4.2 - Genetic inheritance
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
Phenotypic ratios (monohybrid crosses)
all one type, 1:1, 3:1
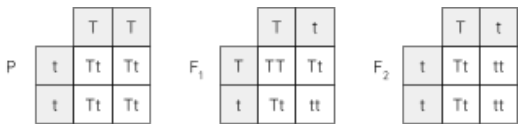
Phenotypic ratios (dihybrid crosses)
all one type, 1:1:1:1, 9:3:3:1, 3:3:1:1
Dominant allele
allele that has the same effect on the phenotype when in either the homozygous or heterozygous state
Recessive allele
allele that only has an effect on the phenotype when in homozygous state
Continuous variation
variation that doesn’t fall into categories, but has a range of measures
Discrete (discontinuous) variation
variation with clearly distinguishable categories with no intermediaries Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNPs)
Codominance
both alleles in the genotype are expressed in the phenotype
Incomplete dominance
the phenotype of heterozygous offspring is a combination of the two homozygous phenotypes (completely new phenotype)
Sex-linked (X-linked) genes
found only on the X chromosome
Examples of x-linked diseases
haemophilia and red-green colourblindness (both recessive)
Pedigree charts
trace the pattern of inheritance of a genetic condition in a family (males squares, females circles)
Example of an autosomal dominant disease
Huntington’s disease
Phenylketonuria (PKU)
autosomal recessive condition, mutates liver enzyme tyrosine hydroxylase (turns phenylalanine into tyrosine) on chromosome 12 so decreased metabolism of amino acid phenylalanine (build up in brain and blood), affects children til puberty
Polygenes
groups of genes which together control a characteristic (often unlinked, create continuous variation like skin colour/height)
Phenotypic plasticity
ability of individual genotypes to produce different phenotypes when exposed to different environmental conditions Polyphenism
Types of polyphenism
seasonal polyphenism (butterfly wings colourful in wet season, dull in dry season), caste polyphenism (ants can develop into queen or sterile worker ant), sexual polyphenism (sex of crocodiles determined by the temperature of egg incubation - aka ESD)
Environmental sex determination (ESD)
determination of sex based on environmental factors like temperature, nutrient availability, photoperiodism (changes in day length), location (some snails form towers: if next to female become male, if alone become female, once female cannot change back to male)
Dihybrid crosses
genetic crosses for two genes
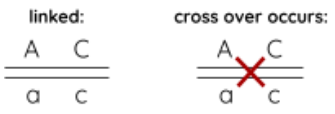
Likelihood of genes inherited together
increased if genes are linked (loci on same chromosomes) and close together (unlikely to cross over), if unlinked (different chromosomes) then Mendelian genetics applies
Linked genes representation
Chi squared test (𝛘2)
𝛘2 = 𝚺(O - E)2/E statistical test to check if the difference between observed and expected results is significant, use a table of values (degrees of freedom or df = n° of phenotypes - 1)
Example of codominance
ABO blood groups (IAIA = A, IBIB = B, IAi = A, ii = O, IAIB = AB)