Genomic Variation & Disease / RNA & Transcriptomics
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is personalised medicine
a medical model that proposes to customize medical decisions, practices, and treatments for the individual patients
what is the aim of personalised medicine
to select appropriate therapies for the individual patient to ensure the best possible outcome and reduce the risk of side effects
what is a biomarker
something that can be measured and points to the presence of:
a disease
a physiological change
a response to treatment
psychological condition
what is gene therapy
process by which a sequence of DNA/RNA is introduced to the cells which results on the formation of a protein which is needed for recovery
what is gene editing
the process by which genetic tools are used to delete or insert sections of DNA to prevent disease/introduce new function
CRISPR-CAS9
endonucleases
what is artificial cell therapy
design a cell programmed to make a native protein from a wildtype gene
deliver cell to parts of the body that require the protein for function
what is protein replacement therapy
process of providing individuals with a supply of functional proteins which may be dysfunction/absent in their body
what are some general struggles with personalised medicine treatments
delivery of treatment to target cells
uptake of treatment by target cells
cost
does this approach actually help the patient
time & cost of creating the drug/protein/cell
early stages of development/needs more research
how is DNA packaged
packaged in nucleosomes, which condense to form chromatin fibres
these are packaged as chromosomes
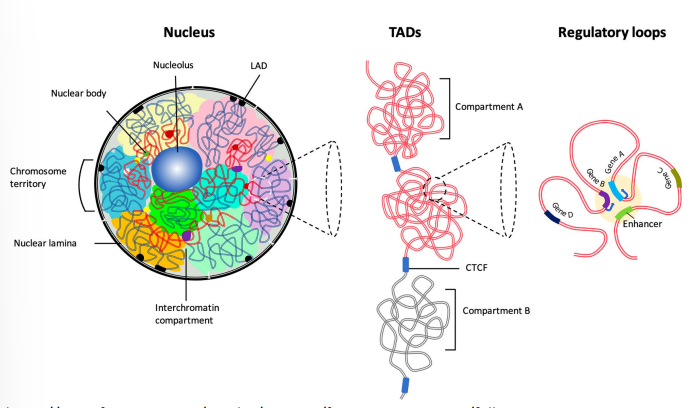
what are lamina associated domains (LADs)
parts of the chromosome that are associated with the nuclear lamina, they are areas of lower gene expression
lamina is an inner layer of the nucleus responsible for structural integrity & gene regulation
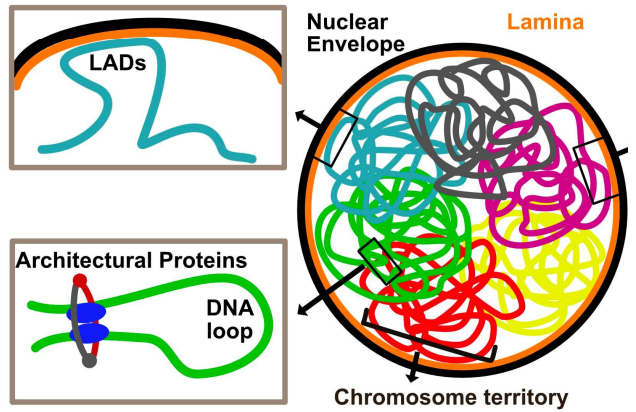
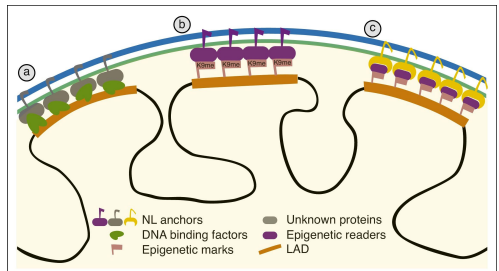
how are LADs formed
via interactions between DNA & anchors in nuclear lamin
some LADs are constitutive (cLADs) or facultative (fLADs)
LADs are dynamic and change during mitosis & cell development
what is important to note about the structure of genes
they are looped, this allows promoters that are a downstream to interact with upstream components
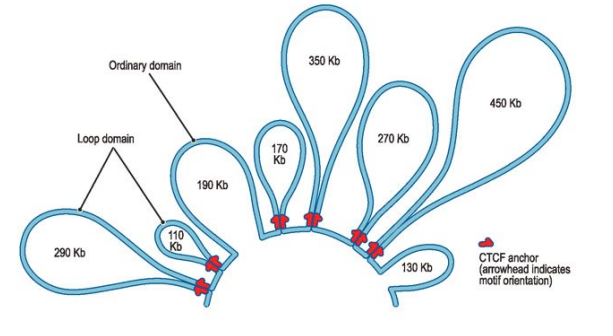
what are TADs
topologically-associating domains
structural units that describe how DNA is folded in the nucleus
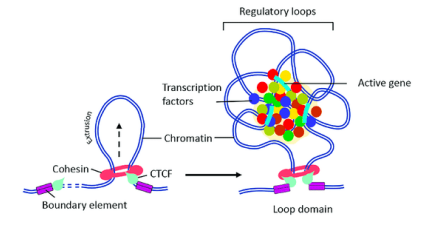
what is CTCF
a zinc finger protein that binds to DNA and demarcates the TAD boundaries
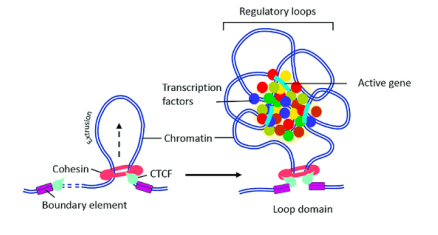
what is cohesion
a circular multi-protein complex that acts as a collar to form the TAD
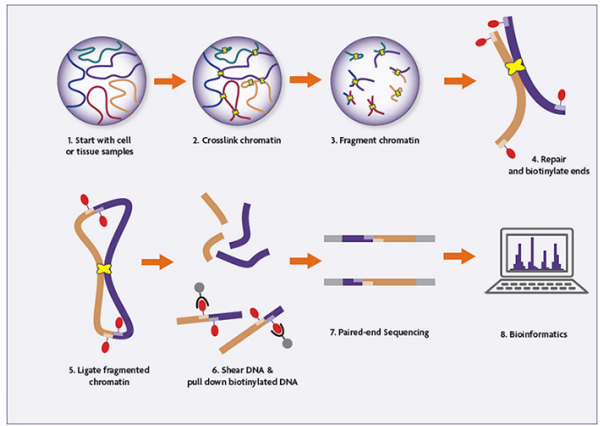
how are TADs identified with Hi-C
what is epigenetics
refers to the alteration of histones to regulate gene expression
methylation, phosphorylation, ubiquitarian, acetylation
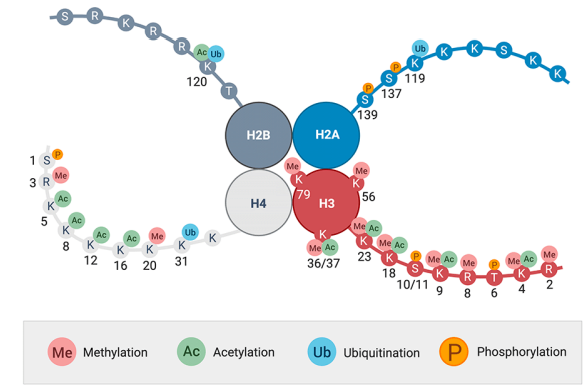
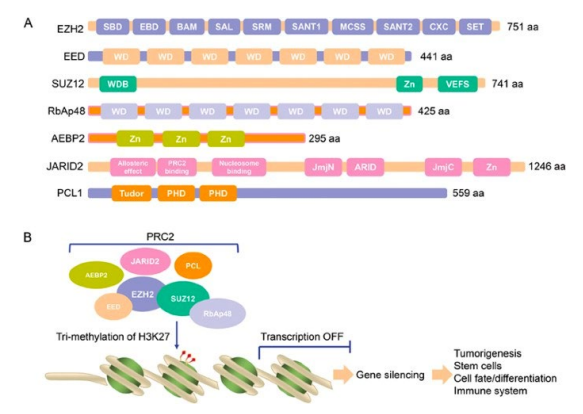
how does H3K27 turn off transcription
requires an enzyme EZH2 which functions in a complex called PRC2
complex adds 3 methyl groups onto K27 which ultimately results in deactivating transcription