Chem 2C Final
1/204
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
205 Terms
Strong Fields
tend to pair electrons, tend to be diamagnetic
Weak Fields
tend to have electrons unpaired, tend to be paramagnetic
What happens when a TM bonded to a weak field ligand switches to bonding with a strong field ligand?
there is a net increase in delta
Main Group Characteristics
group members have analogous valence shell configs
lightest element of each group has unique characteristics
diagonal relationships of similar properties may exist
metallic character decreases as you approach F
Oxide Ion
O²-
Peroxide Ion
O22-
Superoxide Ion
O2-
Alkali Metals
the hydrogen column
only one valence electron
malleable, good conductors
tend to oxidize ns^1→np^1
readily forms oxides based on the radius of the metal
Hydrogen
strange since it is not quite metalloid, not quite halogen
-1 charge, considered with alkali metals
+1 charge, considered with halogens
Alkali Earth Metals
Beryllium column
easily oxidized to a +2 oxidation state
Beryllium: beryllium chloride forms unique planar structures
calcium: creates concrete w/ CaO, also makes chalk
Barium: BaS is opaque to x-rays
General Reaction
M+Z2(or W-Z) → M-Zy
Group 13 (Icosagens)
Al, Ga, In, Tl
have a ns²np^1 electron config
common ox states: +1, +3
can form dimers
Aluminum: AlCl forms unique planar structure, most abundant metal in Earth’s crust, very strong
dimers
where two identical compounds bond together
Inert Pair Effect
occurs for metals and non-metals in groups 13, 14, 15, and 16, where they all have expected charges
nonmetals have negative charges
metals have positive charges
semimetals can be both negative and positive
13: +1, +3
14: +2, +4
15: +3, +5
16: +4, +6
Group 14 (Tetragens)
sn, pb
can form 4 bonds
common charge of +2, +4
Tin can be used for solders, pewter
lead can be used for ammo, piping, storage cells in batteries
Noble Gases
helium column
odorless, colorless, ionizable, electro-negative, nearly ideal gases, not completely inert, can form compounds under certain conditions
Helium: very light, LDF, unreactive, dilutent
Neon: light emits under current
Argon: 3rd most common gas that comprises air
Krypton: product of fission
Group 17 (Halogens)
F column
electron config: ns²np^5
F- is the most reactive becaus eit is the least polarizable
halogens w/ oxygens form oxy acids
other halogen compounds: teflon, Freon, PVC
Hypohalous Acid
HOX, +1
oxy acid
Halous Acid
HOXO, +3
oxy acid
Halic Acid
HOXO2, +5
oxy acid
Perhalic Acid
HOXO3, +7
oxy acid
Group 16 (halcogens)
oxygen column
oxygen: forms lots of things, includes both pi and sigma bonds
sulfur: tends to join to itself, smells bad, forms H2SO4, rubber
Group 15 (Pnictogens)
nitrogen column
can exist in multiple oxidation states, +3 or +5 can give noble gas configuration
Nitrogen: nearly inert, but out of N2 can be explosive like with TNT
phosphorous: common ox states: +3, +5, can make lots of oxides, can create oxy acids
Group 14 (Tetragens)
carbon, silicon, GE
Carbon: super strong compounds, can bond w/ itself and others, creates allotropes, essential to all life
silicon: Si-O bonds stronger than Si-Si, glass dust and sand, amorphous
Group 13 (Icosagens) B
Boron
true semi metal
dopant
can form clusters
behaves more like silicon than aluminum
For the rxn R→ P, what is the tangent line and what is the secant line?
The tangent: the instantaneous rxn rate
the secant: the avg rate in the rexn rate
What does k depend on?
depends on reaction, temperature, and catalyst
Slow reaction speed
rate is small, rate constant is small
Fast reaction speed
rate is large, rate constant is small
The Order
the rxn is the sum of the exponents (m+n)
m and n are usually small, positive numbers and may be equal to zero, but may also be negative or fractions
Zeroth Order Rate Law
for a straight line, [A] vs. t
non-concentration dependent
m+n+…=0
First Order Rate Law
for a straight line, ln[A] vs. t
m+n+…=1
Second Order Rate Law
for a straight line, 1/[A] vs. t
m+n+…=2
Collision theory
a & b need to hit directly
a & b need to enter with a combined kinetic energy that is high enough to make bond formation a viable result
Collision Frequency
number of molecular collisions per unit time
Activation Energy
minimum energy above which collision results in product
as temperature goes up, velocity and kinetic energy go up
Orientation in Space
for a bond to happen, there must be a direct hit
Transition State Theory
when A & B first collide, a transition state between formed and unformed is created. After transition state, reaction can either proceed to products or return to reactions
breaks down when considering quantum mechanics at high temps
peak of activation is the transition state
A
the frequency factor
made up of (Z0)(p)
p= proper orientation when collision occurs
Z0= the frequency of molar collisions
Reaction Mechanisms
a step-by-step description of a chemical reaction where each step is called an elementary process (or step)
Elementary Process Typical Characteristics
uni or bipolar
reaction coefficients are the same as exponents in the rate law
reactions are reversible
intermediates appear in the same steps. an intermediate is a chemical species that appears in the elementary process but not in the overall reaction.
RDS
rate determining step, the slow reaction
r is small… meaning very slow
k is small… since r and k are proportional
Pseudo Steady State Hypothesis (PSSH)
states that at equilibrium, the rate of appearance and disappearance of intermediates are equal
Catalyst
lowers the activation energy
increases the rate of reaction so that it occurs faster
reaction equilibrium (keq) is not affected
Homogeneous Catalysis
occurs when the reaction and catalyst are in the same phase
Heterogeneous Catalysis
occurs when the reaction and catalyst are in different phases
Michcelis-Menten Kinetics
biochemical reactions involving a single substrate
high substance concentrations are zeroth order (enzyme works at maximum rate)
low substance concentrations are first order
Alkanes
saturated hydrocarbon
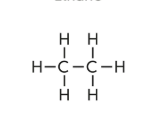
Alkenes
unsaturated hydrocarbon
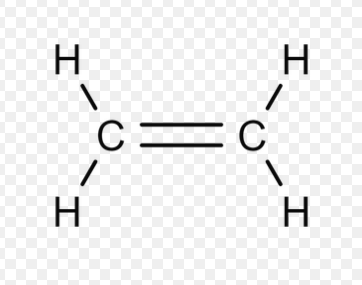
Alkynes
unsaturated hydrocarbon
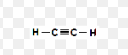
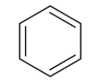
Arenes
aromatic hydrocarbon
R
alkyl groups
Ar
arene, aromatic groups
Organic (or Alkyl) Halides
hydrocarbon derivative (no CO group)
R-X
Ar-X
(x is a halogen atom)
Alcohols
hydrocarbon derivative (no CO group)
R-OH
Phenols
hydrocarbon derivative (no CO group)
Ar-OH
Ethers
hydrocarbon derivative (no CO group)
R-O-R^1
Ar-O-R
Amines
hydrocarbon derivative (no CO group)
R-NH2
Ar-NH2
can have multiple R groups instead of H atoms on the nitrogen
Aldehydes
hydrocarbon derivatives (w/ CO groups)
R can be replaced with Ar

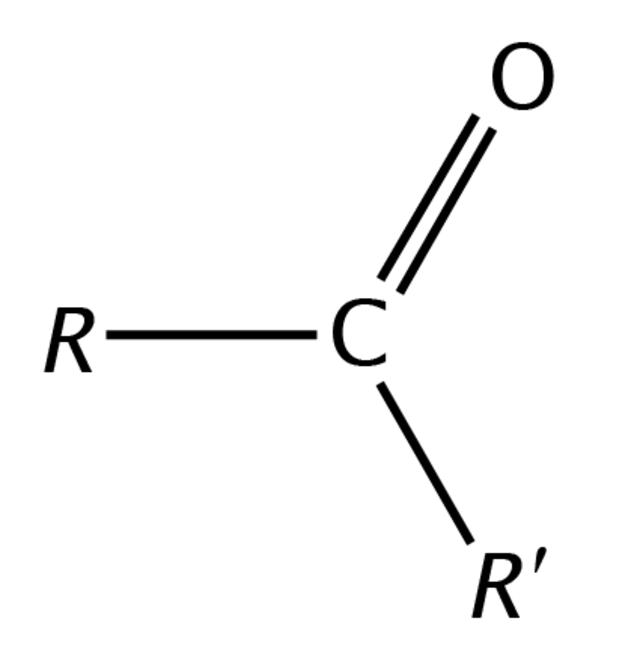
Ketone
hydrocarbon derivatives (w/ CO groups)
R can be replaced with Ar
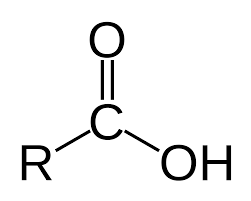
Carboxylic Acids
hydrocarbon derivatives (w/ CO groups)
R can be replaced with Ar
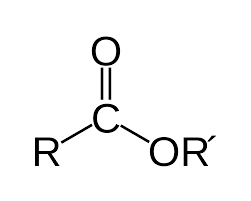
Esters
hydrocarbon derivatives (w/ CO groups)
R can be replaced with Ar
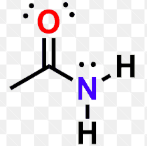
Amides
hydrocarbon derivatives (w/ CO groups)
R can be replaced with Ar
can have multiple R groups instead of H atoms on the nitrogen
Spectroscopy
uses electromagnetic radiation
measures the difference between molecular states to determine information about the molecule
analyzes the structure of the molecule based on the energy of the molecular state
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance
nucleus has a nuclear momentum called spin
when the correct radio-frequency radiation is introduced, the spins are aligned and energized
the change in energy is dependent on the environment of atoms in the molecule. determines carbon-hydrogen framework molecule
Infared Spectroscopy
when infared radiation is introduced into a sample, vibrational states are observed
determines functional groups present in the molecule
Ultraviolet Spectroscopy
when ultraviolet light is introduced into the sample, electrons in conjugated pi systems are excited to higher energy states
determines if a conjugated pi system is present in the molecule
conformations
identical molecules that differ only by their rotation in space
Primary
1 neighboring carbon
Secondary
2 neighboring carbons
Tertiary
3 neighboring carbons
Quartenary
4 neighboring carbons
Alkane
Big main branch
Alkyl
small branches off of the main alkane
1 Alkane
meth-
2 alkanes
eth-
3 alkanes
prop-
4 alkanes
but-
5 alkanes
pent-
Isopropyl
(3) alkane
essentially a tripod
t-butyl
(4) alkane
shaped like a bird foot
(don’t count the ‘t’ when alphabetizing substituents)
Oxidizing Agent
oxidizes compounds or elements in a reaction. the species that is reduced
Reducing Agent
the species oxidized in a reaction. reduces compounds or elements in a reaction
Anode
where oxidation occurs, drawn on the LHS, e- flow, pitting, corrosion (metal→ore)
Cathode
where reduction occurs, drawn on the RHS, current, plating, refining (ore→metal)
Where do electrons flow?
from the anode to the cathode
Standard Hydrogen Electrode (SHE)
assigned 0.00V, a standard
What happens when a half reaction is multiplied by a constant?
E^o does not change
E>0
spontaneous reaction, shift towards products
E<0
nonspontaneous reaction, shift towards reactants
E=0
equilibirum, no shift
Concentration Cells
consists of two half cells having the same reaction but only differ in concentrations
E=0
The reaction is driven forward if the molarity of the cathode>anode
Spontaneous
deltaG<0
E>0
Nonspontaneous
deltaG>0
E<0
Equilibrium
deltaG=0
E=0
K=Q
Primary Cell
reaction is non-reversible. battery eventually goes dead
Dry Cell
hold charge a long time, good for emergency use
zinc is the anode, manganese oxide is cathode, sometimes mercury
can be acidic or alkaline
Button Battery
high storage capacity, very small
Anode=zinc
cathode=silver
Secondary Cell
reaction can be reversed
Lead-Acid (Storage) Battery
concentration cell
can be put together to make car batteries