p1 particle model of matter
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
describe solids
Particles are very close together
Arranged in regular pattern
Vibrate but do not move from place to place
Describe liquid
Particles are close together
Not arranged in regular pattern
Also can move around each other
Gas
Very far apart
Particles not arranged in any pattern
Moving very rapidly
Which is gas
Which is liquid
Which is solid
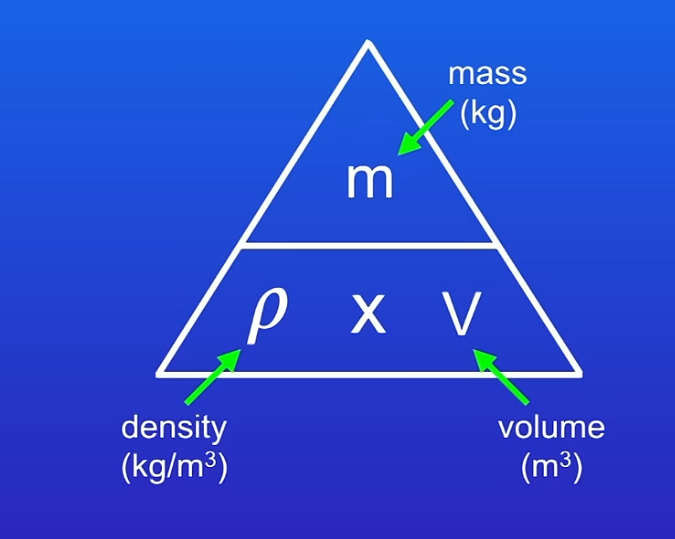
What is density ?
The density of a material tells us the mass for a given volume
An example of density
The brick has high density it has lots of mass packed into its volume
The polystyrene block has a low density it has a lower mass packed into its volume
What is the equation for density
Explaining the density of different materials
Solids usually have a vey high density Bc the particles are packed closely together solids have a lot of mass for their volume
Liquids usually have a high density bc the particles are close together liquids have a lot of mass for their volume
Gases have low density bc the particles are very apart so gases have a small mass for their volume
Polystyrene is a exception for these rules
It’s a solid but it has low density bc it has a very open structure and is full of air spaces it has a small mass for its volume.

What do all 3 particles have in common
Kinetic
Potential energy (intermolecular forces and chemical bonds )- forces
Wat is internal energy
Is the energy stored in a system by the particles
Is the total kinetic energy and potential energy of all the particles (atoms and molecules that make up a system
What happens when we heat a solid?
We increase the internal energy at some point the solid turns to liquid (melting )
What happens if we Continue to heat liquid ?
We increase the internal energy at some point the liquid will turn to a gas that is boiling
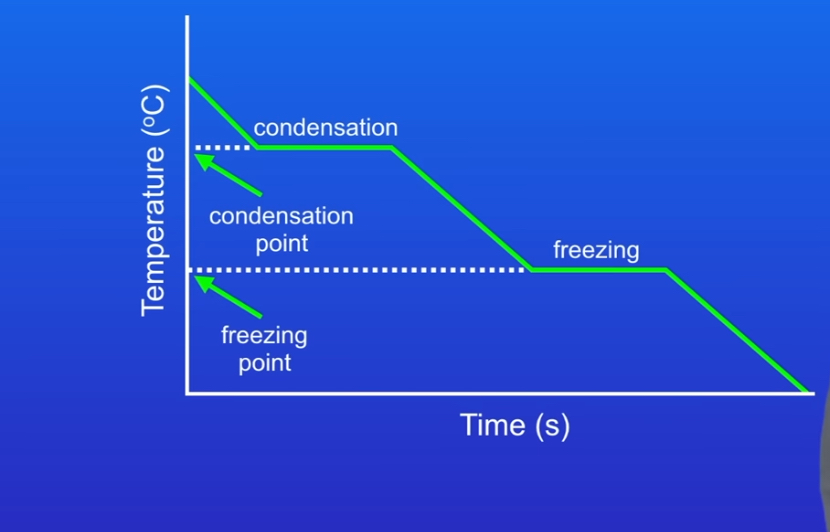
What happens if we cool the gas down?
Then we reduce the internal energy at some point the gas turns back to liquid (condensation )
What happens if we cool liquid even more ?
We reduce internal energy even more and then liquid turns to solid - freezing
Whats it called when a solid turns to gas
Sublimation
What happens when changes of state take place
Mass is always conserved were not adding or taking away any particles
Changes of state are
Physical change not chemical
If we reverse the change the material recovers its original properties
What is evaporation
When a liquid turns to gas but only on the surface of a liquid
In this case only the particles on the surface have enough energy to turn into gas
Specific heat capacity
Example - how much energy is stored in hot water ?
To answer this we need to look at the idea of specie heat capacity
What is specific heat capacity
Of a substance
Is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1kg of the substance by 1 degree
What is the equation for specific heat capacity

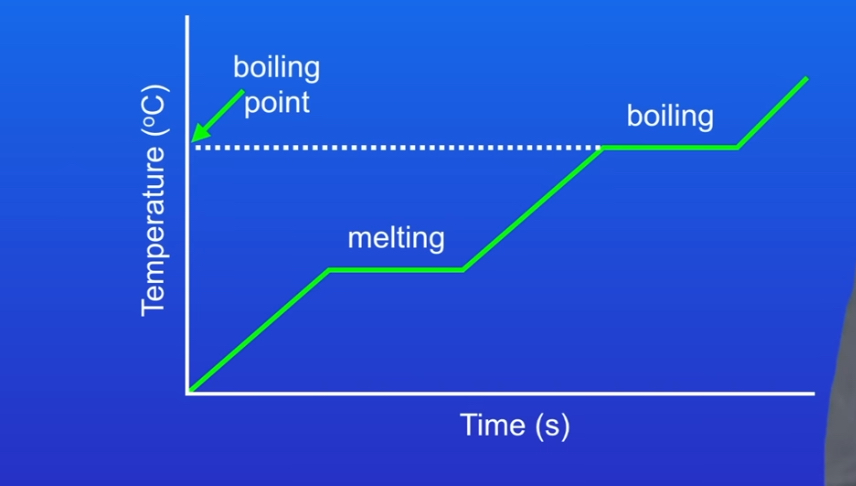
Heating graph 1 parts
The temperature of the solid is rising as we are increasing the energy of the particles
At some point the tem stops rising and the line is now horizontal at this point the solid is changing state and turning in to liquid by melting
The energy we are putting in is weakening or breaking the forces of attraction between the particles allowing substance to change from a solid to liquid scientists call the energy needed for a substance to change state the latent heat
Heating graph2 part
During the change of state we are increasing the internal energy store of the system but we are not changing the tem
The tem that the substance melts at is the boiling point
Eventually alll of the solid will have melted into a liquid and now the tem starts to rise again bc we are increasing the energy of the particles
Heating graph part 3
Tem stops increasing and line becomes horizontal again
The substance is now boiling the energy we are putting in is weakening or breaking the forces of attraction between the particles allowing substance
Once al the liquid has boiled the tem starts to rise again
Cooling graph
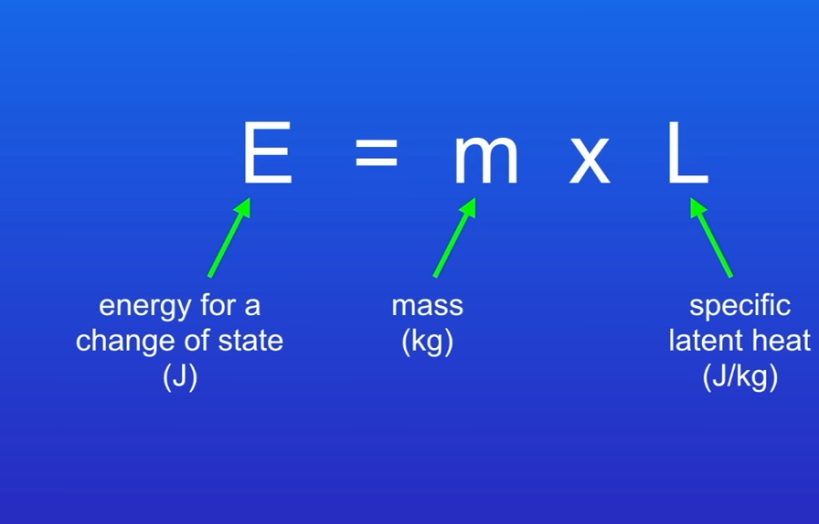
The energy needed for. Substance to change state it the latent heat this is ..
The specific latent heat of a substance is the amount of energy required to change the state of one kilogram of the substance with no change in tem
Specific latent heat example is ice if we wanted to melt 1kg of ice
The energy it would take ..
334 000 J of energy to melt one kilogram of ice scientists call this the specific latent heat of fusion
What is specific latent heat of fusion
The energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a solid to liquid with no change in tem
What if we wanted to change a substance from a liquid to gas how much energy would that take
This is called specific latent heat of vaporisation
the energy required to change 1kg of a substance from a liquid to vapour with no change in tem
We can use the idea of Specific latent heat To calculate energy change when a change of state takes pace calculation
Gas pressure
The pressure of a gas is due to the particles colliding with the walls of the container that the glass is held in
By colliding with the walls of the container the gas particles are exerting a pressure
We can increase the pressure if we increase the number of Collisions per second or the energy of each collision One way to do that is to increase the tem of the gas
Gas pressure 2
The tem of a gas is related to the average kinetic energy of the particles
Gas pressure 3
At low tem particles have lower kinetic energy there are fewer collisions per second these are lower energy collisions
So low tem - low pressure
At high tem particles have higher kinetic energy there are more collisions per second these are higher energy collisions
High tem particles- high pressure