Light and The Eye
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
34 Terms
Retina
the light-sensitive inner surface of the eye, containing photoreceptors including rods and cones plus layers of neurons that begin the processing of visual information
Rod Cells
a type of photoreceptor specialized for low levels of light intensity, such as those found at night
Cone Cells
a type of photoreceptor that operate best in bright light; enable high-acuity, color vision
Lens
the transparent structure behind the pupil that changes shape to help focus images on the retina
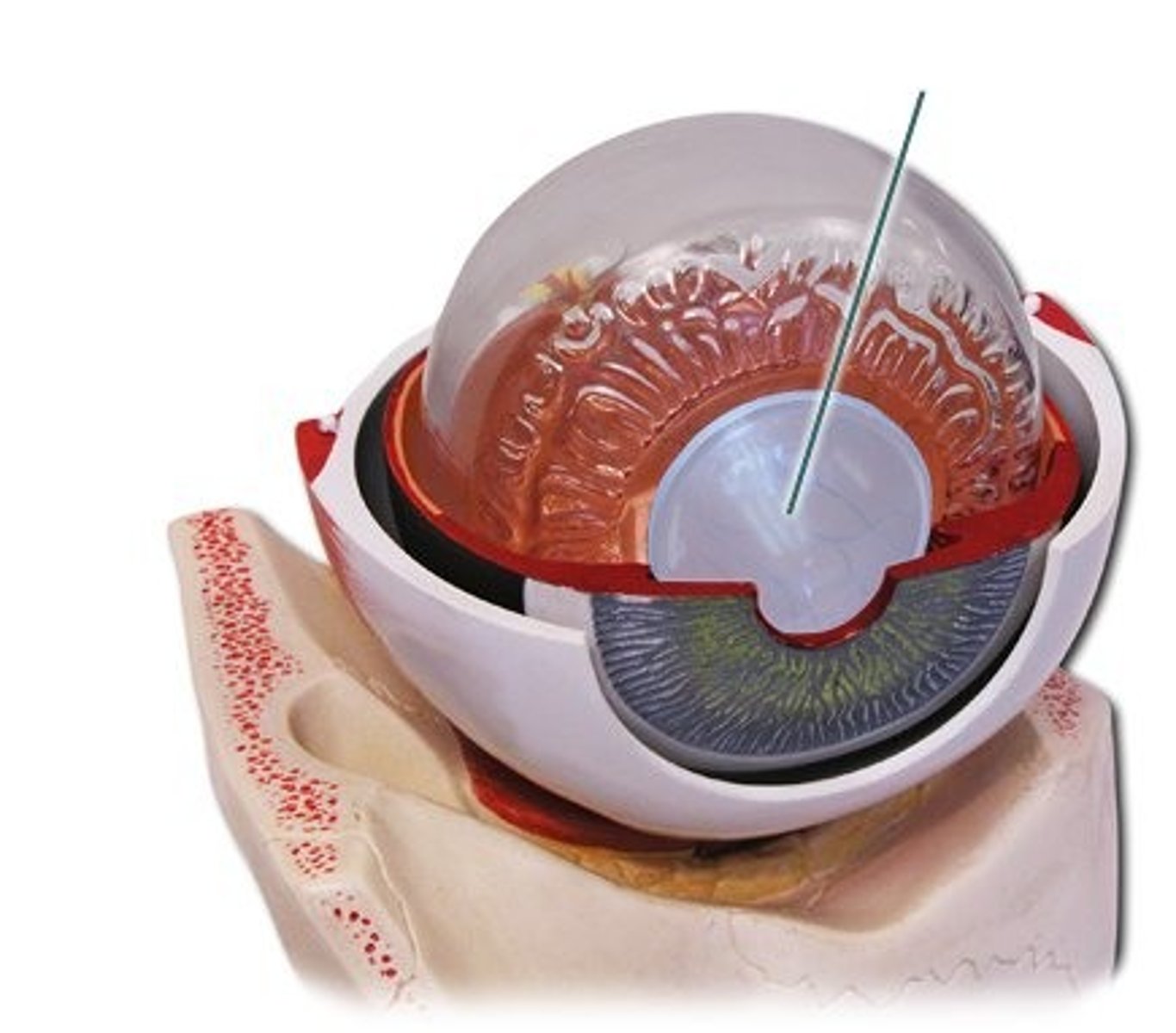
Fovea
the central focal point in the retina, containing the highest density of cone cells in the retina
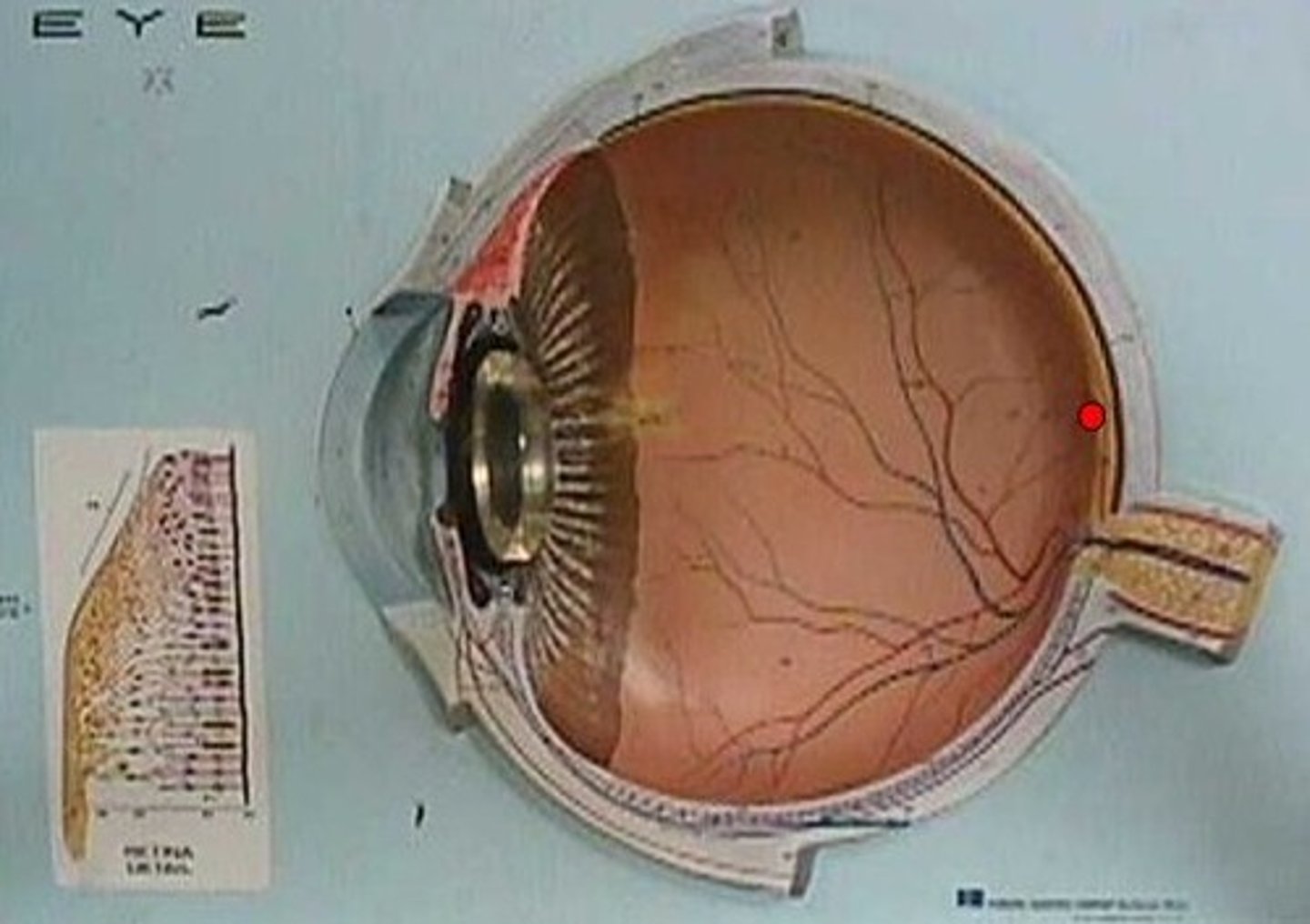
Bipolar cell
a bipolar neuron located in the middle layer of the retina, conveying information from the photoreceptors to the ganglion cells
Ganglion cells
In the retina, the specialized neurons that connect to the bipolar cells; the bundled axons of these cells form the optic nerve.
Visible light
electromagnetic waves ranging from 400-700 nms
Isomerisation
Process by which retinal changes its shape within the disc membrane in the outer segment of photoreceptors, in response to the absorption of light.
Retinal
The light-sensitive part of the visual pigment molecule. It is attached to the protein molecule opsin to form the visual pigment.
Opsin
A class of protein that, together with retinal, constitutes the photopigments
Spatial Summation
The sum of multiple synapses firing at different locations at one time to create a net effect.
Neural Convergence
When several presynaptic neurons synapse with a single postsynaptic neuron. Increases light sensitivity and decreases spatial resolution of rod cells.
Sclera
Hard, white, strucutral part of the eye
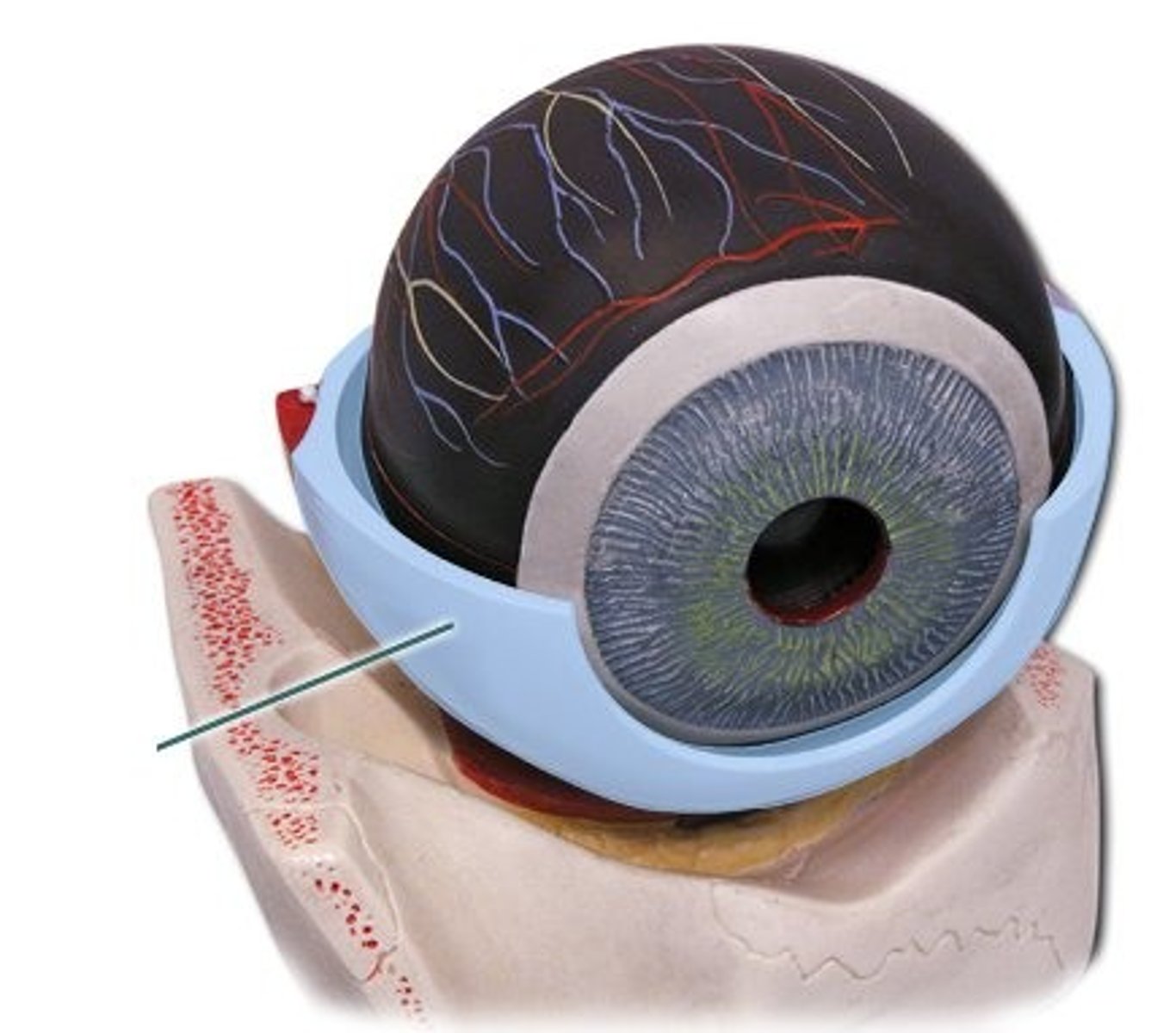
Cornea
The transparent layer forming the front of the eye.
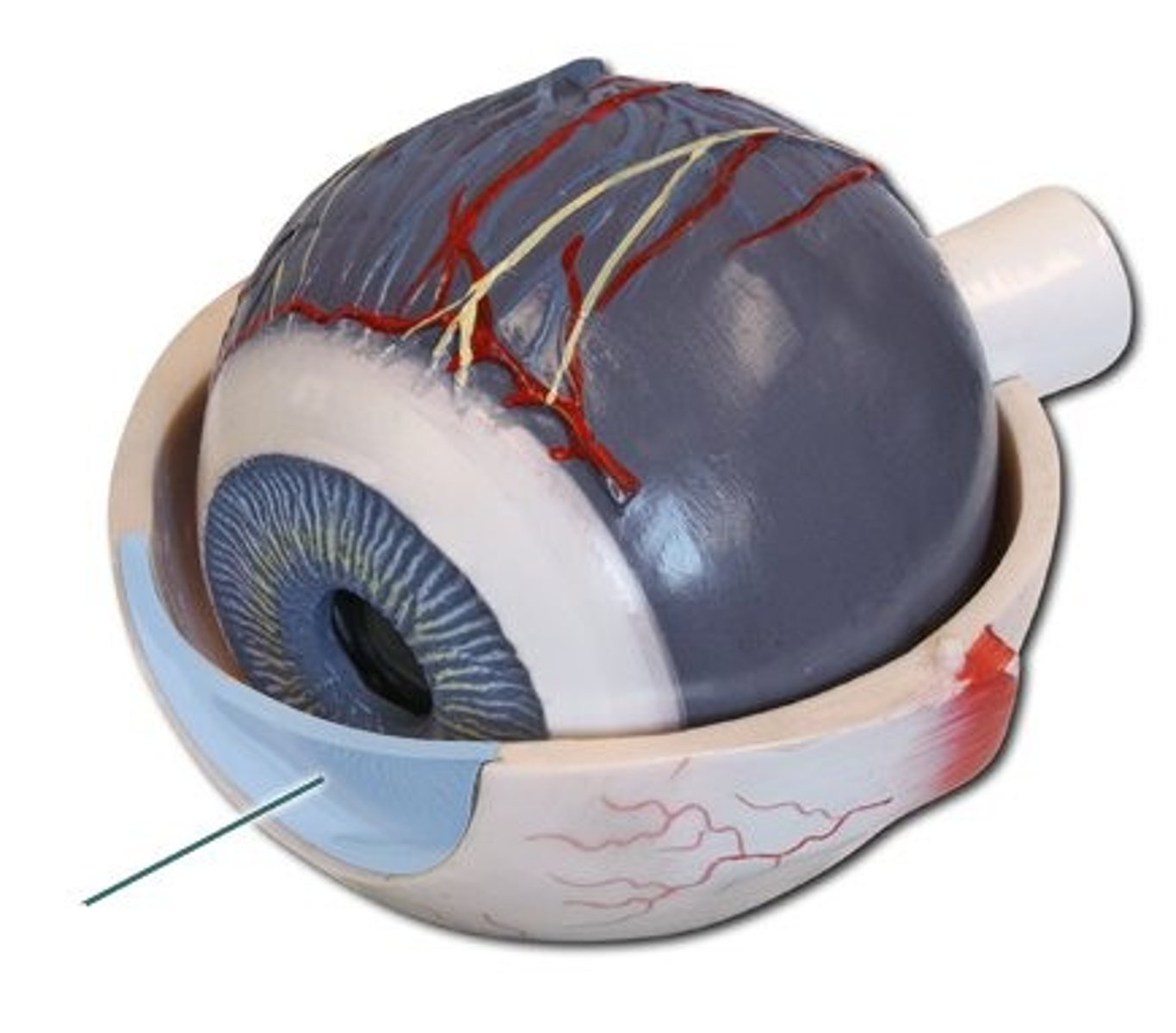
Pupil
The adjustable opening in the centre of the eye through which light enters
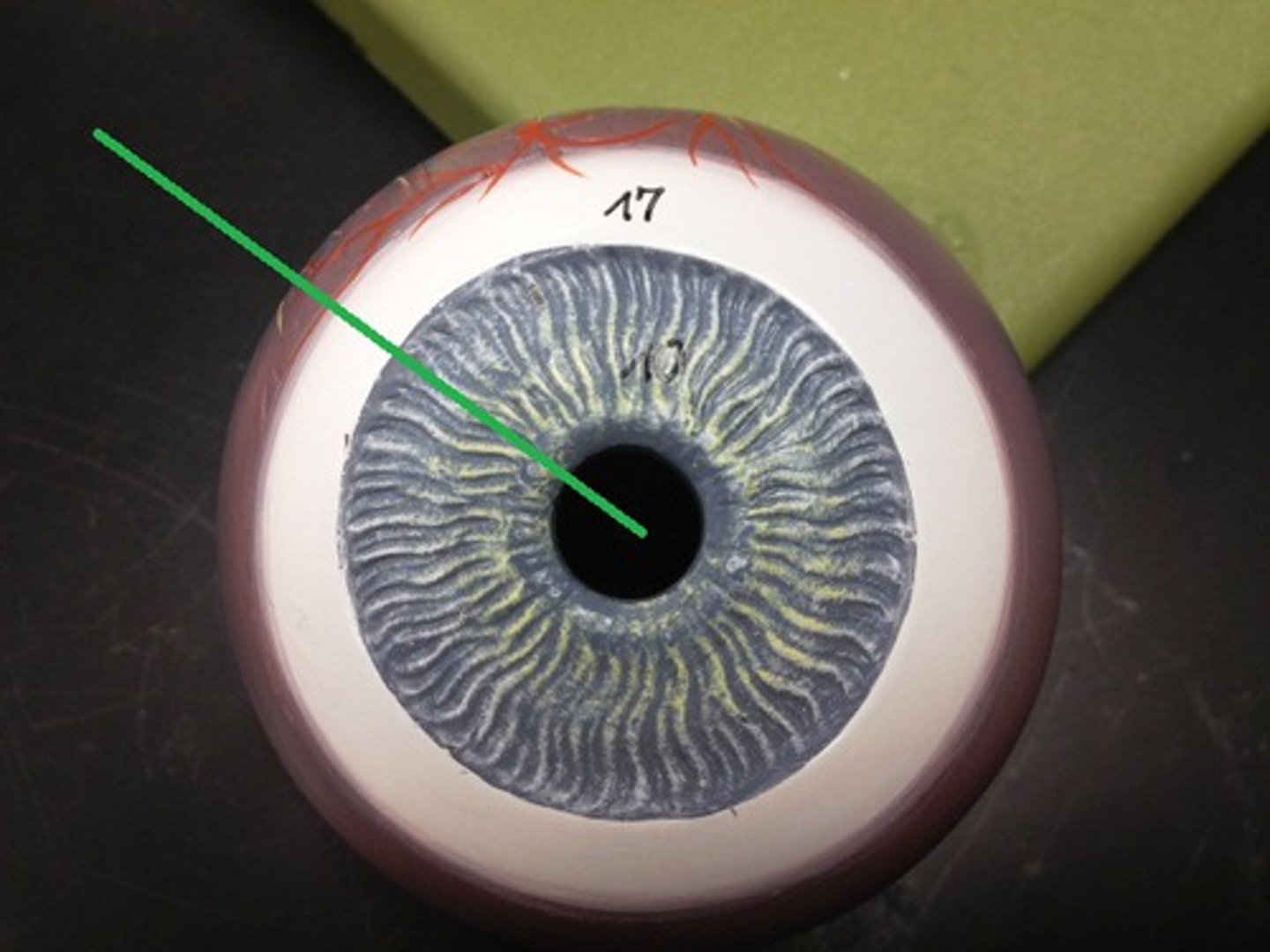
Iris
A ring of muscle tissue that forms the colored portion of the eye around the pupil and controls the size of the pupil opening
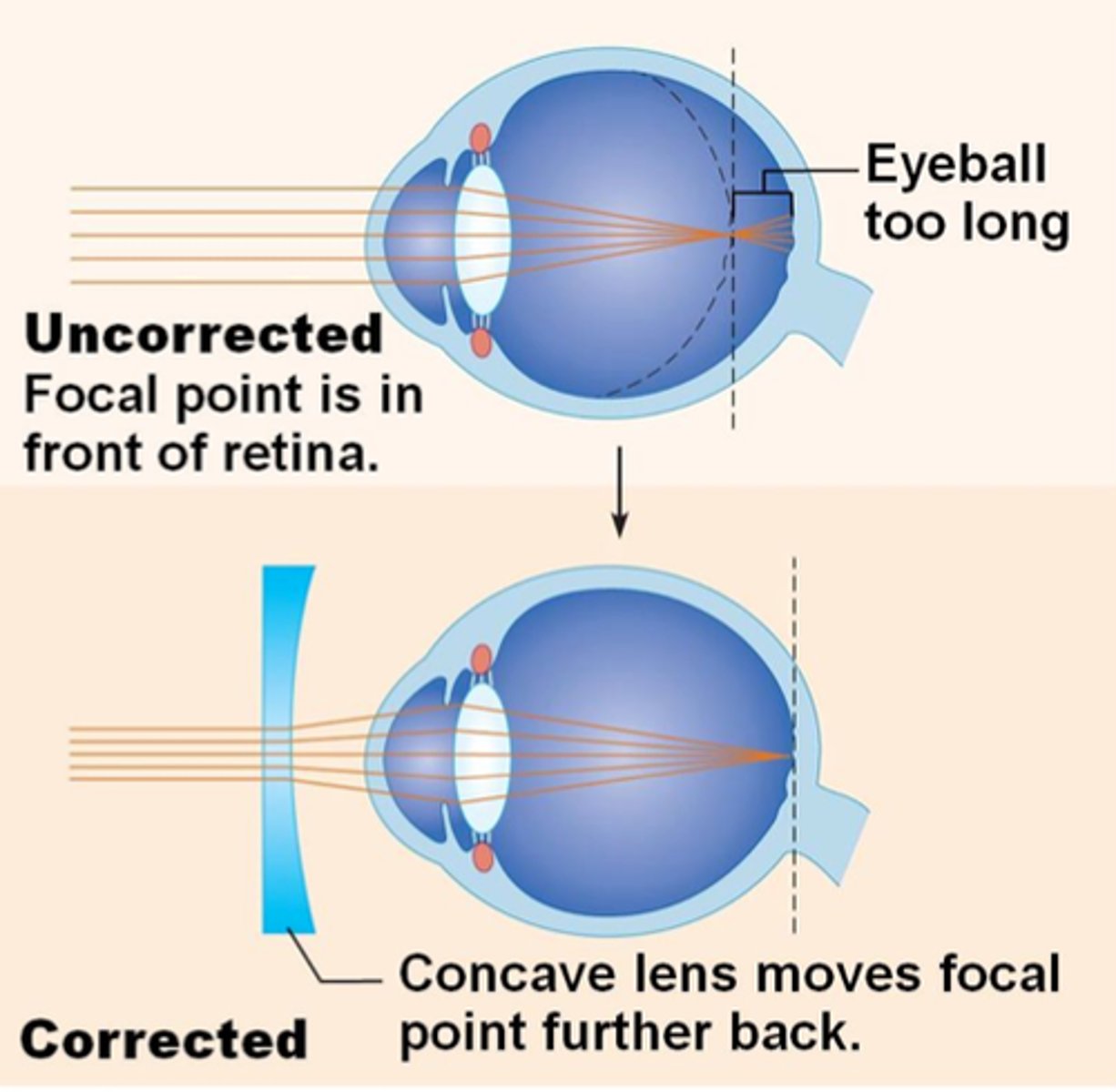
Myopia
Nearsightedness; difficulty seeing distant objects when focal point of light rays falls in front of the retina
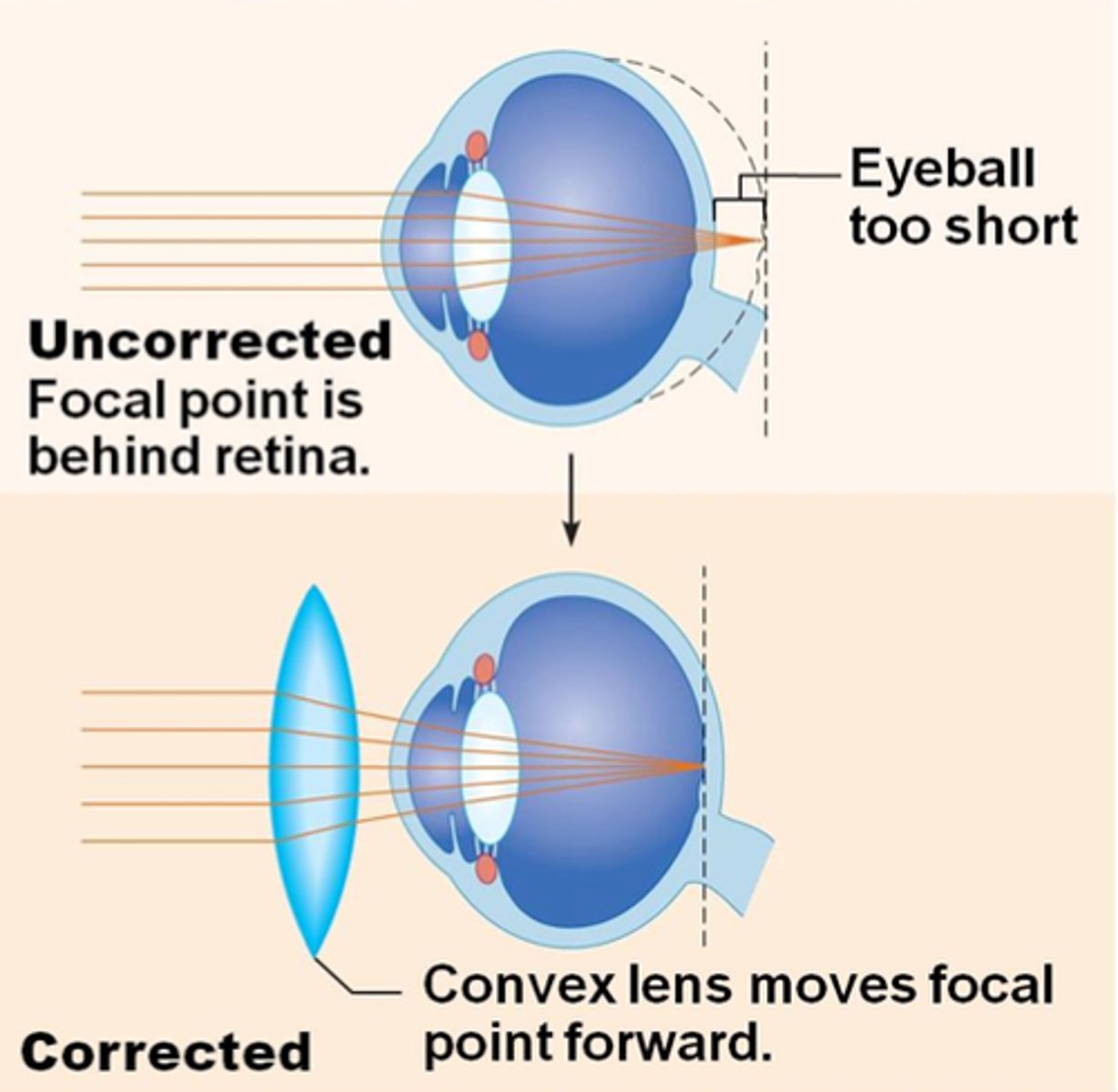
Hyperopia
Farsightedness; difficulty seeing close objects when focal point of light rays falls behind the retina
Presbyobia
Farsightedness; caused by weakening of ciliary muscles and hardening of lens due to aging
Near point
The distance at which the lens can no longer accommodate enough to bring close objects into focus.
Focal point
The point at which rays parallel to the optical axis reflect and meet
Ciliary Muscles
Muscles which relax or contract and alter the shape of the lens
Cone-based Neurotransmission
On average 6 photoreceptors transmitting to a single ganglion cell. Often one-to-one transmission with individual ganglion cells, particularly in the fovea, resulting in high visual acuity but low sensitivity to low levels of light.
Rod-based Neurotransmission
On average 120 photoreceptors transmitting signals to a single ganglion cell. Results in low visual acuity but high sensitivity to low levels of light.
Accommodation
The process by which the eye's lens changes shape to focus near or far objects on the retina
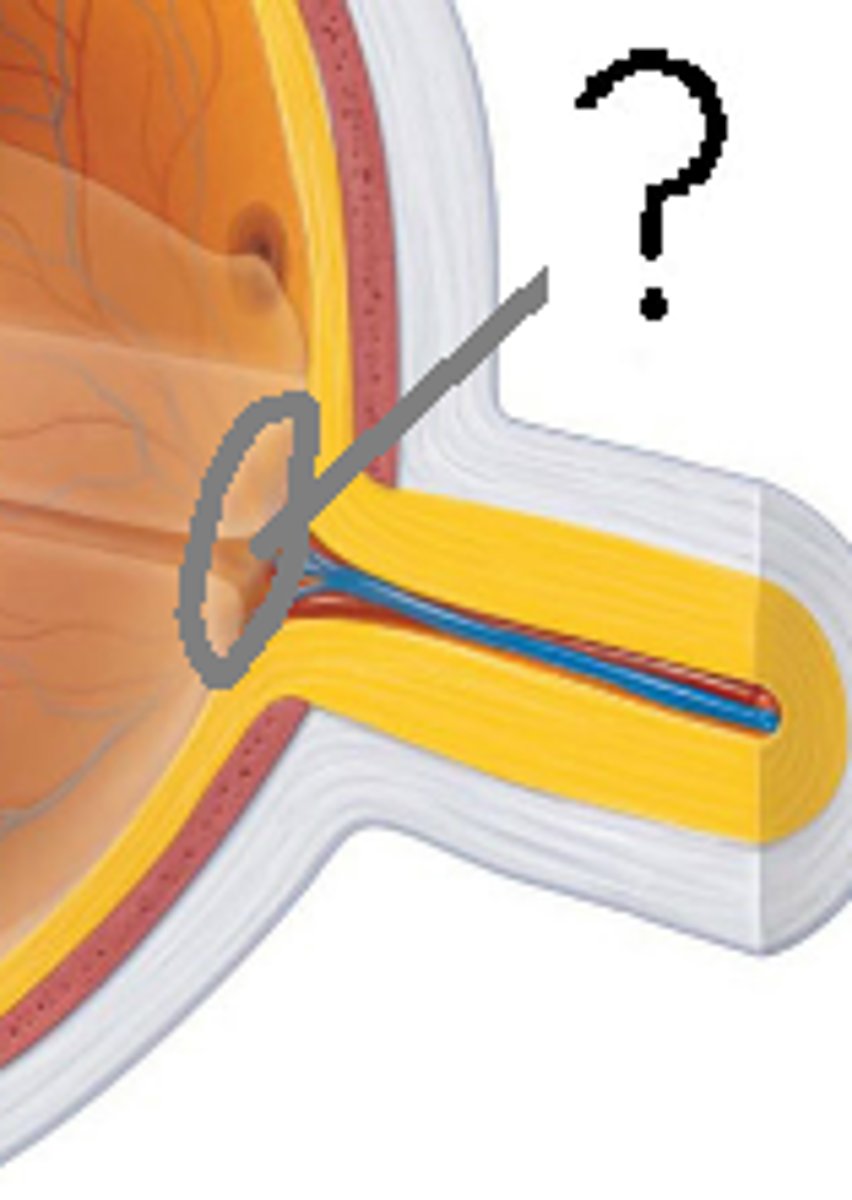
Blind spot
The point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye. No photoreceptors cells are located there, creating a gap in our vision.
Dark Adaptation Curve
The function relating sensitivity to light to time in the dark, beginning when the lights are extinguished
Light Adaptation
The process whereby the eyes become less sensitive to light in high illumination
Rod Monochromats
A person who has a retina in which the only functioning receptors are rods.
Light Sensitivity
The ability to detect an object in dim light
Ultraviolet Light (UV)
Part of the electromagnetic spectrum that consists of wavelengths that are shorter than those of visible light and longer than those of x-rays
Gamma Rays
Electromagnetic waves with the shortest wavelengths and highest frequencies. Penetrating electromagnetic radiation of a kind arising from the radioactive decay of atomic nuclei.
Radio Waves
Electromagnetic waves with the longest wavelengths and lowest frequencies