Pharm 212 Sequential Exam 1 - Drug Receptors
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
what is a molecular complex that binds drugs/endogenous agents resulting in a pharmacological/physiological resonse
receptor
what is a drug that elicits a pharmacological response when it binds to a receptor
agonist
what is an agent that reduced the effectiveness of a corresponding agonist
an antagonist
what is the ability to bind to a receptor
affinity
what is the ability to produce a pharmacological action after binding
intrinsic activity
what is the x-y axis scale for drug-receptor interaction graphs
Log [A] V % maximal response
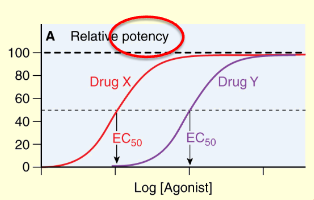
which drug is the more potent drug
Drug X — it requires much less concentration to achieve the same effect
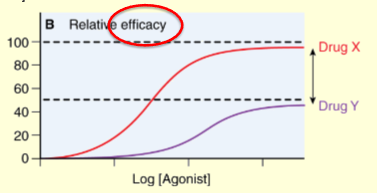
which drug has a higher activity
Drug X — it reaches a higher efficacy than drug Y
which interactions have receptor affinity and intrinsic activity
Agonists
which interactions have receptor affinity but have reduced intrinsic activity
partial agonists
which interactions have receptor affinity but lack intrinsic activity
pure antagonists
which interactions bind to the receptors in an inactive state, which might also show antagonism
inverse agonists
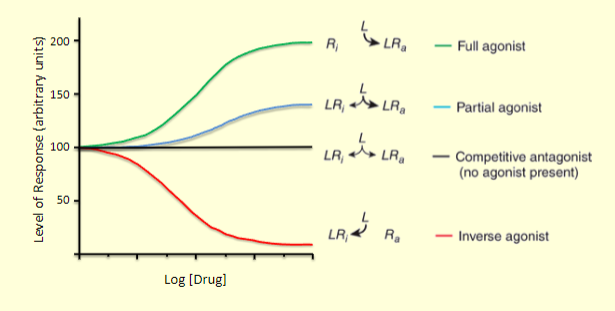
understand the different aspects of this graph
—
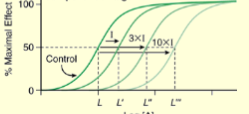
what type of mechanism does this graph indicate
competitive
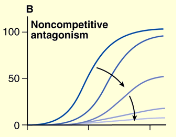
what kind of mechanism does this graph indicate
pseudo-irreversible
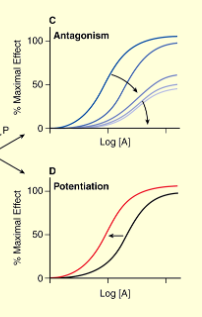
what kind of mechanism does this graph indicate
allosteric
what is the selectivity of agonist/antagonist binding to a specific class of receptors
receptor specificity
how can we quantitatively relate the toxic and therapeutic effects of a drug through dose-response
therapeutic index
how do we calculate therapeutic index

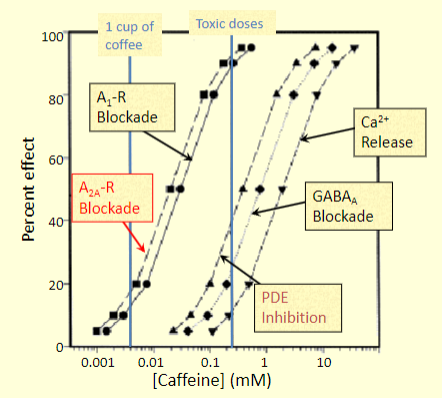
what does this exemplify?
therapeutic index
coupling or signal transduction
what is it called when ligand binding must be transduced into the cell to produce a physiological response
spare receptors
what are unequal proportions or rations between receptors and effectors, either within time or space
what do spare receptors do
serves to make drugs more or less effective by increasing or decreasing sensitivity
what is the clinical definition of spatially spare
when 100% response is elicited by less than full receptor occupancy = spare in numbers
what causes receptor desensitization
due to intracellular signaling feedback inhibiting the receptor machinery
how long does receptor desensitization last
usually a few minutes up to one hour
receptor down-regulation
what results from agonist-induced decreases in receptor number
degradation in lysosomes and recycling to the plasma membrane restoring function
what is are the receptor effects of drug tolerance
super sensitivity
what is the other regulatory response
tachyphylaxis
what is a reduction in response after acute readministration of a drug
hypersensitivity
what is an allergic reaction to an antigen
idiosyncratic reaction
what is an abnormal reaction to a drug that may result from a genetic predisposition
synergy
what is it when two or more drugs result in a response that is greater than the sum of their individual intrinsic activities
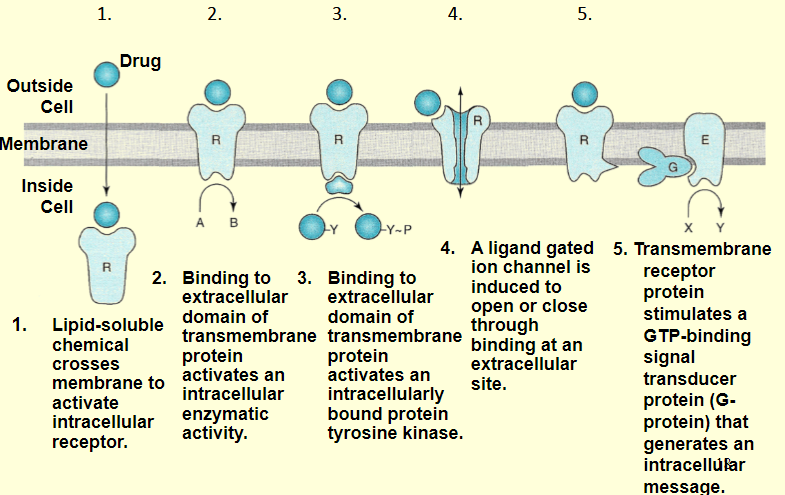
what does the graphic describe
different transmembrane signaling mechanisms
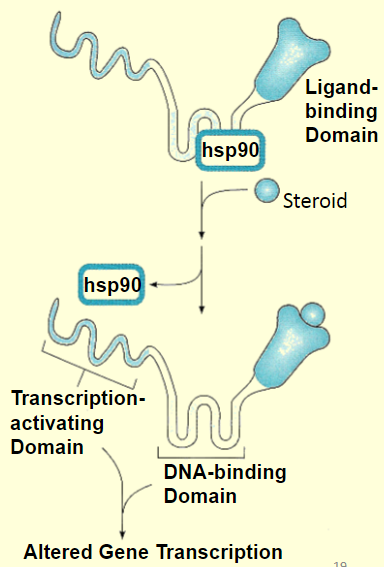
lipid crossing
requires a lag period if 30 minutes to several hours, effects are long lived, several hours to days, even after the ligand has dropped to zero
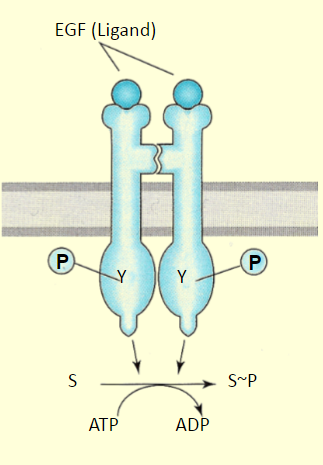
ligand regulated enzymes
the binding of the ligand to receptor does 3 things:
exposes tyrosine sites
activates tyr-kinases
activates kinases to alter cell physiology
what are the consequences of ligand regulated enzymes
cooperative binding and long-lasting effect
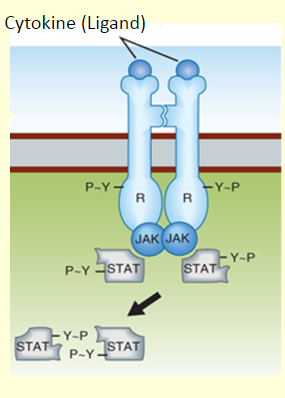
Activation of JAK- STAT
binding of the ligand to the dimer causes:
dimer formation
activates mobile kinase
JAK phosphorylation of receptor protein and STAT transcription factor
STAT can migrate to the nucleus and promote gene transcription
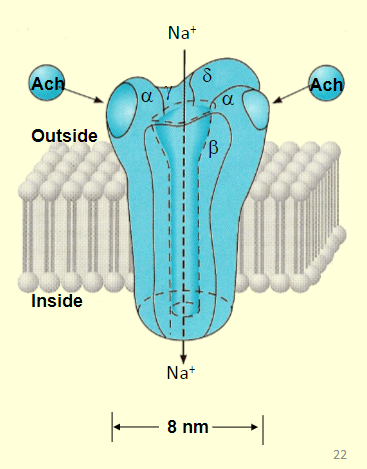
ligand-gated ion channels
binding of the ligand causes:
creates conformational shift in subunit structure
opens aqueous channel allowing sodium ions to enter
features an on/off switch