Biology 100: Photosynthesis, Cellular Respiration, DNA Replication
1/97
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
98 Terms
Do prokaryotes have chloroplasts?
NO they don't but they still do photosynthesis
-to produce the concentration difference, we need to have a membrane
Where do prokaryotes have a membrane?
Their cell membrane (plasma membrane)
What is stomata?
Small openings on the underside of a leaf through which oxygen and carbon dioxide can move
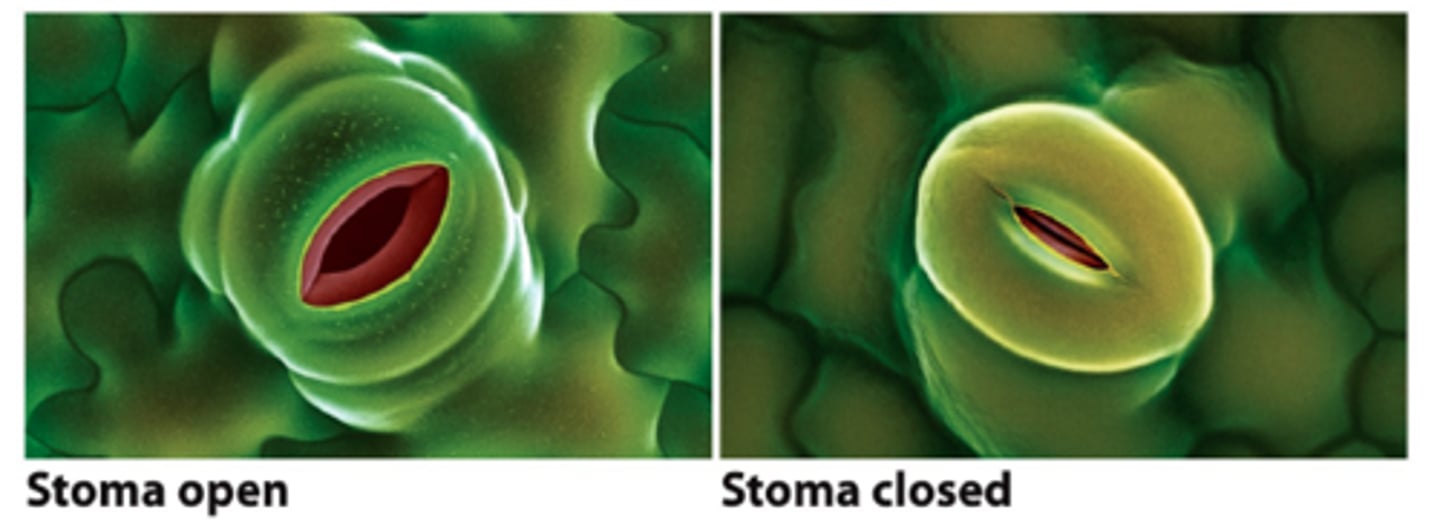
What if water is limited?
- open pores let in CO2
- but closed pores keep in water
- plants can used different strategies depending on costs/benefits of opening pores in the climate they inhabit.
What are C3 plants?
open pores that let in lots of O2, they are good for wet climates (little danger of excess water loss
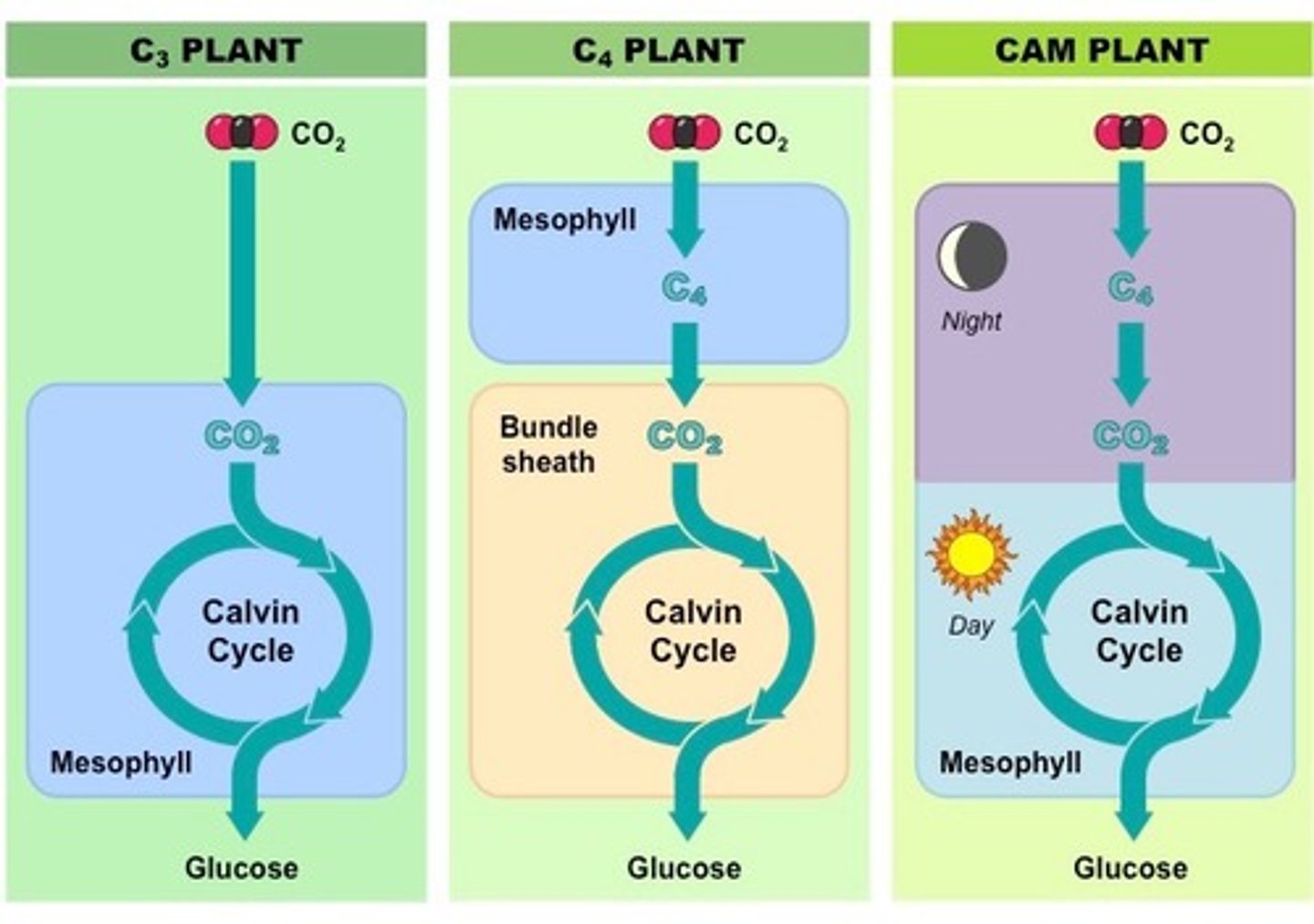
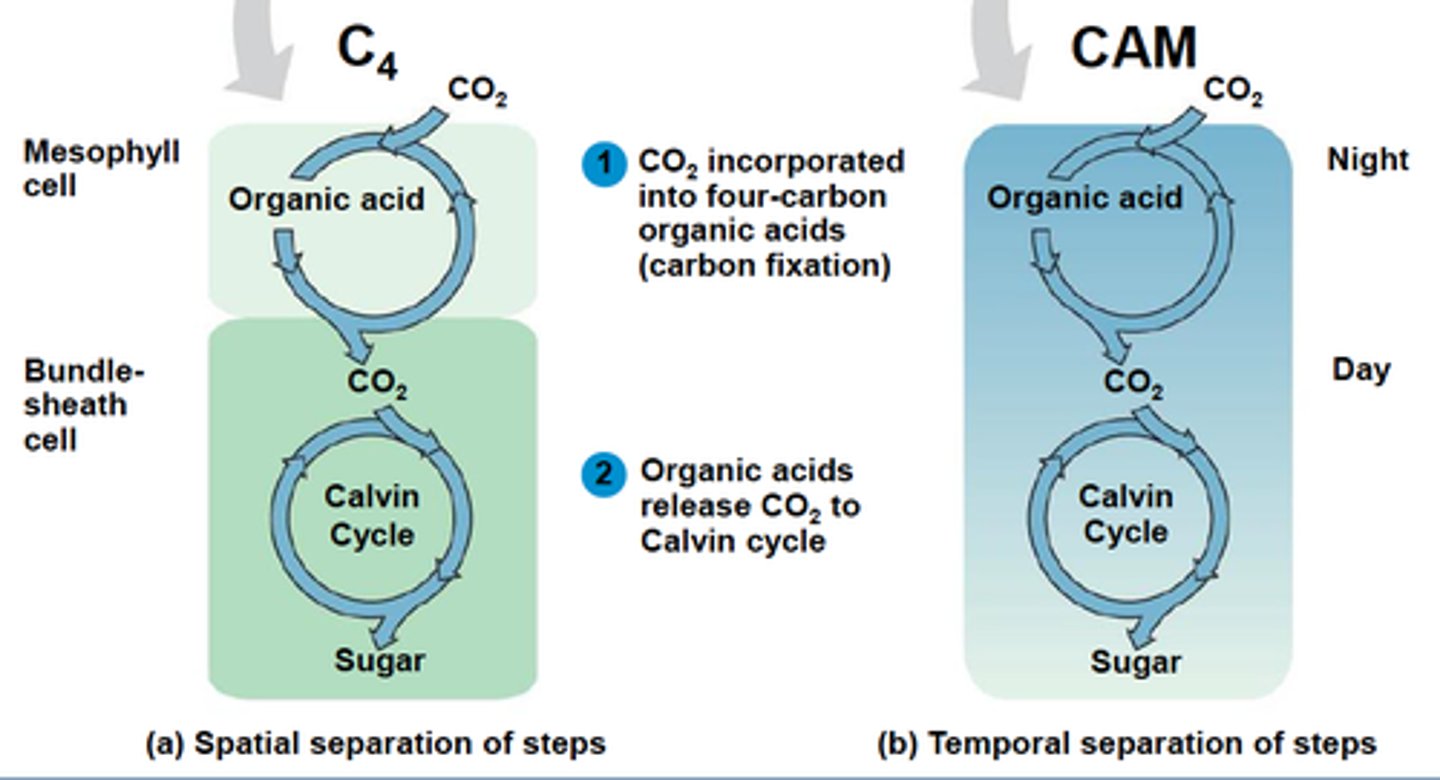
What are C4 and CAM plants?
keep pores closed some of the time, conserve water, good for hot dry climates
What is drawback of C3?
water loss through open pores
Where do C3 plants get CO2 from?
They get it directly from the air and use it!
What do C4 and CaM plants do with CO2?
They store the carbon from it in other carbon compounds
What is drawback of C4 and CAM?
it is less efficient (extra chemical required)
Whats the benefit of understanding Photosynthesis?
- plants are very efficient at converting sunlight to useable energy
-human societies would benefit greatly from efficient harnessing of sun energy
What percent of visible sunlight do plants convert to usable chemical energy?
90%

What do solar panels do?
They convert 10-20% of sunlight to electrical energy and most affordable material converts 5%

What are biofuels?
alternative renewable fuels made from plant materials

What are the pros and cons of corn biofuels?
Technology ready, realtively cheap, reduces food supple, production requires lots of resources

What are the pros and cons of sugar cane biofuels?
Technology ready, limits range where it will grow, production requires lots of resources

What are the pros and cons of switch grass biofuels?
won't complete with food supply, production requires relatively few resources, technology is not ready

What are the pros and cons of algae biofuels?
won't compete with food supply or agricultural land, production requires relatively few resources, potential for HUGE levels of production, technology is not ready.

What cells can do cellular respiration?
Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes
What are the steps of cellular respiration?
1. Glycolysis
2. Citric Acid Cycle aka Krebs Cycle
3. Electron Transport Chain
What cell can only do the citric acid cycle and electron transport cycle?
Eukaryotes because it requires mitochondria
What is glycolysis and where does it occur?
Glycolysis ("sugar splitting") breaks down glucose into 2 molecules of pyruvate. Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm. Gets 2 ATP from it
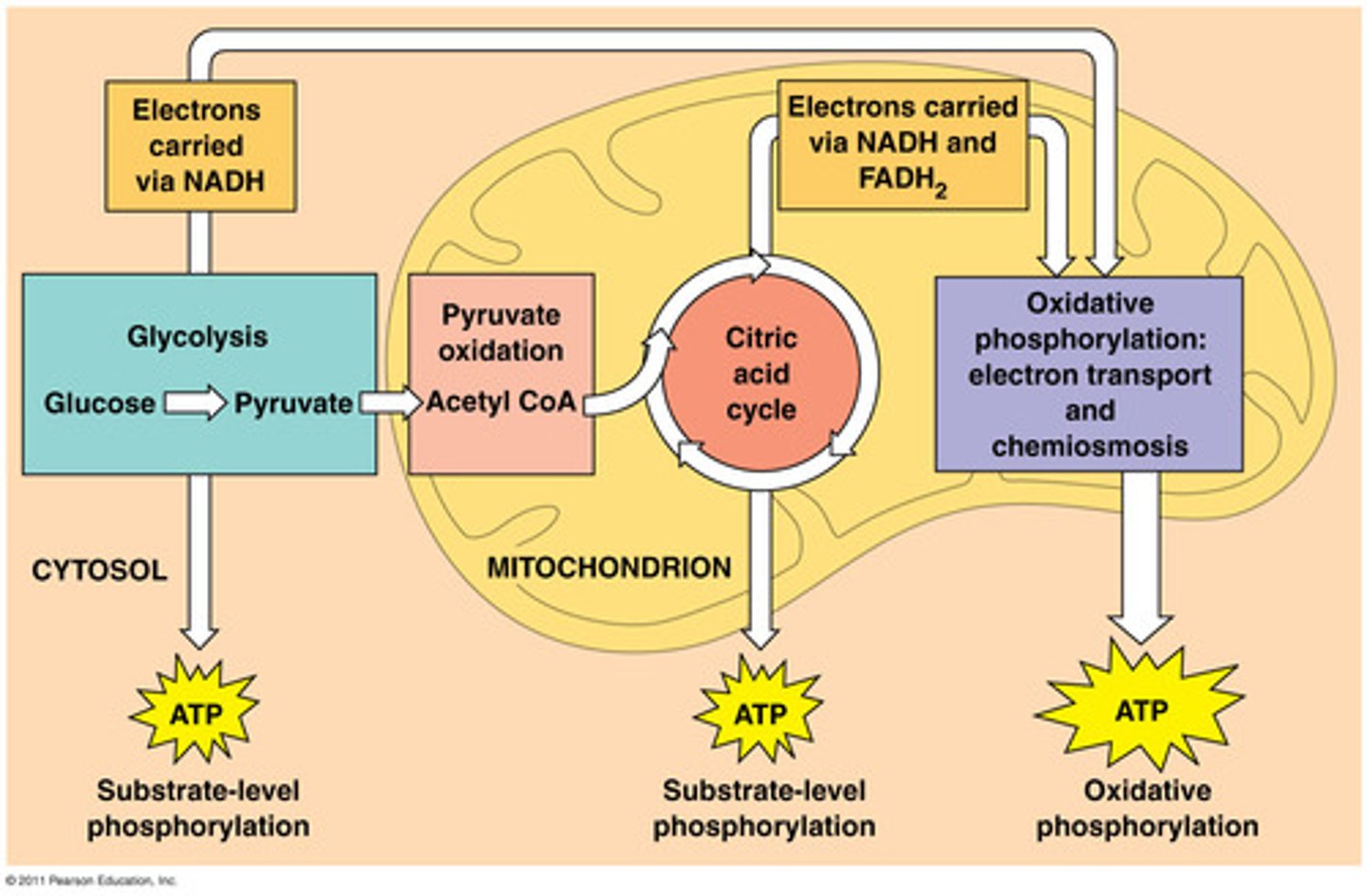
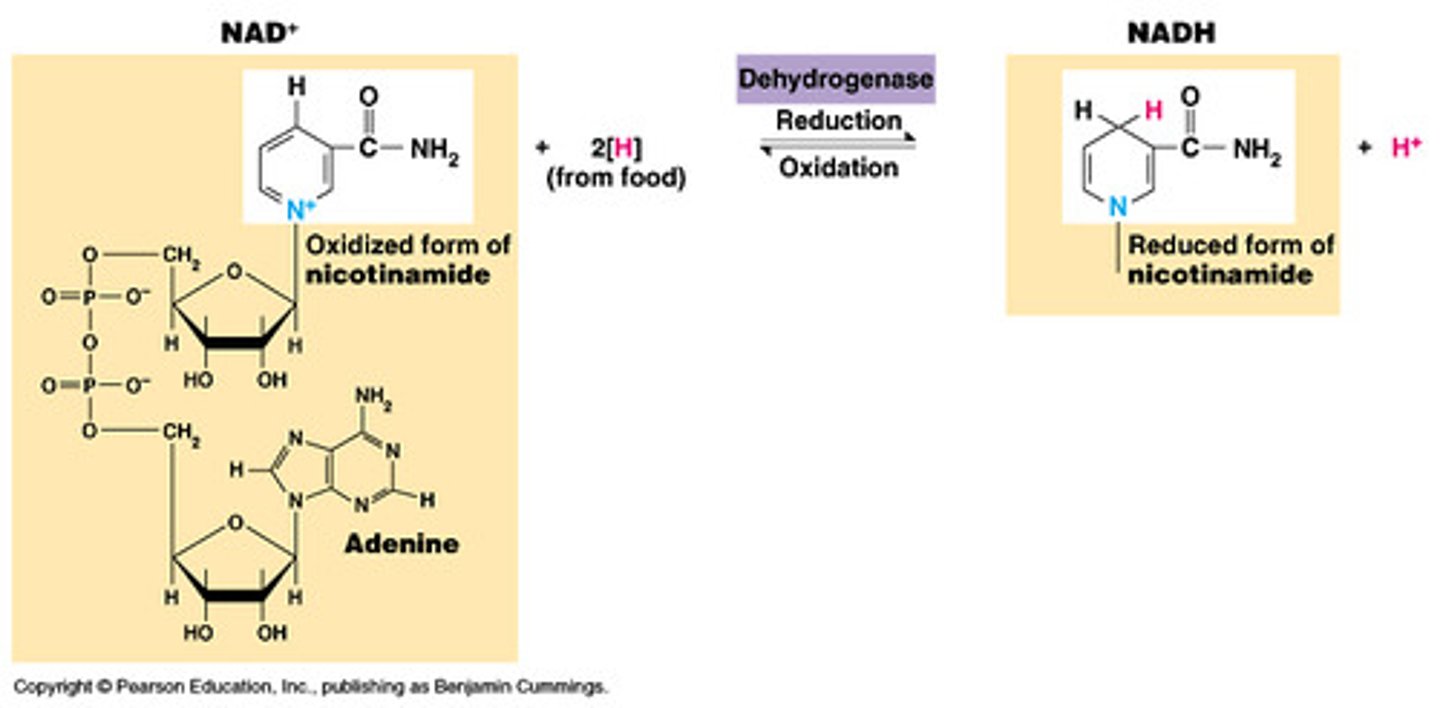
What is NAD+ and NADH?
They are electron carriers and they collect electrons and carry them to where the electrons need to go to produce ATP. They easily receive and give up electrons
At the end of glycolysis we have what?
- 4 molecules of ATP (used 2 of these)
- 2 molecules of NADH (used 2 of these to start process)
- 2 pyruvate molecules
only 10% of energy of one glucose molecule
What happens when we run out of NAD+ or cell only has NADH?
we need some way to replenish NAD+ by using the electrons stored in NADH
What happens in aerobic respiration? (WITH OXYGEN)
we can give extra electrons to oxygen in the electron transport cycle
What happens in anaerobic respiration? (NO OXYGEN)
1) turn pyruvate into latin acid
2) turn pyruvate into alcohol
3) use something other than oxygen

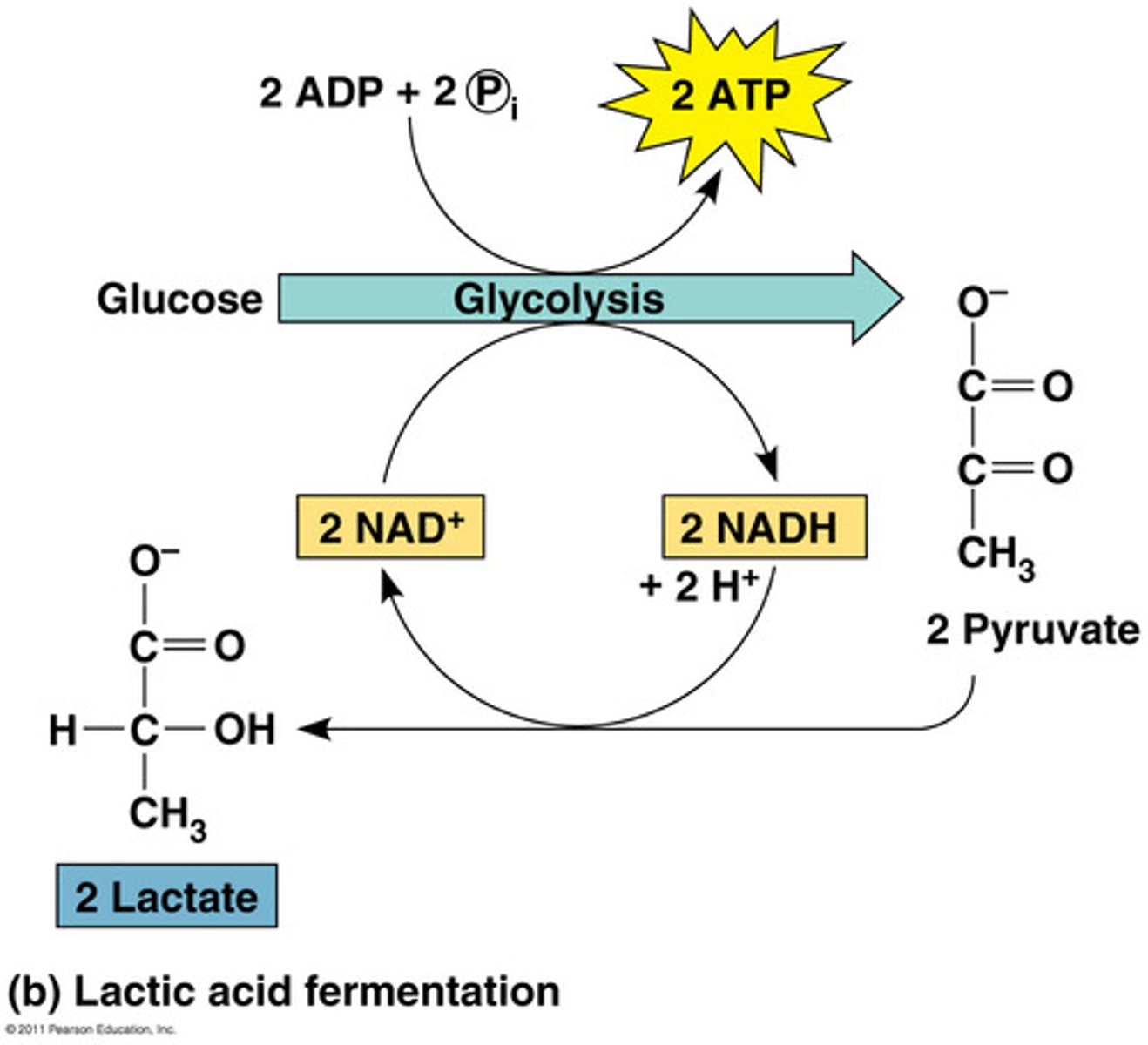
What is lactic acid fermentation?
Lactic acid fermentation is when pyruvate is reduced by NADH, and forms lactate as a waste product, thus releasing no CO2.
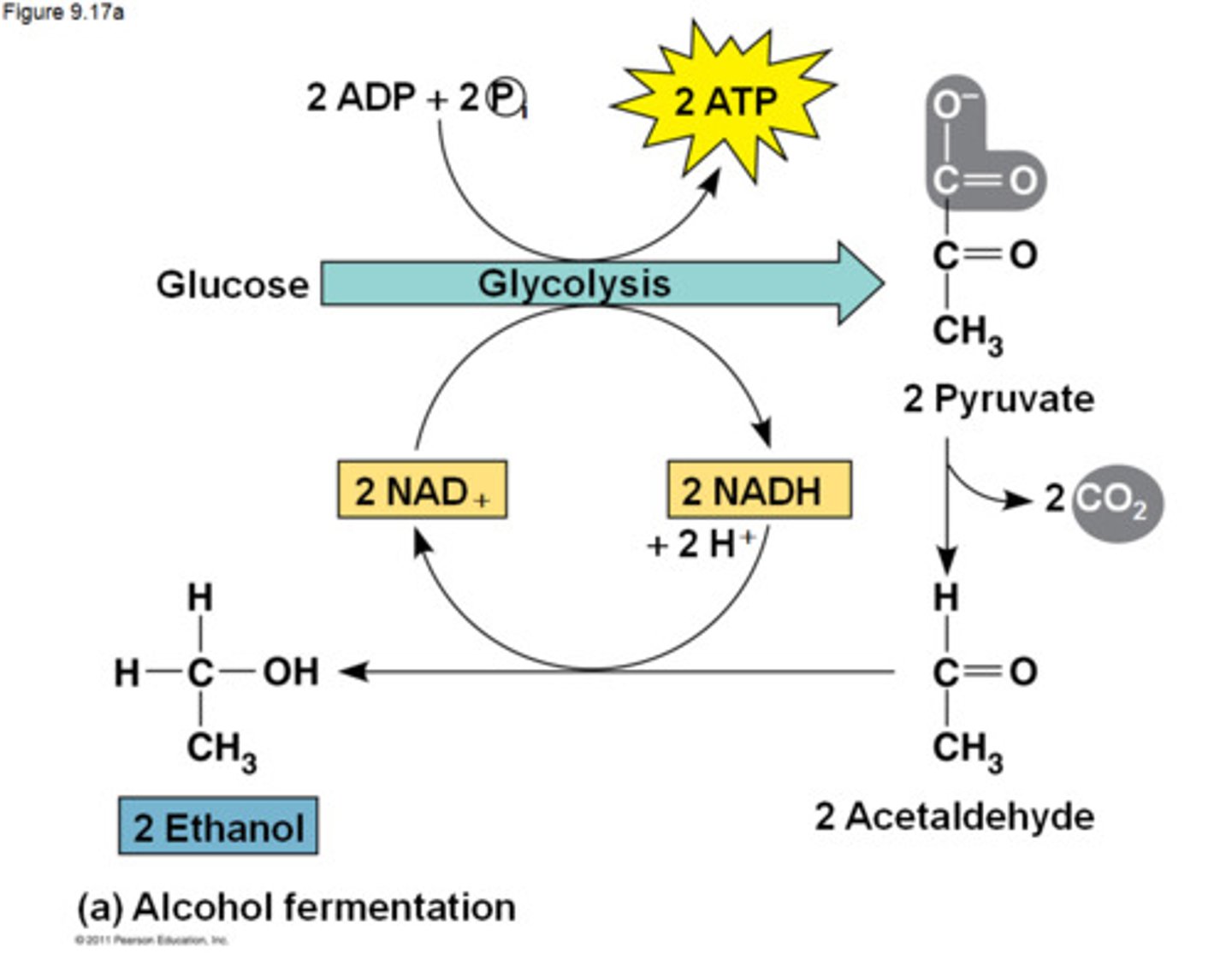
What is alcohol fermentation?
Glycolysis followed by the reduction of pyruvate to ethyl alcohol, regenerating NAD+ and releasing carbon dioxide.
Whats example of lactic fermentation?
human muscles when cells are not get enough O2, they get fatigued
Whats an example of alcohol fermentation?
yeast aka BREAD AND BEER
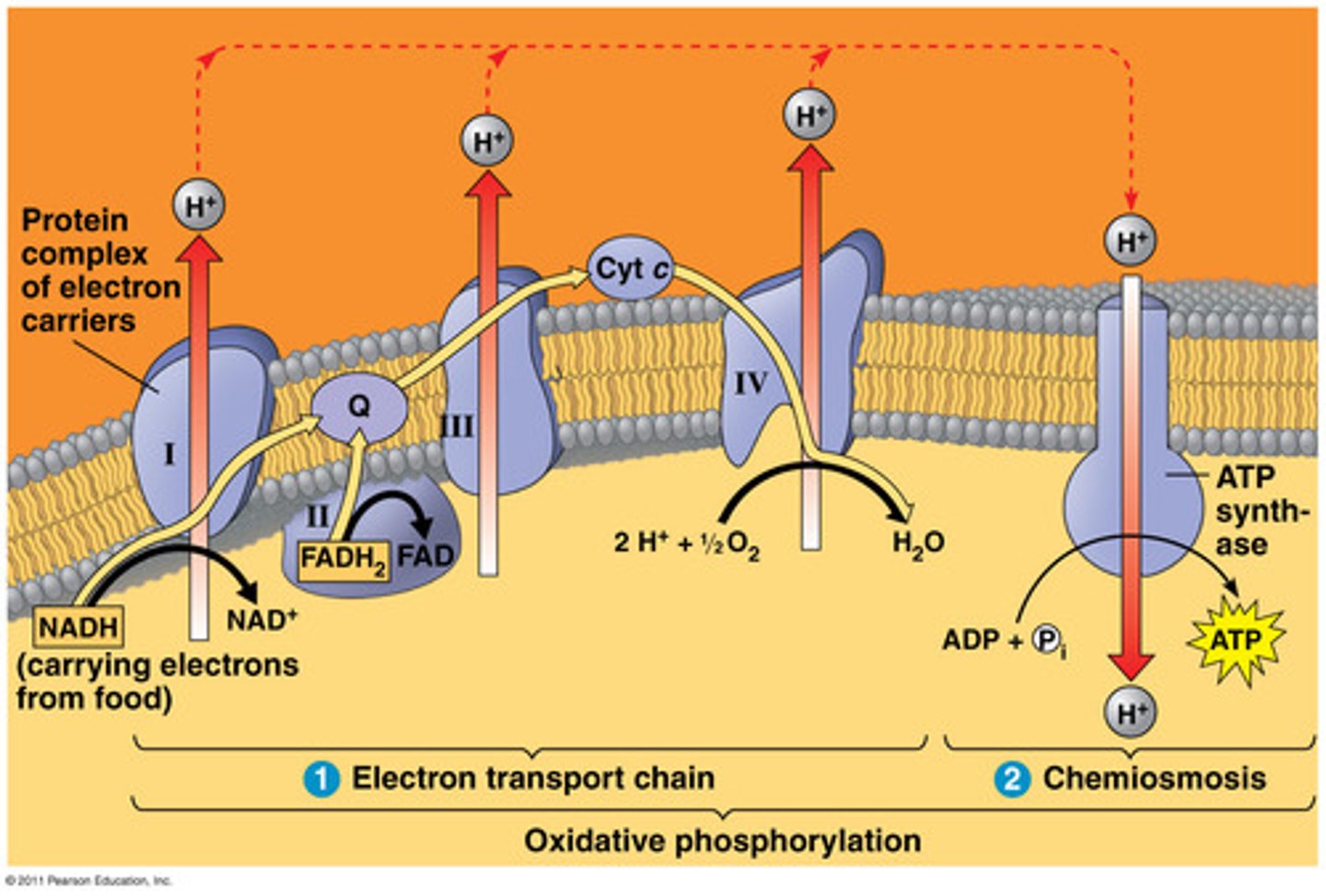
What is the electron transport?
The third stage of cellular respiration. Electrons are captured from food by the NADH formed in the first 2 stages "fall" down electron transport chains to oxygen.
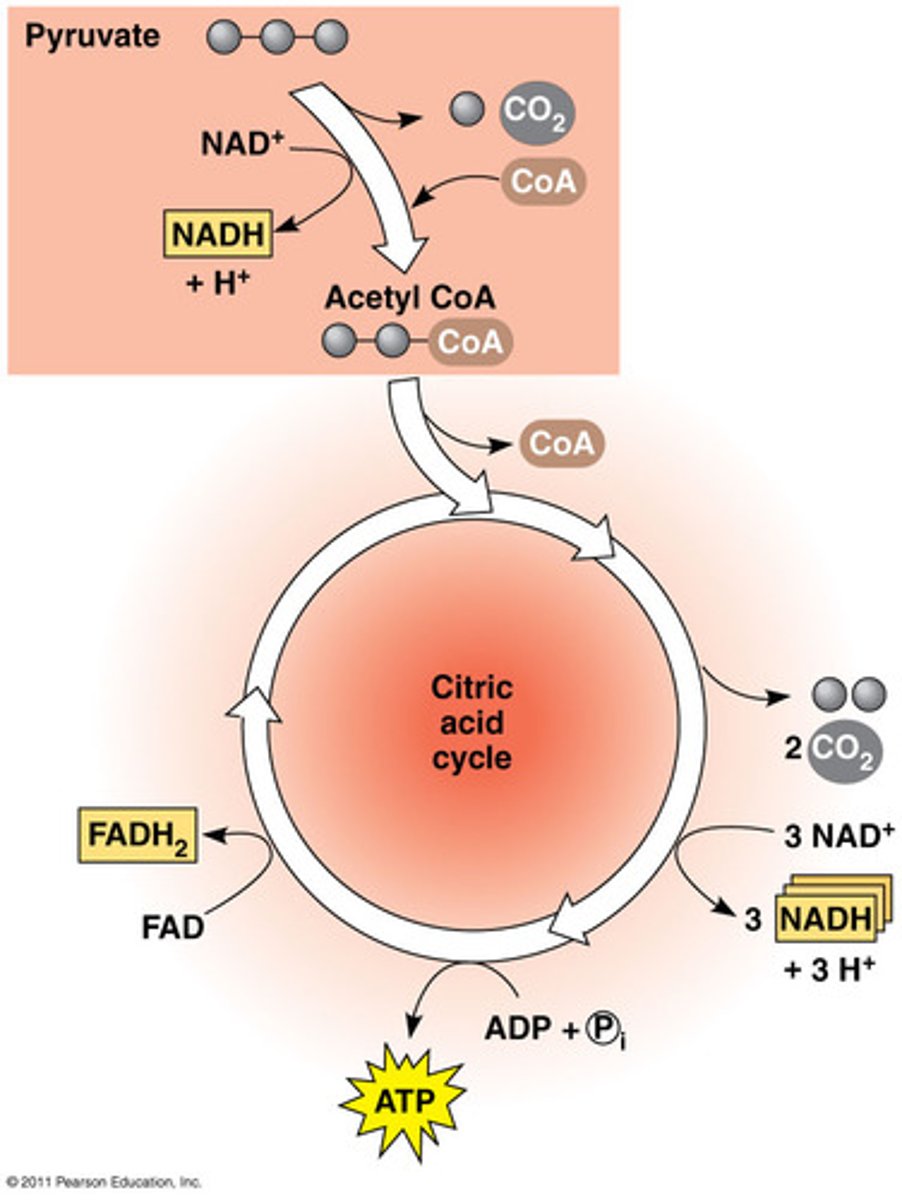
What is the citric acid cycle?
series of redox reactions that result in the breaking down of glucose to CO2
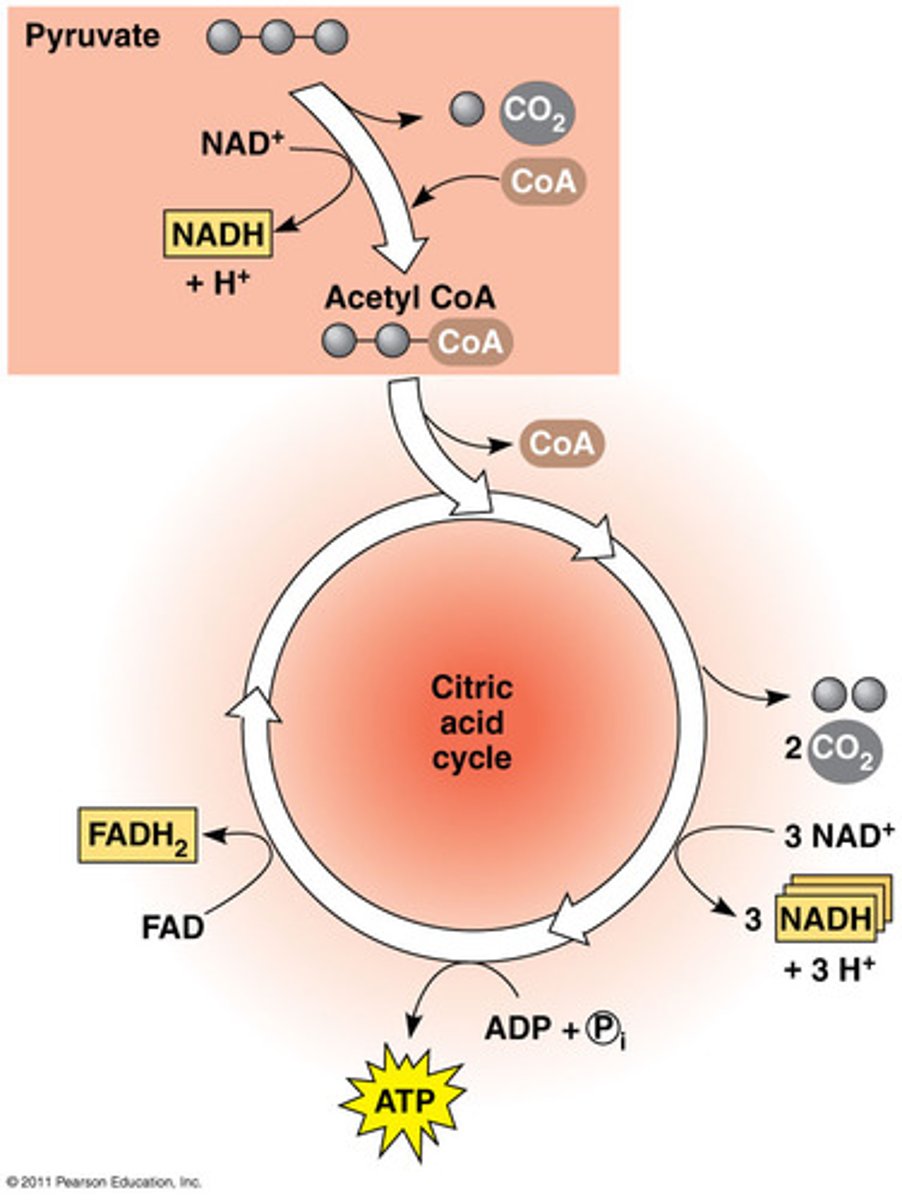
What are the steps in the citric acid cycle?
Step 1: 2 carbons of acetyl-CoA combines with 4-C oxaloacetic acid → citric acid (6-C)
Step 2: CO2 is released
Citric acid is oxidized and NAD+ turns to NADH + H+
Step 3: CO2 is released again
Citric acid is oxidized and NAD+ turns to NADH + H+ again
ADP + P → ATP
Step 4: 4-C compound releases a H+ → FADH2
ATP is formed
Step 5: Hydrogen is released again →NADH
4-C Oxaloacetic acid is regenerated
How much energy does the electron transport chain produce?
34 ATP
Where does the electron transport chain occur?
inner mitochondrial membrane
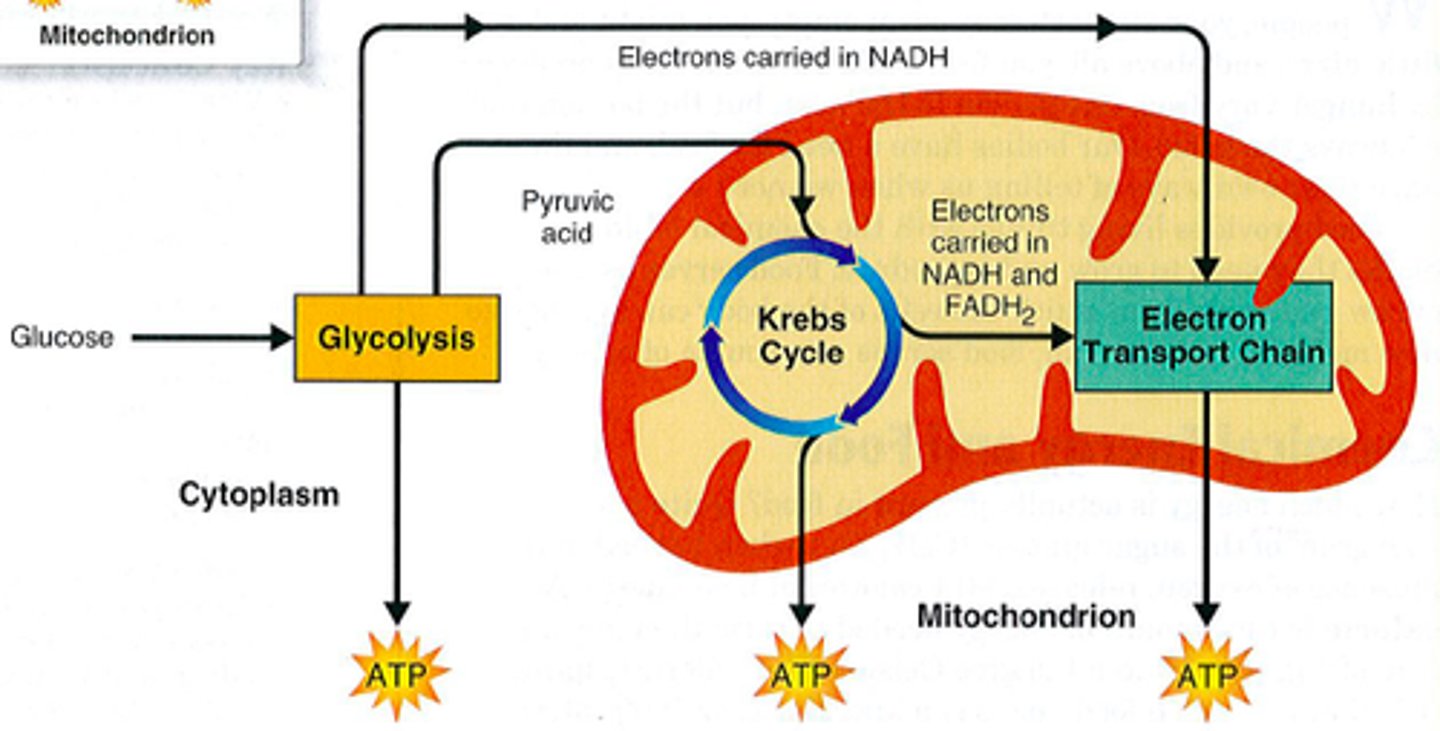
What are the parts of the mitochondria?
inner membrane, outer membrane, cristae, matrix
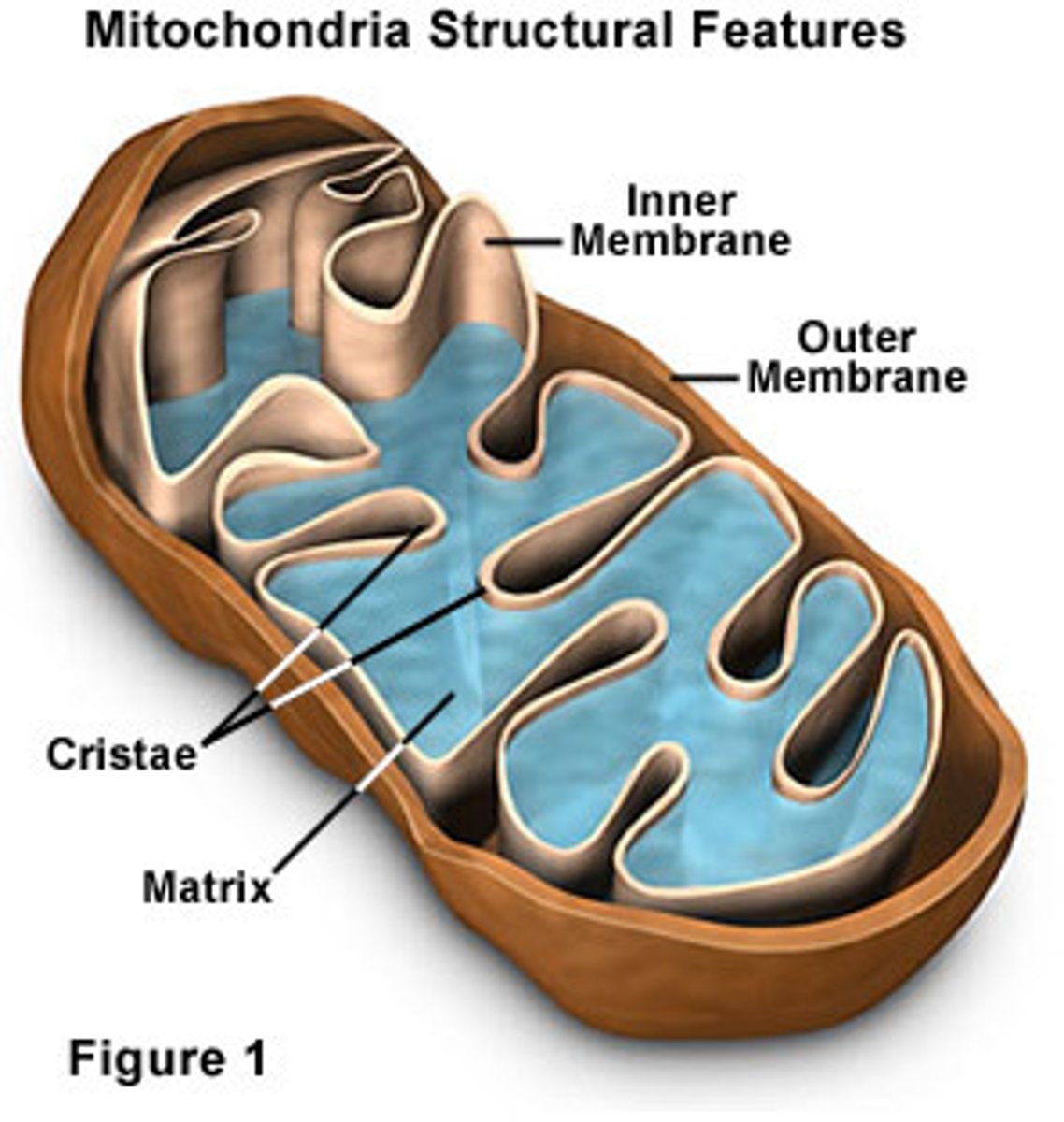
Whats the cristae? (E)
folds in the inner membrane of mitochondria
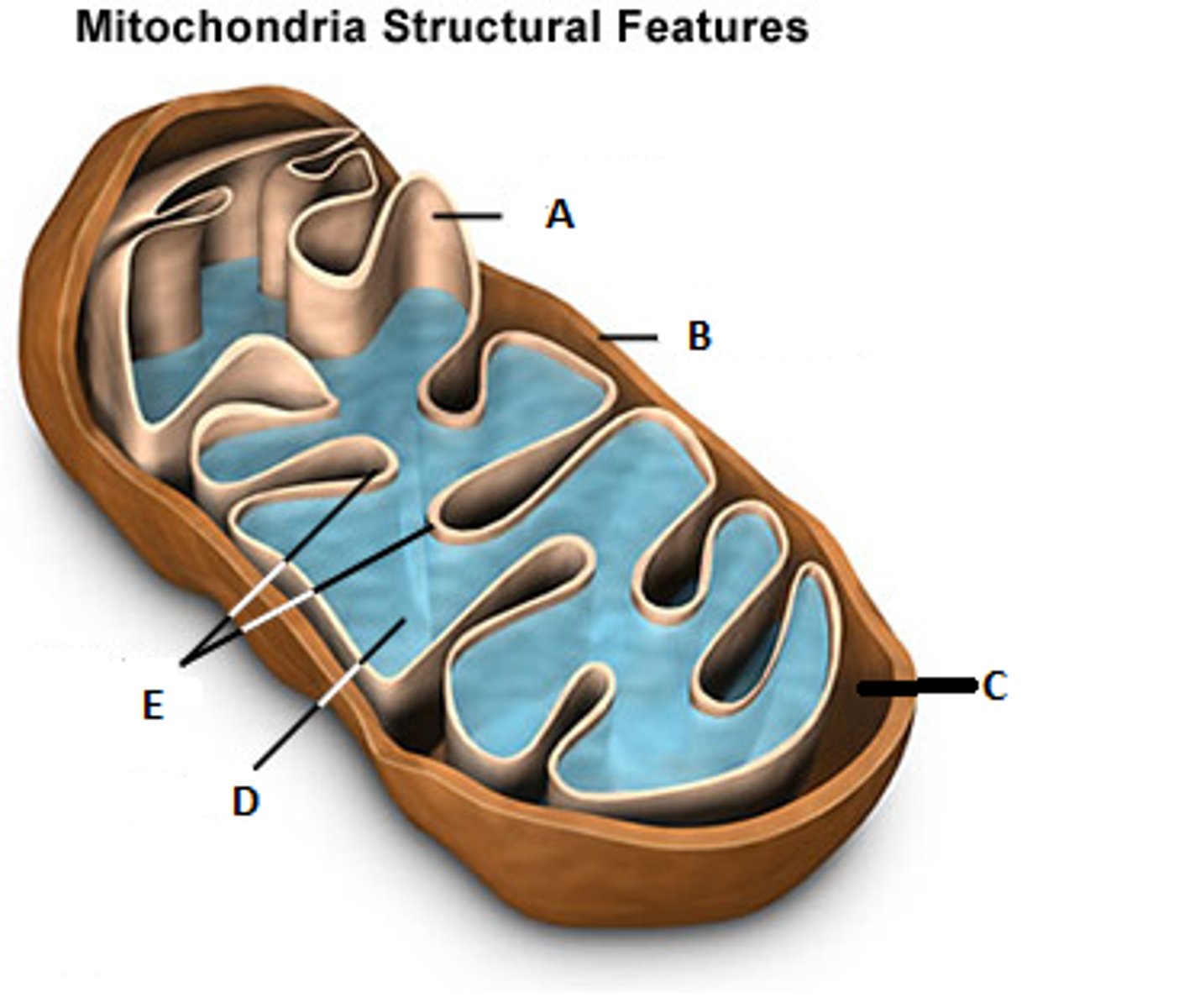
What is the matrix? (D)
Innermost compartment of the mitochondrion
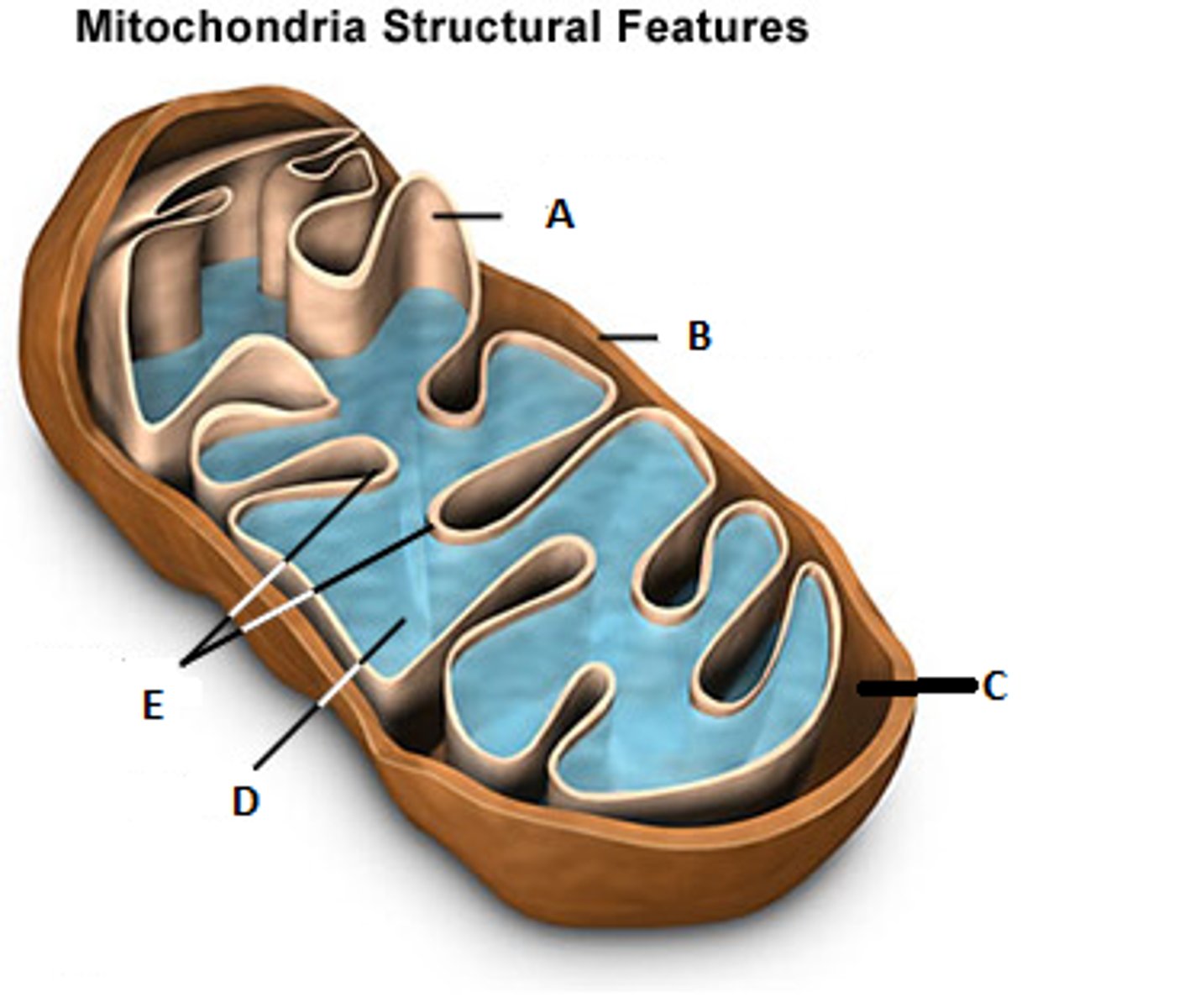
Whats the purpose of Cellular Respiration?
to make ATP (energy)
What step of respiration produces the most ATP?
electron transport chain
What step of respiration requires mitochondria but not oxygen?
Citric Acid Cycle
What type of cells preform cellular respiration (glycolysis, CA cycle, and electron transport)?
ALL EUKARYOTES!
What do prokaryotes do?
make vitamins, break down food, fill niches
What do eukaryotes do?
divide and produce/synthesize enzymes
What is DNA?
deoxyribonucleic acid, a self-replicating material present in nearly all living organisms as the main constituent of chromosomes. It is the carrier of genetic information.
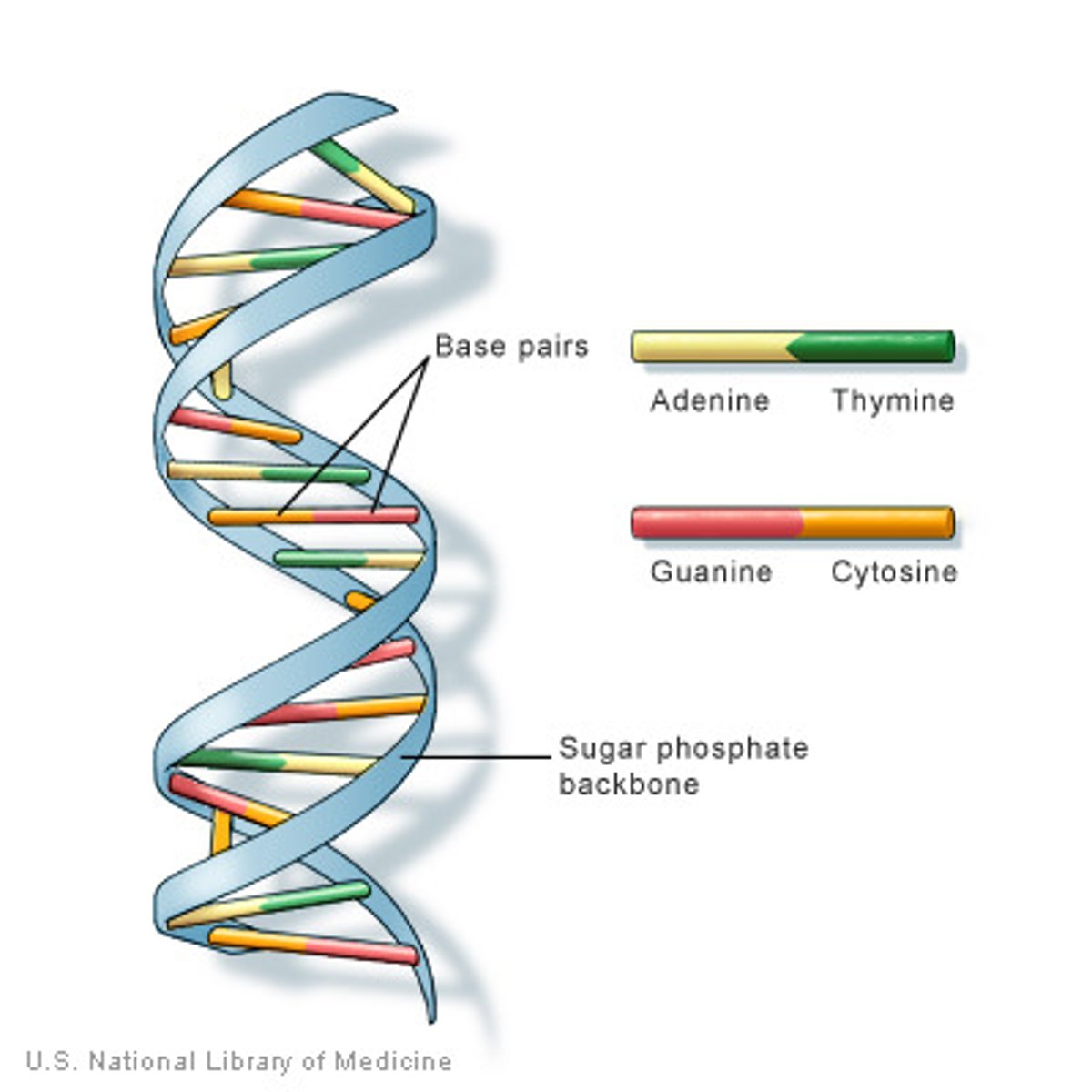
What is the structure of DNA?
double helix (twisted ladder) and stores info for making cell function
What did Watson, Crick, and Franklin do>
- worked out the structure of DNA and used x-ray crystallography in 1950s
- won the nobel prize in 1962
What is a nucleic acid?
DNA and RNA
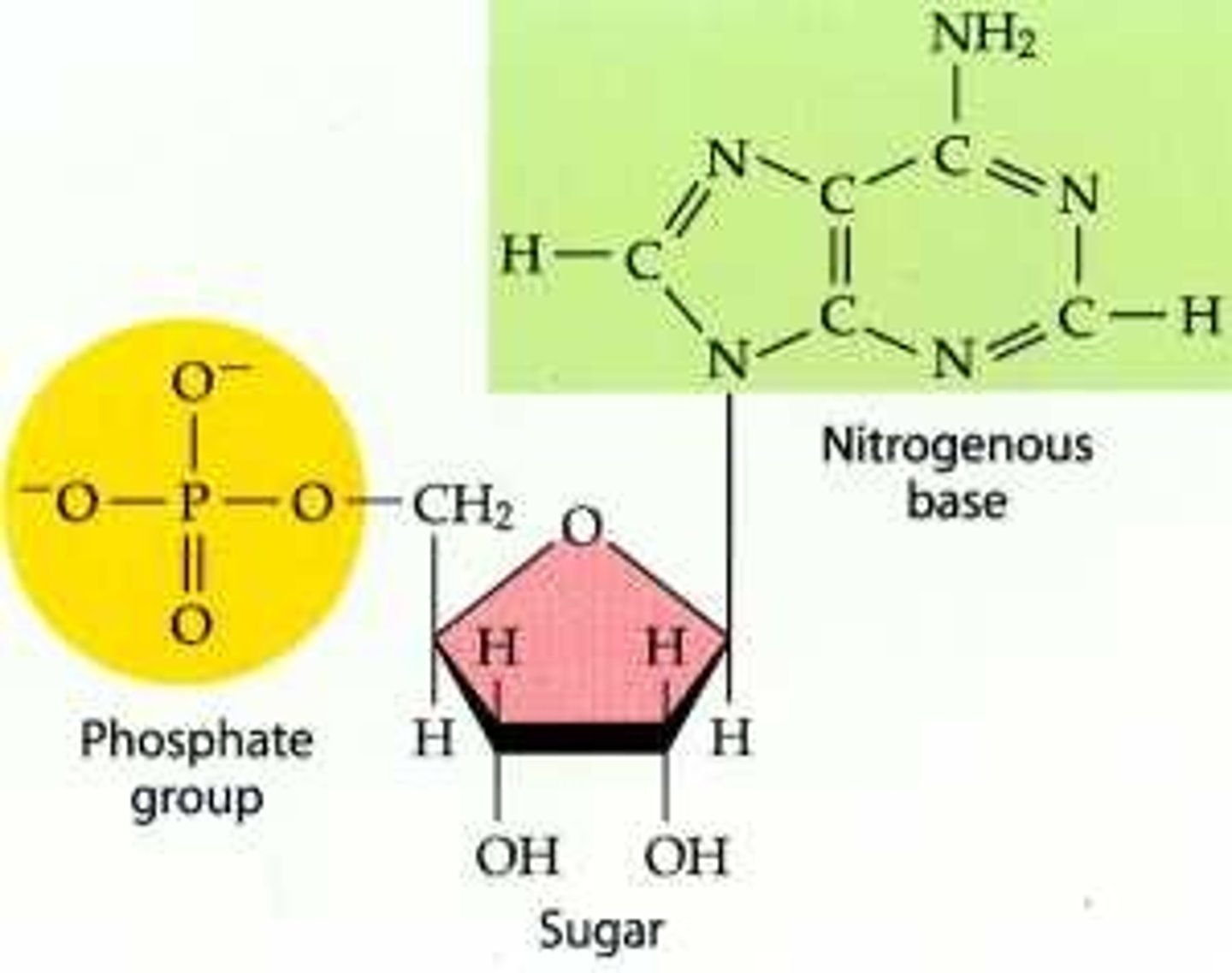
What are the bases in DNA?
Adenine, Thymine, Guanine, Cytosine
How many bonds are between Cytosine and Guanine?
3 hydrogen bonds
How many bonds are between Adenine and Thymine?
2 hydrogen bonds
How many meter of DNA are in a cell?
3 METERS
What is a histone protein?
a protein which acts as a "spool" to keep dna from tangling
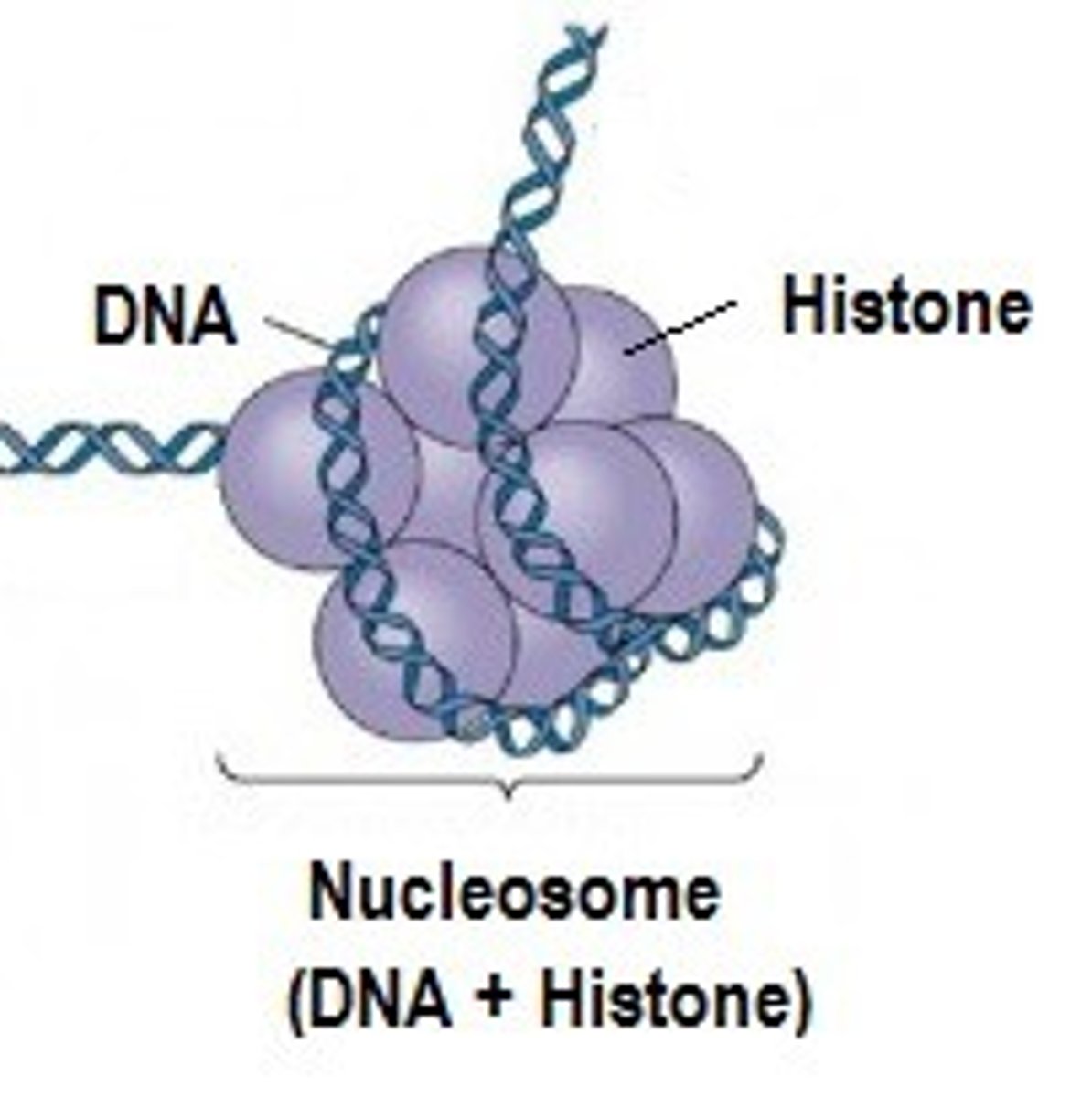
What is a nucleosome?
A region of DNA wound around histone proteins
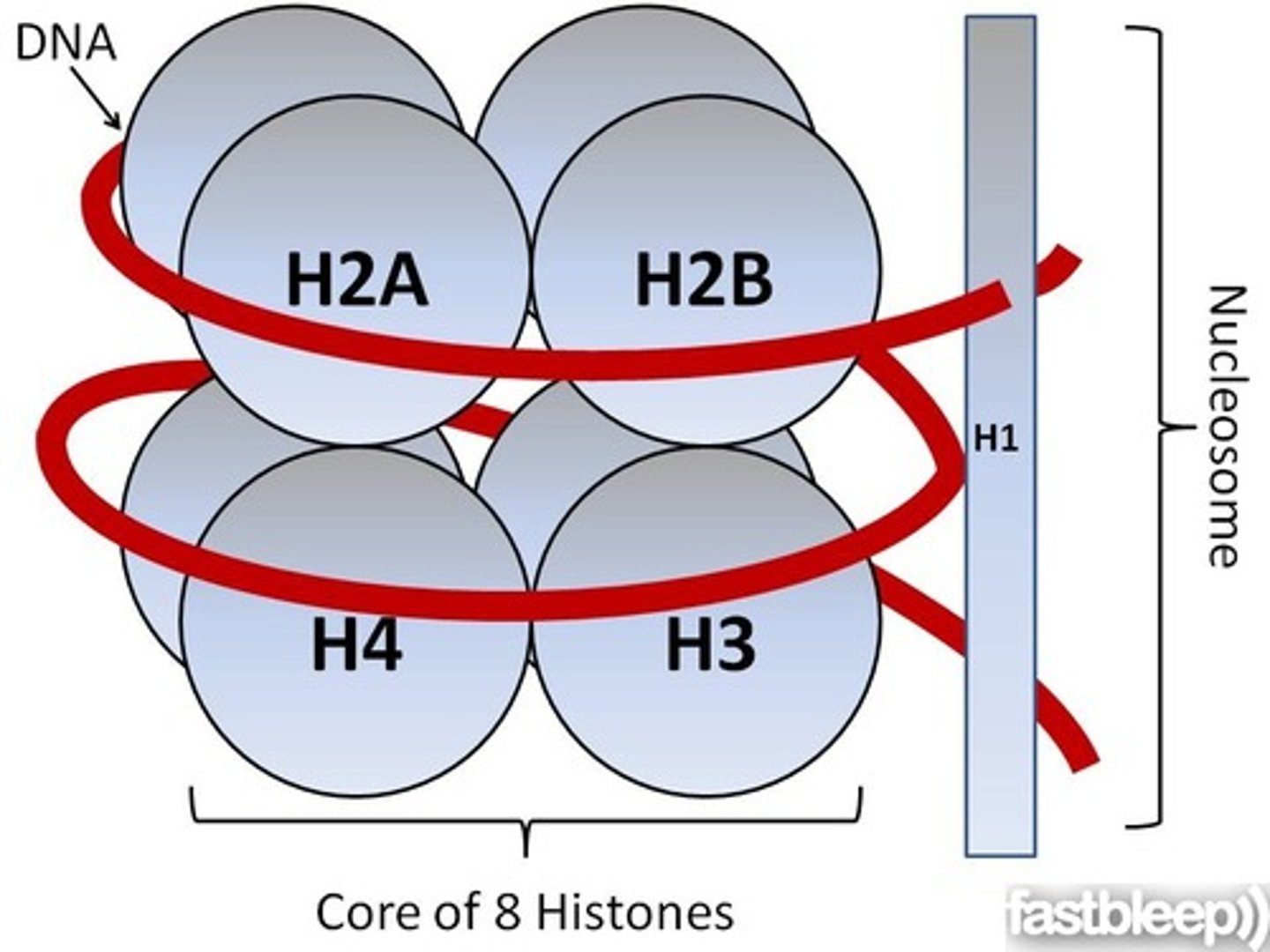
What is chromatin?
a strand of DNA wrapped around proteins
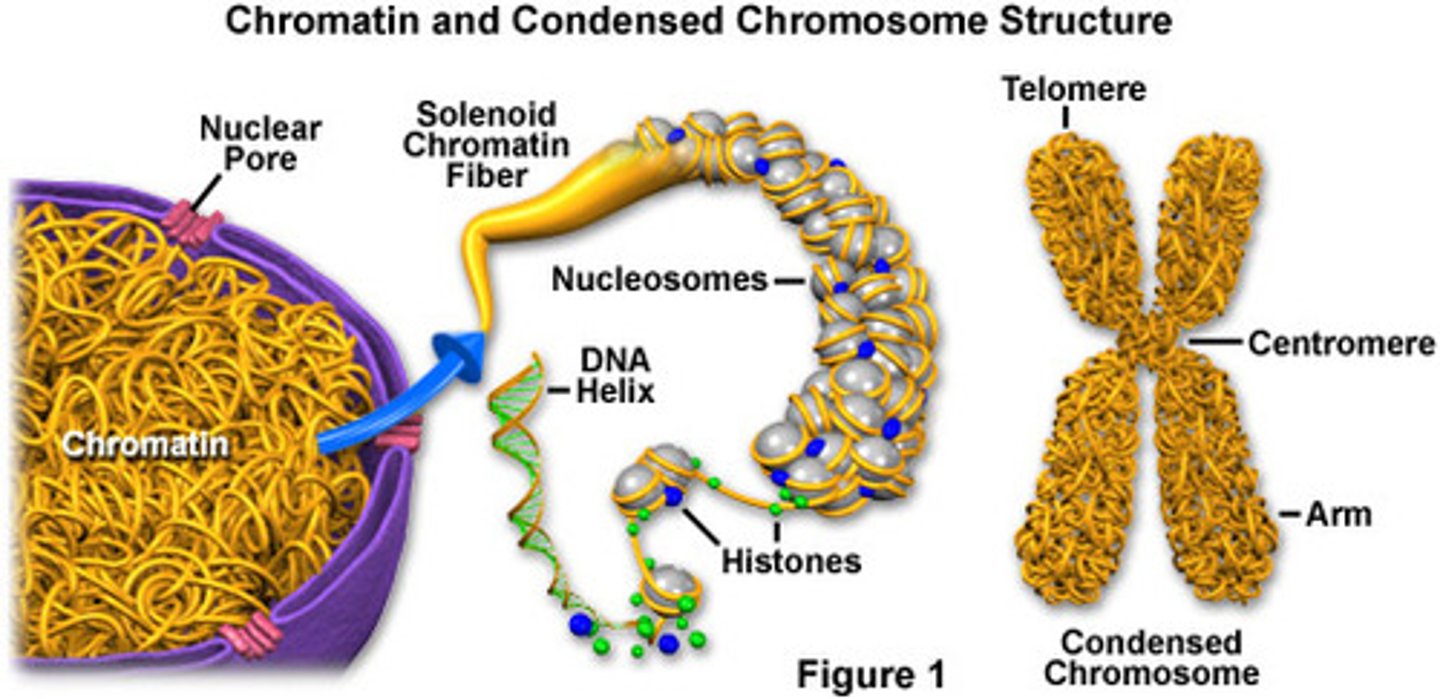
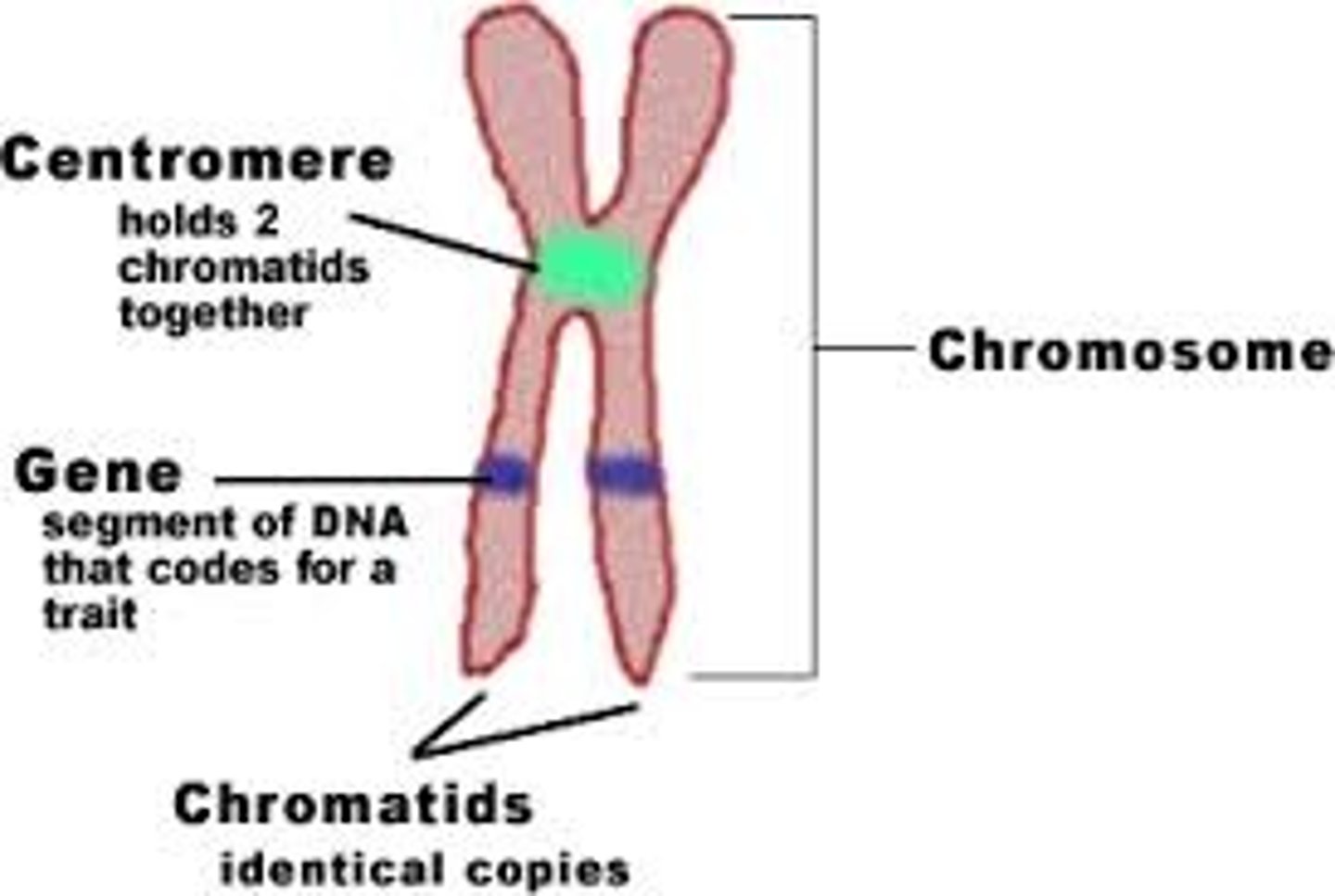
What is a chromosome?
a long continuous chromatin fiber organized so that DNA can still be read (jumbled tangle of thread)
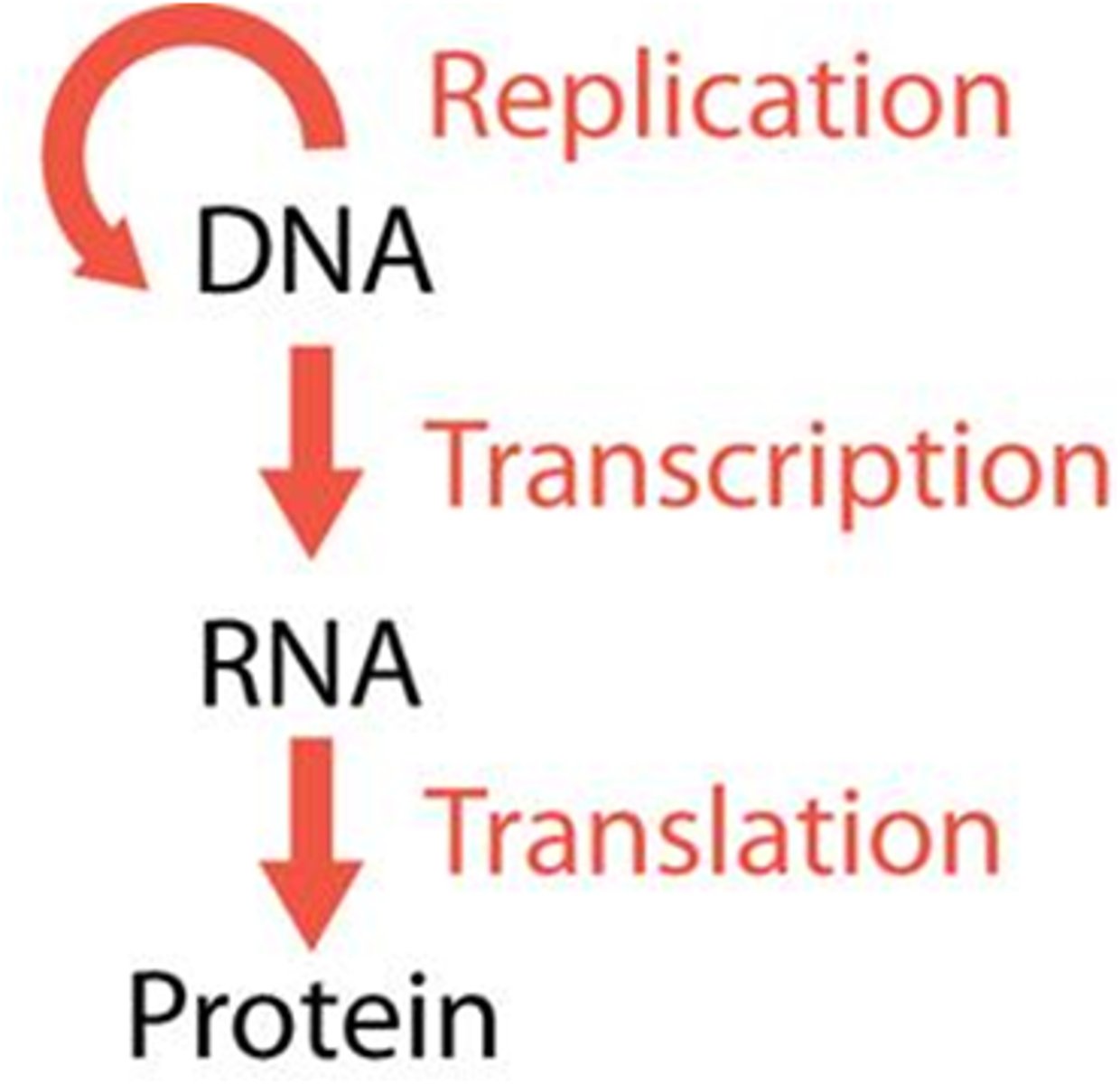
What's the central dogma of biology?
DNA-transcription-RNA-translation-protein
What is RNA?
ribonucleic acid, it moves the code from the nucleus to the outside of nucleus
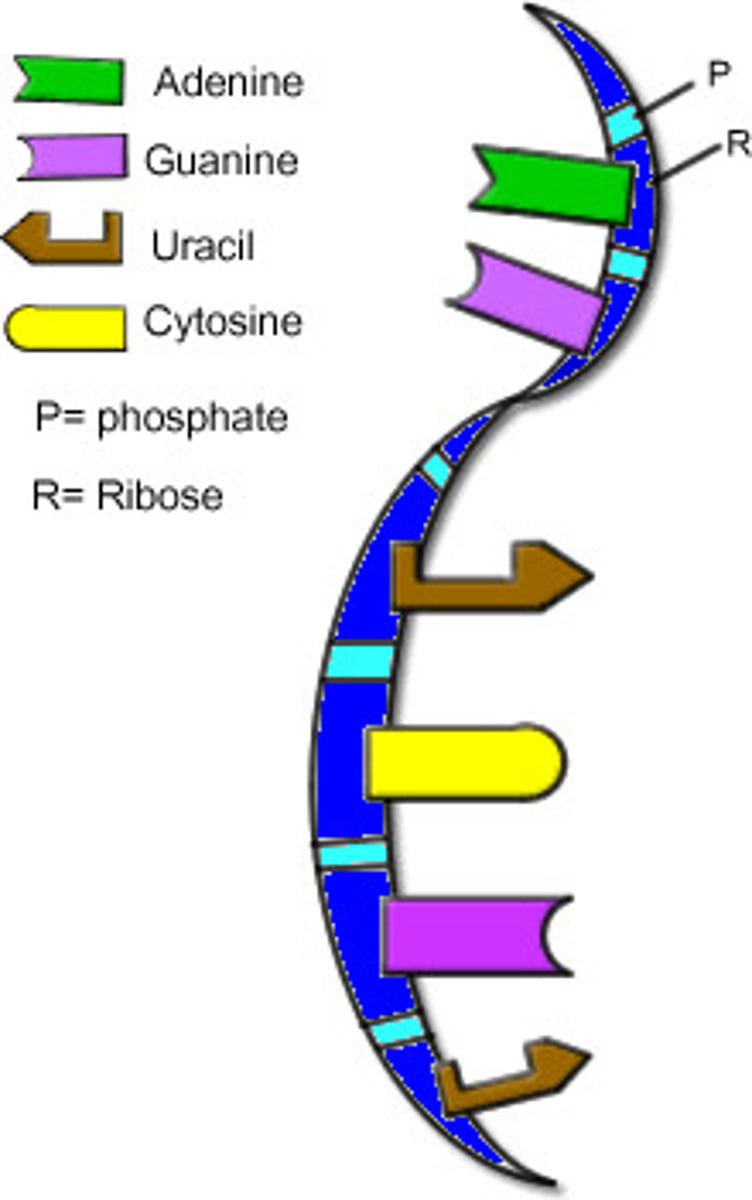
What are the bases of RNA?
Adenine, Uracil, Guanine, Cytosine
What is mRNA?
messenger RNA carries the DNA message from the nucleus to the ribosomes
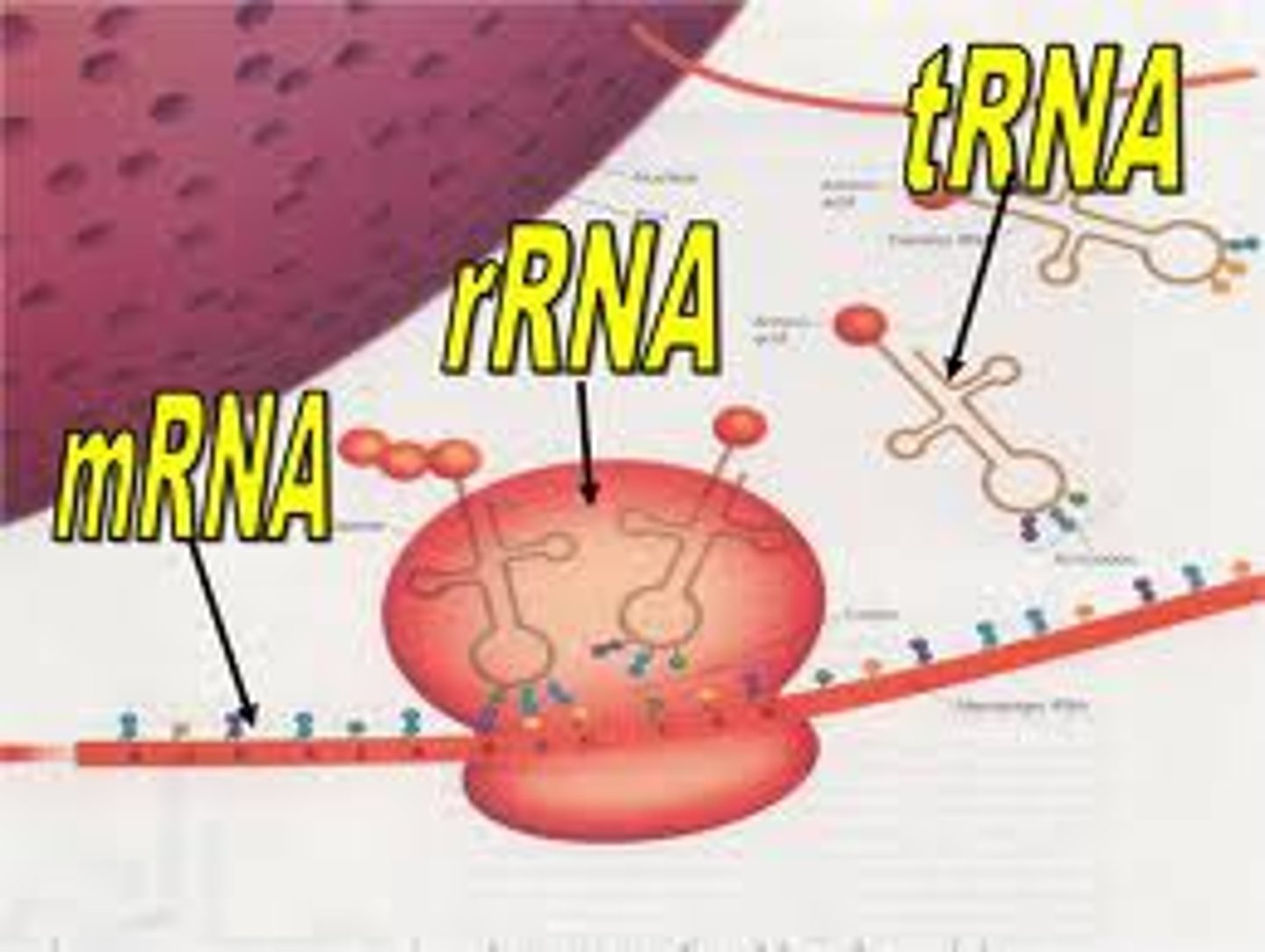
What is tRNA?
tRNA is transfer RNA. It carries amino acids around during translation.
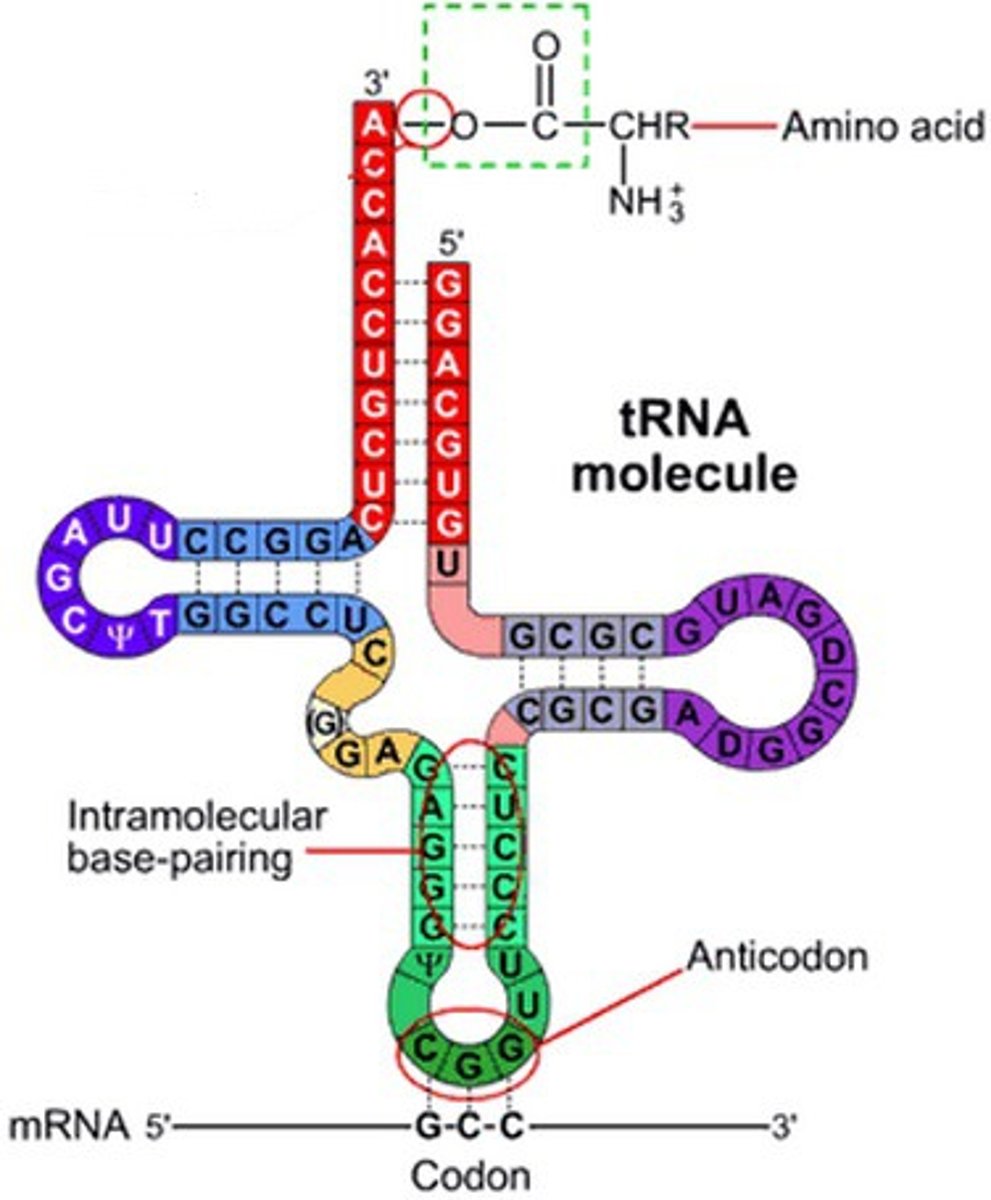
What is rRNA and what does it do?
ribosomal RNA; it makes up the ribosome
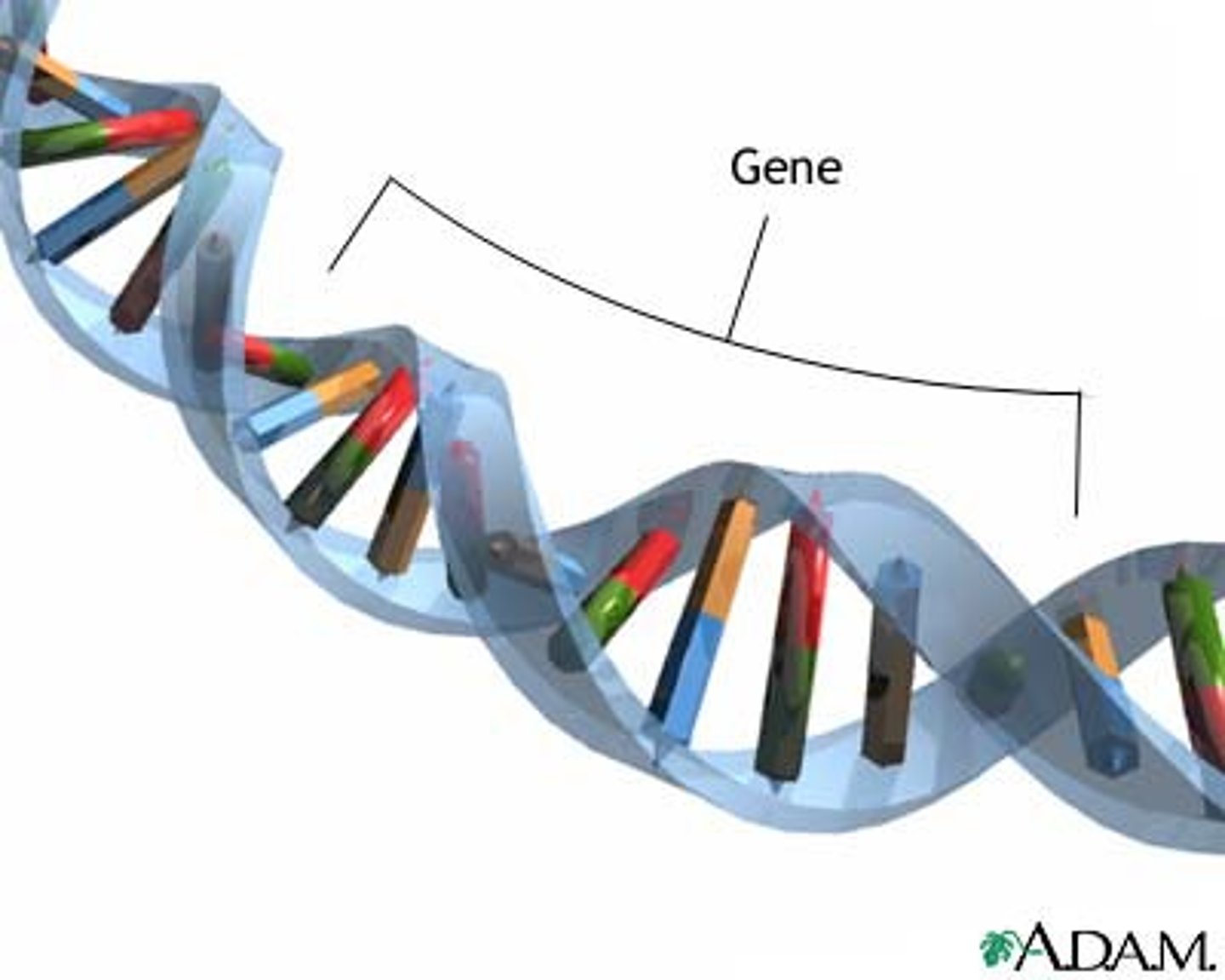
What is a gene?
segment of DNA that codes for a protein
What cell structure is responsible for translation?
Ribosome!
What is the start codon?
AUG (methionine)
What do stop codons do?
signal the end of translation

What is transcription?
The process of making RNA from DNA
What is translation?
the decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
What is mitosis?
Cell division that generates new cells for growth and repair. The division of one cell into two genetically identical daughter cells
What is meiosis?
a type of cell division that results in four daughter cells each with half the number of chromosomes of the parent cell, as in the production of gametes and plant spores.
is mitosis sexual or asexual?
asexual
Is meiosis sexual or asexual reproduction?
sexual
How many chromosomes do humans have?
46 (23 pairs)
Where do chromosomes come from?
in organisms with sexual reproduction; each parent gives the offspring chromosomes containing a full set of genes
Whats the results from mitosis?
2 copies of chromosome and the genes in those chromosomes but may not be same exact sequence
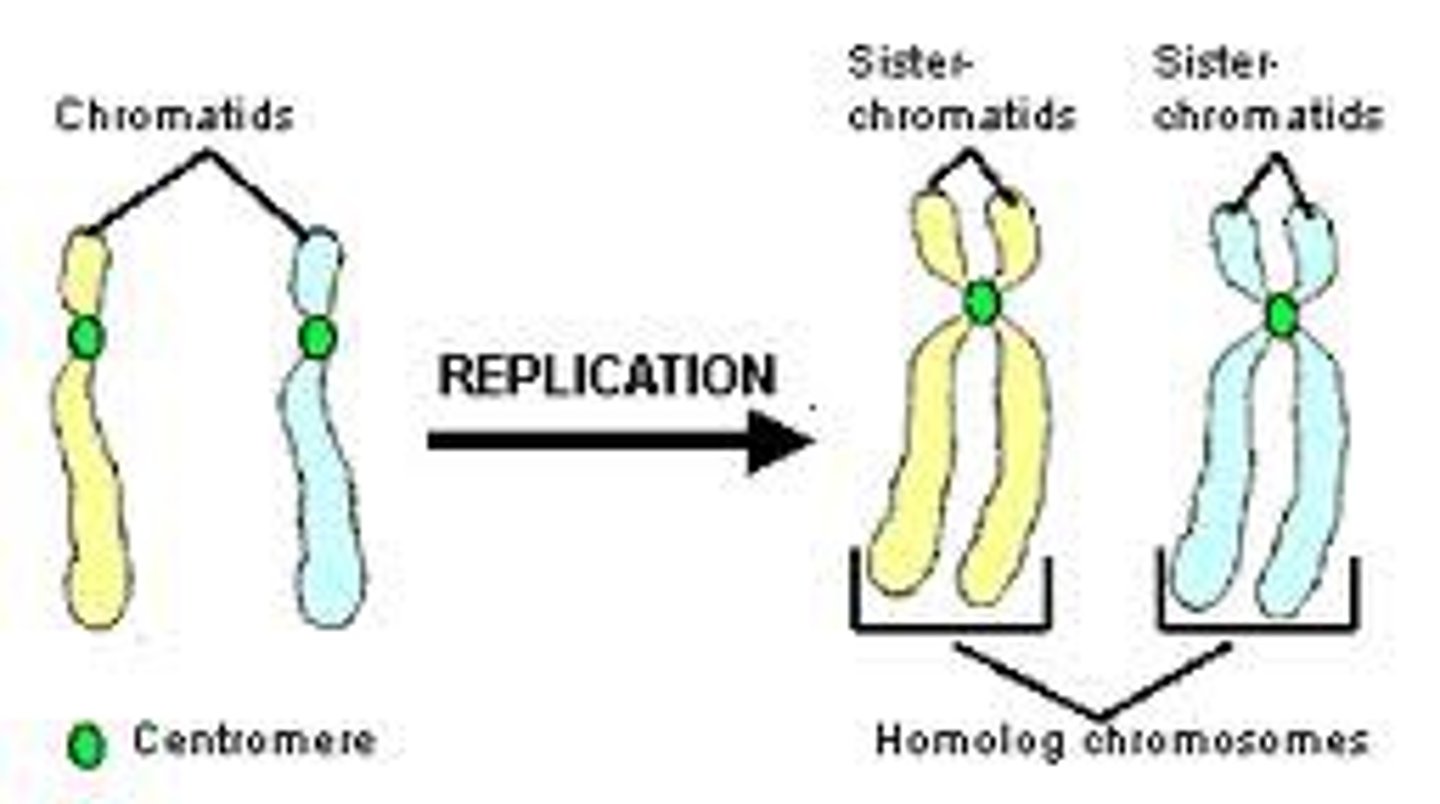
What is a homologous pair?
Two chromosomes of the same type, containing copies of the same genes laid out in the same order.
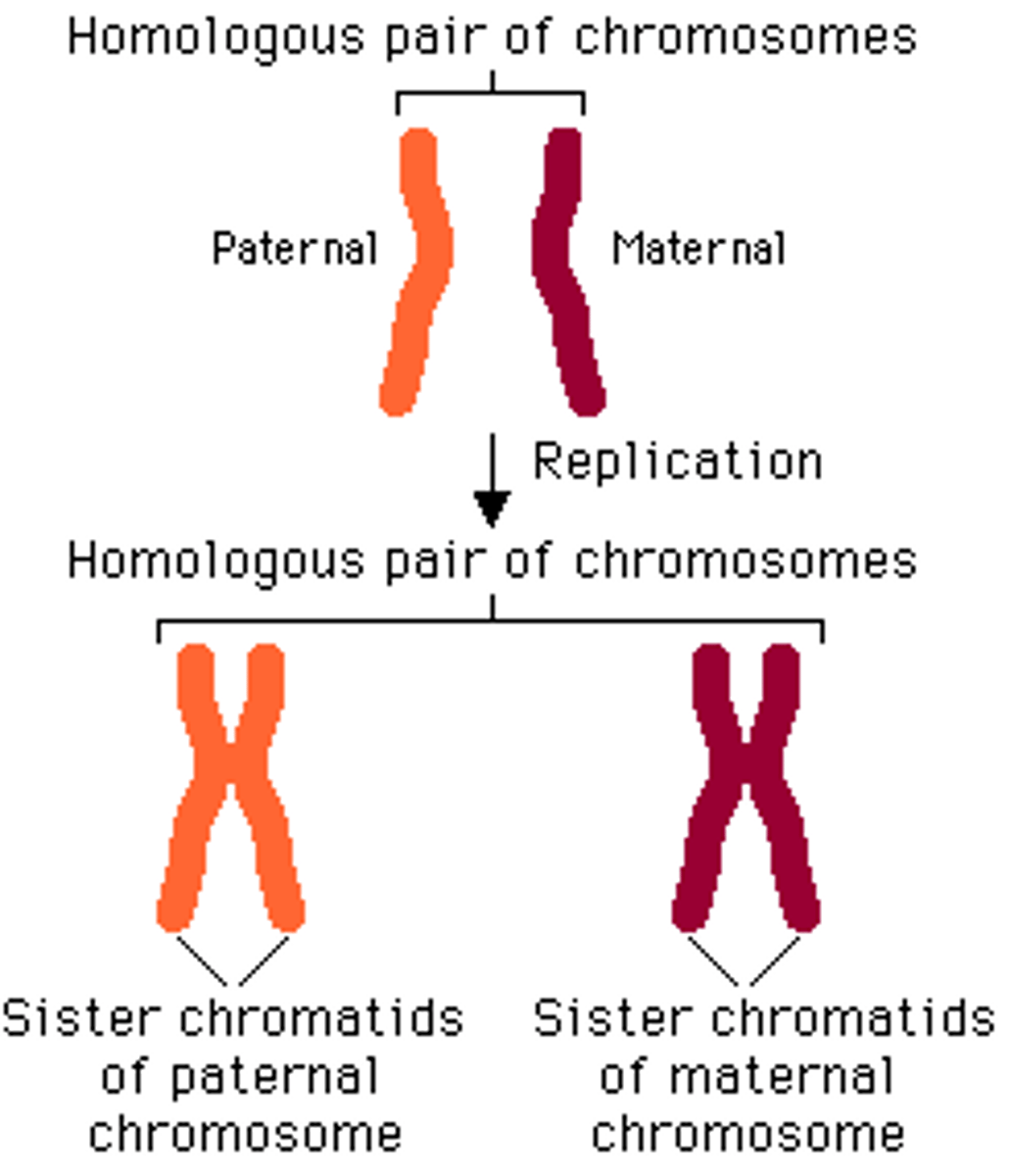
What's cell division?
2 sister chromatids (100% identical copies of the exact same chromosome, attached at centromere
What is the centromere?
usually the middle of chromosome
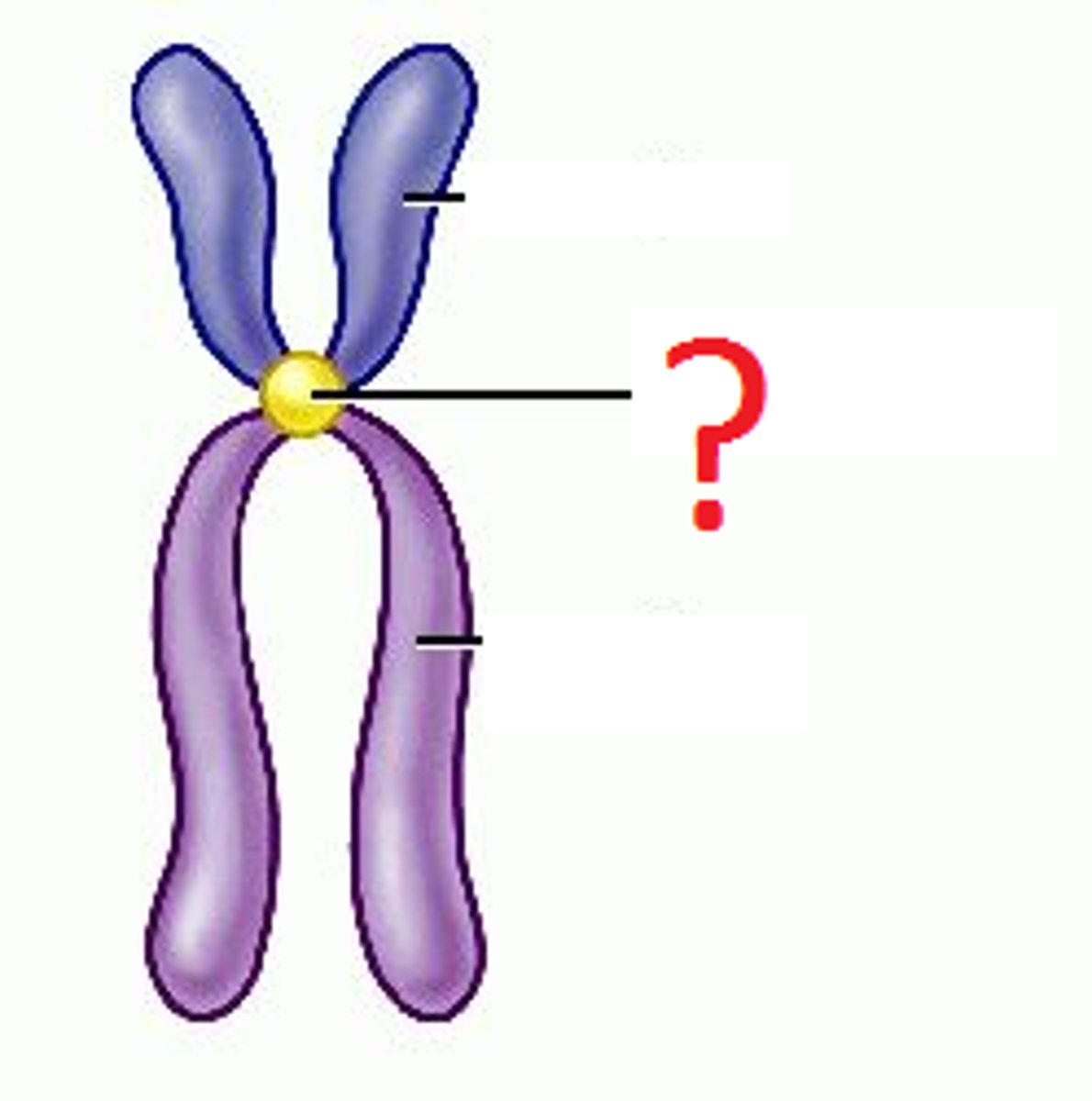
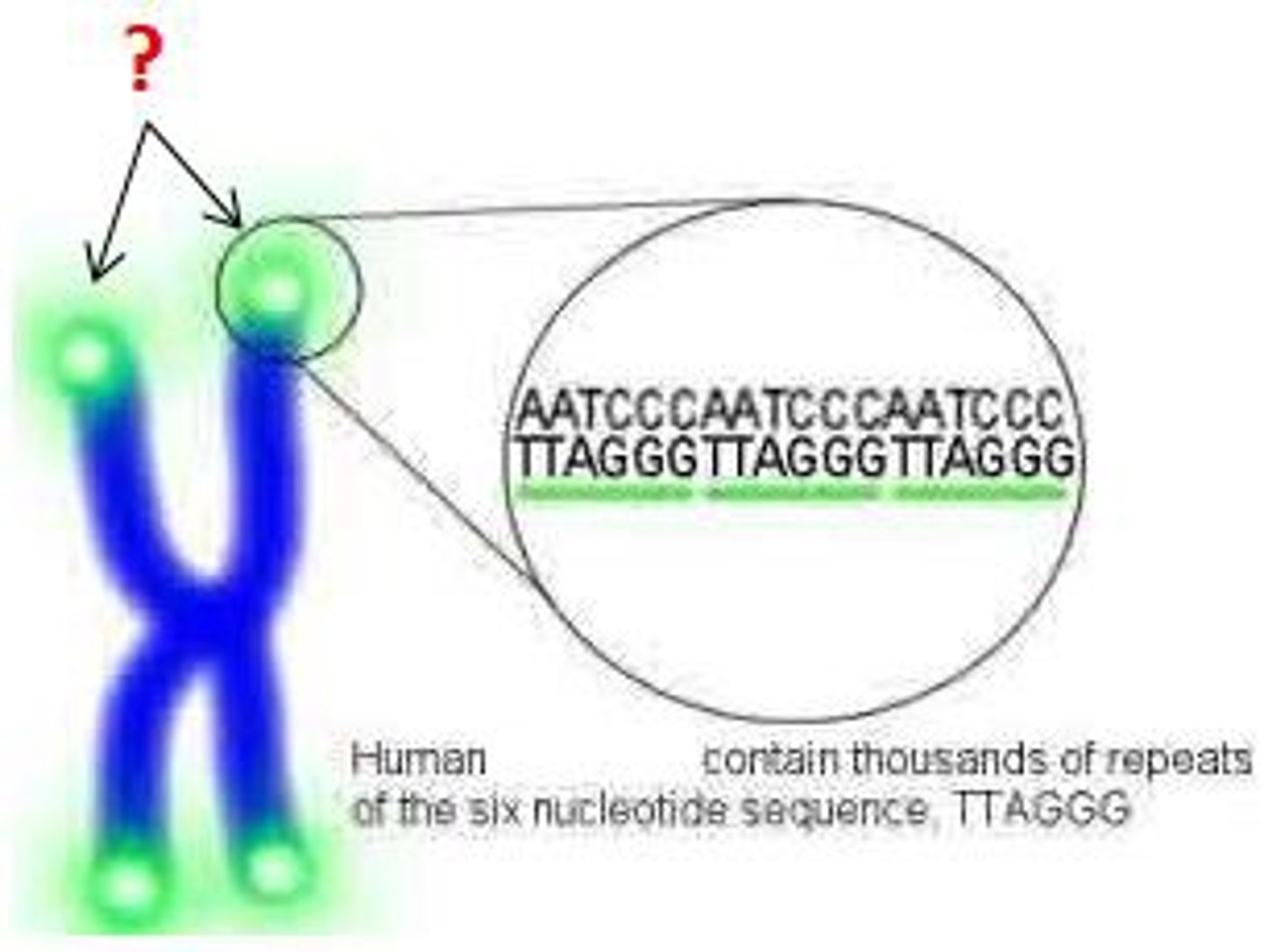
What is telomeres?
end/"caps" of chromosome
What is the DNA replication process?
the process by which a double-stranded DNA molecule is copied to produce two identical DNA molecules
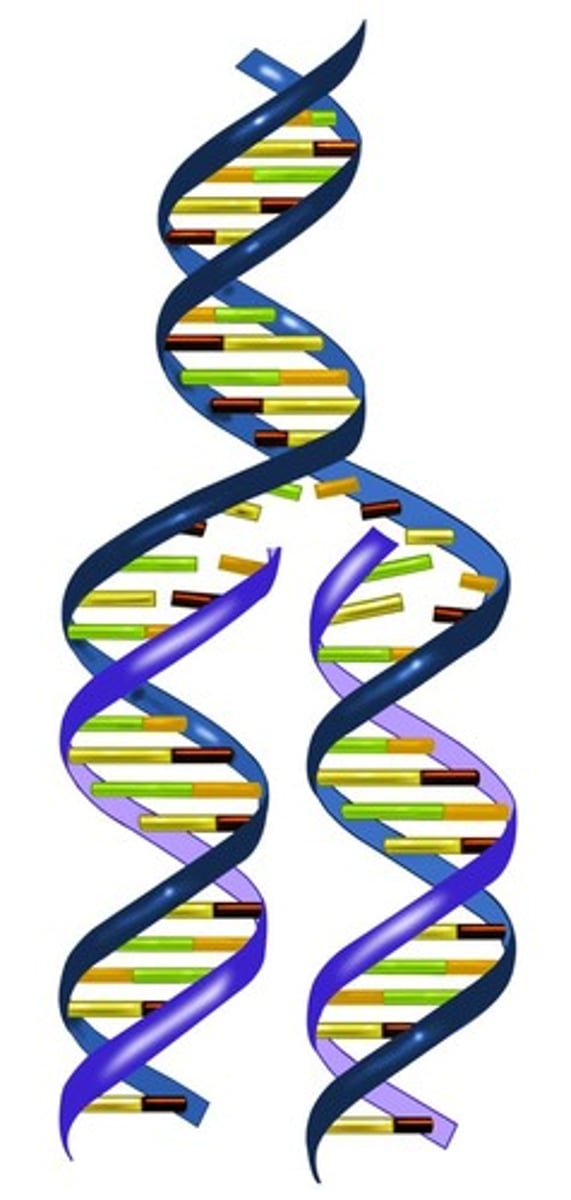

What are sister chromatids?
2 identical copies of DNA held together by a centromere
What is biotechnology?
the manipulation of organisms or their components to make useful products
- making clones
- molecular cloning
- transgenic organisms
Who were the first people to extract insulin?
Frederick Banting and Charles Best in 1922
Who was the first person to get treated with the extracted insulin?
Leonard Thompson, 14 yo
Who put genes into the bacteria Escherichia Coli?
Arthur Riggs, Keiichi Sakura, and Herbert Boyer
What is molecular cloning?
isolation and incorporation of a piece of DNA into a vector so it can be replicated and manipulated
What is the first part of molecular cloning?
Find DNA containing protein that you want to produce
plasmid- a circular piece of DNA used by prokaryotes
What is the second part of molecular cloning?
Fragmentation- cut the DNA into fragments
What is the third part of molecular cloning?
Ligation- give the DNA fragments together, specifically the plasmid and the DNA sequence that codes for your protein
What is the fourth part of molecular cloning?
Transfection- get the plasmid with the DNA sequence for the protein into the cell, often use heat shock
What is the fifth part of molecular cloning?
Screening- determine which cells contain the plasmid withe the DNA sequence- often a color champ and a resistance to antibiotics
What is a transgenic organism?
An organism that contains genes from other species
Who was the first person to have gene editing attempted?
Brian Maduex, 44 and he had Hunters Disease
What is the cell cycle?
series of events that cells go through as they grow and divide
What is cell division?
Process by which a cell divides into two new daughter cells
What are multi-celled organisms?
mitosis produces new body cells
- growth and maintenance
- repair of damaged tissue
What are single celled organisms?
mitosis produces new individuals
-asexual reproduction
- offspring are genetically identical to parent