Lecture 32 - Power and Sample Size
1/17
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
18 Terms
what is the null hypothesis
generally the opposite of what is trying to be proven
e.g. drug A has the same mortality rate as drug B (superiority)
drug A is inferior to drug B (non-inferiority)
drug A and B are outside of the equivalence threshold (equivalence)
what is the alternative hypothesis
generally what the experimenter wishes to demonstrate or test
e.g. drugs A and B will have different mortality rates (superiority)
drug A is not inferior to drug B (non-inferiority)
drug A and B’s mortality rates are within a specified equivalence bound (equivalence)
what is important to note about the null hypothesis
can never accept the null hypothesis (mathematically impossible)
simply conclude the evidence is insufficient to disprove it
what kind of error is it when you reject the null hypothesis when it is actually true
type 1 error
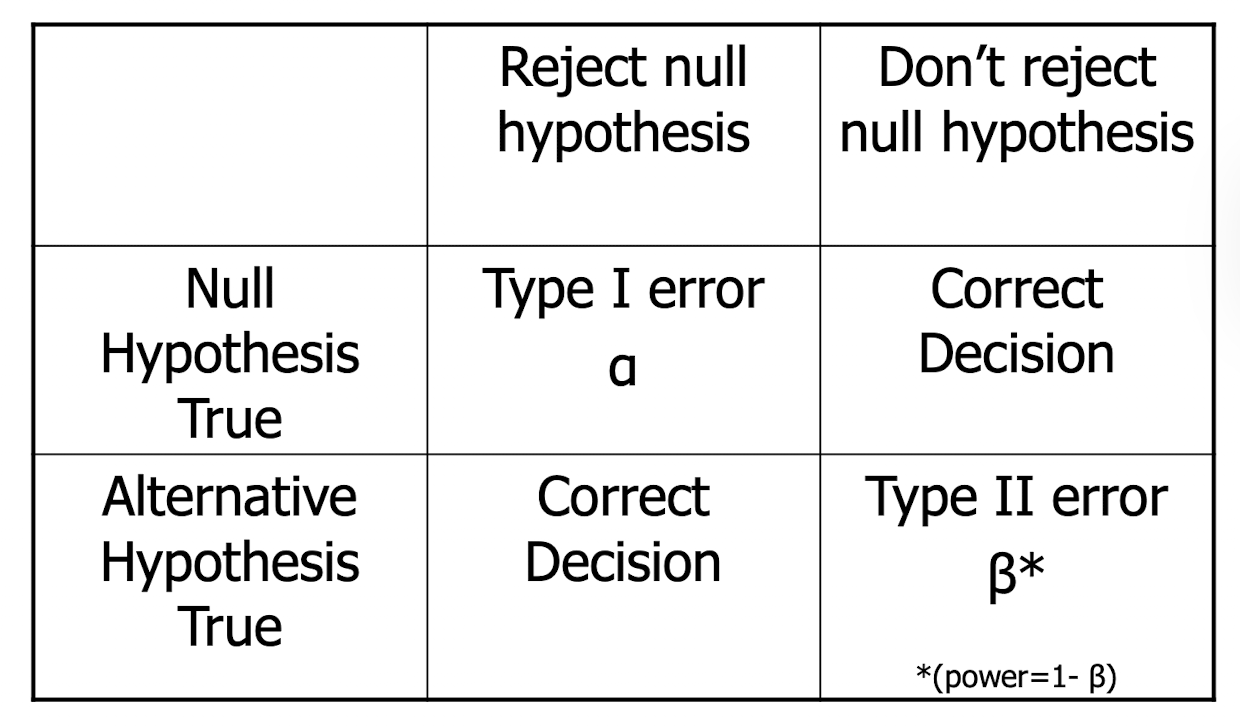
what kind of error is it when you do not reject the null hypothesis when it is false
type 2 error
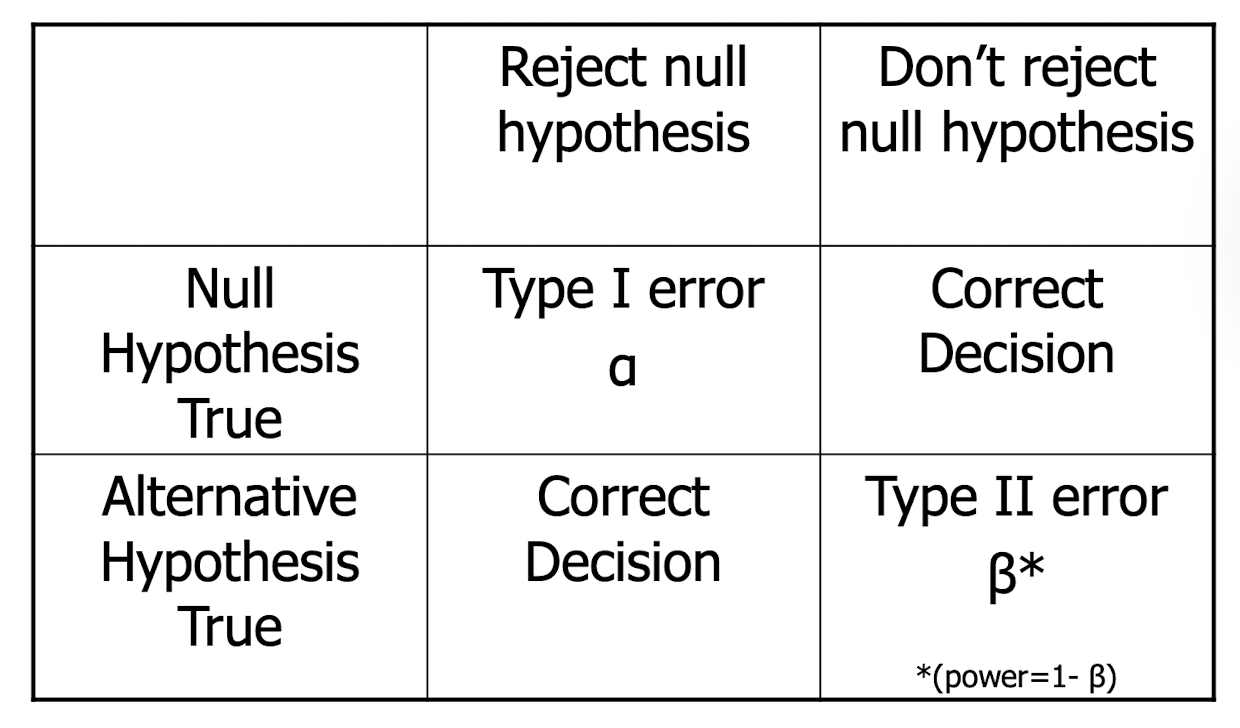
what is the probably of making a type 1 error (when the null hypothesis is true)
alpha
what is the probability of making a type 2 error (when the alternative hypothesis is true)
beta
what is the power of a study
the probability of correctly rejecting the null hypothesis when it is false
power = 1 - beta (and beta = 1- power)
what are alpha and beta commonly set at
alpha = 0.05 (sometimes 0.01 or 0.1)
beta = 0.2 or 0.1 (i.e power is 80% or 90%)
what is the effect of increasing the number of particpants/obersations on alpha and beta
will decrease both alpha and beta
what does the estimation of power assume
the estimation of power (or beta) assumes the alternative hypothesis is true
however, the alternative hypothesis is generally an inequality, so to estimate power, we need to specify a value
how can alpha be interpreted in plain language
e.g alpha = 0.05
if the null hypothesis is true, you will have at most a 5% chance of incorrectly rejecting it
how can power be interpreted in plain language
e.g. power = 90%
if the alternative hypothesis is true, there is a 90% chance you will reject the null hypothesis
what is the risk of too many patients in a RCT
possible overexposure to an inferior treatment
what is the risk of too few patients in a RCT
inconclusive and/or unreliable results
how is sample size estimated
should be based on primary outcome
based on 3 factors set by trialists:
target difference between interventions (determined by clinical expertise)
type 1 error rate (usually alpha = 0.05)
type 2 error rate (usually beta = 0.1 or 0.2 - i.e. power = 90% or 80%)
what are nuisance parameters
parameters that are not of interest in and of themselves, but must be accounted for to estimate those that are of interest
need to be estimated to make a sample size calculation
what are common examples of nuisance parameters
the control event rate (dichotomous outcomes)
the standard deviation (continuous outcomes)