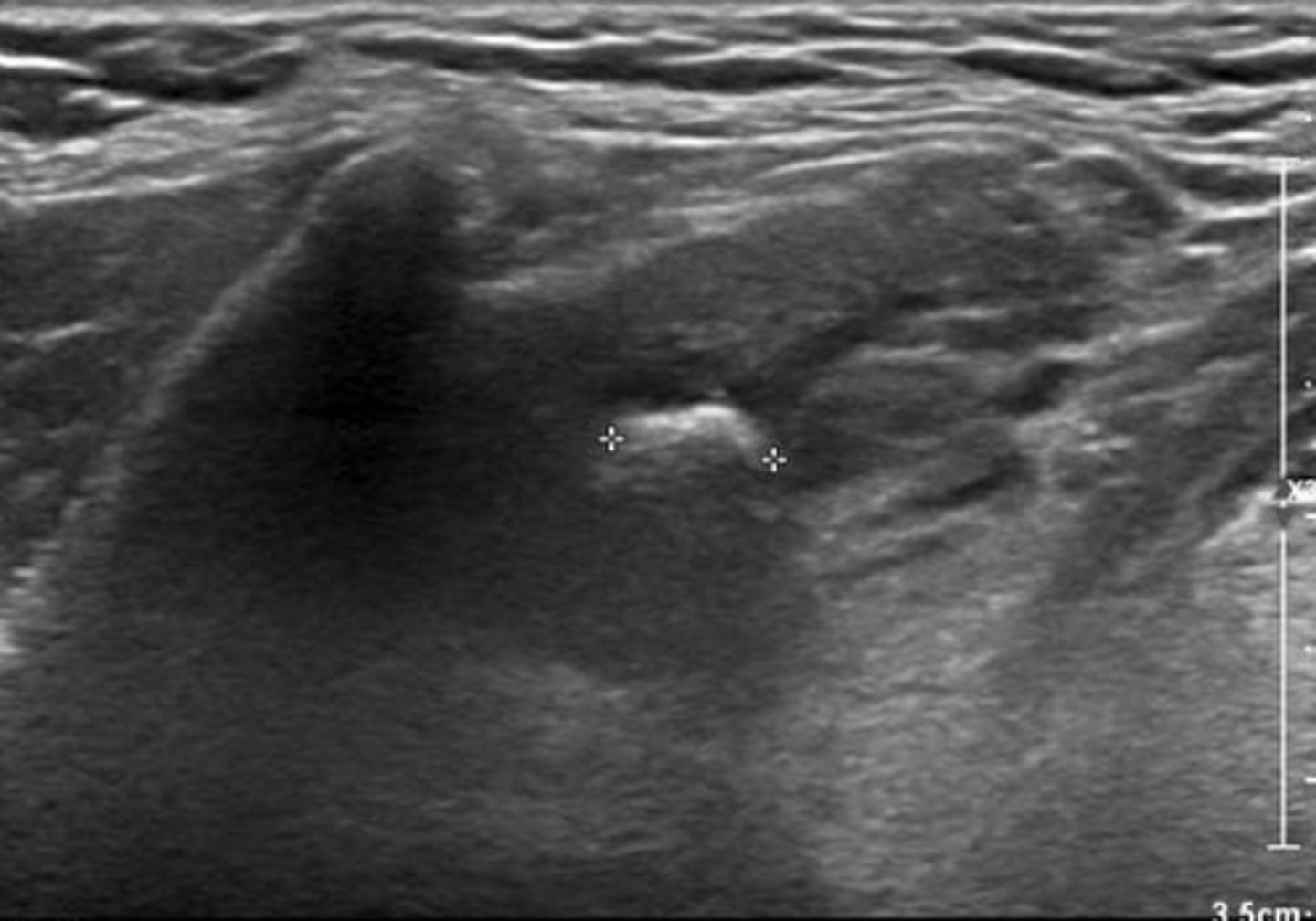
Salivary Gland Pathology - Sialosis:
Etiology
Associated with:
-_____ diseases
-Hepatic _____
-Chronic _____
-Malnutrition
Clinical findings
-_____, painless gland _____
Sonographic findings
-_____, _____echoic gland with increased attenuation
-_____ increase in vascularity
Etiology
Associated with:
-Endocrine diseases
-Hepatic cirrhosis
-Chronic alcoholism
-Malnutrition
Clinical findings
-Recurrent, painless gland swelling
Sonographic findings
-Enlarged, hyperechoic gland with increased attenuation
-No increase in vascularity
Salivary Gland Pathology - Sjogren's Syndrome:
Etiology
-Chronic _____ disease
Clinical findings
-Eye and mouth _____
-Severe _____
-_____ saliva
Sonographic findings
-_____geneous gland with small, oval _____echoic or _____echoic areas
-May demonstrate _____
Etiology
-Chronic autoimmune disease
Clinical findings
-Eye and mouth dryness
-Severe dental caries
-Frothy saliva
Sonographic findings
-Inhomogeneous gland with small, oval hypoechoic or anechoic areas
-May demonstrate hypervascularity